|
Carbomethoxymethylenetriphenylphosphorane
Carbomethoxymethylenetriphenylphosphorane is a chemical compound used in organic syntheses. It contains a phosphorus atom bound to three phenyl groups, and doubly bound to the alpha position of methyl acetate. It undergoes a Wittig reaction. It is used in the Vitamin B12 total synthesis. Production Carbomethoxymethylenetriphenylphosphorane can be made via a multistep reaction using bromoacetic acid, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, and triphenylphosphine. This makes a phosphonium salt, which is converted to the final product by sodium carbonate in water. Reactions Carbomethoxymethylenetriphenylphosphorane reacts with aldehyde In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl grou ...s to give a two carbon atom extension. The carbomethoxymethylene group replaces the oxygen of the aldehyde to give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Substance
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances (substances consisting of a single chemical element), chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical substances are often called 'pure' to set them apart from mixtures. A common example of a chemical substance is pure water; it has the same properties and the same ratio of hydrogen to oxygen whether it is isolated from a river or made in a laboratory. Other chemical substances commonly encountered in pure form are diamond (carbon), gold, table salt (sodium chloride) and refined sugar (sucrose). However, in practice, no substance is entirely pure, and chemical purity is specified according to the intended use of the chemical. Chemical substances exist as solids, liquids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated as white phosphorus in 1669. White phosphorus emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen – hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, meaning 'light-bearer' (Latin ), referring to the " Morning Star", the planet Venus. The term '' phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, derives from this property of phosphorus, although the word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus is caused by oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus — a process now called chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenyl Group
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6 H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. Phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. Phenyl group has six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, phenyl group is chemically aromatic and has equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring. Nomenclature Usually, a "phenyl group" is synonymous with C6H5− and is represented by the symbol Ph or, archaically, Φ. Benzene is sometimes denoted as PhH. Phenyl groups are generally attached to other atoms or groups. For example, triphenylmethane (Ph3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Acetate
Methyl acetate, also known as MeOAc, acetic acid methyl ester or methyl ethanoate, is a carboxylate ester with the formula CH3COOCH3. It is a flammable liquid with a characteristically pleasant smell reminiscent of some glues and nail polish removers. Methyl acetate is occasionally used as a solvent, being weakly polar and lipophilic, but its close relative ethyl acetate is a more common solvent being less toxic and less soluble in water. Methyl acetate has a solubility of 25% in water at room temperature. At elevated temperature its solubility in water is much higher. Methyl acetate is not stable in the presence of strong aqueous bases or aqueous acids. Methyl acetate is not considered a VOC in the USA. Preparation and reactions Methyl acetate is produced industrially via the carbonylation of methanol as a byproduct of the production of acetic acid. Methyl acetate also arises by esterification of acetic acid with methanol in the presence of strong acids such as sulfuric ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wittig Reaction
The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide called a Wittig reagent. Wittig reactions are most commonly used to convert aldehydes and ketones to alkenes. Most often, the Wittig reaction is used to introduce a methylene group using methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph3P=CH2). Using this reagent, even a sterically hindered ketone such as camphor can be converted to its methylene derivative. Stereochemistry For the reaction with aldehydes, the double bond geometry is readily predicted based on the nature of the ylide. With unstabilised ylides (R3 = alkyl) this results in (''Z'')-alkene product with moderate to high selectivity. With stabilized ylides (R3 = ester or ketone), the (''E'')-alkene is formed with high selectivity. The (''E'')/(''Z'') selectivity is often poor with semistabilized ylides (R3 = aryl). To obtain the (''E'')-alkene for unstabilized ylides, the Schlosser modification of the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B12 Total Synthesis
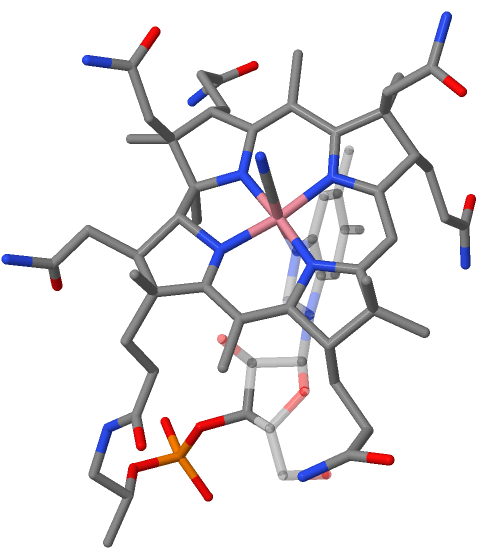
The total synthesis of the complex biomolecule vitamin B12 was accomplished in two different approaches by the collaborating research groups of Robert Burns Woodward at Harvard and Albert Eschenmoser at ETH in 1972. The accomplishment required the effort of no less than 91 postdoctoral researchers (Harvard: 77, ETH: 14), and 12 Ph.D. students (at ETH) from 19 different nations over a period of almost 12 years. The synthesis project induced and involved a major change of paradigm in the field of natural product synthesis. The molecule Vitamin B12, C63H88CoN14O14P, is the most complex of all known vitamins. Its chemical structure had been determined by x-ray crystal structure analysis in 1956 by the research group of Dorothy Hodgkin (Oxford University) in collaboration with Kenneth N. Trueblood at UCLA and John G. White at Princeton University. Core of the molecule is the corrin structure, a nitrogenous tetradentate ligand system. This is biogenetically related to porphyrins a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromoacetic Acid
Bromoacetic acid is the chemical compound with the formula CH2BrCO2H. This colorless solid is a relatively strong alkylating agent. Bromoacetic acid and its esters are widely used building blocks in organic synthesis, for example, in pharmaceutical chemistry. The compound is prepared by bromination of acetic acid, such as by a Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky reaction or using other reagents.. : CH3CO2H + Br2 → CH2BrCO2H + HBr See also * Acetic acid * Chloroacetic acid * Ethyl bromoacetate Ethyl bromoacetate is the chemical compound with the formula CH2BrCO2C2H5. It is the ethyl ester of bromoacetic acid and is prepared in two steps from acetic acid. It is a lachrymator and has a fruity, pungent odor. It is also a highly toxic alky ... References External links The microwave spectrum of bromoacetic acid {{DEFAULTSORT:Bromoacetic Acid Alkylating agents Acetic acids Organobromides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
''N'',''N''′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC or DCCD) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (C6H11N)2C. It is a waxy white solid with a sweet odor. Its primary use is to couple amino acids during artificial peptide synthesis. The low melting point of this material allows it to be melted for easy handling. It is highly soluble in dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile and dimethylformamide, but insoluble in water. Structure and spectroscopy The C−N=C=N−C core of carbodiimides (N=C=N) is linear, being related to the structure of allene. The molecule has idealized C2 symmetry. The N=C=N moiety gives characteristic IR spectroscopic signature at 2117 cm−1. The 15N NMR spectrum shows a characteristic shift of 275 ppm upfield of nitric acid and the 13C NMR spectrum features a peak at about 139 ppm downfield from TMS. Preparation DCC is produced by the decarboxylation of cyclohexylisocyanate using phosphine oxides as a catalyst: :2 C6H11NCO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether. Preparation and structure Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium: :PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl Triphenylphosphine crystallizes in triclinic and monoclinic modification. In both cases, the molecule adopts a pyramidal structure with propeller-like arrangement of the three phenyl groups. Principal reactions with chalcogens, halogens, and acids Oxidation Triphenylphosphine undergoes slow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphonium
In polyatomic cations with the chemical formula (where R is a hydrogen or an alkyl, aryl, or halide group). These cations have tetrahedral structures. The salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions. Types of phosphonium cations Protonated phosphines The parent phosphonium is as found in the iodide salt, phosphonium iodide. Salts of the parent are rarely encountered, but this ion is an intermediate in the preparation of the industrially useful tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride: :PH3 + HCl + 4 CH2O → Many organophosphonium salts are produced by protonation of primary, secondary, and tertiary phosphines: :PR3 + H+ → The basicity of phosphines follows the usual trends, with R = alkyl being more basic than R = aryl. Tetraorganophosphonium cations The most common phosphonium compounds have four organic substituents attached to phosphorus. The quaternary phosphonium cations include tetraphenylphosphonium, (C6H5)4P+ and tetramethylphosphoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Carbonate
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants growing in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process. Hydrates Sodium carbonate is obtained as three hydrates and as the anhydrous salt: * sodium carbonate decahydrate (natron), Na2CO3·10H2O, which readily efflorescence, effloresces to form the monohydrate. * sodium carbonate heptahydrate (not known in mineral form), Na2CO3·7H2O. * sodium carbonate monohydrate (thermonatrite), Na2CO3·H2O. Also known as crystal carbonate. * anhydrous sodium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |