|
Vitamin B12 Total Synthesis
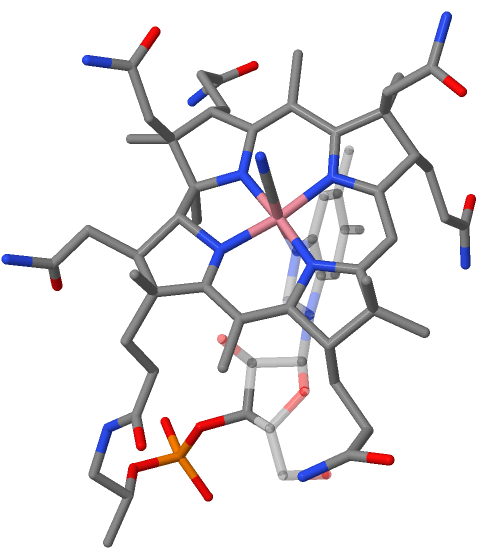
The total synthesis of the complex biomolecule vitamin B12 was accomplished in two different approaches by the collaborating research groups of Robert Burns Woodward at Harvard and Albert Eschenmoser at ETH in 1972. The accomplishment required the effort of no less than 91 postdoctoral researchers (Harvard: 77, ETH: 14), and 12 Ph.D. students (at ETH) from 19 different nations over a period of almost 12 years. The synthesis project induced and involved a major change of paradigm in the field of natural product synthesis. The molecule Vitamin B12, C63H88CoN14O14P, is the most complex of all known vitamins. Its chemical structure had been determined by x-ray crystal structure analysis in 1956 by the research group of Dorothy Hodgkin (Oxford University) in collaboration with Kenneth N. Trueblood at UCLA and John G. White at Princeton University. Core of the molecule is the corrin structure, a nitrogenous tetradentate ligand system. This is biogenetically related to porphyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Synthesis
Total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of a complex molecule, often a natural product, from simple, commercially-available precursors. It usually refers to a process not involving the aid of biological processes, which distinguishes it from semisynthesis. Syntheses may sometimes conclude at a precursor with further known synthetic pathways to a target molecule, in which case it is known as a formal synthesis. Total synthesis target molecules can be natural products, medicinally-important active ingredients, known intermediates, or molecules of theoretical interest. Total synthesis targets can also be organometallic or inorganic, though these are rarely encountered. Total synthesis projects often require a wide diversity of reactions and reagents, and subsequently requires broad chemical knowledge and training to be successful. Often, the aim is to discover a new route of synthesis for a target molecule for which there already exist known routes. Sometimes, however, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California State Normal School (now San José State University). This school was absorbed with the official founding of UCLA as the Southern Branch of the University of California in 1919, making it the second-oldest of the 10-campus University of California system (after UC Berkeley). UCLA offers 337 undergraduate and graduate degree programs in a wide range of disciplines, enrolling about 31,600 undergraduate and 14,300 graduate and professional students. UCLA received 174,914 undergraduate applications for Fall 2022, including transfers, making the school the most applied-to university in the United States. The university is organized into the College of Letters and Science and 12 professional schools. Six of the schools offer undergraduate deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
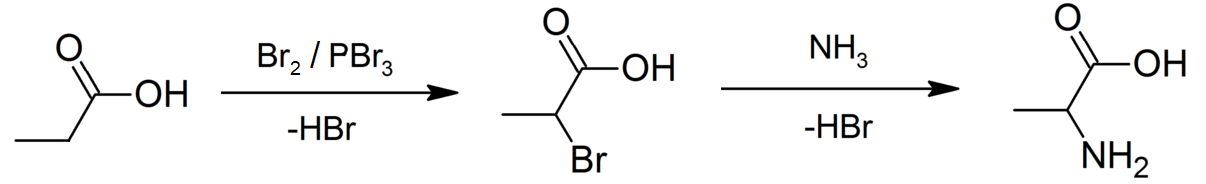
Propionic Acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2CO2H. It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion CH3CH2CO2− as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas established all the acids to be the same compound, which he called propionic acid, from the Greek words πρῶτος (prōtos), meaning ''first'', and πίων (piōn), meaning ''fat'', because it is the smallest H(CH2)''n''COOH acid that ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bounded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For example, protonation of methanol gives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrocyclic Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a macrocyclic ligand is a macrocyclic ring having at least nine atoms (including all hetero atoms) and three or more donor sites that serve as ligands that can bind to a central metal ion. Crown ethers and porphyrins are prominent examples. Macrocyclic ligands exhibit high affinity for metal ions. History Porphyrins and phthalocyanines have long been recognized as potent ligands in coordination chemistry as illustrated by numerous transition metal porphyrin complexes and the commercialization of copper phthalocyanine pigments. In the 1960s the synthesis of macrocylic ligands received much attention. One early contribution involved the synthesis of the "Curtis macrocycles", in which a metal ion serves as a template for ring formation. Polyether macrocycles - or "crown" ligands - were also developed at that time. A few years later, three-dimensional analogs of crown ethers called " cryptands" were reported by Lehn and co-workers. Macrocyclic effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amidine
Amidines are organic compounds with the functional group RC(NR)NR2, where the R groups can be the same or different. They are the imine derivatives of amides (RC(O)NR2). The simplest amidine is formamidine, HC(=NH)NH2. Examples of amidines include: * DBU * diminazene * benzamidine * Pentamidine * Paranyline Preparation A common route to primary amidines is the Pinner reaction. Reaction of the nitrile with alcohol in the presence of acid gives an iminoether. Treatment of the resulting compound with ammonia then completes the conversion to the amidine. Instead of using a Bronsted acid, Lewis acids such as aluminium trichloride promote the direct amination of nitriles. They are also generated by amination of an imidoyl chloride. They are also prepared by the addition of organolithium reagents to diimines, followed by protonation or alkylation. Dimethylformamide acetal reacts with primary amines to give amidines: :Me2NC(H)(OMe)2 + RNH2 → Me2NC=NHR + 2 MeOH Properties and appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinylogy
In organic chemistry, vinylogy is the transmission of electronic effects through a conjugated organic bonding system. The concept was introduced in 1926 by Ludwig Claisen to explain the acidic properties of formylacetone and related ketoaldehydes. Its adjectival form, vinylogous, is used to describe functional groups in which the standard moieties of the group are separated by a carbon–carbon double bond. For example, a carboxylic acid with a carbon-carbon double bond (, a "vinyl" moiety; actually a vinylene group) between a carbonyl group () and a hydroxyl group () is referred to as a ''vinylogous'' carboxylic acid. Due to the transmission of electronic information through conjugation, ''vinylogous'' functional groups often possess "''analogous''" reactivity or chemical properties compared to the parent functional group. Hence, vinylogy is a useful heuristic for the prediction of the behavior of systems that are structurally similar but contain intervening C=C bonds that ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color that is seen by our eyes is the one not absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavelength spectrum of visible light. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two separate molecular orbitals falls within the range of the visible spectrum. Visible light that hits the chromophore can thus be absorbed by exciting an electron from its ground state into an excited state. In biological molecules that serve to capture or detect light energy, the chromophore is the moiety that causes a conformational change in the molecule when hit by light. Conjugated pi-bond system chromophores Just like how two adjacent p-orbitals in a molecule will form a pi-bond, three or more adjacent p-orbitals in a molecule can form a conjugated pi-system. In a conjugated pi-system, electrons are able to capture certain photons as the electrons resonate along a certain di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to absorb energy from light. Chlorophylls absorb light most strongly in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum as well as the red portion. Conversely, it is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum. Hence chlorophyll-containing tissues appear green because green light, diffusively reflected by structures like cell walls, is less absorbed. Two types of chlorophyll exist in the photosystems of green plants: chlorophyll ''a'' and ''b''. History Chlorophyll was first isolated and named by Joseph Bienaimé Caventou and Pierre Joseph Pelletier in 1817. The presence of magnesium in chlorophyll was discovered in 1906, and was that element's first detection in living tissue. After initial work done by German ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). The parent of porphyrin is porphine, a rare chemical compound of exclusively theoretical interest. Substituted porphines are called porphyrins. With a total of 26 π-electrons, of which 18 π-electrons form a planar, continuous cycle, the porphyrin ring structure is often described as aromatic. One result of the large conjugated system is that porphyrins typically absorb strongly in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, i.e. they are deeply colored. The name "porphyrin" derives from the Greek word πορφύρα (''porphyra''), meaning ''purple''. Complexes of porphyrins Concomitant with the displacement of two N-''H'' protons, porphyrins bind metal ions in the N4 "pocket". The metal ion usually has a charge of 2+ or 3+. A schematic equation for these syntheses is shown: :H2porp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism. The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via pepti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpeg/1200px-Fall_Leaves_(199582361).jpeg)
