Biosynthesis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme- catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular
Reactant ->[][enzyme] Product
Some variations of this basic equation which will be discussed later in more detail are:
# Simple compounds which are converted into other compounds, usually as part of a multiple step reaction pathway. Two examples of this type of reaction occur during the formation of + ATP <=> + PP_i
# Simple compounds that are converted into other compounds with the assistance of cofactors. For example, the synthesis of + Cofactor ->[][enzyme] macromolecule
# Simple compounds that join to create a macromolecule. For example, fatty acids join to form phospholipids. In turn, phospholipids and cholesterol interact Noncovalent bonding, noncovalently in order to form the lipid bilayer. This reaction may be depicted as follows:
#:: + Molecule~2 -> macromolecule
 Many intricate macromolecules are synthesized in a pattern of simple, repeated structures. For example, the simplest structures of lipids are fatty acids. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon derivatives; they contain a carboxyl group "head" and a hydrocarbon chain "tail". These fatty acids create larger components, which in turn incorporate noncovalent interactions to form the lipid bilayer.
Fatty acid chains are found in two major components of membrane lipids: phospholipids and sphingolipids. A third major membrane component, cholesterol, does not contain these fatty acid units.
Many intricate macromolecules are synthesized in a pattern of simple, repeated structures. For example, the simplest structures of lipids are fatty acids. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon derivatives; they contain a carboxyl group "head" and a hydrocarbon chain "tail". These fatty acids create larger components, which in turn incorporate noncovalent interactions to form the lipid bilayer.
Fatty acid chains are found in two major components of membrane lipids: phospholipids and sphingolipids. A third major membrane component, cholesterol, does not contain these fatty acid units.
 The pathway starts with glycerol 3-phosphate, which gets converted to lysophosphatidate via the addition of a fatty acid chain provided by
The pathway starts with glycerol 3-phosphate, which gets converted to lysophosphatidate via the addition of a fatty acid chain provided by
 As the image denotes, during sphingosine synthesis, palmitoyl CoA and
As the image denotes, during sphingosine synthesis, palmitoyl CoA and
 More generally, this synthesis occurs in three stages, with the first stage taking place in the cytoplasm and the second and third stages occurring in the endoplasmic reticulum. The stages are as follows:
::1. The synthesis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate, the "building block" of cholesterol
::2. The formation of squalene via the condensation of six molecules of isopentenyl phosphate
::3. The conversion of squalene into cholesterol via several enzymatic reactions
More generally, this synthesis occurs in three stages, with the first stage taking place in the cytoplasm and the second and third stages occurring in the endoplasmic reticulum. The stages are as follows:
::1. The synthesis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate, the "building block" of cholesterol
::2. The formation of squalene via the condensation of six molecules of isopentenyl phosphate
::3. The conversion of squalene into cholesterol via several enzymatic reactions
 The DNA nucleotides
The DNA nucleotides
 Other DNA and RNA nucleotide bases that are linked to the ribose sugar via a glycosidic bond are thymine, cytosine and uracil (which is only found in RNA).
Uridine monophosphate biosynthesis involves an enzyme that is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and multifunctional enzymes that are located in the cytosol.
# The first step involves the enzyme
Other DNA and RNA nucleotide bases that are linked to the ribose sugar via a glycosidic bond are thymine, cytosine and uracil (which is only found in RNA).
Uridine monophosphate biosynthesis involves an enzyme that is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and multifunctional enzymes that are located in the cytosol.
# The first step involves the enzyme 
 Cytosine is a nucleotide that is present in both DNA and RNA. However, uracil is only found in RNA. Therefore, after UTP is synthesized, it is must be converted into a deoxy form to be incorporated into DNA. This conversion involves the enzyme ribonucleoside triphosphate reductase. This reaction that removes the 2'-OH of the ribose sugar to generate deoxyribose is not affected by the bases attached to the sugar. This non-specificity allows ribonucleoside triphosphate reductase to convert all nucleotide triphosphates to deoxyribonucleotide by a similar mechanism.
In contrast to uracil, thymine bases are found mostly in DNA, not RNA. Cells do not normally contain thymine bases that are linked to ribose sugars in RNA, thus indicating that cells only synthesize deoxyribose-linked thymine. The enzyme thymidylate synthetase is responsible for synthesizing thymine residues from
Cytosine is a nucleotide that is present in both DNA and RNA. However, uracil is only found in RNA. Therefore, after UTP is synthesized, it is must be converted into a deoxy form to be incorporated into DNA. This conversion involves the enzyme ribonucleoside triphosphate reductase. This reaction that removes the 2'-OH of the ribose sugar to generate deoxyribose is not affected by the bases attached to the sugar. This non-specificity allows ribonucleoside triphosphate reductase to convert all nucleotide triphosphates to deoxyribonucleotide by a similar mechanism.
In contrast to uracil, thymine bases are found mostly in DNA, not RNA. Cells do not normally contain thymine bases that are linked to ribose sugars in RNA, thus indicating that cells only synthesize deoxyribose-linked thymine. The enzyme thymidylate synthetase is responsible for synthesizing thymine residues from
 Although there are differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA synthesis, the following section denotes key characteristics of DNA replication shared by both organisms.
DNA is composed of nucleotides that are joined by phosphodiester bonds. DNA synthesis, which takes place in the nucleus, is a
Although there are differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA synthesis, the following section denotes key characteristics of DNA replication shared by both organisms.
DNA is composed of nucleotides that are joined by phosphodiester bonds. DNA synthesis, which takes place in the nucleus, is a
 The general structure of the standard amino acids includes a primary amino group, a carboxyl group and the functional group attached to the α-carbon. The different amino acids are identified by the functional group. As a result of the three different groups attached to the α-carbon, amino acids are asymmetrical molecules. For all standard amino acids, except glycine, the α-carbon is a chiral center. In the case of glycine, the α-carbon has two hydrogen atoms, thus adding symmetry to this molecule. With the exception of
The general structure of the standard amino acids includes a primary amino group, a carboxyl group and the functional group attached to the α-carbon. The different amino acids are identified by the functional group. As a result of the three different groups attached to the α-carbon, amino acids are asymmetrical molecules. For all standard amino acids, except glycine, the α-carbon is a chiral center. In the case of glycine, the α-carbon has two hydrogen atoms, thus adding symmetry to this molecule. With the exception of 
 There are two distinct lysine biosynthetic pathways: the diaminopimelic acid pathway and the α-aminoadipate pathway. The most common of the two synthetic pathways is the diaminopimelic acid pathway; it consists of several enzymatic reactions that add carbon groups to aspartate to yield lysine:
# Aspartate kinase initiates the diaminopimelic acid pathway by phosphorylating aspartate and producing aspartyl phosphate.
# Aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase catalyzes the
There are two distinct lysine biosynthetic pathways: the diaminopimelic acid pathway and the α-aminoadipate pathway. The most common of the two synthetic pathways is the diaminopimelic acid pathway; it consists of several enzymatic reactions that add carbon groups to aspartate to yield lysine:
# Aspartate kinase initiates the diaminopimelic acid pathway by phosphorylating aspartate and producing aspartyl phosphate.
# Aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase catalyzes the
 The diaminopimelic acid biosynthetic pathway of lysine belongs to the aspartate family of amino acids. This pathway involves nine enzyme-catalyzed reactions that convert aspartate to lysine.
# Aspartate kinase catalyzes the initial step in the diaminopimelic acid pathway by transferring a phosphoryl from ATP onto the carboxylate group of aspartate, which yields aspartyl-β-phosphate.
# Aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase catalyzes the reduction reaction by dephosphorylation of aspartyl-β-phosphate to yield aspartate-β-semialdehyde.
#
The diaminopimelic acid biosynthetic pathway of lysine belongs to the aspartate family of amino acids. This pathway involves nine enzyme-catalyzed reactions that convert aspartate to lysine.
# Aspartate kinase catalyzes the initial step in the diaminopimelic acid pathway by transferring a phosphoryl from ATP onto the carboxylate group of aspartate, which yields aspartyl-β-phosphate.
# Aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase catalyzes the reduction reaction by dephosphorylation of aspartyl-β-phosphate to yield aspartate-β-semialdehyde.
#

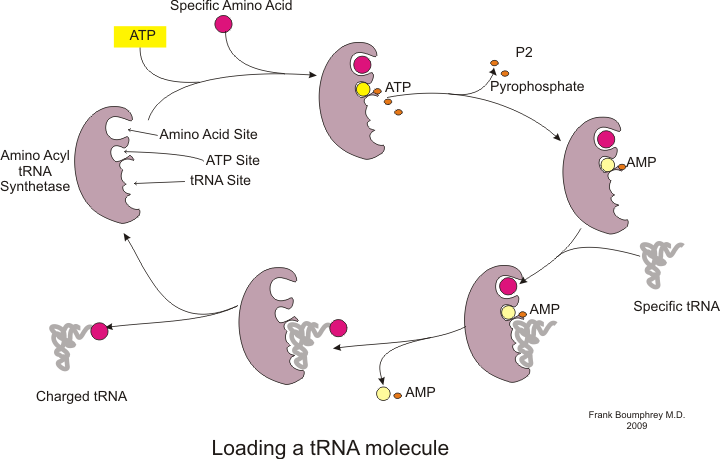 Protein synthesis occurs via a process called translation. During translation, genetic material called mRNA is read by ribosomes to generate a protein
Protein synthesis occurs via a process called translation. During translation, genetic material called mRNA is read by ribosomes to generate a protein
+ ATP <=> + PP_i
This is followed by the transfer of the aminoacyl group from aminoacyl-AMP to a tRNA molecule. The resulting molecule is aminoacyl-tRNA:
: + tRNA <=> + AMP
The combination of these two steps, both of which are catalyzed by aminoacyl tRNA synthetase, produces a charged tRNA that is ready to add amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain.
In addition to binding an amino acid, tRNA has a three nucleotide unit called an anticodon that

 Errors in biosynthetic pathways can have deleterious consequences including the malformation of macromolecules or the underproduction of functional molecules. Below are examples that illustrate the disruptions that occur due to these inefficiencies.
*
Errors in biosynthetic pathways can have deleterious consequences including the malformation of macromolecules or the underproduction of functional molecules. Below are examples that illustrate the disruptions that occur due to these inefficiencies.
*
organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the ...
, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all ...
ous with anabolism
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct molecules from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catabolism is the breaking-do ...
.
The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "How ...
(e.g. ATP
ATP may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* Association of Tennis Professionals, men's professional tennis governing body
* American Technical Publishers, employee-owned publishing company
* ', a Danish pension
* Armenia Tree Project, non ...
), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g. NADH, NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NAD ...
). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
, which are composed of amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.
Properties of chemical reactions
Biosynthesis occurs due to a series of chemical reactions. For these reactions to take place, the following elements are necessary: * Precursor compounds: these compounds are the starting molecules or substrates in a reaction. These may also be viewed as the reactants in a given chemical process. *Chemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "How ...
: chemical energy can be found in the form of high energy molecules. These molecules are required for energetically unfavorable reactions. Furthermore, the hydrolysis of these compounds drives a reaction forward. High energy molecules, such as ATP
ATP may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* Association of Tennis Professionals, men's professional tennis governing body
* American Technical Publishers, employee-owned publishing company
* ', a Danish pension
* Armenia Tree Project, non ...
, have three phosphates. Often, the terminal phosphate is split off during hydrolysis and transferred to another molecule.
* Catalysts: these may be for example metal ions or coenzymes and they catalyze a reaction by increasing the rate of the reaction and lowering the activation energy.
In the simplest sense, the reactions that occur in biosynthesis have the following format:
::nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
s and the charging of tRNA prior to translation. For some of these steps, chemical energy is required:
#::phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ...
s requires acetyl CoA, while the synthesis of another membrane component, sphingolipids, requires NADH and FADH for the formation the sphingosine backbone. The general equation for these examples is:
#::Lipid
 Many intricate macromolecules are synthesized in a pattern of simple, repeated structures. For example, the simplest structures of lipids are fatty acids. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon derivatives; they contain a carboxyl group "head" and a hydrocarbon chain "tail". These fatty acids create larger components, which in turn incorporate noncovalent interactions to form the lipid bilayer.
Fatty acid chains are found in two major components of membrane lipids: phospholipids and sphingolipids. A third major membrane component, cholesterol, does not contain these fatty acid units.
Many intricate macromolecules are synthesized in a pattern of simple, repeated structures. For example, the simplest structures of lipids are fatty acids. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon derivatives; they contain a carboxyl group "head" and a hydrocarbon chain "tail". These fatty acids create larger components, which in turn incorporate noncovalent interactions to form the lipid bilayer.
Fatty acid chains are found in two major components of membrane lipids: phospholipids and sphingolipids. A third major membrane component, cholesterol, does not contain these fatty acid units.
Phospholipids
The foundation of all biomembranes consists of abilayer
A bilayer is a double layer of closely packed atoms or molecules.
The properties of bilayers are often studied in condensed matter physics, particularly in the context of semiconductor devices, where two distinct materials are united to form junc ...
structure of phospholipids. The phospholipid molecule is amphipathic; it contains a hydrophilic polar head and a hydrophobic nonpolar tail. The phospholipid heads interact with each other and aqueous media, while the hydrocarbon tails orient themselves in the center, away from water. These latter interactions drive the bilayer structure that acts as a barrier for ions and molecules.
There are various types of phospholipids; consequently, their synthesis pathways differ. However, the first step in phospholipid synthesis involves the formation of phosphatidate or diacylglycerol 3-phosphate Phosphatidic acids are anionic phospholipids important to cell signaling and direct activation of lipid-gated ion channels. Hydrolysis of phosphatidic acid gives rise to one molecule each of glycerol and phosphoric acid and two molecules of fatty ac ...
at the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ( ...
and outer mitochondrial membrane. The synthesis pathway is found below:
acyl coenzyme A
Acyl-CoA is a group of coenzymes that metabolize fatty acids. Acyl-CoA's are susceptible to beta oxidation, forming, ultimately, acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle, eventually forming several equivalents of ATP. In this wa ...
. Then, lysophosphatidate is converted to phosphatidate via the addition of another fatty acid chain contributed by a second acyl CoA; all of these steps are catalyzed by the glycerol phosphate acyltransferase
Acyltransferase is a type of transferase enzyme that acts upon acyl groups.
Examples include:
* Glyceronephosphate O-acyltransferase
* Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase
*Long-chain-alcohol O-fatty-acyltransferase
In enzymology, a long-chain- ...
enzyme. Phospholipid synthesis continues in the endoplasmic reticulum, and the biosynthesis pathway diverges depending on the components of the particular phospholipid.
Sphingolipids
Like phospholipids, these fatty acid derivatives have a polar head and nonpolar tails. Unlike phospholipids, sphingolipids have a sphingosine backbone. Sphingolipids exist in eukaryotic cells and are particularly abundant in the central nervous system. For example, sphingomyelin is part of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers. Sphingolipids are formed from ceramides that consist of a fatty acid chain attached to the amino group of a sphingosine backbone. These ceramides are synthesized from the acylation of sphingosine. The biosynthetic pathway for sphingosine is found below: As the image denotes, during sphingosine synthesis, palmitoyl CoA and
As the image denotes, during sphingosine synthesis, palmitoyl CoA and serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form un ...
undergo a condensation reaction which results in the formation of dehydrosphingosine. This product is then reduced to form dihydrospingosine, which is converted to sphingosine via the oxidation reaction by FAD.
Cholesterol
This lipid belongs to a class of molecules calledsterols
Sterol is an organic compound with formula , whose molecule is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom in position 3 by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the gon ...
. Sterols have four fused rings and a hydroxyl group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy g ...
. Cholesterol is a particularly important molecule. Not only does it serve as a component of lipid membranes, it is also a precursor to several steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
hormones, including cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
It is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland ...
, testosterone, and estrogen.
Cholesterol is synthesized from acetyl CoA. The pathway is shown below:
Nucleotides
The biosynthesis of nucleotides involves enzyme- catalyzed reactions that convert substrates into more complex products. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA andRNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
. Nucleotides are composed of a five-membered ring formed from ribose sugar in RNA, and deoxyribose sugar in DNA; these sugars are linked to a purine or pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other ...
base with a glycosidic bond and a phosphate group at the 5' location of the sugar.
Purine nucleotides
adenosine
Adenosine ( symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside building ...
and guanosine consist of a purine base attached to a ribose sugar with a glycosidic bond. In the case of RNA nucleotides deoxyadenosine and deoxyguanosine, the purine bases are attached to a deoxyribose sugar with a glycosidic bond. The purine bases on DNA and RNA nucleotides are synthesized in a twelve-step reaction mechanism present in most single-celled organisms. Higher eukaryotes
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
employ a similar reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.
A chemical mechanism is a theoretical conjecture that tries to describe in detail what takes place at each stage of ...
in ten reaction steps. Purine bases are synthesized by converting phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) to inosine monophosphate (IMP), which is the first key intermediate in purine base biosynthesis. Further enzymatic modification of IMP produces the adenosine and guanosine bases of nucleotides.
# The first step in purine biosynthesis is a condensation reaction, performed by glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase. This enzyme transfers the amino group from glutamine to PRPP, forming 5-phosphoribosylamine
Phosphoribosylamine (PRA) is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, and hence is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin also contain fragments derived from PRA. ...
. The following step requires the activation of glycine by the addition of a phosphate group from ATP
ATP may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* Association of Tennis Professionals, men's professional tennis governing body
* American Technical Publishers, employee-owned publishing company
* ', a Danish pension
* Armenia Tree Project, non ...
.
# GAR synthetase performs the condensation of activated glycine onto PRPP, forming glycineamide ribonucleotide (GAR).
# GAR transformylase adds a formyl group onto the amino group of GAR, forming formylglycinamide ribonucleotide (FGAR).
# FGAR amidotransferase catalyzes the addition of a nitrogen group to FGAR, forming formylglycinamidine ribonucleotide (FGAM).
# FGAM cyclase catalyzes ring closure, which involves removal of a water molecule, forming the 5-membered imidazole ring 5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide (AIR).
# N5-CAIR synthetase transfers a carboxyl group, forming the intermediate N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide (N5-CAIR).
# N5-CAIR mutase rearranges the carboxyl functional group and transfers it onto the imidazole ring, forming carboxyamino- imidazole ribonucleotide (CAIR). The two step mechanism of CAIR formation from AIR is mostly found in single celled organisms. Higher eukaryotes contain the enzyme AIR carboxylase, which transfers a carboxyl group directly to AIR imidazole ring, forming CAIR.
# SAICAR synthetase forms a peptide bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
between aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the pro ...
and the added carboxyl group of the imidazole ring, forming N-succinyl-5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (SAICAR).
# SAICAR lyase removes the carbon skeleton of the added aspartate, leaving the amino group and forming 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR).
# AICAR transformylase
In enzymology, a phosphoribosylaminoimidazolecarboxamide formyltransferase (), also known by the shorter name AICAR transformylase, is an enzyme that catalyzes
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by ad ...
transfers a carbonyl group to AICAR, forming N-formylaminoimidazole- 4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (FAICAR).
# The final step involves the enzyme IMP synthase, which performs the purine ring closure and forms the inosine monophosphate intermediate.
Pyrimidine nucleotides
 Other DNA and RNA nucleotide bases that are linked to the ribose sugar via a glycosidic bond are thymine, cytosine and uracil (which is only found in RNA).
Uridine monophosphate biosynthesis involves an enzyme that is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and multifunctional enzymes that are located in the cytosol.
# The first step involves the enzyme
Other DNA and RNA nucleotide bases that are linked to the ribose sugar via a glycosidic bond are thymine, cytosine and uracil (which is only found in RNA).
Uridine monophosphate biosynthesis involves an enzyme that is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and multifunctional enzymes that are located in the cytosol.
# The first step involves the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthase
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase catalyzes the ATP-dependent synthesis
of carbamoyl phosphate from glutamine () or ammonia () and bicarbonate. This enzyme catalyzes the reaction of ATP and bicarbonate to produce carboxy phosphate and ADP. Carb ...
combining glutamine with CO2 in an ATP dependent reaction to form carbamoyl phosphate.
# Aspartate carbamoyltransferase condenses carbamoyl phosphate with aspartate to form uridosuccinate.
# Dihydroorotase performs ring closure, a reaction that loses water, to form dihydroorotate.
# Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DHODH'' gene on chromosome 16. The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the fourth enzymatic step, the ubiquinone-mediated oxidation of dihydroorotate to ...
, located within the mitochondrial inner membrane, oxidizes dihydroorotate to orotate.
# Orotate phosphoribosyl hydrolase (OMP pyrophosphorylase) condenses orotate with PRPP
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) is a pentose phosphate. It is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, as well as in pyrimidine nucleotide formation. Hence it is a building block for DNA ...
to form orotidine-5'-phosphate.
# OMP decarboxylase
Orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase (OMP decarboxylase) or orotidylate decarboxylase is an enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis. It catalyzes the decarboxylation of orotidine monophosphate (OMP) to form uridine monophosphate (UMP). The ...
catalyzes the conversion of orotidine-5'-phosphate to UMP.
After the uridine nucleotide base is synthesized, the other bases, cytosine and thymine are synthesized. Cytosine biosynthesis is a two-step reaction which involves the conversion of UMP to UTP. Phosphate addition to UMP is catalyzed by a kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
enzyme. The enzyme CTP synthase
CTP synthase is an enzyme () involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis that interconverts UTP and CTP.
Reaction mechanism
CTP (cytidine triphosphate) synthetase catalyzes the last committed step in pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis:
ATP + UTP + ...
catalyzes the next reaction step: the conversion of UTP to CTP by transferring an amino group from glutamine to uridine; this forms the cytosine base of CTP. The mechanism, which depicts the reaction UTP + ATP + glutamine ⇔ CTP + ADP + glutamate, is below:
 Cytosine is a nucleotide that is present in both DNA and RNA. However, uracil is only found in RNA. Therefore, after UTP is synthesized, it is must be converted into a deoxy form to be incorporated into DNA. This conversion involves the enzyme ribonucleoside triphosphate reductase. This reaction that removes the 2'-OH of the ribose sugar to generate deoxyribose is not affected by the bases attached to the sugar. This non-specificity allows ribonucleoside triphosphate reductase to convert all nucleotide triphosphates to deoxyribonucleotide by a similar mechanism.
In contrast to uracil, thymine bases are found mostly in DNA, not RNA. Cells do not normally contain thymine bases that are linked to ribose sugars in RNA, thus indicating that cells only synthesize deoxyribose-linked thymine. The enzyme thymidylate synthetase is responsible for synthesizing thymine residues from
Cytosine is a nucleotide that is present in both DNA and RNA. However, uracil is only found in RNA. Therefore, after UTP is synthesized, it is must be converted into a deoxy form to be incorporated into DNA. This conversion involves the enzyme ribonucleoside triphosphate reductase. This reaction that removes the 2'-OH of the ribose sugar to generate deoxyribose is not affected by the bases attached to the sugar. This non-specificity allows ribonucleoside triphosphate reductase to convert all nucleotide triphosphates to deoxyribonucleotide by a similar mechanism.
In contrast to uracil, thymine bases are found mostly in DNA, not RNA. Cells do not normally contain thymine bases that are linked to ribose sugars in RNA, thus indicating that cells only synthesize deoxyribose-linked thymine. The enzyme thymidylate synthetase is responsible for synthesizing thymine residues from dUMP
Dump generally refers to a place for disposal of solid waste, a rubbish dump, or landfill. The word has other uses alone or in combination, and may refer to:
* Midden, historically a dump for domestic waste
* Dump job, a term for criminal disposal ...
to dTMP. This reaction transfers a methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many ...
group onto the uracil base of dUMP to generate dTMP. The thymidylate synthase reaction, dUMP + 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate ⇔ dTMP + dihydrofolate, is shown to the right.
DNA
semiconservative
Semiconservative replication describe the mechanism of DNA replication in all known cells. DNA replication occurs on multiple origins of replication along the DNA template strand (antinsense strand). As the DNA double helix is unwound by helicase, ...
process, which means that the resulting DNA molecule contains an original strand from the parent structure and a new strand. DNA synthesis is catalyzed by a family of DNA polymerases that require four deoxynucleoside triphosphates, a template strand, and a primer
Primer may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Primer'' (film), a 2004 feature film written and directed by Shane Carruth
* ''Primer'' (video), a documentary about the funk band Living Colour
Literature
* Primer (textbook), a t ...
with a free 3'OH in which to incorporate nucleotides.
In order for DNA replication to occur, a replication fork is created by enzymes called helicases which unwind the DNA helix. Topoisomerase
DNA topoisomerases (or topoisomerases) are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues i ...
s at the replication fork remove supercoils caused by DNA unwinding, and single-stranded DNA binding proteins maintain the two single-stranded DNA templates stabilized prior to replication.
DNA synthesis is initiated by the RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the ...
primase, which makes an RNA primer with a free 3'OH. This primer is attached to the single-stranded DNA template, and DNA polymerase elongates the chain by incorporating nucleotides; DNA polymerase also proofreads the newly synthesized DNA strand.
During the polymerization reaction catalyzed by DNA polymerase, a nucleophilic attack occurs by the 3'OH of the growing chain on the innermost phosphorus atom of a deoxynucleoside triphosphate; this yields the formation of a phosphodiester bridge that attaches a new nucleotide and releases pyrophosphate.
Two types of strands are created simultaneously during replication: the leading strand, which is synthesized continuously and grows towards the replication fork, and the lagging strand, which is made discontinuously in Okazaki fragments and grows away from the replication fork. Okazaki fragments are covalently joined by DNA ligase to form a continuous strand.
Then, to complete DNA replication, RNA primers are removed, and the resulting gaps are replaced with DNA and joined via DNA ligase.
Amino acids
A protein is a polymer that is composed fromamino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
s that are linked by peptide bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
s. There are more than 300 amino acids found in nature of which only twenty, known as the standard amino acids, are the building blocks for protein. Only green plants and most microbes are able to synthesize all of the 20 standard amino acids that are needed by all living species. Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s can only synthesize ten of the twenty standard amino acids. The other amino acids, valine, methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
, leucine, isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprot ...
, phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino a ...
, lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −C ...
, threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO� ...
and tryptophan for adults and histidine, and arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the am ...
for babies are obtained through diet.
Amino acid basic structure
proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the prot ...
, all of the amino acids found in life have the L-isoform conformation. Proline has a functional group on the α-carbon that forms a ring with the amino group.
Nitrogen source
One major step in amino acid biosynthesis involves incorporating a nitrogen group onto the α-carbon. In cells, there are two major pathways of incorporating nitrogen groups. One pathway involves the enzyme glutamine oxoglutarate aminotransferase (GOGAT) which removes the amide amino group of glutamine and transfers it onto 2-oxoglutarate, producing twoglutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can syn ...
molecules. In this catalysis reaction, glutamine serves as the nitrogen source. An image illustrating this reaction is found to the right.
The other pathway for incorporating nitrogen onto the α-carbon of amino acids involves the enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH). GDH is able to transfer ammonia onto 2-oxoglutarate and form glutamate. Furthermore, the enzyme glutamine synthetase (GS) is able to transfer ammonia onto glutamate and synthesize glutamine, replenishing glutamine.
The glutamate family of amino acids
Theglutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can syn ...
family of amino acids includes the amino acids that derive from the amino acid glutamate. This family includes: glutamate, glutamine, proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the prot ...
, and arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the am ...
. This family also includes the amino acid lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −C ...
, which is derived from α-ketoglutarate.
The biosynthesis of glutamate and glutamine is a key step in the nitrogen assimilation discussed above. The enzymes GOGAT and GDH catalyze the nitrogen assimilation reactions.
In bacteria, the enzyme glutamate 5-kinase initiates the biosynthesis of proline by transferring a phosphate group from ATP onto glutamate. The next reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase (P5CS), which catalyzes the reduction of the ϒ-carboxyl group of L-glutamate 5-phosphate. This results in the formation of glutamate semialdehyde, which spontaneously cyclizes to pyrroline-5-carboxylate. Pyrroline-5-carboxylate is further reduced by the enzyme pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase (P5CR) to yield a proline amino acid.
In the first step of arginine biosynthesis in bacteria, glutamate is acetylated by transferring the acetyl group from acetyl-CoA at the N-α position; this prevents spontaneous cyclization. The enzyme N-acetylglutamate synthase (glutamate N-acetyltransferase) is responsible for catalyzing the acetylation step. Subsequent steps are catalyzed by the enzymes N-acetylglutamate kinase, N-acetyl-gamma-glutamyl-phosphate reductase
In enzymology, a N-acetyl-gamma-glutamyl-phosphate reductase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:N-acetyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + NADP+ + phosphate \rightleftharpoons N-acetyl-L-glutamyl 5-phosphate + NADPH + H+
The 3 su ...
, and acetylornithine/succinyldiamino pimelate aminotransferase and yield the N-acetyl-L-ornithine. The acetyl group of acetylornithine is removed by the enzyme acetylornithinase Acetylornithinase may refer to:
* Acetylornithine deacetylase, an enzyme
* Glutamate N-acetyltransferase
In enzymology, a glutamate N-acetyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:N2-acetyl-L-ornithine + L-glutamate \rig ...
(AO) or ornithine acetyltransferase (OAT), and this yields ornithine. Then, the enzymes citrulline and argininosuccinate convert ornithine to arginine.
 There are two distinct lysine biosynthetic pathways: the diaminopimelic acid pathway and the α-aminoadipate pathway. The most common of the two synthetic pathways is the diaminopimelic acid pathway; it consists of several enzymatic reactions that add carbon groups to aspartate to yield lysine:
# Aspartate kinase initiates the diaminopimelic acid pathway by phosphorylating aspartate and producing aspartyl phosphate.
# Aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase catalyzes the
There are two distinct lysine biosynthetic pathways: the diaminopimelic acid pathway and the α-aminoadipate pathway. The most common of the two synthetic pathways is the diaminopimelic acid pathway; it consists of several enzymatic reactions that add carbon groups to aspartate to yield lysine:
# Aspartate kinase initiates the diaminopimelic acid pathway by phosphorylating aspartate and producing aspartyl phosphate.
# Aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase catalyzes the NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NAD ...
-dependent reduction of aspartyl phosphate to yield aspartate semialdehyde.
# 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase
4-Hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase (EC 4.3.3.7, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydropicolinate synthetase, dihydrodipicolinic acid synthase, L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing), ''dapA (gene)'') is an en ...
adds a pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic aci ...
group to the β-aspartyl-4-semialdehyde, and a water molecule is removed. This causes cyclization and gives rise to (2S,4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate.
# 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate reductase
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate reductase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:(S)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine-2,6-dicarboxylate + NAD(P)+ + H2O \rightleftharpoons (2S,4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate ...
catalyzes the reduction of (2S,4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate by NADPH to yield Δ'-piperideine-2,6-dicarboxylate (2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate) and H2O.
# Tetrahydrodipicolinate acyltransferase catalyzes the acetylation reaction that results in ring opening and yields N-acetyl α-amino-ε-ketopimelate.
# N-succinyl-α-amino-ε-ketopimelate-glutamate aminotransaminase catalyzes the transamination reaction that removes the keto group of N-acetyl α-amino-ε-ketopimelate and replaces it with an amino group to yield N-succinyl-L-diaminopimelate.
# N-acyldiaminopimelate deacylase catalyzes the deacylation of N-succinyl-L-diaminopimelate to yield L,L-diaminopimelate.
# DAP epimerase catalyzes the conversion of L,L-diaminopimelate to the meso
Meso or mesos may refer to:
* Apache Mesos, a computer clustering management platform
* Meso, in-game currency for the massively multiplayer online role-playing game '' MapleStory''
* Meso compound, a stereochemical classification in chemistry
* ...
form of L,L-diaminopimelate.
# DAP decarboxylase catalyzes the removal of the carboxyl group, yielding L-lysine.
The serine family of amino acids
Theserine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form un ...
family of amino acid includes: serine, cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
, and glycine. Most microorganisms and plants obtain the sulfur for synthesizing methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
from the amino acid cysteine. Furthermore, the conversion of serine to glycine provides the carbons needed for the biosynthesis of the methionine and histidine.
During serine biosynthesis, the enzyme phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase catalyzes the initial reaction that oxidizes
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
3-phospho-D-glycerate to yield 3-phosphonooxypyruvate. The following reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme phosphoserine aminotransferase, which transfers an amino group from glutamate onto 3-phosphonooxypyruvate to yield L-phosphoserine. The final step is catalyzed by the enzyme phosphoserine phosphatase
The enzyme phosphoserine phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.3) catalyzes the reaction
:''O''-phospho-L(or D)-serine + H2O \rightleftharpoons L(or D)-serine + phosphate
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on phosphoric m ...
, which dephosphorylates L-phosphoserine to yield L-serine.
There are two known pathways for the biosynthesis of glycine. Organisms that use ethanol and acetate
An acetate is a salt (chemistry), salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. Alkali metal, alkaline, Alkaline earth metal, earthy, Transition metal, metallic, nonmetallic or radical Radical (chemistry), base). "Acetate" als ...
as the major carbon source utilize the glyconeogenic pathway to synthesize glycine. The other pathway of glycine biosynthesis is known as the glycolytic
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate (). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH ...
pathway. This pathway converts serine synthesized from the intermediates of glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate (). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH ...
to glycine. In the glycolytic pathway, the enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase catalyzes the cleavage of serine to yield glycine and transfers the cleaved carbon group of serine onto tetrahydrofolate, forming 5,10-methylene-tetrahydrofolate.
Cysteine biosynthesis is a two-step reaction that involves the incorporation of inorganic sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
. In microorganisms and plants, the enzyme serine acetyltransferase catalyzes the transfer of acetyl group from acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for ...
onto L-serine to yield O-acetyl-L-serine. The following reaction step, catalyzed by the enzyme O-acetyl serine (thiol) lyase, replaces the acetyl group of O-acetyl-L-serine with sulfide to yield cysteine.
The aspartate family of amino acids
Theaspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the pro ...
family of amino acids includes: threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO� ...
, lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −C ...
, methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
, isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprot ...
, and aspartate. Lysine and isoleucine are considered part of the aspartate family even though part of their carbon skeleton is derived from pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic aci ...
. In the case of methionine, the methyl carbon is derived from serine and the sulfur group, but in most organisms, it is derived from cysteine.
The biosynthesis of aspartate is a one step reaction that is catalyzed by a single enzyme. The enzyme aspartate aminotransferase catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from aspartate onto α-ketoglutarate to yield glutamate and oxaloacetate. Asparagine is synthesized by an ATP-dependent addition of an amino group onto aspartate; asparagine synthetase catalyzes the addition of nitrogen from glutamine or soluble ammonia to aspartate to yield asparagine.  The diaminopimelic acid biosynthetic pathway of lysine belongs to the aspartate family of amino acids. This pathway involves nine enzyme-catalyzed reactions that convert aspartate to lysine.
# Aspartate kinase catalyzes the initial step in the diaminopimelic acid pathway by transferring a phosphoryl from ATP onto the carboxylate group of aspartate, which yields aspartyl-β-phosphate.
# Aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase catalyzes the reduction reaction by dephosphorylation of aspartyl-β-phosphate to yield aspartate-β-semialdehyde.
#
The diaminopimelic acid biosynthetic pathway of lysine belongs to the aspartate family of amino acids. This pathway involves nine enzyme-catalyzed reactions that convert aspartate to lysine.
# Aspartate kinase catalyzes the initial step in the diaminopimelic acid pathway by transferring a phosphoryl from ATP onto the carboxylate group of aspartate, which yields aspartyl-β-phosphate.
# Aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase catalyzes the reduction reaction by dephosphorylation of aspartyl-β-phosphate to yield aspartate-β-semialdehyde.
# Dihydrodipicolinate synthase
4-Hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase (EC 4.3.3.7, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydropicolinate synthetase, dihydrodipicolinic acid synthase, L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing), ''dapA (gene)'') is an enz ...
catalyzes the condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to ...
reaction of aspartate-β-semialdehyde with pyruvate to yield dihydrodipicolinic acid.
# 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate reductase
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate reductase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:(S)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine-2,6-dicarboxylate + NAD(P)+ + H2O \rightleftharpoons (2S,4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate ...
catalyzes the reduction of dihydrodipicolinic acid to yield tetrahydrodipicolinic acid.
# Tetrahydrodipicolinate N-succinyltransferase catalyzes the transfer of a succinyl group from succinyl-CoA on to tetrahydrodipicolinic acid to yield N-succinyl-L-2,6-diaminoheptanedioate.
# N-succinyldiaminopimelate aminotransferase catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from glutamate onto N-succinyl-L-2,6-diaminoheptanedioate to yield N-succinyl-L,L-diaminopimelic acid.
# Succinyl-diaminopimelate desuccinylase
In enzymology, a succinyl-diaminopimelate desuccinylase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:N-succinyl-LL-2,6-diaminoheptanedioate + H2O \rightleftharpoons succinate + LL-2,6-diaminoheptanedioate
Thus, the two substrates of t ...
catalyzes the removal of acyl group from N-succinyl-L,L-diaminopimelic acid to yield L,L-diaminopimelic acid.
# Diaminopimelate epimerase
In enzymology, a diaminopimelate epimerase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:LL-2,6-diaminoheptanedioate \rightleftharpoons meso-diaminoheptanedioate
Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, LL-2,6-diaminoheptanedioate, and o ...
catalyzes the inversion of the α-carbon of L,L-diaminopimelic acid to yield meso-diaminopimelic acid.
# Siaminopimelate decarboxylase catalyzes the final step in lysine biosynthesis that removes the carbon dioxide group from meso-diaminopimelic acid to yield L-lysine.
Proteins
 Protein synthesis occurs via a process called translation. During translation, genetic material called mRNA is read by ribosomes to generate a protein
Protein synthesis occurs via a process called translation. During translation, genetic material called mRNA is read by ribosomes to generate a protein polypeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A p ...
chain. This process requires transfer RNA
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino ac ...
(tRNA) which serves as an adaptor by binding amino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
on one end and interacting with mRNA at the other end; the latter pairing between the tRNA and mRNA ensures that the correct amino acid is added to the chain. Protein synthesis occurs in three phases: initiation, elongation, and termination. Prokaryotic (archaeal
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebact ...
and bacterial) translation differs from eukaryotic translation; however, this section will mostly focus on the commonalities between the two organisms.
Additional background
Before translation can begin, the process of binding a specific amino acid to its corresponding tRNA must occur. This reaction, called tRNA charging, is catalyzed by aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. A specific tRNA synthetase is responsible for recognizing and charging a particular amino acid. Furthermore, this enzyme has special discriminator regions to ensure the correct binding between tRNA and its cognate amino acid. The first step for joining an amino acid to its corresponding tRNA is the formation of aminoacyl-AMP: :base pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
s with specific nucleotide triplets on the mRNA called codons
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links ...
; codons encode a specific amino acid. This interaction is possible thanks to the ribosome, which serves as the site for protein synthesis. The ribosome possesses three tRNA binding sites: the aminoacyl site (A site), the peptidyl site (P site), and the exit site (E site).
There are numerous codons within an mRNA transcript, and it is very common for an amino acid to be specified by more than one codon; this phenomenon is called degeneracy
Degeneracy, degenerate, or degeneration may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Degenerate'' (album), a 2010 album by the British band Trigger the Bloodshed
* Degenerate art, a term adopted in the 1920s by the Nazi Party in Germany to descri ...
. In all, there are 64 codons, 61 of each code for one of the 20 amino acids, while the remaining codons specify chain termination.
Translation in steps
As previously mentioned, translation occurs in three phases: initiation, elongation, and termination.Step 1: Initiation
The completion of the initiation phase is dependent on the following three events: 1. The recruitment of the ribosome to mRNA 2. The binding of a charged initiator tRNA into the P site of the ribosome 3. The proper alignment of the ribosome with mRNA's start codonStep 2: Elongation
Following initiation, the polypeptide chain is extended via anticodon:codon interactions, with the ribosome adding amino acids to the polypeptide chain one at a time. The following steps must occur to ensure the correct addition of amino acids: 1. The binding of the correct tRNA into the A site of the ribosome 2. The formation of apeptide bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
between the tRNA in the A site and the polypeptide chain attached to the tRNA in the P site
3. Translocation
Translocation may refer to:
* Chromosomal translocation, a chromosome abnormality caused by rearrangement of parts
** Robertsonian translocation, a chromosomal rearrangement in pairs 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22
** Nonreciprocal translocation, transfer ...
or advancement of the tRNA-mRNA complex by three nucleotides
Translocation "kicks off" the tRNA at the E site and shifts the tRNA from the A site into the P site, leaving the A site free for an incoming tRNA to add another amino acid.
Step 3: Termination
The last stage of translation occurs when a stop codon enters the A site. Then, the following steps occur: 1. The recognition of codons byrelease factor
A release factor is a protein that allows for the termination of translation by recognizing the termination codon or stop codon in an mRNA sequence. They are named so because they release new peptides from the ribosome.
Background
During t ...
s, which causes the hydrolysis of the polypeptide chain from the tRNA located in the P site
2. The release of the polypeptide chain
3. The dissociation and "recycling" of the ribosome for future translation processes
A summary table of the key players in translation is found below:
Diseases associated with macromolecule deficiency
 Errors in biosynthetic pathways can have deleterious consequences including the malformation of macromolecules or the underproduction of functional molecules. Below are examples that illustrate the disruptions that occur due to these inefficiencies.
*
Errors in biosynthetic pathways can have deleterious consequences including the malformation of macromolecules or the underproduction of functional molecules. Below are examples that illustrate the disruptions that occur due to these inefficiencies.
*Familial hypercholesterolemia
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL cholesterol), in the blood and early cardiovascular disease. The most common mutatio ...
: this disorder is characterized by the absence of functional receptors for LDL. Deficiencies in the formation of LDL receptors may cause faulty receptors which disrupt the endocytic pathway, inhibiting the entry of LDL into the liver and other cells. This causes a buildup of LDL in the blood plasma, which results in atherosclerotic plaques
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usually no sy ...
that narrow arteries and increase the risk of heart attacks.
* Lesch–Nyhan syndrome: this genetic disease is characterized by self- mutilation, mental deficiency, and gout. It is caused by the absence of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) is an enzyme encoded in humans by the ''HPRT1'' gene.
HGPRT is a transferase that catalyzes conversion of hypoxanthine to inosine monophosphate and guanine to guanosine monophosphate. This r ...
, which is a necessary enzyme for purine nucleotide formation. The lack of enzyme reduces the level of necessary nucleotides and causes the accumulation of biosynthesis intermediates, which results in the aforementioned unusual behavior.
* Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID): SCID is characterized by a loss of T cells. Shortage of these immune system components increases the susceptibility to infectious agents because the affected individuals cannot develop immunological memory. This immunological disorder results from a deficiency in adenosine deanimase activity, which causes a buildup of dATP. These dATP molecules then inhibit ribonucleotide reductase, which prevents of DNA synthesis.
* Huntington's disease: this neurological disease is caused from errors that occur during DNA synthesis. These errors or mutations lead to the expression of a mutant huntingtin protein, which contains repetitive glutamine residues that are encoded by expanding CAG trinucleotide repeats in the gene. Huntington's disease is characterized by neuronal loss and gliosis. Symptoms of the disease include: movement disorder, cognitive
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
decline, and behavioral disorder.
See also
* Lipids * Phospholipid bilayer * Nucleotides * DNA * DNA replication * Proteinogenic amino acid *Codon table
A codon table can be used to translate a genetic code into a sequence of amino acids. The standard genetic code is traditionally represented as an RNA codon table, because when proteins are made in a cell by ribosomes, it is messenger RNA (mRNA) t ...
* Prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derive ...
* Porphyrins
* Chlorophylls and bacteriochlorophylls
* Vitamin B12
References
{{Authority control Metabolism