|
Sterols
Sterol is an organic compound with formula , whose molecule is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom in position 3 by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the gonane structure, additional functional groups, and/or modified ring systems derived from gonane are called steroids. Therefore, sterols are a subgroup of the steroids. They occur naturally in most eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi, and can also be produced by some bacteria (however likely with different functions). The most familiar type of animal sterol is cholesterol, which is vital to cell membrane structure, and functions as a precursor to fat-soluble vitamins and steroid hormones. While technically alcohols, sterols are classified by biochemists as lipids ( fats in the broader sense of the term). Types Sterols of plants are called '' phytosterols'' and sterols of animals are called ''zoosterols''. The most impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phytosterols extracted from oils are insoluble in water, relatively insoluble in oil, and soluble in alcohols. Phytosterol-enriched foods and dietary supplements have been marketed for decades. Despite well-documented LDL cholesterol-lowering effects from long-term consumption of phytosterols, there is insufficient evidence for an effect on cardiovascular diseases, fasting blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin, or overall mortality rate. Structure They have a fused polycyclic structure and vary in carbon side chains and / or presence or absence of a double bond (saturation). They are divided into 4,4-dimethyl phytosterols, 4-monomethyl phytosterols, and 4-desmethyl phytosterols based on the location of methyl groups at the carbon-4 position. St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campesterol
Campesterol is a phytosterol whose chemical structure is similar to that of cholesterol, and is one of the ingredients for E number E499. Natural occurrences Many vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds contain campesterol, but in low concentrations. Banana, pomegranate, pepper, coffee, grapefruit, cucumber, onion, oat, potato, and lemon grass (citronella) are few examples of common sources containing campesterol at roughly 1–7 mg/100 g of the edible portion. In contrast, canola and corn oils contain as much as 16–100 mg/100 g. Levels are variable and are influenced by geography and growing environment. In addition, different strains have different levels of plant sterols. A number of new genetic strains are currently being engineered with the goal of producing varieties high in campesterol and other plant sterols. It is also found in dandelion coffee. It is so named because it was first isolated from the rapeseed (''Brassica campestris''). It is thought to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid. Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as '' Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine". Etymology The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek ''chole- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/ unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or that are synthetic in order to increase the quantity of their consumption. The class of nutrient compounds includes vitamins, minerals, fiber, fatty acids, and amino acids. Dietary supplements can also contain substances that have not been confirmed as being essential to life, but are marketed as having a beneficial biological effect, such as plant pigments or polyphenols. Animals can also be a source of supplement ingredients, such as collagen from chickens or fish for example. These are also sold individually and in combination, and may be combined with nutrient ingredients. The European Commission has also established harmonized rules to help insure that food supplements are safe and appropriately labeled. Creating an industry estimated to have a 2020 value of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol ( opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ergosterol
Ergosterol (ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol) is a sterol found in cell membranes of fungi and protozoa, serving many of the same functions that cholesterol serves in animal cells. Because many fungi and protozoa cannot survive without ergosterol, the enzymes that synthesize it have become important targets for drug discovery. In human nutrition, ergosterol is a provitamin form of vitamin D2; exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light causes a chemical reaction that produces vitamin D2. Role in fungi Ergosterol (ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol) is a sterol found in fungi, and named for ergot, the common name of members of the fungal genus '' Claviceps'' from which ergosterol was first isolated. Ergosterol is a component of yeast and other fungal cell membranes, serving many of the same functions that cholesterol serves in animal cells. Its specificity in higher fungi is thought to be related to the climatic instabilities (highly varying humidity and moisture conditions) encountered by these org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
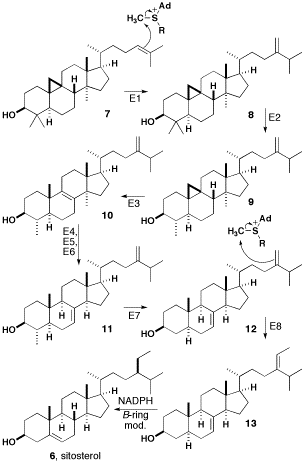
Sitosterol
β-sitosterol (beta-sitosterol) is one of several phytosterols (plant sterols) with chemical structures similar to that of cholesterol. It is a white, waxy powder with a characteristic odor, and is one of the components of the food additive E499. Phytosterols are hydrophobic and soluble in alcohols. Natural occurrences and food β-sitosterol is widely distributed in the plant kingdom. It is found in vegetable oil, nuts, avocados, and derived prepared foods such as salad dressings. Human research β-sitosterol is being studied for its potential to reduce benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and blood cholesterol levels. Genetic disorder While plant sterols are usually beneficial, there is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder phytosterolemia which causes over-absorption of phytosterols. Precursor of anabolic steroid boldenone Being a steroid, β-sitosterol is a precursor of anabolic steroid boldenone. Boldenone undecylenate is commonly used in veterinary medicine to indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stigmasterol
Stigmasterol – a plant sterol (''phytosterol'') – is among the most abundant of plant sterols, having a major function to maintain the structure and physiology of cell membranes. In the European Union, it is a food additive listed with E number E499, and may be used in food manufacturing to increase the phytosterol content, potentially lowering the levels of LDL cholesterol. Discovery Once called ''Wulzen factor'' in the mid-20th century, stigmasterol was discovered by the University of California physiologist Rosalind Wulzen (born 1886). Natural occurrences Stigmasterol is an unsaturated phytosterol occurring in the plant fats or oils of numerous plants, such as soybean, calabar bean, and rape seed, and in herbs used in herbalism practices, including the Chinese herbs '' Ophiopogon japonicus'' (Mai men dong), in ''Mirabilis jalapa''. Stigmasterol is a constituent of various vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and unpasteurized milk. Pasteurization will inactivate st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon- hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Livin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |