|
Captorhinid
Captorhinidae (also known as cotylosaurs) is an extinct family of tetrapods, traditionally considered primitive reptiles, known from the late Carboniferous to the Late Permian. They had a cosmopolitan distribution across Pangea. Description Captorhinids are a clade of small to very large lizard-like reptiles that date from the late Carboniferous through the Permian. Their skulls were much stronger than those of their relatives, the Protorothyrididae, and had teeth that were better able to deal with tough plant material. The postcranial skeleton is very similar to that of advanced reptiliomorph amphibians, so much in fact that the amphibian Seymouriamorpha and Diadectomorpha were thought to be reptiles and grouped together in "Cotylosauria" as the first reptiles in the early 20th century. Captorhinids have broad, robust skulls that are generally triangular in shape when seen in dorsal view. The premaxillae are characteristically downturned. The largest captorhinid, the herbivorous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captorhinus Kierani
''Captorhinus'' (from el, καπτō , 'to gulp down' and el, ῥῑνός , 'nose') is an extinct genus of captorhinid reptiles that lived during the Permian period. Its remains are known from Oklahoma, Texas, Europe, India, the Pedra de Fogo Formation, Parnaíba Basin, Brazil and the Madumabisa Mudstone, Zambia. Description While there are several forms of ''Captorhinus'', there are three main species that are the best known. The previously mentioned ''Captorhinus aguti'' is the type species of ''Captorhinus'', but there is also a fair amount of material collected on ''Captorhinus magnus'' and ''Captorhinus laticeps''. The most distinguishable trait of ''Captorhinus'' is its namesake: the hooking of the snout from prominent ventral angulation of the premaxillary process. Other notable characteristics include the dorsally positioned alary process of the jugal on the medial surface and flushed with the orbital margin, the retroarticular process longer anteroposteriorly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captorhinus
''Captorhinus'' (from el, καπτō , 'to gulp down' and el, ῥῑνός , 'nose') is an extinct genus of captorhinid reptiles that lived during the Permian period. Its remains are known from Oklahoma, Texas, Europe, India, the Pedra de Fogo Formation, Parnaíba Basin, Brazil and the Madumabisa Mudstone, Zambia. Description While there are several forms of ''Captorhinus'', there are three main species that are the best known. The previously mentioned ''Captorhinus aguti'' is the type species of ''Captorhinus'', but there is also a fair amount of material collected on ''Captorhinus magnus'' and ''Captorhinus laticeps''. The most distinguishable trait of ''Captorhinus'' is its namesake: the hooking of the snout from prominent ventral angulation of the premaxillary process. Other notable characteristics include the dorsally positioned alary process of the jugal on the medial surface and flushed with the orbital margin, the retroarticular process longer anteroposteriorly th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
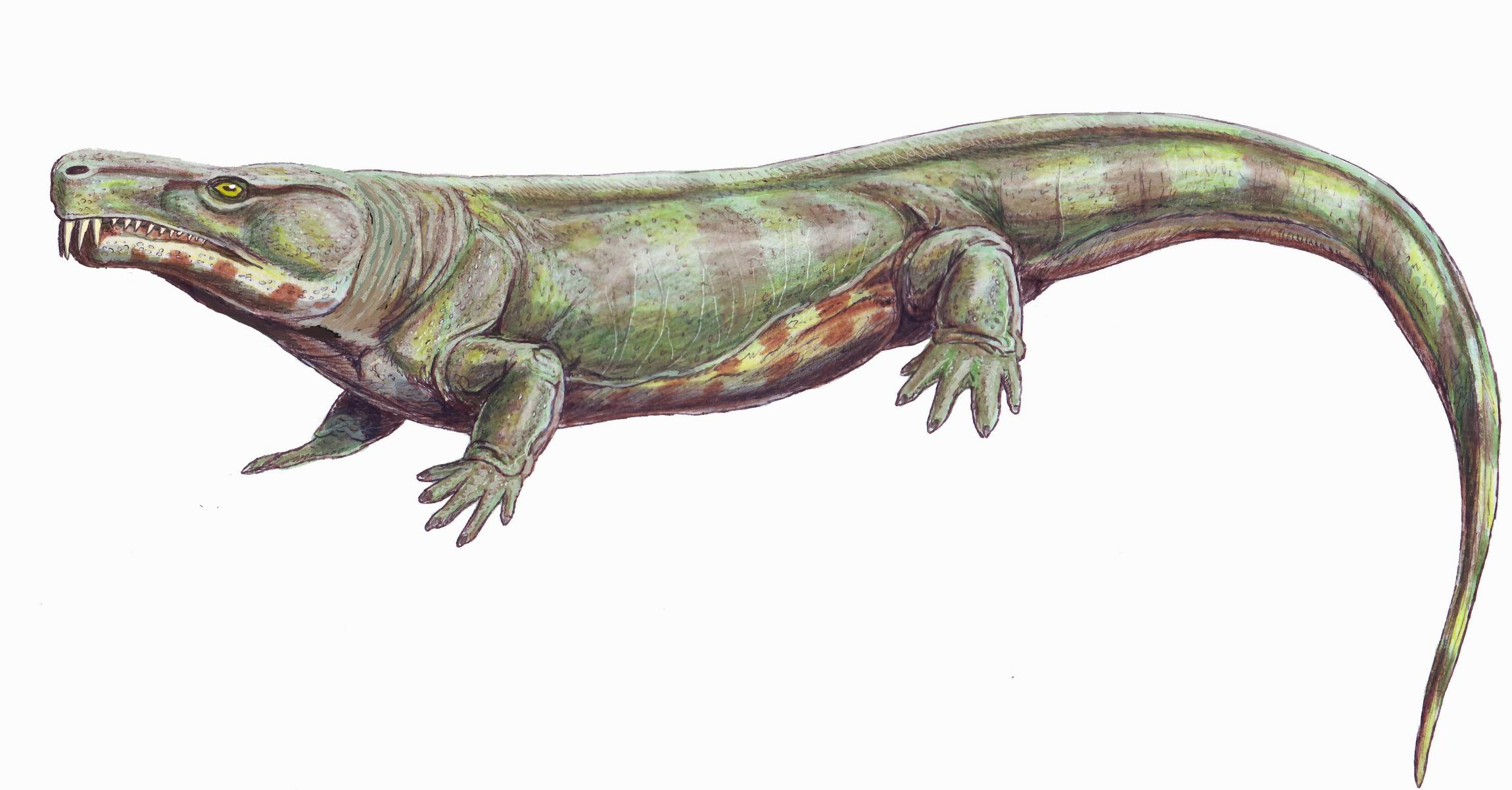
Thuringothyris
''Thuringothyris'' is an extinct genus of Early Permian eureptiles known from the Thuringian Forest in central Germany. Description ''Thuringothyris'' is known from the holotype MNG 7729, articulated well-preserved skull and partial postcranial skeleton, and from the referred specimens MNG 10652, poorly preserved skull and partial vertebral column, MNG 10647, disarticulated cranial and postcranial remains of at least four individuals, MNG 10183, slightly crushed skull and partial postcranial skeleton and MNG 11191, poorly preserved skull and partial limbs. All specimens were collected from the Tambach-Sandstein Member, the uppermost part of the Tambach Formation, dating to the Artinskian stage of the Late Cisuralian Series (or alternatively upper Rotliegend), about 284–279.5 million years ago. They were found in the Bromacker Quarry, the middle part of the Thuringian Forest, near the small town of Tambach-Dietharz. ''Thuringothyris'' was originally tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concordia Cunninghami
''Euconcordia'' is an extinct genus of Late Carboniferous captorhinid known from Greenwood County, Kansas of the United States. Description ''Euconcordia'' is known from the holotype KUVP 8702a&b, well preserved skull in dorsal view along with its counterpart, a partial preserved braincase in ventral view, and from the referred specimen KUVP 96/95, well preserved skull in ventral view and a poorly preserved dorsal counterpart. It was collected in the Hamilton Quarry, from the Calhouns Shale Formation of the Shawnee Group, dating to the Virgilian stage (or alternatively late Kasimovian to early Gzhelian stage) of the Late Pennsylvanian Series, about 300 million years ago. ''Euconcordia'' was originally thought to be the basalmost known member of Captorhinidae. A novel phylogenic study of primitive reptile relationships by Müller & Reisz in 2006 recovered ''Thuringothyris'' as a sister taxon of the Captorhinidae, and therefore, by definition, ''Thuringothyris'' repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiliomorph
Reptiliomorpha (meaning reptile-shaped; in PhyloCode known as ''Pan-Amniota'') is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians ( lissamphibians). It was defined by Michel Laurin (2001) and Vallin and Laurin (2004) as the largest clade that includes ''Homo sapiens'', but not ''Ascaphus truei'' (tailed frog). Laurin and Reisz (2020) defined Pan-Amniota as the largest total clade containing ''Homo sapiens'', but not ''Pipa pipa'', '' Caecilia tentaculata'', and '' Siren lacertina''. The informal variant of the name, "reptiliomorphs", is also occasionally used to refer to stem-amniotes, i.e. a grade of reptile-like tetrapods that are more closely related to amniotes than they are to lissamphibians, but are not amniotes themselves; the name is used in this meaning e.g. by Ruta, Coates and Quicke (2003). An alternative name, "Anthracosauria", is also commonly used for the group, but is confusing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsid, sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, Squamata, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean taxonomy, Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern Cladistics, cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile Order (biology), orders, historically combined with that of modern amphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autotomy
Autotomy (from the Greek language, Greek ''auto-'', "self-" and ''tome'', "severing", wikt:αὐτοτομία, αὐτοτομία) or self-amputation, is the behaviour whereby an animal sheds or discards one or more of its own appendages, usually as a self-preservation, self-defense mechanism to elude a predation, predator's grasp or to distract the predator and thereby allow escape. Some animals have the ability to regeneration (biology), regenerate the lost body part later. Autotomy has multiple evolutionary origins and is thought to have evolved at least nine times independently in animalia. The term was coined in 1883 by Léon Fredericq, Leon Fredericq. Vertebrates Reptiles and amphibians Some lizards, salamanders and tuatara when caught by the tail will shed part of it in attempting to escape. In many species the detached tail will continue to wriggle, creating a deceptive sense of continued struggle, and distracting the predator's attention from the fleeing prey animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labidosaurus
''Labidosaurus'' (from el, λᾰβῐ́δος , 'forceps' and el, σαῦρος , 'lizard') is an extinct genus of reptile from the Permian period of North America. Fossils have been discovered in Texas. It was heavily built, resembling a lizard with a large head, and measuring about long. Unlike many other captorhinids it had a single row of sharp, conical teeth in its jaws, and its dietary habits are assumed to have been omnivore, omnivorous. A lower jaw of ''Labidosaurus'' was described in 2011 that shows evidence of osteomyelitis, or an infection of the bone. It is the earliest known example of an infection in a land vertebrate. The infection probably developed because the Pulp (tooth), pulp cavity of a broken dentary tooth was exposed to bacteria. Although another tooth would have replaced the broken one, regeneration would have been slow. ''Labidosaurus'' and other derived captorhinids had teeth that were deeply implanted in the jaws. This deep implantation limited toot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seymouriamorpha
Seymouriamorpha were a small but widespread group of limbed vertebrates (tetrapods). They have long been considered reptiliomorphs, and most paleontologists may still accept this point of view, but some analyses suggest that seymouriamorphs are stem-tetrapods (not more closely related to Amniota than to Lissamphibia). Many seymouriamorphs were terrestrial or semi-aquatic. However, aquatic larvae bearing external gills and grooves from the lateral line system have been found, making them unquestionably amphibians. The adults were terrestrial. They ranged from lizard-sized creatures (30 centimeters) to crocodile-sized 150 centimeter long animals. They were reptile-like. If seymouriamorphs are reptiliomorphs, they were the distant relatives of amniotes. Seymouriamorphs form into three main groups, Kotlassiidae, Discosauriscidae, and Seymouriidae, a group that includes the best known genus, ''Seymouria''. The last seymouriamorph became extinct by the end of the Permian. Taxonomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadectomorpha
Diadectomorpha is a clade of large tetrapods that lived in Euramerica during the Carboniferous and Early Permian periods and in Asia during Late Permian (Wuchiapingian), They have typically been classified as advanced reptiliomorphs (transitional between "amphibians" ''sensu lato'' and amniotes) positioned close to, but outside of the clade Amniota, though some recent research has recovered them as the sister group to the traditional Synapsida within Amniota, based on inner ear anatomy and cladistic analyses. They include both large (up to 2 meters long) carnivorous and even larger (to 3 meters) herbivorous forms, some semi-aquatic and others fully terrestrial. The diadectomorphs seem to have originated during late Mississippian times, although they only became common after the Carboniferous rainforest collapse and flourished during the Late Pennsylvanian and Early Permian periods. Anatomy Diadectomorphs possessed both amphibian-like and amniote-like characteristics. Originall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvanian (geology)
The Pennsylvanian ( , also known as Upper Carboniferous or Late Carboniferous) is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two period (geology), subperiods (or upper of two system (stratigraphy), subsystems) of the Carboniferous Period. It lasted from roughly . As with most other geochronology, geochronologic units, the stratum, rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain by a few hundred thousand years. The Pennsylvanian is named after the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, where the coal-productive beds of this age are widespread. The division between Pennsylvanian and Mississippian (geology), Mississippian comes from North American stratigraphy. In North America, where the early Carboniferous beds are primarily marine limestones, the Pennsylvanian was in the past treated as a full-fledged geologic period between the Mississippian and the Permian. In parts of Europe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |