|
Battle Of The Tanais River
The Battle of the Tanais River in 373 AD between the Huns and the Alans, was fought on the traditional border between Asia and Europe. The Huns were victorious. Some historians credit this battle as the beginning of the process of Germanic migration, in which the Huns pushed Germanic tribes into central and northern Europe, resulting in many conflicts between those tribes and the Roman Empire. It was followed by a joint Hun-Alan invasion of the Gothic kingdom of Ermanaric. See also * Germanic migrations Sources * Spencer C. Tucker - A Global Chronology of Conflict: From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East volumes From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East - 2777 pages - - p. 162 * John Keegan - A History of Warfare - 1994 - 432 pages - - page 184 Otto Maenchen-Helfen, Otto Helfen «The World of the Huns: Studies in Their History and Culture» Literature * William Rosen - Justinian's Flea: Plague, Empire, and the Birth of Europe - 2007 - Viking - 367 pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time; the Huns' arrival is associated with the migration westward of an Iranian people, the Alans. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, and by 430, they had established a vast, if short-lived, dominion in Europe, conquering the Goths and many other Germanic peoples living outside of Roman borders and causing many others to flee into Roman territory. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they invaded Italy. After the death of Attila in 453, the Huns ceased to be a major thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
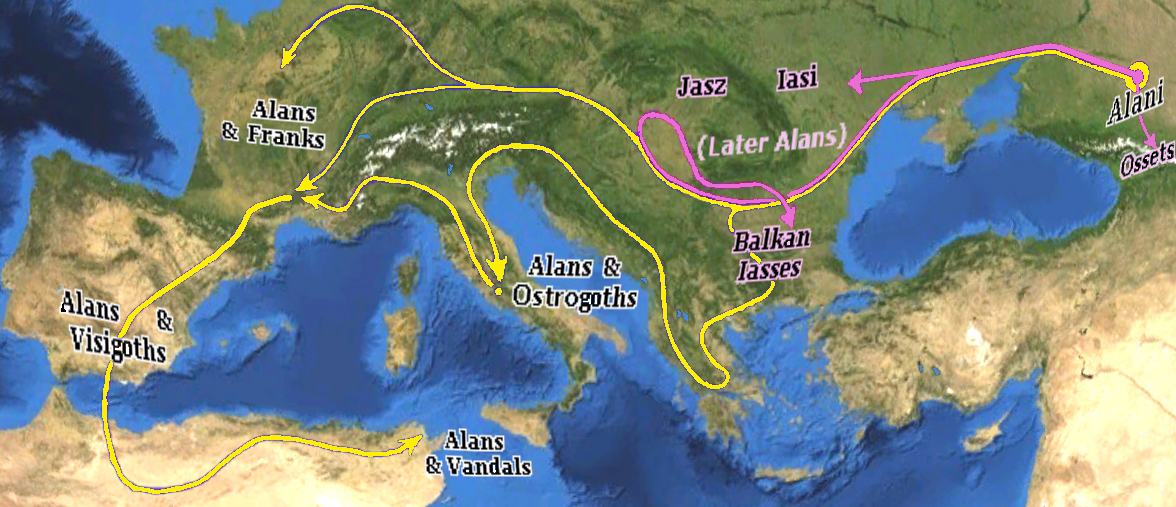
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don River, Russia
The Don ( rus, Дон, p=don) is the fifth-longest river in Europe. Flowing from Central Russia to the Sea of Azov in Southern Russia, it is one of Russia's largest rivers and played an important role for traders from the Byzantine Empire. Its basin is between the Dnieper basin to the west, the lower Volga basin immediately to the east, and the Oka basin (tributary of the Volga) to the north. Native to much of the basin were Slavic nomads. The Don rises in the town of Novomoskovsk southeast of Tula (in turn south of Moscow), and flows 1,870 kilometres to the Sea of Azov. The river's upper half ribbles (meanders subtly) south; however, its lower half consists of a great eastern curve, including Voronezh, making its final stretch, an estuary, run west south-west. The main city on the river is Rostov-on-Don. Its main tributary is the Seversky Donets, centred on the mid-eastern end of Ukraine, thus the other country in the overall basin. To the east of a series of three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area of , about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8.7% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. In general terms, Asia is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents of Earth#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century, having crossed the Lower Danube. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under the influence of the Amal dynasty, the family of Theodoric the Great. After the death of Attila and collapse of the Hunnic empire represented by the Battle of Nedao in 453, the Amal family began to form their kingdom in Pannonia. Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Zeno (emperor), Emperor Zeno played these Pannonian Goths off against the Thracian Goths, but instead the two groups united after the death of the Thracian leader Theoderic Strabo and his son Recitach. Zeno then backed Theodori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ermanaric
Ermanaric; la, Ermanaricus or ''Hermanaricus''; ang, Eormanrīc ; on, Jǫrmunrekkr , gmh, Ermenrîch (died 376) was a Greuthungian Gothic king who before the Hunnic invasion evidently ruled a sizable portion of Oium, the part of Scythia inhabited by the Goths at the time. He is mentioned in two Roman sources: the contemporary writings of Ammianus Marcellinus, and in ''Getica'' by the sixth-century historian Jordanes. He also appears in a fictionalized form in later Germanic heroic legends. Modern historians disagree on the size of Ermanaric's realm. Herwig Wolfram postulates that he at one point ruled a realm stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea as far eastwards as the Ural Mountains. Peter Heather is skeptical of the claim that Ermanaric ruled all Goths except the Tervingi, and furthermore points to the fact that such an enormous empire would have been larger than any known Gothic political unit, that it would have left bigger traces in the sources and that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Migrations
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman kingdoms. The term refers to the important role played by the migration, invasion, and settlement of various tribes, notably the Franks, Goths, Alemanni, Alans, Huns, early Slavs, Pannonian Avars, Magyars, and Bulgars within or into the former Western Empire and Eastern Europe. The period is traditionally taken to have begun in AD 375 (possibly as early as 300) and ended in 568. Various factors contributed to this phenomenon of migration and invasion, and their role and significance are still widely discussed. Historians differ as to the dates for the beginning and ending of the Migration Period. The beginning of the period is widely regarded as the invasion of Europe by the Huns from Asia in about 375 and the ending with the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spencer C
Spencer may refer to: People *Spencer (surname) **Spencer family, British aristocratic family ** List of people with surname Spencer * Spencer (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name) Places Australia *Spencer, New South Wales, on the Central Coast * Spencer Gulf, one of two inlets on the South Australian coast United States *Spencer, Idaho *Spencer, Indiana *Spencer, Iowa *Spencer, Massachusetts **Spencer (CDP), Massachusetts *Spencer, Missouri * Spencer, Nebraska *Spencer, New York **Spencer (village), New York *Spencer, North Carolina *Spencer, Ohio *Spencer, Oklahoma *Spencer, South Dakota *Spencer, Tennessee *Spencer, Virginia *Spencer, West Virginia *Spencer, Wisconsin **Spencer (town), Wisconsin *Spencer County, Indiana *Spencer County, Kentucky Ireland *Spencer Dock, North Wall, Dublin Arts and entertainment Fictional characters *Spencer, character in ''Beyblade'' *Spencer, character from ''Final Fantasy Mystic Quest'' * Spencer family (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Keegan
Sir John Desmond Patrick Keegan (15 May 1934 – 2 August 2012) was an English military historian, lecturer, author and journalist. He wrote many published works on the nature of combat between prehistory and the 21st century, covering land, air, maritime, intelligence warfare and the psychology of battle. Life and career At the age of 13, Keegan contracted orthopaedic tuberculosis, which subsequently affected his gait. The long-term effects of this rendered him unfit for military service, and the timing of his birth made him too young for service in the Second World War, facts he mentioned in his works as an ironic observation on his profession and interests. The illness also interrupted his education in his teenage years, although it included a period at King's College, Taunton and two years at Wimbledon College, which led to entry to Balliol College, Oxford in 1953, where he read history with an emphasis on war theory. After graduation he worked at the American Embassy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)