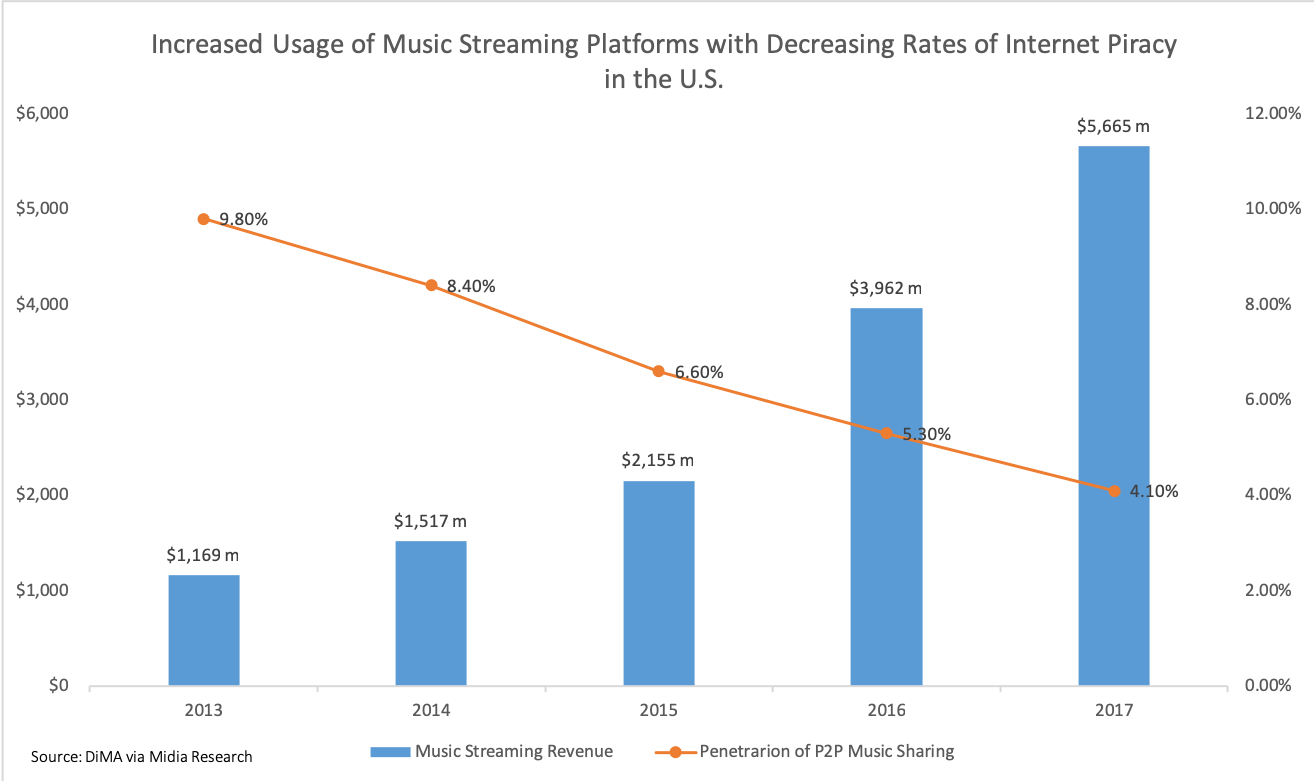
|
Audio Normalization
Audio normalization is the application of a constant amount of gain to an audio recording to bring the amplitude to a target level (the norm). Because the same amount of gain is applied across the entire recording, the signal-to-noise ratio and relative dynamics are unchanged. Normalization is one of the functions commonly provided by a digital audio workstation. Two principal types of audio normalization exist. Peak normalization adjusts the recording based on the highest signal level present in the recording. Loudness normalization adjusts the recording based on perceived loudness. Normalization differs from dynamic range compression, which applies varying levels of gain over a recording to fit the level within a minimum and maximum range. Normalization adjusts the gain by a constant value across the entire recording. Peak normalization One type of normalization is peak normalization, wherein the gain is changed to bring the highest PCM sample value or analog signal peak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio Recording
Sound recording and reproduction is the electrical, mechanical, electronic, or digital inscription and re-creation of sound waves, such as spoken voice, singing, instrumental music, or sound effects. The two main classes of sound recording technology are analog recording and digital recording. Sound recording is the transcription of invisible vibrations in air onto a storage medium such as a phonograph disc. The process is reversed in sound reproduction, and the variations stored on the medium are transformed back into sound waves. Acoustic analog recording is achieved by a microphone diaphragm that senses changes in atmospheric pressure caused by acoustic sound waves and records them as a mechanical representation of the sound waves on a medium such as a phonograph record (in which a stylus cuts grooves on a record). In magnetic tape recording, the sound waves vibrate the microphone diaphragm and are converted into a varying electric current, which is then converted to a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YouTube
YouTube is a global online video platform, online video sharing and social media, social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the List of most visited websites, second most visited website, after Google Search. YouTube has more than 2.5 billion monthly users who collectively watch more than one billion hours of videos each day. , videos were being uploaded at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute. In October 2006, YouTube was bought by Google for $1.65 billion. Google's ownership of YouTube expanded the site's business model, expanding from generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subscription option for watching content without ads. YouTube also approved creators to participate in Google's Google AdSens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normalization (image Processing)
In image processing, normalization is a process that changes the range of pixel intensity values. Applications include photographs with poor contrast due to glare, for example. Normalization is sometimes called contrast stretching or histogram stretching. In more general fields of data processing, such as digital signal processing, it is referred to as dynamic range expansion. The purpose of dynamic range expansion in the various applications is usually to bring the image, or other type of signal, into a range that is more familiar or normal to the senses, hence the term normalization. Often, the motivation is to achieve consistency in dynamic range for a set of data, signals, or images to avoid mental distraction or fatigue. For example, a newspaper will strive to make all of the images in an issue share a similar range of grayscale. Normalization transforms an n-dimensional grayscale image I:\\rightarrow\ with intensity values in the range (\text,\text), into a new image I_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loudness War
The loudness war (or loudness race) is a trend of increasing audio levels in recorded music, which reduces audio fidelity and—according to many critics—listener enjoyment. Increasing loudness was first reported as early as the 1940s, with respect to mastering practices for 7-inch singles. The maximum peak level of analog recordings such as these is limited by varying specifications of electronic equipment along the chain from source to listener, including vinyl and Compact Cassette players. The issue garnered renewed attention starting in the 1990s with the introduction of digital signal processing capable of producing further loudness increases. With the advent of the compact disc (CD), music is encoded to a digital format with a clearly defined maximum peak amplitude. Once the maximum amplitude of a CD is reached, loudness can be increased still further through signal processing techniques such as dynamic range compression and equalization. Engineers can apply an incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialnorm
Dialnorm is the metadata parameter that controls playback gain within the Dolby Laboratories Dolby Digital (AC-3) audio compression system. Dialnorm stands for dialog normalization. Dialnorm is an integer value with range 1 to 31 corresponding to a playback gain of -30 to 0 dB (unity) respectively. Higher values afford more headroom and are appropriate for dynamic material such as an action film. Dolby recommends that the dialnorm value be determined by measurement of average dialog level in the program. The recommended metering approach uses a power sum of the A-weighted audio level in all channels. If every producer and distributor uses this method, consumer dialog levels will be consistent from program to program and channel to channel. The dialog levels will be normalized. Historical basis Audio levels within analog disk, tape and broadcasting have traditionally been adjusted to keep peak levels within the physical and legal modulation limits of the medium. While thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alignment Level
The alignment level in an audio signal chain or on an audio recording is a defined anchor point that represents a reasonable or typical level. It does not represent a particular sound level or signal level or digital representation, but it can be defined as corresponding to particular levels in each of these domains. Example For example, alignment level is commonly 0 dBu (Equal to 0.775 Volts RMS) in broadcast chains and in professional audio what is commonly known as ''0 VU'', which is +4 dBu (equal to 1.227 Volts RMS) in places where the signal exists as analogue voltage. Under normal situations, the "0VU" reference allowed for a headroom of 18 dB or more above the reference level without significant distortion. This is largely due to the use of slow responding VU meters in almost all analogue professional audio equipment which, by their design, and by specification responded to an average level, not peak levels. It most commonly is at −18 dB FS (18& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streaming Media
Streaming media is multimedia that is delivered and consumed in a continuous manner from a source, with little or no intermediate storage in network elements. ''Streaming'' refers to the delivery method of content, rather than the content itself. Distinguishing delivery method from the media applies specifically to telecommunications networks, as most of the traditional media delivery systems are either inherently ''streaming'' (e.g. radio, television) or inherently ''non-streaming'' (e.g. books, videotape, audio CDs). There are challenges with streaming content on the Internet. For example, users whose Internet connection lacks sufficient bandwidth may experience stops, lags, or poor buffering of the content, and users lacking compatible hardware or software systems may be unable to stream certain content. With the use of buffering of the content for just a few seconds in advance of playback, the quality can be much improved. Livestreaming is the real-time delivery of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spotify
Spotify (; ) is a proprietary Swedish audio streaming and media services provider founded on 23 April 2006 by Daniel Ek and Martin Lorentzon. It is one of the largest music streaming service providers, with over 456 million monthly active users, including 195 million paying subscribers, as of September 2022. Spotify is listed (through a Luxembourg City-domiciled holding company, Spotify Technology S.A.) on the New York Stock Exchange in the form of American depositary receipts. Spotify offers digital copyright restricted recorded music and podcasts, including more than 82 million songs, from record labels and media companies. As a freemium service, basic features are free with advertisements and limited control, while additional features, such as offline listening and commercial-free listening, are offered via paid subscriptions. Users can search for music based on artist, album, or genre, and can create, edit, and share playlists. Spotify is available in most of Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EBU R 128
EBU R 128 is a recommendation for loudness normalisation and maximum level of audio signals. It is primarily followed during audio mixing of television and radio programmes and adopted by broadcasters to measure and control programme loudness. It was first issued by the European Broadcasting Union in August 2010 and most recently revised in August 2020. employs an international standard for measuring audio loudness, stated in the ITU-R BS.1770 recommendation and using the loudness measures LU (loudness units) and LUFS (loudness units referenced to full scale), specifically created with this purpose. The EBU Tech 3341 document further clarified loudness metering implementation and practices in 2016. Premise Before the adoption of , normalisation was based on the peak level of audio signals, which led to considerable loudness discrepancies between programmes and between broadcast channels. The same peak level does not necessarily produce the same loudness, because the use of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Radio Exchange
The Public Radio Exchange (PRX) is a non-profit web-based platform for digital distribution, review, and licensing of radio programs. The organization is the largest on-demand catalogue of public radio programs available for broadcast and internet use. History The PRX site and its services launched in September 2003 after a two-year planning, research, and development phase supported by the Corporation for Public Broadcasting, the National Endowment for the Arts, and the Ford Foundation. PRX received additional support from the NTIA Technology Opportunities Program, the MacArthur Foundation, the Open Society Institute, the Surdna Foundation, and Google Grants. PRX offices are located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. On February 28, 2007, PRX and the Corporation for Public Broadcasting announced the Public Radio Talent Quest. It was an open search for new public radio talent, and gave producers the chance to produce a pilot show for public radio. Finalists were to be chosen after a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATSC
Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) standards are an American set of standards for digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable and satellite networks. It is largely a replacement for the analog NTSC standard and, like that standard, is used mostly in the United States, Mexico, Canada, and South Korea. Several former NTSC users, such as Japan, have not used ATSC during their digital television transition, because they adopted other systems such as ISDB developed by Japan, and Digital Video Broadcasting, DVB developed in Europe, for example. The ATSC standards were developed in the early 1990s by the Grand Alliance (HDTV), Grand Alliance, a consortium of electronics and telecommunications companies that assembled to develop a specification for what is now known as HDTV. The standard is now administered by the Advanced Television Systems Committee. It includes a number of patented elements, and licensing is required for devices that use these parts of the stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
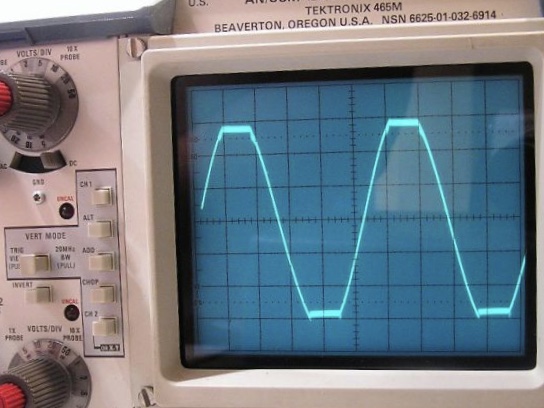
Clipping (audio)
Clipping is a form of waveform distortion that occurs when an amplifier is overdriven and attempts to deliver an output voltage or current beyond its maximum capability. Driving an amplifier into clipping may cause it to output power in excess of its power rating. In the frequency domain, clipping produces strong harmonics in the high-frequency range (as the clipped waveform comes closer to a squarewave). The extra high-frequency weighting of the signal could make tweeter damage more likely than if the signal was not clipped. In some cases, the distortion associated with clipping is unwanted, and is visible on an oscilloscope even if it is inaudible. However, clipping is often used in music for artistic effect, especially in heavier genres. Overview When an amplifier is pushed to create a signal with more power than its power supply can produce, it will amplify the signal only up to its maximum capacity, at which point the signal can be amplified no further. As the signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |