|
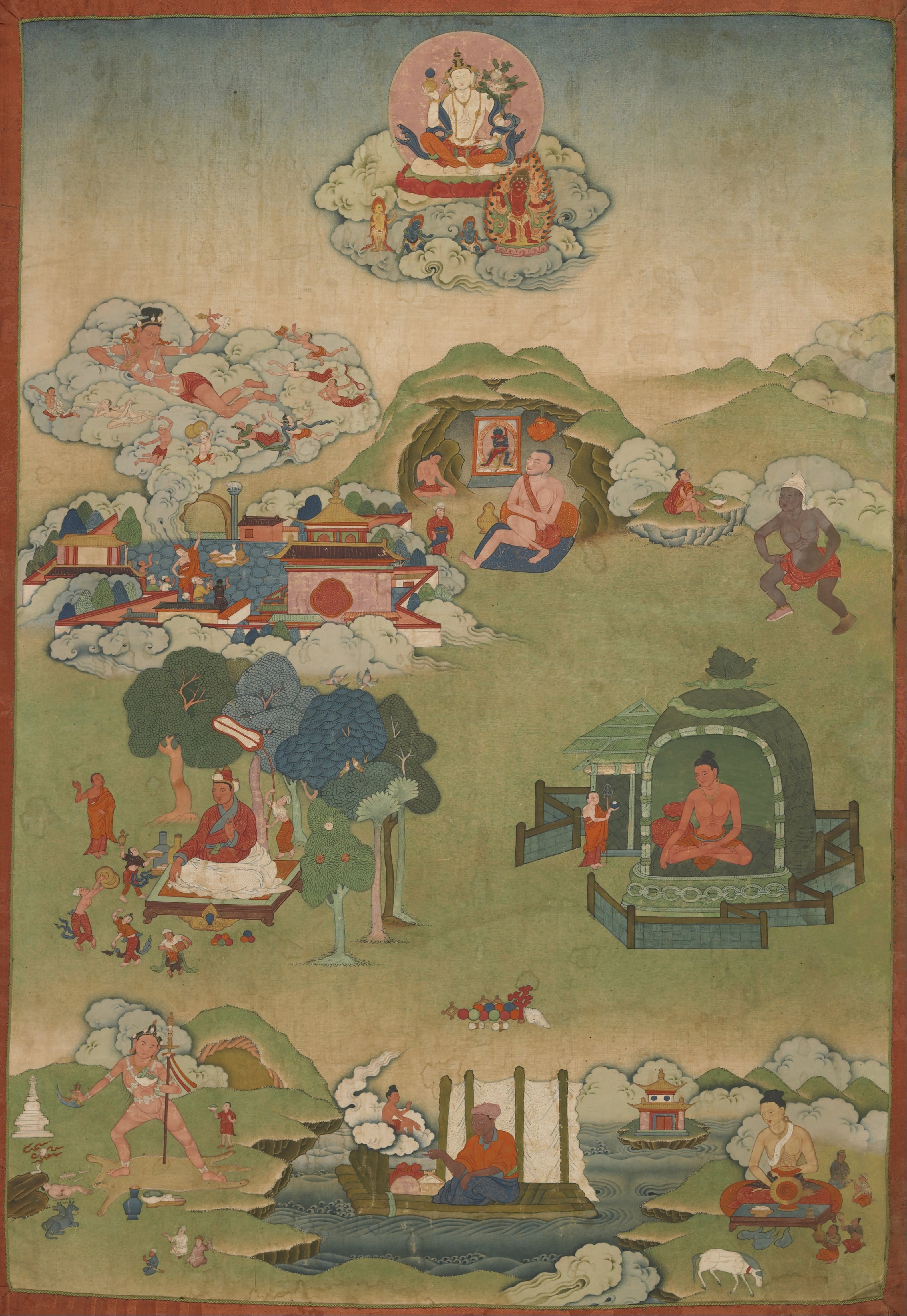
Atiśa
Atish Dipankar Shrijnan (Sanskrit transliteration: Atiśa Dipankara Shrijnana) (c. 982–1054 CE) was a Bengalis, Bengali Buddhist religious teacher and leader. He is generally associated with his body of work authored at Vikramashila, Vikramaśīla Monastery in modern day Bihar, India. He was a major figures in the spread of 11th-century Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhism in Asia and traveled to Sumatra and Tibet. Atiśa, along with this chief disciple Dromtön, is regarded as the founder of the Kadam (Tibetan Buddhism), Kadam school, one of the Sarma (Tibetan Buddhism), New Translation schools of Tibetan Buddhism. In the 14th century, the Kadam school was supplanted by the Gelug tradition, which adopted its teachings and absorbed its monasteries. Biography Early life Atiśa was born as Candragarbha in c. 982 CE as the second of three sons to a ruling family in Bengal in the city of Vikrampura. His father was a king known as Kalyānaśrī and his mother was Prabhavati Sri. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kadam (Tibetan Buddhism)
300px, Tibetan Portrait of Atiśa The Kadam school () of Tibetan Buddhism, or Kadampa was an 11th century Buddhist tradition founded by the great Bengali master Atiśa (982–1054) and his students including Dromtön (1005–1064), a Tibetan Buddhist lay master.Silk, Jonathan A; von Hinüber, Oskar; Eltschinger, Vincent; Bowring, Richard; Radich, Michael (2015). ''Brill's Encyclopedia of Buddhism: Vol. II Lives'', pp. 1145-1158. Brill. The Kadampa stressed compassion, pure discipline and study.Chokyi Dragpa (2015). ''Illuminating the Thirty-Seven Practices of a Bodhisattva'', Glossary. Simon & Schuster. By the 15th century, Tsongkapa is credited with synthesizing and folding Kadampa lineages into the Gelug school. The most evident teachings of that tradition were the graduated teachings on the Mahayana path. These special presentations became known as lojong (mind training) and lamrim (stages of the path). Kadam masters like Atiśa also promoted the study of madhyamaka p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism is a form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet, Bhutan and Mongolia. It also has a sizable number of adherents in the areas surrounding the Himalayas, including the Indian regions of Ladakh, Gorkhaland Territorial Administration, Darjeeling, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh, as well as in Nepal. Smaller groups of practitioners can be found in Central Asia, some regions of China such as Northeast China, Xinjiang, Inner Mongolia and some regions of Russia, such as Tuva, Buryatia, and Kalmykia. Tibetan Buddhism evolved as a form of Mahayana, Mahāyāna Buddhism stemming from the latest stages of Indian Buddhism (which included many Vajrayana, Vajrayāna elements). It thus preserves many Indian Buddhist Tantra, tantric practices of the Gupta Empire, post-Gupta Medieval India, early medieval period (500–1200 CE), along with numerous native Tibetan developments. In the pre-modern era, Tibetan Buddhism spread outside of Tibet primarily due to the influence of the Mongol Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhyamaka
Madhyamaka ("middle way" or "centrism"; ; ; Tibetic languages, Tibetan: དབུ་མ་པ་ ; ''dbu ma pa''), otherwise known as Śūnyavāda ("the Śūnyatā, emptiness doctrine") and Niḥsvabhāvavāda ("the no Svabhava, ''svabhāva'' doctrine"), refers to a tradition of Buddhist philosophy and practice founded by the History of Buddhism in India, Indian Buddhist monk and philosopher Nagarjuna, Nāgārjuna ().Wynne, Alexander (2015) ''Early Buddhist Teaching as Proto-śūnyavāda.'' Journal of the Oxford Centre for Buddhist Studies, 6. pp. 213-241. The foundational text of the Mādhyamaka tradition is Nagarjuna, Nāgārjuna's ''Mūlamadhyamakakārikā'' ("Root Verses on the Middle Way"). More broadly, Madhyamaka also refers to the ultimate nature of phenomena as well as the non-conceptual realization of ultimate reality that is experienced in Buddhist meditation, meditation. Since the 4th century CE onwards, Madhyamaka philosophy had a major influence on the subsequent d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dromtön
Dromtön, Drom Tonpa or Dromtönpa Gyelwé Jungné (, 1004 or 1005–1064) was the chief disciple of the Buddhist master Atiśa, the initiator of the Kadam school of Tibetan Buddhism and the founder of Reting Monastery. Early life and education Dromtönpa was born in Tolung at the beginning of the period of the second propagation of Buddhism in Tibet. "His father was Kushen Yaksherpen (sku gshen yag gsher 'phen) and his mother was Kuoza Lenchikma (khu 'od bza' lan gcig ma)." His father's title ''skugshen'' indicates he was an important figure in the Bon tradition. He began preaching in Tibet in 1042. Career Dromtön is considered to be the 45th incarnation of Avalokiteśvara, an important bodhisattva and thus a member of the early lineage of the Dalai Lamas (the First Dalai Lama is said to have been the 51st incarnation). Dromtön founded Reting Monastery in 1056 in the Reting Tsampo Valley north of Lhasa which became the seat of the Kadampa lineage and brought some relic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahayana
Mahāyāna ( ; , , ; ) is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, Buddhist texts#Mahāyāna texts, texts, Buddhist philosophy, philosophies, and practices developed in ancient India ( onwards). It is considered one of the three main existing branches of Buddhism, the others being Theravāda and Vajrayāna.Harvey (2013), p. 189. Mahāyāna accepts the main scriptures and teachings of Early Buddhist schools, early Buddhism but also recognizes various doctrines and texts that are not accepted by Theravada Buddhism as original. These include the Mahāyāna sūtras and their emphasis on the ''bodhisattva'' path and Prajnaparamita, ''Prajñāpāramitā''. Vajrayāna or Mantra traditions are a subset of Mahāyāna which makes use of numerous Tantra, tantric methods Vajrayānists consider to help achieve Buddhahood. Mahāyāna also refers to the path of the bodhisattva striving to become a fully awakened Buddha for the benefit of all sentience, sentient beings, and is thus also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vajrayana
''Vajrayāna'' (; 'vajra vehicle'), also known as Mantrayāna ('mantra vehicle'), Guhyamantrayāna ('secret mantra vehicle'), Tantrayāna ('tantra vehicle'), Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, is a Mahāyāna Buddhism, Mahāyāna Buddhist tradition that emphasizes Eastern esotericism, esoteric practices and rituals aimed at Sudden awakening, rapid spiritual awakening. Emerging between the 5th and 7th centuries CE in medieval India, Vajrayāna incorporates a Tibetan tantric practice, range of techniques, including the use of mantras (sacred sounds), dhāraṇīs (mnemonic codes), mudrās (symbolic hand gestures), mandalas (spiritual diagrams), and the visualization of Buddhist deities, deities and Buddhahood, Buddhas. These practices are designed to transform ordinary experiences into paths toward Enlightenment in Buddhism, enlightenment, often by engaging with aspects of Taṇhā, desire and Dvesha, aversion in a ritualized context. A distinctive feature of Vajrayāna is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengalis
Bengalis ( ), also rendered as endonym and exonym, endonym Bangalee, are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the Bengal region of South Asia. The current population is divided between the sovereign country Bangladesh and the India, Indian regions of West Bengal, Tripura, Barak Valley of Assam, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and parts of Meghalaya, Manipur and Jharkhand. Most speak Bengali language, Bengali, a classical languages of India, classical language from the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language family. Bengalis are the List of contemporary ethnic groups, third-largest ethnic group in the world, after the Han Chinese and Arabs. They are the largest ethnic group within the Indo-European languages, Indo–European linguistic family and the largest ethnic group in South Asia. Apart from Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura, Manipur, and Assam's Barak Valley, Bengali-majority popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikramashila
Vikramashila ( IAST: ) was a Buddhist monastery situated in what is now modern-day Bihar in India. It was founded by King Dharmapala between the late eighth and early ninth century. It was one of the three most important Buddhist Mahaviharas of its time in India, along with Nalanda and Odantapuri. Its location is now the site of Antichak village near Kahalgaon, Bhagalpur district in Bihar. It was one of the largest Buddhist mahaviharas, with more than one hundred teachers and about one thousand students. It produced eminent scholars who were often invited by foreign countries to spread Buddhist learning, culture and religion including Atiśa and Ratnākaraśānti. Vikramashila was established by the Pala emperor Dharmapala (783 to 820 CE) in response to a supposed decline in the quality of scholarship at Nalanda. It was destroyed by the forces of Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khalji around 1193. History A number of monasteries grew up during the Pāla period in medieva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelug
file:DalaiLama0054 tiny.jpg, 240px, 14th Dalai Lama, The 14th Dalai Lama (center), the most influential figure of the contemporary Gelug tradition, at the 2003 Kalachakra ceremony, Bodh Gaya, Bodhgaya (India) The Gelug (, also Geluk; 'virtuous')Kay, David N. (2007). ''Tibetan and Zen Buddhism in Britain: Transplantation, Development and Adaptation,'' p. 39. Routledge. is the newest of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. It was founded by Je Tsongkhapa (1357–1419), a Tibetan people, Tibetan philosopher, Vajrayana, tantric yogi and lama and further expanded and developed by his disciples (such as Khedrup Gelek Pelzang, 1st Panchen Lama, Khedrup Je, Gyaltsab Je, Gyaltsap Je, Dulzin Drakpa Gyaltsen, and 1st Dalai Lama, Gendün Drubpa). The Gelug school is alternatively known as Kadam (''bKa’-gdams gsar-pa''), since it sees itself as a continuation of the Kadam (Tibetan Buddhism), Kadam tradition of Atiśa, Atisha (c. 11th century). The school of New Kadam, or New Kadampa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahāsāṃghika
The Mahāsāṃghika (Brahmi script, Brahmi: 𑀫𑀳𑀸𑀲𑀸𑀁𑀖𑀺𑀓, "of the Great Sangha (Buddhism), Sangha", ) was a major division (nikāya) of the early Buddhist schools in India. They were one of the two original communities that emerged from the first schism of the Pre-sectarian Buddhism, original pre-sectarian Buddhist tradition (the other being the Sthavira nikāya, Sthavira nikaya). This schism is traditionally held to have occurred after the Second Buddhist council, which occurred at some point during or after the reign of Kalashoka. The Mahāsāṃghika nikāya developed into numerous sects which spread throughout History of India, ancient India. Some scholars think that the Mahāsāṃghika Vinaya (Monasticism, monastic rule) represents the oldest Buddhist monastic source, although some other scholars think that it is not the case. While the Mahāsāṃghika tradition is no longer in existence, many scholars look to the Mahāsāṃghika tradition as an ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikrampura
Bikrampur (lit. City of Courage) was a historic region and a sub-division of Dhaka within the Bengal Presidency during the period of British India. Located along the banks of the Padma River (a major distributary of the Ganges), it was a significant cultural and political centre in both ancient and medieval Bengal. Today, the region is part of the Munshiganj District in Bangladesh. History Pala Era The region was successively ruled by Vigrahapala I, Narayanapala, Rajyapala, Gopala II, Vigrahapala II, Mahipala, Naya Pala, Vigrahapala III, Mahipala II, Shurapala II, Ramapala, Kumarapala, Gopala III and Madanapala. Pala empire disintegrated in 1174 weakened by attacks of the rising Sena dynasty. Chandra Era During the rule of Srichandra (reigned 930 – 975 AD), the administrative centre of the Chandra kingdom was established at Bikrampur. The Varman Dynasty (1035-1150 CE) replaced the Chandras and established their independent kingdom. Varman Era After the fall of the Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |