|
Atelestidae Wing (Atelestus Pulicarius)
Atelestidae is a family (biology), family of Diptera, flies in the Taxonomic rank, superfamily Empidoidea. The four genera were placed in a separate family in 1983; they were formerly either in Platypezidae (which are not even particularly closely related) or considered ''incertae sedis''. While they are doubtless the most basal (evolution), basal of the living Empidoidea, the monophyly of the family is not fully proven. The genus ''Nemedina'' seems to represent a most ancient lineage among the entire superfamily, while ''Meghyperus'' is probably not monophyletic in its present delimitation, and it is liable to be split up eventually, with some species being placed elsewhere. In 2010, the genus ''Alavesia'', previously only known from Cretaceous fossils, was found alive in Namibia, subsequent species were also described from Brazil. Atelestidae has been shown to form the sister group to the remaining members of the Empidoidea superfamily. Subfamilies include Atelestinae and Nemedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atelestus Pulicarius ''
{{genus disambiguation ...
Atelestus may refer to: * ''Atelestus'' (fly), a genus of flies in the family Atelestidae * ''Atelestus'', a genus of beetles in the family Malachiidae; synonym of ''Brachemys ''Brachemys'' is a genus of beetles belonging to the family Melyridae Melyridae (common name: soft-winged flower beetles) are a family of beetles of the superfamily Cleroidea. Description Most are elongate-oval, soft-bodied beetles 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybotidae
Hybotidae, the typical dance flies, are a family of true flies. They belong to the superfamily Empidoidea and were formerly included in the Empididae as a subfamily. Some, such as '' Tachydromia'', are predators that run around on the bark of trees in complex patterns, hence the common name. ''Tachydromia'' species are only about three millimeters long. Description Hybotidae share some similarities with the family Dolichopodidae, when looking at rotation of genitalia and wing characteristics. Male terminalia are rotated dextrally between 45° and 90°, excluding segment 7. Hybotidae wings always have a simple R4+5 vein, where the costa either ends near or at M1/M1+2, or near or at R4+5/R5. Furthermore, it can be distinguished from Dolichopodidae by the point of vein Rs, which it at a distance from the humeral crossvein (h) equal to or longer than the length of h. Systematics The Hybotidae clearly form a lineage quite distinct from the Empididae. Among the Empidoidea, they re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after declaring in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neotropical
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone. Definition In biogeography, the Neotropic or Neotropical realm is one of the eight terrestrial realms. This realm includes South America, Central America, the Caribbean islands, and southern North America. In Mexico, the Yucatán Peninsula and southern lowlands, and most of the east and west coastlines, including the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula are Neotropical. In the United States southern Florida and coastal Central Florida are considered Neotropical. The realm also includes temperate southern South America. In contrast, the Neotropical Floristic Kingdom excludes southernmost South America, which instead is placed in the Antarctic kingdom. The Neotropic is delimited by similarities in fauna or flora. Its fauna and flora are distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holarctic
The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical region (which covers most of North America), and Alfred Wallace's Palearctic zoogeographical region (which covers North Africa, and all of Eurasia except for Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, the southern Arabian Peninsula). These regions are further subdivided into a variety of ecoregions. Many ecosystems and the animal and plant communities that depend on them extend across a number of continents and cover large portions of the Holarctic realm. This continuity is the result of those regions’ shared glacial history. Major ecosystems Within the Holarctic realm, there are a variety of ecosystems. The type of ecosystem found in a given area depends on its latitude and the local geography. In the far north, a band of Arctic tundra en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosternum
The prothorax is the foremost of the three segments in the thorax of an insect, and bears the first pair of legs. Its principal sclerites (exoskeletal plates) are the pronotum (dorsal), the prosternum (ventral), and the propleuron (lateral) on each side. The prothorax never bears wings in extant insects (except in some cases of atavism), though some fossil groups possessed wing-like projections. All adult insects possess legs on the prothorax, though in a few groups (e.g., the butterfly family Nymphalidae) the forelegs are greatly reduced. In many groups of insects, the pronotum is reduced in size, but in a few it is hypertrophied, such as in all beetles (Coleoptera). In most treehoppers (family Membracidae, order Hemiptera), the pronotum is expanded into often fantastic shapes that enhance their camouflage or mimicry. Similarly, in the Tetrigidae, the pronotum is extended backward to cover the flight wings, supplanting the function of the tegmina. See also *Glossary of entomol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect Wing
Insect wings are adult outgrowths of the insect exoskeleton that enable insects to fly. They are found on the second and third thoracic segments (the mesothorax and metathorax), and the two pairs are often referred to as the forewings and hindwings, respectively, though a few insects lack hindwings, even rudiments. The wings are strengthened by a number of longitudinal veins, which often have cross-connections that form closed "cells" in the membrane (extreme examples include the dragonflies and lacewings). The patterns resulting from the fusion and cross-connection of the wing veins are often diagnostic for different evolutionary lineages and can be used for identification to the family or even genus level in many orders of insects. Physically, some insects move their flight muscles directly, others indirectly. In insects with direct flight, the wing muscles directly attach to the wing base, so that a small downward movement of the wing base lifts the wing itself upward. Those i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect Genitalia
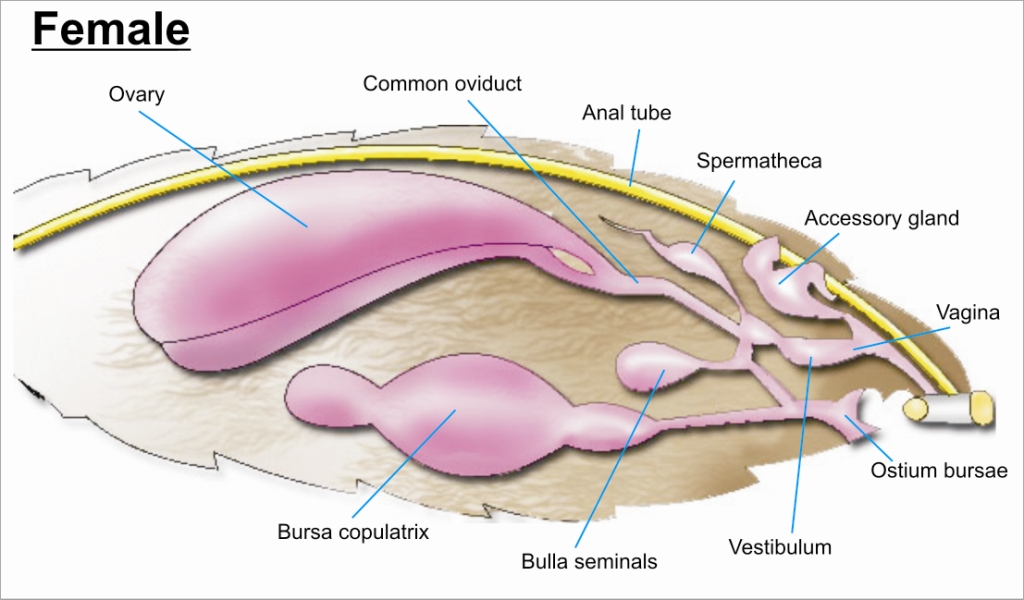
Most insects reproduce oviparously, i.e. by laying eggs. The eggs are produced by the female in a pair of ovaries. Sperm, produced by the male in one testis or more commonly two, is transmitted to the female during mating by means of external genitalia. The sperm is stored within the female in one or more spermathecae. At the time of fertilization, the eggs travel along oviducts to be fertilized by the sperm and are then expelled from the body ("laid"), in most cases via an ovipositor. Internal Female Female insects are able to make eggs, receive and store sperm, manipulate sperm from different males, and lay eggs. Their reproductive systems are made up of a pair of ovaries, accessory glands, one or more spermathecae, and ducts connecting these parts. The ovaries make eggs and accessory glands produce the substances to help package and lay the eggs. Spermathecae store sperm for varying periods of time and, along with portions of the oviducts, can control sperm use. The ducts and sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ragadidae
Ragadidae is a family of true flies in the superfamily Empidoidea. It was formerly considered a lower taxon, but was published as a new subfamily within Empididae in 2016.Sinclair (2016) Since then, it has been classified as the sister group to Empididae, and has been elevated to family level based on the genetic differences which separate it from Empididae.Wahlberg & Johanson (2018) Description Ragadidae are similar to Empididae and Atelestidae in the sense that their genitalia have symmetrical and straight terminalia. In their wings, the point of origin of the Rs vein is located at a distance from the humeral crossvein (h) as long as, or longer than, h. There is also a circumambient costa in the wing, which distinguishes Ragadidae from Atelestidae. Furthermore, the prosternum being separated from the proepisternum sets Ragadidae aside from Empididae—this is true for all except one genera (''Hydropeza'' ''spp''.), which can instead be characterized through its recurved labr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empididae
__NOTOC__ Empididae is a family of flies with over 3,000 described species occurring worldwide in all the biogeographic realms but the majority are found in the Holarctic. They are mainly predatory flies like most of their relatives in the Empidoidea, and exhibit a wide range of forms but are generally small to medium-sized, non-metallic and rather bristly. Common names for members of this family are dagger flies (referring to the sharp piercing mouthparts of some species) and balloon flies. The term "dance flies" is sometimes used for this family too, but the dance flies proper, formerly included herein, are now considered a separate family Hybotidae. Description For terms see Morphology of Diptera. Empididae are small to medium-sized flies, rarely large (1.0 to 15.0mm.). The body is slender, or elongated and rarely thickset. The colour ranges from yellow to black, and they may be pollinose or lustrous, but never have a metallic gloss. The head is often small and rounded with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)

_wing.png)