|
Arthur Erdélyi
Arthur Erdélyi FRS, FRSE (2 October 1908 – 12 December 1977) was a Hungarian-born British mathematician. Erdélyi was a leading expert on special functions, particularly orthogonal polynomials and hypergeometric functions. Biography He was born Arthur Diamant in Budapest, Hungary to Ignác Josef Armin Diamant and Frederike Roth. His name was changed to Erdélyi when his mother remarried to Paul Erdélyi. He attended the primary and secondary schools there from 1914 to 1926. His interest in mathematics dates back to this time. Erdélyi was a Jew, and so it was difficult for him to receive a university education in his native Hungary. He travelled to Brno, Czechoslovakia, to obtain a degree in electrical engineering. However, after his flair for mathematics was discovered (he won several prizes in a competition in his first year), he was persuaded to study the subject. He soon after began to conduct theoretical research into mathematics, and his first paper was publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population of 1,752,286 over a land area of about . Budapest, which is both a city and county, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of and a population of 3,303,786; it is a primate city, constituting 33% of the population of Hungary. The history of Budapest began when an early Celtic settlement transformed into the Roman town of Aquincum, the capital of Lower Pannonia. The Hungarians arrived in the territory in the late 9th century, but the area was pillaged by the Mongols in 1241–42. Re-established Buda became one of the centres of Renaissance humanist culture by the 15th century. The Battle of Mohács, in 1526, was followed by nearly 150 years of Ottoman rule. After the reconquest of Buda in 1686, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
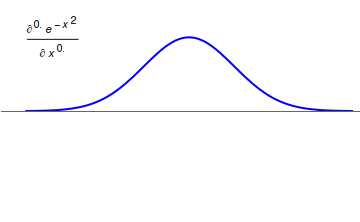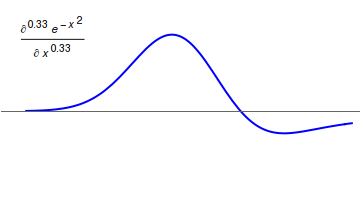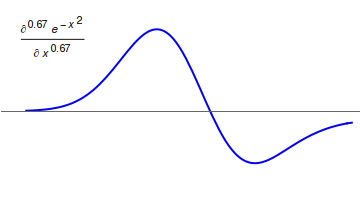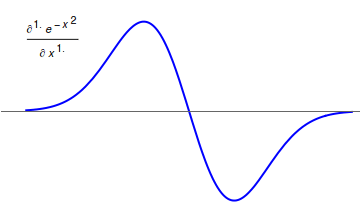
Fractional Calculus
Fractional calculus is a branch of mathematical analysis that studies the several different possibilities of defining real number powers or complex number powers of the differentiation operator D :D f(x) = \frac f(x)\,, and of the integration operator J The symbol J is commonly used instead of the intuitive I in order to avoid confusion with other concepts identified by similar I–like glyphs, such as identities. :J f(x) = \int_0^x f(s) \,ds\,, and developing a calculus for such operators generalizing the classical one. In this context, the term ''powers'' refers to iterative application of a linear operator D to a function f, that is, repeatedly composing D with itself, as in D^n(f) = (\underbrace_n)(f) = \underbrace_n (f)\cdots))). For example, one may ask for a meaningful interpretation of :\sqrt = D^\frac12 as an analogue of the functional square root for the differentiation operator, that is, an expression for some linear operator that, when applied ''twice'' to any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamé Function
In mathematics, a Lamé function, or ellipsoidal harmonic function, is a solution of Lamé's equation, a second-order ordinary differential equation. It was introduced in the paper . Lamé's equation appears in the method of separation of variables applied to the Laplace equation in elliptic coordinates. In some special cases solutions can be expressed in terms of polynomials called Lamé polynomials. The Lamé equation Lamé's equation is :\frac + (A+B\weierp(x))y = 0, where ''A'' and ''B'' are constants, and \wp is the Weierstrass elliptic function. The most important case is when B\weierp(x) = - \kappa^2 \operatorname^2x , where \operatorname is the elliptic sine function, and \kappa^2 = n(n+1)k^2 for an integer ''n'' and k the elliptic modulus, in which case the solutions extend to meromorphic functions defined on the whole complex plane. For other values of ''B'' the solutions have branch points. By changing the independent variable to t with t=\operatorname x, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territories of the United States by population, most populous U.S. state and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 3rd largest by area. It is also the most populated Administrative division, subnational entity in North America and the 34th most populous in the world. The Greater Los Angeles area and the San Francisco Bay Area are the nation's second and fifth most populous Statistical area (United States), urban regions respectively, with the former having more than 18.7million residents and the latter having over 9.6million. Sacramento, California, Sacramento is the state's capital, while Los Angeles is the List of largest California cities by population, most populous city in the state and the List of United States cities by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citizen
Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection". Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and the conditions under which that status will be withdrawn. Recognition by a state as a citizen generally carries with it recognition of civil, political, and social rights which are not afforded to non-citizens. In general, the basic rights normally regarded as arising from citizenship are the right to a passport, the right to leave and return to the country/ies of citizenship, the right to live in that country, and to work there. Some countries permit their citizens to have multiple citizenships, while others insist on exclusive allegiance. Determining factors A person can be recognized or granted citizenship on a number of bases. Usually, citizenship based on circumstances of birth is automatic, but an application may be required. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bateman Manuscript Project
The Bateman Manuscript Project was a major effort at collation and encyclopedic compilation of the mathematical theory of special functions. It resulted in the eventual publication of five important reference volumes, under the editorship of Arthur Erdélyi. Overview The theory of special functions was a core activity of the field of applied mathematics, from the middle of the nineteenth century to the advent of high-speed electronic computing. The intricate properties of spherical harmonics, elliptic functions and other staples of problem-solving in mathematical physics, astronomy and right across the physical sciences, are not easy to document completely, absent a theory explaining the inter-relationships. Mathematical tables to perform actual calculations needed to mesh with an adequate theory of how functions could be transformed into those already tabulated. Harry Bateman, a distinguished applied mathematician, undertook the somewhat quixotic task of trying to collate the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Bateman
Harry Bateman FRS (29 May 1882 – 21 January 1946) was an English mathematician with a specialty in differential equations of mathematical physics. With Ebenezer Cunningham, he expanded the views of spacetime symmetry of Lorentz and Poincare to a more expansive conformal group of spacetime leaving Maxwell's equations invariant. Moving to the U.S.A., and obtaining a Ph.D. in geometry with Frank Morley, he became a professor of mathematics at California Institute of Technology. There he taught fluid dynamics to students going into aerodynamics with Theodore von Karman. Bateman made a broad survey of applied differential equations in his Gibbs Lecture in 1943 titled "The control of an elastic fluid". Biography Bateman was born in Manchester, England on 29 May 1882. He first grew to love mathematics at Manchester Grammar School, and, in his final year, won a scholarship to Trinity College, Cambridge. Bateman studied with coach Robert Alfred Herman preparing for Cambridge Mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pound Sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and the word "pound" is also used to refer to the British currency generally, often qualified in international contexts as the British pound or the pound sterling. Sterling is the world's oldest currency that is still in use and that has been in continuous use since its inception. It is currently the fourth most-traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar, the euro, and the Japanese yen. Together with those three currencies and Renminbi, it forms the basket of currencies which calculate the value of IMF special drawing rights. As of mid-2021, sterling is also the fourth most-held reserve currency in global reserves. The Bank of England is the central bank for sterling, issuing its own banknotes, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Whittaker
Sir Edmund Taylor Whittaker (24 October 1873 – 24 March 1956) was a British mathematician, physicist, and historian of science. Whittaker was a leading mathematical scholar of the early 20th-century who contributed widely to applied mathematics and was renowned for his research in mathematical physics and numerical analysis, including the theory of special functions, along with his contributions to astronomy, celestial mechanics, the history of physics, and digital signal processing. Among the most influential publications in Whittaker’s bibliography, he authored several popular reference works in mathematics, physics, and the history of science, including ''A Course of Modern Analysis'' (better known as ''Whittaker and Watson''), ''Analytical Dynamics of Particles and Rigid Bodies'', and ''A History of the Theories of Aether and Electricity''. Whittaker is also remembered for his role in the relativity priority dispute, as he credited Henri Poincaré and Hendrik Loren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


