|
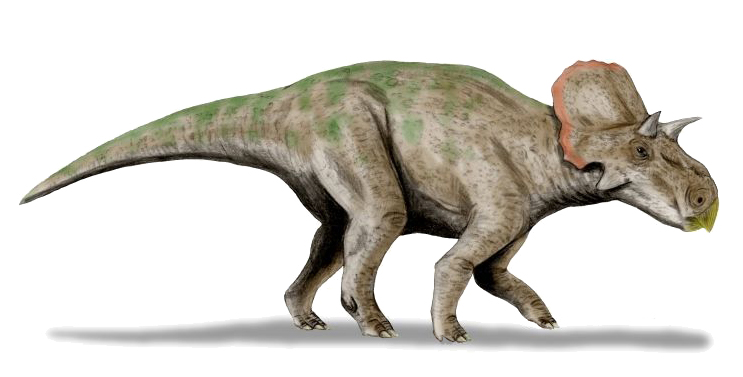
Albertaceratops Scale
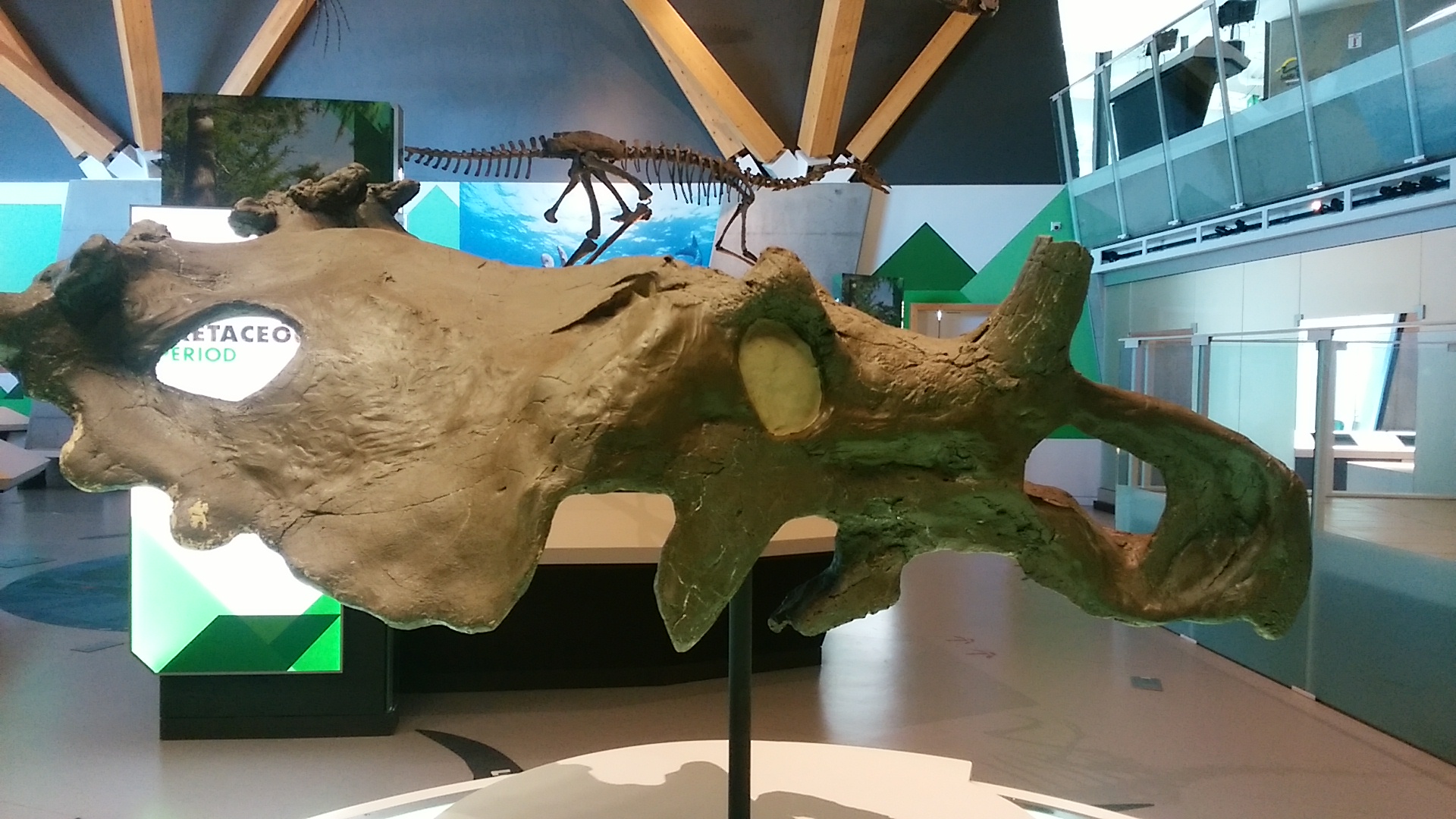
''Albertaceratops'' (meaning "Alberta horned face") was a genus of centrosaurine horned dinosaur from the middle Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Oldman Formation of Alberta, Canada. Description ''Albertaceratops'' is unusual in combining long brow horns with an otherwise centrosaurine skull, as centrosaurines normally possess short brow horns. Over its nose was a bony ridge, and on its frill were two large outwardly-projecting hooks. Its size has been estimated at and . Discovery and naming ''Albertaceratops'' is known from a single complete skull ( TMP.2001.26.1) found in August 2001 and skull and postcranial fragments. A phylogenetic analysis carried out by its describer, Michael J. Ryan, found it to be the most basal centrosaurine. Additional specimens were reported from a bonebed in the Judith River Formation of Montana, which is equivalent to the Oldman Formation and differentiated only by the Canada–US border. However, further study showed these remains to come f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judith River Formation
The Judith River Formation is a fossil-bearing geologic formation in Montana, and is part of the Judith River Group. It dates to the Late Cretaceous, between 79 and 75.3 million years ago, corresponding to the "Judithian" land vertebrate age. It was laid down during the same time period as portions of the Two Medicine Formation of MontanaSullivan, R.M. and Lucas, S. G. (2006). "The Kirtlandian land-vertebrate "age"–faunal composition, temporal position and biostratigraphic correlation in the nonmarine Upper Cretaceous of western North America." Pp. 7-29 in Lucas, S. G. and Sullivan, R.M. (eds.), ''Late Cretaceous vertebrates from the Western Interior. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin 35''. and the Oldman Formation of Alberta. It is an historically important formation, explored by early American paleontologists such as Edward Drinker Cope, who named several dinosaurs from scrappy remains found here on his 1876 expedition (such as ''Monoclonius''). Modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avaceratops
''Avaceratops'' is a genus of small herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaurs which lived during the late Campanian during the Late Cretaceous Period in what are now the Northwest United States. Most fossils come from the Judith River Formation. Discovery and naming The first remains of ''Avaceratops'' were found by fossil dealer Eddie Cole in the Judith River Formation of Montana, in 1981, on land of the Careless Creek Ranch, owned by rancher Arthur J. Lammers."Avaceratops." In: Dodson, Peter & Britt, Brooks & Carpenter, Kenneth & Forster, Catherine A. & Gillette, David D. & Norell, Mark A. & Olshevsky, George & Parrish, J. Michael & Weishampel, David B. ''The Age of Dinosaurs''. Publications International, LTD. p. 129. . They were preserved scattered throughout the remains of a prehistoric stream bed. This ''Avaceratops'' specimen was likely buried in the sandbar after its body was swept downstream by the current. The finds, displayed in Cole's fossil shop, were in October 1981 inspect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasutoceratopsini
Centrosaurinae (from the Greek, meaning "pointed lizards") is a subfamily of ceratopsid dinosaurs, a group of large quadrupedal ornithischians. Centrosaurine fossil remains are known primarily from the northern region of Laramidia (modern day Alberta, Montana, and Alaska) but isolated taxa have been found in China and Utah as well. Defining features of centrosaurines include a large nasal horn, short supratemporal horns, and an ornamented frill projecting from the back of the skull. With the exception of ''Centrosaurus apertus'', all adult centrosaurines have spike-like ornaments midway up the skull. Morphometric analysis shows that centrosaurines differ from other ceratopsian groups in skull, snout, and frill shapes. There is evidence to suggest that male centrosaurines had an extended period of adolescence, and sexual ornamentation did not appear until adulthood. Centrosaurinae was named by paleontologist Lawrence Lambe in 1915, with ''Centrosaurus'' as the type genus. The cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machairoceratops
''Machairoceratops'' (meaning "bent sword horned face"), previously known as the "Wahweap centrosaurine B", is an extinct genus of centrosaurine ceratopsian dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Wahweap Formation (late Campanian stage) of Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument, southern Utah, United States. Discovery It contains a single species, ''M. cronusi'', first described and named in 2016 by Eric K. Lund, Patrick M. O’Connor, Mark A. Loewen and Zubair A. Jinnah. The generic name is derived from Greek ''machairis'', meaning "bent sword", in reference to its unique frill ornamentation showing two forward curving horns on the frill's uppermost part, and Latinized Greek ''ceratops'', meaning "horned-face", which is a common suffix for ceratopsian genera names. The specific name ''cronusi'' refers to Cronus, a Greek god who deposed his father Uranus by castrating him with a sickle or scythe based on the mythology, and as such is shown carrying a curved bladed wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabloceratops
''Diabloceratops'' is an extinct genus of centrosaurine ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 81.4-81 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Utah, in the United States. ''Diabloceratops'' was a medium-sized, moderately built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore, that could grow up to an estimated in length and in body mass. At the time of its discovery, it was the oldest-known ceratopsid, and first centrosaurine known from latitudes south of the U.S. state of Montana. The generic name ''Diabloceratops'' means "devil-horned face," coming from ''Diablo'', Spanish for "devil," and ''ceratops'', Latinized Greek for "horned face." The specific name honors Jeffrey Eaton, a paleontologist at Weber State University and long time friend of the lead author Jim Kirkland. Eaton had a big role in establishing the Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument where the specimen was found. The type species, ''Diabloceratops eatoni'', was n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosaurinae
Centrosaurinae (from the Greek, meaning "pointed lizards") is a subfamily of ceratopsid dinosaurs, a group of large quadrupedal ornithischians. Centrosaurine fossil remains are known primarily from the northern region of Laramidia (modern day Alberta, Montana, and Alaska) but isolated taxa have been found in China and Utah as well. Defining features of centrosaurines include a large nasal horn, short supratemporal horns, and an ornamented frill projecting from the back of the skull. With the exception of ''Centrosaurus apertus'', all adult centrosaurines have spike-like ornaments midway up the skull. Morphometric analysis shows that centrosaurines differ from other ceratopsian groups in skull, snout, and frill shapes. There is evidence to suggest that male centrosaurines had an extended period of adolescence, and sexual ornamentation did not appear until adulthood. Centrosaurinae was named by paleontologist Lawrence Lambe in 1915, with ''Centrosaurus'' as the type genus. The cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about ance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albertaceratops Scale
''Albertaceratops'' (meaning "Alberta horned face") was a genus of centrosaurine horned dinosaur from the middle Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Oldman Formation of Alberta, Canada. Description ''Albertaceratops'' is unusual in combining long brow horns with an otherwise centrosaurine skull, as centrosaurines normally possess short brow horns. Over its nose was a bony ridge, and on its frill were two large outwardly-projecting hooks. Its size has been estimated at and . Discovery and naming ''Albertaceratops'' is known from a single complete skull ( TMP.2001.26.1) found in August 2001 and skull and postcranial fragments. A phylogenetic analysis carried out by its describer, Michael J. Ryan, found it to be the most basal centrosaurine. Additional specimens were reported from a bonebed in the Judith River Formation of Montana, which is equivalent to the Oldman Formation and differentiated only by the Canada–US border. However, further study showed these remains to come f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronosaurus And Albertaceratops
''Coronosaurus'' is a genus of centrosaurine ceratopsian dinosaurs which lived in the Late Cretaceous, in the middle Campanian stage. Its remains, two bone beds, were discovered by Phillip J. Currie in the Oldman Formation of Alberta, Canada, and its type and only species, ''Coronosaurus brinkmani'', was first described in 2005, as a new species within the genus ''Centrosaurus''. Later studies questioned the presence of a direct relationship, and in 2012 it was named as a separate genus. ''Coronosaurus'' means "crowned lizard", coming from "''corona''", Latin for crown, and "''sauros''", Greek for lizard; this name refers to the unique, crown-like shape of the horns on the top of its frill. Like other ceratopsids, ''Coronosaurus'' had a large frill and horns on its head. These include a small pair of brow horns over its eyes, a large nasal horn on its snout, and, unique among ceratopsians, irregular, spiky bone masses on its frill. Growing up to around long and in weight, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manyberries
Manyberries is a hamlet in Alberta, Canada within the County of Forty Mile No. 8. It is located approximately south of Medicine Hat, at the eastern end of Highway 61 (the Red Coat Trail). Climate Manyberries experiences a semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification ''BSk''). Winters are long, cold and dry, while summers are relatively short but very warm. Precipitation is low, with an annual average of 353 mm, and is concentrated in the warmer months. Manyberries is the sunniest spot in Canada, receiving an average of 2,567 hours of sunshine per year. Demographics Manyberries recorded a population of 96 in the 1991 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada. Services Manyberries has a community hall, a curling rink, a park with playground equipment, and a hotel with lounge. Manyberries still has its original Canadian Pacific railway station and a section house, which are both private residences, and are located beside the former Stirling-Weyburn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |