Avaceratops on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Avaceratops'' is a
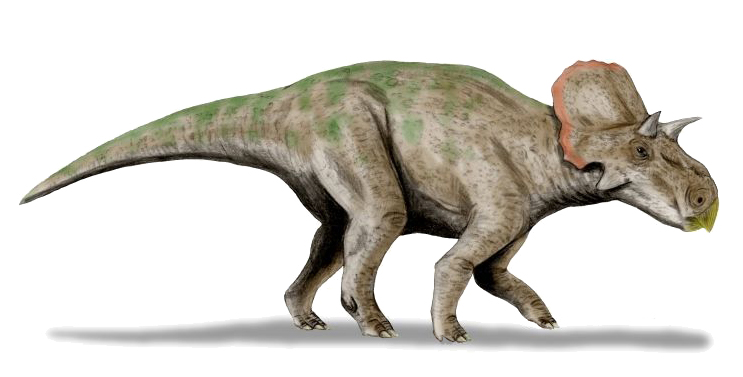 ''Avaceratops'' was originally by Dodson considered to have been an exceptionally small species. He estimated the holotype length at and assumed it had almost attained adult size. However, the second skull (which does not necessarily belong to ''Avaceratops''), MOR 692, indicates a body length of . Paul in 2010 estimated the weight of a four-metre-long animal at one tonne.Paul, G.S., 2010, ''The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs'', Princeton University Press p. 264 Another change in the image of ''Avaceratops'' brought about by MOR 692 concerned the brow horns. These were first thought to be rather short, although this was purely speculative, the holotype not having preserved them. The new skull showed postorbital horn cores with a length of .
''Avaceratops'' has a distinctive frill at the back of the skull. The squamosal, the element at the front of the frill side, is large with a continuously curving instead of a stepped edge. A raised area at the base of the squamosal divides it into two equal halves, whereas more derived species have an enlarged top part. The squamosal is separated from the
''Avaceratops'' was originally by Dodson considered to have been an exceptionally small species. He estimated the holotype length at and assumed it had almost attained adult size. However, the second skull (which does not necessarily belong to ''Avaceratops''), MOR 692, indicates a body length of . Paul in 2010 estimated the weight of a four-metre-long animal at one tonne.Paul, G.S., 2010, ''The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs'', Princeton University Press p. 264 Another change in the image of ''Avaceratops'' brought about by MOR 692 concerned the brow horns. These were first thought to be rather short, although this was purely speculative, the holotype not having preserved them. The new skull showed postorbital horn cores with a length of .
''Avaceratops'' has a distinctive frill at the back of the skull. The squamosal, the element at the front of the frill side, is large with a continuously curving instead of a stepped edge. A raised area at the base of the squamosal divides it into two equal halves, whereas more derived species have an enlarged top part. The squamosal is separated from the
 ''Avaceratops'' was by Dodson in 1986 assigned to the
''Avaceratops'' was by Dodson in 1986 assigned to the
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of small herbivorous ceratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. ...
n dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s which lived during the late Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian s ...
during the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
Period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
in what are now the Northwest United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
. Most fossils come from the Judith River Formation
The Judith River Formation is a fossil-bearing geologic formation in Montana, and is part of the Judith River Group. It dates to the Late Cretaceous, between 79 and 75.3 million years ago, corresponding to the "Judithian" land vertebrate age. It ...
.
Discovery and naming
The first remains of ''Avaceratops'' were found by fossil dealer Eddie Cole in theJudith River Formation
The Judith River Formation is a fossil-bearing geologic formation in Montana, and is part of the Judith River Group. It dates to the Late Cretaceous, between 79 and 75.3 million years ago, corresponding to the "Judithian" land vertebrate age. It ...
of Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
, in 1981, on land of the Careless Creek Ranch, owned by rancher Arthur J. Lammers."Avaceratops." In: Dodson, Peter & Britt, Brooks & Carpenter, Kenneth & Forster, Catherine A. & Gillette, David D. & Norell, Mark A. & Olshevsky, George & Parrish, J. Michael & Weishampel, David B. ''The Age of Dinosaurs''. Publications International, LTD. p. 129. . They were preserved scattered throughout the remains of a prehistoric stream bed. This ''Avaceratops'' specimen was likely buried in the sandbar after its body was swept downstream by the current. The finds, displayed in Cole's fossil shop, were in October 1981 inspected by Peter Dodson
Peter Dodson (born August 20, 1946) is an American paleontologist who has published many papers and written and collaborated on books about dinosaurs. An authority on Ceratopsians, he has also authored several papers and textbooks on hadrosaurs a ...
who in July 1982 during a visit with Cole to the site discovered additional bones, which from 1984 were excavated by Anthony Fiorillo
Anthony Ricardo Fiorillo is a senior fellow at the Institute for the Study of Earth and Man at Southern Methodist University, but for many years he was vice president of research & collections and chief curator at the Perot Museum of Nature & S ...
.
The fossil was formally named and described by Dodson in 1986, as the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
''Avaceratops lammersi''. It was the first ceratopsid named since ''Pachyrhinosaurus
''Pachyrhinosaurus'' (meaning in Greek "thick-nosed lizard", from ' (), thick; ' (), nose; and (), lizard) is an extinct genus of centrosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of North America. The first examples were discove ...
'' in 1950. The genus was named after Ava Cole, Eddie's wife. The specific epithet honors the Lammers family. In 1990 George Olshevsky emended the name to ''A. lammersorum'', with the specific name in the genitive plural because it referred to several people. However, Dodson objected against this change, arguing the genitive singular might also refer to a single family name. In 1990 Thomas Lehman renamed ''A. lammersi'' into ''Monoclonius
''Monoclonius'' (meaning "single sprout") is a dubious genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur found in the Late Cretaceous layers of the Judith River Formation in Montana, United States, and the uppermost rock layers of the Dinosaur Park Forma ...
lammersi''. This alternative name has found no acceptance.
The holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
, ANSP 15800, consists of a partial skeleton containing the lower skull, a left lower jaw, vertebrae, a complete shoulder girdle and most elements of forelimbs and hindlimbs. The type specimen might represent a juvenile or a subadult individual, Dodson in 1986 being inclined to consider it almost fully grown. Kenneth Carpenter
Kenneth Carpenter (born September 21, 1949, in Tokyo, Japan) is a paleontologist. He is the former director of the USU Eastern Prehistoric Museum and author or co-author of books on dinosaurs and Mesozoic life. His main research interests ...
made a reconstruction of the skull, a cast of which was by Leroy Glenn combined with restored parts of the postcranial skeleton to create a mount that in 1986 was displayed in the Academy of Natural Sciences
The Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University, formerly the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, is the oldest natural science research institution and museum in the Americas. It was founded in 1812, by many of the leading natura ...
in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
; a copy of this skeletal mount was donated to the Upper Musselshell Valley Historical Museum
Upper may refer to:
* Shoe#Shoe construction, Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot
* Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both
* ''Upper'', the original film titl ...
in Harlowton
Harlowton is a city in and the county seat of Wheatland County, Montana, United States. The population was 955 at the 2020 census.
Description
The city was once the eastern terminus of electric operations (1914–74) for the "Pacific Extension ...
.
In 1993 Paul Penkalski
Paul may refer to:
*Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name)
* Paul (surname), a list of people
People
Christianity
*Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Chri ...
referred two earlier found squamosal The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral co ...
s to ''Avaceratops'', USNM 4802 and USNM 2415, of larger individuals. In 1999, Penkalski and Dodson described a second skull, MOR 692, again of a larger individual. This specimen includes the upper skull, with the nose and brow horns. However, the assignment of the latter to ''Avaceratops'' has been questioned due to differences in relative chronological position, skull morphology, and lack of intermediate forms; thus, ''Avaceratops'' is only represented by the type specimen.
Description
 ''Avaceratops'' was originally by Dodson considered to have been an exceptionally small species. He estimated the holotype length at and assumed it had almost attained adult size. However, the second skull (which does not necessarily belong to ''Avaceratops''), MOR 692, indicates a body length of . Paul in 2010 estimated the weight of a four-metre-long animal at one tonne.Paul, G.S., 2010, ''The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs'', Princeton University Press p. 264 Another change in the image of ''Avaceratops'' brought about by MOR 692 concerned the brow horns. These were first thought to be rather short, although this was purely speculative, the holotype not having preserved them. The new skull showed postorbital horn cores with a length of .
''Avaceratops'' has a distinctive frill at the back of the skull. The squamosal, the element at the front of the frill side, is large with a continuously curving instead of a stepped edge. A raised area at the base of the squamosal divides it into two equal halves, whereas more derived species have an enlarged top part. The squamosal is separated from the
''Avaceratops'' was originally by Dodson considered to have been an exceptionally small species. He estimated the holotype length at and assumed it had almost attained adult size. However, the second skull (which does not necessarily belong to ''Avaceratops''), MOR 692, indicates a body length of . Paul in 2010 estimated the weight of a four-metre-long animal at one tonne.Paul, G.S., 2010, ''The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs'', Princeton University Press p. 264 Another change in the image of ''Avaceratops'' brought about by MOR 692 concerned the brow horns. These were first thought to be rather short, although this was purely speculative, the holotype not having preserved them. The new skull showed postorbital horn cores with a length of .
''Avaceratops'' has a distinctive frill at the back of the skull. The squamosal, the element at the front of the frill side, is large with a continuously curving instead of a stepped edge. A raised area at the base of the squamosal divides it into two equal halves, whereas more derived species have an enlarged top part. The squamosal is separated from the parietal bone
The parietal bones () are two bones in the Human skull, skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint, form the sides and roof of the Human skull, cranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four borders, an ...
at the rear of the skull by a small indentation. The parietals however, show no indentation at the midline of the frill rear. Also the parietals are probably lacking '' fenestrae'' which are typical of many other genera except ''Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of herbivore, herbivorous Chasmosaurinae, chasmosaurine Ceratopsidae, ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 68 m ...
'', resulting in a solid frill, although damage to the holotype allows for a small opening to be present.
Classification
 ''Avaceratops'' was by Dodson in 1986 assigned to the
''Avaceratops'' was by Dodson in 1986 assigned to the Ceratopsidae
Ceratopsidae (sometimes spelled Ceratopidae) is a family of ceratopsian dinosaurs including ''Triceratops'', ''Centrosaurus'', and ''Styracosaurus''. All known species were quadrupedal herbivores from the Upper Cretaceous. All but one species are k ...
within the Ceratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. ...
(both names being derived from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
for 'horned face'), a group of herbivorous dinosaurs with parrot
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoid ...
-like beaks which thrived in what are now North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
, during the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
Period.
Apart from being a ceratopsian, little is certain about ''Avaceratops's'' taxonomic position. Because most of the skeleton is only known from a juvenile, and juveniles tend to express ancestral traits more strongly, a cladistic
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived char ...
analysis would likely indicate a too basal, low, position in the evolutionary tree. For this reason, ''Avaceratops'' has often been excluded from such analyses. Penkalski and Dodson in 1999 concluded that ''Avaceratops'' most likely occupied a basal position within the Centrosaurinae
Centrosaurinae (from the Greek, meaning "pointed lizards") is a subfamily of ceratopsid dinosaurs, a group of large quadrupedal ornithischians. Centrosaurine fossil remains are known primarily from the northern region of Laramidia (modern day Al ...
but that it was also possible it was a basal member of the Ceratopsinae or just outside the clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
formed by both groups. A phylogenetic analysis performed by Sampson et al. (2013) found that ''Avaceratops'' was the sister taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and t ...
of the new genus ''Nasutoceratops
''Nasutoceratops'' is an extinct genus of ceratopsian dinosaur. It is a basal centrosaurine which lived during the Late Cretaceous Period (late Campanian, about 76.0-75.5 Ma). Fossils have been found in southern Utah, United States. ''Nasutocer ...
'', described and named in 2013
File:2013 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: Edward Snowden becomes internationally famous for leaking classified NSA wiretapping information; Typhoon Haiyan kills over 6,000 in the Philippines and Southeast Asia; The Dhaka garment fact ...
. This clade containing both ''Avaceratops'' and ''Nasutoceratops'' was named the Nasutoceratopsini in 2016.
The cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ...
presented below follows a phylogenetic analysis by Chiba ''et al.'' (2017):
Paleobiology
''Avaceratops'', like all ceratopsians, was aherbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
. During the Cretaceous, flowering plants were "geographically limited on the landscape", so it is likely that this dinosaur fed on the predominant plants of the era: fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except t ...
s, cycad
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk (botany), trunk with a crown (botany), crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants o ...
s and conifer
Conifers are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single ...
s. It would have used its sharp ceratopsian beak to bite off the leaves or needles. The habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
of ''Avaceratops'' was heavily forested and wet.
See also
*Timeline of ceratopsian research
This timeline of ceratopsian research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the ceratopsians, a group of herbivorous marginocephalian dinosaurs that evolved parrot-like beaks, bony frills, and, later, spe ...
References
* https://web.archive.org/web/20050824122458/http://www.vertpaleo.org/jvp/19-692-711.html (online abstract of the preceding) * https://web.archive.org/web/20090531083004/http://www.dinosaurvalley.com/Visiting_Drumheller/Kids_Zone/Groups_of_Dinosaurs/index.php * '' The Humongous Book of Dinosaurs'', published by Stewart Tabori & ChangNotes
{{Taxonbar, from=Q131576 Centrosaurines Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of North America Fossil taxa described in 1986 Taxa named by Peter Dodson Paleontology in Montana Campanian genus first appearances Campanian genus extinctions Ornithischian genera