|
1857 In China
Events from the year 1857 in China. Incumbents * Xianfeng Emperor (7th year) Viceroys * Viceroy of Zhili — Guiliang (- Jan.), Tan Tingxiang (Jan. - ) Events * Nian Rebellion * Second Opium War ** January 4 — Battle of Macao FortFurther Papers Relating to the Proceedings of Her Majesty's Naval Forces at Canton'. London: Harrison and Sons. 1857. pp. 27–31. ** December 28–31 — Battle of Canton (1857) * Taiping Rebellion * Miao Rebellion (1854–73) * Panthay Rebellion * Ningpo massacre * April 20 — James Bruce, 8th Earl of Elgin appointed plenipotentiary to China. Births * Canton — Gin Chow, (1857 – 1933) Chinese immigrant who gained fame in California as a prophet and fortune teller able to predict the weather and other natural events * Penang, British Malaya — Gu Hongming, (1857 – 1928) was a British Malaya born Chinese man of letters. He also used the pen name "Amoy Ku", later served in the Qing government * Chengdu — Li Donghai, (1857–1938 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Malaya
The term "British Malaya" (; ms, Tanah Melayu British) loosely describes a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the island of Singapore that were brought under British hegemony or control between the late 18th and the mid-20th century. Unlike the term "British India", which excludes the Indian princely states, British Malaya is often used to refer to the Federated and Unfederated Malay States, which were British protectorates with their own local rulers, as well as the Straits Settlements, which were under the sovereignty and direct rule of the British Crown, after a period of control by the East India Company. Before the formation of the Malayan Union in 1946, the territories were not placed under a single unified administration, with the exception of the immediate post-war period when a British military officer became the temporary administrator of Malaya. Instead, British Malaya comprised the Straits Settlements, the Federated Malay States, and the Unfederated Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Tape
Mary Tape (1857–1934) was a desegregation activist who fought for Chinese-Americans' access to education, notably in the case ''Tape v. Hurley'' in 1885,"We have always lived as Americans" Chinese American Exclusion/Inclusion, New-York Historical Society. Retrieved 8 Dec 2016. Berkeley Architectural Heritage Association website. Retrieved 8 December 2016 in which the stated that public schools could not exclude her daughter Mamie Tape for being Chinese-American. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, Postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an Eastern China, eastern coastal Provinces of the People's Republic of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its capital in Nanjing. Jiangsu is the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, third smallest, but the List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, fifth most populous and the List of Chinese administrative divisions by population density, most densely populated of the 23 provinces of the People's Republic of China. Jiangsu has the highest GDP per capita of Chinese provinces and second-highest GDP of Chinese provinces, after Guangdong. Jiangsu borders Shandong in the north, Anhui to the west, and Zhejiang and Shanghai to the south. Jiangsu has a coastline of over along the Yellow Sea, and the Yangtze River passes through the southern part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Noble Consort Gongsu
Imperial Noble Consort Gongsu (20 September 1857 – 14 April 1921), of the Manchu Bordered Yellow Banner Arute (阿鲁特) clan, was a consort of the Tongzhi Emperor. She was one year his junior. Life Family background Imperial Noble Consort Gongsu's personal name was not recorded in history. Her family originally belonged to the Mongol Plain Blue Banner. * Father: Saišangga (; 1794–1875), served as the Minister of Works from 1841–1845 ** Paternal grandfather: Jinghui (景辉) ** Paternal grandmother: Lady Zhang (张氏) * Mother: Lady Fuca ** Maternal grandfather: Xingfu (兴福) * Four brothers ** Third elder brother: Chongqi (; 1829–1900), the top candidate in the 1865 imperial examination, served as a fourth rank literary official () in the Hanlin Academy, the Minister of Revenue from 1884–1886 and in 1900 and the Minister of Personnel in 1886, and held the title of a third class duke (), the father of Empress Xiaozheyi (1854–1875) Xianfeng era The future Imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Jingxi
Li Jingxi (; 1857–18 September 1925) was a politician in the Qing Dynasty and Republic of China. He was born in Anhui and was the nephew of Li Hongzhang. He was the Premier of State Council in May–July 1917. During the Qing Dynasty, he was the last viceroy of Yun-Gui The Viceroy of Yun-Gui, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of Yunnan and Guizhou Provinces and the Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Affairs and Food Production, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional viceroys ... from 1909 to 1911. 徐友春主编. 民国人物大辞典 増订版. 河北人民出版社. 2007. References 1857 births 1925 deaths Premiers of the Republic of China Viceroys of Yun-Gui {{China-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze River and the Huai River, bordering Jiangsu to the east, Zhejiang to the southeast, Jiangxi to the south, Hubei to the southwest, Henan to the northwest, and Shandong for a short section in the north. With a population of 63.65 million, Anhui is the 8th most populous province in China. It is the 22nd largest Chinese province based on area, and the 12th most densely-populated region of all 34 Chinese provincial regions. Anhui's population is mostly composed of Han Chinese. Languages spoken within the province include Jianghuai Mandarin, Wu, Hui, Gan and small portion of Zhongyuan Mandarin Chinese. The name "Anhui" derives from the names of two cities: Anqing and Huizhou (now Huangshan City). The abbreviation for Anhui is "" after the histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
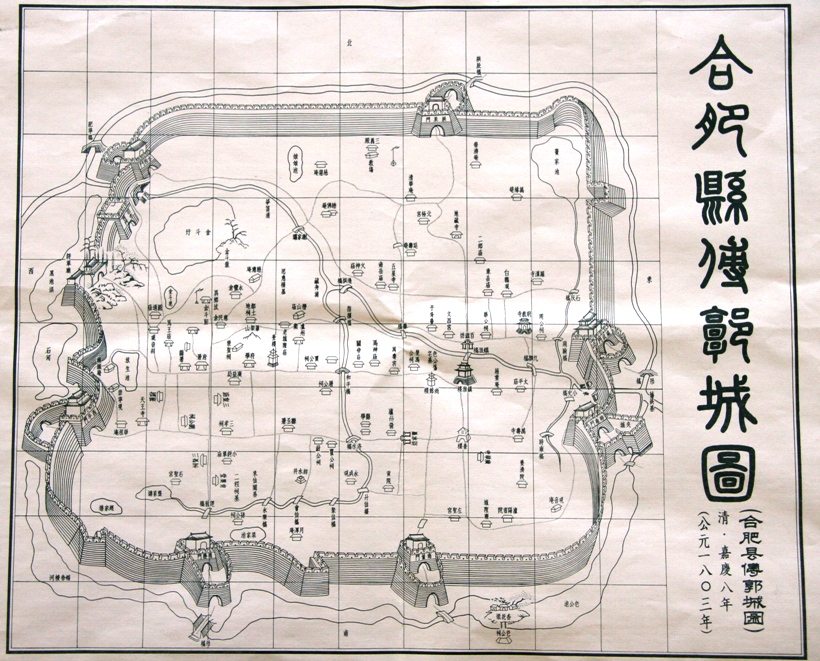
Hefei
Hefei (; ) is the capital and largest city of Anhui Province, People's Republic of China. A prefecture-level city, it is the political, economic, and cultural center of Anhui. Its population was 9,369,881 as of the 2020 census and its built-up (or ''metro'') area made up of four urban districts plus Feidong, Feixi and Changfeng counties being urbanized, was home to 7,754,481 inhabitants. Located in the central portion of the province, it borders Huainan to the north, Chuzhou to the northeast, Wuhu to the southeast, Tongling to the south, Anqing to the southwest and Lu'an to the west. A natural hub of communications, Hefei is situated to the north of Chao Lake and stands on a low saddle crossing the northeastern extension of the Dabie Mountains, which forms the divide between the Huai and Yangtze rivers. The present-day city dates from the Song dynasty. Before World War II, Hefei remained essentially an administrative centre and the regional market for the fertile plain to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xidaotang
Xidaotang (, "Hall of the Western ''Dao''," i.e. Islam)--originally called Jinxingtang , the "Gold Star Hall"; also called the ''Hanxue pai'' , the "Han Studies Sect" —is a Sino-Islamic religious body / special economic community centered in Gansu province. Founded in 1901 by Ma Qixi (1857–1914), a Chinese Muslim from Lintan (formerly Taozhou), it fuses traditional Sunni Hanafi Islam with study of the Confucian classics and the Han Kitab. The group lived communally, supporting itself through a trade network which extended into the Tibetan border regions. In 1914, Hui general Ma Anliang, affiliated with the rival Khufiyya order, slew Ma Qixi, and was nearly successful in exterminating the sect, but a portion evaded capture. Hui warlord Ma Zhongying raided Hui and Tibetan encampments in the 1920s, causing another exodus. The Xidaotang pledged allegiance to the Kuomintang after their rise to power, and in 1941, the Hui General Bai Chongxi introduced Chiang Kai-shek to Xidaotang le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma Qixi
Ma Qixi (1857–1914; , Xiao'erjing: ), a Hui from Gansu, was the founder of the Xidaotang, a Chinese-Islamic school of thought. Education and teaching Ma was born into the family of a Táozhōu ''ahong'' of the Beizhuang ''menhuan'', a Sufi order. At 11 years of age, he studied with a non-Muslim who was an examination graduate at the private academy he attended. He was introduced to the senior licentiate, Fan Shengwu, whose school was at New Taozhou. Ma placed second in the Táozhōu examination and fourth in the prefectural examination in Gongchang, achieving the rank of ''xiucai''. He studied Neo-Confucian texts and the Han Kitab. Wang Daiyu, Ma Zhu, Liu Zhi, and others had synthesized Confucianism with Islam. Ma believed Muslims should use Chinese culture to understand Islam. He opened his own school, Gold Star Hall (''Jinxing Tang'') at a '' gongbei'' of his ''menhuan''. He taught Islam, Chinese curriculum, and the Han Kitab. Ma became an independent instructor; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan and Loess plateaus and borders Mongolia ( Govi-Altai Province), Inner Mongolia and Ningxia to the north, Xinjiang and Qinghai to the west, Sichuan to the south and Shaanxi to the east. The Yellow River passes through the southern part of the province. Part of Gansu's territory is located in the Gobi Desert. The Qilian mountains are located in the south of the Province. Gansu has a population of 26 million, ranking 22nd in China. Its population is mostly Han, along with Hui, Dongxiang and Tibetan minorities. The most common language is Mandarin. Gansu is among the poorest administrative divisions in China, ranking 31st, last place, in GDP per capita as of 2019. The State of Qin originated in what is now southeastern Gansu and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu E (writer)
Liu E (; also spelled Liu O; 18 October 1857 – 23 August 1909), courtesy name Tieyun (), was a Chinese writer, archaeologist and politician of the late Qing Dynasty. Government and politics Liu was a native of Dantu (modern day Zhenjiang). In the government he worked with flood control, famine relief, and railroads. He became disillusioned with official ideas of reform and became a proponent of private economic development modeled after western systems. During the Boxer Uprising he speculated in government rice, distributing it to the poor. He was cashiered for these efforts, but shrewd investments had left him wealthy enough to follow his pioneering archaeological studies and to write fiction. Literature Liu's best known work is ''The Travels of Lao Can'', which the critic C.T. Hsia calls the "most beloved of all the novels" in the last decade of the Qing. Liu E's novels borrowed allusions and images from classical Chinese literature and used extensive symbolism. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)