Hefei on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hefei (; ) is the capital and largest city of
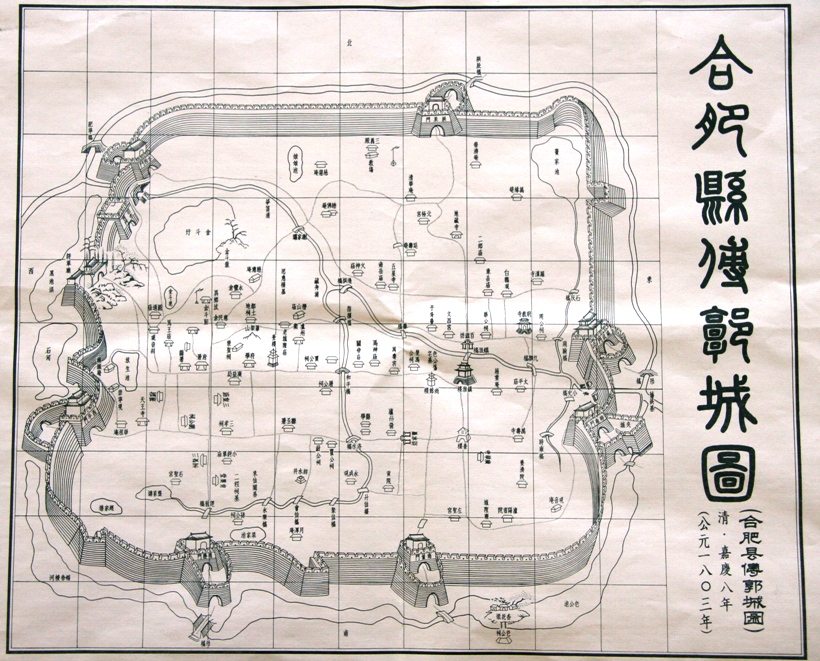 From the 8th to the 6th centuries BC, Hefei was the site of many small states, later a part of the Chu kingdom. Many archaeological finds dating from this period have been made. The name 'Hefei' was first given to the county set up in the area under the
From the 8th to the 6th centuries BC, Hefei was the site of many small states, later a part of the Chu kingdom. Many archaeological finds dating from this period have been made. The name 'Hefei' was first given to the county set up in the area under the
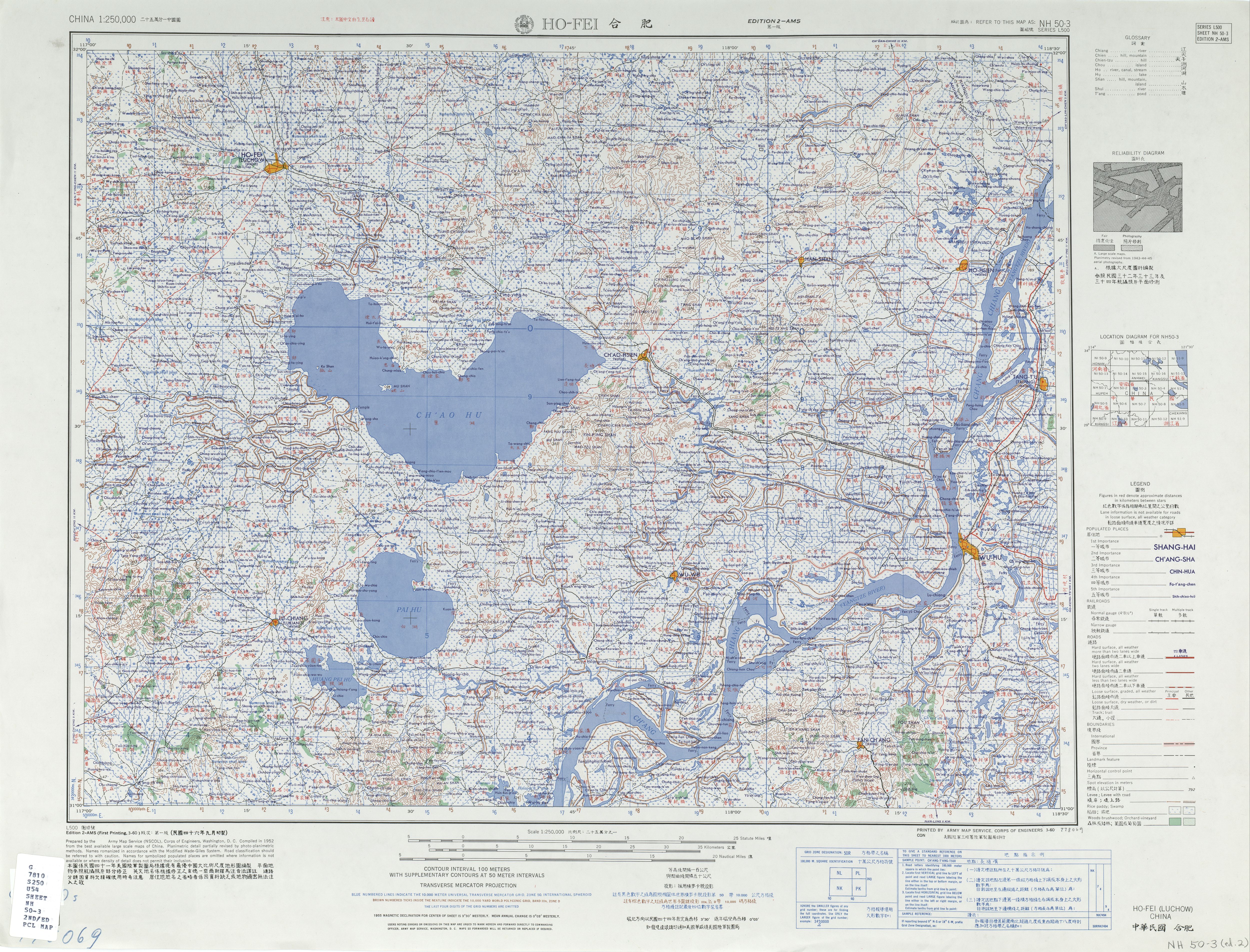 Hefei is located west of
Hefei is located west of
 Hefei has been the provincial capital since 1945 (before it was Lihuang, which is today's Jinzhai) and is a natural center of
Hefei has been the provincial capital since 1945 (before it was Lihuang, which is today's Jinzhai) and is a natural center of
 *
*

 * Sanhe Town, ancient town which has a history of more than 2,500 years.
* Xiaoyaojin Park, a public park sitting on the ancient site of the Battle of Xiaoyao Ford.
*Temple of Lord Bao, built in 1066 near the tomb of Lord Bao.
*
* Sanhe Town, ancient town which has a history of more than 2,500 years.
* Xiaoyaojin Park, a public park sitting on the ancient site of the Battle of Xiaoyao Ford.
*Temple of Lord Bao, built in 1066 near the tomb of Lord Bao.
*
Hefei Online Government
{{Authority control Provincial capitals in China
Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze River ...
Province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
, People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, sli ...
. A prefecture-level city
A prefecture-level city () or prefectural city is an administrative division of the People's Republic of China (PRC), ranking below a province and above a county in China's administrative structure.
During the Republican era, many of China' ...
, it is the political, economic, and cultural center of Anhui. Its population was 9,369,881 as of the 2020 census and its built-up (or ''metro'') area made up of four urban districts plus Feidong, Feixi and Changfeng counties being urbanized, was home to 7,754,481 inhabitants. Located in the central portion of the province, it borders Huainan to the north, Chuzhou to the northeast, Wuhu to the southeast, Tongling to the south, Anqing to the southwest and Lu'an to the west. A natural hub of communications, Hefei is situated to the north of Chao Lake
Chao Lake (), also known by its Chinese name Chao Hu, is a lake wholly situated in Hefei, the capital of Anhui Province. It is the largest lake in Anhui and one of the five largest freshwater lakes in China.
Mythology
According to legend, the ...
and stands on a low saddle crossing the northeastern extension of the Dabie Mountains, which forms the divide between the Huai
The Huai River (), formerly romanized as the Hwai, is a major river in China. It is located about midway between the Yellow River and Yangtze, the two longest rivers and largest drainage basins in China, and like them runs from west to east. ...
and Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flow ...
rivers.
The present-day city dates from the Song dynasty. Before World War II, Hefei remained essentially an administrative centre and the regional market for the fertile plain to the south. It has gone through a growth in infrastructure in recent years. Hefei is the location of Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak, an experimental superconducting tokamak
A tokamak (; russian: токамáк; otk, 𐱃𐰸𐰢𐰴, Toḳamaḳ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being ...
magnetic fusion energy reactor.
Hefei is a world leading city for scientific research, with its ranking placed at 16th globally, 8th in the Asia-Pacific and 6th in China (behind Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
, Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
, Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and t ...
, Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong ...
and Wuhan
Wuhan (, ; ; ) is the capital of Hubei Province in the People's Republic of China. It is the largest city in Hubei and the most populous city in Central China, with a population of over eleven million, the ninth-most populous Chinese city a ...
), as tracked by the Nature Index The Nature Index is a database that tracks institutions and countries and their scientific output since its introduction in November, 2014. Each year, Nature Index ranks the leading institutions (which can be companies, universities, government agen ...
in 2022. The city is represented by several major universities, including the University of Science and Technology of China
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which rou ...
, Hefei University of Technology, Anhui University
Anhui University (), colloquially known in Chinese as An Da (安大, ''Āndà''), is located in Hefei, the capital city of Anhui Province, China. Founded in 1928 in Anqing, named 'National Anhui University' in 1946 and moved to Hefei in 1958, ...
, Anhui Agricultural University
Anhui Agricultural University (AAU) () is in Hefei, the capital city of Anhui, China. AAU is a key university, with a long history specializing in agriculture and forestry. It is jointly funded by Anhui Provincial Government and the Ministry of ...
and Anhui Medical University. Notably, the University of Science and Technology of China
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which rou ...
is one of the top 100th comprehensive public
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichk ...
research universities in the world.
History
 From the 8th to the 6th centuries BC, Hefei was the site of many small states, later a part of the Chu kingdom. Many archaeological finds dating from this period have been made. The name 'Hefei' was first given to the county set up in the area under the
From the 8th to the 6th centuries BC, Hefei was the site of many small states, later a part of the Chu kingdom. Many archaeological finds dating from this period have been made. The name 'Hefei' was first given to the county set up in the area under the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
in the 2nd century BC.
In the 3rd century AD, the Battle of Xiaoyao Ford was fought at Xiaoyao Ford
The Xiaoyao Faction or Xiaoyao Pai (), also known as Tea-drinking Faction (喝茶派), translated into English as Wanderers' Faction or Faction of Bystanders or Carefree Clique, refers to the illiterate or indifferent people who do not belong to ...
() in Hefei. Zhang Liao, a general of the Wei
Wei or WEI may refer to:
States
* Wey (state) (衛, 1040–209 BC), Wei in pinyin, but spelled Wey to distinguish from the bigger Wei of the Warring States
* Wei (state) (魏, 403–225 BC), one of the seven major states of the Warring States per ...
state, led 800 picked cavalry to defeat the 200,000-strong army from Wei's rival state Wu. Several decades of warring in Hefei between Wu and Wei followed this battle.
During the 4th to the 6th centuries AD, this crucial border region between northern and southern states was much fought over; its name and administrative status were consequently often changed. During the Sui (581–618) and Tang (618–907) periods, it became the seat of Lu prefecture—a title it kept until the 15th century, when it became a superior prefecture named Luzhou.
The present city dates from the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
(960–1126), the earlier Hefei having been some distance farther north. In the 10th year of Xining (, 1077 AD), the taxes collected from the Luchow Prefecture were 50315 Guan, approximately 25 million today's Chinese Yuan, with a ranking of the amount of taxes was the 11th(following Kaifeng, Hangzhou, Qinzhou, Chuzhou, Chengdu, Zizhou, Xingyuan, Mianzhou, Zhenzhou, Suzhou) among all the prefectures of Song Dynasty. During the 10th century, it was for a while the capital of the independent Wu kingdom (902–938) and was an important center of the Southern Tang state (937–975).
After 1127 it became a center of the defenses of the Southern Song dynasty (1126–1279) against the Jin ( Jurchen) invaders in the Jin–Song wars
The Jin–Song Wars were a series of conflicts between the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty (1115–1234) and the Han-led Song dynasty (960–1279). In 1115, Jurchen tribes rebelled against their overlords, the Khitan-led Liao dynasty (916–1125) ...
, as well as a flourishing center of trade between the two states. When the Chinese Republic was founded in 1911, the superior prefecture was abolished, and the city took the name of Hefei. The city was known as Luchow or Liu-tcheou (, p ''Luzhou'') during the Ming and Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
dynasties (after the 14th century to the 19th century). Hefei was the temporary capital for Anhui from 1853 to 1862. It was renamed as Hefei County in 1912. Following the Chinese victory in the Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Thea ...
in 1945, Hefei was made the capital of Anhui.
Before World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Hefei remained essentially an administrative center and the regional market for the fertile plain to the south. It was a collecting center for grain, beans, cotton, and hemp, as well as a center for handicraft industries manufacturing cloth, leather, bamboo goods, and ironware.
The construction in 1912 of the Tianjin–Pukou railway, farther east, for a while made Hefei a provincial backwater, and much of its importance passed to Bengbu
Bengbu () is a city in northern Anhui Province, China. Its population was 3,296,408 registered residents at the 2020 census. 1,968,027 lived in the built-up area made of four Bengbu urban districts and Fengyang County in Chuzhou Prefecture, larg ...
. In 1932–36, however, a Chinese company built a railway linking Hefei with Yuxikou (on the Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flow ...
opposite Wuhu) to the southeast and with the Huai River
The Huai River (), formerly romanized as the Hwai, is a major river in China. It is located about midway between the Yellow River and Yangtze, the two longest rivers and largest drainage basins in China, and like them runs from west to east ...
at Huainan to the north. While this railway was built primarily to exploit the rich coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen ...
field in northern Anhui, it also did much to revive the economy of the Hefei area by taking much of its produce to Wuhu and Nanjing.
Although Hefei was a quiet market town of only about 30,000 in the mid-1930s, its population grew more than tenfold in the following 20 years. The city's administrative role was strengthened by the transfer of the provincial government from Anqing in 1945, but much of its new growth derived from its development as an industrial city. A cotton mill
A cotton mill is a building that houses spinning (textiles), spinning or weaving machinery for the production of yarn or cloth from cotton, an important product during the Industrial Revolution in the development of the factory system.
Althou ...
was opened in 1958, and a thermal generating plant, using coal from Huainan, was established in the early 1950s. It also became the seat of an industry producing industrial chemicals and chemical fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s. In the late 1950s an iron and steel complex was built. In addition to a machine-tool works and engineering and agricultural machinery factories, the city has developed an aluminum industry and a variety of light industries. There are several universities based in the city.
Geography
 Hefei is located west of
Hefei is located west of Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and t ...
in south-central Anhui. Chao Lake
Chao Lake (), also known by its Chinese name Chao Hu, is a lake wholly situated in Hefei, the capital of Anhui Province. It is the largest lake in Anhui and one of the five largest freshwater lakes in China.
Mythology
According to legend, the ...
, a lake southeast of the city, is one of the largest fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does incl ...
lakes in China. Though, the lake has unfortunately been polluted with nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seve ...
and phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ea ...
, in recent decades, the situation is improving due to efforts by both the government and the people.
Climate
Hefei features a humid subtropical climate ( Köppen ''Cfa'') with four distinct seasons. Hefei's annual average temperature is . Its annualprecipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hai ...
is just slightly over , being heavier from May through August. Winters are damp and cold, with January lows dipping just below freezing and January averaging . The city sees irregular snowfalls that rarely turn significant. Springs are generally relatively pleasant if somewhat erratic. Summers here are oppressively hot and humid, with a July average of . In the months of June, July, August, and often September, daily temperatures can reach or surpass with high humidity levels being the norm. Autumn in Hefei sees a gradual cooling and drying. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 35 percent in March to 50 percent in August, the city receives 1,868 hours of bright sunshine annually. Extremes since 1951 have ranged from on 6 January 1955 to on 27 July 2017.
Air Pollution
Air quality typically diminishes in May and June when the city is blanketed by smog caused by the smoke generated as farmers outside the city burn their fields in preparation for planting the next crop.Administrative divisions and demographics
Demographics
The majority of the population in Hefei areHan Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive v ...
. There are a comparatively small number of Hui Chinese
The Hui people ( zh, c=, p=Huízú, w=Hui2-tsu2, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Хуэйзў, ) are an East Asian ethnoreligious group predominantly composed of Chinese-speaking adherents of Islam. They are distributed throughout China, mainly in the n ...
living in the city, for whom a few mosques have been constructed. Of the more than five million people in the city, some are migrant workers from other parts of Anhui.
Administration
Theprefecture-level city
A prefecture-level city () or prefectural city is an administrative division of the People's Republic of China (PRC), ranking below a province and above a county in China's administrative structure.
During the Republican era, many of China' ...
of Hefei administers 9 county-level divisions, including 4 districts, 1 County-city and 4 counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
.
Hefei subdivisions area (km²), population (According to 2010 Census) and population density (per km²).
Economy
The GDP was ¥1141.28 billion in 2021. The GDP per capita was ¥121187(ca.US$18784) in 2021.Ranked top 20 cities of China. Before theChinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on main ...
, Hefei's main industry was agriculture. After World War II, the capital of Anhui was moved from Anqing to Hefei. To assist the development of the city, many talented people were sent in from other parts of the country. Modern-day Hefei has machinery, electronics, chemistry, steel, textile, and cigarette industries, among others.
In the summer of 2005, the municipal government implemented changes designed to beautify the city by demolishing thousands of illegally built
Illegal construction (also known as illegal building or illegal housing) is construction work (or the result of such) without a valid construction permit. Besides the potential technical hazards on uncontrolled construction sites and in finished ...
structures, and clearing away long-established marketplaces in many parts of the city. While these actions removed many unlicensed, and often poorly-constructed food stalls which had been contributing to the spread of disease and which posed fire hazards, these changes also removed longstanding businesses that had lined many streets throughout the city overnight. The impact on the local economy was felt immediately as hundreds, if not thousands, of low paid workers no longer had employment.
Hefei has been identified by the Economist Intelligence Unit
The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) is the research and analysis division of the Economist Group, providing forecasting and advisory services through research and analysis, such as monthly country reports, five-year country economic forecasts, ...
in the November 2010 Access China White Paper as a member of the CHAMPS ( Chongqing, Hefei, Anshan, Ma'anshan, Pingdingshan and Shenyang), an economic profile of the top 20 emerging cities in China.
Hefei was identified by ''The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Econ ...
'' in December 2012 as the world's No.1 fastest growing metropolitan economy.
Transportation
 Hefei has been the provincial capital since 1945 (before it was Lihuang, which is today's Jinzhai) and is a natural center of
Hefei has been the provincial capital since 1945 (before it was Lihuang, which is today's Jinzhai) and is a natural center of transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipel ...
, being situated to the north of Lake Chao and standing on a low saddle crossing the northeastern extension of the Dabie Mountains, which form the divide between the Huai
The Huai River (), formerly romanized as the Hwai, is a major river in China. It is located about midway between the Yellow River and Yangtze, the two longest rivers and largest drainage basins in China, and like them runs from west to east. ...
and Yangtze river
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flow ...
s. From Hefei there is easy water transport
Maritime transport (or ocean transport) and hydraulic effluvial transport, or more generally waterborne transport, is the transport of people ( passengers) or goods ( cargo) via waterways. Freight transport by sea has been widely used th ...
via the lake to the Yangtze River opposite Wuhu.
Land
Important land routes run through Hefei, including: 1. G3 Beijing-Taipei Expressway (京台高速公路 FromBeijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
to Pingtan, and was designed to cross the Taiwan Strait
The Taiwan Strait is a -wide strait separating the island of Taiwan and continental Asia. The strait is part of the South China Sea and connects to the East China Sea to the north. The narrowest part is wide.
The Taiwan Strait is itself ...
to connect the highways in Taipei
Taipei (), officially Taipei City, is the capital and a special municipality of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Located in Northern Taiwan, Taipei City is an enclave of the municipality of New Taipei City that sits about southwest of the ...
)
2. G40 Shanghai-Xi'an Expressway (沪陕高速公路 From Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
to Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by #Name, other names, is the list of capitals in China, capital of Shaanxi, Shaanxi Province. A Sub-provincial division#Sub-provincial municipalities, sub-provincial city o ...
)
3. G42 Shanghai-Chengdu Expressway
G4 or G.IV may refer to:
Transport
* AEG G.IV, a German World War I heavy bomber
* Allegiant Air, by IATA airline designator
* Caudron G.4, a 1915 French biplane
* Friedrichshafen G.IV, a 1918 German medium bomber
* Gotha G.IV, a 1916 German he ...
(沪蓉高速公路 From Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
to Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
)
4. G4212 Hefei-Anqing Expressway
G4 or G.IV may refer to:
Transport
* AEG G.IV, a German World War I heavy bomber
* Allegiant Air, by IATA airline designator
* Caudron G.4, a 1915 French biplane
* Friedrichshafen G.IV, a 1918 German medium bomber
* Gotha G.IV, a 1916 German he ...
(合安高速公路 From Hefei to Anqing, a spur of G42)
5. G5011 Wuhu-Hefei Expressway
G5, G.V, G.5 or G-5 may refer to:
Businesses and companies
* G5 Entertainment, a video game developer and publisher; see list of PlayStation minis
* G5, IATA code for China Express Airlines
Electronics and software
* Canon PowerShot G5, a digita ...
(芜合高速公路 From Wuhu to Hefei, a spur of G50)
6. China National Highway 206 (烟汕线 From Yantai
Yantai, formerly known as Chefoo, is a coastal prefecture-level city on the Shandong Peninsula in northeastern Shandong province of People's Republic of China. Lying on the southern coast of the Bohai Strait, Yantai borders Qingdao on the ...
to Shantou
Shantou, Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanization of Chinese, romanized as Swatow and sometimes known as Santow, is a prefecture-level city on the eastern coast of Guangdong, China, with a total population of 5,502,031 as of the 2 ...
)
7. China National Highway 312 (沪霍线 From Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
to Khorgas)
8. China National Highway 346
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
(沪康线 From Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
to Ankang
Ankang () is a prefecture-level city in the south of Shaanxi Province in the People's Republic of China, bordering Hubei province to the east, Chongqing municipality to the south, and Sichuan province to the southwest.
History
The se ...
)
9. S24 Changshu-Hefei Expressway
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ess'' (pronounced ), plural ''esses''.
History ...
(常合高速公路 From Changshu to Hefei)
10.S17 Bengbu-Hefei Expressway S17 may refer to:
Aviation
* Rans S-17 Stinger, an American ultralight aircraft
* Saab 17, a Swedish reconnaissance aircraft
* Short S.17 Kent, a British flying boat airliner
* SIAI S.17, an Italian racing flying boat
* Sikorsky S-17, a Russ ...
(蚌合高速公路 From Bengbu
Bengbu () is a city in northern Anhui Province, China. Its population was 3,296,408 registered residents at the 2020 census. 1,968,027 lived in the built-up area made of four Bengbu urban districts and Fengyang County in Chuzhou Prefecture, larg ...
to Hefei)
11. G3W Dezhou-Shangrao Expressway (德上高速公路 From Dezhou to Shangrao)
There are two main train stations in Hefei. The newest one is Hefei South railway station (Hefeinan station, 合肥火车南站) where most high-speed trains pass through. Many city buses serve this station, for instance the 108 from the East gate of the University of Science and Technology's East campus on Susong road. It has a very comprehensive taxi rank with multiple queues to avoid a long wait. There are many fast food restaurants in the departure hall with seating. There are not so many options for arrivals, a small cafe and a takeaway kfc booth. There is an ATM in the ticket sales area next to the security gates for the departure hall.
The alternative station is Hefei railway station
The Hefei railway station () is a major railway station in Hefei, Anhui, China.
It was built in 1934, and served as of 2019 by the Hening Passenger Railway, Western Union Railway, Huainan Railway
Huainan () is a prefecture-level city wi ...
() which is smaller and older. This has only one taxi queue, directly opposite the main exit. There is fast food, a post office and a China mobile store in the same courtyard next to the arrival gates.
There are some small stations such as Feidong Station (), Feixi Station (), Shuijiahu Station (), Chaohu Station (), Chaohu East railway station
Chaohu East railway station () is a railway station in Chaohu, Hefei, Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest ...
(Chaohudong station; 巢湖火车东站), Hefeibeicheng Station (Hefei Northtown Station 合肥北城火车站), Lujiang Station () and so on. These stations are mostly located in small towns or played commuting roles.
Important railways that run through Hefei, including:
1. Shanghai-Wuhan-Chengdu High-Speed Railway ()
2. Hefei-Fuzhou high-speed railway (合福高速铁路 Play as part of Beijing-Taipei high-speed railway)
3. Hefei-Bengbu high-speed railway (合蚌高速铁路 A spur of Beijing-Shanghai high-speed railway)
4. Shangqiu-Hangzhou high-speed railway (商合杭高速铁路 The northern part, Shangqiu-Hefei High-Speed Railway will play as a part of Beijing-Hong Kong high-speed railway. Under Construction)
5. Hefei-Anqing-Jiujiang high-speed railway (合安九高速铁路 Play as a part of Beijing-Hong Kong High-Speed Railway.)
6. Hefei-Qingdao high-speed railway (合青高速铁路 Proposed)
7. Nanjing-Xi'an high-speed railway (宁西高速铁路 Proposed)
8. Huainan railway (淮南铁路 From Huainan- Wuhu)
9. Hefei-Jiujiang railway ()
10. Nanjing-Xi'an railway ()
11. Lujiang-Tongling railway (庐铜铁路 Under Construction)
In 2008 the thoroughfare Chang Jiang Road () is undergoing a renovation project to widen the roads and to create a bus route in the center of the road, with bus stations at islands that are connected to the sidewalks by skyways. The First Ring Road is also undergoing construction, with traffic lights being replaced by overpasses and ramps built to connect the First Ring Road and all major intersecting roads. Both projects are intended to ease the traffic Hefei now experiences at rush hour.
Air
Hefei Xinqiao International Airport replaced the old Hefei Luogang International Airport and started its operation on May 30, 2013 00:00. This new domestic aviation hub is located in Gaoliu Village situated in the northwestern part of Hefei City. The first arriving flight wasChina Eastern Airlines
China Eastern Airlines Corporation Limited (), also known as China Eastern, is an airline headquartered in the China Eastern Airlines Building, on the grounds of Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport in Changning District, Shanghai. It is ...
flight MU5172 from Beijing Capital International Airport
Beijing Capital International Airport is one of two international airports serving Beijing, the other one being Beijing Daxing International Airport (PKX). It is located northeast of Beijing's city center, in an exclave of Chaoyang District ...
. The first departing flight was China Eastern Airlines
China Eastern Airlines Corporation Limited (), also known as China Eastern, is an airline headquartered in the China Eastern Airlines Building, on the grounds of Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport in Changning District, Shanghai. It is ...
MU5468 to Shanghai Pudong International Airport.
Hefei Xinqiao International Airport provides scheduled passenger service to major airports in China and other international cities. Destinations include Hong Kong, Macao, Singapore, Taipei (Taoyuan, Songshan), Kaohsiung, Taichung, Seoul, Cheongju, Yangyang, Jeju, Osaka, Nagoya, Shizuoka, Okayama, Boracay Island, Bali Island, Frankfurt, Siem Reap, Bangkok, Phuket Island and Krabi Island.
Subway
Hefei Metro is a rapid transit rail network under construction that will eventually serve both urban and rural areas of Hefei. As planned,Line 1 Line 1 or 1 line may refer to:
Public transport Africa
* Line 1 (Algiers Metro), Algeria
* Cairo Metro Line 1, Egypt
Asia China
* Line 1 (Beijing Subway)
* Line 1 (Changchun Rail Transit)
* Line 1 (Changsha Metro)
* Line 1 (Changzhou Metro)
* L ...
covers a total distance of starting from Hefei Railway Station. It was inaugurated in December 2016.
In February 2013, Metro Line 2 Line 2 or 2 Line may refer to:
Public transport Americas
*2 (New York City Subway service), a rapid transit service in the A Division of the New York City Subway
*2 Line (Sound Transit), a light rail line in Seattle, Washington
*Line 2 Bloor–Dan ...
also began its construction. It is being built alongside the Changjiang Dong Road, Changjiang Zhong Road and Changjiang Xi Road, which is a major passenger corridor in the east–west direction. It will pass through the city center area and connect to a transit point where passengers will be able to take the shuttle bus to Hefei Xinqiao International Airport. The Line 2 was opened on December 26, 2017.
In November 2015, Metro Line 3 construction began. Line 3 was opened on December 26, 2019. Line 3 connects the New Station Exploitative-experimental Zone and the Economic Technology Development District, from the vocational education town to the university town.
In 2016, Metro Line 4 construction began. Line 4 was opened on December 26, 2021. Line 4 connects the New Station Exploitative-experimental Zone and the High Technology Development District.
In 2017, Metro Line 5 construction began. The south part of Line 5 was opened on December 26, 2020. Line 5 connects Binhu New District and the Beicheng (North city) New District. The north part of Line 5 is expected to open at the end of 2022.
Alongside Line 1, Line 2, Line 3, Line 4 and Line 5, Hefei is also planning to build other 12 metro lines, 4 lines of intra-metropolitan rail transit (to Lu'an, Huainan, Lujiang and Chaohu) and 3 lines of tram and hopefully accomplish the project by 2030.
Bus
Normal buses included 1-33, 35–53, 56,57,59-68, 70, 72, 76, 78, 99, 101–141, 143, 145–150, 152, 154–159, 161–163, 166, 226, 232–235, 300–305, 350–359, 399, 401, 502–513, 516–519, 521, 522, 525–533, 535–539, 577, 601–606, 621, 622, 650–657, 665, 670, 681–683, 686, 690–699, 702–710, 801–805,809,810,901–903. And there are also several buses lines which severed for Feixi county(begins with X, such as X201), Feidong county(begins with D, such as D199), Changfeng county (begins with C, such as C131) and Chaohu city (begins with H, such as H105). There are 8 major lines of Bus Rapid Transit in Hefei, including: Bus Rapid Transit Line 1 (B1): from the downtown to the Binhu New Area. () Bus Rapid Transit Line 2 (B2): from Previous Research Institute of China University of Science and Technology to Wang Tong Bus Station (Along Wangjiang Rd. ) Bus Rapid Transit Line 3 (B3): from No.2 buses company to Hefei No.2 Hospital New Area (Along Changjiang Rd. ) Bus Rapid Transit Line 4 (B4): from Hefei Information Technology University to Binhu International Convention and Exhibition Center (Along Ziyun Rd. ) Bus Rapid Transit Line 5 (B5): from Hefeinan Railway Station to Binhu Wanda Bus Station (Along Baohe Avenue. ) Bus Rapid Transit Line 7 (B7): from Provincial Administrative Center to Xinghua Park (Along Baohe Avenue. ) Bus Rapid Transit Line 9 (B9): from Road Bus Station to City Square (Along Fuyang North Road. ) Bus Rapid Transit Line 11 (B11): from Feixi Railway Station to Nanqili Station (Along Jinzhai South Road. ) And there are several commuter lines operating, which only run at designated time or having a large interval, including: T1 from West Bus Terminus () to No.7 High School New Campus (), T2 from Liushutang () to No.7 High School New Campus, T3 from North Square of Hefei Railway Station () to Hefei Economic and Trade Tourism School (), T5 from North Square of Hefei Railway Station to Gongda Vocational and Technical College (), T6 from North Square of Hefei Railway Station to Hefei Industrial School (), T7 from Hefeinan Railway Station () to University Park (), T8 from Gedadian () to E-Commerce Park of the Youth (), T9 from Public Transportation Group (No.2 Hospital) () to No.10 High School New Campus (), T10 from Shifu Square () to No.10 High School New Campus, T12 from Anjuyuan() to Provincial Administration Center (), T13 from CPPCC of Anhui Province () to Provincial Administration Center, T15 from Binhu Vanke City () to Provincial Administration Center, T16 from Wanghucheng () to Provincial Administration Center, T18 as a loop line of the CBD of Binhu New Area (), T19 as a loop line of the Promoting Zone of Binhu New Area (), T21 from Cuozhen () to Fuxing Community (), T22 from Shuidong Rd. () to Sanlian University Branch Campus (), T24 from Cuozhen to Qiaotouji (), T26 from Feihe () to Hefei International Port ().Research
Hefei plays an important role in scientific research in China. It has seven national laboratories, second only to Beijing: The National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory (), the Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale (), both of which are under theUniversity of Science and Technology of China
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which rou ...
. It also has the Institute of Solid State Physics, Institute of Plasma Physics, Institute of Intelligent Machines, High Magnetic Field Laboratory (founded in 2008), Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, all of which are under the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science which belongs to the Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS); ), known by Academia Sinica in English until the 1980s, is the national academy of the People's Republic of China for natural sciences. It has historical origins in the Academia Sinica during the Repub ...
.
Hefei is the location of Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak, an experimental superconducting tokamak
A tokamak (; russian: токамáк; otk, 𐱃𐰸𐰢𐰴, Toḳamaḳ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being ...
magnetic fusion energy reactor.
The No. 105 Hospital of the People's Liberation Army, located in Hefei, is reportedly the site of the first human trials using CRISPR
CRISPR () (an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. These sequences are derived from DNA fragments of bac ...
genome editing, doing so in 2015.
Universities
 *
*University of Science and Technology of China
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which rou ...
(USTC)
* Hefei University of Technology (HFUT)
*Anhui University
Anhui University (), colloquially known in Chinese as An Da (安大, ''Āndà''), is located in Hefei, the capital city of Anhui Province, China. Founded in 1928 in Anqing, named 'National Anhui University' in 1946 and moved to Hefei in 1958, ...
(AHU)
*Anhui Agricultural University
Anhui Agricultural University (AAU) () is in Hefei, the capital city of Anhui, China. AAU is a key university, with a long history specializing in agriculture and forestry. It is jointly funded by Anhui Provincial Government and the Ministry of ...
(AHAU)
* Anhui Medical University (AHMU)
* Anhui University of Chinese Medicine (AUCM)
* Anhui Jianzhu University (AHJU)
* Hefei Normal University (HNU)
* Hefei University (HU)
* Beihang University (BUAA) - Hefei Campus
* National University of Defense Technology (NUDT) - Hefei Campus
* Beijing Foreign Studies University (BFSU) - Hefei Campus
* Tianjin University (TJU) - Hefei Graduate School
*Peking University
Peking University (PKU; ) is a public research university in Beijing, China. The university is funded by the Ministry of Education.
Peking University was established as the Imperial University of Peking in 1898 when it received its royal charte ...
(PKU) - Hefei Graduate School
*Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University (; abbr. THU) is a national public research university in Beijing, China. The university is funded by the Ministry of Education.
The university is a member of the C9 League, Double First Class University Plan, Projec ...
(THU) - Hefei Institute of Public Safety Research
Yicheng Prison
Yicheng Prison is located within the city. It was built during the 1983 "Strike Hard" campaign and was formerly Hefei Zhenxing Machine Parts Factory. On June 15, 1984, the Prov. Justice Dept. decided to change the name of the Machine Parts Factory's Internal Dept. to the Prov. Independent LRC. On March 17, 1986, the City's Party Committee and government agreed to the change. On April 26 more than 400 inmates were transferred to Hefei Shangzhangwei Farm and Baihu Farm. In February 1992 a secondary country level prison was created at the Shangzhangwei Farm. In August 1992 the Hefei City LRD level was upgraded by the government. June 1996 the prison was changed to its present name. It is currently controlled by Hefei city. It mainly houses prisoners with sentences of less than 5 years and houses up to 1000 prisoners a year. In the past 20 years, nearly 20,000 inmates have completed their sentences here. The prison mainly cultivates vegetables and rice but also cooperates with the Zhejiang Rongguang Group and produces soccer training shoes, soccer balls, tourism products, and other products.Sport
Hefei has its own football team calledAnhui Jiufang
Anhui Jiufang Football Club () is a defunct Chinese football club from Hefei, Anhui. The club is owned by Anhui Jiarun Group () with 15,000,000 RMB registered capital. At the end of the 2008 season, Anhui Jiufang qualified from China League Two ( ...
, who in the 2007–08 season were promoted from the Chinese Football Association Yi League
The Chinese Football Association Division Two League (Simplified Chinese: 中国足球协会乙级联赛), or China League Two, is the third tier league of the People's Republic of China. The league is under the auspices of the Chinese Football As ...
to the Chinese Football Association Jia League which is the second highest tier of Chinese football. It was acquired by Tianjin Runyulong in 2011.
Sites of interest
Li Hongzhang
Li Hongzhang, Marquess Suyi ( zh, t=李鴻章; also Li Hung-chang; 15 February 1823 – 7 November 1901) was a Chinese politician, general and diplomat of the late Qing dynasty. He quelled several major rebellions and served in important ...
's Former Residence (), built in the late 19th century and fully restored by the 1990s.
*Hui Garden () (Opened to the public in September 2001)
*Children's Welfare Institute (a.k.a. "Social Welfare Institute"), children's orphanage
* Anhui Laomingguang Stadium, the home ground of Anhui Jiufang
Anhui Jiufang Football Club () is a defunct Chinese football club from Hefei, Anhui. The club is owned by Anhui Jiarun Group () with 15,000,000 RMB registered capital. At the end of the 2008 season, Anhui Jiufang qualified from China League Two ( ...
, but also used for other public sporting events.
Notable people
* Bao Zheng (999–1062),Northern Song dynasty
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a ...
bureaucrat and judge whose name has become synonymous with judicial wisdom and uprightness.
*Li Hongzhang
Li Hongzhang, Marquess Suyi ( zh, t=李鴻章; also Li Hung-chang; 15 February 1823 – 7 November 1901) was a Chinese politician, general and diplomat of the late Qing dynasty. He quelled several major rebellions and served in important ...
(1823–1901), prominent late Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
bureaucrat and diplomat.
* Liu Mingchuan (1836–1896). Statesman during the late Qing dynasty, first governor of Taiwan.
* Duan Qirui (1865–1936), the Provisional Chief Executive of Republic of China (in Beijing) from November 24, 1924, to April 20, 1926.
*Susan Wu Rathbone
Susan Wu Rathbone (; October 29, 1921 – November 22, 2019), also known as Wu Shih-san and "Auntie Wu", was a Chinese-born community leader in New York City. She was founder and head of the Chinese Immigrants Service and the Queens Chinese Women ...
(1921–2019), community leader in Queens, New York
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long Is ...
.
* Yang Chen-Ning, (b. 1922), 1957 Nobel Physics Prize laureate, for their work on parity nonconservation of weak interaction. One of the two earliest Chinese to receive the prize.
* Wu Bangguo(b. 1941), Chinese politician.
* Li Keqiang(b. 1955), PM of Chinese government.
* Yang Yuanqing (b. 1964), Chairman of Board of Lenovo
Lenovo Group Limited, often shortened to Lenovo ( , ), is a Chinese multinational technology company specializing in designing, manufacturing, and marketing consumer electronics, personal computers, software, business solutions, and related se ...
.
* Han Qizhi, (b. 1970), first person to climb the Jin Mao Tower, then the tallest building in China.
*Jin Jing
Jin Jing (Chinese: 金晶; Pinyin: Jīn Jīng; born 1981 in Hefei, Anhui, China) is a Chinese female Paralympic fencer. She was a torchbearer carrying the Olympic torch amid political protests during the 2008 Summer Olympics torch relay in ...
(b. 1981), Paralympic fencer.
* Xu Song (b. 1986), Chinese singer.
* Chen Xiao (b. 1987), actor.
* Yang Yang (b. 1991), actor.
* Hu Bingqing (b. 1992), actress.
Sister cities
* Kurume,Fukuoka
is the List of Japanese cities by population, sixth-largest city in Japan, the second-largest port city after Yokohama, and the capital city of Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. The city is built along the shores of Hakata Bay, and has been a center ...
, Japan (1980)
* Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational an ...
, Sierra Leone (1984)
* Bujumbura
Bujumbura (; ), formerly Usumbura, is the economic capital, largest city and main port of Burundi. It ships most of the country's chief export, coffee, as well as cotton and tin ore. Bujumbura was formerly the country's normal capital. In la ...
, Burundi (1986)
* Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
, United States (1988)
* Aalborg
Aalborg (, , ) is Denmark's fourth largest town (behind Copenhagen, Aarhus, and Odense) with a population of 119,862 (1 July 2022) in the town proper and an urban population of 143,598 (1 July 2022). As of 1 July 2022, the Municipality of ...
, Denmark (1989)
* Lleida, Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
, Spain (1998)
* Wonju, Gwandong, South Korea (2002)
* Darebin, Victoria, Australia (2003)
* Belfast
Belfast ( , ; from ga, Béal Feirste , meaning 'mouth of the sand-bank ford') is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingd ...
, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom (2005)
* Osnabrück
Osnabrück (; wep, Ossenbrügge; archaic ''Osnaburg'') is a city in the German state of Lower Saxony. It is situated on the river Hase in a valley penned between the Wiehen Hills and the northern tip of the Teutoburg Forest. With a populat ...
, Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
, Germany (2006)
* Ufa, Bashkortostan
The Republic of Bashkortostan or Bashkortostan ( ba, Башҡортостан Республикаһы, Bashqortostan Respublikahy; russian: Республика Башкортостан, Respublika Bashkortostan),; russian: Респу́блик� ...
, Russia (2016)
See also
* List of twin towns and sister cities in ChinaReferences
External links
*Hefei Online Government
{{Authority control Provincial capitals in China