|
Zhang Liao
Zhang Liao () (169–222), courtesy name Wenyuan, was a Chinese military general serving under the warlord Cao Cao in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He served briefly in the state of Cao Wei, founded by Cao Cao's successor Cao Pi, in the early Three Kingdoms period before his death. Formerly a subordinate of other warlords such as Ding Yuan, Dong Zhuo and Lü Bu, Zhang Liao joined Cao Cao around 198 after Lü Bu's downfall at the Battle of Xiapi. Since then, he participated in many of Cao Cao's military campaigns, including those against Yuan Shao's heirs and the Wuhuan tribes from 201 to 207. He is best known for his pivotal role in the Battle of Xiaoyao Ford in 214–215, in which he successfully defended Hefei from the forces of the warlord Sun Quan. Chen Shou, who wrote the third-century historical text '' Sanguozhi'', named Zhang Liao as one of the Five Elite Generals of his time, alongside Yu Jin, Zhang He, Yue Jin and Xu Huang. Early career and service under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtesy Name
A courtesy name (), also known as a style name, is a name bestowed upon one at adulthood in addition to one's given name. This practice is a tradition in the East Asian cultural sphere, including China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ..., Japan, Korea, and Vietnam.Ulrich TheobaldNames of Persons and Titles of Rulers/ref> A courtesy name is not to be confused with an art name, another frequently mentioned term for an alternative name in East Asia, which is closer to the concept of a pen name or a pseudonym. Usage A courtesy name is a name traditionally given to Chinese men at the age of 20 East Asian age reckoning, ''sui'', marking their coming of age. It was sometimes given to women, usually upon marriage. The practice is no longer common in modern Chinese socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
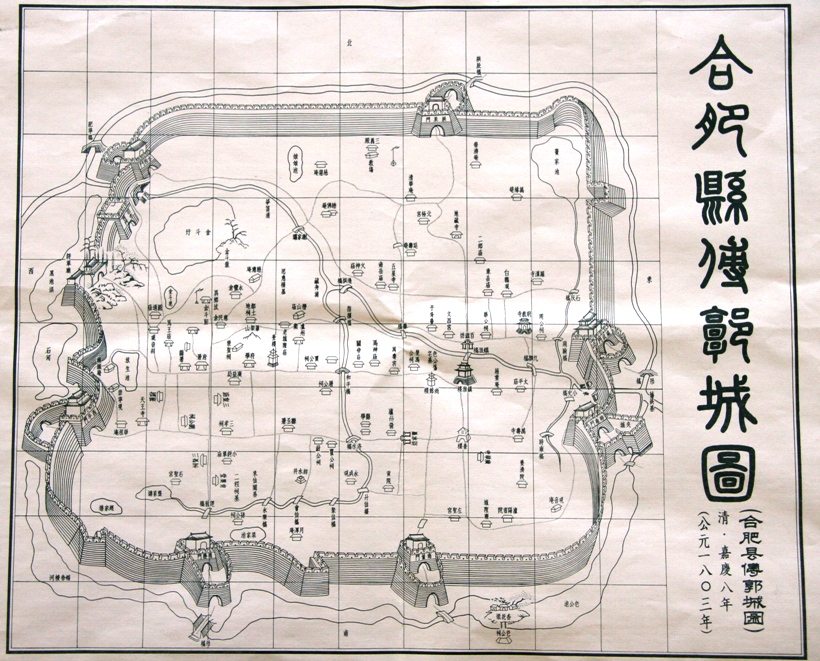
Hefei
Hefei (; ) is the capital and largest city of Anhui Province, People's Republic of China. A prefecture-level city, it is the political, economic, and cultural center of Anhui. Its population was 9,369,881 as of the 2020 census and its built-up (or ''metro'') area made up of four urban districts plus Feidong, Feixi and Changfeng counties being urbanized, was home to 7,754,481 inhabitants. Located in the central portion of the province, it borders Huainan to the north, Chuzhou to the northeast, Wuhu to the southeast, Tongling to the south, Anqing to the southwest and Lu'an to the west. A natural hub of communications, Hefei is situated to the north of Chao Lake and stands on a low saddle crossing the northeastern extension of the Dabie Mountains, which forms the divide between the Huai and Yangtze rivers. The present-day city dates from the Song dynasty. Before World War II, Hefei remained essentially an administrative centre and the regional market for the fertile plain to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Xiaoyao Ford
The Battle of Xiaoyao Ford, also known as the Battle of Leisure Ford, Battle of Hefei, and Hefei Campaign, was fought between the warlords Cao Cao and Sun Quan between 214 and 215 in the late Eastern Han dynasty. The two contending sides were fighting for control over a strategic fortress at Hefei, which was defended by Cao Cao's general Zhang Liao. Towards the end of the campaign, Zhang Liao made use of force concentration and launched a sneak counteroffensive on Sun Quan at Leisure Ford, where Sun only had 1,000 soldiers with him at the time. Amidst the chaos, Sun Quan barely escaped capture with the aid of his general Ling Tong. This action raised Zhang Liao to primacy among Cao Cao's generals. Background Long before Sun Quan solidified his control over southeastern China, Cao Cao had appointed Liu Fu as the Inspector of Yang Province, and had him build fortifications against besiegers. Liu Fu oversaw the construction of Hefei fortress (), stocked with boulders, logs, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuhuan
The Wuhuan (, < : *''ʔɑ-ɣuɑn'', < (c. 78 BCE): *''ʔâ-wân'' < *''Awar''Schuessler, Axel (2014) "Phonological Notes on Hàn Period Transcriptions of Foreign Names and Words" in ''Studies in Chinese and Sino-Tibetan Linguistics: Dialect, Phonology, Transcription and Text''. Series: Language and Linguistics Monograph. Issue 53. p. 257 of 249-292) were a Proto-Mongolic nomadic people who inhabited |
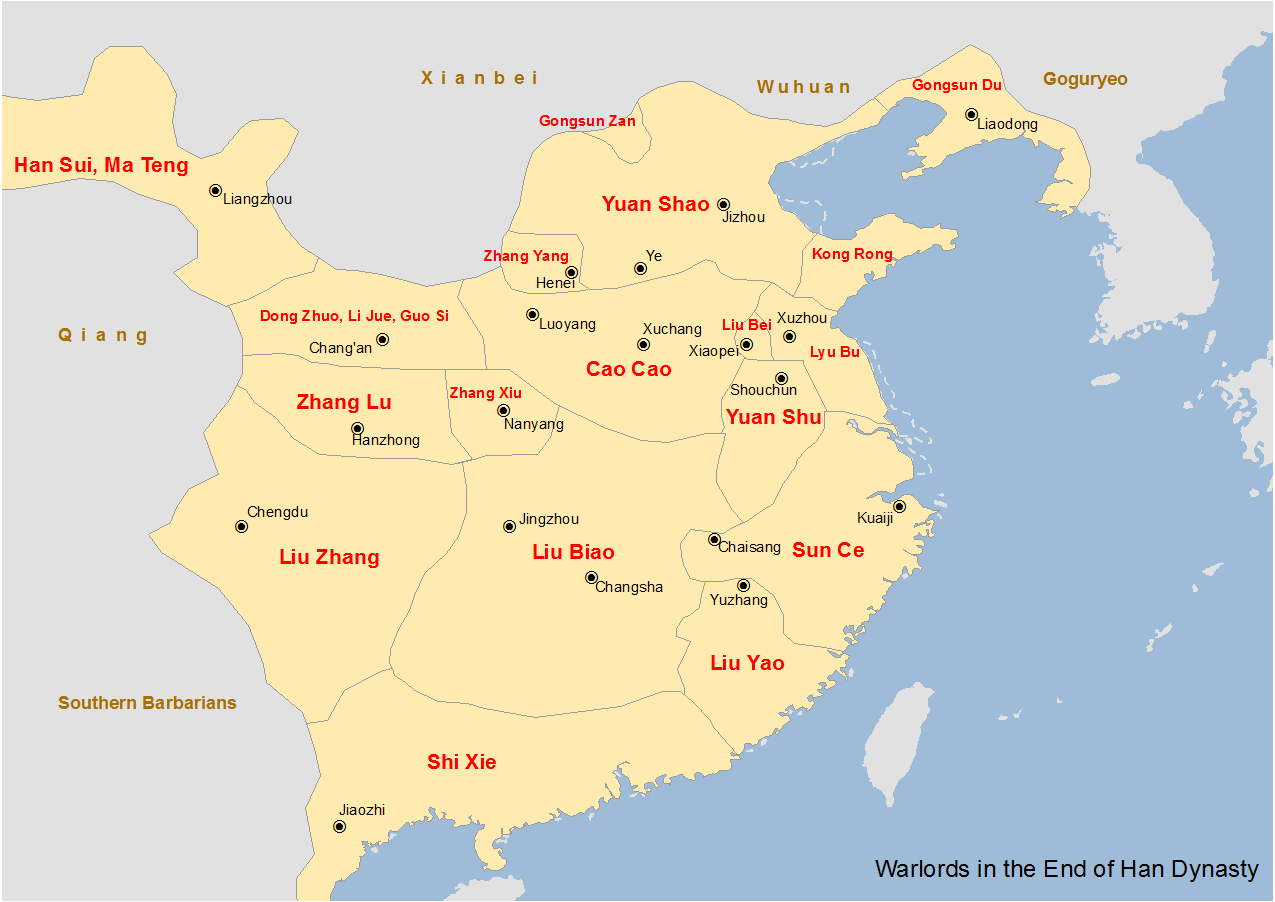
Yuan Shao
Yuan Shao (, ; died 28 June 202), courtesy name Benchu (), was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. He occupied the northern territories of China during the civil wars that occurred towards the end of the Han dynasty. He was also an elder half-brother of Yuan Shu, a warlord who controlled the Huai River region, though the two were not on good terms with each other. One of the most powerful warlords of his time, Yuan Shao spearheaded a coalition of warlords against Dong Zhuo, who held Emperor Xian hostage in the imperial capital, Luoyang, but failed due to internal disunity. In 200, he launched a campaign against his rival Cao Cao but was defeated at the Battle of Guandu. He died of illness two years later in Ye. His eventual failure despite his illustrious family background and geographical advantages was commonly blamed on his indecisiveness and inability to heed the advice of his advisors. Family background Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Xiapi
The Battle of Xiapi was fought between the forces of Lü Bu against the allied armies of Cao Cao and Liu Bei from the winter of 198 to 7 February 199 towards the end of the Eastern Han dynasty in China. The battle concluded with victory for Cao Cao and Liu Bei, with Lü Bu being subsequently executed. Background In 194, while Cao Cao was away attacking Tao Qian in Xu Province, his subordinates Chen Gong and Zhang Miao rebelled against him and aided Lü Bu in invading his base in Yan Province. Cao Cao abandoned his invasion of Xu Province and turned back to attack Lü Bu, culminating in the Battle of Yan Province which lasted more than 100 days. By 195, Cao Cao had retaken all his cities in Yan Province and defeated Lü Bu at Juye. Lü Bu and his men fled east to join Liu Bei, who had succeeded Tao Qian as Governor () of Xu Province. In 196, Cao Cao found Emperor Xian in the ruins of Luoyang and brought him to Xuchang, where the new capital and imperial court would be bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dong Zhuo
Dong Zhuo () (died 22 May 192), courtesy name Zhongying, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr .... At the end of the reign of the Eastern Han, Dong Zhuo was a general and powerful minister of the imperial government. Yet he forced the young Liu Bian, Emperor Shao of Han to abdicate and replaced him with his half-brother Emperor Xian of Han while he sought to become the de facto ruler of China in the boy-emperor's name. The Eastern Han dynasty regime survived in name only. Dong Zhuo seized control of the imperial capital Luoyang in 189 when it entered a state of turmoil following the death of Emperor Ling of Han and a massacre of the Ten Attendants, eunuch faction by the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ding Yuan
Ding Yuan () (died 189), courtesy name Jianyang, was a Chinese politician and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. In 189, both he and Dong Zhuo were summoned into the capital Luoyang with their individual troops to assist in the struggle against the powerful eunuch faction. Ding Yuan, however, was eventually killed by his trusted aide Lü Bu, who had been bought over by Dong Zhuo. Life According to the ''Records of Heroes'' (英雄記) by Wang Can, Ding Yuan was born in a poor family. Uncouth but brave, he was adept in horse riding and archery. During his early career as a county magistrate, he never turned away from his responsibility no matter the adversity or risk. He always pitched himself in front during confrontations with fugitive criminals and bandits. He was eventually promoted to Inspector of Bing Province (并州; present-day Shanxi) when he met Lü Bu. The martial prowess of the young warrior greatly impressed Ding Yuan, who made him Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the Jin dynasty (266–420), Western Jin dynasty. The short-lived state of Yan (Three Kingdoms), Yan on the Liaodong Peninsula, which lasted from 237 to 238, is sometimes considered as a "4th kingdom". Academically, the period of the Three Kingdoms refers to the period between the establishment of Cao Wei in 220 and the Conquest of Wu by Jin, conquest of the Eastern Wu by the Western Jin in 280. The earlier, "unofficial" part of the period, from 184 to 220, was marked by chaotic infighting between warlords in various parts of China during the end of the Han dynasty, downfall of the Eastern Han dynasty. The middle part of the period, from 220 to 263, was marked by a more militarily stable arrangement between three rival states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Wei
Wei (Hanzi: 魏; pinyin: ''Wèi'' < Middle Chinese: *''ŋjweiC'' < Eastern Han Chinese: *''ŋuiC'') (220–266), known as Cao Wei or Former Wei in historiography, was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the period (220–280). With its capital initially located at , and thereafter Luoyang, the state was established by [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the " Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as " Han characters". The emperor was at the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
