|
Superconducting
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered, even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete cancellation of the magnetic field in the interior of the superconductor during its transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuprate Superconductor
Cuprate superconductors are a family of High-temperature superconductivity, high-temperature superconducting materials made of layers of copper oxides () alternating with layers of other metal oxides, which act as charge reservoirs. At ambient pressure, cuprate superconductors are the highest temperature superconductors known. Cuprates have a structure close to that of a two-dimensional material. Their superconducting properties are determined by electrons moving within weakly coupled copper-oxide () layers. Neighbouring layers contain ions such as lanthanum, barium, strontium, or other atoms that act to stabilize the structures and dope electrons or holes onto the copper-oxide layers. The undoped "parent" or "mother" compounds are Mott insulator, Mott insulators with long-range antiferromagnetic order at sufficiently low temperatures. Single Electronic band structure, band models are generally considered to be enough to describe the electronic properties. The cuprate supercon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
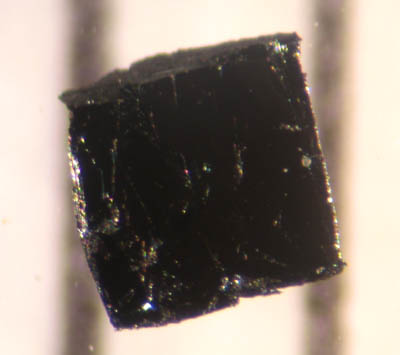
YBCO
Yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) is a family of crystalline chemical compounds that display high-temperature superconductivity; it includes the first material ever discovered to become superconductivity, superconducting above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen [] at about . Many YBCO compounds have the general formula (also known as Y123), although materials with other Y:Ba:Cu ratios exist, such as (Y124) or (Y247). At present, there is no singularly recognised theory for high-temperature superconductivity. It is part of the more general group of rare-earth barium copper oxides (ReBCO) in which, instead of yttrium, other rare earths are present. History In April 1986, Georg Bednorz and Karl Alexander Müller, Karl Müller, working at IBM Research – Zurich, IBM in Zurich, discovered that certain semiconducting oxides became superconducting at relatively high temperature, in particular, a lanthanum barium copper oxide becomes superconducting at 35 K. This oxide was an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconducting Wire
Superconducting wires are electrical wires made of superconductive material. When cooled below their transition temperatures, they have zero electrical resistance. Most commonly, conventional superconductors such as niobium–titanium are used, but high-temperature superconductors such as YBCO are entering the market. Superconducting wire's advantages over copper or aluminum include higher maximum current densities and zero power dissipation. Its disadvantages include the cost of refrigeration of the wires to superconducting temperatures (often requiring cryogens such as liquid nitrogen or liquid helium), the danger of the wire quenching (a sudden loss of superconductivity), the inferior mechanical properties of some superconductors, and the cost of wire materials and construction. Its main application is in superconducting magnets, which are used in scientific and medical equipment where high magnetic fields are necessary. Important parameters The construction and ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meissner Effect
In condensed-matter physics, the Meissner effect (or Meißner–Ochsenfeld effect) is the expulsion of a magnetic field from a superconductor during its transition to the superconducting state when it is cooled below the critical temperature. This expulsion will repel a nearby magnet. The German physicists Walther Meissner, Walther Meißner (anglicized ''Meissner'') and Robert Ochsenfeld discovered this phenomenon in 1933 by measuring the magnetic field distribution outside superconducting tin and lead samples. The samples, in the presence of an applied magnetic field, were cooled below their Superconductivity#Superconducting phase transition, superconducting transition temperature, whereupon the samples cancelled nearly all interior magnetic fields. They detected this effect only indirectly because the magnetic flux is conserved by a superconductor: when the interior field decreases, the exterior field increases. The experiment demonstrated for the first time that superconducto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-temperature Superconductors
High-temperature superconductivity (high-c or HTS) is superconductivity in materials with a critical temperature (the temperature below which the material behaves as a superconductor) above , the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. They are "high-temperature" only relative to previously known superconductors, which function only closer to absolute zero. The first high-temperature superconductor was discovered in 1986 by IBM researchers Georg Bednorz and K. Alex Müller. Although the critical temperature is around , this material was modified by Ching-Wu Chu to make the first high-temperature superconductor with critical temperature . Bednorz and Müller were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1987 "for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials". Most high-c materials are type-II superconductors. The major advantage of high-temperature superconductors is that they can be cooled using liquid nitrogen, in contrast to previously k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures. The 13th International Institute of Refrigeration's (IIR) International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington, DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of "cryogenics" and "cryogenic" by accepting a threshold of to distinguish these terms from conventional refrigeration. This is a logical dividing line, since the normal boiling points of the so-called permanent gases (such as helium, hydrogen, neon, nitrogen, oxygen, and normal air) lie below 120 K, while the Freon refrigerants, hydrocarbons, and other common refrigerants have boiling points above 120 K. Discovery of superconducting materials with critical temperatures significantly above the boiling point of nitrogen has provided new interest in reliable, low-cost methods of producing high-temperature cryogenic refrigeration. The term "high temperature cryogenic" describes temperatures ranging from above the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Transition
In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic State of matter, states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma (physics), plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical property, physical properties. During a phase transition of a given medium, certain properties of the medium change as a result of the change of external conditions, such as temperature or pressure. This can be a discontinuous change; for example, a liquid may become gas upon heating to its boiling point, resulting in an abrupt change in volume. The identification of the external conditions at which a transformation occurs defines the phase transition point. Types of phase transition States of matter Phase transitions commonly refer to when a substance tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perovskite (structure)
A perovskite is a crystalline material of formula ABX3 with a crystal structure similar to that of the mineral perovskite, this latter consisting of calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO3). The mineral was first discovered in the Ural mountains of Russia by Gustav Rose in 1839 and named after Russian mineralogist L. A. Perovski (1792–1856). In addition to being one of the most abundant structural families, perovskites have wide-ranging properties and applications. Structure Perovskite structures are adopted by many compounds that have the chemical formula ABX3. 'A' and 'B' are positively charged ions (i.e. cations), often of very different sizes, and X is a negatively charged ion (an anion, frequently oxide) that bonds to both cations. The 'A' atoms are generally larger than the 'B' atoms. The ideal cubic structure has the B cation in 6-fold coordination, surrounded by an octahedron of anions, and the A cation in 12-fold cuboctahedral coordination. Additional perovskite for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Helium
Liquid helium is a physical state of helium at very low temperatures at standard atmospheric pressures. Liquid helium may show superfluidity. At standard pressure, the chemical element helium exists in a liquid form only at the extremely low temperature of . Its boiling point and critical point depend on the isotope of helium present: the common isotope helium-4 or the rare isotope helium-3. These are the only two stable isotopes of helium. See the table below for the values of these physical quantities. The density of liquid helium-4 at its boiling point and a pressure of one atmosphere (101.3 kilopascals) is about , or about one-eighth the density of liquid water. Liquefaction Helium was first liquefied on July 10, 1908, by the Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes at the University of Leiden in the Netherlands. At that time, helium-3 was unknown because the mass spectrometer had not yet been invented. In more recent decades, liquid helium has been used as a cryogenic refriger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and has often been classified as a "rare-earth element". Yttrium is almost always found in combination with lanthanide elements in rare-earth minerals and is never found in nature as a free element. 89Y is the only stable isotope and the only isotope found in the Crust (geology), Earth's crust. The most important present-day use of yttrium is as a component of phosphors, especially those used in LEDs. Historically, it was once widely used in the red phosphors in television set cathode ray tube displays. Yttrium is also used in the production of electrodes, electrolytes, electronic filters, lasers, superconductors, various medical applications, and Trace element, tracing various materials to enhance their properties. Yttrium has no known Biology, biological role. Exposure to yttrium compounds can cause Respiratory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Resistance And Conductance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its Multiplicative inverse, reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The International System of Units, SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (unit), siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by electrical resistivity and conductivity, resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) is nitrogen in a liquid state at cryogenics, low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, mobile liquid whose viscosity is about one-tenth that of acetone (i.e. roughly one-thirtieth that of water at room temperature). Liquid nitrogen is widely used as a coolant. Physical properties The diatomic character of the N2 molecule is retained after liquefaction. The weak van der Waals interaction between the N2 molecules results in little interatomic attraction. This is the cause of nitrogen's unusually low boiling point. The temperature of liquid nitrogen can readily be reduced to its freezing point by placing it in a vacuum chamber pumped by a vacuum pump. Liquid nitrogen's efficiency as a coolant is limited by the fact that it boils immediately on contact with a warmer object, enveloping the object in an insulating layer of nitrogen gas bubbles. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |