Wa'a on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Outrigger boats are various  Unlike a single-hulled vessel, an outrigger or double-hull vessel generates stability as a result of the distance between its hulls rather than due to the shape of each individual hull. As such, the hulls of outrigger or double-hull boats are typically longer, narrower and more hydrodynamically efficient than those of single-hull vessels. Compared to other types of canoes, smaller outrigger canoes can be quite fast, yet are also capable of being paddled and sailed in rougher water. This paddling technique, however, differs greatly from
Unlike a single-hulled vessel, an outrigger or double-hull vessel generates stability as a result of the distance between its hulls rather than due to the shape of each individual hull. As such, the hulls of outrigger or double-hull boats are typically longer, narrower and more hydrodynamically efficient than those of single-hull vessels. Compared to other types of canoes, smaller outrigger canoes can be quite fast, yet are also capable of being paddled and sailed in rougher water. This paddling technique, however, differs greatly from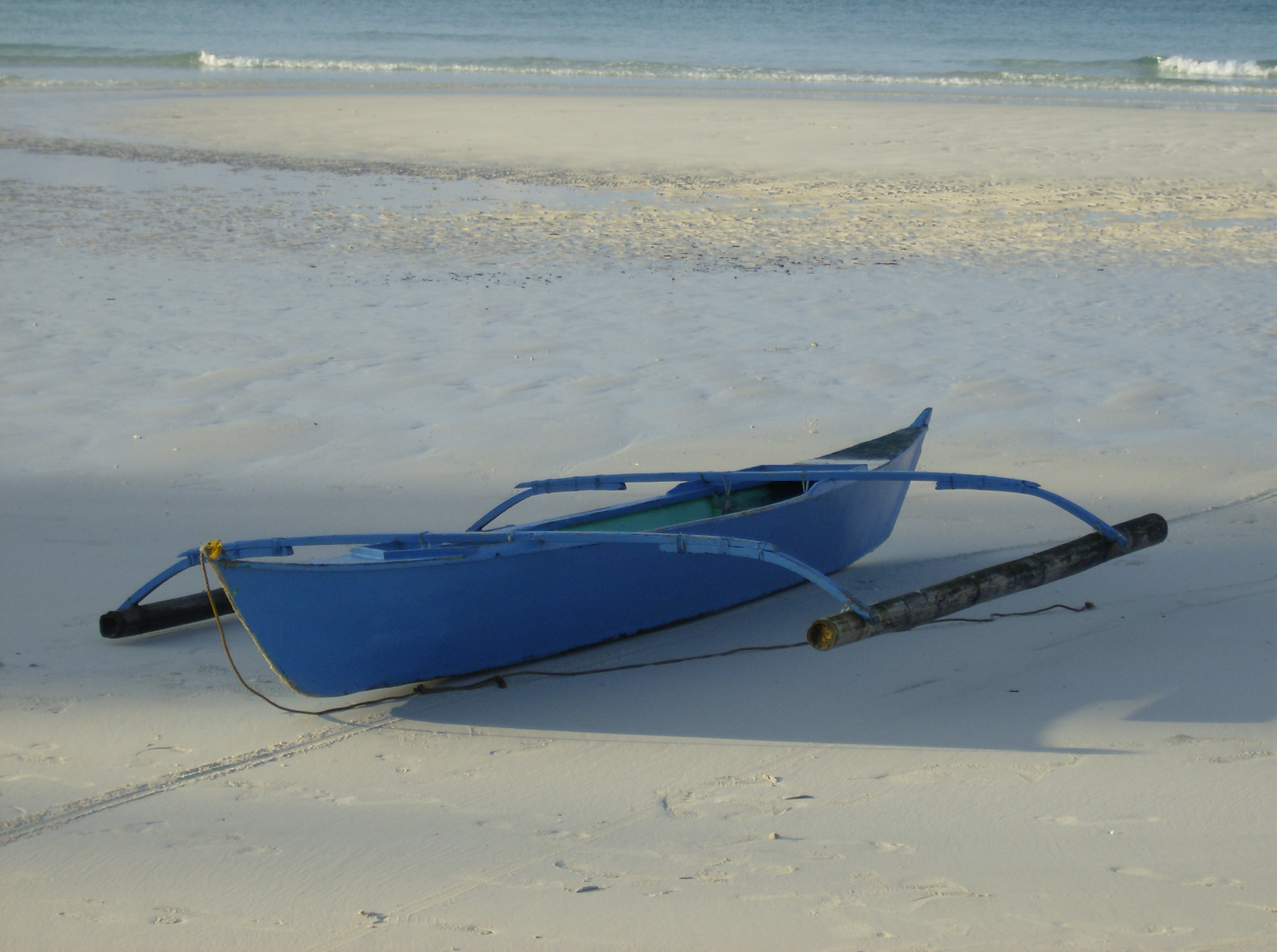  These vessels were the first true ocean-going ships, and are an important part of the
These vessels were the first true ocean-going ships, and are an important part of the
 Outrigger boats were originally developed by the
Outrigger boats were originally developed by the  The simplest form of all ancestral Austronesian boats had five parts. The bottom part consists of single piece of hollowed-out log. At the sides were two planks, and two horseshoe-shaped wood pieces formed the
The simplest form of all ancestral Austronesian boats had five parts. The bottom part consists of single piece of hollowed-out log. At the sides were two planks, and two horseshoe-shaped wood pieces formed the  The technology has persisted into the modern age. Outrigger boats can be quite large
The technology has persisted into the modern age. Outrigger boats can be quite large
 *
*
 * Armadahan
* Balación
*
* Armadahan
* Balación
*
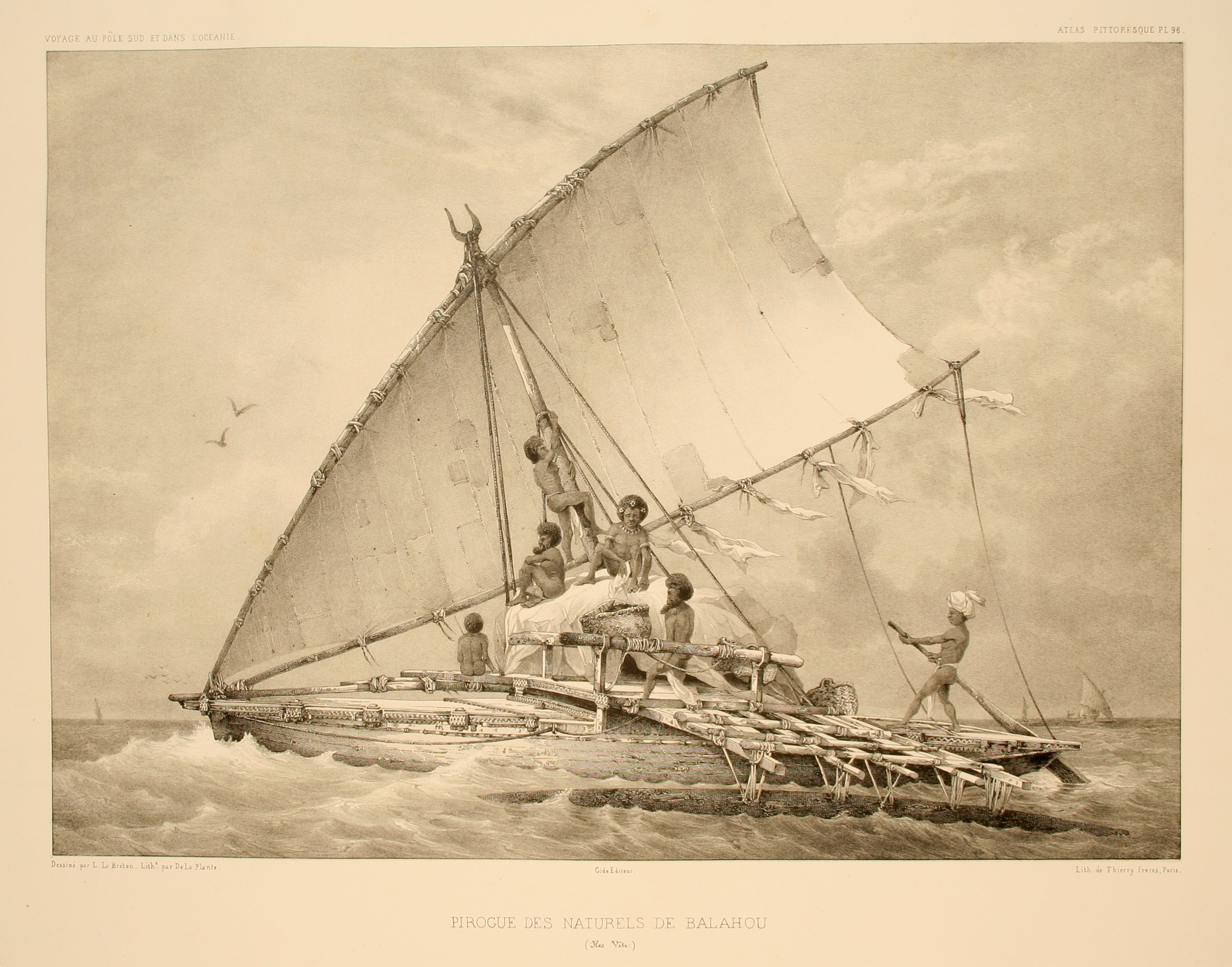


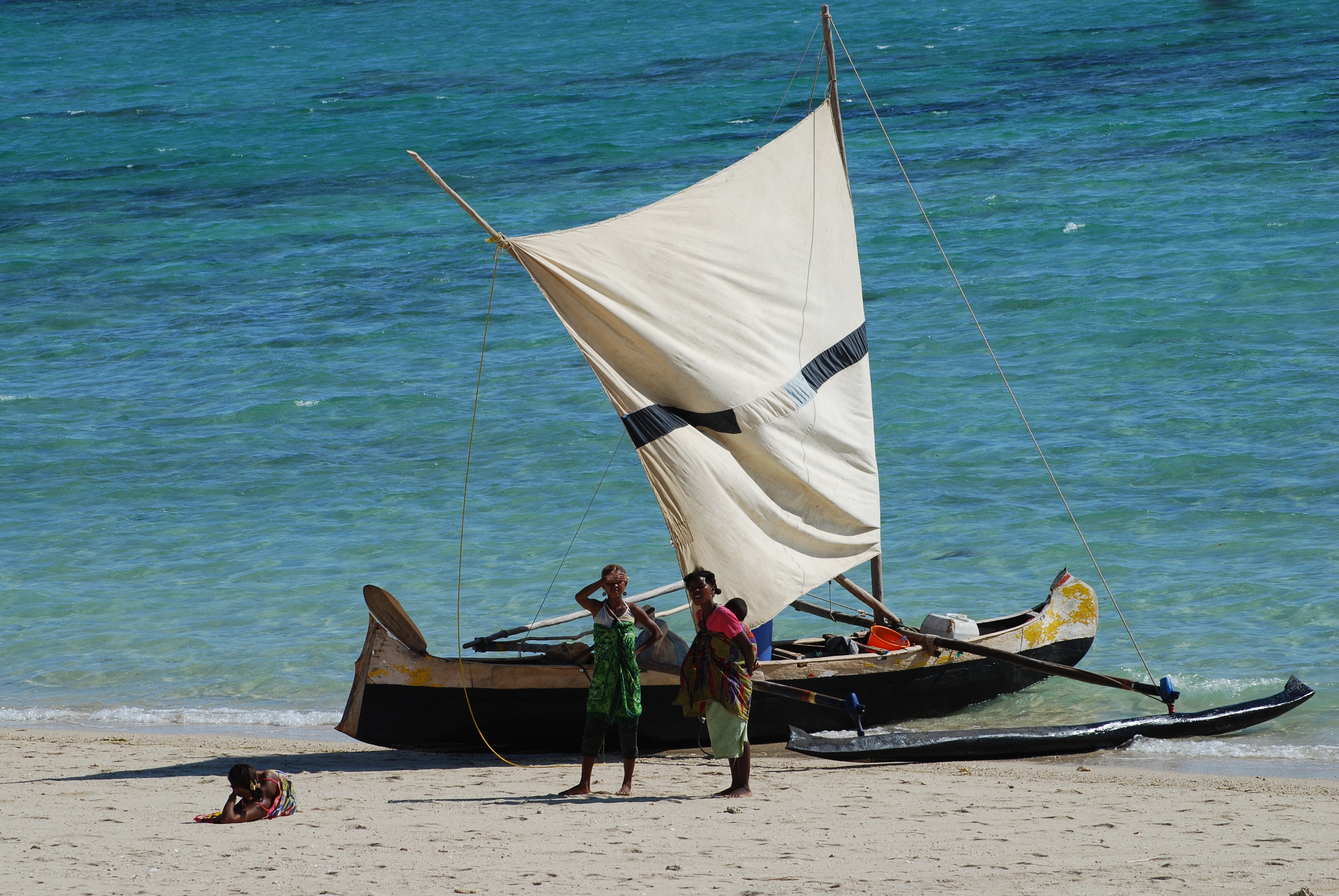 * Lakana
* Lakana
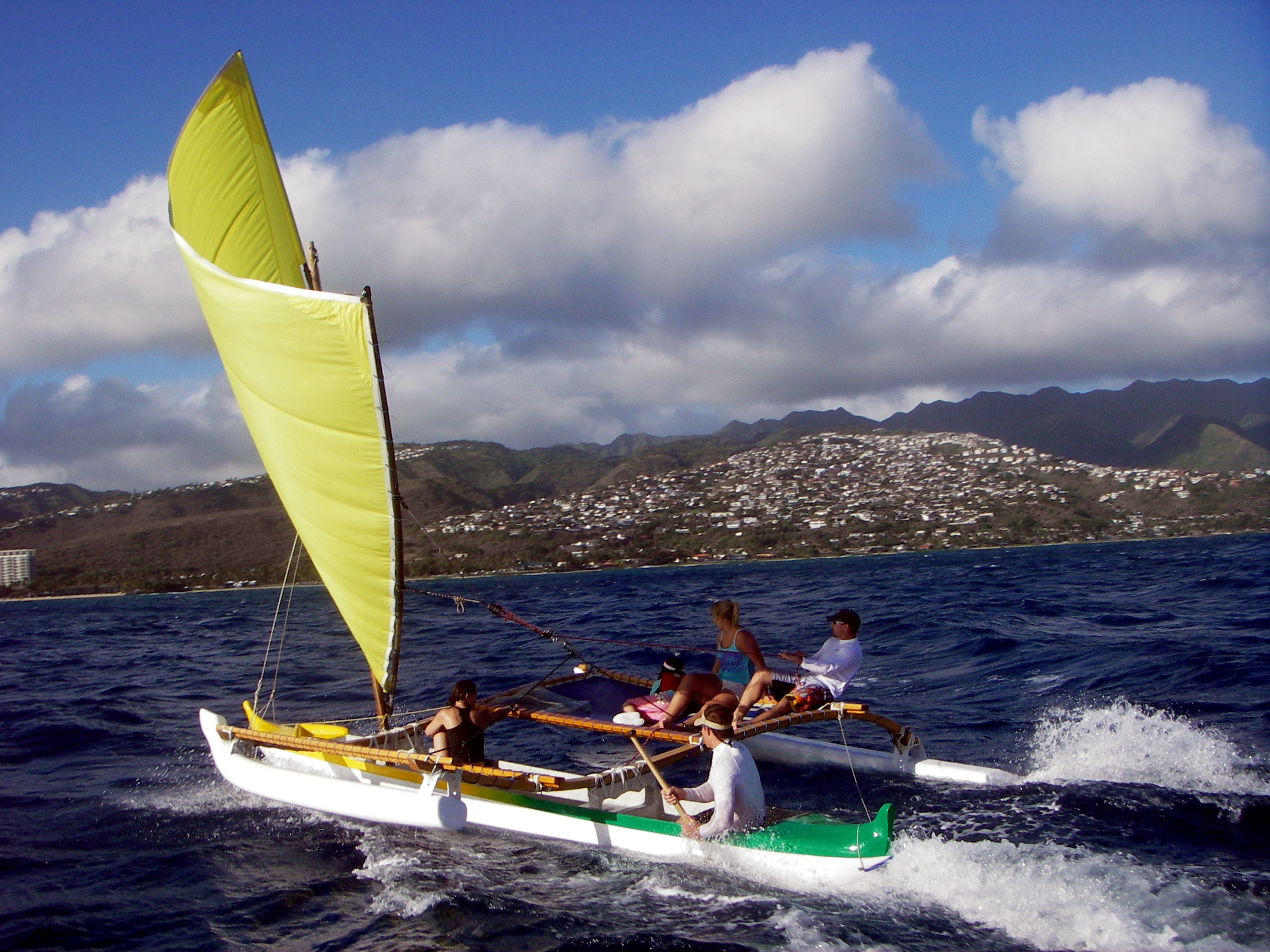 In modern sport outrigger canoeing, ships are classified according to the configuration and number of the hulls and the number of paddlers, including the OC1, OC2, OC3, OC4 and OC6 (with the respective number of paddlers using a single-hull outrigger canoe), and the DC12 or OC12 (with twelve paddlers using a double-hull outrigger canoe, two six-person canoes rigged together like a
In modern sport outrigger canoeing, ships are classified according to the configuration and number of the hulls and the number of paddlers, including the OC1, OC2, OC3, OC4 and OC6 (with the respective number of paddlers using a single-hull outrigger canoe), and the DC12 or OC12 (with twelve paddlers using a double-hull outrigger canoe, two six-person canoes rigged together like a
 A good steersman is able to maintain the
A good steersman is able to maintain the
 The longer races are typically conducted in the open ocean, e.g., between islands in the South Pacific. The Molokai Hoe in Hawaii, The Hamilton Cup in Australia, The Vaka Eiva in Rarotonga (Cook Islands), The Motu2Motu in Aitutaki (Cook Islands) and the Catalina Channel crossing in California are four examples of races involving water changes.
Paddlers and crews are usually classified by gender and age. Gender classification is typically straightforward, with male, female, and coed classifications, with the latter being a crew with equal numbers of male and female paddlers (different rules may apply to nine-person coed crews doing a race with paddler replacements). Age classifications typically include youth divisions like 19-and-under, 16-and-under, etc., master divisions with minimum ages typically starting at 35 or 40 years of age, and an open division which allows paddlers of any age. A novice division for paddlers with less than a specified number of years of race experience (usually one or two) may also exist in a given association.
In some races, a particular type of outrigger canoe, usually a more traditional design for the region, may be given its own racing classification. For example, races in Hawaii have a
The longer races are typically conducted in the open ocean, e.g., between islands in the South Pacific. The Molokai Hoe in Hawaii, The Hamilton Cup in Australia, The Vaka Eiva in Rarotonga (Cook Islands), The Motu2Motu in Aitutaki (Cook Islands) and the Catalina Channel crossing in California are four examples of races involving water changes.
Paddlers and crews are usually classified by gender and age. Gender classification is typically straightforward, with male, female, and coed classifications, with the latter being a crew with equal numbers of male and female paddlers (different rules may apply to nine-person coed crews doing a race with paddler replacements). Age classifications typically include youth divisions like 19-and-under, 16-and-under, etc., master divisions with minimum ages typically starting at 35 or 40 years of age, and an open division which allows paddlers of any age. A novice division for paddlers with less than a specified number of years of race experience (usually one or two) may also exist in a given association.
In some races, a particular type of outrigger canoe, usually a more traditional design for the region, may be given its own racing classification. For example, races in Hawaii have a
Kanuculture
* Steve West (2014) ''Outrigger Canoeing – The Art and Skill of Steering'', Batini Books
Kanuculture
* Steve West (2014) ''Outrigger Canoeing – OC1 a Paddlers Guide'', Batini Books
Kanuculture
* Steve West (2014) ''Outrigger Canoeing – V1 a Paddlers Guide'', Batini Book
Kanuculture
(Drua) in the
Original Outrigger Canoe
in the
watercraft
A watercraft or waterborne vessel is any vehicle designed for travel across or through water bodies, such as a boat, ship, hovercraft, submersible or submarine.
Types
Historically, watercraft have been divided into two main categories.
*Raf ...
featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outrigger
An outrigger is a projecting structure on a boat, with specific meaning depending on types of vessel. Outriggers may also refer to legs on a wheeled vehicle that are folded out when it needs stabilization, for example on a crane that lifts he ...
s, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* The hull of an armored fighting vehicle, housing the chassis
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a sea-going craft
* Submarine hull
Ma ...
. They can range from small dugout canoe
A canoe is a lightweight, narrow watercraft, water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using paddles.
In British English, the term ' ...
s to large plank-built vessels. Outrigger boats can also vary in their configuration, from the ancestral double-hull configuration (catamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
s), to single-outrigger vessels prevalent in the Pacific Islands
The Pacific islands are a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean. They are further categorized into three major island groups: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Depending on the context, the term ''Pacific Islands'' may refer to one of several ...
and Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
, to the double-outrigger vessels (trimaran
A trimaran (or double-outrigger) is a multihull boat that comprises a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls (or "floats") which are attached to the main hull with lateral beams. Most modern trimarans are sailing yachts designed for recrea ...
s) prevalent in Island Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.
The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as Mari ...
. They are traditionally fitted with Austronesian sails, like the crab claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples by at least 2000 BCE. It is sometimes known as the Oceanic lateen or the Oceanic ...
s and tanja sail
Tanja sail ( Malay: ''layar tanjak'') or tanja rig is a type of sail commonly used by the Austronesian people, particularly in Maritime Southeast Asia. It is also known as the tilted square sail, canted rectangular sail, rectangular balance lug ...
s, but in modern times are often fitted with petrol engines.
 Unlike a single-hulled vessel, an outrigger or double-hull vessel generates stability as a result of the distance between its hulls rather than due to the shape of each individual hull. As such, the hulls of outrigger or double-hull boats are typically longer, narrower and more hydrodynamically efficient than those of single-hull vessels. Compared to other types of canoes, smaller outrigger canoes can be quite fast, yet are also capable of being paddled and sailed in rougher water. This paddling technique, however, differs greatly from
Unlike a single-hulled vessel, an outrigger or double-hull vessel generates stability as a result of the distance between its hulls rather than due to the shape of each individual hull. As such, the hulls of outrigger or double-hull boats are typically longer, narrower and more hydrodynamically efficient than those of single-hull vessels. Compared to other types of canoes, smaller outrigger canoes can be quite fast, yet are also capable of being paddled and sailed in rougher water. This paddling technique, however, differs greatly from kayak
]
A kayak is a small, narrow human-powered watercraft typically propelled by means of a long, double-bladed paddle. The word ''kayak'' originates from the Inuktitut word '' qajaq'' (). In British English, the kayak is also considered to be ...
ing or Watercraft rowing, rowing. The paddle
A paddle is a handheld tool with an elongated handle and a flat, widened end (the ''blade'') used as a lever to apply force onto the bladed end. It most commonly describes a completely handheld tool used to propel a human-powered watercraft by p ...
, or blade, used by the paddler is single sided, with either a straight or a double-bend shaft.
 These vessels were the first true ocean-going ships, and are an important part of the
These vessels were the first true ocean-going ships, and are an important part of the Austronesian
Austronesian may refer to:
*The Austronesian languages
*The historical Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Sout ...
heritage. They were the vessels that enabled the Austronesian expansion
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesi ...
from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
into the islands of both the Indian and Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
from around 3000 BC. They comprise the bulk of traditional boats in Island Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.
The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as Mari ...
, Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology a ...
, Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
, Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
, and Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
. They have spread to other cultures Austronesians came into contact with, notably in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
and southern India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
as well as in the coast of East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
. In modern times, outrigger vessels are used in the sport of sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, Windsurfing, windsurfer, or Kitesurfing, kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (Land sa ...
. Catamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
and trimaran configurations are also widely used for high speed craft.
History
Austronesian
Austronesian may refer to:
*The Austronesian languages
*The historical Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Sout ...
-speaking peoples of the islands of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
for sea travel. It is believed that the use of outriggers may have been initially caused by the need for stability on small watercraft after the invention of crab claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples by at least 2000 BCE. It is sometimes known as the Oceanic lateen or the Oceanic ...
s some time around 1500 BCE.
Outrigger boats were essential in the transportation of Austronesians both eastward to Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
and New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
and westward across the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
as far as Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
during the Austronesian
Austronesian may refer to:
*The Austronesian languages
*The historical Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Sout ...
migration period. The Austronesian peoples ( Malagasy, Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.
The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as ...
n, Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
n, Melanesian, Taiwanese indigenous peoples
Taiwanese indigenous peoples, formerly called Taiwanese aborigines, are the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, with the nationally recognized subgroups numbering about 600,303 or 3% of the Geography of Taiwan, island's population. This total is incr ...
, and Polynesian peoples) continue to be the primary users of the outrigger boats.
 The simplest form of all ancestral Austronesian boats had five parts. The bottom part consists of single piece of hollowed-out log. At the sides were two planks, and two horseshoe-shaped wood pieces formed the
The simplest form of all ancestral Austronesian boats had five parts. The bottom part consists of single piece of hollowed-out log. At the sides were two planks, and two horseshoe-shaped wood pieces formed the prow
The bow () is the forward part of the hull (watercraft), hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern.
Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the f ...
and stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. O ...
. These were "sewn" together with dowel
The dowel is a cylindrical shape made of wood, plastic, or metal. In its original manufactured form, a dowel is long and called a ''dowel rod'', which are often cut into shorter ''dowel pins''. Dowels are commonly used as structural reinforceme ...
s and lashings. They had no central rudders but were instead steered using an oar on one side. The ancestral rig was the mastless triangular crab claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples by at least 2000 BCE. It is sometimes known as the Oceanic lateen or the Oceanic ...
which had two booms that could be tilted to the wind. These were built in the double-canoe configuration or had a single outrigger on the windward side. In Island Southeast Asia, these developed into double outriggers on each side that provided greater stability. The triangular crab claw sails also later developed into square or rectangular tanja sail
Tanja sail ( Malay: ''layar tanjak'') or tanja rig is a type of sail commonly used by the Austronesian people, particularly in Maritime Southeast Asia. It is also known as the tilted square sail, canted rectangular sail, rectangular balance lug ...
s, which like crab claw sails, had booms spanning the upper and lower edges. Fixed masts also developed later in both Southeast Asia (usually as bipod or tripod masts) and Oceania.
Early researchers like Heine-Geldern (1932) and Hornell (1943) once believed that catamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
s evolved from outrigger boats, but modern authors specializing in Austronesian cultures like Doran (1981) and Mahdi (1988) now believe it to be the opposite.
Two canoes bound together developed directly from minimal raft technologies of two logs tied together. Over time, the double-hulled canoe form developed into the asymmetric double canoe, where one hull is smaller than the other. Eventually the smaller hull became the prototype outrigger
An outrigger is a projecting structure on a boat, with specific meaning depending on types of vessel. Outriggers may also refer to legs on a wheeled vehicle that are folded out when it needs stabilization, for example on a crane that lifts he ...
, giving way to the single outrigger canoe, which diverged into the reversible single outrigger canoe in Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its co ...
. Finally, the single outrigger types developed into the double outrigger canoe (or trimaran
A trimaran (or double-outrigger) is a multihull boat that comprises a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls (or "floats") which are attached to the main hull with lateral beams. Most modern trimarans are sailing yachts designed for recrea ...
s).
This would also explain why older Austronesian populations in Island Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.
The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as Mari ...
tend to favor double outrigger boats, as it keeps the boats stable when tacking. But they still have small regions where catamarans and single-outrigger boats are still used. In contrast, more distant outlying descendant populations in Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
, Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
, and the Comoros
The Comoros, officially the Union of the Comoros, is an archipelagic country made up of three islands in Southeastern Africa, located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city is Moroni, ...
retained the double-hull and the single outrigger boat types, for the technology of double outriggers never reached them (exceptions being western Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Vanu ...
). To deal with the problem of the instability of the boat when the outrigger faces leeward when tacking, they instead developed the shunting technique in sailing, in conjunction with reversible single-outriggers.
When Magellan's ships first encountered the Chamorros
The Chamorro people (; also Chamoru) are the Indigenous people of the Mariana Islands, politically divided between the United States territory of Guam and the encompassing Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands in Micronesia, a commonweal ...
of the Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands ( ; ), also simply the Marianas, are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, between the 12th and 21st pa ...
in 1521, Antonio Pigafetta
Antonio Pigafetta (; – c. 1531) was a Venetian scholar and explorer. In 1519, he joined the Spanish expedition to the Spice Islands led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan, the world's first Magellan's circumnavigation, circumnavigation, ...
recorded that the Chamorros' sailboats far surpassed Magellan's in speed and maneuverability. Similarly, the Spanish priest Francisco Combés
Francisco Combés (5 October 1620 – 29 December 1665) was a Spanish Jesuit priest who established Christian monasteries in the Philippines in the 17th century.
Life
Combés was born in Zaragoza (Spain) in 1620. When he was twelve, he joined ...
, describing the large ''karakoa
''Karakoa'' were large outrigger warships from the Philippines. They were used by native Filipinos, notably the Kapampangans and the Visayans, during seasonal sea raids. ''Karakoa'' were distinct from other traditional Philippine sailing vesse ...
'' outrigger warships of the Visayan Islands
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands ( Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; Filipino: ''Kabisayaan'' ), are one of the three principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the arch ...
in the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, remarked:
Outrigger fishing canoes are also used among certain non-Austronesian groups, such as the Sinhalese in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
, where they are known as ''oruwa'', as well as among some groups in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India comprising 572 islands, of which only 38 are inhabited. The islands are grouped into two main clusters: the northern Andaman Islands and the southern Nicobar Islands, separated by a ...
. They can also be found in East Africa (e.g., the '' ungalawa'' of Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
).
The acquisition of the catamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
and outrigger boat technology by the non-Austronesian peoples in Sri Lanka and southern India is the result of very early Austronesian contact with the region, including the Maldives
The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, and historically known as the Maldive Islands, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in South Asia located in the Indian Ocean. The Maldives is southwest of Sri Lanka and India, abou ...
and Laccadive Islands
The Laccadive Islands ( ) or Kannur Islands (formerly spelled Cannanore, ) are one of the three island subgroups in the Union Territory of Lakshadweep, India. It is the central subgroup of the Lakshadweep, separated from the Amindivi Islands ...
. This is estimated to have occurred around 1000 to 600 BCE and onwards. This may have possibly included limited colonization that have since been assimilated. This is still evident in Sri Lankan and South Indian languages. For example, Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
People, culture and language
* Tamils, an ethno-linguistic group native to India, Sri Lanka, and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka
** Myanmar or Burmese Tamils, Tamil people of Ind ...
''paṭavu'', Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of South India
** Telugu literature, is the body of works written in the Telugu language.
* Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Tel ...
''paḍava'', and Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
''paḍahu'', all meaning "ship", are all derived from Proto-Hesperonesian ''*padaw'', "sailboat", with Austronesian cognates like Javanese ''perahu
The ProA is the second-tier league of professional club basketball in Germany. The league comprises 16 teams. Officially the ProA is part of the '' 2. Basketball Bundesliga'', which consists of the two hierarchical leagues ''ProA'' and ''ProB'' ...
'', Kadazan ''padau'', Maranao
The Maranao people ( Maranao: ''Bangsa'' ''Mëranaw''; Filipino: ''mga'' ''Maranaw''), also spelled Meranaw, Maranaw, and Mëranaw, is a predominantly Muslim Filipino ethnic group native to the region around Lanao Lake in the island of Mi ...
''padaw'', Cebuano ''paráw
Paraw (also spelled ''parao'') are various double Outrigger canoe, outrigger sail boats in the Philippines. It is a general term (similar to the term ''bangka (boat), bangka'') and thus can refer to a range of ship types, from small fishing ...
'', Samoan ''folau'', Hawaiian ''halau'', and Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
''wharau''.
 The technology has persisted into the modern age. Outrigger boats can be quite large
The technology has persisted into the modern age. Outrigger boats can be quite large fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
or transport vessels. In the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, outrigger boats (called ''bangka'' or ''paraw
Paraw (also spelled ''parao'') are various double outrigger sail boats in the Philippines. It is a general term (similar to the term '' bangka'') and thus can refer to a range of ship types, from small fishing canoes to large merchant lashe ...
'') are often fitted with petrol engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American and Canadian English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends ...
s. The links between seafaring and outrigger boats in the Philippines extend through to political life, in which the smallest political unit in the country is still called "barangay
The barangay (; abbreviated as Brgy. or Bgy.), historically referred to as ''barrio'', is the smallest Administrative divisions of the Philippines, administrative division in the Philippines. Named after the Precolonial barangay, precolonial po ...
" after the historical ''balangay
A balangay, or barangay, is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The ...
'' outrigger boats used in the original migrations of the first Austronesian people
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesi ...
s across the archipelago and beyond. The Polynesian Voyaging Society
The Polynesian Voyaging Society (PVS) is a non-profit research and educational corporation based in Honolulu, Hawaii. PVS was established to research and perpetuate traditional Polynesian voyaging methods. Using replicas of traditional double-hul ...
has two double-hull sailing catamarans, '' Hokulea'' and '' Hawaiiloa'', and sails them between various islands in the Pacific using traditional Polynesian navigation
Polynesian navigation or Polynesian wayfinding was used for thousands of years to enable long voyages across thousands of kilometres of the Pelagic zone, open Pacific Ocean. Polynesians made contact with nearly every island within the vast Poly ...
methods without instruments. The ''Hikianalia'' and ''Alingano Maisu
''Alingano Maisu'', also known as ''Maisu'' , is a double-hulled voyaging canoe built in Kawaihae, Hawaii, by members of Na Kalai Waa Moku o Hawaii and Ohana Wa'a members from throughout the Pacific and abroad as a gift and tribute to Satawales ...
'' are other extant double-hulled voyaging canoes.
Terminology and linguistics
The Germanlinguist
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds ...
Otto Dempwolff
Otto Dempwolff (25 May 1871 in Pillau, Province of Prussia – 27 November 1938, in Hamburg) was a German physician, linguist and anthropologist who specialized in the study of the Austronesian language family.
Initially trained as a physician, ...
(1871-1938) originally reconstructed the Proto-Austronesian
Proto-Austronesian (commonly abbreviated as PAN or PAn) is a proto-language. It is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austronesian languages, one of the world's major language families. Proto-Austronesian is assumed to have begun to diversify in ...
word for "boat" as *waŋkaŋ, and included the reflexes
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a Stimulus (physiology), stimulus.
Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous s ...
for both *baŋkaʔ and *waŋkaʔ as its descendants. However modern linguists like Robert Blust
Robert A. Blust (; zh, c=白樂思, p=Bái Lèsī; May 9, 1940 – January 5, 2022) was an American linguist who worked in several areas, including historical linguistics, lexicography and ethnology. He was Professor of Linguistics at the Uni ...
generally reject this. Mahdi (2016) instead reconstructs four words for "boat" in the Austronesian languages
The Austronesian languages ( ) are a language family widely spoken throughout Maritime Southeast Asia, parts of Mainland Southeast Asia, Madagascar, the islands of the Pacific Ocean and Taiwan (by Taiwanese indigenous peoples). They are spoken ...
, all ultimately derived from the monosyllabic protoforms *Cu and *baŋ. They are:
:a) *qaCu - cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language.
Because language change can have radical effects on both the s ...
s include Squliq-Atayal ''qasuʔ'', Pazeh ''ʔasuʔ'', and Bunun ''hatoʔ''
:b) *qabaŋ - cognates include Kanakanavu ''abaŋɯ'', Oponohu-Rukai ''havaŋu'', Siraya ''avang'', Gaddang ''ʔabaŋ'', Tiruray ''ʔawaŋ'', Iranun
The Iranun are an Austronesian ethnic group native to southwestern Mindanao, Philippines. They are ethnically and culturally closely related to the Maranao, and Maguindanaon, all three groups being denoted as speaking Danao languages and giv ...
''awaŋ'', Mentawai ''abak'', and Moken
The Moken (also Mawken or Morgan; ; ) are an Austronesian people of the Mergui Archipelago, a group of approximately 800 islands claimed by both Myanmar and Thailand, and the Surin Islands. Most of the Moken live a semi-nomadic hunter-gatherer ...
''kabaŋ''
:c) *baŋkaʔ - cognates include Kavalan ''baŋka'', Tagalog ''baŋkaʔ'', Tausug ''baŋkaʔ'', Mori
Mori is a Japanese and Italian surname. It is also the name of two clans in Japan, and one clan in India.
Italian surname
* Camilo Mori, Chilean painter
* Cesare Mori, Italian "Iron Prefect"
* Claudia Mori, Italian actress, singer, televisio ...
and Muna ''baŋka'', and Sumbawa
Sumbawa, is an Indonesian island, located in the middle of the Lesser Sunda Islands chain, with Lombok to the west, Flores to the east, and Sumba further to the southeast. Along with Lombok, it forms the province of West Nusa Tenggara, but th ...
''baŋka''
:d) *waŋkaʔ' - cognates include Manggarai and Rembong ''waŋka'', Tobati ''wăgě'', Yabem ''waŋ'', Suau ''waga'', Hiw ''wakə'', Mota ''aka'', Fijian ''waqa'', Tongan ''vaka'', Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
'' waka'' and Hawaiian ''waa''; Tahitian and Samoan '' vaa''
Instead of being cognates, the protoforms *baŋkaʔ and *waŋkaʔ are believed to be doublets. The protoforms *qabaŋ and *baŋkaʔ are composites with a common precursor, with the ''*qa-'' and ''-*ka'' positioned differently. Only *qaCu and *qabaŋ can be traced back to Proto-Austronesian
Proto-Austronesian (commonly abbreviated as PAN or PAn) is a proto-language. It is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austronesian languages, one of the world's major language families. Proto-Austronesian is assumed to have begun to diversify in ...
, with the rest being later developments.
The outrigger float is called the '' ama'' in many Polynesian languages
The Polynesian languages form a genealogical group of languages, itself part of the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian family.
There are 38 Polynesian languages, representing 7 percent of the 522 Oceanic languages, and 3 percent of the Austr ...
(compare Hawaiian ''ama'', Māori ''ama'', and Samoan ''ama'', all meaning 'outrigger float'), realisations of Proto-Malayo-Polynesian
Proto-Malayo-Polynesian (PMP) is the reconstructed ancestor of the Malayo-Polynesian languages, which is by far the largest branch (by current speakers) of the Austronesian language family. Proto-Malayo-Polynesian is ancestral to all Austronesia ...
*saRman 'outrigger float'. Similar terms also exist in other Malayo-Polynesian languages, such as Pohnpeian ''dahm'', Yapese ''thaam'', Ambonese Malay
Ambonese Malay or simply Ambonese is a Malay-based creole language spoken on Ambon Island in the Maluku Islands of Eastern Indonesia. It was first brought by traders from Western Indonesia, then developed when the Dutch Empire colonised the M ...
''semang'', all meaning 'outrigger float', as well as Chamorro '' sakman'' meaning ' large canoe.' The outrigger boom—spars connecting the ''ama'' to the main hull (or the two hulls in a double-hull canoe)—are called '' iako'' in Hawaiian and ''kiato'' in Māori (with similar words in other Polynesian languages), ultimately from Proto-Oceanic
Proto-Oceanic (abbreviated as POc) is a proto-language that comparative linguistics, historical linguists since Otto Dempwolff have reconstructed as the hypothetical common ancestor of the Oceanic languages, Oceanic subgroup of the Austronesian ...
*kiajo or its doublet *kayajo both meaning 'outrigger boom' (compare Loniu
Loniu is an Austronesian language spoken along the southern coast of Los Negros Island in the Manus Province, immediately east of Manus Island in Manus Province, Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Pap ...
''kiec'', Kiribati
Kiribati, officially the Republic of Kiribati, is an island country in the Micronesia subregion of Oceania in the central Pacific Ocean. Its permanent population is over 119,000 as of the 2020 census, and more than half live on Tarawa. The st ...
''kiaro'', and Tongan ''kiato'', as well as Seimat ''ayas'' and Gedaged ''ayad'', all meaning 'outrigger boom'). In Philippine languages
The Philippine languages or Philippinic are a proposed group by R. David Paul Zorc (1986) and Robert Blust (1991; 2005; 2019) that include all the languages of the Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia—except Sama–Bajaw (language ...
, the outrigger floats are called ''katig'' or ''kate'', from Proto-Philippine
The Proto-Philippine language is a reconstructed ancestral proto-language of the Philippine languages, a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian languages which includes all languages within the Philippines (except for the Sama–Bajaw languages) ...
*katiR.
Types
Double-outrigger boats are more prevalent inSoutheast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, though single-outriggers and catamarans also exist. They have two outrigger floats connected to spars lashed across a single hull. They range in size from small vessels like the ''jukung
A jukung or kano, also known as cadik is a small wooden Indonesian outrigger canoe. It is a traditional fishing boat, but newer uses include "Jukung Dives", using the boat as a vehicle for small groups of SCUBA divers.
The double outrigger jukun ...
'', ''vinta
The vinta is a traditional outrigger boat from the Philippine island of Mindanao. The boats are made by Sama-Bajau, Tausug and Yakan peoples living in the Sulu Archipelago, Zamboanga peninsula, and southern Mindanao. It is also made by t ...
'', and the ''paraw
Paraw (also spelled ''parao'') are various double outrigger sail boats in the Philippines. It is a general term (similar to the term '' bangka'') and thus can refer to a range of ship types, from small fishing canoes to large merchant lashe ...
''; to medium-sized trading and fishing vessels like the ''balangay
A balangay, or barangay, is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The ...
'' and '' basnigan''; to very large warships like the ''karakoa
''Karakoa'' were large outrigger warships from the Philippines. They were used by native Filipinos, notably the Kapampangans and the Visayans, during seasonal sea raids. ''Karakoa'' were distinct from other traditional Philippine sailing vesse ...
'' and ''kora kora
A kora-kora or kora kora or coracora is a traditional canoe from the Maluku (Moluccas) Islands, Indonesia. They are naval boat for carrying men on raids for plunder or for slaves. In Maritime Southeast Asia, raiding for slaves was an honourable w ...
''. In Philippine vessels, additional booms called ''batangan'' are usually added across the outrigger spars (''tadik''), in between the outrigger floats (''katig'') and the main hull (''bangka''). In modern terminology, especially in leisure or sport boating, double-outrigger ships are usually termed trimaran
A trimaran (or double-outrigger) is a multihull boat that comprises a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls (or "floats") which are attached to the main hull with lateral beams. Most modern trimarans are sailing yachts designed for recrea ...
or triple-hull ships.
An unusual type of double-outrigger boat design, preserved in scale models in the Pitt Rivers Museum
Pitt Rivers Museum is a museum displaying the archaeological and anthropological collections of the University of Oxford in England. The museum is located to the east of the Oxford University Museum of Natural History, and can only be accessed ...
, forms a triangle shape. The front ends of the outriggers are attached directly to the hull, while the rear ends are splayed out. These boats were small and used exclusively as passenger ferries in the Pasig River
The Pasig River (; ) is a water body in the Philippines that connects Laguna de Bay to Manila Bay. Stretching for , it bisects the Philippine capital of Manila and Metro Manila, its surrounding urban area into northern and southern halves. Its m ...
of the Philippines.
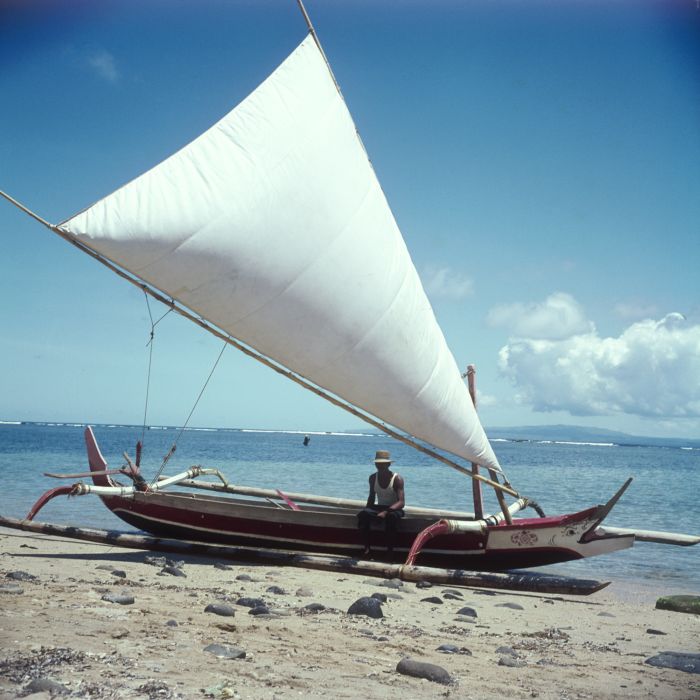
Catamarans and single-outrigger canoes are the traditional configurations in Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
, Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
, and Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
. In the Pacific Islands, a single outrigger float is called an ''ama''. It is connected to the main hull by spars called ''iako'' ( Hawaiian), ''iato'' ( Tahitian), or ''kiato'' (Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
). The ama, which is usually rigged on the left side, provides stability. The paddlers need to be careful to avoid leaning too far on the opposite side of the ama, as that may cause the canoe to capsize ( ''huli'' or ''lumai''). Double-outrigger configurations, a later innovation from Southeast Asian Austronesians, never reached Oceania.
Single-outrigger dugout canoe
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed-out tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' (tr ...
s also exist in the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
. Examples include canoes from Laguna de Bay
Laguna de Bay ( Spanish for "Lagoon/Lake of Bay"; , ), also known as Laguna Lake and alternatively spelled "Laguna de Bae", is the largest lake in the Philippines. It is located southeast of Metro Manila, between the provinces of Laguna to t ...
, as well as boats from Lake Bulusan and Lake Buhi of the Bicol Region
The Bicol Region, designated as Region V, is an administrative region of the Philippines. It comprises six Provinces of the Philippines, provinces, four on the Bicol Peninsula (the luzon#Southeastern Luzon, southeastern end of Luzon): Albay, Ca ...
. A notable example is the '' armadahan'' of Laguna de Bay
Laguna de Bay ( Spanish for "Lagoon/Lake of Bay"; , ), also known as Laguna Lake and alternatively spelled "Laguna de Bae", is the largest lake in the Philippines. It is located southeast of Metro Manila, between the provinces of Laguna to t ...
, which were dugouts typically long and wide. They were equipped with two masts. The single outrigger float () on the starboard side was either two bamboo poles lashed together or a flattened elongated beam. It also featured a counter-balance beam projecting off the port side known as the . In modern times, these types of boats are usually motorized or paddled. And the single outrigger is used to provide lateral stability, while still allowing fishermen to work with fishing net
A fishing net or fish net is a net (device), net used for fishing. Fishing nets work by serving as an improvised fish trap, and some are indeed rigged as traps (e.g. #Fyke nets, fyke nets). They are usually wide open when deployed (e.g. by cast ...
s. They were more widespread in the Philippines in the past, with a specimen in the University of Southampton
The University of Southampton (abbreviated as ''Soton'' in post-nominal letters) is a public university, public research university in Southampton, England. Southampton is a founding member of the Russell Group of research-intensive universit ...
from Manila Bay
Manila Bay (; ) is a natural harbor that serves the Port of Manila (on Luzon), in the Philippines. Strategically located around the Manila, capital city of the Philippines, Manila Bay facilitated commerce and trade between the Philippines and ...
collected in the 1940s for example. But they have largely disappeared in modern times, partly due to the scarcity of suitable timber and partly due to the relative cheapness of fiberglass boats.
List of traditional outrigger vessels by region
The following is an incomplete list of traditional Austronesian outrigger vessels. It also includescatamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
s.
Island Southeast Asia
Indonesia
 *
*Borobudur ship
A Borobudur ship is an 8th to 9th-century wooden double outrigger sailing vessel of Maritime Southeast Asia, depicted in some bas-reliefs of the Borobudur Buddhist monument in Central Java, Indonesia. It is a ship of the Javanese people, and de ...
* Jellore
*Jukung
A jukung or kano, also known as cadik is a small wooden Indonesian outrigger canoe. It is a traditional fishing boat, but newer uses include "Jukung Dives", using the boat as a vehicle for small groups of SCUBA divers.
The double outrigger jukun ...
* Knabat bogolu
*Kora kora
A kora-kora or kora kora or coracora is a traditional canoe from the Maluku (Moluccas) Islands, Indonesia. They are naval boat for carrying men on raids for plunder or for slaves. In Maritime Southeast Asia, raiding for slaves was an honourable w ...
* Londe
* Paduwang
* Paledang
* Pangajava
* Pangkur
*Pelang
Pelang or pilang is a traditional boat from Indonesia and Malaysia. It may refer to several different types of boats in the Nusantara, but commonly they refer to an outrigger canoe. The function differs from where they were used, from transport ...
*Perahu
The ProA is the second-tier league of professional club basketball in Germany. The league comprises 16 teams. Officially the ProA is part of the '' 2. Basketball Bundesliga'', which consists of the two hierarchical leagues ''ProA'' and ''ProB'' ...
*Sandeq
A Sandeq is a type of outrigger sailboat or trimaran used by the Mandarese people for fishing and as a means of transportation between islands. The size of Sandeq varies, with hulls ranging from long and wide. Its carrying capacity ranges fr ...
Malaysia
*Penjajap
Penjajap, also pangajava and pangayaw, were native galley-like warships used by several Austronesian ethnic groups in maritime Southeast Asia. They were typically very long and narrow, and were very fast. They are mentioned as being used by native ...
*Pelang
Pelang or pilang is a traditional boat from Indonesia and Malaysia. It may refer to several different types of boats in the Nusantara, but commonly they refer to an outrigger canoe. The function differs from where they were used, from transport ...
*Perahu
The ProA is the second-tier league of professional club basketball in Germany. The league comprises 16 teams. Officially the ProA is part of the '' 2. Basketball Bundesliga'', which consists of the two hierarchical leagues ''ProA'' and ''ProB'' ...
Philippines
 * Armadahan
* Balación
*
* Armadahan
* Balación
*Balangay
A balangay, or barangay, is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The ...
(Baloto, Biray, Biroko)
* Bangka (Sakayan)
* Bangka anak-anak
* Basnigan
*Bigiw
Bigiw is a small Outrigger canoe, double-outrigger sailboat native to the islands of Mindanao (particularly in the Island Garden City of Samal), Visayas, and Palawan in the Philippines. It is used for personal transport or small-scale fishing an ...
* Casco
*Djenging
Djenging is a type of large double-outrigger plank boat built by the Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Loca ...
(Balutu, Kubu)
* Guilalo
* Junkun
*Karakoa
''Karakoa'' were large outrigger warships from the Philippines. They were used by native Filipinos, notably the Kapampangans and the Visayans, during seasonal sea raids. ''Karakoa'' were distinct from other traditional Philippine sailing vesse ...
*Lanong
''Lanong'' were large outrigger warships used by the Iranun and the Banguingui people of the Philippines. They could reach up to in length and had two biped shear masts which doubled as boarding ladders. They also had one to three banks of o ...
* Pangayaw
*Paraw
Paraw (also spelled ''parao'') are various double outrigger sail boats in the Philippines. It is a general term (similar to the term '' bangka'') and thus can refer to a range of ship types, from small fishing canoes to large merchant lashe ...
* Salisipan
* Tataya
*Vinta
The vinta is a traditional outrigger boat from the Philippine island of Mindanao. The boats are made by Sama-Bajau, Tausug and Yakan peoples living in the Sulu Archipelago, Zamboanga peninsula, and southern Mindanao. It is also made by t ...
(Dapang, Pilang)
Melanesia
Fiji
* Camakau *Drua
Drua, also known as na drua, n'drua, ndrua or waqa tabu ("sacred canoe", ), is a double-hull sailing boat that originated in the south-western Pacific islands. Druas do not tack but rather shunt (stern becomes the bow and vice versa). Both ends ...
(Wangga tabu)
* Takia
Papua New Guinea
*Lakatoi
Lakatoi (also Lagatoi) are multiple-hulled sailing watercraft of Papua New Guinea. They are named in the Motu language and traditionally used in the Hiri trade cycle.
Lakatoi (whose literal meaning is ''three dugouts)'' are fashioned from two ...
Solomon Islands
* TepukeiVanuatu
* Aka * Angga *Wangga
Wangga (sometimes spelled Wongga) is an Aboriginal Australian genre of traditional music and ceremony which originated in Northern Territory and north Western Australia. Specifically, from South Alligator River south east towards Ngukurr, sou ...
Australia (Torres strait islands)
* kulbasaibaiMicronesia

Caroline Islands
* Wa * Wahr * WaserakKiribati
* BauruaMarshall Islands
* Korkor * Tipnol * WalapMariana Islands, incl. Guam
* Ladjak * Sakman (Flying proa)Palau
*Kaep
Kaep is a traditional type of double-ended Proa sailboat native to Palau. Some of the essential design elements have also been adopted as a modern smaller multihull prototype variant.
Larger context
The Pacific Ocean and particularly Micronesia ...
* Wa
Yap
* Chugpin * Popow * WaPolynesia

Cook Islands
* Vaka *Vaka katea
Vaka katea are the traditional sailing double canoe watercraft of the Cook Islands.
See also
* Rarotonga
Rarotonga is the largest and most populous of the Cook Islands. The island is volcanic, with an area of , and is home to almost 75% of t ...
Hawaii
* Malia * Wa'a * Wa'a kauluaMarquesas
* Vaka touuaNew Zealand
* Waka ama *Waka hourua
WAKA (channel 8) is a television station licensed to Selma, Alabama, United States, serving as the CBS affiliate for the Montgomery area. It is owned by Bahakel Communications alongside Tuskegee-licensed CW+ affiliate WBMM (channel 22); Bah ...
Samoa
*Alia
Alia or ALIA may refer to:
People
*Alia (name), a list of people with the surname or given name
Places
*Alia, Sicily, Italy, a comune
* Alia (Phrygia), a town of ancient Phrygia which remains a Roman Catholic titular bishopric
* Alía, Spain, a ...
* Amatasi
* Laau
* Lualua (Foulua)
* Paopao
* Vaa
* Vaa-alo
* Vaa-tele
Society Islands
* Ivahah * Pahi *Tipairua
Tipairua were large traditional sailing canoes of Tahiti that were of stately bearing and significance. They were often used for deep sea voyages, had low heads, high upturned stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, t ...
* Vaa
Tonga
* Hamatafua * Kalia * Pōpao *Tongiaki
Tongiaki are native watercraft of Tonga. They are double-hulled canoes in the Austronesian tradition, similar to catamarans.
See also
*outrigger canoe
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known ...
Tuvalu
* PaopaoMadagascar
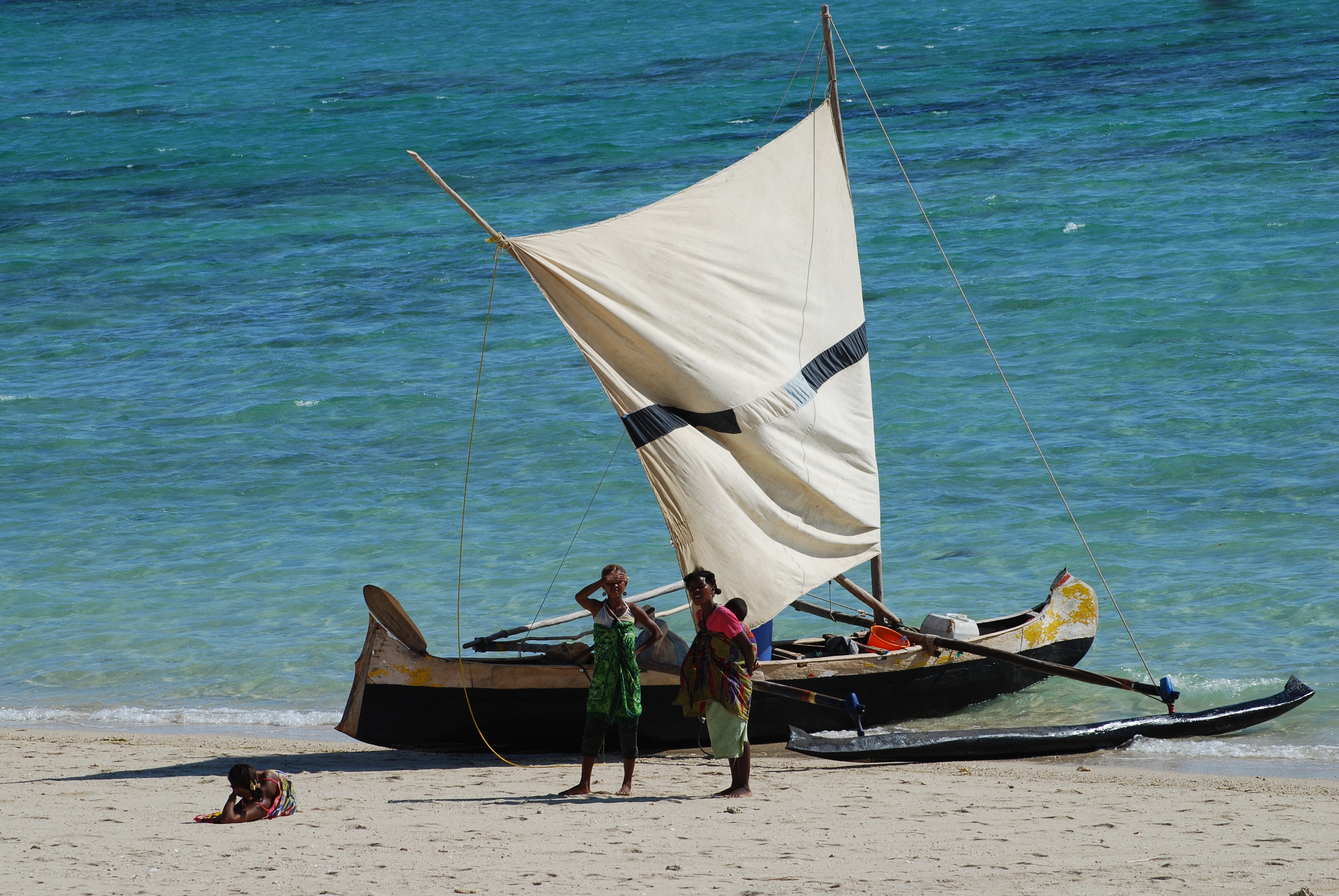 * Lakana
* Lakana
Non-Austronesian outrigger boats
The following are traditional outrigger boats acquired by other cultures from contact with Austronesian sailors.Sri Lanka
* Oruwa * Yathra doniEast Africa
*Ngalawa
The ngalawa or ungalawa is a traditional, outrigger canoe, double-outrigger canoe of the Swahili people living in Zanzibar and the Tanzanian coast. It is usually 5–6 m long and has two outriggers, a centrally-placed mast (often inclining slightl ...
* Laana
northern Australia (Aboriginal)
* Aboriginal single outrigger canoe * Aboriginal double outrigger canoeModern sport
Outrigger canoe racing has become a popularcanoeing
Canoeing is an activity which involves paddling a canoe with a single-bladed paddle. In some parts of Europe, canoeing refers to both canoeing and kayaking, with a canoe being called an 'open canoe' or Canadian.
A few of the recreational ...
sport, with numerous clubs located around the world. Outrigger Canoe Racing is the State sport of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
and an interscholastic high school sport. In Hawaii, entire families participate in summer regatta
Boat racing is a sport in which boats, or other types of watercraft, race on water. Boat racing powered by oars is recorded as having occurred in ancient Egypt, and it is likely that people have engaged in races involving boats and other wa ...
s with age groups from keiki (children as young as 6 with an adult steersperson) and age 12 through age 60+.
Major races in Hawaii include the Molokai Hoe men's race from the island of Molokai
Molokai or Molokai ( or ; Molokaʻi dialect: Morotaʻi ) is the fifth most populated of the eight major islands that make up the Hawaiian Islands archipelago in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. It is 38 by 10 miles (61 by 16 km) at its g ...
to Oahu
Oahu (, , sometimes written Oahu) is the third-largest and most populated island of the Hawaiian Islands and of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oahu's southeast coast. The island of Oahu and the uninhabited Northwe ...
across the Kaiwi Channel, Na Wahine O Ke Kai (same race for women) and the Queen Liliuokalani Race held near Kona on the Island of Hawai.
 In modern sport outrigger canoeing, ships are classified according to the configuration and number of the hulls and the number of paddlers, including the OC1, OC2, OC3, OC4 and OC6 (with the respective number of paddlers using a single-hull outrigger canoe), and the DC12 or OC12 (with twelve paddlers using a double-hull outrigger canoe, two six-person canoes rigged together like a
In modern sport outrigger canoeing, ships are classified according to the configuration and number of the hulls and the number of paddlers, including the OC1, OC2, OC3, OC4 and OC6 (with the respective number of paddlers using a single-hull outrigger canoe), and the DC12 or OC12 (with twelve paddlers using a double-hull outrigger canoe, two six-person canoes rigged together like a catamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
). Outriggers without a rudder are referred to as V1, V2, etc. (where V refers to ''vaa'').
Six-person outrigger canoes (or OC6) are among the most commonly used for sport use; single-person outrigger canoes (or OC1) are also very common. Two and four-person outrigger canoes are also sometimes used, and two six-person outrigger canoes are sometimes rigged together like a catamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
to form a twelve-person double canoe.
Modern OC6 hulls and amas are commonly made from glass-reinforced plastic
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass ( Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass c ...
. However, some canoes are made of more traditional materials. In Ancient Hawaii
Ancient Hawaii is the period of Hawaiian history preceding the establishment in 1795 of the Kingdom of Hawaii by Kamehameha the Great. Traditionally, researchers estimated the first settlement of the Hawaiian islands as having occurred sporad ...
, canoes were carved from the trunks of very old koa
KOA (short for Kampgrounds of America) is an American franchise of privately owned campgrounds. Having more than 500 locations across the United States and Canada, it is the world's largest system of privately owned campgrounds. It was founded ...
trees. These canoes, although rare, are still very much in use today. The iako are usually made of wood; the iako-ama and iako-hull connections are typically done with rope wrapped and tied in an interlocking fashion to reduce the risk of the connection coming completely apart if the rope breaks.
Modern OC1 hulls and amas are commonly made from glass-reinforced plastic
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass ( Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass c ...
, carbon fiber reinforced plastic, and/or Kevlar
Kevlar (para-aramid) is a strong, heat-resistant synthetic fiber, related to other aramids such as Nomex and Technora. Developed by Stephanie Kwolek at DuPont in 1965, the high-strength material was first used commercially in the early 1970s as ...
to produce a strong but light canoe. OC1 are often made with rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, airship, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (usually air or water). On an airplane, the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw ...
s operated by foot pedals. More traditional designs do not have rudders. OC1 commonly use iako made of aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
or carbon fiber, with a mechanism for quickly assembling and disassembling the canoe (snap buttons, large wing nuts, etc.).
Roles
In an outrigger canoe, the paddlers sit in line, facing toward the bow of the canoe (i.e., forward, in the direction of travel, unlike Watercraft rowing, rowing). The seats are numbered from 1 (closest to the bow) to the number of seats in the canoe, usually 6. The ''steerer'' (or ''steersman'' or ''steersperson'') sits in the last seat of the canoe (seat 6 in the common OC6) and, as the name indicates, is primarily responsible forsteering
Steering is the control of the direction of motion or the components that enable its control. Steering is achieved through various arrangements, among them ailerons for airplanes, rudders for boats, cylic tilting of rotors for helicopters, ...
. The paddler sitting in seat 1 is called the ''stroke'' (or ''stroker'') and is responsible for setting the pace of the paddle strokes. The stroker should have a high level of endurance to keep the rate (the number of strokes taken in a given amount of time) manageable for whatever the situation may be. The first two positions may also be involved in certain steering manoeuvers. This usually involves the draw stroke. During a tight turn, the one seat might poke to make the canoe turn the opposite way. In the middle of the canoe ''(seats number 3 and 4)'' known as the powerhouse are the strong and powerful paddlers. Any of the 2 can be the 'caller' who directs when to switch over their blades, when to pick up or slow down the stroking pace, etc. Whoever is caller must have very good leadership skills and know how to think off the top of their heads in any situation. Every position has an important role to play in the canoe.
In an OC1, the single paddler must also steer the canoe. Some OC1s have rudders operated by foot pedals, while OC1s without rudders must be steered by drawing and paddling as needed for steering purposes while paddling to move the canoe forward.
Steersman
 A good steersman is able to maintain the
A good steersman is able to maintain the straight
Straight may refer to:
Slang
* Straight, slang for heterosexual
** Straight-acting, normal person
* Straight, a member of the straight edge subculture
Sport and games
* Straight, an alternative name for the cross, a type of punch in boxing
* Str ...
attitude of the canoe throughout the course of a race, and also keep the boat and the crew safe in rough sea conditions. They may also take advantage of water conditions to gain extra speed by surfing
Surfing is a surface water sport in which an individual, a surfer (or two in tandem surfing), uses a board to ride on the forward section, or face, of a moving wave of water, which usually carries the surfer towards the shore. Waves suita ...
. The steersman uses a single bladed steering paddle which has a larger blade than a standard outrigger paddle, is built stronger, and has less or no bend in its shaft. They steer by the following methods:
* Poking: holding the paddle vertically against the side of the canoe, causing drag on that side to cause the canoe to turn that direction. (left to go left and right to go right)
* Drawing: paddling at a 45 to 90-degree angle to pull water under the canoe, causing the canoe to turn the opposite direction.
* Posting: holding the paddle in the water out to the side with the forward edge angled opposite to the desired turn direction, usually as a prelude to drawing.
* Paddling: by applying power on one side of the canoe, the steersman can influence to a small degree which way the canoe will turn. Paddling also increases the total power moving the canoe forward compared to the other steering methods. The steersman should try and paddle as much as possible so he or she doesn't slow down the canoe by contributing to the amount of weight in the canoe.
A steersman also skippers the canoe and instructs all other paddlers as necessary. As an outrigger canoe is a long narrow canoe with the steersman placed at the very end, the steersman must give instructions sufficiently loudly and clearly for the entire crew to hear. From a water safety
Safety is the state of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
The word 'safety' entered the English language in the 1 ...
perspective the steersman should also be among the most experienced crew members, and be knowledgeable with the waterways and weather conditions, relevant maritime rules and other safety considerations such as the use of personal flotation devices, rigging of the canoe, placement of paddlers in the various seating positions, and recovery from a huli by righting the canoe and bailing out the water. The steersman should also be able to keep the ama down during rough water.
Paddlers
Paddlers use single-bladed paddles, usually with single or double bent shafts. The paddling stroke is similar to that of most other racing canoe paddling strokes, involving primarily core and lat strength. Generally, each paddler paddles on the opposite side from the paddler in directly front (for example, in an OC6, paddlers in seats 1, 3, and 5 paddle on one side, while paddlers in seats 2 and 4 paddle on the other side). All paddlers switch sides simultaneously on a call from one who is the designated caller. The steerer may paddle either side or switch sides as needed for steering purposes. The steersman will also switch sides to keep the ama from popping up and capsizing the canoe. Stronger paddlers are typically placed in the middle of the canoe, while paddlers with the most endurance tend to be placed at the front, as the lead paddler sets the pace for the crew. All other paddlers synchronize their strokes to the paddler in front of them (whom they can directly see). In rough water, it is often desirable to have a paddler with steering skill in seat 5 (of an OC6), to allow for the steerer to have that paddler also take steering strokes if needed in some situations. In conditions when the boat is surfing, the stern of the canoe will be so far out of the water that seat 5 will have to keep the boat on course. A seat 5 paddler with steering skill can also assist in preventing a huli by staying on the ama side during a particularly rough stretch of water. In water rough enough to splash into the canoe, paddlers also need to pay attention to the water level in the canoe, report the situation to the steerer, and bail out the water as necessary. Paddlers also need to know how to recover from a huli under the steerer's direction. In a quick turn situation, paddlers at the front may also be instructed to ''une'' (poke steer, causes the canoe to turn the opposite direction) or ''kahi'' (post and draw steer, pulls the canoe to the side where this is done) to help bring the canoe around a turn quickly.Racing
The length of a race ranges from short sprints (e.g., 250–500 metres for the OC1 and the OC12, 500–2000 metres (usually includes turns) for the OC6) to longer events, including marathons (e.g., 42 kilometres). A number of races are raced over distances that far exceed 42 kilometres, including the Molokai Hoe that crosses the Kaiwi Channel between the islands of Molokai and Oahu in Hawaii. However, long-distance races of 20 to 30 kilometres are more common, with shorter 5 to 8 kilometre courses typically being offered to novice paddlers and those under 20 years of age. Longer races involving the OC6 often involve paddler replacements, which involve exit and entry to the canoe directly from the water while the canoe is underway (this is called a ''water change''). Typically, nine paddlers form a crew, with six paddling the OC6 and the other three resting, drinking, and/or eating on an escort boat. Replacement typically occurs at 20 to 30 minute intervals; the escort boat drops the relief paddlers into the water ahead of the OC6, which is steered toward them. The relief paddlers climb in on the ama side as those they are replacing roll out into the water on the opposite side. The escort boat then picks up the paddlers in the water so that they can rest, drink, and/or eat before they, in turn, relieve some of the paddlers in the OC6. The longer races are typically conducted in the open ocean, e.g., between islands in the South Pacific. The Molokai Hoe in Hawaii, The Hamilton Cup in Australia, The Vaka Eiva in Rarotonga (Cook Islands), The Motu2Motu in Aitutaki (Cook Islands) and the Catalina Channel crossing in California are four examples of races involving water changes.
Paddlers and crews are usually classified by gender and age. Gender classification is typically straightforward, with male, female, and coed classifications, with the latter being a crew with equal numbers of male and female paddlers (different rules may apply to nine-person coed crews doing a race with paddler replacements). Age classifications typically include youth divisions like 19-and-under, 16-and-under, etc., master divisions with minimum ages typically starting at 35 or 40 years of age, and an open division which allows paddlers of any age. A novice division for paddlers with less than a specified number of years of race experience (usually one or two) may also exist in a given association.
In some races, a particular type of outrigger canoe, usually a more traditional design for the region, may be given its own racing classification. For example, races in Hawaii have a
The longer races are typically conducted in the open ocean, e.g., between islands in the South Pacific. The Molokai Hoe in Hawaii, The Hamilton Cup in Australia, The Vaka Eiva in Rarotonga (Cook Islands), The Motu2Motu in Aitutaki (Cook Islands) and the Catalina Channel crossing in California are four examples of races involving water changes.
Paddlers and crews are usually classified by gender and age. Gender classification is typically straightforward, with male, female, and coed classifications, with the latter being a crew with equal numbers of male and female paddlers (different rules may apply to nine-person coed crews doing a race with paddler replacements). Age classifications typically include youth divisions like 19-and-under, 16-and-under, etc., master divisions with minimum ages typically starting at 35 or 40 years of age, and an open division which allows paddlers of any age. A novice division for paddlers with less than a specified number of years of race experience (usually one or two) may also exist in a given association.
In some races, a particular type of outrigger canoe, usually a more traditional design for the region, may be given its own racing classification. For example, races in Hawaii have a koa
KOA (short for Kampgrounds of America) is an American franchise of privately owned campgrounds. Having more than 500 locations across the United States and Canada, it is the world's largest system of privately owned campgrounds. It was founded ...
division, while southern California has a Bradley OC6 division and northern California OC1 sprint races have a traditional (no rudder) division.
Paddling Around the World
The sport of outrigging has travelled worldwide and is now prominent in countries around the world. Clubs exist worldwide in the countries detailed below Hawaii: Outrigger canoe paddling is a popular sport and cultural tradition, with many clubs and competitions. Fiji: Outrigger canoe racing (va'a) is a significant part of Fijian culture and is even featured in the Pacific Games,. Tahiti: Outrigger canoes, known as va'a, are a national sport and are used for various purposes like fishing, travel, and racing. Hong Kong: A Hong Kong group has introduced and promotes outrigger canoes and their cultural significance. There are many clubs within the special administrative region such as the Victoria Recreational Club (VRC), The Royal Hong Kong Yacht Club (RHKYC), and the Lamma Outrigger Canoe Club located around Hong Kong Sri Lanka: Outrigger canoes are used for fishing, and research is ongoing to improve their design and materials, according to the FAO. East Africa: While less prominent than in the Pacific, outrigger canoes like the ungalawa are used in Tanzania for fishing and transportation.Organisations
The International Va'a Federation (IVF) overseesva'a
Vaʻa is a word in Samoan language, Samoan, Hawaiian language, Hawaiian and Tahitian language, Tahitian which means 'boat', 'canoe' or 'ship'. It is cognate with other Polynesian words such as ''vaka (sailing), vaka'' or the Māori language, Māo ...
racing worldwide, including the IVF World Championships and at the Pacific Games
The Pacific Games (French: Jeux du Pacifique), is a continent, continental multi-sport event held every four years among athletes from Oceania. The inaugural Games took place in 1963 South Pacific Games, 1963 in Suva, Fiji, and most recently i ...
.
Outrigger racing organizations in the United States include the East Coast Outrigger Racing Association (ECORA), the Hawaiian Canoe Racing Association (HCRA), the Northern California Outrigger Canoe Association (NCOCA), the Southern California Outrigger Canoe Association (SCORA), and several more.
See also
* Ama and Aka *Austronesian maritime trade network
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over land or water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a singl ...
* Burulan
Burulan is a Visayan term referring to fighting platforms on the traditional large trimaran warships (''balangay'') of the Philippines. They were made from bamboo and were distinctively raised from the deck. They carried the warrior-nobility of t ...
* Canoe sailing
* Catamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
* Crab claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples by at least 2000 BCE. It is sometimes known as the Oceanic lateen or the Oceanic ...
* Daramba
* Hiri trade cycle
Hiri is the name for the traditional trade voyages that formed an important part of the culture of the Motu people of Papua New Guinea.
Origins
The Motu live in a comparative rain shadow – the dry season is unusually harsh, and there are not ...
* Kula ring
Kula, also known as the Kula exchange or Kula ring, is a ceremonial exchange system conducted in the Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea. The Kula ring was made famous by Bronisław Malinowski, considered the father of modern anthropology. He ...
* Lapita culture
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian peoples, Austronesian people and their distinct material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. The Lapita people are believed t ...
* Lashed-lug boat
Lashed-lug boats are ancient boat-building techniques of the Austronesian peoples. It is characterized by the use of raised lugs (also called "cleats") on the inner face of hull planks. These lugs have holes drilled in them so that other hull com ...
* Maritime Silk Road
The Maritime Silk Road or Maritime Silk Route is the maritime section of the historic Silk Road that connected Southeast Asia, East Asia, the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian Peninsula, eastern Africa, and Europe. It began by the 2nd century BCE ...
* Marshall Islands stick chart
Stick charts were made and used by the Marshallese people, Marshallese to navigate the Pacific Ocean by canoe off the coast of the Marshall Islands. The charts represented major swell (ocean), ocean swell patterns and the ways the islands disru ...
* Multihull
A multihull is a boat or ship with more than one Hull (watercraft), hull, whereas a vessel with a single hull is a monohull. The most common multihulls are catamarans (with two hulls), and trimarans (with three hulls). There are other types, wi ...
* Polynesian multihull terminology
Polynesian multihull terminology, such as "ama", "aka" and "vaka" (or "waka") are multihull terms that have been widely adopted beyond the South Pacific where these terms originated. This Polynesian terminology is in common use in the Americas an ...
* Polynesian navigation
Polynesian navigation or Polynesian wayfinding was used for thousands of years to enable long voyages across thousands of kilometres of the Pelagic zone, open Pacific Ocean. Polynesians made contact with nearly every island within the vast Poly ...
* Proa
The ProA is the German basketball league system, second-tier Sports league, league of professional club basketball in Germany. The league comprises 16 teams. Officially the ProA is part of the ''2. Basketball Bundesliga'', which consists of the t ...
* Sa Huynh-Kalanay Interaction Sphere
The Kalanay Cave is a small cave located on the island of Masbate in the central Philippines. The cave is located specifically at the northwest coast of the island within the municipality of Aroroy. The artifacts recovered from the site were sim ...
* Tanja sail
Tanja sail ( Malay: ''layar tanjak'') or tanja rig is a type of sail commonly used by the Austronesian people, particularly in Maritime Southeast Asia. It is also known as the tilted square sail, canted rectangular sail, rectangular balance lug ...
* Trimaran
A trimaran (or double-outrigger) is a multihull boat that comprises a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls (or "floats") which are attached to the main hull with lateral beams. Most modern trimarans are sailing yachts designed for recrea ...
* Weriyeng
References
Further reading
* * Steve West (2012) ''Outrigger Canoeing – The Ancient Sport of Kings – A Paddlers Guide'', Batini BooksKanuculture
* Steve West (2014) ''Outrigger Canoeing – The Art and Skill of Steering'', Batini Books
Kanuculture
* Steve West (2014) ''Outrigger Canoeing – OC1 a Paddlers Guide'', Batini Books
Kanuculture
* Steve West (2014) ''Outrigger Canoeing – V1 a Paddlers Guide'', Batini Book
Kanuculture
External links
*(Drua) in the
Fiji Museum
The Fiji Museum is a museum in Suva, Fiji, located in the capital city's botanical gardens, Thurston Gardens.
Background
The museum is a statutory body and is under the administration of the Fiji Museum Act and the Preservation of Objects of A ...
Original Outrigger Canoe
in the
National Maritime Museum Cornwall
The National Maritime Museum, Cornwall (NMMC) is located in a harbourside building at Falmouth in Cornwall, England. The building was designed by architect M. J. Long, following an architectural design competition managed by RIBA Competition ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Outrigger Boat
Exploration ships
Polynesian navigation
Sailboat types
Austronesian culture