|
Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania. It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds'' See also Archaeology and social history * Austronesian peoples * Lapita culture * Micronesian navigation * Polynesian navigation Human geography * East Melanesian Islands * Near Oceania * Remote Oceania Languages * Central–Eastern Oceanic languages * Oceanic languages * Remote Oceanic languages * Southern Oceanic languages Nations * Bougainville * Fiji * New Caledonia * Solomon Islands * Vanuatu Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (; ), is an island country in Melanesia located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, east o ... References Geography of Melanesia Regions of Oceania Geography of New Caledonia Geography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Subregion
A subregion is a part of a larger geographical region or continent. Cardinal directions are commonly used to define subregions. There are many criteria for creating systems of subregions; this article is focusing on the United Nations geoscheme, which is a changing, constantly updated, UN tool based on specific political geography and demography considerations relevant in UN statistics. United Nations subregions The Statistics Division of the United Nations (UN) is in charge of the collection, processing, and dissemination of statistical information for the UN. In 1999, it developed a system of macro-geographical (continental) regions, subregions, and other selected economic groups to report advances towards achieving numerous Millennium Development Goals worldwide. These statistical divisions were devised for statistical purposes and is used for carrying out statistical analysis. The division's first publication was the book ''World's Women 2000: Trends and Statistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oceanic Languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they retain a rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geography Of The Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country in the South Pacific Ocean, that lies east of Papua New Guinea. Islands The major part of the nation of Solomon Islands is the mountainous volcanic islands of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), which includes Choiseul, the Shortland Islands, the New Georgia Islands, Santa Isabel, the Russell Islands, the Florida Islands, Tulagi, Malaita, Maramasike, Ulawa, Owaraha (Santa Ana), Makira (San Cristobal), and the main island of Guadalcanal. (The largest island in the archipelago is Bougainville, but it is politically an autonomous region of the neighbouring country of Papua New Guinea.) Solomon Islands also includes isolated low-lying atolls and volcanic islands such as Sikaiana, Rennell Island, Bellona Island, the Santa Cruz Islands and the remote, tiny outliers, Tikopia, Anuta, and Fatutaka. The distance between the most western and most eastern islands is about . Especially the Santa Cruz Islands, north of Vanuatu, are isolate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geography Of Papua New Guinea
The geography of Papua New Guinea describes the eastern half of the island of New Guinea, the islands of New Ireland, New Britain and Bougainville, and smaller nearby islands. Together these make up the nation of Papua New Guinea in tropical Oceania, located in the western edge of the Pacific Ocean. Papua New Guinea is largely mountainous, and much of it is covered with tropical rainforest. The New Guinea Highlands (or Central Range) run the length of New Guinea, and the highest areas receive snowfall—a rarity in the tropics. Within Papua New Guinea Mount Wilhelm is the highest peak, at . There are several major rivers, notably the Sepik River, which is long, which winds through lowland swamp plains to the north coast, and the Fly River at in length, which flows through one of the largest swamplands in the world to the south coast. The Highlands consist of a number of smaller ranges running west to east, such as the Finisterre Range which dominates the Huon Peninsula t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geography Of New Caledonia
The geography of New Caledonia (''Nouvelle-Calédonie''), an overseas collectivity of France located in the subregion of Melanesia, makes the continental island group unique in the southwest Pacific. Among other things, the island chain has played a role in preserving unique biological lineages from the Mesozoic. It served as a waystation in the expansion of the predecessors of the Polynesians, the Lapita culture. Under the Free French it was a vital naval base for Allied Forces during the War in the Pacific. The archipelago is located east of Australia, north of New Zealand, south of the Equator, and just west of Fiji and Vanuatu. New Caledonia comprises a main island, Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, and several smaller islands. Approximately half the size of Taiwan, the group has a land area of . The islands have a coastline of . New Caledonia claims an exclusive fishing zone to a distance of and a territorial sea of from shore. New Caledonia is one of the northernmost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Regions Of Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its continental landmass. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, at the centre of the water hemisphere, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of about and a population of around 46.3 million as of 2024. Oceania is the smallest continent in land area and the second-least populated after Antarctica. Oceania has a diverse mix of economies from the highly developed and globally competitive financial markets of Australia, French Polynesia, Hawaii, New Caledonia, and New Zealand, which rank high in quality of life and Human Development Index, to the much less developed economies of Kiribati, Papua New Guinea, Tuvalu, Vanuatu, and Western New Guinea. The largest and most populous country in Oceania is Australia, and the largest city is Sydney. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
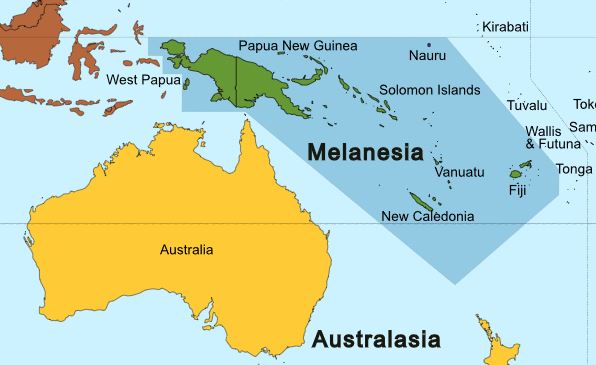
Geography Of Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea. The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Vanuatu, Solomon Islands, and Papua New Guinea. It also includes the Indonesian part of New Guinea, the French overseas collectivity of New Caledonia, and the Torres Strait Islands. Almost all of the region is in the Southern Hemisphere; only a few small islands that are not politically considered part of Oceania—specifically the northwestern islands of Western New Guinea—lie in the Northern Hemisphere. The name ''Melanesia'' (in French, ''Mélanésie'') was first used in 1832 by French navigator Jules Dumont d'Urville: he coined the terms ''Melanesia'' and ''Micronesia'' to go alongside the pre-existing ''Polynesia'' to designate what he viewed as the three main ethnic and geographical regions forming the Pacific. The indigenous people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (; ), is an island country in Melanesia located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji. Vanuatu was first inhabited by Melanesians, Melanesian people. The first Europeans to visit the islands were a Spanish expedition led by Portuguese navigator Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, Fernandes de Queirós, who arrived on the largest island, Espíritu Santo, in 1606. Queirós claimed the archipelago for Spain, as part of the colonial Spanish East Indies and named it . In the 1880s, France and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom claimed parts of the archipelago, and in 1906, they agreed on a framework for jointly managing the archipelago as the New Hebrides through an Anglo-French condominium (international law), condominium. An independence movem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, to the northeast of Australia. It is directly adjacent to Autonomous Region of Bougainville, Bougainville, a part of Papua New Guinea to the west, Australia to the southwest, New Caledonia and Vanuatu to the southeast, Fiji, Wallis and Futuna, and Tuvalu to the east, and Nauru and the Federated States of Micronesia to the north. It has a total area of 28,896 square kilometres (11,157 sq mi), and a population of 734,887 according to the official estimates for mid-2023. Its capital and largest city, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), Solomon Islands archipelago, which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about 110 are permanently inhabited—and more than 500 islets, amounting to a total land area of about . The most outlying island group is Ono-i-Lau. About 87% of the total population live on the two major islands, Viti Levu and Vanua Levu. About three-quarters of Fijians live on Viti Levu's coasts, either in the capital city of Suva, or in smaller urban centres such as Nadi (where tourism is the major local industry) or Lautoka (where the Sugarcane, sugar-cane industry is dominant). The interior of Viti Levu is sparsely inhabited because of its terrain. The majority of Fiji's islands were formed by Volcano, volcanic activity starting around 150 million years ago. Some geothermal activity still occurs today on the islands of Vanua Levu and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Autonomous Region Of Bougainville
In developmental psychology and morality, moral, political, and bioethics, bioethical philosophy, autonomy is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be defined from a human resources perspective, where it denotes a (relatively high) level of discretion granted to an employee in his or her work. In such cases, autonomy is known to generally increase job satisfaction. Self-actualization, Self-actualized individuals are thought to operate autonomously of external expectations. In a Medicine, medical context, respect for a patient's personal autonomy is considered one of many fundamental Medical ethics, ethical principles in medicine. Sociology In the sociology of knowledge, a controversy over the boundaries of autonomy inhibited analysis of any concept beyond relative autonomy, until a typology of autonomy was created and developed within science and technology studies. Acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Southern Oceanic Languages
The Southern Oceanic languages are a linkage (rather than family) of Oceanic languages spoken in Vanuatu and New Caledonia. It was proposed by John Lynch in 1995 and supported by later studies. It appears to be a linkage rather than a language family with a clearly defined internal nested structure. Classification Clark (2009) groups the North Vanuatu and Central Vanuatu languages together into a North-Central Vanuatu (NCV) group and also reconstructs Proto-North-Central Vanuatu, but this is not accepted by Lynch (2018). In addition to the Temotu languages and the Northwest Solomonic languages of the western Solomon Islands, Geraghty (2017) notes that many Southern Oceanic languages are often lexically and typologically aberrant, likely with Papuan substrata - particularly the Espiritu Santo, Malakula, South Vanuatu, and New Caledonian languages, and perhaps also some Central Vanuatu languages of Ambrym and Efate. Nevertheless, languages in the eastern Solomon Isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |