|
Steering
Steering is the control of the direction of motion or the components that enable its control. Steering is achieved through various arrangements, among them ailerons for airplanes, rudders for boats, cylic tilting of rotors for helicopters, and many more. Aircraft Aircraft flight control systems are normally steered when airborne by the use of ailerons, spoileron, or both to bank the aircraft into a turn; although the rudder can also be used to turn the aircraft, it is usually used to minimize adverse yaw, rather than as a means to directly cause the turn. On the ground, aircraft are generally steered at low speeds by turning the nosewheel or tailwheel (using a tiller or the rudder pedals) or through differential braking, and by the rudder at high speeds. Missiles, airships and large hovercraft are usually steered by a rudder, thrust vectoring, or both. Small sport hovercraft have similar rudders, but steer mostly by the pilot shifting their weight from side to side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steering Box
Steering is the control of the direction of motion or the components that enable its control. Steering is achieved through various arrangements, among them ailerons for airplanes, rudders for boats, cylic tilting of rotors for helicopters, and many more. Aircraft Aircraft flight control systems are normally steered when airborne by the use of ailerons, spoileron, or both to bank the aircraft into a turn; although the rudder can also be used to turn the aircraft, it is usually used to minimize adverse yaw, rather than as a means to directly cause the turn. On the ground, aircraft are generally steered at low speeds by turning the nosewheel or tailwheel (using a tiller or the rudder pedals) or through differential braking, and by the rudder at high speeds. Missiles, airships and large hovercraft are usually steered by a rudder, thrust vectoring, or both. Small sport hovercraft have similar rudders, but steer mostly by the pilot shifting their weight from side to side and u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
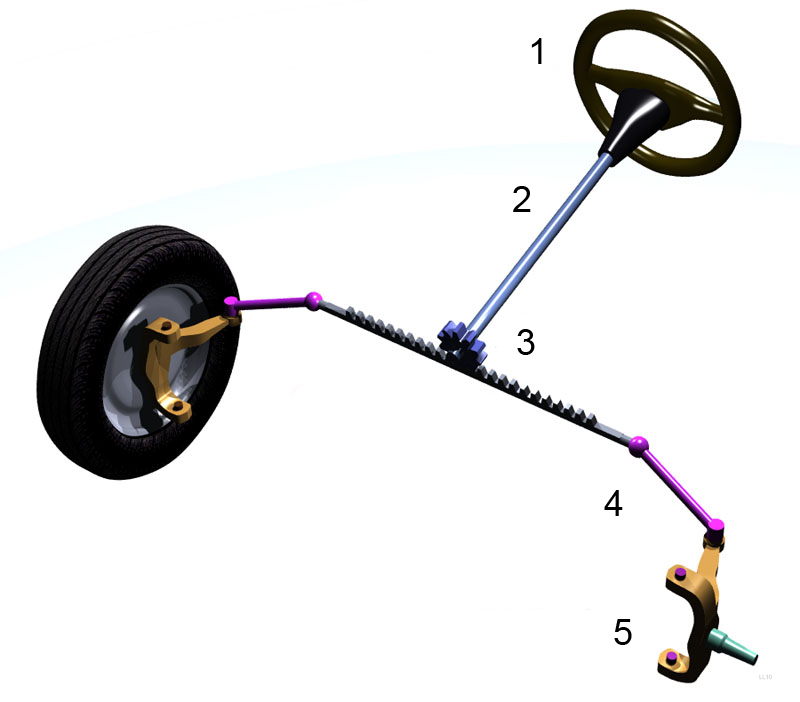
Steering Wheel
A steering wheel (also called a driving wheel, a hand wheel, or simply wheel) is a type of steering control in vehicles. Steering wheels are used in most modern land vehicles, including all mass-production automobiles, buses, light and heavy trucks, as well as tractors and tanks. The steering wheel is the part of the steering system that the driver manipulates; the rest of the steering system responds to such driver inputs. This can be through direct mechanical contact as in recirculating ball or rack and pinion steering gears, without or with the assistance of hydraulic power steering, HPS, or as in some modern production cars with the help of computer-controlled motors, known as Power steering#Electric systems, electric power steering. History Near the start of the 18th century, many sea vessels appeared using the ship's wheel design. However, historians are unclear when that approach to steering was first used. The first automobiles were steered with a Tiller (automobi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Steering
Power steering is a system for reducing a driver's effort to turn a steering wheel of a motor vehicle, by using a power source to assist steering. Hydraulic or electric actuators add controlled energy to the steering mechanism, so the driver can provide less effort to turn the steered wheels when driving at typical speeds, and considerably reduce the physical effort necessary to turn the wheels when a vehicle is stopped or moving slowly. Power steering can also be engineered to provide some artificial feedback of forces acting on the steered wheels. Hydraulic power steering systems for cars augment steering effort via an actuator, a hydraulic cylinder that is part of a servo system. These systems have a direct mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the steering linkage that steers the wheels. This means that power-steering system failure (to augment effort) still permits the vehicle to be steered using manual effort alone. Electric power steering systems use elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Steering
Differential steering is the means of steering a land vehicle by applying more drive torque to one side of the vehicle than the other. Differential steering is the primary means of steering tracked vehicles, such as tanks and bulldozers, is also used in certain wheeled vehicles commonly known as skid-steer, and even implemented in some automobiles, where it is called torque vectoring, to augment steering by changing wheel direction relative to the vehicle. Differential steering is distinct from torque steer, which is usually considered a negative side effect of drive-train design choices. History A British agricultural company, Richard Hornsby & Sons, Hornsby in Grantham, developed a continuous track, which was patented in 1905. The Hornsby tractors featured a track-steer clutch arrangement. Mechanisms There are several mechanisms that have been developed to vary the torque applied to different sides of a vehicle. These include ''clutch-brake'' steering, ''braked-differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudders
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, airship, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (usually aircraft, air or watercraft, water). On an airplane, the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull (watercraft), hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yaw (rotation), yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or afterend. Often rudders are shaped to minimize Drag (physics), hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may link rudders to steering wheels. In typical aircraft, the rudder is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiller
A tiller or till is a lever used to steer a vehicle. The mechanism is primarily used in watercraft, where it is attached to an outboard motor, rudder post, rudder post or stock to provide leverage in the form of torque for the helmsman to turn the rudder. A tiller may also be used in vehicles outside of water, and was seen in early automobiles. On vessels, a tiller can be used by the helmsman directly pulling or pushing it, but it may also be moved remotely using tiller lines or a ship's wheel. Rapid or excessive movement of the tiller results in an increase in drag and will result in braking or slowing the boat. Description A tiller is a lever used to steer a vehicle. It provides leverage in the form of torque to turn the device that changes the direction of the vehicle, such as a rudder on a watercraft or the surface wheels on a wheeled vehicle. A tiller can be used by directly pulling or pushing it, but it may also be moved remotely using a whipstaff, tiller lines, or a sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steering Column
The automotive steering column is a device intended primarily for connecting the steering wheel to the steering mechanism. Secondary functions A steering column may also perform the following secondary functions: *energy dissipation management in the event of a frontal collision; *provide mounting for: the multi-function switch, column lock, column wiring, column shroud(s), transmission gear selector, gauges or other instruments as well as the electro motor and gear units found in EPAS and SbW systems; *offer (height and/or length) adjustment to suit driver preference Steering lock Modern vehicles are fitted with a steering lock which is an anti-theft device. It is fitted to the steering column usually below the steering wheel. The lock is combined with the ignition switch and engaged and disengaged either by a mechanical ignition key or electronically from the vehicles electronic control unit. These locks were introduced on many General Motors products in 1969 drastically r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recirculating Ball
Recirculating ball, also known as recirculating ball and nut or worm and sector, is a steering mechanism commonly found in older automobiles, off-road vehicles, and some trucks. Most newer cars use the more economical rack and pinion steering instead, but some upmarket manufacturers (such as BMW and Mercedes-Benz) held on to the design until well into the 1990s for the durability and strength inherent in the design. A few, including Chrysler, General Motors, Lada and Ineos, still use this technology in certain models including the Jeep Wrangler,{{Cite book , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HlbCM7VEmroC&q=wrangler+Recirculating+ball&pg=PA91 , title=High-Performance Jeep Wrangler TJ Builder's Guide, isbn=9781932494266, last1=Lee, first1=Christian, year=2007, publisher=CarTech, Incorporated the Ineos Grenadier Quartermaster and the Lada Niva. Mechanism The recirculating ball steering mechanism contains a worm gear inside a block with a threaded hole in it; this bloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rack And Pinion
rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a circular gear (the '' pinion'') engaging a linear gear (the ''rack''). Together, they convert between rotational motion and linear motion: rotating the pinion causes the rack to be driven in a line. Conversely, moving the rack linearly will cause the pinion to rotate. The rack and pinion mechanism is used in rack railways, where the pinion mounted on a locomotive or a railroad car engages a rack usually placed between the rails, and helps to move the train up a steep gradient. It is also used in arbor presses and drill presses, where the pinion is connected to a lever and displaces a vertical rack (the ram). In pipelines and other industrial piping systems, a rack displaced by a linear actuator turns a pinion to open or close a valve. Stairlifts, lock gates, electric gates, and the mechanical steering mechanism of cars are other notable applications. The term "rack and pinion" may be used also when the rac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idler Arm
An idler arm is a pivoting support for a conventional parallelogram steering linkage on some cars and trucks. The idler arm supports the end of the center link on the passenger's side of the vehicle. The idler arm bolts to the vehicle's frame or subframe. Generally, an idler arm is attached between the opposite side of the center link from the Pitman arm and the vehicle's frame to hold the center link at the proper height. Idler arms are generally more vulnerable to wear than Pitman arms because of the pivot function built into them. If the idler arm is fitted with grease fittings, these should be lubricated with a Grease gun (tool), grease gun at each oil change. References Automotive steering technologies Auto parts {{Automotive-part-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |