Sultanate of Delhi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Temple desecration in pre-modern India
Frontline, p. 73, item 16 of the Table, Archived by Columbia University File:Benares- The Golden Temple, India, ca. 1915 (IMP-CSCNWW33-OS14-66).jpg, The Kashi Vishwanath Temple was destroyed by Muhammad of Ghor along with thousand other temples in
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a
Encyclopædia Britannica The
"Growth and Development of Oriental Libraries in India"
''Library Philosophy and Practice'',
 His rule was challenged several times, such as by Qubacha, and this led to a series of wars. Iltutmish conquered
His rule was challenged several times, such as by Qubacha, and this led to a series of wars. Iltutmish conquered
UNESCO During the Mamluk dynasty, many nobles from Afghanistan and Persia migrated and settled in India, as West Asia came under
 The
The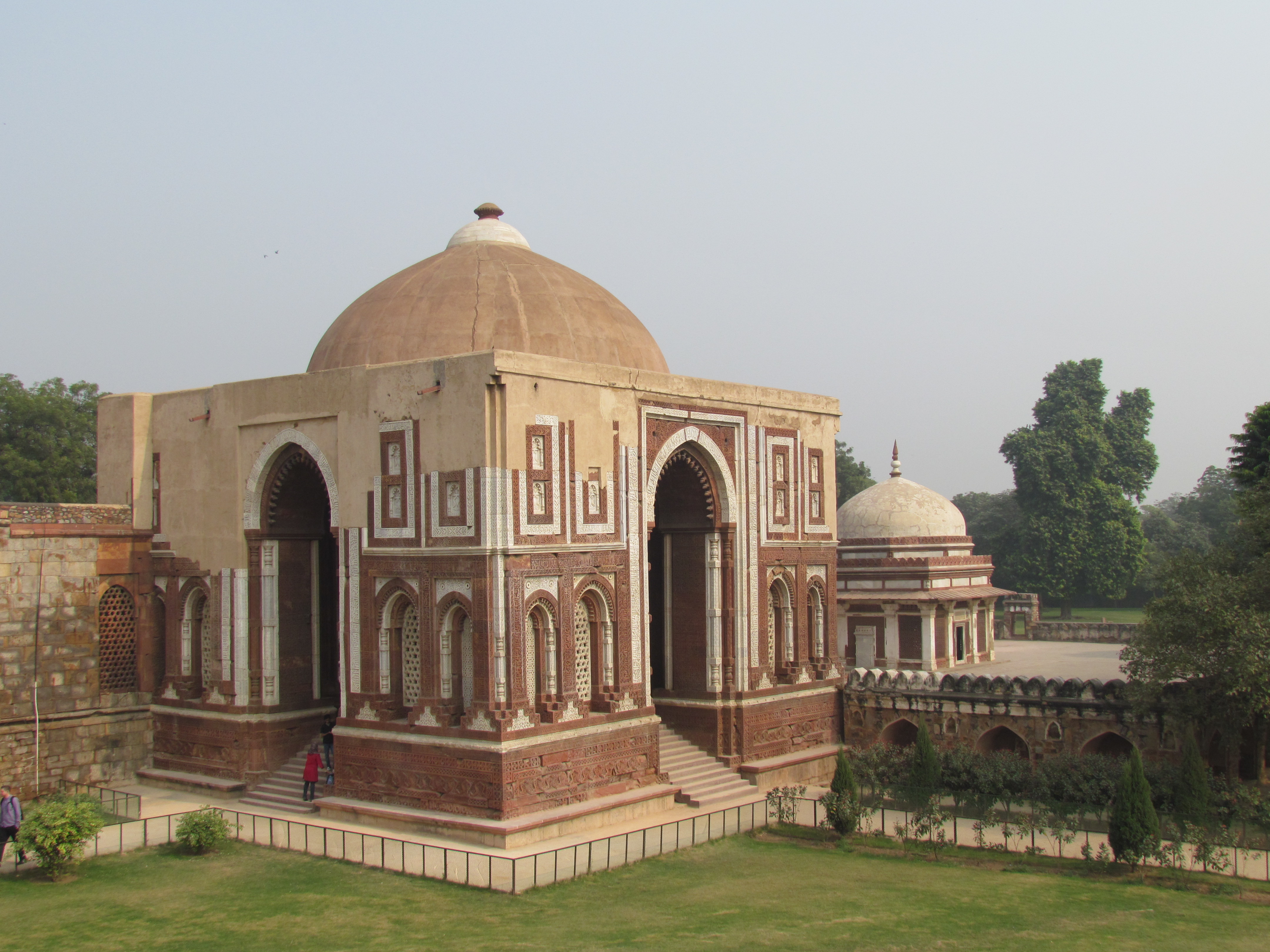  Historians note Ala ud-Din Khalji as being a
Historians note Ala ud-Din Khalji as being a
 The
The
Encyclopædia Britannica Muhammad bin Tughlaq was an intellectual, with extensive knowledge of the Quran,
Futuhat-i Firoz Shahi – Autobiographical memoirs
Translated in 1871 by Elliot and Dawson, Volume 3 –The History of India, Cornell University Archives, pp 377–381. Firuz Shah Tughlaq also lists his accomplishments to include converting Hindus to Sunni Islam by announcing an exemption from taxes and jizya for those who convert, and by lavishing new converts with presents and honours.Futuhat-i Firoz Shahi
Simultaneously, he raised taxes and jizya, assessing it at three levels, and stopping the practice of his predecessors who had historically exempted all Hindu The death of Firuz Shah Tughlaq created anarchy and disintegration of the kingdom. Firuz Shah's successor, Ghiyath-ud-Din Shah II was young and inexperienced and gave himself up to wine and pleasure. The nobles rose against him killed the Sultan and his vizier, and installed
The death of Firuz Shah Tughlaq created anarchy and disintegration of the kingdom. Firuz Shah's successor, Ghiyath-ud-Din Shah II was young and inexperienced and gave himself up to wine and pleasure. The nobles rose against him killed the Sultan and his vizier, and installed
 The
The
 The Lodi dynasty was an Afghan, or Turco-Afghan dynasty, related to the
The Lodi dynasty was an Afghan, or Turco-Afghan dynasty, related to the
''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2009) Babur defeated and killed Ibrahim Lodi in the Battle of Panipat in 1526. The death of Ibrahim Lodi ended the Delhi Sultanate, and the
 According to historians Arnold Pacey and
According to historians Arnold Pacey and
pages 241–242
,
page 236
,
 The start of the Delhi Sultanate in 1206 under
The start of the Delhi Sultanate in 1206 under
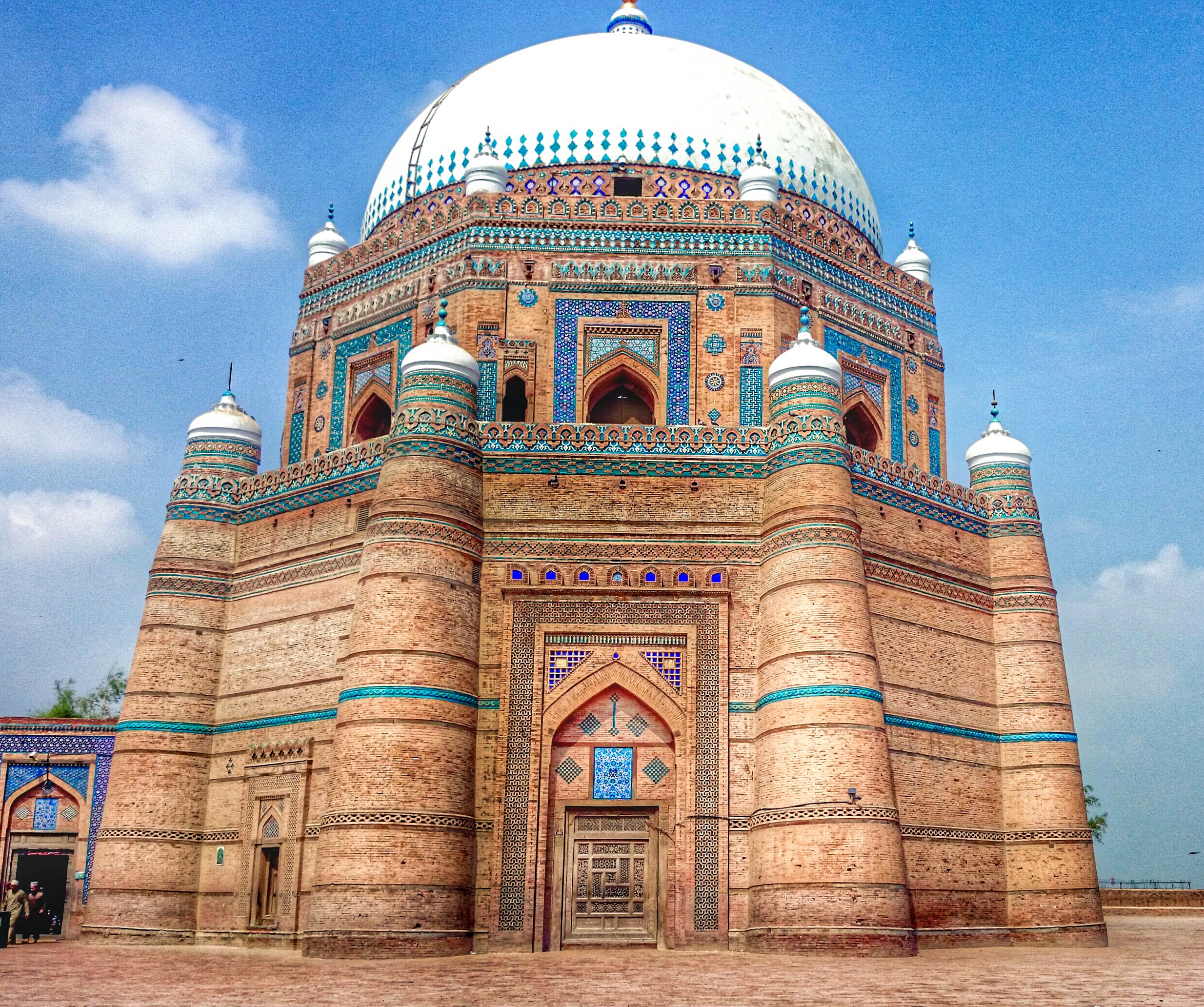 The tomb of Shah Rukn-e-Alam (built 1320 to 1324) in
The tomb of Shah Rukn-e-Alam (built 1320 to 1324) in
File:Adhai Din Ka Jhonpra (literally "shed of 2½ days").jpg, Screen of the Adhai Din Ka Jhonpra mosque,
Iconoclasm
Iconoclasm ()From . ''Iconoclasm'' may also be considered as a back-formation from ''iconoclast'' (Greek: εἰκοκλάστης). The corresponding Greek word for iconoclasm is εἰκονοκλασία, ''eikonoklasia''. is the social belie ...
under the Delhi Sultanate">
File:Somnath temple ruins (1869).jpg, The Somnath Temple in Gujarat was repeatedly destroyed by Delhi Sultanate armies and rebuilt by Chaulukya armies. It was destroyed by the Delhi Sultanate's army in 1299 and was rebuilt afterwards.Eaton (2000)late medieval
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the period of European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renai ...
empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ...
primarily based in Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
for more than three centuries.Delhi SultanateEncyclopædia Britannica The
sultanate
Sultan (; ', ) is a Royal and noble ranks, position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". La ...
was established around in the former Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-so ...
(1206–1290), Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid
''Sayyid'' is an honorific title of Hasanid and Husaynid lineage, recognized as descendants of the Islamic prophet Muhammad through his daughter Fatima and Ali's sons Hasan ibn Ali, Hasan and Husayn ibn Ali, Husayn. The title may also refer ...
(1414–1451), and Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
, Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, as well as some parts of southern Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
.
The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad Ghori, who routed the Rajput Confederacy, led by Ajmer ruler Prithviraj Chauhan
Prithviraja III (IAST: Pṛthvī-rāja; 22 May 1166 – February 1192), popularly known as Prithviraj Chauhan or Rai Pithora, was a king from the Chahamanas of Shakambhari, Chauhan (Chahamana) dynasty who ruled the territory of Sapadalaksha, w ...
, in 1192 near Tarain in a reversal of an earlier battle. As a successor to the Ghurid dynasty, the Delhi Sultanate was originally one of several principalities ruled by the Turkic slave-generals of Muhammad Ghori, including Taj al-Din Yildiz, Qutb ud-Din Aibak, Bahauddin Tughril and Nasir ad-Din Qabacha, that had inherited and divided the Ghurid territories amongst themselves. Khalji and Tughlaq rule ushered a new wave of rapid and continual Muslim conquests The Muslim conquests, Muslim invasions, Islamic conquests, including Arab conquests, Arab Islamic conquests, also Iranian Muslim conquests, Turkic Muslim conquests etc.
*Early Muslim conquests
** Ridda Wars
**Muslim conquest of Persia
*** Muslim co ...
deep into South India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
. The sultanate finally reached the peak of its geographical reach during the Tughlaq dynasty, occupying most of the Indian subcontinent under Muhammad bin Tughluq
Muhammad bin Tughluq (; ; 1290 – 20 March 1351), or Muhammad II, also named Jauna Khan as Crown Prince, further known by his epithets, The Eccentric Prince, or The Mad Sultan, was the eighteenth Sultan of Delhi. He reigned from 4 February 1 ...
. A major political transformation occurred across North India
North India is a geographical region, loosely defined as a cultural region comprising the northern part of India (or historically, the Indian subcontinent) wherein Indo-Aryans (speaking Indo-Aryan languages) form the prominent majority populati ...
, triggered by the Central Asian king Timur
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeat ...
's devastating raid on Delhi in 1398, followed soon afterwards by the re-emergence of rival Hindu powers such as Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Kingdom, was a late medieval Hinduism, Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, belongi ...
and Kingdom of Mewar
The Kingdom of Mewar was an independent Hindu kingdom that existed in the Rajputana region of the Indian subcontinent and later became a dominant state in medieval India. The kingdom was initially founded and ruled by the Guhila dynasty, foll ...
asserting independence, and new Muslim sultanates such as the Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
and Bahmani Sultanate
The Bahmani Kingdom or the Bahmani Sultanate was a late medieval Persianate kingdom that ruled the Deccan plateau in India. The first independent Muslim sultanate of the Deccan, the Bahmani Kingdom came to power in 1347 during the rebellio ...
s breaking off. In 1526, Timurid ruler Babur
Babur (; 14 February 148326 December 1530; born Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad) was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also ...
invaded northern India and conquered the Sultanate, leading to its succession by the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
.
The establishment of the Sultanate drew the Indian subcontinent more closely into international and multicultural Islamic social and economic networks, as seen concretely in the development of the Hindustani language
Hindustani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in North India and Pakistan as the lingua franca of the region. It is also spoken by the Deccani people, Deccani-speaking community in the Deccan plateau. Hindustani is a pluricentric language w ...
and Indo-Islamic architecture. It was also one of the few powers to repel attacks by the Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
(from the Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, also known as the Chagatai Ulus, was a Mongol and later Turkification, Turkicized khanate that comprised the lands ruled by Chagatai Khan, second son of Genghis Khan, and his descendants and successors. At its height in the l ...
) and saw the enthronement of one of the few female rulers in Islamic history
The history of Islam is believed, by most historians, to have originated with Muhammad's mission in Mecca and Medina at the start of the 7th century CE, although Muslims regard this time as a return to the original faith passed down by the Abra ...
, Razia Sultana, who reigned from 1236 to 1240. During the sultanate's rule, there was no mass forcible conversion of Hindus, Buddhists, and other dharmic faiths, and Hindu officials and vassals were readily accepted. However, there were cases like Bakhtiyar Khalji's annexations, which involved a large-scale desecration of Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
and Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
temples and the destruction of universities and libraries.Gul and Khan (200"Growth and Development of Oriental Libraries in India"
''Library Philosophy and Practice'',
University of Nebraska–Lincoln
The University of Nebraska–Lincoln (Nebraska, NU, or UNL) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Lincoln, Nebraska, United States. Chartered in 1869 by the Nebraska Legislature as part of the M ...
Richard Eaton, , (2004) Mongolian raids on West
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance langu ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
set the scene for centuries of migration of fleeing soldiers, intelligentsia, mystics, traders, artists, and artisans from those regions into the subcontinent, thereby establishing Islamic culture
Islamic cultures or Muslim cultures refers to the historic cultural practices that developed among the various peoples living in the Muslim world. These practices, while not always religious in nature, are generally influenced by aspects of Islam ...
there.
Name
Although conventionally named after its principal capital city,Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
, the terminology applied to domains under Delhi Sultanate was often unspecified. It was called as "Empire of Delhi" ''( Persian: Mamalik-i-Delhi)'' by Juzjani and Barani while Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
called the empire under Muhammad bin Tughlaq
Muhammad bin Tughluq (; ; 1290 – 20 March 1351), or Muhammad II, also named Jauna Khan as Crown Prince, further known by his epithets, The Eccentric Prince, or The Mad Sultan, was the eighteenth Sultan of Delhi. He reigned from 4 February 1 ...
as " Hind and Sind". The Delhi Sultanate was also known as the "Empire of Hindustan
''Hindūstān'' ( English: /ˈhɪndustæn/ or /ˈhɪndustɑn/, ; ) was a historical region, polity, and a name for India, historically used simultaneously for northern Indian subcontinent and the entire subcontinent, used in the modern day ...
" ''( Persian: Mamalik-i-Hindustan)'', a name that gained currency during the period.
History
Background
The rise of the Delhi Sultanate in India was part of a wider trend affecting much of theAsia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
n continent, including the whole of southern and western Asia: the influx of nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic Turkic peoples
Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members ...
from the Central Asian steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
s. This can be traced back to the 9th century when the Islamic Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
began fragmenting in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, where Muslim rulers in rival states began enslaving non-Muslim nomadic Turks from the Central Asian steppes and raising many of them to become loyal army slaves called Mamluk
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-so ...
s. Soon, Turks were migrating to Muslim lands and becoming Islamicized. Many of the Turkic Mamluk slaves eventually rose to become rulers and conquered large parts of the Muslim world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
, establishing Mamluk Sultanates from Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
to present-day Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, before turning their attention to the Indian subcontinent.
It is also part of a longer trend predating the spread of Islam
The spread of Islam spans almost 1,400 years. The early Muslim conquests that occurred following the death of Muhammad in 632 CE led to the creation of the caliphates, expanding over a vast geographical area; conversion to Islam was boosted ...
. Like other settled
A settler or a colonist is a person who establishes or joins a permanent presence that is separate to existing communities. The entity that a settler establishes is a settlement. A settler is called a pioneer if they are among the first settli ...
, agrarian societies in history, those in the Indian subcontinent have been attacked by nomadic tribes throughout its long history. In evaluating the impact of Islam on the subcontinent, one must note that the northwestern subcontinent was a frequent target of tribes raiding from Central Asia in the pre-Islamic era. In that sense, the Muslim intrusions and later Muslim invasions were not dissimilar to those of the earlier invasions during the 1st millennium.
By 962 AD, Hindu and Buddhist kingdoms in South Asia faced a series of raids from Muslim armies from Central Asia.See:
* M. Reza Pirbha, Reconsidering Islam in a South Asian Context, , Brill
* The Islamic frontier in the East: Expansion into South Asia, Journal of South Asian Studies, 4(1), pp. 91–109
* Sookoohy M., Bhadreswar – Oldest Islamic Monuments in India, , Brill Academic; see discussion of earliest raids in Gujarat Among them was Mahmud of Ghazni
Abu al-Qasim Mahmud ibn Sabuktigin (; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi (), was Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, ruling from 998 to 1030. During his reign and in medieval sources, he is usuall ...
, the son of a Turkic Mamluk military slave, who raided and plundered kingdoms in northern India from east of the Indus river to west of the Yamuna river seventeen times between 997 and 1030. Mahmud of Ghazni raided the treasuries but retreated each time, only extending Islamic rule into western Punjab.
The series of raids on northern and western Indian kingdoms by Muslim warlords continued after Mahmud of Ghazni. The raids did not establish or extend the permanent boundaries of the Islamic kingdoms. In contrast, the Ghurid
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; ; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Tajik people, Tajik origin, which ruled from the 8th-century in the region of Ghor, and became an Emp ...
Sultan Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad Ghori (commonly known as Muhammad of Ghor) began a systematic war of expansion into northern India in 1173. He sought to carve out a principality for himself and expand the Islamic world. Muhammad of Ghor created a Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
Islamic kingdom of his own extending east of the Indus river, and he thus laid the foundation for the Muslim kingdom called the Delhi Sultanate. Some historians chronicle the Delhi Sultanate from 1192 due to the presence and geographical claims of Muhammad Ghori in South Asia by that time.
Muhammad Ghori was assassinated in 1206, by Ismāʿīlī Shia Muslims. After the assassination, one of Ghori's slaves (or Mamluks), the Turkic Qutb al-Din Aibak, assumed power, becoming the first Sultan of Delhi.
Dynasties
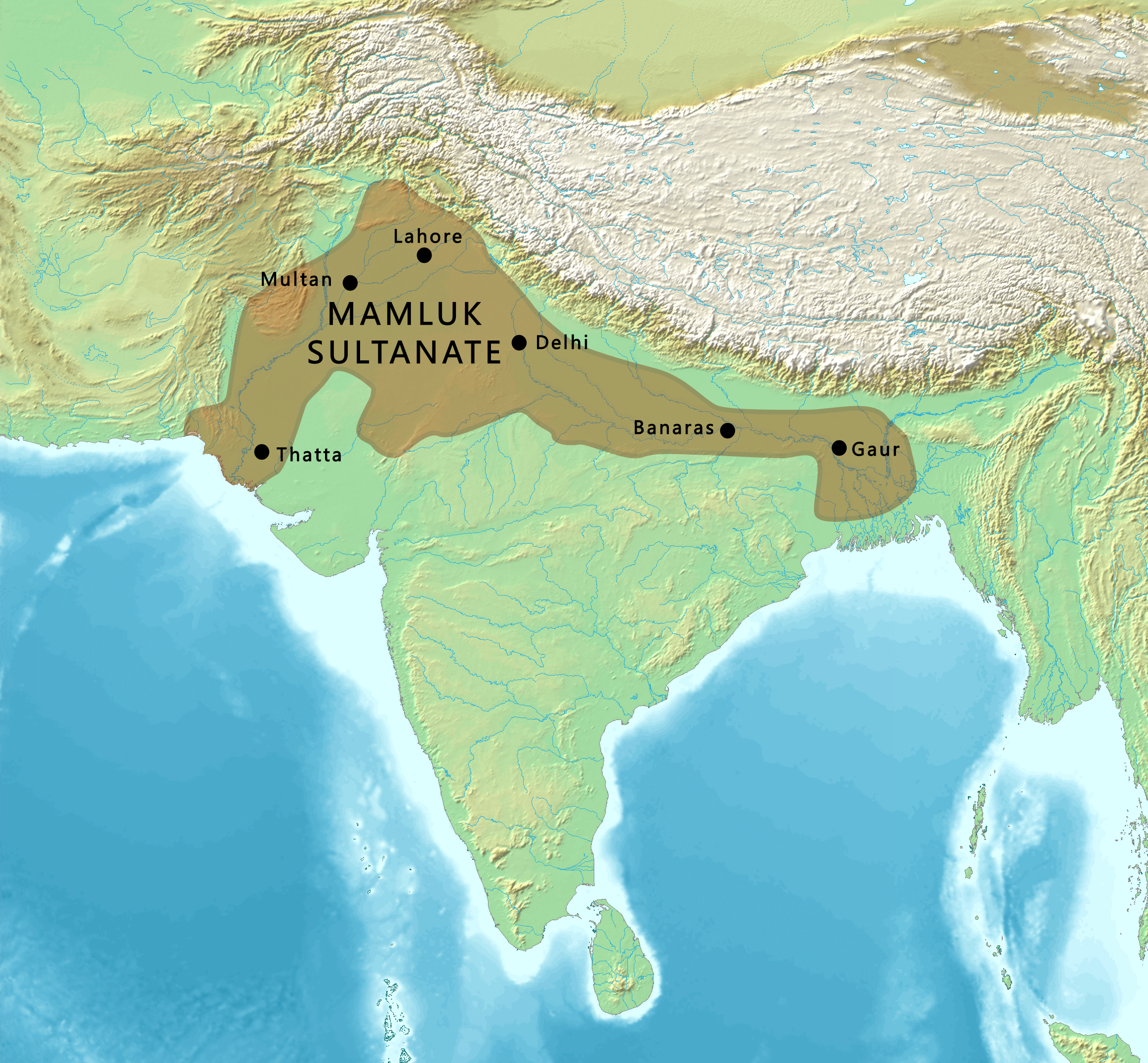
Mamluk dynasty (1206–1290)

Qutb al-Din Aibak
Qutb ud-Din Aibak (; 1150 – 4 November 1210) was a Turkic general of the Ghurid emperor Muhammad Ghori. He was in charge of the Ghurid territories in northern India, and after Muhammad Ghori's assassination in 1206, he established his ow ...
, a former slave of Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad Ghori, was the first ruler of the Delhi Sultanate. Aibak was of Turkic Cuman
The Cumans or Kumans were a Turkic nomadic people from Central Asia comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation who spoke the Cuman language. They are referred to as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Rus' chronicles, as " ...
- Kipchak origin, and due to his lineage, his dynasty is known as the Mamluk dynasty. Aibak reigned as the Sultan of Delhi for four years, from 1206 to 1210. Aibak was praised by the contemporary and later accounts for his generosity and due to this was called with the sobriquet of ''Lakhbaksh'' (provider of lakhs).
After Aibak died, Aram Shah
Aram Shah (; 1176 – June 1211) was the second sultan of the Mamluk Sultanate. He briefly held the throne from Lahore after the unexpected death of Qutb ud-Din Aibak before being defeated and dethroned by Iltutmish who began ruling from Delhi ...
assumed power in 1210, but he was assassinated in 1211 by Aibak's son-in-law, Shams ud-Din Iltutmish. Iltutmish's power was precarious, and several Muslim amirs (nobles) challenged his authority as they had been supporters of Qutb al-Din Aibak. After a series of conquests and brutal executions of opposition, Iltutmish consolidated his power.
 His rule was challenged several times, such as by Qubacha, and this led to a series of wars. Iltutmish conquered
His rule was challenged several times, such as by Qubacha, and this led to a series of wars. Iltutmish conquered Multan
Multan is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fifth-most populous city in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the List of cities in Pakistan by populatio ...
and Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
from contesting Muslim rulers, as well as Ranthambore and Sivalik from the Hindu rulers. He also attacked, defeated, executed Taj al-Din Yildiz, who asserted his rights as heir to Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad Ghori.Anzalone, Christopher (2008), "Delhi Sultanate", in Ackermann, M. E. etc. (Editors), Encyclopedia of World History 2, Iltutmish's rule lasted until 1236. Following his death, the Delhi Sultanate saw a succession of weak rulers, disputing Muslim nobility, assassinations, and short-lived tenures. Power shifted from Rukn ud-Din Firuz to Razia Sultana and others, until Ghiyas ud-Din Balban came to power and ruled from 1266 to 1287. Ghiyasuddin Balban destroyed the power of the Corps of Forty, a council of 40 Turkic slaves who had played a role as kingmakers and had been independent of the Sultan. He was succeeded by 17-year-old Muiz ud-Din Qaiqabad, who appointed Jalal ud-Din Firuz Khalji as the commander of the army. Khalji assassinated Qaiqabad and assumed power in the Khalji Revolution, thus ending the Mamluk dynasty and starting the Khalji dynasty.
Qutb al-Din Aibak initiated the construction of the Qutb Minar
The Qutb Minar, also spelled Qutub Minar and Qutab Minar, is a minaret and victory tower comprising the Qutb complex, which lies at the site of Delhi's oldest fortified city, Lal Kot, founded by the Tomar Rajputs. It is a UNESCO World Heritage ...
but died before it was completed. It was later completed by his son-in-law, Iltutmish. The Quwwat-ul-Islam (Might of Islam) Mosque was built by Aibak, now a UNESCO world heritage site. The Qutub Minar Complex was expanded by Iltutmish, and later by Ala ud-Din Khalji in the early 14th century.Qutb Minar and its Monuments, DelhiUNESCO During the Mamluk dynasty, many nobles from Afghanistan and Persia migrated and settled in India, as West Asia came under
Mongol
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China (Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of M ...
siege.
Khalji dynasty (1290–1320)
 The
The Khalji dynasty
The Khalji or Khilji dynasty was a Turco-Afghan dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate for three decades between 1290 and 1320. It was the second dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate which covered large swaths of the Indian subcontinent.
was of Turko-Afghan heritage. They were originally Turkic, but due to their long presence in Afghanistan, they were treated by others as Afghan
Afghan or Afgan may refer to:
Related to Afghanistan
*Afghans, historically refers to the Pashtun people. It is both an ethnicity and nationality. Ethnicity wise, it refers to the Pashtuns. In modern terms, it means both the citizens of Afghanist ...
as they adopted Afghan habits and customs.
The first ruler of the Khalji dynasty was Jalal ud-Din Firuz Khalji. He was around 70 years old at the time of his ascension and was known as a mild-mannered, humble and kind monarch to the general public. Jalal ud-Din Firuz ruled for 6 years before he was murdered in 1296 by Muhammad Salim of Samana, on the orders of his nephew and son-in-law Juna Muhammad Khalji, who later came to be known as Ala ud-Din Khalji.
Ala ud-Din began his military career as governor of Kara province, from where he led two raids on the Kingdom of Malwa (1292) and Devagiri (1294) for plunder and loot. After he acceded to the throne, expansions towards these kingdoms were renewed including Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
which was conquered by the Grand Vizier
Grand vizier (; ; ) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. It was first held by officials in the later Abbasid Caliphate. It was then held in the Ottoman Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Soko ...
Nusrat Khan Jalesari, the kingdom of Malwa by Ainul Mulk Multani, as well as Rajputana
Rājputana (), meaning Land of the Rajputs, was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the entire present-day States of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, parts of the neighboring states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and adjo ...
. However, these victories were cut short because of Mongol attacks and plunder raids from the northwest. The Mongols withdrew after plundering and stopped raiding northwest parts of the Delhi Sultanate.
After the Mongols withdrew, Ala ud-Din Khalji continued to expand the Delhi Sultanate into southern India with the help of Indian slave generals such as Malik Kafur and Khusro Khan. They collected much war booty (anwatan) from those they defeated. His commanders collected war spoils and paid ghanima (Arabic: الْغَنيمَة, a tax on spoils of war), which helped strengthen the Khalji rule. Among the spoils was the Warangal
Warangal () is a city in the Indian state of Telangana and the district headquarters of Warangal district. It is the second largest city in Telangana with a population of 811,844 per 2011 Census of India, and spreading over an .
Warangal serv ...
loot that included the famous Koh-i-Noor diamond.
Ala ud-Din Khalji changed tax policies, raising agriculture taxes from 20% to 50% (payable in grain and agricultural produce), eliminating payments and commissions on taxes collected by local chiefs, banning socialization among his officials as well as inter-marriage between noble families to help prevent any opposition forming against him, and he cut salaries of officials, poets, scholars. These tax policies and spending controls strengthened his treasury to pay the keep of his growing army; he also introduced price controls on all agricultural produce and goods in the kingdom, as well as controls on where, how, by whom these goods could be sold. Markets called "shahana-i-mandi" were created. Muslim merchants were granted exclusive permits and monopoly in these "mandis" to buy and resell at official prices. No one other than these merchants could buy from farmers or sell in cities. Those found violating these "mandi" rules were severely punished, often by mutilation. Taxes collected in the form of grain were stored in the kingdom's storage. During famines that followed, these granaries ensured sufficient food for the army.
tyrant
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to ...
. Anyone Ala ud-Din suspected of being a threat to this power was killed along with the men, women, and children of that family. He grew to eventually distrust the majority of his nobles and favoured only a handful of his slaves and family. In 1298, between 15,000 and 30,000 Mongols near Delhi, who had recently converted to Islam, were slaughtered in a single day, due to a mutiny during an invasion of Gujarat. He is also known for his cruelty against kingdoms he defeated in battle.
After Ala ud-Din died in 1316 by assassination through his nobles, his general Malik Kafur, who was born to a Hindu family but converted to Islam, assumed de facto power and was supported by non-Khalji nobles like Kamal al-Din Gurg. However, he lacked the support of the majority of Khalji's nobles who had him assassinated, hoping to take power for themselves.Holt et al., The Cambridge History of Islam – The Indian sub-continent, south-east Asia, Africa and the Muslim west, , pp 9–13 However, the new ruler had the killers of Kafur executed.
The last Khalji ruler was Ala ud-Din Khalji's 18-year-old son Qutb ud-Din Mubarak Shah Khalji, who ruled for four years before he was killed by Khusro Khan, another slave-general with Hindu origins, who reverted from Islam and favoured his Hindu Baradu military clan in the nobility. Khusro Khan's reign lasted only a few months, when Ghazi Malik, later to be called Ghiyath al-Din Tughlaq, defeated and killed him and assumed power in 1320, thus ending the Khalji dynasty and starting the Tughlaq dynasty.
Tughlaq dynasty (1320–1413)
 The
The Tughlaq dynasty
The Tughlaq dynasty (also known as the Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty; ) was the third dynasty to rule over the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath ...
was a Turko-Mongol or Turkic Muslim dynasty, which lasted from 1320 to 1413. The first ruler was Ghiyath al-Din Tughlaq. Ghiyath al-Din ruled for five years and built a town near Delhi named Tughlaqabad. His son Juna Khan and general Ainul Mulk Multani conquered Warangal
Warangal () is a city in the Indian state of Telangana and the district headquarters of Warangal district. It is the second largest city in Telangana with a population of 811,844 per 2011 Census of India, and spreading over an .
Warangal serv ...
in south India. According to some historians such as Vincent Smith, he was killed by his son Juna Khan, who then assumed power in 1325.
Juna Khan renamed himself as Muhammad bin Tughlaq
Muhammad bin Tughluq (; ; 1290 – 20 March 1351), or Muhammad II, also named Jauna Khan as Crown Prince, further known by his epithets, The Eccentric Prince, or The Mad Sultan, was the eighteenth Sultan of Delhi. He reigned from 4 February 1 ...
and ruled for 26 years. During his rule, the Delhi Sultanate reached its peak in terms of geographical reach, covering most of the Indian subcontinent.Muḥammad ibn TughluqEncyclopædia Britannica Muhammad bin Tughlaq was an intellectual, with extensive knowledge of the Quran,
Fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ) is the term for Islamic jurisprudence.Fiqh
Encyclopædia Britannica ''Fiqh'' is of ...
, poetry and other fields. He was also deeply suspicious of his kinsmen and wazirs (ministers), extremely severe with his opponents, and took decisions that caused economic upheaval. For example, he ordered the minting of coins from base metals with face value of silver coins – a decision that failed because ordinary people minted counterfeit coins from base metal they had in their houses and used them to pay taxes and Encyclopædia Britannica ''Fiqh'' is of ...
jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
.
Muhammad bin Tughlaq chose the city of Deogiri in the present-day Indian state of Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
(renaming it Daulatabad), as the second administrative capital of the Delhi Sultanate. He ordered a forced migration of the Muslim population of Delhi, including his royal family, the nobles, Syeds, Sheikhs and 'Ulema to settle in Daulatabad. The purpose of transferring the entire Muslim elite to Daulatabad was to enrol them in his mission of world conquest. He saw their role as propagandists who would adapt Islamic religious symbolism to the rhetoric of empire, and that the Sufis could by persuasion bring many of the inhabitants of the Deccan to become Muslim. Tughluq cruelly punished the nobles who were unwilling to move to Daulatabad seeing their non-compliance with his order as equivalent to rebellion. According to Ferishta, when the Mongols arrived in Punjab, the Sultan returned the elite to Delhi, although Daulatabad remained an administrative centre. One result of the transfer of the elite to Daulatabad was the hatred of the nobility to the Sultan, which remained in their minds for a long time. The other result was that he managed to create a stable Muslim elite and result in the growth of the Muslim population of Daulatabad who did not return to Delhi, without which the rise of the Bahmanid kingdom to challenge the Vijayanagara kingdom would not have been possible. Muhammad bin Tughlaq's adventures in the Deccan region also marked campaigns of destruction and desecration temples, for example, the Svayambhu Shiva Temple and the Thousand Pillar Temple in Warangal
Warangal () is a city in the Indian state of Telangana and the district headquarters of Warangal district. It is the second largest city in Telangana with a population of 811,844 per 2011 Census of India, and spreading over an .
Warangal serv ...
.
Revolts against Muhammad bin Tughlaq began in 1327, continued over his reign, and over time the geographical reach of the Sultanate shrunk. The Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Kingdom, was a late medieval Hinduism, Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, belongi ...
originated in southern India as a direct response to attacks from the Delhi Sultanate, and liberated south India from the Delhi Sultanate's rule. In the 1330s, Muhammad bin Tughlaq ordered an invasion of China, sending part of his forces over the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
. However, they were defeated by the Kangra State
Kangra-Lambagraon was a historical state and later princely estate (''jagir'') of British India located in the present-day state of Himachal Pradesh.
The rulers of the estate belonged to the ancient Katoch dynasty which had ruled the former ...
. During his reign, state revenues collapsed from his policies such as the base metal coins from 1329 to 1332. Famines, widespread poverty, and rebellion grew across the kingdom. In 1338 his nephew rebelled in Malwa, whom he attacked, caught, flayed alive, and killed ultimately. By 1339, the eastern regions under local Muslim governors and southern parts led by Hindu kings had revolted and declared independence from the Delhi Sultanate. Muhammad bin Tughlaq did not have the resources or support to respond to the shrinking kingdom. The historian Walford chronicled that Delhi and most of India faced severe famines during Muhammad bin Tughlaq's rule in the years after the base metal coin experiment. In 1335, Jalaluddin Ahsan Khan, a Sayyid native of Kaithal in North India, revolted and founded the Madurai Sultanate
Ma'bar Sultanate, also known as the Madurai Sultanate, was a short lived kingdom based in the city of Madurai in Tamil Nadu, India. It was dominated by Hindustani speaking Muslims. The sultanate was proclaimed in 1335 CE in Madurai led by Jala ...
in South India. By 1347, the Bahmani Sultanate had become independent through the rebellion of Ismail Mukh. It became a competing Muslim kingdom in the Deccan region of South Asia, founded by Ala-ud-Din Bahman Shah
Ala-ud-Din Hasan Bahman Shah (; died 10 February 1358) whose original name was Zafar Khan or Hasan Gangu, was the founder of the Bahmani Sultanate.
Ancestry and early life
Hasan Gangu, the founder of the Bahmani Sultanate, was either of Afgha ...
.
Muhammad bin Tughlaq died in 1351 while trying to chase and punish people in Gujarat who were rebelling against the Delhi Sultanate. He was succeeded by Firuz Shah Tughlaq
Firuz Shah Tughlaq (1309 – 20 September 1388), also known as Firuz III, was Sultan of Delhi from 1351 until his death in 1388. He succeeded his cousin Muhammad bin Tughlaq following the latter's death at Thatta, Sindh. His father was ...
(1351–1388), who tried to regain the old kingdom, boundary by waging a war with Bengal for 11 months in 1359. However, Bengal did not fall. Firuz Shah ruled for 37 years. His reign was marked with prosperity much of which was due to the wise and capable Grand Vizier, Khan-i-Jahan Maqbul, a South Indian Telugu Muslim. His reign attempted to stabilize the food supply and reduce famines by commissioning an irrigation canal from the Yamuna river. An educated sultan, Firuz Shah left a memoir. In it he wrote that he banned the practice of torture, such as amputations, tearing out of eyes, sawing people alive, crushing people's bones as punishment, pouring molten lead into throats, setting people on fire, driving nails into hands and feet, among others. He also wrote that he did not tolerate attempts by Rafawiz Shia
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (imam). However, his right is understood ...
Muslim and Mahdi
The Mahdi () is a figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the Eschatology, End of Times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a descendant of Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad, and will appear shortly before Jesu ...
sects from proselytizing people into their faith, nor did he tolerate Hindus who tried to rebuild temples that his armies had destroyed.Firoz Shah TughlakFutuhat-i Firoz Shahi – Autobiographical memoirs
Translated in 1871 by Elliot and Dawson, Volume 3 –The History of India, Cornell University Archives, pp 377–381. Firuz Shah Tughlaq also lists his accomplishments to include converting Hindus to Sunni Islam by announcing an exemption from taxes and jizya for those who convert, and by lavishing new converts with presents and honours.Futuhat-i Firoz Shahi
Simultaneously, he raised taxes and jizya, assessing it at three levels, and stopping the practice of his predecessors who had historically exempted all Hindu
Brahmin
Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). Th ...
s from the jizya. He also vastly expanded the number of slaves in his service and those of Muslim nobles, who were converted to Islam, taught to read and memorize the Quran, and employed in many offices especially in the military, out of which he was able to amass a large army. These slaves were known as the Ghulaman-i-Firuz Shahi formed an elite guard which later became influential in the state. The reign of Firuz Shah Tughlaq was marked by reduction in extreme forms of torture, elimination of favours to select parts of society, but also increased intolerance and persecution of targeted groups, the latter of which resulting in conversion of significant parts of the population to Islam.
 The death of Firuz Shah Tughlaq created anarchy and disintegration of the kingdom. Firuz Shah's successor, Ghiyath-ud-Din Shah II was young and inexperienced and gave himself up to wine and pleasure. The nobles rose against him killed the Sultan and his vizier, and installed
The death of Firuz Shah Tughlaq created anarchy and disintegration of the kingdom. Firuz Shah's successor, Ghiyath-ud-Din Shah II was young and inexperienced and gave himself up to wine and pleasure. The nobles rose against him killed the Sultan and his vizier, and installed Abu Bakr Shah
Abu Bakr Shah Tughlaq (; reigned 1389–1390), was a Muslim ruler of the Tughlaq dynasty. He was the son of Zafar Khan and the grandson of Sultan Feroze Shah Tughluq.
Life
After Ghiyas-ud-Din Tughlaq II (who had succeeded Sultan Feroze Sha ...
on the throne. However, the old Ghulaman-i-Firuz Shahi turned against Abu Bakr, who fled, and on their invitation Nasir-ud-Din Muhammad Shah was installed on the throne. The anamalous institution of the Ghulaman-i-Firuz Shahi became a corrupting influence on the successive Sultans following Firuz Shah. The last rulers of this dynasty both called themselves Sultan from 1394 to 1397: Nasir ud-Din Mahmud Shah Tughlaq, the grandson of Firuz Shah Tughlaq who ruled from Delhi, and Nasir ud-Din Nusrat Shah Tughlaq, another relative of Firuz Shah Tughlaq who ruled from Firozabad
Firozabad () is a city near Agra in Firozabad district in the state of Uttar Pradesh in India. It is the centre of India's glassmaking industry and is known for the quality of the bangles and glassware produced here.
During the reign of Akba ...
, which was a few miles from Delhi. The battle between the two relatives continued until Timur's invasion in 1398. Timur
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeat ...
, also known as Tamerlane in Western scholarly literature, was the Turkicized Mongol ruler of the Timurid Empire
The Timurid Empire was a late medieval, culturally Persianate, Turco-Mongol empire that dominated Greater Iran in the early 15th century, comprising modern-day Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, much of Central Asia, the South Caucasus, and parts of co ...
. He became aware of the weakness and quarrelling of the rulers of the Delhi Sultanate, so he marched with his army to Delhi, plundering and killing all the way. Estimates for the massacre by Timur in Delhi range from 100,000 to 200,000 people. Timur had no intention of staying in or ruling India. He looted the lands he crossed, then plundered and burnt Delhi. Over fifteen days, Timur and his army raged a massacre. Then he collected wealth, captured women and men and children, and enslaved people (particularly skilled artisans), and returning with this loot to Samarkand. The people and lands within the Delhi Sultanate were left in a state of anarchy, chaos, and pestilence. Nasir ud-Din Mahmud Shah Tughlaq, who had fled to Gujarat during Timur's invasion, returned and nominally ruled as the last ruler of the Tughlaq dynasty, as a puppet of the various factions at the court.Annemarie Schimmel, Islam in the Indian Subcontinent, , Brill Academic, Chapter 2
Sayyid dynasty (1414–1450)
 The
The Sayyid dynasty
The Sayyid dynasty was the fourth dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, with four rulers ruling from 1414 to 1451 for 37 years.See:
* M. Reza Pirbha, Reconsidering Islam in a South Asian Context, , Brill
* The Islamic frontier in the east: Expansion ...
was founded by Khizr Khan and it ruled the Delhi Sultanate from 1415 to 1451. Members of the dynasty derived their title, Sayyid
''Sayyid'' is an honorific title of Hasanid and Husaynid lineage, recognized as descendants of the Islamic prophet Muhammad through his daughter Fatima and Ali's sons Hasan ibn Ali, Hasan and Husayn ibn Ali, Husayn. The title may also refer ...
, or the descendants of the Islamic prophet, Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
, based on the claim that they belonged to his lineage through his daughter Fatima
Fatima bint Muhammad (; 605/15–632 CE), commonly known as Fatima al-Zahra' (), was the daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his wife Khadija. Fatima's husband was Ali, the fourth of the Rashidun caliphs and the first Shia imam. ...
. Abraham Eraly thinks his forebears were likely that Khizr Khan's ancestors were likely descendants of an Arab family who had long ago settled in the region of Multan during the early Tughluq period, but he doubts his Sayyid lineage. A.L. Srivastava shares a similar viewpoint. According to Richard M. Eaton and Simon Digby, Khizr Khan was a Punjabi chieftain from Khokhar clan. The Timurid invasion and plunder had left the Delhi Sultanate in shambles, and little is known about the rule by the Sayyid dynasty. Annemarie Schimmel notes the first ruler of the dynasty as Khizr Khan, who assumed power as a vassal of the Timurid Empire
The Timurid Empire was a late medieval, culturally Persianate, Turco-Mongol empire that dominated Greater Iran in the early 15th century, comprising modern-day Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, much of Central Asia, the South Caucasus, and parts of co ...
. His successor was Mubarak Khan, who renamed himself Mubarak Shah, discontinued his father's nominal allegiance to Timur and unsuccessfully tried to regain lost territories in Punjab from Khokhar warlords.
With the power of the Sayyid dynasty faltering, Islam's history on the Indian subcontinent underwent a profound change, according to Schimmel. The previously dominant Sunni sect of Islam became diluted, alternate Muslim sects such as Shia rose, and new competing centres of Islamic culture took roots beyond Delhi.
In the course of the late Sayyid dynasty, the Delhi Sultanate shrank until it became a minor power. By the time of the last Sayyid ruler, Alam Shah (whose name translated to "king of the world"), this resulted in a common northern Indian witticism, according to which the "kingdom of the king of the world extends from Delhi to Palam", i.e. merely . Historian Richard M. Eaton noted that this saying showcased how the "once-mighty empire had become a joke". The Sayyid dynasty was displaced by the Lodi dynasty in 1451, however, resulting in a resurgence of the Delhi Sultanate.
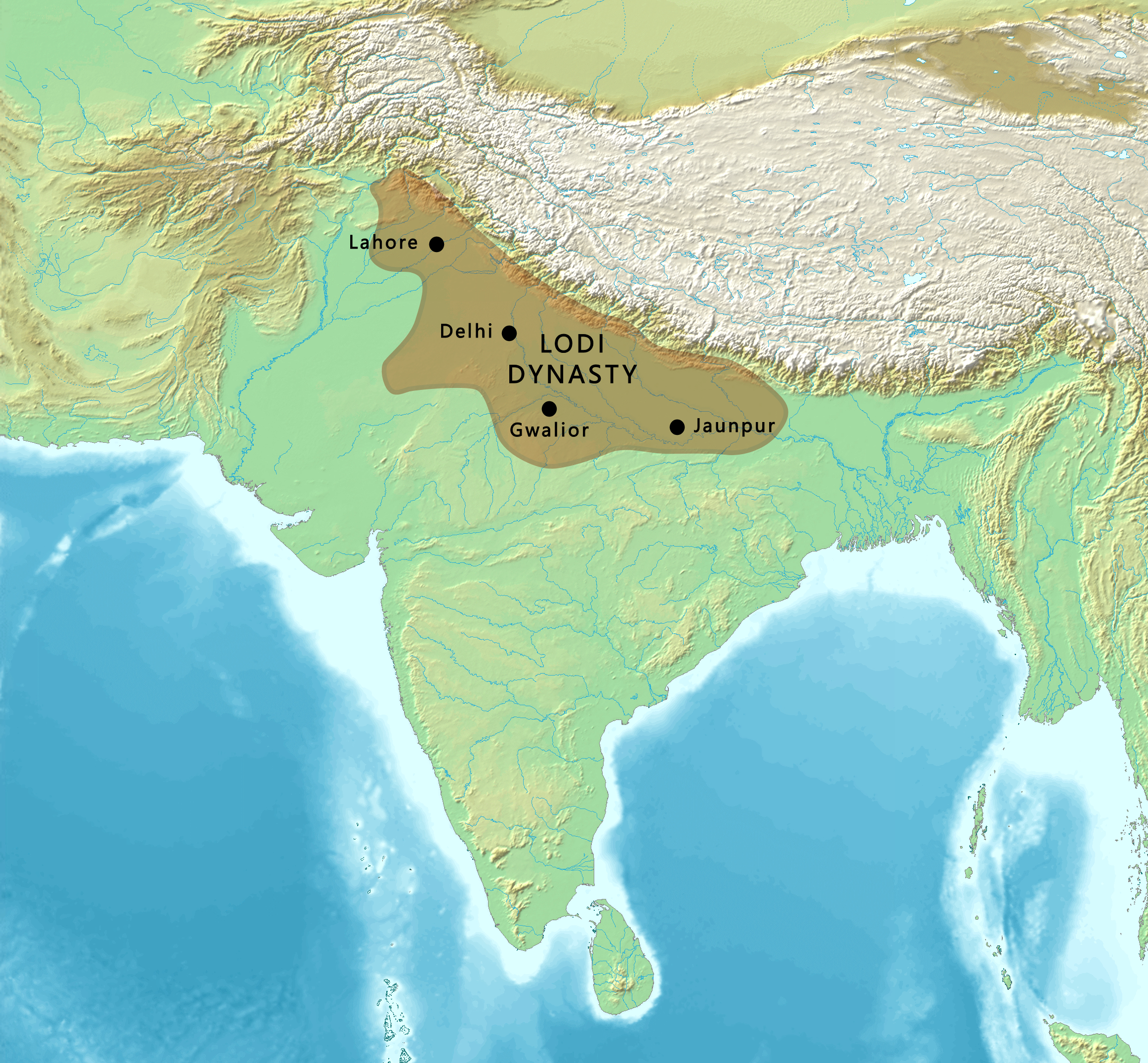
Lodi dynasty (1451–1526)
 The Lodi dynasty was an Afghan, or Turco-Afghan dynasty, related to the
The Lodi dynasty was an Afghan, or Turco-Afghan dynasty, related to the Pashtun
Pashtuns (, , ; ;), also known as Pakhtuns, or Pathans, are an Iranic ethnic group primarily residing in southern and eastern Afghanistan and northwestern Pakistan. They were historically also referred to as Afghans until 1964 after the ...
(Afghan
Afghan or Afgan may refer to:
Related to Afghanistan
*Afghans, historically refers to the Pashtun people. It is both an ethnicity and nationality. Ethnicity wise, it refers to the Pashtuns. In modern terms, it means both the citizens of Afghanist ...
) Lodi tribe. The founder of the dynasty, Bahlul Khan Lodi, was a Khalji of the Lodi clan. He started his reign by attacking the Muslim Jaunpur Sultanate
The Jaunpur Sultanate () was a late medieval Indian Muslim state which ruled over much of what is now the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar and southern Nepal between 1394 and 1494. It was founded in 1394 by Khwajah-i-Jahan Malik Sarwar ...
to expand the influence of the Delhi Sultanate and was partially successful through a treaty. Thereafter, the region from Delhi to Varanasi
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic tradition of I ...
(then at the border of Bengal province), was back under the influence of the Delhi Sultanate.
After Bahlul Lodi died, his son Nizam Khan assumed power, renamed himself Sikandar Lodi and ruled from 1489 to 1517. One of the better-known rulers of the dynasty, Sikandar Lodi expelled his brother Barbak Shah from Jaunpur, installed his son Jalal Khan as the ruler, then proceeded east to make claims on Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
. The Muslim governors of Bihar agreed to pay tribute and taxes but operated independently of the Delhi Sultanate. Sikandar Lodi led a campaign of destruction of temples, particularly around Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
. He also moved his capital and court from Delhi to Agra
Agra ( ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is the ...
, an ancient Hindu city that had been destroyed during the plunder and attacks of the early Delhi Sultanate period. Sikandar thus erected buildings with Indo-Islamic architecture in Agra during his rule, and the growth of Agra continued during the Mughal Empire, after the end of the Delhi Sultanate.
Sikandar Lodi died a natural death in 1517, and his second son Ibrahim Lodi assumed power. Ibrahim did not enjoy the support of Afghan and Persian nobles or regional chiefs. Ibrahim attacked and killed his elder brother Jalal Khan, who was installed as the governor of Jaunpur by his father and had the support of the amirs and chiefs. Ibrahim Lodi was unable to consolidate his power, and after Jalal Khan's death, the governor of Punjab, Daulat Khan Lodi, reached out to the Mughal Babur
Babur (; 14 February 148326 December 1530; born Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad) was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also ...
and invited him to attack the Delhi Sultanate.Lodi Dynasty''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2009) Babur defeated and killed Ibrahim Lodi in the Battle of Panipat in 1526. The death of Ibrahim Lodi ended the Delhi Sultanate, and the
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
replaced it.
Government and politics
The historianPeter Jackson
Sir Peter Robert Jackson (born 31 October 1961) is a New Zealand filmmaker. He is best known as the director, writer, and producer of the ''Lord of the Rings'' trilogy (2001–2003) and the ''Hobbit'' trilogy (2012–2014), both of which ar ...
explains in ''The New Cambridge History of Islam
''The New Cambridge History of Islam'' is a six volume history of Islam published by Cambridge University Press in 2010. The general editor is Michael Cook (historian), Michael Cook.
The history replaced the original ''Cambridge History of Islam ...
'': "The elite of the early Delhi sultanate comprised overwhelmingly first-generation immigrants from Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
: Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
, Turks, Ghūrīs, Khalaj from the hot regions (''garmsīr'') of modern Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
".
Political system
Medieval scholars such as Isami and Barani suggested that the prehistory of the Delhi Sultanate lay in theGhaznavid
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a Persianate Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin. It ruled the Ghaznavid Empire or the Empire of Ghazni from 977 to 1186, which at its greatest extent, extended from the Oxus to the Indus Va ...
state and that its ruler, Mahmud Ghaznavi, provided the foundation and inspiration integral in the making of the Delhi regime. The Mongol and Hindu monarchies were the great "Others" in these narratives and the Persianate and class-conscious, aristocratic virtues of the ideal state were creatively memorialized in the Ghaznavid state, now the templates for the Delhi Sultanate. Cast within a historical narrative it allowed for a more self-reflective, linear rooting of the Sultanate in the great traditions of Muslim statecraft. Over time, successive Muslim dynasties created a "centralized structure in the Persian tradition whose task was to mobilize human and material resources for the ongoing armed struggle against both Mongol and Hindu monarchies
In Hinduism, kingship was a monarchy institution guided by the religious laws of Hinduism, with corresponding complex and hierarchical structure. Hindu monarchies headed by Hindu kings were widespread in South Asia since about 1500 BC and later in ...
". The monarch was not the Sultan of the Hindus or of, say, the people of Haryana, rather in the eyes of the Sultanate's chroniclers, the Muslims constituted what in more recent times would be termed a "Staatsvolk". For many Muslim observers, the ultimate justification for any ruler within the Islamic world was the protection and advancement of the faith. For the Sultans, as for their Ghaznavid and Ghurid predecessors, this entailed the suppression of heterodox Muslims, and Firuz Shah attached some importance to the fact that he had acted against the ashab-i had-u ibadat (deviators and latitudinarians). It also involved plundering and extorting tribute from, independent Hindu principalities. Firuz Shah, who believed that India was changed into a Muslim nation, declared that "no zimmi living in a Musalman country might dare to act".
The Hindu kingdoms who submitted to Islamic rule qualified as "protected peoples" according to the wide spectrum of the educated Muslim community within the subcontinent. The balance of the evidence is that in the latter half of the fourteenth century, if not before, the jizyah was levied as a discriminatory tax on non-Muslims, although even then it is difficult to see how such a measure could have been enforced outside the principal centres of Muslim authority. The Delhi Sultanate also continued the governmental conventions of the previous Hindu polities, claiming paramountcy of some of its subjects rather than exclusive supreme control. Accordingly, it did not interfere with the autonomy and military of certain conquered Hindu rulers and freely included Hindu vassals and officials.
Economic policy and administration
The economic policy of the Delhi Sultanate was characterized by greater government involvement in the economy relative to the Classical Hindu dynasties, and increased penalties for private businesses that broke government regulations. Alauddin Khalji replaced the private markets with four centralized government-run markets, appointed a "market controller", and implemented strict price controls on all kinds of goods, "fromcap
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. The origin of the word "cap" comes from the Old French word "chapeau" which means "head co ...
s to sock
A sock is a piece of clothing worn on the feet and often covering the ankle or some part of the Calf (leg), calf. Some types of shoes or boots are typically worn over socks. In ancient times, socks were made from leather or matted animal hair. ...
s; from comb
A comb is a tool consisting of a shaft that holds a row of teeth for pulling through the hair to clean, untangle, or style it. Combs have been used since prehistoric times, having been discovered in very refined forms from settlements dating ba ...
s to pins; from vegetable
Vegetables are edible parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. This original meaning is still commonly used, and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including edible flower, flo ...
s to soup
Soup is a primarily liquid food, generally served warm or hot – though it is sometimes served chilled – made by cooking or otherwise combining meat or vegetables with Stock (food), stock, milk, or water. According to ''The Oxford Compan ...
s, from sweetmeats to chapati
Chapati (alternatively spelled chapathi; pronounced as IAST: ), also known as ''roti'', ''rooti'', ''rotee'', ''rotli'', '' rotta'', ''safati'', ''shabaati'', ''phulka'', ''chapo'' (in East Africa), ''sada roti'' (in the Caribbean), ''poli'' (i ...
s" (according to Ziauddin Barani . 1357. The price controls were inflexible even during droughts. Capitalist investors were completely banned from participating in the horse trade, animal and slave brokers were forbidden from collecting commissions, and private merchants were eliminated from all animal and slave markets. Bans were instituted against hoarding
Hoarding is the act of engaging in excessive acquisition of items that are not needed or for which no space is available.
Civil unrest or the threat of natural disasters may lead people to hoard foodstuffs, water, gasoline, and other essentials ...
and regrating, granaries were nationalized and limits were placed on the amount of grain that could be used by cultivators for personal use.
Various licensing rules were imposed. Registration of merchants was required, and expensive goods such as certain fabrics were deemed "unnecessary" for the general public and required a permit from the state to be purchased. These licenses were issued to '' amirs'', '' maliks'', and other important persons in government. Agricultural taxes were raised to 50%.
Traders regarded the regulations as burdensome, and violations were severely punished, leading to further resentment among the traders. A network of spies was instituted to ensure the implementation of the system; even after price controls were lifted after Khalji's death, Barani claims that the fear of his spies remained and that people continued to avoid trading in expensive commodities.
Social policies
The sultanate enforced Islamic religious prohibitions on anthropomorphic representations in art.Military
The army of the Delhi sultans initially consisted of nomadic TurkicMamluk
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-so ...
military slaves belonging to Muhammad of Ghor.
The nucleus of this Southeast Asian sultanate military were the Turco-Afghani regular units named ''Wajih'', which were composed of elite household cavalry archers who came from slave backgrounds. A major military contribution of the Delhi Sultanate was their successful campaigns repelling the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
's invasions of India, which could have been devastating for the Indian subcontinent, like the Mongol invasions of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. Were it not for the Delhi Sultanate, the Mongol Empire may have been successful in invading India.
The strength of the armies changes according to time. Historians state the Delhi sultanate during the Khalji dynasty maintained 300,000–400,000 horse cavalry and 2500–3000 war elephant
A war elephant is an elephant that is Animal training, trained and guided by humans for combat purposes. Historically, the war elephant's main use was to charge (warfare), charge the enemy, break their ranks, and instill terror and fear. Elep ...
as a standing army. Its successor state, the Tughlaq dynasty
The Tughlaq dynasty (also known as the Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty; ) was the third dynasty to rule over the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath ...
further expanded into 500,000 horse cavalry in their force.
Economy
Some historians argue that the Delhi Sultanate was responsible for making India more multicultural and cosmopolitan. The establishment of the Delhi Sultanate in India has been compared to the expansion of theMongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
and called "part of a larger trend occurring throughout much of Eurasia, in which nomadic people migrated from the steppes of Inner Asia and became politically dominant".
According to Angus Maddison
Angus Maddison (6 December 1926 – 24 April 2010) was a distinguished British economist specialising in quantitative macro economic history, including the measurement and analysis of economic growth and development.
Maddison lectured at sev ...
, between the years 1000 and 1500, India's GDP, of which the sultanates represented a significant part, grew nearly 8% to $60.5 billion in 1500. Though the overall the percentage of the GDP share reduced from 33% to 22% According to Maddison's estimates, India's population grew from 85 million in 1200 to 101 million in 1500 AD in the period.
The Delhi Sultanate period coincided with more use of mechanical technology in the Indian subcontinent. India previously already had highly sophisticated agriculture, food crops, textiles, medicine, minerals, and metals. Water wheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a large wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with numerous b ...
s also previously existed in India, as described by various Chinese monks and Arab travellers and writers in their books. During the Delhi Sultanate, various mechanical devices were introduced from the Islamic world to India, such as gear
A gear or gearwheel is a rotating machine part typically used to transmit rotational motion and/or torque by means of a series of teeth that engage with compatible teeth of another gear or other part. The teeth can be integral saliences or ...
ed water-raising wheels and other machine
A machine is a physical system that uses power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromol ...
s with gears, pulley
Sheave without a rope
A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft enabling a taut cable or belt passing over the wheel to move and change direction, or transfer power between itself and a shaft.
A pulley may have a groove or grooves between flan ...
s, cams, and cranks. Later, Mughal emperor Babur provided a description on the use of water wheels in the Delhi Sultanate.
 According to historians Arnold Pacey and
According to historians Arnold Pacey and Irfan Habib
Irfan Habib (born 10 August 1931) is an Indian historian of ancient and medieval India, following the methodology of Marxist historiography in his contributions to economic history. He is known for his strong stance against Hindutva. He has au ...
, the spinning wheel
A spinning wheel is a device for spinning thread or yarn from fibres. It was fundamental to the textile industry prior to the Industrial Revolution. It laid the foundations for later machinery such as the spinning jenny and spinning frame, ...
was introduced to India from Iran during the Delhi Sultanate. Smith and Cothren suggested that it was invented in India during the latter half of the first millennium, but Pacey and Habib said these early references to cotton spinning do not identify a wheel, but more likely refer to hand spinning. The earliest unambiguous reference to a spinning wheel in India is dated to 1350. The worm gear roller cotton gin
A cotton gin—meaning "cotton engine"—is a machine that quickly and easily separates cotton fibers from their seeds, enabling much greater productivity than manual cotton separation.. Reprinted by McGraw-Hill, New York and London, 1926 (); ...
was invented in the thirteenth or fourteenth centuries; Habib states that the development may likely occurred in peninsular India, before becoming more widespread across India during the Mughal era. The incorporation of the crank handle in the cotton gin may have appeared sometime during the late Delhi Sultanate or the early Mughal Empire.
India and China have connections throughout the thousands of years of history. Paper had already reached some parts of India as early as the 6th or 7th century,Harrison, Frederick. ''A Book about Books''. London: John Murray, 1943. p. 79. Mandl, George. "Paper Chase: A Millennium in the Production and Use of Paper". Myers, Robin & Michael Harris (eds). ''A Millennium of the Book: Production, Design & Illustration in Manuscript & Print, 900–1900''. Winchester: St. Paul's Bibliographies, 1994. p. 182.
Mann, George. ''Print: A Manual for Librarians and Students Describing in Detail the History, Methods, and Applications of Printing and Paper Making''. London: Grafton & Co., 1952. p. 79. McMurtrie, Douglas C. ''The Book: The Story of Printing & Bookmaking''. London: Oxford University Press, 1943. p. 63. initially through Chinese travellers and the ancient silk road which India was very well connected with. Earlier some historians believed that paper failed to catch on as palmyra leaves and birch bark remained far more popular but this theory was discredited later on. On the other hand, the paper may have arrived in Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
from a separate route, as 15th-century Chinese traveller Ma Huan remarked that Bengali paper was white and made from "bark of a tree" similar to the Chinese method of papermaking (as opposed to the Middle-Eastern method of using rags and waste material), suggesting a direct route from China for the arrival of paper in Bengal and paper was already very well established and widespread in that part of the subcontinent.
Factors
Demographics
According to one set of very uncertain estimates by modern historians, the total Indian population had largely been stagnant at 75 million during the Middle Kingdoms era from 1 AD to 1000 AD. During theMedieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
Delhi Sultanate era from 1000 to 1500, India as a whole experienced lasting population growth for the first time in a thousand years, with its population increasing nearly 50% to 110 million by 1500 AD.Angus Maddison
Angus Maddison (6 December 1926 – 24 April 2010) was a distinguished British economist specialising in quantitative macro economic history, including the measurement and analysis of economic growth and development.
Maddison lectured at sev ...
(2001), '' The World Economy: A Millennial Perspective''pages 241–242
,
OECD Development Centre
The OECD Development Centre was established in 1961 as an independent platform for knowledge sharing and policy dialogue between Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Devel ...
Angus Maddison
Angus Maddison (6 December 1926 – 24 April 2010) was a distinguished British economist specialising in quantitative macro economic history, including the measurement and analysis of economic growth and development.
Maddison lectured at sev ...
(2001), '' The World Economy: A Millennial Perspective''page 236
,
OECD Development Centre
The OECD Development Centre was established in 1961 as an independent platform for knowledge sharing and policy dialogue between Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Devel ...
Culture
While the Indian subcontinent has had invaders from Central Asia since ancient times, what made the Muslim invasions different is that unlike the preceding invaders who assimilated into the prevalent social system, the successful Muslim conquerors retained their Islamic identity and created new legal and administrative systems that challenged and usually in many cases superseded the existing systems of social conduct and ethics, even influencing the non-Muslim rivals and common masses to a large extent, though the non-Muslim population was left to their laws and customs. They also introduced new cultural codes that in some ways were very different from the existing cultural codes. This led to the rise of a new Indian culture that was mixed in nature, different from ancient Indian culture. The overwhelming majority of Muslims in India were Indian natives converted to Islam. This factor also played an important role in the synthesis of cultures. TheHindustani language
Hindustani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in North India and Pakistan as the lingua franca of the region. It is also spoken by the Deccani people, Deccani-speaking community in the Deccan plateau. Hindustani is a pluricentric language w ...
(Hindi) began to emerge in the Delhi Sultanate period, developed from the Middle Indo-Aryan
The Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Middle Indic languages, sometimes conflated with the Prakrits, which are a stage of Middle Indic) are a historical group of languages of the Indo-Aryan family. They are the descendants of Old Indo-Aryan (OIA; ...
'' apabhramsha'' vernacular
Vernacular is the ordinary, informal, spoken language, spoken form of language, particularly when perceptual dialectology, perceived as having lower social status or less Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige than standard language, which is mor ...
s of North India
North India is a geographical region, loosely defined as a cultural region comprising the northern part of India (or historically, the Indian subcontinent) wherein Indo-Aryans (speaking Indo-Aryan languages) form the prominent majority populati ...
. Amir Khusrau
Abu'l Hasan Yamīn ud-Dīn Khusrau (1253 – 1325 AD), better known as Amīr Khusrau, sometimes spelled as, Amir Khusrow or Amir Khusro, was an Indo-Persian Sufi singer, musician, poet and scholar, who lived during the period of the Delhi Sult ...
, who lived in the 13th century CE during the Delhi Sultanate period in North India, used a form of Hindustani, which was the ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
'' of the period, in his writings and referred to it as ''Hindavi''.
The officers, the Sultans, Khans, Maliks and the soldiers wore the Islamic qabas dress in the style of Khwarezm, which were tucked in the middle of the body, while the turban and kullah were common headwear. The turbans were wrapped around the kullah (caps), and the feet were covered with red boots. The Wazirs and Katibs also dressed like the soldiers, except they did not use belts, and often let down a piece of cloth in front of them in the manner of the Sufis. The judges and the learned men wore ample gowns (farajiyat) and an Arabic garment (durra).
Architecture
 The start of the Delhi Sultanate in 1206 under
The start of the Delhi Sultanate in 1206 under Qutb al-Din Aibak
Qutb ud-Din Aibak (; 1150 – 4 November 1210) was a Turkic general of the Ghurid emperor Muhammad Ghori. He was in charge of the Ghurid territories in northern India, and after Muhammad Ghori's assassination in 1206, he established his ow ...
introduced a large Islamic state to India, using Central Asian styles. The types and forms of large buildings required by Muslim elites, with mosque
A mosque ( ), also called a masjid ( ), is a place of worship for Muslims. The term usually refers to a covered building, but can be any place where Salah, Islamic prayers are performed; such as an outdoor courtyard.
Originally, mosques were si ...
s and tombs much the most common, were very different from those previously built in India. The exteriors of both were very often topped by large dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
s and made extensive use of arch
An arch is a curved vertical structure spanning an open space underneath it. Arches may support the load above them, or they may perform a purely decorative role. As a decorative element, the arch dates back to the 4th millennium BC, but stru ...
es. Both of these features were hardly used in Hindu temple architecture
Hindu temple architecture as the main form of Hindu architecture has many different styles, though the basic nature of the Hindu temple remains the same, with the essential feature an inner sanctum, the ''Garbhagriha, garbha griha'' or womb-ch ...
and other indigenous Indian styles. Both types of building essentially consist of a single large space under a high dome, and completely avoid the figurative sculpture so important to Hindu temple architecture.
The important Qutb Minar complex in Delhi was begun under Muhammad of Ghor, by 1199, and continued under Qutb al-Din Aibak and later sultans. The Quwwat-ul-Islam Mosque, now a ruin, was the first structure. Like other early Islamic buildings, it re-used elements such as columns from destroyed Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
and Jain temples, including one on the same site whose platform was reused. The style was Iranian, but the arches were still corbelled in the traditional Indian way.
Beside it is the extremely tall Qutb Minar
The Qutb Minar, also spelled Qutub Minar and Qutab Minar, is a minaret and victory tower comprising the Qutb complex, which lies at the site of Delhi's oldest fortified city, Lal Kot, founded by the Tomar Rajputs. It is a UNESCO World Heritage ...
, a minaret
A minaret is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generally used to project the Muslim call to prayer (''adhan'') from a muezzin, but they also served as landmarks and symbols of Islam's presence. They can h ...
or victory tower, whose original four stages reach 73 meters (with a final stage added later). Its closest comparator is the 62-metre all-brick Minaret of Jam in Afghanistan, of , a decade or so before the probable start of the Delhi tower. The surfaces of both are elaborately decorated with inscriptions and geometric patterns; in Delhi the shaft is fluted with "superb stalactite
A stalactite (, ; , ) is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension (chemistry ...
bracketing under the balconies" at the top of each stage. In general minarets were slow to be used in India, and are often detached from the main mosque where they exist.
The Tomb of Iltutmish
Shams ud-Din Iltutmish (1192 – 30 April 1236) was the third of the Mamluk kings who ruled the former Ghurid territories in northern India. He was the first Muslim sovereign to rule from Delhi, and is thus considered the effective founder of ...
was added by 1236; its dome, the squinches again corbelled, and is now missing, and the intricate carving has been described as having an "angular harshness", from carvers working in an unfamiliar tradition. Other elements were added to the complex over the next two centuries.
Another very early mosque, begun in the 1190s, is the Adhai Din Ka Jhonpra in Ajmer
Ajmer () is a city in the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Ajmer district and Ajmer division. It lies at the centre of Rajasthan, earning it the ...
, Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; Literal translation, lit. 'Land of Kings') is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the List of states and union territories of ...
, built for the same Delhi rulers, again with corbelled arches and domes. Here Hindu temple columns (and possibly some new ones) are piled up in threes to achieve extra height. Both mosques had large detached screens with pointed corbelled arches added in front of them, probably under Iltutmish a couple of decades later. In these, the central arch is taller, in imitation of an iwan
An iwan (, , also as ''ivan'' or ''ivān''/''īvān'', , ) is a rectangular hall or space, usually vaulted, walled on three sides, with one end entirely open. The formal gateway to the iwan is called , a Persian term for a portal projecting ...
. At Ajmer, the smaller screen arches are tentatively cusped, for the first time in India.
By around 1300 true domes and arches with voussoir
A voussoir ( UK: ; US: ) is a wedge-shaped element, typically a stone, which is used in building an arch or vault.“Voussoir, N., Pronunciation.” Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford UP, June 2024, https://doi.org/10.1093/OED/7553486115. Acces ...
s were being built; the ruined Tomb of Balban (d. 1287) in Delhi may be the earliest survival. The Alai Darwaza gatehouse at the Qutb complex, from 1311, still shows a cautious approach to the new technology, with very thick walls and a shallow dome, only visible from a certain distance or height. Bold contrasting colours of masonry, with red sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
and white marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
, introduce what was to become a common feature of Indo-Islamic architecture, substituting for the polychrome tiles used in Persia and Central Asia. The pointed arches come together slightly at their base, giving a mild horseshoe arch
The horseshoe arch (; ), also called the Moorish arch and the keyhole arch, is a type of arch in which the circular curve is continued below the horizontal line of its diameter, so that the opening at the bottom of the arch is narrower than the ar ...
effect, and their internal edges are not cusped but lined with conventionalized "spearhead" projections, possibly representing lotus buds. Jali, stone openwork
In art history, architecture, and related fields, openwork or open-work is any decorative technique that creates holes, piercings, or gaps through a solid material such as metal, wood, stone, pottery, cloth, leather, or ivory. Such techniques ha ...
screens, are introduced here; they already had been long used in temples.
Tughlaq architecture
 The tomb of Shah Rukn-e-Alam (built 1320 to 1324) in
The tomb of Shah Rukn-e-Alam (built 1320 to 1324) in Multan
Multan is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fifth-most populous city in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the List of cities in Pakistan by populatio ...
, Pakistan is a large octagonal brick-built mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be considered a type o ...
with polychrome glazed decoration that remains much closer to the styles of Iran and Afghanistan. Timber is also used internally. This was the earliest major monument of the Tughlaq dynasty
The Tughlaq dynasty (also known as the Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty; ) was the third dynasty to rule over the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath ...
(1320–1413), built during the unsustainable expansion of its massive territory. It was built for a Sufi saint
The term ''wali'' is most commonly used by Muslims to refer to a saint, or literally a "friend of God in Islam, God".John Renard, ''Friends of God: Islamic Images of Piety, Commitment, and Servanthood'' (Berkeley: University of California Press ...
rather than a sultan, and most of the many Tughlaq tombs are much less exuberant. The tomb of the founder of the dynasty, Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq (d. 1325) is more austere, but impressive; like a Hindu temple, it is topped with a small amalaka and a round finial
A finial () or hip-knob is an element marking the top or end of some object, often formed to be a decorative feature.
In architecture, it is a small decorative device, employed to emphasize the Apex (geometry), apex of a dome, spire, tower, roo ...
like a kalasha
A kalasha, also called Pūrṇa-Kalaśa, Pūrṇa-Kumbha, Pūrṇa-Ghaṭa, also called ghat or ghot or kumbh ( , Telugu: కలశము Kannada: ಕಳಶ literally "pitcher, pot"), is a metal (brass, copper, silver or gold) pot with a large ...
. Unlike the buildings mentioned previously, it completely lacks carved texts and sits in a compound with high walls and battlements. Both these tombs have external walls sloping slightly inwards, by 25° in the Delhi tomb, like many fortifications including the ruined Tughlaqabad Fort opposite the tomb, intended as the new capital.
The Tughlaqs had a corps of government architects and builders, and in this and other roles employed many Hindus. They left many buildings and a standardized dynastic style. The third sultan, Firuz Shah (r. 1351–88) is said to have designed buildings himself and was the longest ruler and greatest builder of the dynasty. His Firoz Shah Palace Complex (started 1354) at Hisar, Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
is a ruin, but parts are in fair condition. Some buildings from his reign take forms that had been rare or unknown in Islamic buildings. He was buried in the large Hauz Khas Complex in Delhi, with many other buildings from his period and the later Sultanate, including several small domed pavilion
In architecture, ''pavilion'' has several meanings;
* It may be a subsidiary building that is either positioned separately or as an attachment to a main building. Often it is associated with pleasure. In palaces and traditional mansions of Asia ...
s supported only by columns.
By this time Islamic architecture in India had adopted some features of earlier Indian architecture, such as the use of a high plinth
A pedestal or plinth is a support at the bottom of a statue, vase, column, or certain altars. Smaller pedestals, especially if round in shape, may be called socles. In civil engineering, it is also called ''basement''. The minimum height o ...
, and often mouldings around its edges, as well as columns and brackets and hypostyle
In architecture, a hypostyle () hall has a roof which is supported by columns.
Etymology
The term ''hypostyle'' comes from the ancient Greek ὑπόστυλος ''hypóstȳlos'' meaning "under columns" (where ὑπό ''hypó'' means below or und ...
halls. After the death of Firoz the Tughlaqs declined, and the following Delhi dynasties were weak. Most of the monumental buildings constructed were tombs, although the impressive Lodi Gardens in Delhi (adorned with fountains, '' charbagh'' gardens, ponds, tombs and mosques) were constructed by the late Lodi dynasty. The architecture of other regional Muslim states was often more impressive.
Ajmer
Ajmer () is a city in the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Ajmer district and Ajmer division. It lies at the centre of Rajasthan, earning it the ...
, ; Corbel arch
A corbel arch (or corbeled / corbelled arch) is an arch-like construction method that uses the architecture, architectural technique of corbeling to span a space or void in a structure, such as an entranceway in a wall or as the span of a bridge ...
es, some cusped.
File:Tomb of Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq and side tomb (3319047170).jpg, Tomb of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq (d. 1325), Delhi
File:Balban Khan's Tomb 029.jpg, Possibly the first "true" arches in India; Tomb of Balban (d. 1287) in Delhi
File:The tomb of Ferozshah ii ag61.jpg, Pavilions in the Hauz Khas Complex, Delhi
File:The Tomb of Sikander Lodi, seen from the Sheesh Gumbad.JPG, The Shish Gumbad in the Lodi Gardens
Lodi Gardens is a city park situated in New Delhi. Spread over , it contains Muhammad Shah IV, Muhammad Shah's tomb, the tomb of Sikandar Lodi, the Shisha Gumbad and the Bara Gumbad. These monuments date from the late Delhi Sultanate, during the ...
, Delhi
File:Tomb_of_Sikandar_Lodi_in_Lodi_Garden_08.jpg, Tomb of Sikandar Lodi in the Lodi Gardens
Lodi Gardens is a city park situated in New Delhi. Spread over , it contains Muhammad Shah IV, Muhammad Shah's tomb, the tomb of Sikandar Lodi, the Shisha Gumbad and the Bara Gumbad. These monuments date from the late Delhi Sultanate, during the ...
, Delhi
List of rulers
Downfall
Cities
While the sacking of cities was not uncommon in medieval warfare, the army of the Delhi Sultanate also often destroyed cities in their military expeditions. According to Jain chronicler Jinaprabha Suri, Nusrat Khan's conquests destroyed hundreds of towns including Ashapalli (modern-dayAhmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ), also spelled Amdavad (), is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 ...
), Anhilvad (modern-day Patan), Vanthali and Surat
Surat (Gujarati Language, Gujarati: ) is a city in the western Indian States and territories of India, state of Gujarat. The word Surat directly translates to ''face'' in Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of t ...
in Gujarat. This account is corroborated by Ziauddin Barani.
Battles and massacres
*Ghiyas ud din Balban
Al-Sultan al-Azam Ghiyath al-Dunya Wal Din Abu'l Muzaffar Balban al-Sultan (; 1216 – 13 January 1287), more famously known as Ghiyath al-Din Balban or simply Balban, was the ninth Mamluk sultan of Delhi. He had been the regent of the last S ...
wiped out the Rajputs of Mewar
Mewar, also spelled as Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasth ...
and Awadh
Awadh (), known in British Raj historical texts as Avadh or Oudh, is a historical region in northern India and southern Nepal, now constituting the North-central portion of Uttar Pradesh. It is roughly synonymous with the ancient Kosala Regio ...
, killing approximately 100,000 people.
* Alauddin Khalji ordered the killing of 30,000 people at Chittor.
* Alauddin Khalji ordered the killing Brahmins during his raid on Devagiri.
* According to a hymn, Muhammad bin Tughlaq is said to have killed 12,000 Hindu ascetics during the sacking of Srirangam
Srirangam is a neighbourhood in the city of Tiruchirappalli in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. A river island, Srirangam is bounded by the Kaveri River on one side and its distributary Kollidam on the other side. Considered as the first among ...
.
* Firuz Shah Tughlaq
Firuz Shah Tughlaq (1309 – 20 September 1388), also known as Firuz III, was Sultan of Delhi from 1351 until his death in 1388. He succeeded his cousin Muhammad bin Tughlaq following the latter's death at Thatta, Sindh. His father was ...
killed 180,000 people during his invasion of Odisha
Odisha (), formerly Orissa (List of renamed places in India, the official name until 2011), is a States and union territories of India, state located in East India, Eastern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by ar ...
.
Desecration
Historian Richard Eaton has tabulated a campaign of destruction of idols and temples by Delhi Sultans, intermixed with certain years where the temples were protected from desecration. In his paper, he has listed 37 instances ofHindu temple
A Hindu temple, also known as Mandir, Devasthanam, Pura, or Kovil, is a sacred place where Hindus worship and show their devotion to Hindu deities, deities through worship, sacrifice, and prayers. It is considered the house of the god to who ...
s being desecrated or destroyed in India during the Delhi Sultanate, from 1234 to 1518, for which reasonable evidences are available. He notes that this was not unusual in medieval India, as there were numerous recorded instances of temple desecration by Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
and Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
kings against rival Indian kingdoms between 642 and 1520, involving conflict between devotees of different Hindu deities, as well as between Hindus, Buddhists and Jains at small scales. He also noted there were also many instances of Delhi sultans, who often had Hindu ministers, ordering the protection, maintenance and repairing of temples, according to both Muslim and Hindu sources. For example, a Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
inscription notes that Sultan Muhammad bin Tughluq
Muhammad bin Tughluq (; ; 1290 – 20 March 1351), or Muhammad II, also named Jauna Khan as Crown Prince, further known by his epithets, The Eccentric Prince, or The Mad Sultan, was the eighteenth Sultan of Delhi. He reigned from 4 February 1 ...
repaired a Shiva and Parvati temple in Bidar
Bidar ( ) is a city and headquarters of the Bidar district in Karnataka state of India. Bidar is a prominent place on the archaeological map of India, it is well known for architectural, historical religious and rich heritage sites. Pictures ...
after his Deccan
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound by the mount ...
conquest. There was often a pattern of Delhi sultans plundering or damaging temples during the conquest and then patronizing or repairing temples after the conquest. This pattern came to an end with the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
, where Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, – ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
's chief minister Abu'l-Fazl criticized the excesses of earlier sultans such as Mahmud of Ghazni
Abu al-Qasim Mahmud ibn Sabuktigin (; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi (), was Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, ruling from 998 to 1030. During his reign and in medieval sources, he is usuall ...
.
In the majority of cases, the demolished remains, rocks and broken statue pieces of temples destroyed by Delhi sultans were reused to build mosques and other buildings. For example, the Qutb complex in Delhi was built from stones from 27 demolished Hindu and Jain temples by some accounts. Similarly, the Muslim mosque in Khanapur, Maharashtra was built from the looted parts and demolished remains of Hindu temples. Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khalji
Ikhtiyār al-Dīn Muḥammad Bin Bakhtiyār Khaljī, also known as Bakhtiyar Khalji, was a Turko-Afghan Military General of the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor, who led the Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim conquests of the easte ...
destroyed Buddhist Religious Centres such as Odantapuri & Vikramshila in 1193 at the beginning of the Delhi Sultanate.
The first historical record of a campaign of destruction of temples and defacement of faces or heads of Hindu idols lasted from 1193 to 1194 in Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh under the command of Ghuri. Under the Mamluks and Khaljis, the campaign of temple desecration expanded to Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat and Maharashtra, and continued through the late 13th century. The campaign extended to Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu under Malik Kafur and Ulugh Khan in the 14th century, and by the Bahmanis in the 15th century. Orissa temples were destroyed in the 14th century under the Tughlaqs.
Beyond destruction and desecration, the sultans of the Delhi Sultanate in some cases had forbidden the reconstruction or repair of damaged Hindu, Jain and Buddhist temples. In certain cases, the Sultanate would grant a permit for repairs and construction of temples if the patron or religious community paid jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
(fee, tax). For example, a proposal by the Chinese to repair Himalayan Buddhist temples destroyed by the Sultanate army was refused, because such temple repairs were only allowed if the Chinese agreed to pay jizya tax to the treasury of the Sultanate. According to Eva De Clercq, an expert in the study of Jainism, the Delhi Sultans did not strictly prohibit construction of new temples in the sultanate, Islamic law notwithstanding. In his memoirs, Firoz Shah Tughlaq describes how he destroyed temples and built mosques instead and killed those who dared build new temples. Other historical records from ''wazirs'', ''amirs'' and the court historians of various Sultans of the Delhi Sultanate describe the grandeur of idols and temples they witnessed in their campaigns and how these were destroyed and desecrated.
Temple desecration in pre-modern India
Frontline, p. 73, item 16 of the Table, Archived by Columbia University File:Benares- The Golden Temple, India, ca. 1915 (IMP-CSCNWW33-OS14-66).jpg, The Kashi Vishwanath Temple was destroyed by Muhammad of Ghor along with thousand other temples in
Varanasi
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic tradition of I ...
.
File:Temple de Mînâkshî01.jpg, The armies of the Delhi Sultanate led by their Delhi Sultanate commander Malik Kafur demolished and plundered the Meenakshi Temple of Madurai
Madurai ( , , ), formerly known as Madura, is a major city in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the cultural capital of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Madurai District, which is ...
and looted it of all its wealth.
File:Warangal fort.jpg, Kakatiya Kala Thoranam (Warangal Gate) built by the Kakatiya dynasty
The Kakatiya dynasty (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: Kākatīya) was a Andhras, Telugu dynasty that ruled most of eastern Deccan Plateau, Deccan region in present-day India between 12th and 14th centuries. Their ter ...
in ruins; one of the many temple complexes destroyed by the Delhi Sultanate.
File:Rani ki vav1.jpg, Rani ki Vav
Rani Ki Vav () is a stepwell situated in the town of Patan, Gujarat, Patan in Gujarat, India. It is located on the banks of the Saraswati River, Gujarat, Saraswati River. Its construction is attributed to Udayamati, the spouse of the 11th-centur ...
is a stepwell, built by the Chaulukya dynasty, located in Patan; the city was sacked by Sultan of Delhi Qutb ud-Din Aibak between 1200 and 1210, and again by the Allauddin Khalji in 1298.
File:Elevation of Kirtistambh Rudramahalaya Sidhpur Gujarat India.jpg, Artistic rendition of the Kirtistambha at Rudra Mahalaya Temple. The temple was destroyed by Alauddin Khalji
Alauddin Khalji (; ), born Ali Gurshasp, was a ruler from the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the Indian subcontinent. Alauddin instituted a number of significant administrative changes in the Delhi Sultanate, related to revenue ...
.
File:Exteriors Carvings of Shantaleshwara Shrine 02.jpg, Exterior wall reliefs at Hoysaleshvara Temple. The temple was twice sacked and plundered by the Delhi Sultanate.
See also
* Mongol invasions of India * Delhi Sultanate literature *Iconoclasm
Iconoclasm ()From . ''Iconoclasm'' may also be considered as a back-formation from ''iconoclast'' (Greek: εἰκοκλάστης). The corresponding Greek word for iconoclasm is εἰκονοκλασία, ''eikonoklasia''. is the social belie ...
* Ibrahim Lodi's Tomb
* Persianate states
* Tomb of Bahlol Lodi
* Turkish slaves in the Delhi Sultanate
* Islam in South Asia
Islam is the second-largest religion in South Asia, with more than 650 million Muslims living there, forming about one-third of the region's population. Islam first spread along the coastal regions of the Indian subcontinent and Sri Lanka, almo ...
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * ** * * . * Majumdar, R. C., Raychaudhuri, H., & Datta, K. (1951). An advanced history of India: 2. London: Macmillan. * Majumdar, R. C., & Munshi, K. M. (1990). The Delhi Sultanate. Bombay: Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan. * Prasad, Pushpa (1990). ''Sanskrit Inscriptions of Delhi Sultanate 1191-1526''. Oxford University Press. * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * *External links
* * {{Authority control States and territories established in 1206 Former monarchies of India Former sultanates Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent 1206 establishments in Asia 13th-century establishments in India 1526 disestablishments in India States and territories disestablished in 1526