|
Khusrau Khan
Nasir ud-Din Khusrau Shah, better known as Khusrau Khan, was an Indian Sultan of Delhi for around two months in 1320. Originally from the Gujarat region, he was captured by the Delhi army during Alauddin Khalji's conquest of Malwa in 1305. After being brought to Delhi as a slave, he was converted to Islam. After ascending the throne in 1316, Mubarak Shah gave him the title "Khusrau Khan", and greatly favoured him. Khusrau Khan led a successful campaign to reassert Delhi's control over Devagiri in 1317. The next year, he led an army that besieged Warangal, forcing the Kakatiya ruler Prataparudra to resume tribute payments to Delhi. In 1320, he led a group of Baradus and disgruntled nobles to assassinate Mubarak Shah, and ascended the throne with the regnal name Nasiruddin. However, he was soon deposed by a group of rebels led by the noble ''Malik'' Tughluq, who succeeded him on the throne. Early life According to the Delhi chronicler Amir Khusrau, Khusrau Khan and his br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
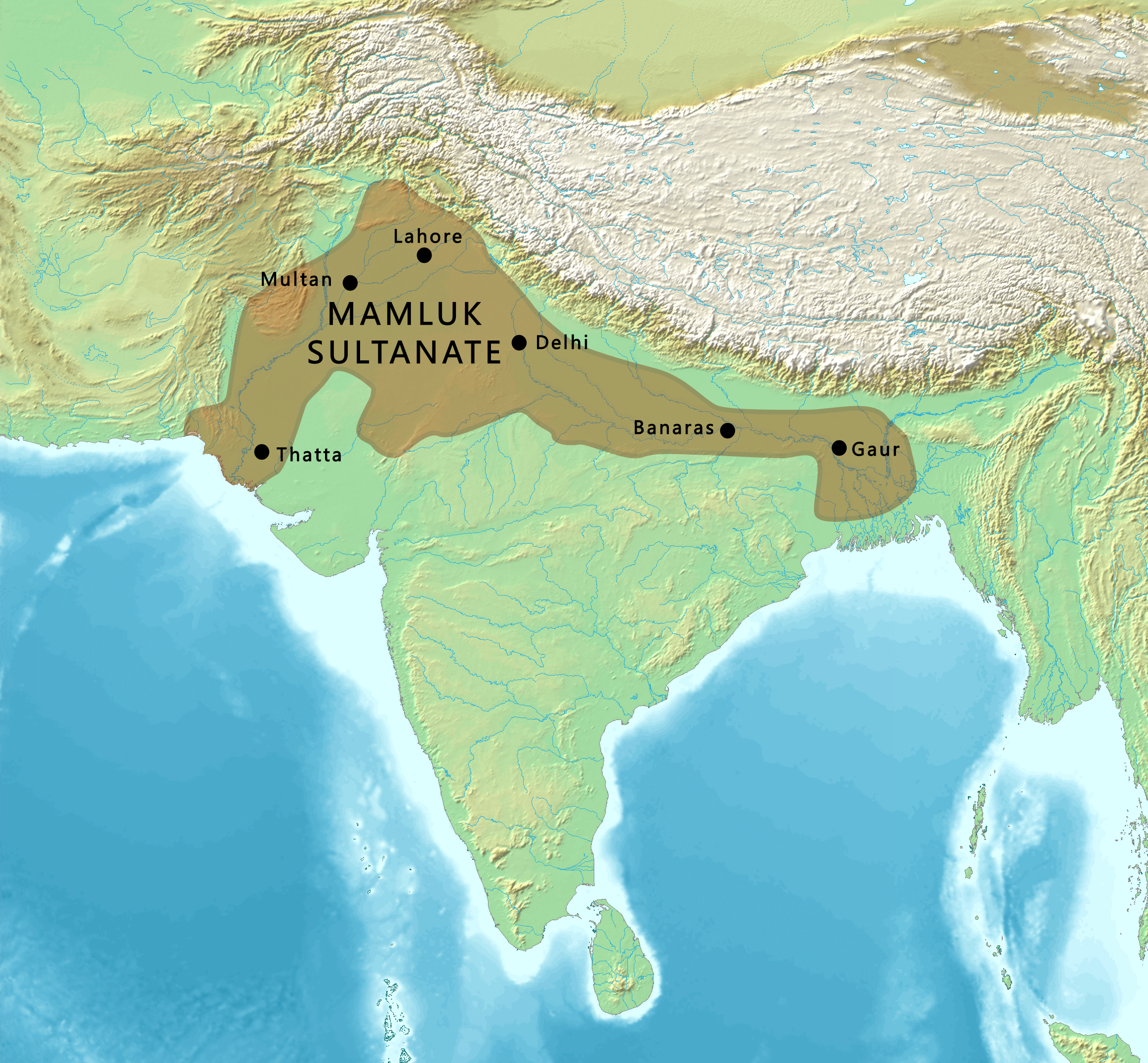
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bharwad
The Bharwad are a Hindu caste found in the state of Gujarat in India, primarily engaged in herding livestock. History According to Sudipta Mitra, historians believe the Bharwards arrived in northern Gujarat in the 10th century, fleeing the Muslim invasions of Sindh. They then spread out throughout Saurashtra. Origin myths According to their origin myth, the goddess Parvati fashioned animals and four men from the sweat and bodily dirt from Shiva's meditation, which Shiva then gave life to. Shamal was the rudest of the four, and he became a camel herder and progenitor of the Rabari camel herders. The better mannered Bharvad received sheep and goats. The handsome and best-mannered Charan became guardian of Nandi and ancestor of cattle herders. Finally, Ahir received land. The four men then married four apsara sisters. In another origin myth, Krishna burned three rolls of dirt on a fire, which he then shaped into Gowals (to watch over his cattle). Krishna had many wives, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dervish
Dervish, Darvesh, or Darwīsh (from ) in Islam can refer broadly to members of a Sufi fraternity (''tariqah''), or more narrowly to a religious mendicant, who chose or accepted material poverty. The latter usage is found particularly in Persian and Turkish (''derviş'') as well as in Tamazight (''Aderwic''), corresponding to the Arabic term '' faqīr''. Their focus is on the universal values of love and service, deserting the illusions of ego (''nafs'') to reach God. In most Sufi orders, a dervish is known to practice ''dhikr'' through physical exertions or religious practices to attain the ecstatic trance to reach God. Their most popular practice is Sama, which is associated with the 13th-century mystic Rumi. In folklore and with adherents of Sufism, dervishes are often credited with the ability to perform miracles and ascribed supernatural powers. Historically, the term Dervish has also been used more loosely, as the designation of various Islamic political movements or mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Firishta
Firishta or Ferešte (), full name Muhammad Qasim Hindu Shah Astarabadi (), was a Persian historian, who later settled in India and served the Deccan Sultans as their court historian. He was born in 1570 and died between 1611 and 1623. Life Firishta was born at Astarabad on the shores of the Caspian Sea to Gholam Ali Hindu Shah. While Firishta was still a child, his father was summoned away from his native country to Ahmednagar, India, to teach Persian to the young prince Miran Husain Nizam Shah, with whom Firishta studied. In 1587 Firishta was serving as the captain of guards of King Murtaza Nizam Shah I when Prince Miran overthrew his father and claimed the throne of Ahmednagar. At this time, the Sunni Deccani Muslims committed a general massacre of the foreign population, especially Shias of Iranian origin, of which Firishta was one of. However, Prince Miran spared the life of his former friend, who then left for Bijapur to enter the service of King Ibrahim Adil II i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
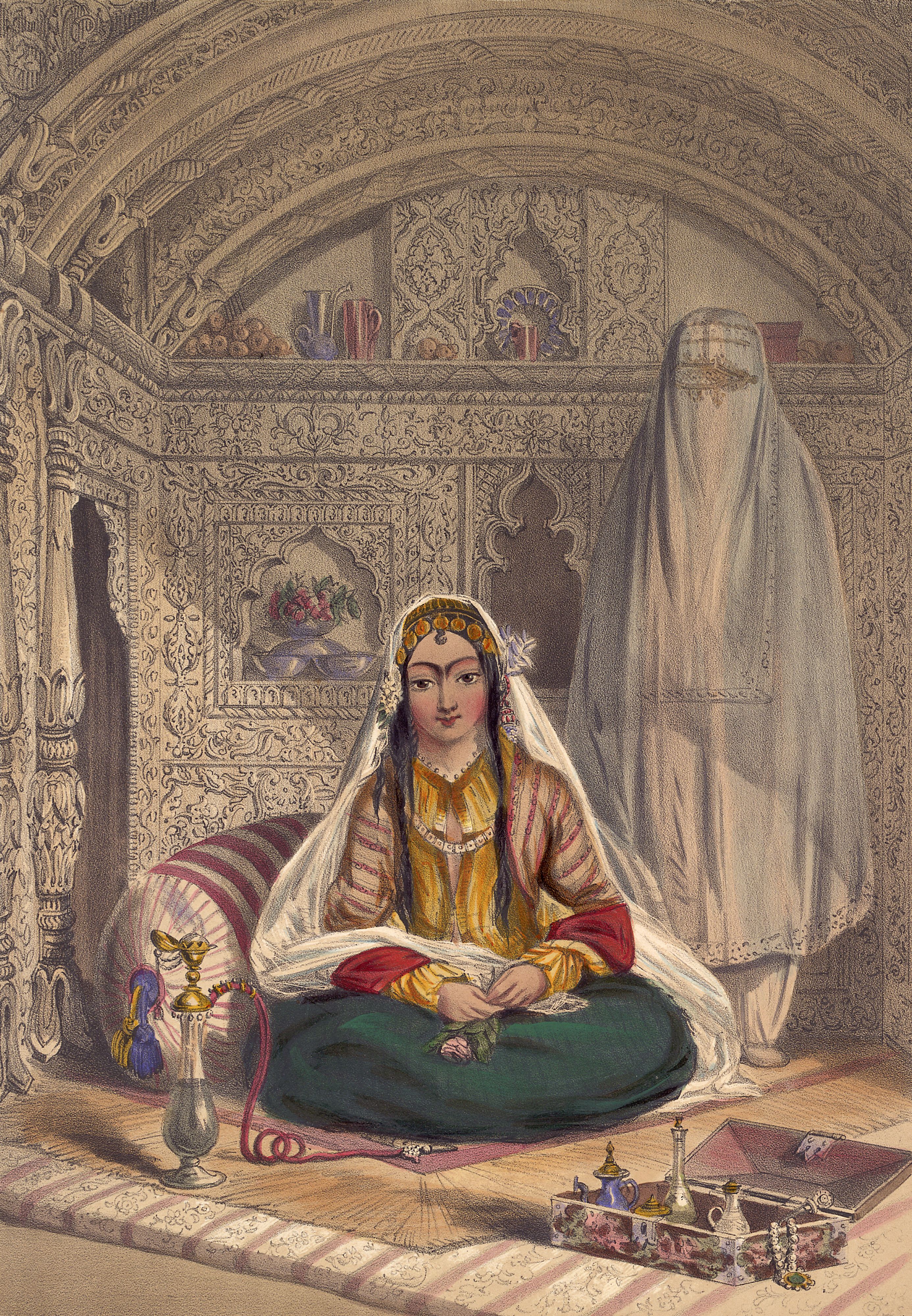
Harem
A harem is a domestic space that is reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A harem may house a man's wife or wives, their pre-pubescent male children, unmarried daughters, female domestic Domestic worker, servants, and other unmarried female relatives. In the past, during the history of slavery in the Muslim world, era of slavery in the Muslim world, harems also housed enslaved Concubinage in Islam, concubines. In former times, some harems were guarded by eunuchs who were allowed inside. The structure of the harem and the extent of monogamy or polygyny have varied depending on the family's personalities, socio-economic status, and local customs. Similar institutions have been common in other Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean and Middle Eastern civilizations, especially among royal and upper-class families, and the term is sometimes used in other contexts. In traditional Persian residential architecture, the women's quarters were known as (), and in the Indian s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Paan
Betel nut chewing, also called betel quid chewing or areca nut chewing, is a practice in which areca nuts (also called "betel nuts") are chewed together with slaked lime and betel leaves for their stimulant and narcotic effects, the primary psychoactive compound being arecoline. The practice is widespread in Southeast Asia, Micronesia, Island Melanesia, and South Asia. It is also found among both Han Chinese immigrants and indigenous peoples of Taiwan, Madagascar, and parts of southern China. It was introduced to the Caribbean in colonial times. The preparation combining the areca nut, slaked lime, and betel (Piper betle) leaves is known as a betel quid (also called ''paan'' or ''pan'' in South Asia), but the exact composition of the mixture varies geographically. It can sometimes include other substances for flavoring and to freshen the breath, like coconut, dates, sugar, menthol, saffron, cloves, aniseed, cardamom, and many others. The areca nut can be replaced with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mount Abu
Mount Abu (), known as Arbudgiri in Jain tradition, is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in the Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India. Here, the mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. It is referred to as 'an oasis in the desert' as its heights are home to rivers, lakes, waterfalls and evergreen forests. It is also home to numerous Jain and Hindu temples. History The ancient name of Mount Abu is Arbuda. In the Puranas, the region has been referred to as ''Arbudaranya'' ("forest of ''Arbuda''") and 'Abu' is a diminutive of this ancient name. It is believed that sage Vashistha retired to the southern spur at Mount Abu following his differences with sage Vishvamitra. There is another history story according to which a serpent named "Arbuda" saved the life of Nandi (Lord Shiva's bull). The incident happened on the mountain that is currently known as Mount Abu and so the mountain is named "Arbudaranya" after that incident which grad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Narmada River
The Narmada River, previously also known as ''Narbada'' or anglicised as ''Nerbudda'', is the 5th longest river in India and overall the longest west-flowing river in the country. It is also the largest flowing river in the state of Madhya Pradesh. This river flows through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat in India. It is also known as the "Lifeline of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat" due to its huge contribution to the two states in many ways. The Narmada River rises from the Amarkantak, Amarkantak Plateau in Anuppur district in Madhya Pradesh. It forms the traditional boundary between North India, North and South India and flows westwards for before draining through the Gulf of Khambhat into the Arabian Sea, west of Bharuch city of Gujarat. It is one of only two major rivers in peninsular India that runs from east to west (longest west flowing river), along with the Tapti River. It is one of the rivers in India that flows in a rift valley, bordered by the Satpura and Vindhy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
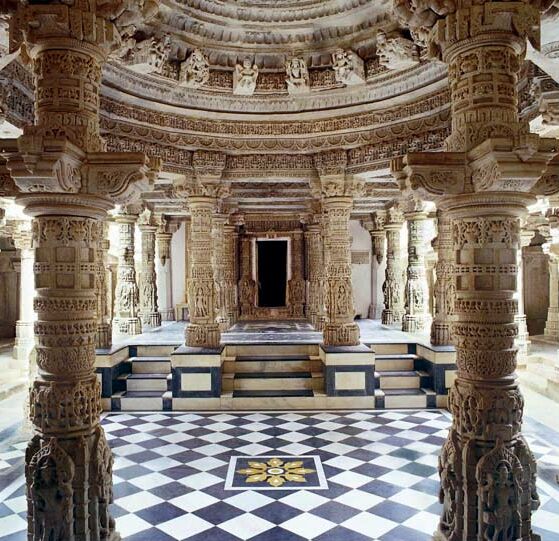
Ellora
The Ellora Caves are a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Aurangabad, India. It is one of the largest rock-cut cave complexes in the world, with artwork dating from the period 600–1000 AD, including Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain caves., Quote: "These 34 monasteries and temples, extending over more than 2 km, were dug side by side in the wall of a high basalt cliff, not far from Aurangabad, in Maharashtra. Ellora, with its uninterrupted sequence of monuments dating from AD 600 to 1000, brings the civilization of ancient India to life. Not only is the Ellora complex a unique artistic creation and a technological exploit but, with its sanctuaries devoted to Hinduism, it illustrates the spirit of tolerance that was characteristic of ancient India." The complex is a leading example of Indian rock-cut architecture, and several are not strictly "caves" in that they have no roof. Cave 16 features the largest single monolithic rock excavation in the world, the Kailash temple, a chariot-shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ziauddin Barani
Ziauddin Barani (; 1285–1357) was an Indian political thinker of the Delhi Sultanate located in present-day Northern India during Muhammad bin Tughlaq and Firuz Shah's reign. He was best known for composing the ''Tarikh-i-Firoz Shahi'' (also called ''Tarikh-i-Firuz Shahi''), a work on medieval India, which covers the period from the reign of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq to the first six years of the reign of Firoz Shah Tughluq; and the ''Fatwa-i-Jahandari'' which promoted a hierarchy among Muslim communities in the Indian subcontinent, although according to M. Athar Ali it was not based on race or even like the caste system, but taking as a model of Sassanid Iran, which promoted an idea of aristocracy through birth and which was claimed by Persians to be "fully in accordance with the main thrust of Islamic thought as it had developed by that time", including in the works of his near-contemporary Ibn Khaldun. Life Barani was born in 1285, to an Indian Muslim family native t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vizier
A vizier (; ; ) is a high-ranking political advisor or Minister (government), minister in the Near East. The Abbasids, Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a helper but afterwards became the representative and successor of the ''dapir'' (official scribe or secretary) of the Sasanian Empire, Sassanian kings. In modern usage, the term has been used for government Minister (government), ministers in much of the Middle East and beyond. Several alternative spellings are used in English, such as ''vizir'', ''wazir'', and ''vezir''. Etymology Vizier may be derived from the Arabic ''wazara'' (), from the Semitic root ''W-Z-R''. The word is mentioned in the Quran, where Aaron is described as the ''wazir'' (helper) of Moses, as well as the word ''wizr'' (burden) which is also derived from the same root. It was later adopted as a title, in the form of ''wazīr āl Muḥammad'' () by the proto-Shi'a leaders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shihabuddin Omar
Shihab-ud-din Omar (1316) was the third Sultan of the Khalji dynasty and fourteenth Sultan of Delhi Sultanate in India. After the death of his father Alauddin Khalji in 1316, he ascended the throne as a toddler, with the support of Alauddin's slave-general Malik Kafur. His brother Qutb-ud-din Mubarak became the regent after the assassination of Kafur and subsequently dethroned him to become the Sultan. Early life According to the 14th century chronicler Isami, Shihab-ud-Din was Alauddin's son from Jhatyapali, the daughter of Alauddin's Yadava feudatory Ramachandra. Ascension to the throne Alauddin fell seriously ill during his last years, and the administration was controlled by his slave-general Malik Kafur. After Alauddin's original heir apparent Khizr Khan was imprisoned at Gwalior for allegedly conspiring to kill him, Malik Kafur convened a meeting of important officers at Alauddin's bedside. It was decided at this meeting that Shihabuddin would succeed Alauddin, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |