metal physics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Metallurgy is a domain of

 The earliest metal employed by humans appears to be
The earliest metal employed by humans appears to be
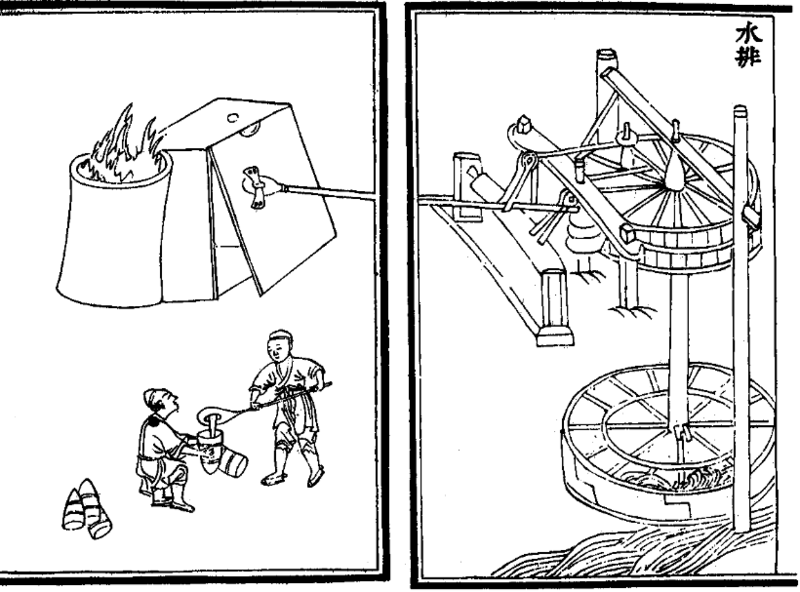
 Much effort has been placed on understanding
Much effort has been placed on understanding
 *
*
 Metals can be heat-treated to alter the properties of strength, ductility, toughness, hardness and resistance to corrosion. Common heat treatment processes include annealing,
Metals can be heat-treated to alter the properties of strength, ductility, toughness, hardness and resistance to corrosion. Common heat treatment processes include annealing,

materials science and engineering
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries.
The intellectual origins of materials scien ...
that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
lic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s.
Metallurgy encompasses both the science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
and the technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible too ...
of metals, including the production of metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
s and the engineering of metal components used in products for both consumers and manufacturers. Metallurgy is distinct from the craft
A craft or trade is a pastime or an occupation that requires particular skills and knowledge of skilled work. In a historical sense, particularly the Middle Ages and earlier, the term is usually applied to people occupied in small scale pr ...
of metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on e ...
. Metalworking relies on metallurgy in a similar manner to how medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
relies on medical science for technical advancement. A specialist practitioner of metallurgy is known as a metallurgist.
The science of metallurgy is further subdivided into two broad categories: chemical metallurgy Chemical metallurgy is the science of obtaining metals from their concentrates, semi products, recycled bodies and solutions, and of considering reactions of metals with an approach of disciplines belonging to chemistry. As such, it involves reacti ...
and physical metallurgy
Physical metallurgy is one of the two main branches of the scientific approach to metallurgy, which considers in a systematic way the physical properties of metals and alloys. It is basically the fundamentals and applications of the theory of ...
. Chemical metallurgy is chiefly concerned with the reduction and oxidation of metals, and the chemical performance of metals. Subjects of study in chemical metallurgy include mineral processing
Mineral processing is the process of separating commercially valuable minerals from their ores in the field of extractive metallurgy. Depending on the processes used in each instance, it is often referred to as ore dressing or ore milling.
Be ...
, the extraction of metals, thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, Work (thermodynamics), work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed b ...
, electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between Electric potential, electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve Electron, electrons moving via an electronic ...
, and chemical degradation (corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
). In contrast, physical metallurgy
Physical metallurgy is one of the two main branches of the scientific approach to metallurgy, which considers in a systematic way the physical properties of metals and alloys. It is basically the fundamentals and applications of the theory of ...
focuses on the mechanical properties of metals, the physical properties of metals, and the physical performance of metals. Topics studied in physical metallurgy include crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In J ...
, material characterization, mechanical metallurgy, phase transformations, and failure mechanisms
Failure causes are defects in design, process, quality, or part application, which are the underlying cause of a failure or which initiate a process which leads to failure. Where failure depends on the user of the product or process, then human er ...
.
Historically, metallurgy has predominately focused on the production of metals. Metal production begins with the processing of ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically including metals, concentrated above background levels, and that is economically viable to mine and process. The grade of ore refers to the concentration ...
s to extract the metal, and includes the mixture of metals to make alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s. Metal alloys are often a blend of at least two different metallic elements. However, non-metallic elements are often added to alloys in order to achieve properties suitable for an application. The study of metal production is subdivided into ferrous metallurgy
Ferrous metallurgy is the metallurgy of iron and its alloys. The earliest surviving prehistoric iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting of iron from ...
(also known as ''black metallurgy'') and non-ferrous metallurgy
In metallurgy, non-ferrous metals are metals or alloys that do not contain iron ( allotropes of iron, ferrite, and so on) in appreciable amounts.
Generally more costly than ferrous metals, non-ferrous metals are used because of desirable prope ...
, also known as colored metallurgy.
Ferrous metallurgy involves processes and alloys based on iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, while non-ferrous metallurgy involves processes and alloys based on other metals. The production of ferrous metals accounts for 95% of world metal production.
Modern metallurgists work in both emerging and traditional areas as part of an interdisciplinary team alongside material scientists and other engineers. Some traditional areas include mineral processing, metal production, heat treatment, failure analysis
Failure analysis is the process of collecting and analyzing data to determine the cause of a failure, often with the goal of determining corrective actions or liability.
According to Bloch and Geitner, ”machinery failures reveal a reaction chain ...
, and the joining of metals (including welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melting, melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Co ...
, brazing
Brazing is a metal-joining process in which two or more metal items are joined by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint, with the filler metal having a lower melting point than the adjoining metal.
Brazing differs from welding in ...
, and soldering
Soldering (; ) is a process of joining two metal surfaces together using a filler metal called solder. The soldering process involves heating the surfaces to be joined and melting the solder, which is then allowed to cool and solidify, creatin ...
). Emerging areas for metallurgists include nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing propertie ...
, superconductors
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases ...
, composites, biomedical materials, electronic materials (semiconductors) and surface engineering.
Etymology and pronunciation
''Metallurgy'' derives from theAncient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
, , "worker in metal", from , , "mine, metal" + , , "work" The word was originally an alchemist
Alchemy (from the Arabic word , ) is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first ...
's term for the extraction of metals from minerals, the ending ''-urgy'' signifying a process, especially manufacturing: it was discussed in this sense in the 1797 ''Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...
''.
In the late 19th century, metallurgy's definition was extended to the more general scientific study of metals, alloys, and related processes. In English, the pronunciation is the more common one in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. The pronunciation is the more common one in the US and is the first-listed variant in various American dictionaries, including ''Merriam-Webster Collegiate'' and ''American Heritage''.
History

gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, which can be found "native
Native may refer to:
People
* '' Jus sanguinis'', nationality by blood
* '' Jus soli'', nationality by location of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Nat ...
". Small amounts of natural gold, dating to the late Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
period, 40,000 BC, have been found in Spanish caves. Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, tin
Tin is a chemical element; it has symbol Sn () and atomic number 50. A silvery-colored metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, a bar of tin makes a sound, the ...
and meteoric iron
Meteoric iron, sometimes meteoritic iron, is a native metal and early-universe protoplanetary-disk remnant found in meteorites and made from the elements iron and nickel, mainly in the form of the mineral phases kamacite and taenite. Meteoric ...
can also be found in native form, allowing a limited amount of metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on e ...
in early cultures. Early cold metallurgy, using native copper
Native copper is an uncombined form of copper that occurs as a natural mineral. Copper is one of the few metallic elements to occur in native form, although it most commonly occurs in oxidized states and mixed with other elements. Native coppe ...
not melted from mineral has been documented at sites in Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and at the site of Tell Maghzaliyah in Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
, dating from the 7th/6th millennia BC.
The earliest archaeological support of smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron-making, iron, copper extraction, copper ...
(hot metallurgy) in Eurasia is found in the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
and Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinav ...
, as evidenced by findings of objects made by metal casting and smelting dated to around 6200–5000 BC, with the invention of copper metallurgy. Certain metals, such as tin, lead, and copper can be recovered from their ores by simply heating the rocks in a fire or blast furnace in a process known as smelting. The first evidence of copper smelting, dating from the 6th millennium BC, has been found at archaeological sites in Majdanpek
Majdanpek ( sr-cyr, Мајданпек; ) is a town and municipality located in the Bor District of the eastern Serbia, and is not far from the border of Romania. According to 2022 census, the municipality of Majdanpek had a population of 14,559 ...
, Jarmovac and Pločnik, in present-day Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
. The site of Pločnik has produced a smelted copper axe dating from 5,500 BC, belonging to the Vinča culture
The Vinča culture , also known as Turdaș culture, Turdaș–Vinča culture or Vinča-Turdaș culture, is a Neolithic archaeological culture of Southeast Europe, dated to the period 5400–4500 BC. It is named for its type site, Vinča-Belo B ...
. The Balkans and adjacent Carpathian
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at ...
region were the location of major Chalcolithic
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in di ...
cultures including Vinča
Vinča ( sr-cyr, Винча, ) is a List of Belgrade neighborhoods, suburban settlement of Belgrade, Serbia. It is part of the municipality of Grocka. Vinča-Belo Brdo, an important archaeological site that gives its name to the Neolithic Vinča c ...
, Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city
** Varna Province
** Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
** Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
* Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
* Varna (Šabac), a village in Serbia
Asia
* Var ...
, Karanovo, Gumelnița and Hamangia, which are often grouped together under the name of ' Old Europe'. With the Carpatho-Balkan region described as the 'earliest metallurgical province in Eurasia', its scale and technical quality of metal production in the 6th–5th millennia BC totally overshadowed that of any other contemporary production centre.
The earliest documented use of lead (possibly native or smelted) in the Near East dates from the 6th millennium BC, is from the late Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
settlements of Yarim Tepe and Arpachiyah in Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
. The artifacts suggest that lead smelting may have predated copper smelting. Metallurgy of lead has also been found in the Balkans during the same period.
Copper smelting is documented at sites in Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and at the site of Tal-i Iblis in southeastern Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
from .
Copper smelting is first documented in the Delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
region of northern Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
in , associated with the Maadi culture. This represents the earliest evidence for smelting in Africa.
The Varna Necropolis
The Varna Necropolis (), or Varna Cemetery, is a burial site in the western industrial zone of Varna, Bulgaria, Varna (approximately half a kilometre from Lake Varna and 4 km from the city centre), internationally considered one of the key a ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, is a burial site located in the western industrial zone of Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city
** Varna Province
** Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
** Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
* Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
* Varna (Šabac), a village in Serbia
Asia
* Var ...
, approximately 4 km from the city centre, internationally considered one of the key archaeological sites in world prehistory. The oldest gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
treasure in the world, dating from 4,600 BC to 4,200 BC, was discovered at the site. The gold piece dating from 4,500 BC, found in 2019 in Durankulak, near Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city
** Varna Province
** Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
** Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
* Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
* Varna (Šabac), a village in Serbia
Asia
* Var ...
is another important example. Other signs of early metals are found from the third millennium BC in Palmela
Palmela () is a town and municipality in Portugal. As of 2011, the population was 62,831, covering an area of 465.12 km².
The municipality is located in the Lisboa Region and Setúbal District, about south of Lisbon. The municipal holiday ...
, Portugal, Los Millares, Spain, and Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric Megalith, megalithic structure on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, to ...
, United Kingdom. The precise beginnings, however, have not be clearly ascertained and new discoveries are both continuous and ongoing.
In approximately 1900 BC, ancient iron smelting sites existed in Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
.
In the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
, about 3,500 BC, it was discovered that by combining copper and tin, a superior metal could be made, an alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
called bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
. This represented a major technological shift known as the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
.
The extraction of iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
from its ore into a workable metal is much more difficult than for copper or tin. The process appears to have been invented by the Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
in about 1200 BC, beginning the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
. The secret of extracting and working iron was a key factor in the success of the Philistines
Philistines (; LXX: ; ) were ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan during the Iron Age in a confederation of city-states generally referred to as Philistia.
There is compelling evidence to suggest that the Philistines origi ...
.W. Keller (1963) ''The Bible as History''. p. 156.
Historical developments in ferrous metallurgy can be found in a wide variety of past cultures and civilizations. This includes the ancient and medieval kingdoms and empires of the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
and Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
, ancient Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, ancient Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, ancient Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
, and Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
in present-day Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, Ancient Nok, Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
, the Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
, Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
and Romans of ancient Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, medieval Europe, ancient and medieval China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, ancient and medieval India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, ancient and medieval Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, amongst others.
A 16th century book by Georg Agricola
Georgius Agricola (; born Georg Bauer; 24 March 1494 – 21 November 1555) was a German Humanist scholar, mineralogist and metallurgist. Born in the small town of Glauchau, in the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire, he was broa ...
, '' De re metallica'', describes the highly developed and complex processes of mining metal ores, metal extraction, and metallurgy of the time. Agricola has been described as the "father of metallurgy".
Extraction

Extractive metallurgy
Extractive metallurgy is a branch of metallurgical engineering wherein process and methods of extraction of metals from their natural mineral deposits are studied. The field is a materials science, covering all aspects of the types of ore, was ...
is the practice of removing valuable metals from an ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically including metals, concentrated above background levels, and that is economically viable to mine and process. The grade of ore refers to the concentration ...
and refining the extracted raw metals into a purer form. In order to convert a metal oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
or sulphide
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families of i ...
to a purer metal, the ore must be reduced physically, chemically, or electrolytically. Extractive metallurgist
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
s are interested in three primary streams: feed, concentrate (metal oxide/sulphide) and tailings
In mining, tailings or tails are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction (gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different from overburden, which is the waste rock or other material ...
(waste).
After mining, large pieces of the ore feed are broken through crushing or grinding in order to obtain particles small enough, where each particle is either mostly valuable or mostly waste. Concentrating the particles of value in a form supporting separation enables the desired metal to be removed from waste products.
Mining may not be necessary, if the ore body and physical environment are conducive to leaching. Leaching dissolves minerals in an ore body and results in an enriched solution. The solution is collected and processed to extract valuable metals. Ore bodies often contain more than one valuable metal.
Tailings of a previous process may be used as a feed in another process to extract a secondary product from the original ore. Additionally, a concentrate may contain more than one valuable metal. That concentrate would then be processed to separate the valuable metals into individual constituents.
Metal and its alloys
 Much effort has been placed on understanding
Much effort has been placed on understanding iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
–carbon alloy system, which includes steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
s and cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
s. Plain carbon steels (those that contain essentially only carbon as an alloying element) are used in low-cost, high-strength applications, where neither weight nor corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
are a major concern. Cast irons, including ductile iron
Ductile iron, also known as ductile cast iron, nodular cast iron, spheroidal graphite iron, spheroidal graphite cast iron and SG iron, is a type of graphite-rich cast iron discovered in 1943 by Keith Millis. While most varieties of cast iron are ...
, are also part of the iron-carbon system. Iron-Manganese-Chromium alloys (Hadfield-type steels) are also used in non-magnetic applications such as directional drilling.
Other engineering metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
s include aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
, chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
, titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, and silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
. These metals are most often used as alloys with the noted exception of silicon, which is not a metal. Other forms include:
* Stainless steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromi ...
, particularly Austenitic stainless steel
Austenitic stainless steel is one of the five families of stainless steel (along with ferritic, martensitic, duplex and precipitation hardened). Its primary crystalline structure is austenite (face-centered cubic). Such steels are not hardena ...
s, galvanized steel
Galvanization ( also spelled galvanisation) is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, to prevent rusting. The most common method is hot-dip galvanizing, in which the parts are coated by submerging them in a bath of ...
, nickel alloys
This is a list of named alloys grouped alphabetically by the metal with the highest percentage. Within these headings, the alloys are also grouped alphabetically. Some of the main alloying elements are optionally listed after the alloy names.
Al ...
, titanium alloys
Titanium alloys are alloys that contain a mixture of titanium and other chemical elements. Such alloys have very high tensile strength and toughness (even at extreme temperatures). They are light in weight, have extraordinary corrosion resistance ...
, or occasionally copper alloys
Copper alloys are metal Alloy, alloys that have copper as their principal component. They have high resistance against corrosion. Of the large number of different types, the best known traditional types are bronze, where tin is a significant addi ...
are used, where resistance to corrosion is important.
* Aluminium alloys and magnesium alloys are commonly used, when a lightweight strong part is required such as in automotive and aerospace applications.
* Copper-nickel alloys (such as Monel
Monel is a group of alloys of nickel (from 52 to 68%) and copper, with small amounts of iron, manganese, carbon, and silicon. Monel is not a cupronickel alloy because it has less than 60% copper.
Stronger than pure nickel, Monel alloys are res ...
) are used in highly corrosive environments and for non-magnetic applications.
* Nickel-based superalloy
A superalloy, or high-performance alloy, is an alloy with the ability to operate at a high fraction of its melting point. Key characteristics of a superalloy include mechanical strength, thermal creep deformation resistance, surface stability, ...
s like Inconel
Inconel is a nickel-chromium-based superalloy often utilized in extreme environments where components are subjected to high temperature, pressure or Mechanical load, mechanical loads. Inconel alloys are oxidation- and corrosion-resistant. When he ...
are used in high-temperature applications such as gas turbine
A gas turbine or gas turbine engine is a type of Internal combustion engine#Continuous combustion, continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas gene ...
s, turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into th ...
s, pressure vessel
A pressure vessel is a container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure.
Construction methods and materials may be chosen to suit the pressure application, and will depend on the size o ...
s, and heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contac ...
s.
* For extremely high temperatures, single crystal
In materials science, a single crystal (or single-crystal solid or monocrystalline solid) is a material in which the crystal lattice of the entire sample is continuous and unbroken to the edges of the sample, with no Grain boundary, grain bound ...
alloys are used to minimize creep. In modern electronics, high purity single crystal silicon is essential for metal-oxide-silicon transistors (MOS) and integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
s.
Production
Inproduction engineering
Manufacturing engineering or production engineering is a branch of professional engineering that shares many common concepts and ideas with other fields of engineering such as mechanical, chemical, electrical, and industrial engineering.
Manufac ...
, metallurgy is concerned with the production of metallic components for use in consumer or engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
products. This involves production of alloys, shaping, heat treatment and surface treatment of product. The task of the metallurgist is to achieve balance between material properties, such as cost, weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is a quantity associated with the gravitational force exerted on the object by other objects in its environment, although there is some variation and debate as to the exact definition.
Some sta ...
, strength
Strength may refer to:
Personal trait
*Physical strength, as in people or animals
*Character strengths like those listed in the Values in Action Inventory
*The exercise of willpower
Physics
* Mechanical strength, the ability to withstand ...
, toughness
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing.hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion ...
, corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
, fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
resistance and performance in temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
extremes. To achieve this goal, the operating environment must be carefully considered.
Determining the hardness of the metal using the Rockwell, Vickers, and Brinell hardness scales is a commonly used practice that helps better understand the metal's elasticity and plasticity for different applications and production processes. In a saltwater environment, most ferrous metals and some non-ferrous alloys corrode quickly. Metals exposed to cold or cryogenic
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.
The 13th International Institute of Refrigeration's (IIR) International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington, DC in 1971) endorsed a univers ...
conditions may undergo a ductile to brittle transition and lose their toughness, becoming more brittle and prone to cracking. Metals under continual cyclic loading can suffer from metal fatigue
In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striation (fatigue), striati ...
. Metals under constant stress at elevated temperatures can creep.
Metalworking processes
 *
* Casting
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or ...
– molten metal is poured into a shaped mold
A mold () or mould () is one of the structures that certain fungus, fungi can form. The dust-like, colored appearance of molds is due to the formation of Spore#Fungi, spores containing Secondary metabolite#Fungal secondary metabolites, fungal ...
. Variants of casting include sand casting
Sand casting, also known as sand molded casting, is a metal casting process characterized by using sand—known as ''casting sand''—as the mold material. The term "sand casting" can also refer to an object produced via the sand casting proces ...
, investment casting
Investment casting is an industrial process based on lost-wax casting, one of the oldest known metal-forming techniques. The term "lost-wax casting" can also refer to modern investment casting processes.
Investment casting has been used in vari ...
, also called the lost wax process, die casting
Die casting is a casting (metalworking), metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel die (manufacturing), dies which have been ...
, centrifugal casting, both vertical and horizontal, and continuous castings. Each of these forms has advantages for certain metals and applications considering factors like magnetism and corrosion.
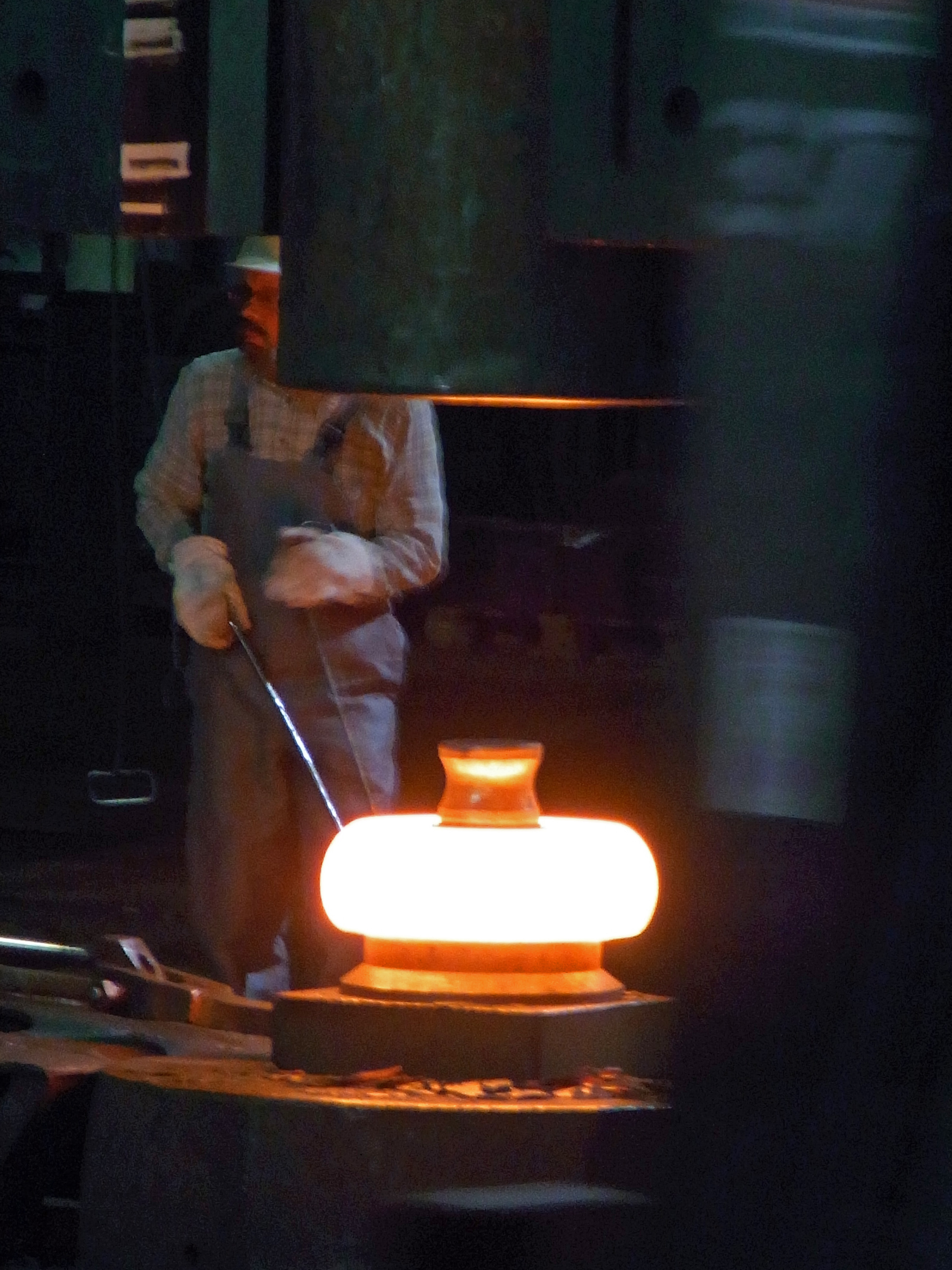
* Forging
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compression (physics), compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die (manufacturing), die. Forging is often classif ...
– a red-hot billet
In European militaries, a billet is a living-quarters to which a soldier is assigned to sleep. In American usage, it refers to a specific personnel position, assignment, or duty station to which a soldier can be assigned. Historically, a billet w ...
is hammered into shape.
* Rolling
Rolling is a Motion (physics)#Types of motion, type of motion that combines rotation (commonly, of an Axial symmetry, axially symmetric object) and Translation (geometry), translation of that object with respect to a surface (either one or the ot ...
– a billet is passed through successively narrower rollers to create a sheet.
* Extrusion
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross section (geometry), cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a Die (manufacturing), die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing pro ...
– a hot and malleable metal is forced under pressure through a die, which shapes it before it cools.
* Machining
Machining is a manufacturing process where a desired shape or part is created using the controlled removal of material, most often metal, from a larger piece of raw material by cutting. Machining is a form of subtractive manufacturing, which util ...
– lathes
A lathe () is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece about an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, threading and turning, with tools that are applied to the ...
, milling machine
Milling is the process of machining using rotary cutters to remove material by advancing a cutter into a workpiece. This may be done by varying directions on one or several axes, cutter head speed, and pressure. Milling covers a wide variety of ...
s and drill
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a drill bit for making holes, or a screwdriver bit for securing fasteners. Historically, they were powered by hand, and later mains power, but cordless b ...
s cut the cold metal to shape.
* Sintering
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, plas ...
– a powdered metal is heated in a non-oxidizing environment after being compressed into a die.
* Fabrication
Fabrication may refer to:
* Manufacturing, specifically the crafting of individual parts as a solo product or as part of a larger combined product.
Processes in arts, crafts and manufacturing
*Semiconductor device fabrication, the process used t ...
– sheets of metal are cut with guillotine
A guillotine ( ) is an apparatus designed for effectively carrying out executions by Decapitation, beheading. The device consists of a tall, upright frame with a weighted and angled blade suspended at the top. The condemned person is secur ...
s or gas cutters and bent and welded into structural shape.
* Laser cladding – metallic powder is blown through a movable laser beam (e.g. mounted on a NC 5-axis machine). The resulting melted metal reaches a substrate to form a melt pool. By moving the laser head, it is possible to stack the tracks and build up a three-dimensional piece.
* 3D printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer ...
– Sintering or melting amorphous powder metal in a 3D space to make any object to shape.
Cold-working processes, in which the product's shape is altered by rolling, fabrication or other processes, while the product is cold, can increase the strength of the product by a process called work hardening
Work hardening, also known as strain hardening, is the process by which a material's load-bearing capacity (strength) increases during plastic (permanent) deformation. This characteristic is what sets ductile materials apart from brittle materi ...
. Work hardening creates microscopic defects in the metal, which resist further changes of shape.
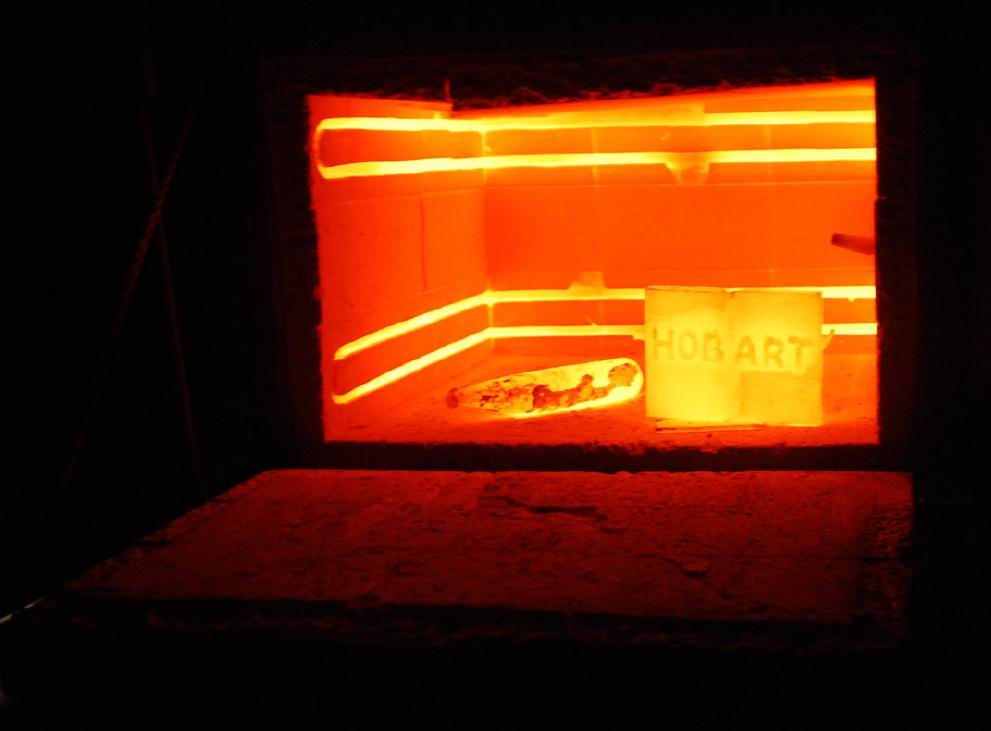
Heat treatment
 Metals can be heat-treated to alter the properties of strength, ductility, toughness, hardness and resistance to corrosion. Common heat treatment processes include annealing,
Metals can be heat-treated to alter the properties of strength, ductility, toughness, hardness and resistance to corrosion. Common heat treatment processes include annealing, precipitation strengthening
Precipitation hardening, also called age hardening or particle hardening, is a heat treatment technique used to increase the Yield (engineering), yield strength of malleable materials, including most structural alloys of aluminium, magnesium, nic ...
, quenching, and tempering:
* Annealing process softens the metal by heating it and then allowing it to cool very slowly, which gets rid of stresses in the metal and makes the grain structure large and soft-edged so that, when the metal is hit or stressed it dents or perhaps bends, rather than breaking; it is also easier to sand, grind, or cut annealed metal.
* Quenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, gas, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, suc ...
is the process of cooling metal very quickly after heating, thus "freezing" the metal's molecules in the very hard martensite form, which makes the metal harder.
* Tempering relieves stresses in the metal that were caused by the hardening process; tempering makes the metal less hard while making it better able to sustain impacts without breaking.
Often, mechanical and thermal treatments are combined in what are known as thermo-mechanical treatments for better properties and more efficient processing of materials. These processes are common to high-alloy special steels, superalloy
A superalloy, or high-performance alloy, is an alloy with the ability to operate at a high fraction of its melting point. Key characteristics of a superalloy include mechanical strength, thermal creep deformation resistance, surface stability, ...
s and titanium alloys.
Plating
Electroplating
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the redox, reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct current, direct electric cur ...
is a chemical surface-treatment technique. It involves bonding a thin layer of another metal such as gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
or zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
to the surface of the product. This is done by selecting the coating material electrolyte solution, which is the material that is going to coat the workpiece (gold, silver, zinc). There needs to be two electrodes of different materials: one the same material as the coating material and one that is receiving the coating material. Two electrodes are electrically charged and the coating material is stuck to the work piece. It is used to reduce corrosion as well as to improve the product's aesthetic appearance. It is also used to make inexpensive metals look like the more expensive ones (gold, silver).
Shot peening
Shot peening is a cold working process used to finish metal parts. In the process of shot peening, small round shot is blasted against the surface of the part to be finished. This process is used to prolong the product life of the part, prevent stress corrosion failures, and also prevent fatigue. The shot leaves small dimples on the surface like a peen hammer does, which cause compression stress under the dimple. As the shot media strikes the material over and over, it forms many overlapping dimples throughout the piece being treated. The compression stress in the surface of the material strengthens the part and makes it more resistant to fatigue failure, stress failures, corrosion failure, and cracking.Thermal spraying
Thermal spraying techniques are another popular finishing option, and often have better high temperature properties than electroplated coatings. Thermal spraying, also known as a spray welding process, is an industrial coating process that consists of a heat source (flame or other) and a coating material that can be in a powder or wire form, which is melted then sprayed on the surface of the material being treated at a high velocity. The spray treating process is known by many different names such as HVOF (High Velocity Oxygen Fuel), plasma spray, flame spray, arc spray and metalizing.Electroless deposition
Electroless deposition (ED) or electroless plating is defined as the autocatalytic process through which metals and metal alloys are deposited onto nonconductive surfaces. These nonconductive surfaces include plastics, ceramics, and glass etc., which can then become decorative, anti-corrosive, and conductive depending on their final functions. Electroless deposition is a chemical processes that createmetal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
coatings on various materials by autocatalytic chemical reduction of metal cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s in a liquid bath.
Characterization

Metallurgist
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
s study the microscopic and macroscopic structure of metals using metallography
Metallography is the study of the physical structure and components of metals, by using microscopy.
Ceramic and polymeric materials may also be prepared using metallographic techniques, hence the terms ceramography, plastography and, collecti ...
, a technique invented by Henry Clifton Sorby
Henry Clifton Sorby (10 May 1826 – 9 March 1908) was an English amateur microscopist and geologist. His major contribution was the development of techniques for thin sectioning of rocks and minerals with polarized light under a microscope whi ...
.
In metallography, an alloy of interest is ground flat and polished to a mirror finish. The sample can then be etched to reveal the microstructure and macrostructure of the metal. The sample is then examined in an optical or electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing it ...
, and the image contrast provides details on the composition, mechanical properties, and processing history.
Crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In J ...
, often using diffraction
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the Wave propagation ...
of x-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s or electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s, is another valuable tool available to the modern metallurgist. Crystallography allows identification of unknown materials and reveals the crystal structure of the sample. Quantitative crystallography can be used to calculate the amount of phases present as well as the degree of strain to which a sample has been subjected.
Current advanced characterization techniques, which are used frequently in this field are: Scanning Electron Microscopy
A scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces images of a sample by scanning the surface with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that ...
(SEM), Transmission Electron Microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a g ...
(TEM), Electron Backscattered Diffraction (EBSD) and Atom-Probe Tomography
The atom probe was introduced at th14th Field Emission Symposium in 1967by Erwin Wilhelm Müller and J. A. Panitz. It combined a field ion microscope with a mass spectrometer having a single particle detection capability and, for the first time ...
(APT).
See also
*Adrien Chenot
Adrien C. B. Chenot (born on August 30, 1803; died November 27, 1855) was a French engineer best known for his inventions in metallurgy as well as his research on manufactured gases. He is notably the inventor of one of the first modern methods of ...
* Archaeometallurgy
* Blacksmith
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from #Other metals, other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such ...
* CALPHAD
* Carbonyl metallurgy
* Cupellation
Cupellation is a refining process in metallurgy in which ores or alloyed metals are treated under very high temperatures and subjected to controlled operations to separate noble metals, like gold and silver, from base metals, like lead, co ...
* Experimental archaeometallurgy
* Forging
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compression (physics), compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die (manufacturing), die. Forging is often classif ...
* Goldbeating
upA gold nugget of 5 mm (0.2 in) in diameter (bottom) can be expanded through hammering into a gold foil of about 0.5 m2 (5.4 sq ft). The Japan.html" ;"title="Toi gold mine museum, Japan">Toi gold mine museum, Japan.
Gold leaf is gold that has ...
* Gold phosphine complex
* Metallurgical failure analysis
Metallurgical failure analysis is the process to determine the mechanism that has caused a metal component to fail. It can identify the cause of failure, providing insight into the root cause and potential solutions to prevent similar failures in ...
* Metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on e ...
* Mineral industry
* Pyrometallurgy
* Welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melting, melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Co ...
References
{{Authority control Metals