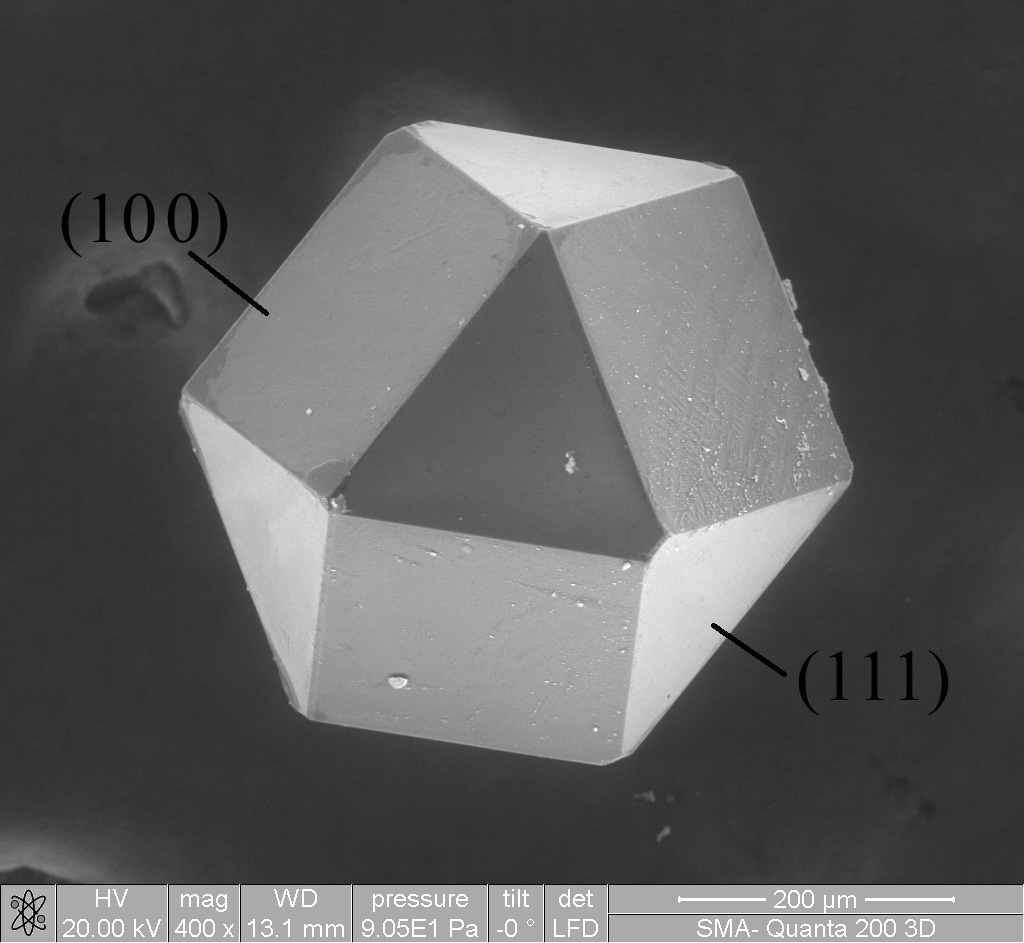
|
Single Crystal
In materials science, a single crystal (or single-crystal solid or monocrystalline solid) is a material in which the crystal lattice of the entire sample is continuous and unbroken to the edges of the sample, with no Grain boundary, grain boundaries. The absence of the crystallographic defect, defects associated with grain boundaries can give monocrystals unique properties, particularly mechanical, optical and electrical, which can also be anisotropic, depending on the type of crystallography, crystallographic structure. These properties, in addition to making some gems precious, are industrially used in technological applications, especially in optics and electronics. Because entropy, entropic effects favor the presence of some imperfections in the microstructure of solids, such as impurity, impurities, inhomogeneous strain and crystallographic defects such as dislocations, perfect single crystals of meaningful size are exceedingly rare in nature. The necessary laboratory condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materials Science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries. The intellectual origins of materials science stem from the Age of Enlightenment, when researchers began to use analytical thinking from chemistry, physics, and engineering to understand ancient, phenomenological observations in metallurgy and mineralogy. Materials science still incorporates elements of physics, chemistry, and engineering. As such, the field was long considered by academic institutions as a sub-field of these related fields. Beginning in the 1940s, materials science began to be more widely recognized as a specific and distinct field of science and engineering, and major technical universities around the world created dedicated schools for its study. Materials scientists emphasize understanding how the history of a material (''processing'') influences its struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracrystalline
In materials science, paracrystalline materials are defined as having short- and medium-range ordering in their lattice (similar to the liquid crystal phases) but lacking crystal-like long-range ordering at least in one direction. Origin and definition The words "paracrystallinity" and "paracrystal" were coined by the late Friedrich Rinne in the year 1933. Their German equivalents, e.g. "Parakristall", appeared in print one year earlier. A general theory of paracrystals has been formulated in a basic textbook, and then further developed/refined by various authors. Rolf Hosemann's definition of an ideal paracrystal is: "The electron density distribution of any material is equivalent to that of a paracrystal when there is for every building block one ideal point so that the distance statistics to other ideal points are identical for all of these points. The electron configuration of each building block around its ideal point is statistically independent of its counterpart in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz Synthese
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is, therefore, classified structurally as a framework silicate mineral and compositionally as an oxide mineral. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Vapor Deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high-quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films. In typical CVD, the wafer (electronics), wafer (substrate) is exposed to one or more Volatility (chemistry), volatile wikt:precursor, precursors, which chemical reaction, react and/or chemical decomposition, decompose on the substrate surface to produce the desired deposit. Frequently, volatile by-products are also produced, which are removed by gas flow through the reaction chamber. Microfabrication processes widely use CVD to deposit materials in various forms, including: Single crystal, monocrystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, and Epitaxy, epitaxial. These materials include: silicon (Silicon dioxide, dioxide, silicon carbide, carbide, silicon nitride, nitride, silicon oxynitride, oxynitride), carbon (carbon (fiber), fiber, carbon nanofibers, nanofibers, carbon nanot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verneuil Method
The Verneuil method (or Verneuil process or Verneuil technique), also called flame fusion, was the first commercially successful method of manufacturing synthetic gemstones, developed in the late 1883 by the French chemist Auguste Verneuil. It is primarily used to produce the ruby, sapphire and padparadscha varieties of corundum, as well as the diamond simulants rutile, strontium titanate and spinel. The principle of the process involves melting a finely powdered substance using an oxyhydrogen flame, and crystallising the melted droplets into a boule. The process is considered to be the founding step of modern industrial crystal growth technology, and remains in wide use to this day. History Since the study of alchemy began, there have been attempts to synthetically produce precious stones, and ruby, being one of the prized cardinal gems, has long been a prime candidate. In the 19th century, significant advances were achieved, with the first ruby formed by melting two sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyropoulos Method
The Kyropoulos method, also known as the KY method or Kyropoulos technique, is a method of bulk crystal growth used to obtain single crystals. The largest application of the Kyropoulos method is to grow large boules of single crystal sapphire used to produce substrates for the manufacture gallium nitride-based LEDs, and as a durable optical material.Dobrovinskaya, Elena R., Leonid A. Lytvynov, and Valerian Pishchik. Sapphire: material, manufacturing, applications. Springer Science & Business Media, 2009. History The method is named for , who proposed the technique in 1926 as a method to grow brittle alkali halide and alkali earth metal crystals for precision optics. The method was a response to the limited boule sizes attainable by the Czochralski and Verneuil methods at the time. The Kyropoulos method was applied to sapphire crystal growth in the 1970s in the Soviet Union. The method The feedstock is melted in a crucible. (For sapphire crystal growth, the feed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recrystallization (chemistry)
Recrystallization is a broad class of List of purification methods in chemistry , chemical purification techniques characterized by the dissolution of an impure sample in a solvent or solvent mixture, followed by some change in conditions that encourages the formation of pure isolate as solid crystals. Recrystallization as a purification technique is driven by spontaneous process , spontaneous processes of molecular self-assembly , self-assembly that leverage the highly ordered (i.e. low-entropy) and periodic characteristics of a crystal's molecular structure to produce purification. Basic principles The driving force of this purification emerges from the difference in molecular interactions between the isolate and the impurities: if a molecule of the desired isolate interacts with any isolate crystal present, it is likely the molecule Deposition (chemistry) , deposits on the crystal's ordered surface and contributes to the crystal's growth; if a molecule of the impurity inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sublimation (chemistry)
Sublimation is the Phase transition, transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas state, without passing through the liquid state. The verb form of sublimation is ''sublime'', or less preferably, ''sublimate''. ''Sublimate'' also refers to the product obtained by sublimation. The point at which sublimation occurs rapidly (for further details, see #False correspondence with vaporization, below) is called critical sublimation point, or simply sublimation point. Notable examples include sublimation of dry ice at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, and that of solid iodine with heating. The reverse process of sublimation is deposition (phase transition), ''deposition'' (also called ''desublimation''), in which a substance passes directly from a gas to a solid phase, without passing through the liquid state. Technically, all solids may sublime, though most sublime at extremely low rates that are hardly detectable under usual conditions. At standard condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrothermal Synthesis
Hydrothermal synthesis includes the various techniques of synthesizing substances from high-temperature aqueous solutions at high pressures; also termed "hydrothermal method". The term "hydrothermal" is of geologic origin. Geochemists and mineralogists have studied hydrothermal phase equilibria since the beginning of the twentieth century. George W. Morey at the Carnegie Institution and later, Percy W. Bridgman at Harvard University did much of the work to lay the foundations necessary to containment of reactive media in the temperature and pressure range where most of the hydrothermal work is conducted. In the broadest definition, a process is considered hydrothermal if it involves water temperatures above and pressures above 1 atm. In the context of material science, hydrothermal synthesis focuses on the production of single crystal. Under high temperature > (300 °C) and pressure (> 100 atm), ordinarily insoluble minerals become soluble in water. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Telephone Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the company operates several laboratories in the United States and around the world. As a former subsidiary of the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T), Bell Labs and its researchers have been credited with the development of radio astronomy, the transistor, the laser, the photovoltaic cell, the charge-coupled device (CCD), information theory, the Unix operating system, and the programming languages B (programming language), B, C (programming language), C, C++, S (programming language), S, SNOBOL, AWK, AMPL, and others, throughout the 20th century. Eleven Nobel Prizes and five Turing Awards have been awarded for work completed at Bell Laboratories. Bell Labs had its origin in the complex corporate organization of the Bell System telepho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zone Melting
Zone melting (or zone refining, or floating-zone method, or floating-zone technique) is a group of similar methods of purifying crystals, in which a narrow region of a crystal is melted, and this molten zone is moved through the crystal. The molten region melts impure solid at its forward edge and leaves a wake of purer material solidified behind it as it moves through the ingot. The impurities concentrate in the melt, and are moved to one end of the ingot. Zone refining was invented by John Desmond Bernal and further developed by William G. PfannWilliam G. Pfann (1966) ''Zone Melting'', 2nd edition, John Wiley & Sons in Bell Labs as a method to prepare high-purity materials, mainly semiconductors, for manufacturing transistors. Its first commercial use was in germanium, refined to one atom of impurity per ten billion,”Zone melting”, entry in ''The World Book Encyclopedia'', Volume 21, W-X-Y-Z, 1973, page 501. but the process can be extended to virtually any solute–solvent sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |