|
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide (TiO2), is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and cata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or Colour Index International, CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble in water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structures of rutile and anatase are tetragonal in symmetry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
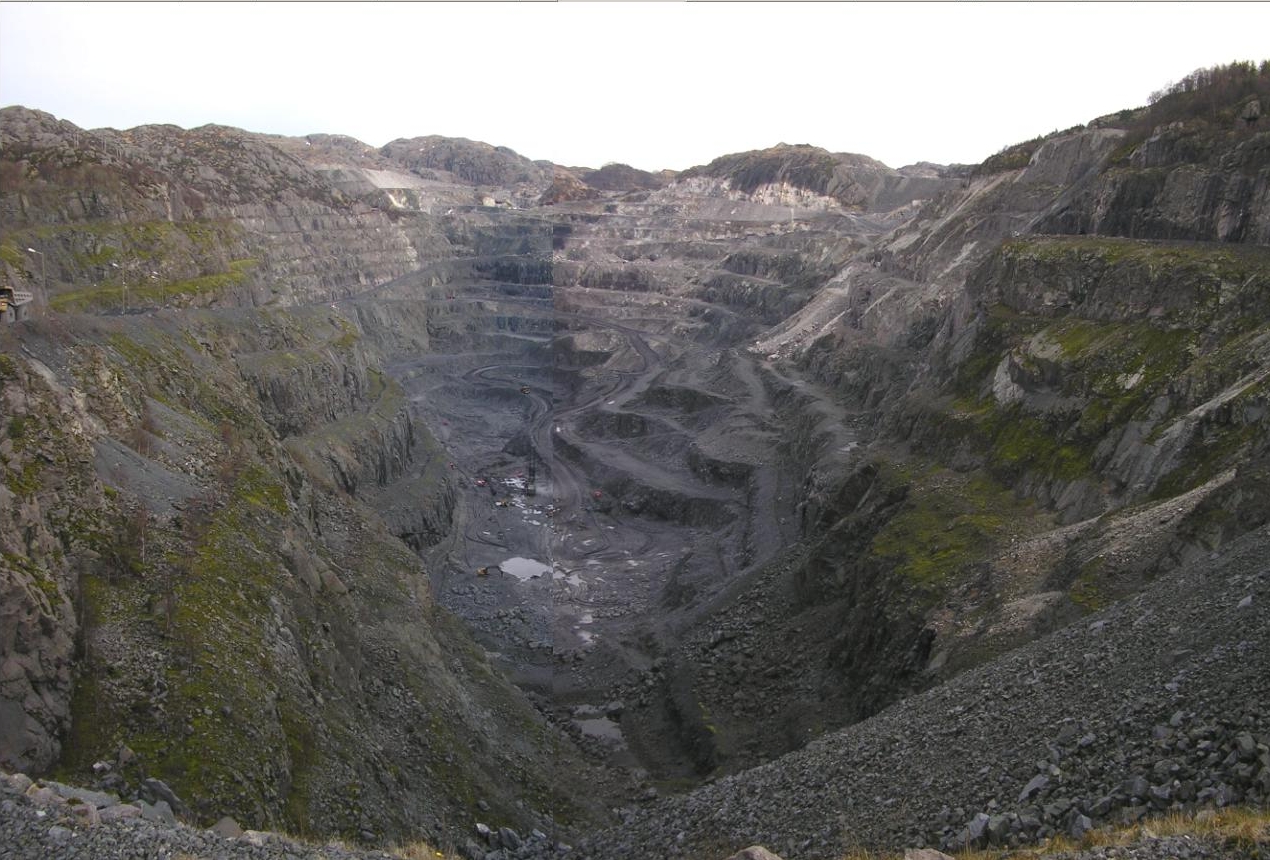
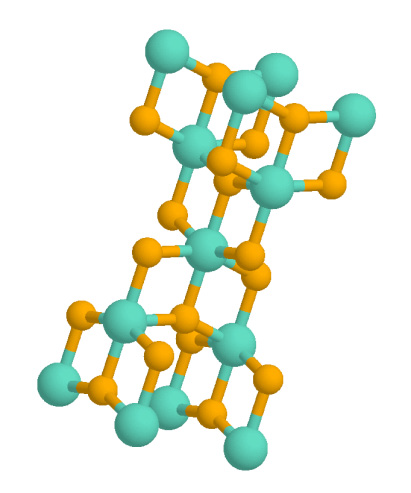
Ilmenite
Ilmenite is a titanium-iron oxide mineral with the idealized formula . It is a weakly magnetic black or steel-gray solid. Ilmenite is the most important ore of titanium and the main source of titanium dioxide, which is used in paints, printing inks, fabrics, plastics, paper, sunscreen, food and cosmetics. Structure and properties Ilmenite is a heavy (specific gravity 4.7), moderately hard (Mohs hardness 5.6 to 6), opaque black mineral with a submetallic luster. It is almost always massive, with thick tabular crystals being quite rare. It shows no discernible cleavage, breaking instead with a conchoidal to uneven fracture. Ilmenite crystallizes in the trigonal system with space group ''R''. The ilmenite crystal structure consists of an ordered derivative of the corundum structure; in corundum all cations are identical but in ilmenite Fe2+ and Ti4+ ions occupy alternating layers perpendicular to the trigonal c axis. Pure ilmenite is paramagnetic (showing only very weak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Titanium Tetrachloride
Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide () and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4", as a phonetic representation of the symbols of its molecular formula (). Properties and structure is a dense, colourless liquid, although crude samples may be yellow or even red-brown. It is one of the rare transition metal halides that is a liquid at room temperature, being another example. This property reflects the fact that molecules of weakly self-associate. Most metal chlorides are polymers, wherein the chloride atoms bridge between the metals. Its melting point is similar to that of . has a "closed" electronic shell, with the same number of electrons as the nobl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Titanium(III) Chloride
Titanium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl3. At least four distinct species have this formula; additionally hydrated derivatives are known. TiCl3 is one of the most common halides of titanium and is an important catalyst for the manufacture of polyolefins. Structure and bonding In TiCl3, each titanium atom has one ''d'' electron, rendering its derivatives paramagnetic, that is, the substance is attracted into a magnetic field. Solutions of titanium(III) chloride are violet, which arises from excitations of its ''d''-electron. The colour is not very intense since the transition is forbidden by the Laporte selection rule. Four solid forms or polymorphs of TiCl3 are known. All feature titanium in an octahedral coordination sphere. These forms can be distinguished by crystallography as well as by their magnetic properties, which probes exchange interactions. β-TiCl3 crystallizes as brown needles. Its structure consists of chains of TiCl6 octahedra th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kroll Process
The Kroll process is a pyrometallurgical industrial process used to produce metallic titanium from titanium tetrachloride. As of 2001 William Justin Kroll's process replaced the Hunter process for almost all commercial production. Process In the Kroll process, titanium tetrachloride is reduced by liquid magnesium to give titanium metal: : + 2 ->[825~^\mathrm] + 2 The reduction is conducted at 800–850 °C in a stainless steel retort. Complications result from partial reduction of the TiCl4, giving to the lower chlorides Titanium(II) chloride, TiCl2 and Titanium(III) chloride, TiCl3. The magnesium chloride, MgCl2 can be further refined back to magnesium. Appurtenant processes The resulting porous metallic titanium sponge is purified by Tank leaching, leaching or vacuum distillation. The sponge is crushed, and pressed before it is melted in a consumable electrode vacuum Electric arc furnace, arc furnace, "backfilled with pure gettered argon of a pressure high enough to avoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rutile
Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite. Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at visible wavelengths of any known crystal and also exhibits a particularly large birefringence and high dispersion. Owing to these properties, it is useful for the manufacture of certain optical elements, especially polarization optics, for longer visible and infrared wavelengths up to about 4.5 micrometres. Natural rutile may contain up to 10% iron and significant amounts of niobium and tantalum. Rutile derives its name from the Latin ('red'), in reference to the deep red color observed in some specimens when viewed by transmitted light. Rutile was first described in 1803 by Abraham Gottlob Werner using specimens obtained in Horcajuelo de la Sierra, Madrid (Spain), which is consequently the type locality. Occurrence Rutile is a comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hunter Process
The Hunter process was the first industrial process to produce pure metallic titanium. It was invented in 1910 by Matthew A. Hunter, a chemist born in New Zealand who worked in the United States. The process involves reducing titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) with sodium (Na) in a batch reactor with an inert atmosphere at a temperature of 1,000 °C. Diluted hydrochloric acid is then used to leach the salt from the product. :TiCl4(g) + 4 Na(l) → 4 NaCl(l) + Ti(s) Prior to the Hunter process, all efforts to produce Ti metal afforded highly impure material, often titanium nitride (which resembles a metal). The Hunter process was used until 1993, when it was replaced by the more economical Kroll process, which was developed in the 1940s. In the Kroll process, TiCl4 is reduced by magnesium instead of sodium. Both methods share the same initial step, obtaining TiCl4 from ore by chlorination and carbothermic reduction of the oxygen. The Kroll process is now the most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Smoke Screen
A smoke screen is smoke released to mask the movement or location of military units such as infantry, tanks, aircraft, or ships. Smoke screens are commonly deployed either by a canister (such as a grenade) or generated by a vehicle (such as a tank or a warship). Whereas smoke screens were originally used to hide movement from enemies' line of sight, modern technology means that they are now also available in new forms; they can screen in the infrared as well as visible spectrum of light to prevent detection by infrared sensors or viewers, and they are also available for vehicles in a super-dense form used to block laser beams of enemy laser designators or rangefinders. Technology Smoke grenades These are canister-type grenades used as a ground-to-ground or ground-to-air signalling device. The body consists of a steel sheet metal cylinder with a few emission holes on the top and/or bottom to allow smoke release when the smoke composition inside the grenade is ignited. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engineering is the field dedicated to controlling and preventing corrosion. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metal in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen, hydrogen, or hydroxide. Rusting, the formation of red-orange iron oxides, is a well-known example of electrochemical corrosion. This type of corrosion typically produces oxides or salts of the original metal and results in a distinctive coloration. Corrosion can also occur in materials other than metals, such as ceramics or polymers, although in this context, the term "degradation" is more common. Corrosion degrades the useful properties of materials and structures including mechanical strength, appearance, and permeability to liquids and ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
William Gregor
William Gregor (25 December 1761 – 11 June 1817) was a British clergyman and mineralogist who discovered the elemental metal Titanium. Early years He was born at the Trewarthenick Estate in Cornwall, the son of Francis Gregor and Mary Copley and the brother of Francis Gregor, MP for Cornwall. He was educated at Bristol Grammar School, where he became interested in chemistry, then after two years with a private tutor entered St John's College, Cambridge, graduating BA in 1784 and MA in 1787. He was ordained in the Church of England. He became vicar of St Mary's Church Diptford near Totnes, Devon. He married Charlotte Anne Gwatkin in 1790 and they had one daughter, Charlotte-Anne Gregor. Discovery of titanium After a brief interval at Bratton Clovelly, in 1793 William and his family moved permanently to the rectory of Creed in Cornwall. Here he continued his remarkably accurate chemical analysis of minerals, most of which came from Cornwall, such as the zeolites found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of (called a passivation layer) that protects the foil from further oxidation.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. . Stoichiometry Oxides are extraordinarily diverse in terms of stoichiometries (the measurable relationship between reactants and chemical equations of an equation or reaction) and in terms of the structures of each stoichiometry. Most elements form oxides of more than one stoichiometry. A well known example is carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Martin Heinrich Klaproth
Martin Heinrich Klaproth (1 December 1743 – 1 January 1817) was a German chemist. He trained and worked for much of his life as an apothecary, moving in later life to the university. His shop became the second-largest apothecary in Berlin, and the most productive artisanal chemical research center in Europe. Klaproth was a major systematizer of analytical chemistry, and an independent inventor of gravimetric analysis. His attention to detail and refusal to ignore discrepancies in results led to improvements in the use of apparatus. He was a major figure in understanding the composition of minerals and characterizing the elements. Klaproth discovered uranium (1789) and zirconium (1789). He was also involved in the discovery or co-discovery of titanium (1795), strontium (1793), cerium (1803), and chromium (1797) and confirmed the previous discoveries of tellurium (1798) and beryllium (1798). Klaproth was a member and director of the Berlin Academy of Scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |