On 26 April 1986, the no. 4 reactor of the
Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, located near
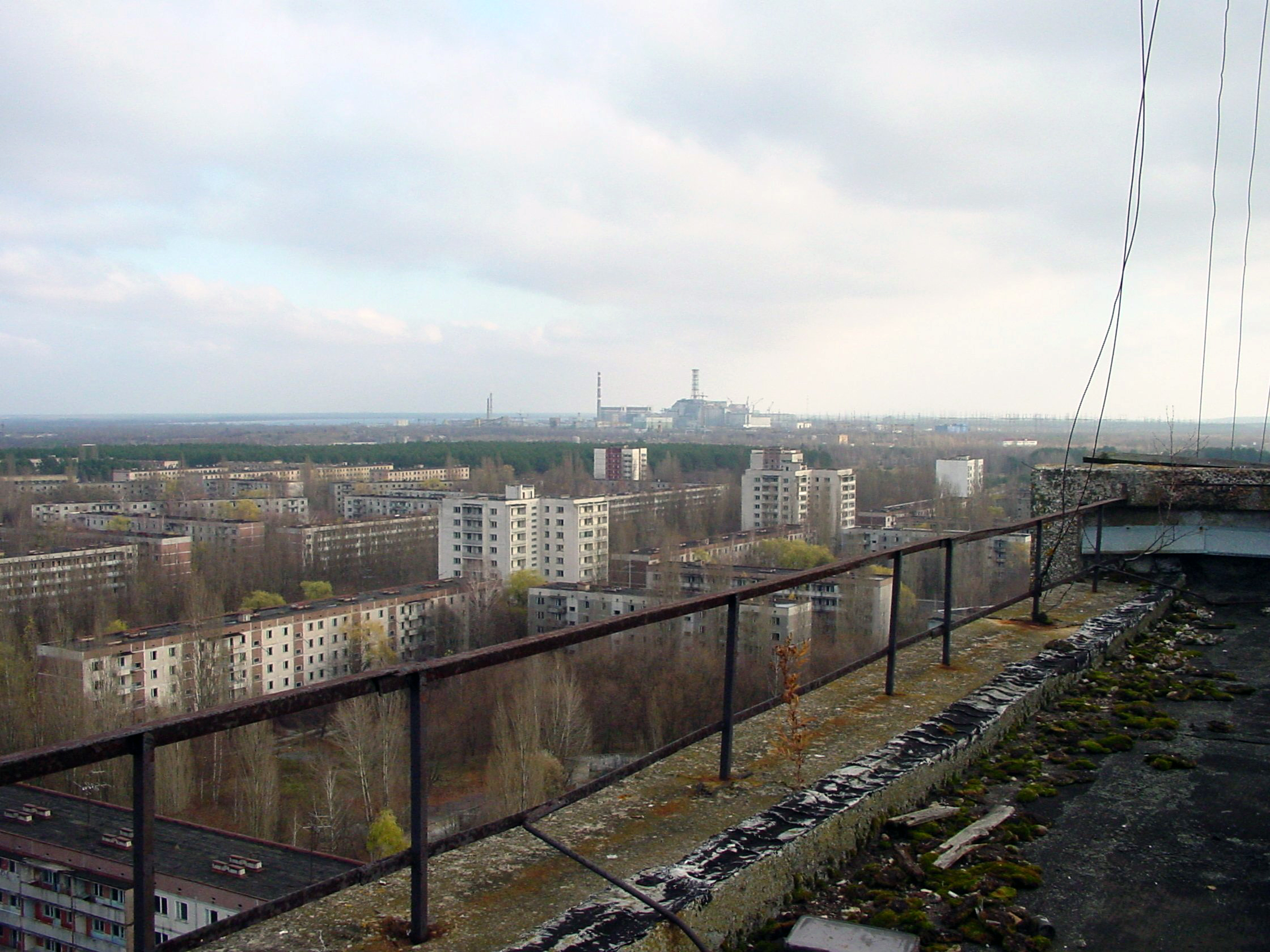
Pripyat
Pripyat, also known as Prypiat, is an abandoned industrial city in Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat (river), Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 1970 as the ninth ''atomgrad'' ...
,
Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
,
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
(now
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
), exploded. With dozens of direct casualties, it is one of only two nuclear energy accidents rated at the maximum severity on the
International Nuclear Event Scale, the other being the 2011
Fukushima nuclear accident. The response involved more than
500,000 personnel and cost an estimated 18billion
rubles
The ruble or rouble (; rus, рубль, p=rublʲ) is a currency unit. Currently, currencies named ''ruble'' in circulation include the Russian ruble (RUB, ₽) in Russia and the Belarusian ruble (BYN, Rbl) in Belarus. These currencies are su ...
(about $84.5billion USD in 2025).
It remains the worst nuclear disaster and the
most expensive disaster in history, with an estimated cost of
US$700 billion.
The disaster occurred while running a test to simulate cooling the reactor during an accident in blackout conditions. The operators carried out the test despite an accidental drop in reactor power, and due to a design issue, attempting to shut down the reactor in those conditions resulted in a dramatic power surge. The reactor components ruptured and lost coolants, and the resulting steam explosions and
meltdown destroyed the Reactor building no. 4, followed by a reactor core fire that spread radioactive contaminants across the Soviet Union and
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. A
exclusion zone was established 36 hours after the accident, initially evacuating around 49,000 people. The exclusion zone was later expanded to , resulting in the evacuation of approximately 68,000 more people.
Following the explosion, which killed two engineers and severely burned two others, an emergency operation began to put out the fires and stabilize the reactor. Of the 237 workers hospitalized, 134 showed symptoms of
acute radiation syndrome
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS), also known as radiation sickness or radiation poisoning, is a collection of health effects that are caused by being exposed to high amounts of ionizing radiation in a short period of time. Symptoms can start wit ...
(ARS); 28 of them died within three months. Over the next decade, 14 more workers (nine of whom had ARS)
died of various causes mostly unrelated to radiation exposure.
It is the only instance in commercial nuclear power history where radiation-related fatalities occurred. As of 2005, 6000 cases of childhood
thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck, ...
occurred within the affected populations, "a large fraction" being attributed to the disaster.
The
United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation estimates fewer than 100 deaths have resulted from the fallout. Predictions of the eventual total death toll vary; a 2006 World Health Organization study projected 9,000 cancer-related fatalities in Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia.
Pripyat was abandoned and replaced by the purpose-built city of
Slavutych. The
Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant sarcophagus, completed in December 1986, reduced the spread of
radioactive contamination
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological pollution, is the deposition of, or presence of Radioactive decay, radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids, or gases (including the human body), where their presence is uni ...
and provided
radiological protection for the crews of the undamaged reactors. In 2016–2018, the
Chernobyl New Safe Confinement
The New Safe Confinement (NSC or New Shelter; ) is a structure put in place in 2016 to confine the remains of the number 4 reactor unit at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, in Ukraine, which was destroyed during the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 ...
was constructed around the old sarcophagus to enable the removal of the reactor debris, with clean-up scheduled for completion by 2065.
Accident sequence
Background
Reactor cooling after shutdown

In nuclear reactor operation, most heat is generated by
nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactiv ...
, but over 6% comes from
radioactive decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
heat, which continues after the reactor shuts down. Continued coolant circulation is essential to prevent core overheating or a
core meltdown.
RBMK reactors, like those at Chernobyl, use water as a coolant, circulated by electrically driven pumps. Reactor No. 4 had 1,661 individual fuel channels, requiring over per hour for the entire reactor.
In case of a total power loss, each of Chernobyl's reactors had three backup
diesel generators, but they took 60–75 seconds to reach full load and generate the 5.5 MW needed to run one main pump.
Special counterweights on each pump provided coolant via inertia to bridge the gap to generator startup. However, a potential safety risk existed in the event that a station blackout occurred simultaneously with the rupture of a coolant pipe. In this scenario the
emergency core cooling system (ECCS) is needed to pump additional water into the core.
[
It had been theorized that the rotational momentum of the reactor's ]steam turbine
A steam turbine or steam turbine engine is a machine or heat engine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work utilising a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Par ...
could be used to generate the required electrical power to operate the ECCS via the feedwater pumps. The turbine's speed would run down as energy was taken from it, but analysis indicated that there might be sufficient energy to provide electrical power to run the coolant pumps for 45 seconds.[.]
Safety test
The turbine run-down energy capability still needed to be confirmed experimentally, and previous tests had ended unsuccessfully. An initial test carried out in 1982 indicated that the excitation voltage of the turbine-generator was insufficient. The electrical system was modified and the test was repeated in 1984, but again proved unsuccessful. In 1985, the test was conducted a third time, but also yielded no results due to a problem with the recording equipment. The test procedure was to be run again in 1986 and was scheduled to take place during a controlled power-down of reactor No. 4, which was preparatory to a planned maintenance outage.[
A test procedure had been written, but the authors were not aware of the unusual RBMK-1000 reactor behaviour under the planned operating conditions.][ It was regarded as purely an electrical test of the generator, even though it involved critical unit systems. According to the existing regulations, such a test did not require approval by either the chief design authority for the reactor (NIKIET) or the nuclear safety regulator.][ The test program called for disabling the emergency core cooling system, a passive/active system of core cooling intended to provide water to the core in a loss-of-coolant accident. Approval from the site chief engineer had been obtained according to regulations.][
The test procedure was intended to run as follows:
# The reactor thermal power was to be reduced to between 700 MW and 1,000 MW (to allow for adequate cooling, as the turbine would be spun at operating speed while disconnected from the power grid)
# The steam-turbine generator was to be run at normal operating speed
# Four out of eight main circulating pumps were to be supplied with off-site power, while the other four would be powered by the turbine
# When the correct conditions were achieved, the steam supply to the turbine generator would be closed, which would trigger an automatic reactor shutdown in ordinary conditions
# The voltage provided by the coasting turbine would be measured, along with the voltage and revolutions per minute (RPMs) of the four main circulating pumps being powered by the turbine
# When the emergency generators supplied full electrical power, the turbine generator would be allowed to continue free-wheeling down
]
Test delay and shift change

 The test was to be conducted during the day-shift of 25 April 1986 as part of a scheduled reactor shutdown. The day shift had been instructed in advance on the reactor operating conditions to run the test, and a special team of
The test was to be conducted during the day-shift of 25 April 1986 as part of a scheduled reactor shutdown. The day shift had been instructed in advance on the reactor operating conditions to run the test, and a special team of electrical engineer
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
s was present to conduct the electrical test once the correct conditions were reached. As planned, a gradual reduction in the output of the power unit began at 01:06 on 25 April, and the power level had reached 50% of its nominal 3,200 MW thermal level by the beginning of the day shift.[
The day shift was scheduled to perform the test at 14:15.][ Meanwhile, another regional power station unexpectedly went offline. At 14:00,][ the ]Kiev
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2, ...
electrical grid controller requested that the further reduction of Chernobyl's output be postponed, as power was needed to satisfy peak evening demand.
Soon, the day shift was replaced by the evening shift.[ which in practice meant that two or three people spent the whole shift manually turning sailboat-helm-sized valve wheels.][
At 23:04, the Kiev grid controller allowed the reactor shutdown to resume. The day shift had long since departed, the evening shift was also preparing to leave, and the night shift would not take over until midnight, well into the job. According to plan, the test should have been finished during the day shift, and the night shift would only have had to maintain decay heat cooling systems in an otherwise shut-down plant.]Anatoly Dyatlov
Anatoly Stepanovich Dyatlov (; 3 March 1931 – 13 December 1995) was a Soviet engineer who was the deputy chief engineer for the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant. He supervised the safety test which resulted in the 1986 Chernobyl disaster, for wh ...
, deputy chief-engineer of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant (ChNPP), was present to direct the test. He was one of the test's chief authors and he was the highest-ranking individual present. Unit Shift Supervisor Aleksandr Akimov was in charge of the Unit 4 night shift, and Leonid Toptunov
Leonid Fedorovych Toptunov (, ; 16 August 1960 – 14 May 1986) was a Soviet nuclear engineer who was the senior reactor control chief engineer at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Reactor Unit 4 on the night of the Chernobyl disaster, 26 April ...
was the Senior Reactor Control Engineer responsible for the reactor's operational regimen, including the movement of the control rods. 25-year-old Toptunov had worked independently as a senior engineer for approximately three months.
Unexpected drop of the reactor power
The test plan called for a gradual decrease in reactor power to a thermal level of 700–1000 MW, and an output of 720 MW was reached at 00:05 on 26 April.[ However, due to the reactor's production of a fission byproduct, ]xenon-135
Xenon-135 (135Xe) is an Isotope#Radioactive, primordial, and stable isotopes, unstable isotope of xenon with a half-life of about 9.2 hours. 135Xe is a fission product of uranium and it is the most powerful known neutron-absorbing nuclear poison ...
, which is a reaction-inhibiting neutron absorber, power continued to decrease in the absence of further operator action, a process known as reactor poisoning. In steady-state operation, this is avoided because xenon-135 is "burned off" as quickly as it is created, becoming the highly stable xenon-136. With reactor power reduced, high quantities of previously produced iodine-135 were decaying into the neutron-absorbing xenon-135 faster than the reduced neutron flux could "burn it off".[ AR-1 then activated, removing all four of AR-1's control rods automatically, but AR-2 failed to activate due to an imbalance in its ionization chambers. In response, Toptunov reduced power to stabilize the automatic regulators' ionization sensors. The result was a sudden power drop to an unintended near- shutdown state, with a power output of 30 MW thermal or less. The exact circumstances that caused the power drop are unknown. Most reports attribute the power drop to Toptunov's error, but Dyatlov reported that it was due to a fault in the AR-2 system.][
The reactor was now producing only 5% of the minimum initial power level prescribed for the test.][ This low reactivity inhibited the burn-off of xenon-135][ within the reactor core and hindered the rise of reactor power. To increase power, control-room personnel removed numerous control rods from the reactor. Several minutes elapsed before the reactor was restored to 160 MW at 00:39, at which point most control rods were at their upper limits, but the rod configuration was still within its normal operating limit, with Operational Reactivity Margin (ORM) equivalent to having more than 15 rods inserted. Over the next twenty minutes, reactor power would be increased further to 200 MW.][
The operation of the reactor at the low power level was accompanied by unstable core temperatures and coolant flow, and possibly by instability of neutron flux. The control room received repeated emergency signals regarding the low levels in one half of the steam/water separator drums, with accompanying drum separator pressure warnings. In response, personnel triggered rapid influxes of feedwater. Relief valves opened to relieve excess steam into a turbine condenser.
]
Reactor conditions priming the accident
When a power level of 200 MW was reattained, preparation for the experiment continued, although the power level was much lower than the prescribed 700 MW. As part of the test, two additional main circulating pumps were activated at 01:05. The increased coolant flow lowered the overall core temperature and reduced the existing steam voids in the core. Because water absorbs neutrons better than steam, neutron flux and reactivity decreased. The operators responded by removing more manual control rods to maintain power.light-water reactor
The light-water reactor (LWR) is a type of thermal-neutron reactor that uses normal water, as opposed to heavy water, as both its coolant and neutron moderator; furthermore a solid form of fissile elements is used as fuel. Thermal-neutron reacto ...
designs, the RBMK design at that time had a positive void coefficient
In nuclear engineering, the void coefficient (more properly called void coefficient of reactivity) is a number that can be used to estimate how much the reactivity of a nuclear reactor changes as voids (typically steam bubbles) form in the reactor ...
of reactivity at typical fuel burnup levels. This meant that the formation of steam bubbles (voids) from boiling cooling water intensified the nuclear chain reaction owing to voids having lower neutron absorption than water. Unknown to the operators, the void coefficient was not counterbalanced by other reactivity effects in the given operating regime, meaning that any increase in boiling would produce more steam voids which further intensified the chain reaction, leading to a positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects ...
loop. Given this characteristic, reactor No.4 was now at risk of a runaway increase in its core power with nothing to restrain it. The reactor was now very sensitive to the regenerative effect of steam voids on reactor power.[
]
Accident
Test execution
 At 01:23:04, the test began.
At 01:23:04, the test began.momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (: momenta or momentums; more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. ...
of the turbine generator decreased, so did the power it produced for the pumps. The water flow rate decreased, leading to increased formation of steam voids in the coolant flowing up through the fuel pressure tubes.
Reactor shutdown and power excursion
At 01:23:40, a scram (emergency shutdown) of the reactor was initiated as the experiment was wrapping-up.[.] The scram was started when the AZ-5 button of the reactor emergency protection system was pressed: this engaged the drive mechanism on all control rods to fully insert them, including the manual control rods that had been withdrawn earlier.
The personnel had intended to shut down using the AZ-5 button in preparation for scheduled maintenance and the scram preceded the sharp increase in power.[ However, the reason why the button was pressed at that time is not certain, as only the deceased Akimov and Toptunov made that decision, though the atmosphere in the control room was calm, according to eyewitnesses. The RBMK designers claim the button had to have been pressed only after the reactor already began to self-destruct.
When the AZ-5 button was pressed, the insertion of control rods into the reactor core began. The control rod insertion mechanism moved the rods at , so that the rods took 18 to 20 seconds to travel the full height of the core, about . A bigger problem was the design of the RBMK control rods, each of which had a graphite neutron moderator section attached to its end to boost reactor output by displacing water when the control rod section had been fully withdrawn from the reactor. That is, when a control rod was at maximum extraction, a neutron-moderating graphite extension was centred in the core with columns of water above and below it.][
Consequently, injecting a control rod downward into the reactor in a scram initially displaced neutron-absorbing water in the lower portion of the reactor with neutron-moderating graphite. Thus, an emergency scram could initially increase the reaction rate in the lower part of the core.][ This behaviour was discovered when the initial insertion of control rods in another RBMK reactor at Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant in 1983 induced a power spike. Procedural countermeasures were not implemented in response to Ignalina. The IAEA investigative report INSAG-7 later stated, "Apparently, there was a widespread view that the conditions under which the positive scram effect would be important would never occur. However, they did appear in almost every detail in the course of the actions leading to the Chernobyl accident."][
A few seconds into the scram, a power spike occurred, and the core overheated, causing some of the ]fuel rod
Nuclear fuel refers to any substance, typically fissile material, which is used by nuclear power stations or other nuclear devices to generate energy.
Oxide fuel
For fission reactors, the fuel (typically based on uranium) is usually based o ...
s to fracture. Some have speculated that this also blocked the control rod columns, jamming them at one-third insertion. Within three seconds the reactor's output rose above 530 MW.
Explosions
As the scram continued, the reactor output jumped to around 30,000 MW thermal, 10 times its normal operational output, the indicated last reading on the control panel. Some estimate the power spike may have gone 10 times higher than that. It was not possible to reconstruct the precise sequence of the processes that led to the destruction of the reactor and the power unit building, but a steam explosion
A steam explosion is an explosion caused by violent boiling or flashing of water or ice into steam, occurring when water or ice is either superheated, rapidly heated by fine hot debris produced within it, or heated by the interaction of molten ...
appears to have been the next event. There is a general understanding that it was explosive steam pressure from the damaged fuel channels escaping into the reactor's exterior cooling structure that caused the explosion that destroyed the reactor casing, tearing off and blasting the upper plate called the upper biological shield,[
A second, more powerful explosion occurred about two or three seconds after the first; this explosion dispersed the damaged core and effectively terminated the nuclear chain reaction. This explosion compromised more of the reactor containment vessel and ejected hot lumps of graphite moderator. The ejected graphite and the demolished channels still in the remains of the reactor vessel caught fire on exposure to air, significantly contributing to the spread of radioactive fallout.]
Possible causes for the second explosion
There were initially several hypotheses about the nature of the second, larger explosion. One view was that the second explosion was caused by the combustion of hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
, which had been produced either by the overheated steam- zirconium reaction or by the reaction of red-hot graphite with steam that produced hydrogen and carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
. Another hypothesis, by Konstantin Checherov, published in 1998, was that the second explosion was a thermal explosion of the reactor due to the uncontrollable escape of fast neutrons caused by the complete water loss in the reactor core.
Fizzled nuclear explosion hypothesis
The force of the second explosion and the ratio of xenon radioisotopes released after the accident led Sergei A. Pakhomov and Yuri V. Dubasov in 2009 to theorize that the second explosion could have been an extremely fast nuclear power transient resulting from core material melting in the absence of its water coolant and moderator. Pakhomov and Dubasov argued that there was no delayed supercritical increase in power but a runaway prompt criticality, similar to the explosion of a fizzled nuclear weapon.[
Their evidence came from Cherepovets, a city northeast of Chernobyl, where physicists from the V.G. Khlopin Radium Institute measured anomalous high levels of ]xenon-135
Xenon-135 (135Xe) is an Isotope#Radioactive, primordial, and stable isotopes, unstable isotope of xenon with a half-life of about 9.2 hours. 135Xe is a fission product of uranium and it is the most powerful known neutron-absorbing nuclear poison ...
—a short half-life isotope—four days after the explosion. This meant that a nuclear event in the reactor may have ejected xenon to higher altitudes in the atmosphere than the later fire did, allowing widespread movement of xenon to remote locations.joule
The joule ( , or ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of SI base units, one joule corresponds to one kilogram- metre squared per second squared One joule is equal to the amount of work d ...
s, the equivalent of about 10 tons of TNT.
Immediate response
Fire containment
Contrary to safety regulations, bitumen
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscosity, viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American Engl ...
, a combustible material, had been used in the construction of the roof of the reactor building and the turbine hall. Ejected material ignited at least five fires on the roof of adjacent reactor No. 3, which was still operating. It was imperative to put out those fires and protect the cooling systems of reactor No. 3.respirator
A respirator is a device designed to protect the wearer from inhaling hazardous atmospheres including lead, lead fumes, vapors, gases and particulate matter such as dusts and airborne pathogens such as viruses. There are two main categories o ...
s and potassium iodide tablets and told to continue working. At 05:00, Bagdasarov made his own decision to shut down the reactor,boron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three ...
onto the burning reactor. It is now known that virtually none of these materials reached the core.Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
physicist who died days after a fatal radiation overdose from a criticality accident.nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel refers to any substance, typically fissile material, which is used by nuclear power stations or other atomic nucleus, nuclear devices to generate energy.
Oxide fuel
For fission reactors, the fuel (typically based on uranium) is ...
and more dangerous fission products into the air. Residents of the surrounding area observed the radioactive cloud on the night of the explosion.
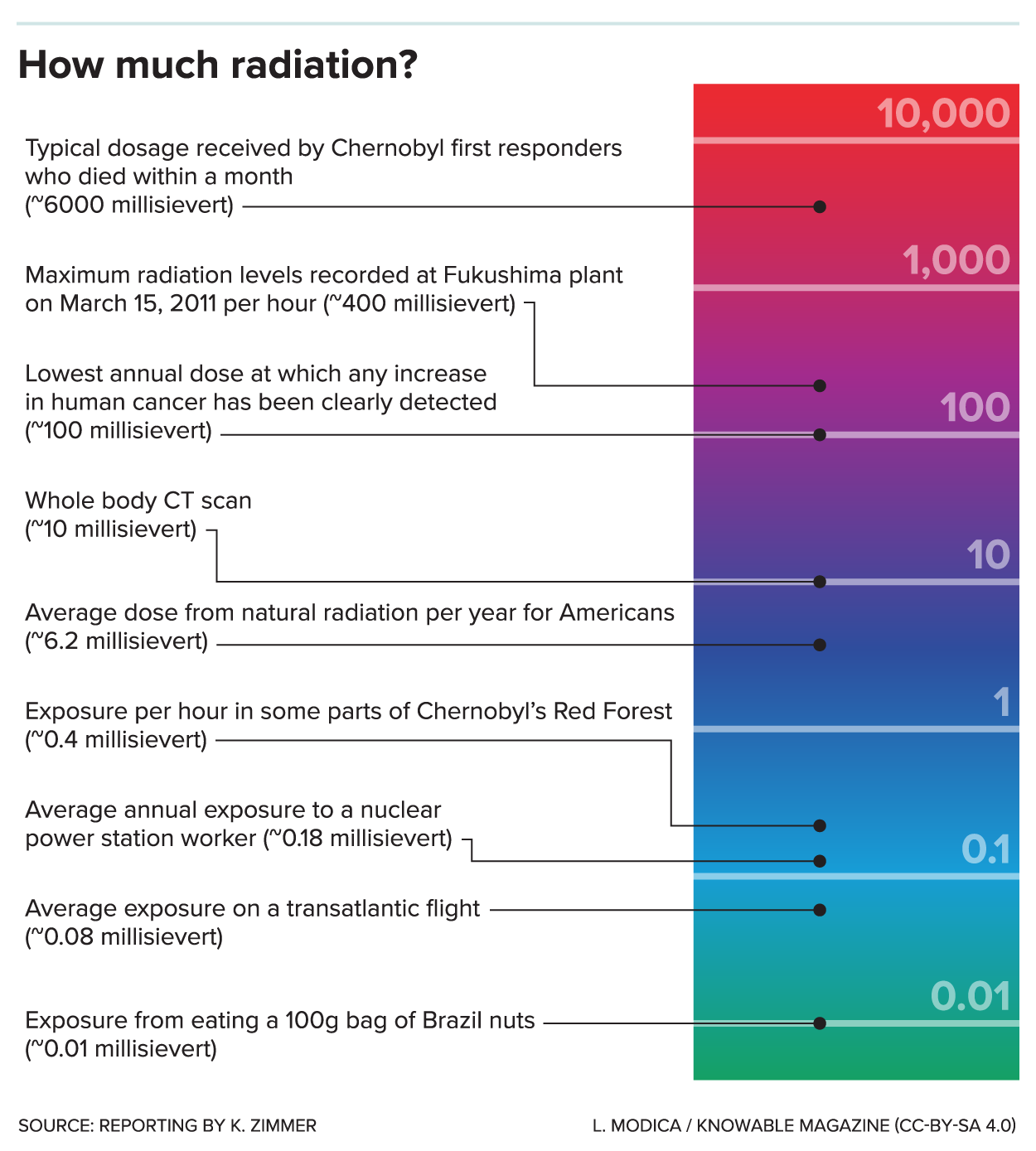
Radiation levels
The ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
levels in the worst-hit areas of the reactor building have been estimated to be 5.6 roentgens per second (R/s), equivalent to more than 20,000 roentgens per hour. A lethal dose is around 500 roentgens (~5 Gray (Gy) in modern radiation units) over five hours. In some areas, unprotected workers received fatal doses in less than a minute. A dosimeter
A radiation dosimeter is a device that measures the equivalent dose, dose uptake of external ionizing radiation. It is worn by the person being monitored when used as a personal dosimeter, and is a record of the radiation dose received. Modern el ...
capable of measuring up to 1,000 R/s was buried in the rubble of a collapsed part of the building, and another one failed when turned on. Most remaining dosimeters had limits of 0.001 R/s and therefore read "off scale". The reactor crew could ascertain only that the radiation levels were somewhere above 0.001 R/s (3.6 R/h), while the true levels were vastly higher in some areas.
Accident investigation
The IAEA
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 ...
had created the International Nuclear Safety Advisory Group (INSAG) in 1985. INSAG produced two significant reports on Chernobyl: INSAG-1 in 1986, and a revised report, INSAG-7, in 1992. According to INSAG-1, the main cause of the accident was the operators' actions, but according to INSAG-7, the main cause was the reactor's design.
Crisis management
Evacuation
 The nearby city of Pripyat was not immediately evacuated and the townspeople were not alerted during the night to what had just happened. However, within a few hours, dozens of people fell ill. Later, they reported severe headaches and metallic tastes in their mouths, along with uncontrollable fits of coughing and vomiting.
The nearby city of Pripyat was not immediately evacuated and the townspeople were not alerted during the night to what had just happened. However, within a few hours, dozens of people fell ill. Later, they reported severe headaches and metallic tastes in their mouths, along with uncontrollable fits of coughing and vomiting.Verkhovna Rada
The Verkhovna Rada ( ; VR), officially the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, is the unicameralism, unicameral parliament of Ukraine. It consists of 450 Deputy (legislator), deputies presided over by a speaker. The Verkhovna Rada meets in the Verkhovn ...
of the Ukrainian SSR, said that Ukraine's acting Minister of Internal Affairs Vasyl Durdynets phoned her at work at 09:00 to report current affairs; only at the end of the conversation did he add that there had been a fire at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, but it was extinguished and everything was fine. When Shevchenko asked "How are the people?", he replied that there was nothing to be concerned about: "Some are celebrating a wedding, others are gardening, and others are fishing in the Pripyat River". A commission was established later in the day to investigate the accident. It was headed by Valery Legasov, First Deputy Director of the Kurchatov Institute of Atomic Energy, and included leading nuclear specialist Evgeny Velikhov, hydro-meteorologist Yuri Izrael, radiologist Leonid Ilyin, and others. They flew to Boryspil International Airport and arrived at the power plant in the evening of 26 April.
A commission was established later in the day to investigate the accident. It was headed by Valery Legasov, First Deputy Director of the Kurchatov Institute of Atomic Energy, and included leading nuclear specialist Evgeny Velikhov, hydro-meteorologist Yuri Izrael, radiologist Leonid Ilyin, and others. They flew to Boryspil International Airport and arrived at the power plant in the evening of 26 April.Dnieper
The Dnieper or Dnepr ( ), also called Dnipro ( ), is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Approximately long, with ...
marshes to house Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant employees instead of Pripyat, with a direct rail connection to the Chernobyl NPP.
Official announcement
 Evacuation began one and a half days before the accident was publicly acknowledged by the Soviet Union. On the morning of 28 April, radiation levels set off alarms at the Forsmark Nuclear Power Plant in
Evacuation began one and a half days before the accident was publicly acknowledged by the Soviet Union. On the morning of 28 April, radiation levels set off alarms at the Forsmark Nuclear Power Plant in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
,International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear technology, nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was ...
that the Soviet government admitted that an accident had taken place at Chernobyl.Vremya
''Vremya'' (, lit. "Time") is the main evening newscast in Russia, airing on Channel One Russia (Russian: , Pervy kanal) and previously on Programme One of the Central Television of the USSR (CT USSR, Russian: ). The programme has been on th ...
'': "There has been an accident at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant. One of the nuclear reactors was damaged. The effects of the accident are being remedied. Assistance has been provided for any affected people. An investigative commission has been set up."[ .]
This was the first time the Soviet Union had officially announced a nuclear accident. The Telegraph Agency of the Soviet Union (TASS) then discussed the Three Mile Island accident
The Three Mile Island accident was a partial nuclear meltdown of the Unit 2 reactor (TMI-2) of the Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station, located on the Susquehanna River in Londonderry Township, Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, Londonderry T ...
and other American nuclear accidents, which Serge Schmemann of ''The New York Times'' wrote was an example of the common Soviet tactic of whataboutism. The mention of a commission also indicated to observers the seriousness of the incident,ABC News ABC News most commonly refers to:
* ABC News (Australia), a national news service of the Australian Broadcasting Corporation
* ABC News (United States), a news-gathering and broadcasting division of the American Broadcasting Company
ABC News may a ...
released its report about the disaster. Shevchenko was the first of the Ukrainian state top officials to arrive at the disaster site early on 28 April. She returned home near midnight, stopping at a radiological checkpoint in Vilcha, one of the first that were set up soon after the accident.International Workers' Day
International Workers' Day, also called Labour Day in some countries and often referred to as May Day, is a celebration of Wage labour, labourers and the working classes that is promoted by the international labour movement and occurs every yea ...
celebrations in Kiev. On 30 April a meeting of the Political bureau of the Central Committee of the CPSU took place to discuss the plan for the celebration. Scientists were reporting that the radiological background level in Kiev was normal. It was decided to shorten celebrations from the regular three and a half to four hours to under two hours.
Core meltdown risk mitigation
Bubbler pools
Two floors of bubbler pools beneath the reactor served as a large water reservoir for the emergency cooling pumps and as a pressure suppression system capable of condensing steam in case of a small broken steam pipe; the third floor above them, below the reactor, served as a steam tunnel. The steam released by a broken pipe was supposed to enter the steam tunnel and be led into the pools to bubble through a layer of water. After the disaster, the pools and the basement were flooded because of ruptured cooling water pipes and accumulated firefighting water.
The smoldering graphite, fuel and other material, at more than ,lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fractu ...
.diving suit
A diving suit is a garment or device designed to protect a diver from the underwater environment. A diving suit may also incorporate a breathing gas supply (such as for a standard diving dress or atmospheric diving suit), but in most cases th ...
s and respirator
A respirator is a device designed to protect the wearer from inhaling hazardous atmospheres including lead, lead fumes, vapors, gases and particulate matter such as dusts and airborne pathogens such as viruses. There are two main categories o ...
s, and equipped with dosimeter
A radiation dosimeter is a device that measures the equivalent dose, dose uptake of external ionizing radiation. It is worn by the person being monitored when used as a personal dosimeter, and is a record of the radiation dose received. Modern el ...
s, entered the knee-deep radioactive water and opened the valves.
Foundation protection measures
The government commission was concerned that the molten core would burn into the earth and contaminate groundwater. To reduce the likelihood of this, it was decided to freeze the earth beneath the reactor, which would also stabilize the foundations. Using oil well drilling equipment, injection of liquid nitrogen began on 4 May. It was estimated that of liquid nitrogen per day would be required to keep the soil frozen at .
Site cleanup
Debris removal
In the months after the explosion, attention turned to removing the radioactive debris from the roof.
Construction of the sarcophagus
 With the extinguishing of the open air reactor fire, the next step was to prevent the spread of contamination due to wind or birds which could land within the wreckage and then carry contamination elsewhere. In addition, rainwater could wash contamination into the sub-surface water table, where it could migrate outside the site area. Rainwater falling on the wreckage could also accelerate corrosion of steelwork in the remaining reactor structure. A further challenge was to reduce the large amount of emitted
With the extinguishing of the open air reactor fire, the next step was to prevent the spread of contamination due to wind or birds which could land within the wreckage and then carry contamination elsewhere. In addition, rainwater could wash contamination into the sub-surface water table, where it could migrate outside the site area. Rainwater falling on the wreckage could also accelerate corrosion of steelwork in the remaining reactor structure. A further challenge was to reduce the large amount of emitted gamma radiation
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
, which was a hazard to the workforce operating adjacent reactor No. 3.
The solution chosen was to enclose the wrecked reactor by the construction of a huge composite steel and concrete shelter, which became known as the "Sarcophagus". It had to be erected quickly and within the constraints of high levels of ambient gamma radiation. The design started on 20 May 1986, 24 days after the disaster, and construction was from June to late November.
The construction workers had to be protected from radiation, and techniques such as crane drivers working from lead-lined control cabins were employed. The construction work included erecting walls around the perimeter, clearing and surface concreting the surrounding ground to remove sources of radiation and to allow access for large construction machinery, constructing a thick radiation shielding wall to protect the workers in reactor No. 3, fabricating a high-rise buttress to strengthen parts of the old structure, constructing an overall roof, and provisioning a ventilation
Ventilation may refer to:
* Ventilation (physiology), the movement of air between the environment and the lungs via inhalation and exhalation
** Mechanical ventilation, in medicine, using artificial methods to assist breathing
*** Respirator, a ma ...
extract system to capture any airborne contamination within the shelter.
Investigations of the reactor condition
During the construction of the sarcophagus, a scientific team, as part of an investigation dubbed "Complex Expedition", re-entered the reactor to locate and contain nuclear fuel to prevent another explosion. These scientists manually collected cold fuel rods, but great heat was still emanating from the core. Rates of radiation in different parts of the building were monitored by drilling holes into the reactor and inserting long metal detector tubes. The scientists were exposed to high levels of radiation.
Area cleanup
The official contaminated zones saw a massive clean-up effort lasting seven months.
Site remediation
Questions arose about the future of the plant and its fate. All work on the unfinished reactors No. 5 and No. 6 was halted three years later. The damaged reactor was sealed off and of concrete was placed between the disaster site and the operational buildings. The Ukrainian government allowed the three remaining reactors to continue operating because of an energy shortage.
In October 1991, a fire occurred in the turbine building of reactor No. 2; the authorities subsequently declared the reactor damaged beyond repair, and it was taken offline. Reactor No. 1 was decommissioned in November 1996 as part of a deal between the Ukrainian government and international organizations such as the IAEA to end operations at the plant. On 15 December 2000, then-President Leonid Kuchma personally turned off reactor No. 3 in an official ceremony, shutting down the entire site.
No. 4 reactor confinement
 Soon after the accident, the reactor building was quickly encased by a mammoth concrete sarcophagus. Crane operators worked blindly from inside lead-lined cabins taking instructions from distant radio observers, while gargantuan pieces of concrete were moved to the site on custom-made vehicles. The purpose of the sarcophagus was to stop any further release of radioactive particles into the atmosphere, isolate the exposed core from the weather and provide safety for the continued operations of adjacent reactors one through three.
Soon after the accident, the reactor building was quickly encased by a mammoth concrete sarcophagus. Crane operators worked blindly from inside lead-lined cabins taking instructions from distant radio observers, while gargantuan pieces of concrete were moved to the site on custom-made vehicles. The purpose of the sarcophagus was to stop any further release of radioactive particles into the atmosphere, isolate the exposed core from the weather and provide safety for the continued operations of adjacent reactors one through three.Chernobyl Shelter Fund The Chernobyl Shelter Fund (CSF) was set up in December 1997 with the purpose of funding the Shelter Implementation Plan (SIP). The aim of the fund is to create conditions for the dismantling and decomposition of the radiation contaminated structure ...
was founded to design and build a more permanent cover for the unstable and short-lived sarcophagus. It received €864 million from international donors in 2011 and was managed by the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development
The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, shortened to EBRD ( French: ''Banque européenne pour la reconstruction et le développement'' or ''BERD''), is an international financial institution founded in 1991 in Paris. As a multilat ...
(EBRD). The new shelter was named the New Safe Confinement and construction began in 2010. It is a metal arch high and spanning built on rails adjacent to the reactor No. 4 building so that it could be slid over the top of the existing sarcophagus. The New Safe Confinement was completed in 2016 and slid into place over the sarcophagus on 29 November. Unlike the original sarcophagus, the New Safe Confinement is designed to allow the reactor to be safely dismantled using remotely operated equipment.
Waste management
Used fuel from units 1–3 was stored in the units' cooling ponds, and in an interim spent fuel storage facility pond, ISF-1, which now holds most of the spent fuel from units 1–3, allowing those reactors to be decommissioned under less restrictive conditions. Approximately 50 of the fuel assemblies from units 1 and 2 were damaged and required special handling. Moving fuel to ISF-1 was thus carried out in three stages: fuel from unit 3 was moved first, then all undamaged fuel from units 1 and 2, and finally the damaged fuel from units 1 and 2. Fuel transfers to ISF-1 were completed in June 2016.
A need for larger, longer-term radioactive waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. It is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, nuclear decommissioning, rare-earth mining, and nuclear ...
management at the site is to be fulfilled by a new facility designated ISF-2. This facility serves as dry storage for used fuel assemblies from units 1–3 and other operational wastes, as well as material from decommissioning units 1–3.
A contract was signed in 1999 with Areva NP ( Framatome) for construction of ISF-2. In 2003, after a significant part of the storage structures had been built, technical deficiencies in the design concept became apparent. In 2007, Areva withdrew and Holtec International was contracted for a new design and construction of ISF-2. The new design was approved in 2010, work started in 2011, and construction was completed in August 2017.
ISF-2 is the world's largest nuclear fuel storage facility, expected to hold more than 21,000 fuel assemblies for at least 100 years. The project includes a processing facility able to cut the RBMK fuel assemblies and to place the material in canisters, to be filled with inert gas
An inert gas is a gas that does not readily undergo chemical reactions with other chemical substances and therefore does not readily form chemical compounds. Though inert gases have a variety of applications, they are generally used to prevent u ...
and welded shut. The canisters are then to be transported to dry storage vaults, where the fuel containers will be enclosed for up to 100 years. Expected processing capacity is 2,500 fuel assemblies per year.
Fuel-containing materials
The radioactive material consists of core fragments, dust, and lava-like "fuel containing materials" (FCM)—also called " corium"—that flowed through the wrecked reactor building before hardening into a ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
form.
Three different lavas are present in the basement of the reactor building: black, brown, and a porous ceramic. The lava materials are silicate glasses with inclusions of other materials within them. The porous lava is brown lava that dropped into water and thus cooled rapidly. It is unclear how long the ceramic form will retard the release of radioactivity. From 1997 to 2002, a series of published papers suggested that the self-irradiation of the lava would convert all into a submicrometre and mobile powder within a few weeks.
It has been reported that the degradation of the lava is likely to be a slow, gradual process.uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
from the wrecked reactor is only per year; this low rate of uranium leaching suggests that the lava is resisting its environment.AK-47
The AK-47, officially known as the Avtomat Kalashnikova (; also known as the Kalashnikov or just AK), is an assault rifle that is chambered for the 7.62×39mm cartridge. Developed in the Soviet Union by Russian small-arms designer Mikhail Kala ...
round to remove a chunk, had softened to a texture similar to sand.neutron moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely ...
, triggering increased fission in the remaining materials, risking criticality. Gadolinium nitrate solution was used to quench neutrons to slow the fission. Even after completion of the building, fission reactions may be increasing; scientists are working to understand the cause and risks. While neutron activity has declined across most of the destroyed fuel, from 2017 until late 2020 a doubling in neutron density was recorded in the sub-reactor space, before levelling off in early 2021. This indicated increasing levels of fission as water levels dropped, the opposite of what had been expected, and atypical compared to other fuel-containing areas. The fluctuations have led to fears that a self-sustaining reaction could be created, which would likely spread more radioactive dust and debris throughout the New Safe Confinement, making future cleanup even more difficult. Potential solutions include using a robot to drill into the fuel and insert boron carbide control rods.
Exclusion zone

 The Exclusion Zone was originally an area with a radius of in all directions from the plant, but was subsequently greatly enlarged to include an area measuring approximately , officially called the " zone of alienation". The area has largely reverted to forest and was overrun by wildlife due to the lack of human competition for space and resources.
The Exclusion Zone was originally an area with a radius of in all directions from the plant, but was subsequently greatly enlarged to include an area measuring approximately , officially called the " zone of alienation". The area has largely reverted to forest and was overrun by wildlife due to the lack of human competition for space and resources.
Forest fire concerns
During the dry season, forest fires A forest fire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a bushfire ( in Au ...
are a perennial concern in areas contaminated by radioactive material. Dry conditions and build-up of debris make the forests a ripe breeding ground for wildfires. Depending on prevailing atmospheric conditions, smoke from wildfires could potentially spread more radioactive material outside the exclusion zone. In Belarus, the Bellesrad organization is tasked with overseeing food cultivation and forestry management in the area.
In April 2020, forest fires spread through of the exclusion zone, causing increased radiation from the release of caesium-137 and strontium-90 from the ground and biomass. The increase in radioactivity was detectable by the monitoring network but did not pose a threat to human health. The average radiation dose that Kyiv residents received as a result of the fires was estimated to be 1 nSv.
Recovery projects
The Chernobyl Trust Fund was created in 1991 by the United Nations to help victims of the Chernobyl accident. It is administered by the , which also manages strategy formulation, resource mobilization, and advocacy efforts.United Nations Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human development. The UNDP emphasizes on developing local capacity towar ...
, the fund shifted its focus from emergency assistance to long-term development.Chernobyl Shelter Fund The Chernobyl Shelter Fund (CSF) was set up in December 1997 with the purpose of funding the Shelter Implementation Plan (SIP). The aim of the fund is to create conditions for the dismantling and decomposition of the radiation contaminated structure ...
was established in 1997 at the G8 summit in Denver to finance the Shelter Implementation Plan (SIP). The plan called for transforming the site into an ecologically safe condition through stabilization of the sarcophagus and construction of the New Safe Confinement structure. While the original cost estimate for the SIP was US$768 million, the 2006 estimate was $1.2 billion.
In 2003, the United Nations Development Programme launched the Chernobyl Recovery and Development Programme (CRDP) for the recovery of affected areas. The programme was initiated in February 2002 based on the recommendations in the report on Human Consequences of the Chernobyl Nuclear Accident. The main goal of the CRDP was to support the Government of Ukraine
The Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine (), commonly referred to as the Government of Ukraine (), is the highest body of state Executive (government), executive power in Ukraine. As the Cabinet of Ministers of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republi ...
in mitigating the long-term social, economic, and ecological consequences of the Chernobyl catastrophe. CRDP works in the four most affected Ukrainian areas: Kyivska, Zhytomyrska, Chernihivska and Rivnenska.
More than 18,000 Ukrainian children affected by the disaster have been treated in the resort town
A resort town, resort city or resort destination is an urban area where tourism or vacationing is the primary component of the local culture and economy. A typical resort town has one or more actual resorts in the surrounding area. Sometimes ...
of Tarará, Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
, since 1990.
The International Project on the Health Effects of the Chernobyl Accident was created and received US$20 million, mainly from Japan, in the hope of discovering the main cause of health problems due to iodine-131 radiation. These funds were divided among Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia for the investigation of health effects. As there was significant corruption in former Soviet countries, most foreign aid was given to Russia, and no results from the funding were demonstrated.
Tourism
First limited guided tours were begun in 2002. The 2007 release of the video game '' S.T.A.L.K.E.R.'' increased the site popularitymicrobiology
Microbiology () is the branches of science, scientific study of microorganisms, those being of unicellular organism, unicellular (single-celled), multicellular organism, multicellular (consisting of complex cells), or non-cellular life, acellula ...
and immunology
Immunology is a branch of biology and medicine that covers the study of Immune system, immune systems in all Organism, organisms.
Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the Physiology, physiological functioning of the immune system in ...
teacher at Georgetown's School of Medicine, recommends that tourists wear clothes and shoes they are comfortable throwing away and to avoid plant life.Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
in early 2022 meant the Chernobyl area saw active fighting and the exclusion zone closed to all visitors. It remained closed to tourism as of summer 2024.
A parallel "stalker" subculture developed of illegal visitors roaming the area for prolonged periods, with some hiking into the zone over 100 times, often without taking appropriate precautions against radiation.
Long-term effects
Release and spread of radioactive materials
Although it is difficult to compare the Chernobyl accident with a deliberate air burst nuclear detonation, it is estimated that Chernobyl released about 400 times more radioactive material than the combined atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
On 6 and 9 August 1945, the United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, respectively, during World War II. The aerial bombings killed between 150,000 and 246,000 people, most of whom were civili ...
. However, the Chernobyl disaster released only about one-hundredth to one-thousandth of the total radioactivity released during nuclear weapons testing
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine the performance of nuclear weapons and the effects of Nuclear explosion, their explosion. Nuclear testing is a sensitive political issue. Governments have often performed tests to si ...
at the height of the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, due to varying isotope abundances.
Approximately of land was significantly contaminated, with the worst-affected areas in Belarus, Ukraine, and Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
.Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
.Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
, the Welsh mountains and the Scottish Highlands
The Highlands (; , ) is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Scottish Lowlands, Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Scots language, Lowland Scots language replaced Scottish Gae ...
, where adiabatic cooling caused radioactive rainfall. The resulting patches of contamination were often highly localized, and localized water-flows contributed to large variations in radioactivity over small areas. Sweden and Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
also received heavy fallout when the contaminated air collided with a cold front, bringing rain.Soviet Air Force
The Soviet Air Forces (, VVS SSSR; literally "Military Air Forces of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics"; initialism VVS, sometimes referred to as the "Red Air Force") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Sovie ...
to remove radioactive particles from clouds heading toward highly populated areas. Heavy, black-coloured rain fell on the city of Gomel
Gomel (, ) or Homyel (, ) is a city in south-eastern Belarus. It serves as the administrative centre of Gomel Region and Gomel District, though it is administratively separated from the district. As of 2025, it is the List of cities and largest ...
. Reports from Soviet and Western scientists indicate that the Belarusian SSR received about 60% of the contamination that fell on the former Soviet Union. However, the 2006 TORCH report stated that up to half of the volatile particles had actually landed outside the former USSR area currently making up Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia. An unconnected large area in Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
south of Bryansk
Bryansk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Bryansk Oblast, Russia, situated on the Desna (river), Desna River, southwest of Moscow. It has a population of 379,152 at the 2021 census.
Bryans ...
was also contaminated, as were parts of northwestern Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
. Studies in surrounding countries indicate that more than one million people could have been affected by radiation.
Relative isotopic abundances
The Chernobyl release was characterized by the physical and chemical properties of the radio-isotopes in the core. Particularly dangerous were the highly radioactive fission products, those with high nuclear decay rates that accumulate in the food chain, such as some of the isotopes of iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
, caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling; also spelled cesium in American English) is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only f ...
and strontium
Strontium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, it is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to ...
. Iodine-131 was and caesium-137 remains the two most responsible for the radiation exposure received by the general population. At different times after the accident, different
At different times after the accident, different isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
s were responsible for the majority of the external dose. The remaining quantity of any radioisotope, and therefore the activity of that isotope, after 7 decay half-lives have passed, is less than 1% of its initial magnitude, and it continues to reduce beyond 0.78% after 7 half-lives to 0.10% remaining after 10 half-lives have passed and so on. Some radionuclides have decay products that are likewise radioactive, which is not accounted for here. The release of radioisotopes from the nuclear fuel was largely controlled by their boiling point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding envi ...
s, and the majority of the radioactivity
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
present in the core was retained in the reactor.
* All of the noble gas
The noble gases (historically the inert gases, sometimes referred to as aerogens) are the members of Group (periodic table), group 18 of the periodic table: helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), radon (Rn) and, in some ...
es, including krypton
Krypton (from 'the hidden one') is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless noble gas that occurs in trace element, trace amounts in the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere and is of ...
and xenon
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
, contained within the reactor were released immediately into the atmosphere by the first steam explosion.radioiodine
There are 40 known isotopes of iodine (53I) from 108I to 147I; all undergo radioactive decay except 127I, which is stable. Iodine is thus a monoisotopic element.
Its longest-lived radioactive isotope, 129I, has a half-life of 16.14 million ye ...
in the reactor, about 1760 PBq (), or about , was released, as a mixture of sublimed vapour, solid particles, and organic iodine compounds. Iodine-131 has a half-life of 8 days.aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be generated from natural or Human impact on the environment, human causes. The term ''aerosol'' co ...
form; caesium-137, along with isotopes of strontium, are the two primary elements preventing the Chernobyl exclusion zone being re-inhabited.nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel refers to any substance, typically fissile material, which is used by nuclear power stations or other atomic nucleus, nuclear devices to generate energy.
Oxide fuel
For fission reactors, the fuel (typically based on uranium) is ...
material released to the environment was %; this was later revised to %. This corresponds to the atmospheric emission of of fragmented fuel.
Environmental impact
Water bodies
The Chernobyl nuclear power plant is located next to the Pripyat River, which feeds into the Dnieper reservoir system, one of the largest surface water systems in Europe, which at the time supplied water to Kiev's 2.4 million residents, and was still in spring flood when the accident occurred.[ Guidelines for levels of radioiodine in drinking water were temporarily raised to 3,700 Bq/L, allowing most water to be reported as safe.][ Officially it was stated that all contaminants had settled to the bottom "in an insoluble phase" and would not dissolve for 800–1000 years.]Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
was not badly affected by the Chernobyl accident since radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ...
s with short half-lives decayed away long before they could affect groundwater supplies, and longer-lived radionuclides such as radiocaesium and radiostrontium were adsorbed to surface soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
s before they could transfer to groundwater.waste disposal
Waste management or waste disposal includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final Waste disposal, disposal. This includes the Waste collection, collection, transport, Sewage treatment, treatm ...
sites in the exclusion zone around Chernobyl. Although there is a potential for transfer of radionuclides from these disposal sites off-site, the IAEA Chernobyl Report[ argues that this is not significant in comparison to washout of surface-deposited radioactivity.
]
Bio-accumulation
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance faster than it can be lost or eliminated by catabolism and excretion. Th ...
of radioactivity in fish[ Guideline maximum levels for radiocaesium in fish vary but are approximately 1000 Bq/kg in the ]European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
.[EURATOM Council Regulations No. 3958/87, No. 994/89, No. 2218/89, No. 770/90.] In the Kiev Reservoir in Ukraine, concentrations in fish were in the range of 3000 Bq/kg during the early years after the accident.[ In small "closed" lakes in Belarus and the Bryansk region of Russia, concentrations in a number of fish species varied from 100 to 60,000 Bq/kg during 1990–1992.][
]
Flora, fauna, and funga
 After the disaster, of
After the disaster, of pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as cu ...
forest directly downwind of the reactor turned reddish-brown and died, earning the name " Red Forest".domestic animal
This page gives a list of domesticated animals, also including a list of animals which are or may be currently undergoing the process of domestication and animals that have an extensive relationship with humans beyond simple predation. This includ ...
s were removed from the exclusion zone, but horses left on an island in the Pripyat River from the power plant died when their thyroid glands were destroyed by radiation doses of 150–200 Sv.Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
mutant that was hyper-resistant to a variety of DNA-damaging elements, including x-ray radiation, UV-C, and 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4NQO). Cladosporium sphaerospermum, a species of fungus that has thrived in the Chernobyl contaminated area, has been investigated for the purpose of using the fungus' particular melanin to protect against high-radiation environments, such as space travel. The disaster has been described by lawyers, academics and journalists as an example of ecocide
Ecocide (from Greek 'home' and Latin 'to kill') is the destruction of the natural environment, environment by humans. Ecocide threatens all human populations that are dependent on natural resources for maintaining Ecosystem, ecosystems and ensu ...
.
Human food chain
With radiocaesium binding less with humic acid, peaty soils than the known binding "fixation" that occurs on kaolinite
Kaolinite ( ; also called kaolin) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina () ...
-rich clay soils, many marshy areas of Ukraine had the highest soil to dairy-milk transfer coefficients, of soil activity in ~ 200 kBq/m2 to dairy milk activity in Bq/L, that had ever been reported, with the transfer, from initial land activity into milk activity, ranging from 0.3−2 to 20−2 times that which was on the soil.countermeasure
A countermeasure is a measure or action taken to counter or offset another one. As a general concept, it implies precision and is any technological or tactical solution or system designed to prevent an undesirable outcome in the process. The fi ...
s were used when cultivation did occur, to further reduce the soil to human transfer as much as possible. The expected highest body activity was in the first few years, where the unabated ingestion of local food resulted in the transfer of activity from soil to body. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of ...
, the now reduced scale initiative to monitor human body activity in these regions of Ukraine, recorded a small and gradual half-decade-long rise in internal committed dose before returning to the previous trend of observing lower body counts each year.
This momentary rise is hypothesized to be due to the cessation of the Soviet food imports together with many villagers returning to older dairy food cultivation practices and large increases in wild berry and mushroom foraging. In a 2007 paper, a robot sent into the No. 4 reactor returned with samples of black,
In a 2007 paper, a robot sent into the No. 4 reactor returned with samples of black, melanin
Melanin (; ) is a family of biomolecules organized as oligomers or polymers, which among other functions provide the pigments of many organisms. Melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes.
There are ...
-rich radiotrophic fungi that grow on the reactor's walls.
Of the 440,350 wild boar killed in the 2010 hunting season in Germany, approximately one thousand were contaminated with levels of radiation above the permitted limit of 600 becquerels of caesium per kilogram, of dry weight, due to residual radioactivity from Chernobyl. Because '' Elaphomyces'' fungal species bioaccumulate radiocaesium, boars of the Bavarian Forest
image:Zell-bayerischer-wald.jpg, The village of Zell in the Bavarian Forest
The Bavarian Forest ( or ''Bayerwald'' ; ) is a wooded, low-mountain region in Bavaria, Germany, that is about 100 kilometres long. It runs along the Czech Republic, C ...
that consume these "deer truffles" are contaminated at higher levels than their environment's soil. Given that nuclear weapons release a higher 135Cs/137Cs ratio than nuclear reactors, the high 135Cs content in these boars suggests that their radiological contamination can be largely attributed to the Soviet Union's nuclear weapons testing in Ukraine, which peaked during the late 1950s and early 1960s.
In 2015, long-term empirical data showed no evidence of a negative influence of radiation on mammal abundance.
Precipitation on distant high ground
On high ground, such as mountain ranges, there is increased precipitation due to adiabatic cooling. This resulted in localized concentrations of contaminants in distant areas; higher in Bq/m2 values to many lowland areas much closer to the source of the plume.
The Norwegian Agricultural Authority reported that in 2009, a total of 18,000 livestock in Norway required uncontaminated feed for a period before slaughter, to ensure that their meat had an activity below the government permitted value of caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling; also spelled cesium in American English) is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only f ...
per kilogram deemed suitable for human consumption. This contamination was due to residual radioactivity from Chernobyl in the mountain plants they grazed on in the wild during the summer. 1,914 sheep required uncontaminated feed for a time before slaughter during 2012, with these sheep located in only 18 of Norway's municipalities, a decrease from the 35 municipalities in 2011 and the 117 municipalities affected during 1986.
Human impact

Acute radiation effects and immediate aftermath
The only known causal deaths from the accident involved plant workers and firefighters. The reactor explosion killed two engineers, and 28 others died within three months from acute radiation syndrome
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS), also known as radiation sickness or radiation poisoning, is a collection of health effects that are caused by being exposed to high amounts of ionizing radiation in a short period of time. Symptoms can start wit ...
(ARS).[Mould (2000), p. 29. "The number of deaths in the first three months were 31."] due to poorly substantiated reports of an individual who died during the evacuation of Pripyat from coronary thrombosis attributed to stress.
Most serious ARS cases were treated with the assistance of American specialist Robert Peter Gale, who supervised bone marrow transplant procedures, although these were unsuccessful. The fatalities were largely due to wearing dusty, soaked uniforms causing beta burns over large areas of skin,
Long-term impact
In the 10 years following the accident, 14 more people who had been initially hospitalized died, mostly from causes unrelated to radiation exposure, with only two deaths resulting from myelodysplastic syndrome.[International Atomic Energy Agency, Chernobyl's Legacy: Health, Environmental and Socio-Economic Impacts and Recommendations to the Governments of Belarus, the Russian Federation, and Ukraine, The Chernobyl Forum: 2003–2005.] However, childhood thyroid cancer increased, with about 4,000 new cases reported by 2002 in contaminated areas of Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine, largely due to high levels of radioactive iodine
There are 40 known isotopes of iodine (53I) from 108I to 147I; all undergo radioactive decay except 127I, which is stable. Iodine is thus a monoisotopic element.
Its longest-lived radioactive isotope, 129I, has a half-life of 16.14 million year ...
. The recovery rate is ~99%, with 15 terminal cases reported.
Effects of main harmful radionuclides
The four most harmful radionuclides spread from Chernobyl were iodine-131, caesium-134, caesium-137 and strontium-90
Strontium-90 () is a radioactive isotope of strontium produced by nuclear fission, with a half-life of 28.79 years. It undergoes β− decay into yttrium-90, with a decay energy of 0.546 MeV. Strontium-90 has applications in medicine a ...
, with half-lives of 8 days, 2.07 years, 30.2 years and 28.8 years respectively.lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), an ...
s.
Disputed investigation
The mutation rates among animals in the Chernobyl zone have been a topic of ongoing scientific debate, notably regarding the research conducted by Anders Moller and Timothy Mousseau.
Withdrawn investigation
In 1996, geneticist Ronald Chesser and Robert Baker published a paper on the thriving vole
Voles are small rodents that are relatives of lemmings and hamsters, but with a stouter body; a longer, hairy tail; a slightly rounder head; smaller eyes and ears; and differently formed molars (high-crowned with angular cusps instead of lo ...
population within the exclusion zone, in which the central conclusion was essentially that "The mutation rate in these animals is hundreds and probably thousands of times greater than normal". This claim occurred after they had done a comparison of the mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
of the "Chernobyl voles" with that of a control group
In the design of experiments, hypotheses are applied to experimental units in a treatment group.
In comparative experiments, members of a control group receive a standard treatment, a placebo, or no treatment at all. There may be more than one tr ...
of voles from outside the region. The authors discovered they had incorrectly classified the species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
of vole and were genetically comparing two different vole species. They issued a retraction in 1997.[
]
Abortions
Following the accident, journalists encouraged public mistrust of medical professionals.intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability (in the United Kingdom), and formerly mental retardation (in the United States), Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010).Archive is a generalized neurodevelopmental ...
and lower verbal IQ. The Chernobyl liquidators fathered children without an increase in developmental anomalies or a significant rise in germline mutation
A germline mutation, or germinal mutation, is any detectable variation within germ cells (cells that, when fully developed, become sperm and Egg cell, ova). Mutations in these cells are the only mutations that can be passed on to offspring, when e ...
s.
Cancer assessments
A report by the International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear technology, nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was ...
examines the environmental consequences of the accident.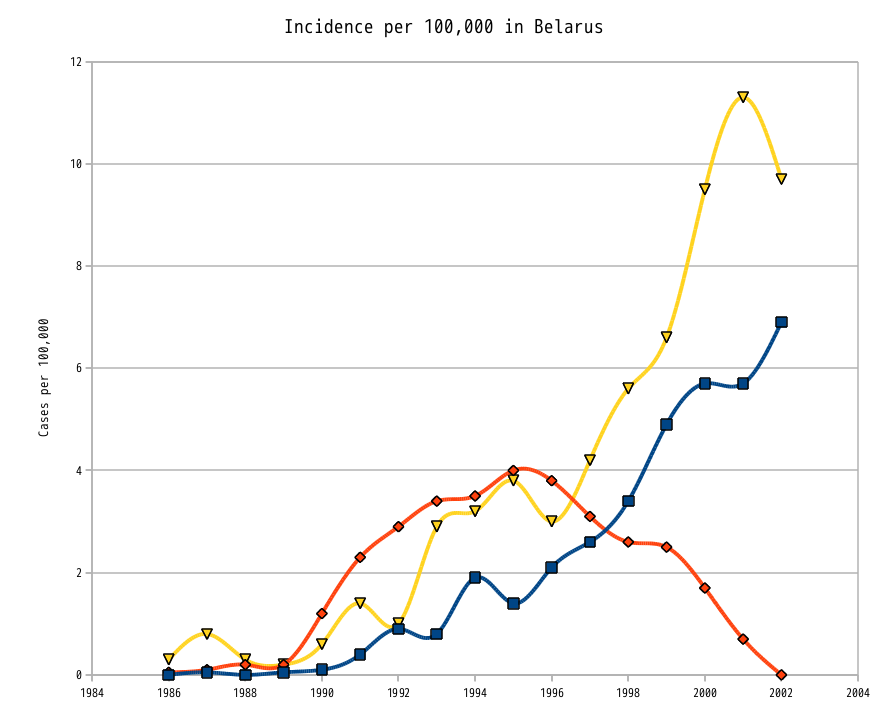 The Chernobyl Forum predicts an eventual death toll of up to 4,000 among those exposed to the highest radiation levels (200,000 emergency workers, 116,000 evacuees, and 270,000 residents of the most contaminated areas), including around 50 emergency workers who died shortly after the accident, 15 children who died of
The Chernobyl Forum predicts an eventual death toll of up to 4,000 among those exposed to the highest radiation levels (200,000 emergency workers, 116,000 evacuees, and 270,000 residents of the most contaminated areas), including around 50 emergency workers who died shortly after the accident, 15 children who died of thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck, ...
, and a predicted 3,935 deaths from radiation-induced cancer and leukemia.[ The IAEA states that there has been no increase in birth defects, solid cancers, or other abnormalities, corroborating UN assessments.]mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
s among children born in 1994. However, the risk of thyroid cancer associated with the Chernobyl accident remains high according to published studies.
Other disorders
Fred Mettler, a radiation expert, estimated 9,000 Chernobyl-related cancer deaths worldwide, noting that while small relative to normal cancer risks, the numbers are large in absolute terms.
Long-term radiation deaths
The potential deaths from the Chernobyl disaster are heavily debated. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
predicted 4,000 future cancer deaths in surrounding countries,
Socio-economic impact
It is difficult to establish the total economic cost of the disaster. According to Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the last leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
, the Soviet Union spent 18 billion Rbls ($ in today's dollars) on containment and decontamination, virtually bankrupting itself.[ (see 1996 interview with Mikhail Gorbachev).] In 2005, the total cost over 30 years for Belarus was estimated at US$235 billion.glasnost
''Glasnost'' ( ; , ) is a concept relating to openness and transparency. It has several general and specific meanings, including a policy of maximum openness in the activities of state institutions and freedom of information and the inadmissi ...
,Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
.Holodomor
The Holodomor, also known as the Ukrainian Famine, was a mass famine in Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Ukraine from 1932 to 1933 that killed millions of Ukrainians. The Holodomor was part of the wider Soviet famine of 1930–193 ...
. Commentators have argued that the Chernobyl disaster was more likely to occur in a communist
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, di ...
country than in a capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
one. Soviet power plant administrators were reportedly not empowered to make crucial decisions during the crisis.
Significance
Nuclear debate
 Because of the distrust many had in the Soviet authorities, who engaged in a cover-up, a great deal of debate about the situation occurred in the
Because of the distrust many had in the Soviet authorities, who engaged in a cover-up, a great deal of debate about the situation occurred in the First World
The concept of the First World was originally one of the " Three Worlds" formed by the global political landscape of the Cold War, as it grouped together those countries that were aligned with the Western Bloc of the United States. This groupin ...
during the early days of the event. Journalists mistrusted many professionals, and in turn encouraged the public to mistrust them as well.
 The accident also raised concerns about the cavalier safety culture in the Soviet nuclear power industry, slowing industry growth and forcing the Soviet government to become less secretive about its operating procedures.
The accident also raised concerns about the cavalier safety culture in the Soviet nuclear power industry, slowing industry growth and forcing the Soviet government to become less secretive about its operating procedures.glasnost
''Glasnost'' ( ; , ) is a concept relating to openness and transparency. It has several general and specific meanings, including a policy of maximum openness in the activities of state institutions and freedom of information and the inadmissi ...
, which "paved the way for reforms leading to the Soviet collapse." Numerous structural and construction quality issues, as well as deviations from the original plant design, had been known to the KGB since at least 1973 and passed on to the Central Committee, which took no action and classified the information.
In Italy, political fallout from the Chernobyl accident was reflected in the outcome of the 1987 nuclear power referendum. As a result, Italy began phasing out its nuclear power plants in 1988, a decision that was effectively reversed in 2008. A 2011 referendum reiterated Italians' objections to nuclear power, thus abrogating the government's 2008 decision.
In Germany, the Chernobyl accident led to the creation of a federal environment ministry. The German environmental minister was given authority over reactor safety as well, a responsibility the minister still holds today. The Chernobyl disaster is also credited with strengthening the anti-nuclear movement in Germany
The anti-nuclear movement in Germany has a long history dating back to the early 1970s when large demonstrations prevented the construction of a nuclear plant at Wyhl. The Wyhl protests were an example of a local community challenging the nuc ...
, which culminated in the decision to Nuclear power phase-out#Germany, end the use of nuclear power made by the 1998–2005 Schröder government. A temporary reversal of this policy ended with the Fukushima nuclear disaster.
In direct response to the Chernobyl disaster, a conference to create a Convention on Early Notification of a Nuclear Accident was called in 1986 by the International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear technology, nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was ...
. The resulting treaty has bound members to provide notification of any nuclear and radiation accidents that occur that could affect other states, along with the Convention on Assistance in the Case of a Nuclear Accident or Radiological Emergency.
Chernobyl has been used as a case study in research concerning the root causes of such disasters, such as sleep deprivation and mismanagement.
In popular culture
The Chernobyl tragedy has inspired many artists across the world to create works of art, animation, video games, theatre and cinema about the disaster. The HBO series ''Chernobyl (miniseries), Chernobyl'' and the book ''Voices from Chernobyl'' by the Ukrainian-Belarusian writer Svetlana Alexievich are two well-known works. The Ukrainian artist Roman Gumanyuk created a series of artworks called "Pripyat Lights, or Chernobyl shadows" that includes 30 oil paintings about the Chernobyl accident, exhibited in 2012–2013.
The video game S.T.A.L.K.E.R.: Shadow of Chernobyl, ''S.T.A.L.K.E.R.: Shadows of Chernobyl'', developed by GSC Game World and released by THQ in 2007, is a first-person shooter game set in the Exclusion zone. A prequel called ''S.T.A.L.K.E.R.: Clear Sky'' was released in 2008 following with a sequel ''S.T.A.L.K.E.R.: Call of Pripyat'' released in 2010. Finally, the horror film ''Chernobyl Diaries'' released in 2012 is about six tourists that hire a tour guide to take them to the abandoned city of Pripyat
Pripyat, also known as Prypiat, is an abandoned industrial city in Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat (river), Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 1970 as the ninth ''atomgrad'' ...
where they discover they are not alone.
Filmmaking, Filmmakers have created documentaries that examine the aftermath of the disaster over the years. Documentaries like the Oscar-winning ''Chernobyl Heart'' released in 2003, explore how radiation affected people living in the area and information about the long-term side effects of radiation exposure. ''The Babushkas of Chernobyl'' (2015) is a documentary about three women who decided to return to the exclusion zone after the disaster. In the documentary, the Babushkas show the polluted water, their food from radioactive gardens, and explain how they manage to survive in this exclusion zone despite the radioactive levels. The documentary ''The Battle of Chernobyl'' (2006) shows rare original footage a day before the disaster in the city of Pripyat, then through different methods goes in depth on the chronological events that led to the explosion of the reactor No. 4 and the disaster response.
See also
* Capture of Chernobyl – part of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Consequences of the Chernobyl disaster in France
Notes
References
Works cited
*
Further reading
External links
Official UN Chernobyl site
International Chernobyl Portal chernobyl.info, UN Inter-Agency Project ICRIN
Frequently Asked Chernobyl Questions
by the IAEA
Chernobyl disaster facts and information
by National Geographic
Chernobyl Recovery and Development Programme (United Nations Development Programme)
Footage and documentary films about Chernobyl disaster
o
Net-Film Newsreels and Documentary Films Archive
Photographs from inside the zone of alienation and City of Prypyat (2010)
Photographs from the City of Pripyat, and of those affected by the disaster
English Russia Photos of a RBMK-based power plant
showing details of the reactor hall, pumps, and the control room
Post-Soviet Pollution: Effects of Chernobyl
from theDean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
Map of residual radioactivity around Chernobyl
{{coord, 51, 23, 23, N, 30, 05, 57, E, region:UA_type:landmark, display=title, name=Chernobyl disaster
Chernobyl disaster,
1986 health disasters
1986 in Belarus
1986 in the Soviet Union
1986 in Ukraine
1986 industrial disasters
1986 disasters in Belarus
1986 disasters in the Soviet Union
1986 disasters in Ukraine
April 1986 in Europe
April 1986 in the Soviet Union
Chernobyl, Ukraine
Civilian nuclear power accidents
Disasters in the Soviet Union
Environment of the Soviet Union
Environmental disasters in Europe
Environmental disasters in Ukraine
Explosions in 1986
Industrial fires and explosions in Ukraine
Health disasters in Ukraine
INES Level 7 accidents
Man-made disasters in Belarus
Man-made disasters in the Soviet Union
Pripyat
Radiation accidents and incidents
Soviet cover-ups
 A commission was established later in the day to investigate the accident. It was headed by Valery Legasov, First Deputy Director of the Kurchatov Institute of Atomic Energy, and included leading nuclear specialist Evgeny Velikhov, hydro-meteorologist Yuri Izrael, radiologist Leonid Ilyin, and others. They flew to Boryspil International Airport and arrived at the power plant in the evening of 26 April. By that time two people had already died and 52 were hospitalized. The delegation soon had ample evidence that the reactor was destroyed and that extremely high levels of radiation had caused a number of cases of radiation exposure. In the early daylight hours of 27 April, they ordered the evacuation of Pripyat.
A translated excerpt of the evacuation announcement follows:
To expedite the evacuation, residents were told to bring only what was necessary, and that they would remain evacuated for approximately three days. As a result, most personal belongings were left behind, and residents were only allowed to recover certain items after months had passed. By 15:00, 53,000 people were evacuated to the Kiev region. The next day, talks began for evacuating people from the zone. Ten days after the accident, the evacuation area was expanded to . The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Exclusion Zone has remained ever since, although its shape has changed and its size has expanded.
The surveying and detection of isolated fallout hotspots outside this zone over the following year eventually resulted in 135,000 long-term evacuees in total. The years between 1986 and 2000 saw the near tripling in the total number of permanently resettled persons from the most severely contaminated areas to approximately 350,000. A new city of Slavutych has been built across the
A commission was established later in the day to investigate the accident. It was headed by Valery Legasov, First Deputy Director of the Kurchatov Institute of Atomic Energy, and included leading nuclear specialist Evgeny Velikhov, hydro-meteorologist Yuri Izrael, radiologist Leonid Ilyin, and others. They flew to Boryspil International Airport and arrived at the power plant in the evening of 26 April. By that time two people had already died and 52 were hospitalized. The delegation soon had ample evidence that the reactor was destroyed and that extremely high levels of radiation had caused a number of cases of radiation exposure. In the early daylight hours of 27 April, they ordered the evacuation of Pripyat.
A translated excerpt of the evacuation announcement follows:
To expedite the evacuation, residents were told to bring only what was necessary, and that they would remain evacuated for approximately three days. As a result, most personal belongings were left behind, and residents were only allowed to recover certain items after months had passed. By 15:00, 53,000 people were evacuated to the Kiev region. The next day, talks began for evacuating people from the zone. Ten days after the accident, the evacuation area was expanded to . The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Exclusion Zone has remained ever since, although its shape has changed and its size has expanded.
The surveying and detection of isolated fallout hotspots outside this zone over the following year eventually resulted in 135,000 long-term evacuees in total. The years between 1986 and 2000 saw the near tripling in the total number of permanently resettled persons from the most severely contaminated areas to approximately 350,000. A new city of Slavutych has been built across the  Evacuation began one and a half days before the accident was publicly acknowledged by the Soviet Union. On the morning of 28 April, radiation levels set off alarms at the Forsmark Nuclear Power Plant in
Evacuation began one and a half days before the accident was publicly acknowledged by the Soviet Union. On the morning of 28 April, radiation levels set off alarms at the Forsmark Nuclear Power Plant in  With the extinguishing of the open air reactor fire, the next step was to prevent the spread of contamination due to wind or birds which could land within the wreckage and then carry contamination elsewhere. In addition, rainwater could wash contamination into the sub-surface water table, where it could migrate outside the site area. Rainwater falling on the wreckage could also accelerate corrosion of steelwork in the remaining reactor structure. A further challenge was to reduce the large amount of emitted
With the extinguishing of the open air reactor fire, the next step was to prevent the spread of contamination due to wind or birds which could land within the wreckage and then carry contamination elsewhere. In addition, rainwater could wash contamination into the sub-surface water table, where it could migrate outside the site area. Rainwater falling on the wreckage could also accelerate corrosion of steelwork in the remaining reactor structure. A further challenge was to reduce the large amount of emitted  Soon after the accident, the reactor building was quickly encased by a mammoth concrete sarcophagus. Crane operators worked blindly from inside lead-lined cabins taking instructions from distant radio observers, while gargantuan pieces of concrete were moved to the site on custom-made vehicles. The purpose of the sarcophagus was to stop any further release of radioactive particles into the atmosphere, isolate the exposed core from the weather and provide safety for the continued operations of adjacent reactors one through three.
The concrete sarcophagus was never intended to last very long, with a lifespan of only 30 years. On 12 February 2013, a section of the roof of the turbine-building collapsed, adjacent to the sarcophagus, causing a new release of radioactivity and a temporary evacuation of the area. At first, it was assumed that the roof collapsed because of the weight of snow, however the amount of snow was not exceptional, and the report of a Ukrainian fact-finding panel concluded that the collapse was the result of sloppy repair work and aging of the structure. Experts warned the sarcophagus itself was on the verge of collapse.
In 1997, the international
Soon after the accident, the reactor building was quickly encased by a mammoth concrete sarcophagus. Crane operators worked blindly from inside lead-lined cabins taking instructions from distant radio observers, while gargantuan pieces of concrete were moved to the site on custom-made vehicles. The purpose of the sarcophagus was to stop any further release of radioactive particles into the atmosphere, isolate the exposed core from the weather and provide safety for the continued operations of adjacent reactors one through three.
The concrete sarcophagus was never intended to last very long, with a lifespan of only 30 years. On 12 February 2013, a section of the roof of the turbine-building collapsed, adjacent to the sarcophagus, causing a new release of radioactivity and a temporary evacuation of the area. At first, it was assumed that the roof collapsed because of the weight of snow, however the amount of snow was not exceptional, and the report of a Ukrainian fact-finding panel concluded that the collapse was the result of sloppy repair work and aging of the structure. Experts warned the sarcophagus itself was on the verge of collapse.
In 1997, the international  After the disaster, of
After the disaster, of  In a 2007 paper, a robot sent into the No. 4 reactor returned with samples of black,
In a 2007 paper, a robot sent into the No. 4 reactor returned with samples of black, 
 The Chernobyl Forum predicts an eventual death toll of up to 4,000 among those exposed to the highest radiation levels (200,000 emergency workers, 116,000 evacuees, and 270,000 residents of the most contaminated areas), including around 50 emergency workers who died shortly after the accident, 15 children who died of
The Chernobyl Forum predicts an eventual death toll of up to 4,000 among those exposed to the highest radiation levels (200,000 emergency workers, 116,000 evacuees, and 270,000 residents of the most contaminated areas), including around 50 emergency workers who died shortly after the accident, 15 children who died of  Because of the distrust many had in the Soviet authorities, who engaged in a cover-up, a great deal of debate about the situation occurred in the
Because of the distrust many had in the Soviet authorities, who engaged in a cover-up, a great deal of debate about the situation occurred in the 
 The accident also raised concerns about the cavalier safety culture in the Soviet nuclear power industry, slowing industry growth and forcing the Soviet government to become less secretive about its operating procedures. The government cover-up of the Chernobyl disaster was a catalyst for
The accident also raised concerns about the cavalier safety culture in the Soviet nuclear power industry, slowing industry growth and forcing the Soviet government to become less secretive about its operating procedures. The government cover-up of the Chernobyl disaster was a catalyst for