Arkansas Razorbacks Men's Basketball Players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked
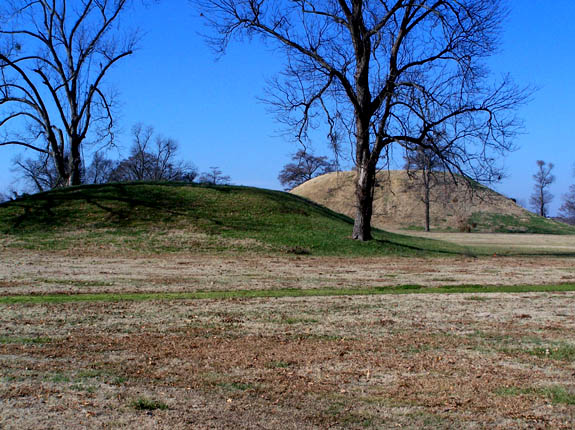 Before European settlement of North America, Arkansas was inhabited by indigenous peoples for thousands of years. The
Before European settlement of North America, Arkansas was inhabited by indigenous peoples for thousands of years. The

accessed April 3, 2008. Five whites also died in the incident. The governor accompanied the troops to the scene; President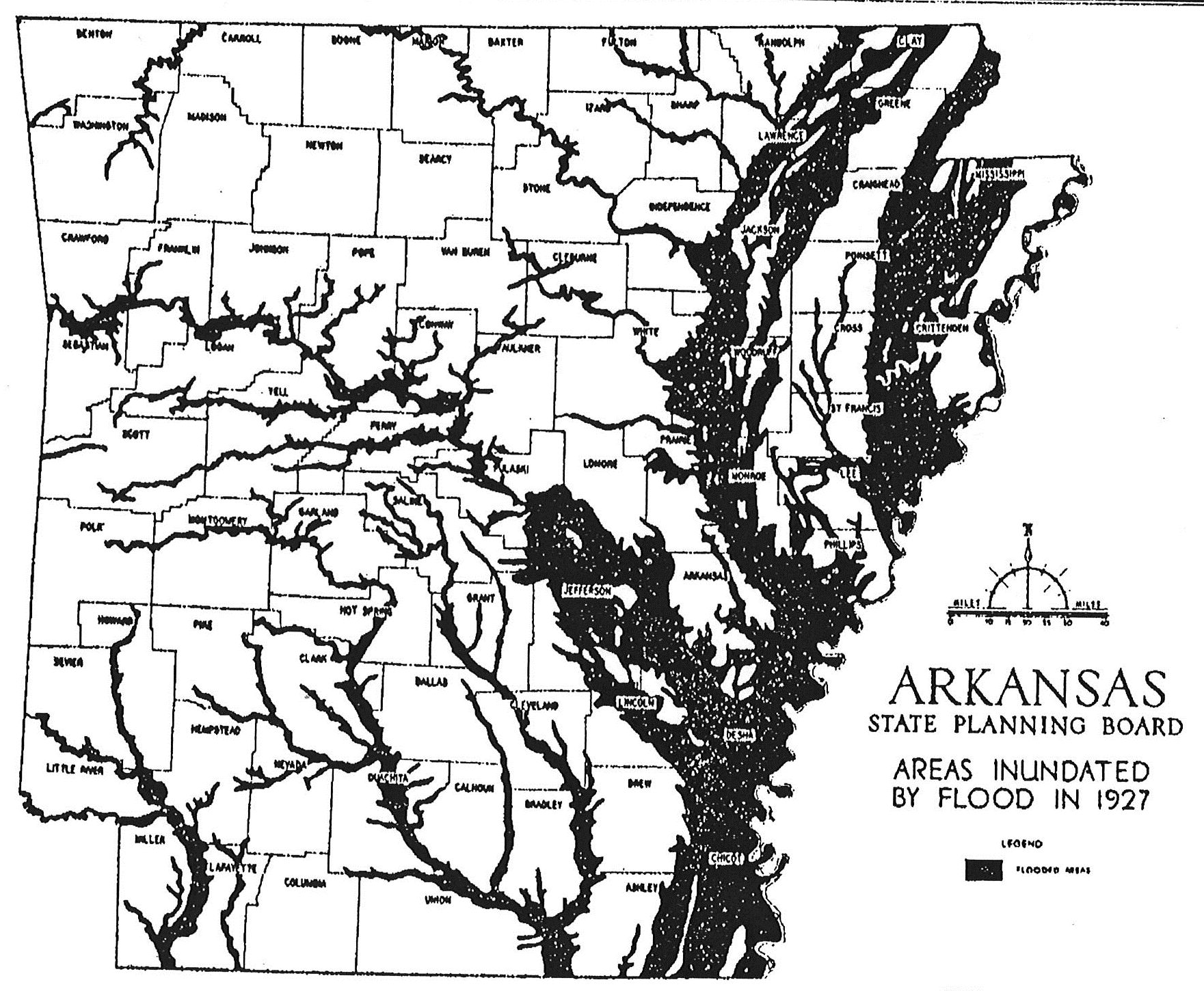 The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 flooded the areas along the Ouachita Rivers along with many other rivers.
Based on the order of President
The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 flooded the areas along the Ouachita Rivers along with many other rivers.
Based on the order of President

 Arkansas can generally be split into two halves, the highlands in the northwest and the lowlands of the southeast. The highlands are part of the Southern Interior Highlands, including
Arkansas can generally be split into two halves, the highlands in the northwest and the lowlands of the southeast. The highlands are part of the Southern Interior Highlands, including
 Arkansas has many rivers, lakes, and reservoirs within or along its borders. Major tributaries to the Mississippi River include the
Arkansas has many rivers, lakes, and reservoirs within or along its borders. Major tributaries to the Mississippi River include the


 European Americans have a strong presence in the northwestern
European Americans have a strong presence in the northwestern
 Once a state with a cashless society in the uplands and
Once a state with a cashless society in the uplands and
 Transportation in Arkansas is overseen by the
Transportation in Arkansas is overseen by the  Arkansas is served by of railroad track divided among twenty-six railroad companies including three Class I railroads. Freight railroads are concentrated in southeast Arkansas to serve the industries in the region. The
Arkansas is served by of railroad track divided among twenty-six railroad companies including three Class I railroads. Freight railroads are concentrated in southeast Arkansas to serve the industries in the region. The
 As of 2012, Arkansas, as with many Southern states, has a high incidence of premature death, infant mortality, cardiovascular deaths, and occupational fatalities compared to the rest of the United States. The state is tied for 43rd with New York in percentage of adults who regularly exercise. Arkansas is usually ranked as one of the least healthy states due to high obesity, smoking, and sedentary lifestyle rates, but according to a Gallup poll, Arkansas made the most immediate progress in reducing its number of uninsured residents after the
As of 2012, Arkansas, as with many Southern states, has a high incidence of premature death, infant mortality, cardiovascular deaths, and occupational fatalities compared to the rest of the United States. The state is tied for 43rd with New York in percentage of adults who regularly exercise. Arkansas is usually ranked as one of the least healthy states due to high obesity, smoking, and sedentary lifestyle rates, but according to a Gallup poll, Arkansas made the most immediate progress in reducing its number of uninsured residents after the
 The culture of Arkansas includes distinct cuisine, dialect, and traditional festivals. Sports are also very important to the culture, including football, baseball, basketball, hunting, and fishing. Perhaps the best-known aspect of Arkansas's culture is the stereotype that its citizens are shiftless hillbillies. The reputation began when early explorers characterized the state as a savage wilderness full of outlaws and thieves. The most enduring icon of Arkansas's hillbilly reputation is '' The Arkansas Traveller'', a painted depiction of a folk tale from the 1840s. Though intended to represent the divide between rich southeastern plantation Arkansas planters and the poor northwestern hill country, the meaning was twisted to represent a Northerner lost in the Ozarks on a white horse asking a backwoods Arkansan for directions. The state also suffers from the racial stigma common to former Confederate states, with historical events such as the
The culture of Arkansas includes distinct cuisine, dialect, and traditional festivals. Sports are also very important to the culture, including football, baseball, basketball, hunting, and fishing. Perhaps the best-known aspect of Arkansas's culture is the stereotype that its citizens are shiftless hillbillies. The reputation began when early explorers characterized the state as a savage wilderness full of outlaws and thieves. The most enduring icon of Arkansas's hillbilly reputation is '' The Arkansas Traveller'', a painted depiction of a folk tale from the 1840s. Though intended to represent the divide between rich southeastern plantation Arkansas planters and the poor northwestern hill country, the meaning was twisted to represent a Northerner lost in the Ozarks on a white horse asking a backwoods Arkansan for directions. The state also suffers from the racial stigma common to former Confederate states, with historical events such as the
 Team sports and especially collegiate football are important to Arkansans. College football in Arkansas began from humble beginnings, when the
Team sports and especially collegiate football are important to Arkansans. College football in Arkansas began from humble beginnings, when the
 * Arkansas Post National Memorial at Gillett, Arkansas, Gillett
* Blanchard Springs Caverns
*
* Arkansas Post National Memorial at Gillett, Arkansas, Gillett
* Blanchard Springs Caverns
*
Hamilton, Peter Joseph. ''The Reconstruction Period''
(1906), full length history of era; Dunning School approach; 570 pp; ch 13 on Arkansas * Hanson, Gerald T. and Carl H. Moneyhon. ''Historical Atlas of Arkansas'' (1992) * Key, V. O. ''Southern Politics'' (1949) * Kirk, John A., ''Redefining the Color Line: Black Activism in Little Rock, Arkansas, 1940–1970'' (2002). * McMath, Sidney S. ''Promises Kept'' (2003) * Moore, Waddy W. ed., ''Arkansas in the Gilded Age, 1874–1900'' (1976). * Peirce, Neal R. ''The Deep South States of America: People, Politics, and Power in the Seven Deep South States'' (1974). * Thompson, Brock. ''The Un-Natural State: Arkansas and the Queer South'' (2010) * Thompson, George H. ''Arkansas and Reconstruction'' (1976) * Whayne, Jeannie M. ''Arkansas Biography: A Collection of Notable Lives'' (2000) * White, Lonnie J. ''Politics on the Southwestern Frontier: Arkansas Territory, 1819–1836'' (1964) * Williams, C. Fred. ed. ''A Documentary History Of Arkansas'' (2005)
Arkansas.gov
€”Official State Website
Arkansas State Facts from USDA
Official State tourism website
''Encyclopedia of Arkansas''
Energy & Environmental Data for Arkansas
2000 Census of Population and Housing for Arkansas
U.S. Census Bureau
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Arkansas
Arkansas Summer Camps
Arkansas Shakespeare Theatre
* *
Arkansas State Code (the state statutes of Arkansas)
Arkansas State Databases
€”Annotated list of searchable databases produced by Arkansas state agencies and compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association. {{Coord, 35, -92, dim:300000_region:US-AR_type:adm1st, name=State of Arkansas, display=title Arkansas, 1836 establishments in the United States Contiguous United States South Central United States Southern United States States and territories established in 1836 States of the Confederate States of America States of the United States
state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
in the West South Central region of the Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is List of regions of the United States, census regions defined by the United States Cens ...
. It borders Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
to the north, Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
and Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
to the east, Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
to the south, Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
to the southwest, and Oklahoma
Oklahoma ( ; Choctaw language, Choctaw: , ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northea ...
to the west. Its name derives from the Osage language
Osage (; Osage: ''Wažáže ie'') is a Siouan language spoken by the people of the Osage Nation in northern Oklahoma. Their original territory was in the present-day Ohio River Valley, which they shared with other Siouan language nations. Slow ...
, and refers to their relatives, the Quapaw
The Quapaw ( , Quapaw language, Quapaw: ) or Arkansas, officially the Quapaw Nation, is a List of federally recognized tribes in the United States, U.S. federally recognized tribe comprising about 6,000 citizens. Also known as the Ogáxpa or †...
people. The state's diverse geography ranges from the mountainous regions of the Ozark and Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thru ...
, which make up the U.S. Interior Highlands
The U.S. Interior Highlands is a mountainous region in the Central United States spanning northern and western Arkansas, southern Missouri, eastern Oklahoma, and southern Illinois. The name is designated by the United States Geological Survey to ...
, to the densely forested land in the south known as the Arkansas Timberlands, to the eastern lowlands along the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
and the Arkansas Delta
The Arkansas Delta is one of the six natural regions of the state of Arkansas. Willard B. Gatewood Jr., author of ''The Arkansas Delta: Land of Paradox'', says that rich cotton lands of the Arkansas Delta make that area "The Deepest of the Deep ...
.
Previously part of French Louisiana
The term French Louisiana ( ; ) refers to two distinct regions:
* First, to Louisiana (New France), historic French Louisiana, comprising the massive, middle section of North America claimed by Early Modern France, France during the 17th and 18th ...
and the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase () was the acquisition of the Louisiana (New France), territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River#Watershed, Mississipp ...
, the Territory of Arkansas was admitted to the Union as the 25th state on June 15, 1836. Much of the Delta had been developed for cotton plantations, and landowners there largely depended on enslaved African Americans' labor. In 1861, Arkansas seceded from the United States and joined the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), also known as the Confederate States (C.S.), the Confederacy, or Dixieland, was an List of historical unrecognized states and dependencies, unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United State ...
during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
. On returning to the Union in 1868, Arkansas continued to suffer economically, due to its overreliance on the large-scale plantation economy. Cotton remained the leading commodity crop, and the cotton market declined. Because farmers and businessmen did not diversify and there was little industrial investment, the state fell behind in economic opportunity. In the late 19th century, the state instituted various Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were U.S. state, state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, "Jim Crow (character), Ji ...
to disenfranchise and segregate the African-American population. White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
interests dominated Arkansas's politics, with disenfranchisement of African Americans and refusal to reapportion the legislature; only after the federal legislation passed were more African Americans able to vote. During the civil rights movement of the 1950s and 1960s, Arkansas and particularly Little Rock were major battlegrounds for efforts to integrate schools. Following World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
in the 1940s, Arkansas began to diversify its economy and see prosperity. During the 1960s, the state became the base of the Walmart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores in the United States and 23 other ...
corporation, the world's largest company by revenue, headquartered in Bentonville.
Arkansas is the 29th largest by area and the 33rd most populous state, with a population of just over three million at the 2020 census. The capital and most populous city is Little Rock
Little Rock is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Arkansas, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The city's population was 202,591 as of the 2020 census. The six-county Central Arkan ...
, in the central part of the state, a hub for transportation, business, culture, and government. The northwestern corner of the state, namely the Fayetteville–Springdale–Rogers Metropolitan Area, is a population, education, cultural, and economic center. The Fort Smith Metropolitan Area
The Fort Smith Metropolitan Statistical Area, as defined by the United States Census Bureau, is a five-county area including three Arkansas county, counties and two Oklahoma counties, and anchored by the city of Fort Smith, Arkansas. The total M ...
is also an economic center and is known for its historic sites related to western expansion and the persecution of Native Americans. The largest city in the state's eastern part is Jonesboro. The largest city in the state's southeastern part is Pine Bluff.
In the 21st century, Arkansas's economy is based on service industries, aircraft, poultry, steel, and tourism, along with important commodity crops of cotton, soybeans
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source of f ...
and rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
. The state supports a network of public universities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
and colleges, including two major university systems: Arkansas State University System
The Arkansas State University System, based in Little Rock, serves almost 40,000 students annually on campuses in Arkansas and Querétaro, Queretaro, Mexico, and globally online.
The Arkansas State University System includes Arkansas State Unive ...
and University of Arkansas System
The University of Arkansas System is a state university system in the U.S. state of Arkansas. It comprises six campuses; a medical school; two law schools; a graduate school focused on public service; a historically black college, statewide rese ...
. Arkansas's culture is observable in museums, theaters, novels, television shows, restaurants, and athletic venues across the state.
Etymology
The name ''Arkansas'' initially applied to theArkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in Colorado, specifically ...
. It derives from a French term, ''Arcansas'', their plural term for their transliteration of ''akansa'', an Algonquian term for the Quapaw
The Quapaw ( , Quapaw language, Quapaw: ) or Arkansas, officially the Quapaw Nation, is a List of federally recognized tribes in the United States, U.S. federally recognized tribe comprising about 6,000 citizens. Also known as the Ogáxpa or †...
people, which is believed to translate to "south wind people." These were a Dhegiha Siouan-speaking people who settled in Arkansas around the 13th century. ''Kansa'' is likely also the root term for Kansas
Kansas ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named a ...
, which was named after the related Kaw people
The Kaw Nation (or Kanza or Kansa) is a federally recognized Native American tribe in Oklahoma and parts of Kansas. The Kaw people historically lived in the central Midwestern United States. They have also been called the "People of the Sou ...
.
The name has been pronounced and spelled in a variety of ways. In 1881, the state legislature defined the official pronunciation of Arkansas as having the final "s" be silent (as it would be in French). A dispute had arisen between the state's two senators over the pronunciation issue. One favored (), the other ().
In 2007, the state legislature passed a non-binding resolution declaring that the possessive form of the state's name is ''Arkansas's'', which the state government has increasingly followed.
History
Early history
 Before European settlement of North America, Arkansas was inhabited by indigenous peoples for thousands of years. The
Before European settlement of North America, Arkansas was inhabited by indigenous peoples for thousands of years. The Caddo
The Caddo people comprise the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe headquartered in Binger, Oklahoma. They speak the Caddo language.
The Caddo Confederacy was a network of Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, who ...
, Osage, and Quapaw
The Quapaw ( , Quapaw language, Quapaw: ) or Arkansas, officially the Quapaw Nation, is a List of federally recognized tribes in the United States, U.S. federally recognized tribe comprising about 6,000 citizens. Also known as the Ogáxpa or †...
peoples encountered European explorers. The first of these Europeans was Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1497 – 21 May 1542) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, ...
in 1541, who crossed the Mississippi and marched across central Arkansas and the Ozark Mountains. After finding nothing he considered of value and encountering native resistance the entire way, he and his men returned to the Mississippi River where de Soto fell ill. From his deathbed he ordered his men to massacre all the men of the nearby village of Anilco, who he feared had been plotting with a powerful polity down the Mississippi River, '' Quigualtam''. His men obeyed and did not stop with the men, but were said to have massacred women and children as well. He died the following day in what is believed to be the vicinity of modern-day McArthur, Arkansas
McArthur is an unincorporated community in Clayton Township, Desha County, Arkansas. It is located on Arkansas Highway 1 northeast of McGehee.
McArthur is one of two possible sites of the death of Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1 ...
, in May 1542. His body was weighted down with sand and he was consigned to a watery grave in the Mississippi River under cover of darkness by his men. De Soto had attempted to deceive the native population into thinking he was an immortal deity, sun of the sun, in order to forestall attack by outraged Native Americans on his by then weakened and bedraggled army. In order to keep the ruse up, his men informed the locals that de Soto had ascended into the sky. His will at the time of his death listed "four Indian slaves, three horses and 700 hogs" which were auctioned off. The starving men, who had been living off maize stolen from natives, immediately started butchering the hogs and later, commanded by former aide-de-camp Moscoso, attempted an overland return to Mexico. They made it as far as Texas before running into territory too dry for maize farming and too thinly populated to sustain themselves by stealing food from the locals. The expedition promptly backtracked to Arkansas. After building a small fleet of boats they then headed down the Mississippi River and eventually on to Mexico by water.
Later explorers included the French Jacques Marquette
Jacques Marquette, Society of Jesus, S.J. (; June 1, 1637 – May 18, 1675), sometimes known as Père Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Society of Jesus, Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Ste. M ...
and Louis Jolliet
Louis Jolliet (; September 21, 1645after May 1700) was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, a Jesuit Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to explore ...
in 1673, and Frenchmen Robert La Salle and Henri de Tonti
Henri de Tonti (born Enrico Tonti; – September 1704) was an Italian-born French military officer and explorer who assisted René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle during the French colonization of the Americas from 1678 to 1686."A tour of M ...
in 1681. Tonti established Arkansas Post
The Arkansas Post (; ), officially the Arkansas Post National Memorial, was the first European colonization of the Americas, European settlement located along the Mississippi River, in the Mississippi Alluvial Plain, and in the present-day U. ...
at a Quapaw village in 1686, making it the first European settlement in the territory.Arnold 1992, p. 75. The early Spanish or French explorers of the state gave it its name, which is probably a phonetic spelling of the Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
tribe's name for the Quapaw
The Quapaw ( , Quapaw language, Quapaw: ) or Arkansas, officially the Quapaw Nation, is a List of federally recognized tribes in the United States, U.S. federally recognized tribe comprising about 6,000 citizens. Also known as the Ogáxpa or †...
people, who lived downriver from them. The name Arkansas has been pronounced and spelled in a variety of fashions. The region was organized as the Territory of Arkansaw on July 4, 1819, with the territory admitted to the United States as the state of Arkansas on June 15, 1836. The name was historically , , and several other variants. Historically and modernly, the people of Arkansas call themselves either "Arkansans" or "Arkansawyers". In 1881, the Arkansas General Assembly
The General Assembly of Arkansas is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The legislature is a bicameral body composed of the upper house Arkansas Senate with 35 members, and the lower Arkansas House of Representatives with 1 ...
passed Arkansas Code 1-4-105 (official text):
Whereas, confusion of practice has arisen in the pronunciation of the name of our state and it is deemed important that the true pronunciation should be determined for use in oral official proceedings.
And, whereas, the matter has been thoroughly investigated by the State Historical Society and the Eclectic Society of Little Rock, which have agreed upon the correct pronunciation as derived from history, and the early usage of the American immigrants.
Be it therefore resolved by both houses of the General Assembly, that the only true pronunciation of the name of the state, in the opinion of this body, is that received by the French from the native Indians and committed to writing in the French word representing the sound. It should be pronounced in three (3) syllables, with the final "s" silent, the "a" in each syllable with the Italian sound, and the accent on the first and last syllables. The pronunciation with the accent on the second syllable with the sound of "a" in "man" and the sounding of the terminal "s" is an innovation to be discouraged.Citizens of the
state of Kansas
Kansas ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named a ...
often pronounce the Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in Colorado, specifically ...
as , in a manner similar to the common pronunciation of the name of their state.
Settlers, such as fur trappers, moved to Arkansas in the early 18th century. These people used Arkansas Post as a home base and entrepĂ´t
An entrepĂ´t ( ; ) or transshipment port is a port, city, or trading post where merchandise may be imported, stored, or traded, usually to be exported again. Such cities often sprang up and such ports and trading posts often developed into comm ...
. During the colonial period, Arkansas changed hands between France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
following the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
, although neither showed interest in the remote settlement of Arkansas Post. In April 1783, Arkansas saw its only battle of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
, a brief siege
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict charact ...
of the post by British Captain James Colbert with the assistance of the Choctaw
The Choctaw ( ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States, originally based in what is now Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama. The Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choct ...
and Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, United States. Their traditional territory was in northern Mississippi, northwestern and northern Alabama, western Tennessee and southwestern Kentucky. Their language is ...
.
Purchase and statehood
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
sold French Louisiana
The term French Louisiana ( ; ) refers to two distinct regions:
* First, to Louisiana (New France), historic French Louisiana, comprising the massive, middle section of North America claimed by Early Modern France, France during the 17th and 18th ...
to the United States in 1803, including all of Arkansas, in a transaction known today as the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase () was the acquisition of the Louisiana (New France), territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River#Watershed, Mississipp ...
. French soldiers remained as a garrison at Arkansas Post
The Arkansas Post (; ), officially the Arkansas Post National Memorial, was the first European colonization of the Americas, European settlement located along the Mississippi River, in the Mississippi Alluvial Plain, and in the present-day U. ...
. Following the purchase, the balanced give-and-take relationship between settlers and Native Americans began to change all along the frontier, including in Arkansas. Following a controversy over allowing slavery in the territory, the Territory of Arkansas was organized on July 4, 1819. Gradual emancipation in Arkansas was struck down by one vote, the Speaker of the House Henry Clay
Henry Clay (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the United States Senate, U.S. Senate and United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives. He was the seventh Spea ...
, allowing Arkansas to organize as a slave territory.
Slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
became a wedge issue in Arkansas, forming a geographic divide that remained for decades. Owners and operators of the cotton plantation economy in southeast Arkansas firmly supported slavery, as they perceived slave labor
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
as the best or "only" economically viable method of harvesting their commodity crops. The "hill country" of northwest Arkansas was unable to grow cotton and relied on a cash-scarce, subsistence farming
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow crops on smallholdings to meet the needs of themselves and their families. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements. Planting decisions occ ...
economy.
As European Americans settled throughout the East Coast and into the Midwest, in the 1830s the United States government forced the removal of many Native American tribes to Arkansas and Indian Territory
Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United States, ...
west of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
.
Additional Native American removals began in earnest during the territorial period, with final Quapaw removal complete by 1833 as they were pushed into Indian Territory. The capital was relocated from Arkansas Post to Little Rock
Little Rock is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Arkansas, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The city's population was 202,591 as of the 2020 census. The six-county Central Arkan ...
in 1821, during the territorial period.
When Arkansas applied for statehood, the slavery issue was again raised in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
Congress eventually approved the Arkansas Constitution
The Constitution of Arkansas is the primary organizing law for the U.S. state of Arkansas delineating the duties, powers, structures, and functions of the state government. Arkansas' original constitution was adopted at a constitutional conv ...
after a 25-hour session, admitting Arkansas on June 15, 1836, as the 25th state and the 13th slave state
In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were prohibited. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave s ...
, having a population of about 60,000. Arkansas struggled with taxation to support its new state government, a problem made worse by a state banking scandal and worse yet by the Panic of 1837
The Panic of 1837 was a financial crisis in the United States that began a major depression (economics), depression which lasted until the mid-1840s. Profits, prices, and wages dropped, westward expansion was stalled, unemployment rose, and pes ...
.
Civil War and Reconstruction
In early antebellum Arkansas, the southeast Arkansas slave-based economy developed rapidly. On the eve of the American Civil War in 1860, enslaved African Americans numbered 111,115 people, just over 25% of the state's population. A plantation system based largely on cotton agriculture developed that, after the war, kept the state and region behind the nation for decades. The wealth developed among planters of southeast Arkansas caused a political rift between the northwest and southeast.Bolton 1999, p. 22. Many politicians were elected to office from the Family, the Southern rights political force in antebellum Arkansas. Residents generally wanted to avoid a civil war. When the Gulf states seceded in early 1861, delegates to a convention called to determine whether Arkansas should secede referred the question back to the voters for a referendum to be held in August. Arkansas did not secede untilAbraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
demanded Arkansas troops be sent to Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter is a historical Coastal defense and fortification#Sea forts, sea fort located near Charleston, South Carolina. Constructed on an artificial island at the entrance of Charleston Harbor in 1829, the fort was built in response to the W ...
to quell the rebellion there. On May 6, the members of the state convention, having been recalled by the convention president, voted to terminate Arkansas's membership in the Union and join the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), also known as the Confederate States (C.S.), the Confederacy, or Dixieland, was an List of historical unrecognized states and dependencies, unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United State ...
.
Arkansas held a very important position for the Rebels, maintaining control of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
and surrounding Southern states. The bloody Battle of Wilson's Creek
The Battle of Wilson's Creek, also known as the Battle of Oak Hills, was the first major battle of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War. It was fought on August 10, 1861, near Springfield, Missouri.
In August, Confe ...
just across the border in Missouri shocked many Arkansans who thought the war would be a quick and decisive Southern victory. Battles early in the war took place in northwest Arkansas, including the Battle of Cane Hill, Battle of Pea Ridge
The Battle of Pea Ridge (March 7–8, 1862), also known as the Battle of Elkhorn Tavern, took place during the American Civil War near Leetown, Arkansas, Leetown, northeast of Fayetteville, Arkansas, Fayetteville, Arkansas. United States, Feder ...
, and Battle of Prairie Grove. Union general Samuel Curtis swept across the state to Helena in the Delta in 1862. Little Rock was captured the following year. The government shifted the state Confederate capital to Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a Spring (hydrology), spring produced by the emergence of Geothermal activity, geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow ...
, and then again to Washington from 1863 to 1865, for the remainder of the war. Throughout the state, guerrilla
Guerrilla warfare is a form of unconventional warfare in which small groups of irregular military, such as rebels, Partisan (military), partisans, paramilitary personnel or armed civilians, which may include Children in the military, recruite ...
warfare ravaged the countryside and destroyed cities. Passion for the Confederate cause waned after implementation of programs such as the draft, high taxes, and martial law.
Under the Military Reconstruction Act, Congress declared Arkansas restored to the Union in June 1868, after the Legislature accepted the 14th Amendment. The Republican-controlled reconstruction legislature established universal male suffrage (though temporarily disfranchising former Confederate Army officers, who were all Democrats), a public education system for blacks and whites, and passed general issues to improve the state and help more of the population. The State soon came under control of the Radical Republicans and Unionists, and led by Governor Powell Clayton
Powell Foulk Clayton (August 7, 1833August 25, 1914) was an American politician, diplomat, and businessman who served as the 9th List of Governors of Arkansas, governor of Arkansas from 1868 to 1871, as a Republican Party (United States), Repub ...
, they presided over a time of great upheaval as Confederate sympathizers and the Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to KKK or Klan, is an American Protestant-led Christian terrorism, Christian extremist, white supremacist, Right-wing terrorism, far-right hate group. It was founded in 1865 during Reconstruction era, ...
fought the new developments, particularly voting rights for African Americans.
End of Reconstruction and late 19th century
In 1874, the Brooks-Baxter War, a political struggle between factions of the Republican Party shook Little Rock and the state governorship. It was settled only when PresidentUlysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
ordered Joseph Brooks to disperse his militant supporters.
Following the Brooks-Baxter War, a new state constitution was ratified, re-enfranchising former Confederates and effectively bringing an end to Reconstruction.
In 1881, the Arkansas state legislature enacted a bill that adopted an official pronunciation of the state's name, to combat a controversy then simmering. (See Law and Government below.)
After Reconstruction, the state began to receive more immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short- ...
and migrants. Chinese, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
, and Syrian
Syrians () are the majority inhabitants of Syria, indigenous to the Levant, most of whom have Arabic, especially its Levantine and Mesopotamian dialects, as a mother tongue. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend ...
men were recruited for farm labor in the developing Delta region. None of these nationalities stayed long at farm labor; the Chinese especially, as they quickly became small merchants in towns around the Delta. Many Chinese became such successful merchants in small towns that they were able to educate their children at college.
Construction of railroads enabled more farmers to get their products to market. It also brought new development into different parts of the state, including the Ozarks, where some areas were developed as resorts. In a few years at the end of the 19th century, for instance, Eureka Springs in Carroll County grew to 10,000 people, rapidly becoming a tourist destination and the fourth-largest city of the state. It featured newly constructed, elegant resort hotels and spas planned around its natural springs, considered to have healthful properties. The town's attractions included horse racing and other entertainment. It appealed to a wide variety of classes, becoming almost as popular as Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a Spring (hydrology), spring produced by the emergence of Geothermal activity, geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow ...
.
Rise of the Jim Crow laws and early 20th century
In the late 1880s, the worsening agricultural depression catalyzed Populist and third party movements, leading to interracial coalitions. Struggling to stay in power, in the 1890s the Democrats in Arkansas followed other Southern states in passing legislation and constitutional amendments that disfranchised blacks and poor whites. In 1891 state legislators passed a requirement for a literacy test, knowing it would exclude many blacks and whites. At the time, more than 25% of the population could neither read nor write. In 1892, they amended the state constitution to require apoll tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources. ''Poll'' is an archaic term for "head" or "top of the head". The sen ...
and more complex residency requirements, both of which adversely affected poor people and sharecroppers, forcing most blacks and many poor whites from voter rolls.
By 1900 the Democratic Party expanded use of the white primary in county and state elections, further denying blacks a part in the political process. Only in the primary was there any competition among candidates, as Democrats held all the power. The state was a Democratic one-party state for decades, until after passage of the federal Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
and Voting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights move ...
to enforce constitutional rights.
Between 1905 and 1911, Arkansas began to receive a small immigration of German, Slovak, and Scots-Irish from Europe. The German and Slovak peoples settled in the eastern part of the state known as the Prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
, and the Irish founded small communities in the southeast part of the state. The Germans were mostly Lutheran and the Slovaks were primarily Catholic. The Irish were mostly Protestant from Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
, of Scots and Northern Borders descent. Some early 20th-century immigration included people from eastern Europe. Together, these immigrants made the Delta more diverse than the rest of the state. In the same years, some black migrants moved into the area because of opportunities to develop the bottomlands and own their own property.
Black sharecroppers began to try to organize a farmers' union after World WarI. They were seeking better conditions of payment and accounting from white landowners of the area cotton plantations. Whites resisted any change and often tried to break up their meetings. On September 30, 1919, two white men, including a local deputy, tried to break up a meeting of black sharecroppers who were trying to organize a farmers' union. After a white deputy was killed in a confrontation with guards at the meeting, word spread to town and around the area. Hundreds of whites from Phillips and neighboring areas rushed to suppress the blacks, and started attacking blacks at large. Governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
Charles Hillman Brough requested federal troops to stop what was called the Elaine massacre. White mobs spread throughout the county, killing an estimated 237 blacks before most of the violence was suppressed after October 1.Elaine Massacre, Arkansas Encyclopedia of History and Cultureaccessed April 3, 2008. Five whites also died in the incident. The governor accompanied the troops to the scene; President
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
had approved their use.
 The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 flooded the areas along the Ouachita Rivers along with many other rivers.
Based on the order of President
The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 flooded the areas along the Ouachita Rivers along with many other rivers.
Based on the order of President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
given shortly after Imperial Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
's attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Empire of Japan on the United States Pacific Fleet at Naval Station Pearl Harbor, its naval base at Pearl Harbor on Oahu, Territory of ...
, nearly 16,000 Japanese Americans
are Americans of Japanese ancestry. Japanese Americans were among the three largest Asian Americans, Asian American ethnic communities during the 20th century; but, according to the 2000 United States census, 2000 census, they have declined in ...
were forcibly removed from the West Coast of the United States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast and the Western Seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the Contiguous United States, contig ...
and incarcerated in two internment camps in the Arkansas Delta
The Arkansas Delta is one of the six natural regions of the state of Arkansas. Willard B. Gatewood Jr., author of ''The Arkansas Delta: Land of Paradox'', says that rich cotton lands of the Arkansas Delta make that area "The Deepest of the Deep ...
. The Rohwer Camp in Desha County operated from September 1942 to November 1945 and at its peak interned 8,475 prisoners. The Jerome War Relocation Center
The Jerome War Relocation Center was a Japanese American internment camp located in southeastern Arkansas, near the town of Jerome, Arkansas, Jerome in the Arkansas Delta. Open from October 6, 1942, until June 30, 1944, it was the last American ...
in Drew County operated from October 1942 to June 1944 and held about 8,000.
Fall of segregation
After theSupreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
ruled segregation in public schools unconstitutional in ''Brown ''v.'' Board of Education of Topeka, Kansas'' (1954), some students worked to integrate schools in the state. The Little Rock Nine
The Little Rock Nine were a group of nine African American students enrolled in Little Rock Central High School in 1957. Their enrollment was followed by the Little Rock Crisis, in which the students were initially prevented from entering th ...
brought Arkansas to national attention in 1957 when the federal government had to intervene to protect African-American students trying to integrate a high school in the capital. Governor Orval Faubus
Orval Eugene Faubus ( ; January 7, 1910 – December 14, 1994) was an American politician who served as the List of governors of Arkansas, 36th Governor of Arkansas from 1955 to 1967, as a member of the Democratic Party (United States), D ...
had ordered the Arkansas National Guard
The Arkansas National Guard (ARNG), commonly known as the Arkansas Guard, is a component of the Politics and government of Arkansas, Government of Arkansas and the National Guard of the United States. It is composed of Arkansas Army National Guar ...
to help segregationists prevent nine African-American students from enrolling at Little Rock's Central High School. After attempting three times to contact Faubus, President Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was the 34th president of the United States, serving from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionar ...
sent 1,000 troops from the active-duty 101st Airborne Division to escort and protect the African-American students as they entered school on September 25, 1957. In defiance of federal court orders to integrate, the governor and city of Little Rock decided to close the high schools for the remainder of the school year. By the fall of 1959, the Little Rock high schools were completely integrated.
Geography

Boundaries
Arkansas bordersLouisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
to the south, Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
to the southwest, Oklahoma
Oklahoma ( ; Choctaw language, Choctaw: , ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northea ...
to the west, Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
to the north, and Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
and Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
to the east. The United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
classifies Arkansas as a southern state, sub-categorized among the West South Central States. The Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
forms most of its eastern border, except in Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
and Greene counties, where the St. Francis River forms the western boundary of the Missouri Bootheel
The Missouri Bootheel is a Salient (geography), salient (protrusion) located in the southeasternmost part of the U.S. state of Missouri, extending south of 36°30′ north latitude, so called because its shape in relation to the rest of the sta ...
, and in many places where the channel of the Mississippi has meandered (or been straightened by man) from its original 1836 course.
Terrain
 Arkansas can generally be split into two halves, the highlands in the northwest and the lowlands of the southeast. The highlands are part of the Southern Interior Highlands, including
Arkansas can generally be split into two halves, the highlands in the northwest and the lowlands of the southeast. The highlands are part of the Southern Interior Highlands, including The Ozarks
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, and Oklahoma, as well as a small area in the southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cover ...
and the Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thru ...
. The southern lowlands include the Gulf Coastal Plain
The Gulf Coastal Plain extends around the Gulf of Mexico in the Southern United States and eastern Mexico.
This coastal plain reaches from the Florida Panhandle, southwest Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, the southern two-thirds of Alabama, over m ...
and the Arkansas Delta
The Arkansas Delta is one of the six natural regions of the state of Arkansas. Willard B. Gatewood Jr., author of ''The Arkansas Delta: Land of Paradox'', says that rich cotton lands of the Arkansas Delta make that area "The Deepest of the Deep ...
. This split can yield to a regional division into northwest, southwest, northeast, southeast, and central Arkansas. These regions are broad and not defined along county lines. Arkansas has seven distinct natural regions: the Ozark Mountains, Ouachita Mountains, Arkansas River Valley, Gulf Coastal Plain, Crowley's Ridge
Crowley's Ridge (also Crowleys Ridge) is a geological formation that rises 250 to above the alluvial plain of the Mississippi embayment in a line from southeastern Missouri to the Mississippi River near Helena, Arkansas. It is the most p ...
, and the Arkansas Delta, with Central Arkansas
Central Arkansas, also known as the Little Rock metro, designated by the United States Office of Management and Budget as the Little Rock-North Little Rock-Conway Metropolitan Statistical Area, is the most populous metro area in the U.S. state ...
sometimes included as a blend of multiple regions.
The southeastern part of Arkansas along the Mississippi Alluvial Plain
The Mississippi River Alluvial Plain is an alluvial plain created by the Mississippi River on which lie parts of seven U.S. states, from southern Louisiana to southern Illinois (Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, Lo ...
is sometimes called the Arkansas Delta. This region is a flat landscape of rich alluvial soils formed by repeated flooding of the adjacent Mississippi. Farther from the river, in the southeastern part of the state, the Grand Prairie has a more undulating landscape. Both are fertile agricultural areas. The Delta region is bisected by a geological formation known as Crowley's Ridge
Crowley's Ridge (also Crowleys Ridge) is a geological formation that rises 250 to above the alluvial plain of the Mississippi embayment in a line from southeastern Missouri to the Mississippi River near Helena, Arkansas. It is the most p ...
. A narrow band of rolling hills, Crowley's Ridge rises above the surrounding alluvial plain and underlies many of eastern Arkansas's major towns.
Northwest Arkansas is part of the Ozark Plateau
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, and Oklahoma, as well as a small area in the southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cov ...
including the Ozark Mountains
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, and Oklahoma, as well as a small area in the southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cover ...
, to the south are the Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thru ...
, and these regions are divided by the Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in Colorado, specifically ...
; the southern and eastern parts of Arkansas are called the Lowlands. These mountain ranges are part of the U.S. Interior Highlands
The U.S. Interior Highlands is a mountainous region in the Central United States spanning northern and western Arkansas, southern Missouri, eastern Oklahoma, and southern Illinois. The name is designated by the United States Geological Survey to ...
region, the only major mountainous region between the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
and the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
. The state's highest point is Mount Magazine in the Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thru ...
, which is above sea level.
Arkansas is home to many caves
Caves or caverns are natural voids under the Earth's surface. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. Exogene caves are smaller openings that extend a relatively short distance underground (such as rock ...
, such as Blanchard Springs Caverns. The State Archeologist has catalogued more than 43,000 Native American living, hunting and tool-making sites, many of them Pre-Columbian burial mounds and rock shelters. Crater of Diamonds State Park
Crater of Diamonds State Park is a List of Arkansas state parks, Arkansas state park in Pike County, Arkansas, Pike County, Arkansas, in the United States. The park features a plowed field, one of the few diamond-bearing sites accessible to th ...
near Murfreesboro is the world's only diamond-bearing site accessible to the public for digging. Arkansas is home to a dozen Wilderness Areas totaling . These areas are set aside for outdoor recreation and are open to hunting, fishing, hiking, and primitive camping. No mechanized vehicles nor developed campgrounds are allowed in these areas.
Hydrology
 Arkansas has many rivers, lakes, and reservoirs within or along its borders. Major tributaries to the Mississippi River include the
Arkansas has many rivers, lakes, and reservoirs within or along its borders. Major tributaries to the Mississippi River include the Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in Colorado, specifically ...
, the White River, and the St. Francis River.Federal Writers' Project 1987, p. 8. The Arkansas is fed by the Mulberry
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of 19 species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 subordinat ...
and Fourche LaFave Rivers in the Arkansas River Valley, which is also home to Lake Dardanelle
Lake Dardanelle is a major reservoir on the Arkansas River in Arkansas, USA. and is an integral part of the McClellan-Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System (MKARNS), which allows barge transportation from the Mississippi River to the Tulsa Port o ...
. The Buffalo, Little Red, Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
and Cache Rivers are all tributaries to the White River, which also empties into the Mississippi. Bayou Bartholomew and the Saline, Little Missouri, and Caddo River
The Caddo River is a tributary of the Ouachita River in the U.S. state of Arkansas. The river is about long.Calculated in Google Maps and Google Earth
Course
The Caddo River flows out of the Ouachita Mountains through Montgomery, Pike, and C ...
s are all tributaries to the Ouachita River
The Ouachita River ( ) is a river that runs south and east through the United States, U.S. U.S. state, states of Arkansas and Louisiana, joining the Tensas River to form the Black River (Louisiana), Black River near Jonesville, Louisiana. It i ...
in south Arkansas, which empties into the Mississippi in Louisiana. The Red River briefly forms the state's boundary with Texas. Arkansas has few natural lakes and many reservoirs, such as Bull Shoals Lake
Bull Shoals Lake is an artificial lake or reservoir in the Ozark Mountains of northern Arkansas and southern Missouri, United States. It has hundreds of miles of lake arms and coves, and common activities include boating, water sports, swimming, ...
, Lake Ouachita
Lake Ouachita (''Pronounced WAH-shi-tah'') is a reservoir created by the damming of the Ouachita River by Blakely Mountain Dam ().
Blakely Mountain Dam was built by the United States Army Corps of Engineers from 1948 to 1953 for hydroelectric ...
, Greers Ferry Lake
Greers Ferry Lake is the reservoir formed by Greers Ferry Dam, a United States Army Corps of Engineers dam in Northern Arkansas. It is located about north of Little Rock, Arkansas, Little Rock.
Geography
The reservoir consists of two lakes co ...
, Millwood Lake, Beaver Lake, Norfork Lake
Norfork Dam impounds the North Fork River in the U.S. state of Arkansas, creating Norfork Lake. The large reservoir is maintained by the United States Army Corps of Engineers and spans Baxter County, Arkansas, Fulton County, Arkansas and Ozar ...
, DeGray Lake, and Lake Conway
Lake Conway is a lake in Arkansas. Lake Conway is the largest lake ever created by a state wildlife commission and the first to be created by the Arkansas Game and Fish Commission. Lake Conway is located directly east of Mayflower, Arkansas, and ...
.
Flora and fauna
Arkansas's mix of warm temperate moist forest and subtropical bottomland is divided into three broad ecoregions: the ''Ozark, Ouachita-Appalachian Forests'', the ''Mississippi Alluvial and Southeast USA Coastal Plains'', and the ''Southeastern USA Plains''. The state is further divided into seven subregions: the Arkansas Valley,Boston Mountains
The Boston Mountains is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. states of Arkansas and Oklahoma. Part of the Ozarks, the Boston Mountains are a deeply dissected plateau. The ecoregion is steepe ...
, Mississippi Alluvial Plain
The Mississippi River Alluvial Plain is an alluvial plain created by the Mississippi River on which lie parts of seven U.S. states, from southern Louisiana to southern Illinois (Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, Lo ...
, Mississippi Valley Loess Plain, Ozark Highlands, Ouachita Mountains, and the South Central Plains. A 2010 United States Forest Service
The United States Forest Service (USFS) is an agency within the United States Department of Agriculture, U.S. Department of Agriculture. It administers the nation's 154 United States National Forest, national forests and 20 United States Natio ...
survey determined of Arkansas's land is forestland, or 56% of the state's total area. Dominant species in Arkansas's forests include ''Quercus
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
'' (oak), ''Carya
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes 19 species accepted by ''Plants of the World Online''.
Seven species are native to southeast Asia in China, Indochina, and northeastern India (Assam), and twelve ...
'' (hickory), ''Pinus echinata
The shortleaf pine or ''Pinus echinata'' is a species of coniferous tree endemic to the United States. The shortleaf pine is sometimes referred to as the "old field", "spruce", "rosemary", "yellow", "two-leaf" and "heart" pine. The common name " ...
'' (shortleaf pine) and ''Pinus taeda
''Pinus taeda'', commonly known as loblolly pine, is one of several pines native to the Southeastern United States, from East Texas to Florida, and north to southern New Jersey. The wood industry classifies the species as a southern yellow pine. ...
'' (loblolly pine).
Arkansas's plant life varies with its climate and elevation. The pine belt stretching from the Arkansas delta to Texas consists of dense oak-hickory-pine growth. Lumbering and paper milling activity is active throughout the region. In eastern Arkansas, one can find ''Taxodium
''Taxodium'' is a genus of one to three species (depending on taxonomic opinion) of extremely flood-tolerant conifers in the cypress family, Cupressaceae. The name is derived from the Latin word ''taxus'', meaning " yew", and the Greek word ' ...
''(cypress), ''Quercus nigra
''Quercus nigra'', the water oak, is an oak in the red oak group (''Quercus'' sect. ''Lobatae''), native to the eastern and south-central United States, found in all the coastal states from New Jersey to Texas, and inland as far as Oklahoma, Ke ...
'' (water oaks), and hickories with their roots submerged in the Mississippi Valley bayous indicative of the Deep South. Saw palmetto and needle palm both range into Arkansas. Nearby Crowley's Ridge is the only home of the tulip tree in the state, and generally hosts more northeastern plant life such as the beech
Beech (genus ''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to subtropical (accessory forest element) and temperate (as dominant element of Mesophyte, mesophytic forests) Eurasia and North America. There are 14 accepted ...
tree. The northwestern highlands are covered in an oak-hickory mixture, with Ozark white cedars, ''cornus
''Cornus'' is a genus of about 30–60 species of woody plants in the family Cornaceae, commonly known as dogwoods or cornels, which can generally be distinguished by their blossoms, berries, and distinctive bark. Most are deciduous ...
'' (dogwoods), and '' Cercis canadensis'' (redbuds) also present. The higher peaks in the Arkansas River Valley play host to scores of ferns, including the ''Physematium scopulinum
''Physematium scopulinum'', also called ''Woodsia scopulina'', is a deciduous perennial fern in the family Woodsiaceae, with the common name Rocky Mountain woodsia.
This plant is native to the western and northern United States and Canada
...
'' and '' Adiantum'' (maidenhair fern) on Mount Magazine. The white-tailed deer is the official state mammal.
Climate
Arkansas generally has ahumid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between ...
. While not bordering the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
, Arkansas, is still close enough to the warm, large body of water for it to influence the weather in the state. Generally, Arkansas, has hot, humid summers and slightly drier, mild to cool winters. In Little Rock
Little Rock is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Arkansas, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The city's population was 202,591 as of the 2020 census. The six-county Central Arkan ...
, the daily high temperatures average around with lows around in July. In January highs average around and lows around . In Siloam Springs in the northwest part of the state, the average high and low temperatures in July are and in January the average high and low are . Annual precipitation throughout the state averages between about ; it is somewhat wetter in the south and drier in the northern part of the state. Snowfall is infrequent but most common in the northern half of the state. The half of the state south of Little Rock is more apt to see ice storms. Arkansas's record high is at Ozark on August 10, 1936; the record low is at Gravette, on February 13, 1905.
Arkansas is known for extreme weather and frequent storms. A typical year brings thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hail. Occasional cold snaps stand to bring varying amounts of snow, as well as ice storms. Between both the Great Plains
The Great Plains is a broad expanse of plain, flatland in North America. The region stretches east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. They are the western part of the Interior Plains, which include th ...
and the Gulf States, Arkansas, receives around 60 days of thunderstorms. Arkansas is located in Dixie alley, and very near tornado alley
Tornado Alley, also known as Tornado Valley, is a loosely defined location of the central United States and, in the 21st century, Canada where tornadoes are most frequent. The term was first used in 1952 as the title of a research project to st ...
. As a result, a few of the most destructive tornadoes in U.S. history have struck the state. While sufficiently far from the coast to avoid a direct hit from a hurricane, Arkansas can often get the remnants of a tropical system, which dumps tremendous amounts of rain in a short time and often spawns smaller tornadoes.
Cities and towns

Little Rock
Little Rock is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Arkansas, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The city's population was 202,591 as of the 2020 census. The six-county Central Arkan ...
has been Arkansas's capital city
A capital city, or just capital, is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state (polity), state, province, department (administrative division), department, or other administrative division, subnational division, usually as its ...
since 1821 when it replaced Arkansas Post
The Arkansas Post (; ), officially the Arkansas Post National Memorial, was the first European colonization of the Americas, European settlement located along the Mississippi River, in the Mississippi Alluvial Plain, and in the present-day U. ...
as the capital of the Territory of Arkansas. The state capitol was moved to Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a Spring (hydrology), spring produced by the emergence of Geothermal activity, geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow ...
and later Washington during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
when the Union armies threatened the city in 1862, and state government did not return to Little Rock until after the war ended. Today, the Little Rock–North Little Rock–Conway metropolitan area is the largest in the state, with a population of 724,385 in 2013.
The Fayetteville–Springdale–Rogers Metropolitan Area is the second-largest metropolitan area in Arkansas, growing at the fastest rate due to the influx of businesses and the growth of the University of Arkansas
The University of Arkansas (U of A, UArk, or UA) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Fayetteville, Arkansas, United States. It is the Flagship campus, flagship campus of the University of Arkan ...
and Walmart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores in the United States and 23 other ...
.
The state has eight cities with populations above 50,000 (based on 2010 census). In descending order of size, they are Little Rock
Little Rock is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Arkansas, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The city's population was 202,591 as of the 2020 census. The six-county Central Arkan ...
, Fort Smith, Fayetteville, Springdale, Jonesboro, North Little Rock
North Little Rock (often abbreviated "NLR") is a city in Pulaski County, Arkansas, United States. Located on the north side of the Arkansas River, it is the twin city of Little Rock. In the late nineteenth century, it was annexed by Little Ro ...
, Conway
Conway may refer to:
Places
United States
* Conway, Arkansas
* Conway County, Arkansas
* Lake Conway, Arkansas
* Conway, Florida
* Conway, Iowa
* Conway, Kansas
* Conway, Louisiana
* Conway, Massachusetts
* Conway, Michigan
* Conway Townshi ...
, and Rogers. Of these, only Fort Smith and Jonesboro are outside the two largest metropolitan areas. Other cities in Arkansas include Pine Bluff, Crossett, Bryant, Lake Village, Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a Spring (hydrology), spring produced by the emergence of Geothermal activity, geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow ...
, Bentonville, Texarkana
The Texarkana metropolitan statistical area (MSA), as defined by the United States Office of Management and Budget, is a two-county region anchored by the Twin cities (geographical proximity), twin cities of Texarkana, Texas (population 37,33 ...
, Sherwood, Jacksonville
Jacksonville ( ) is the most populous city proper in the U.S. state of Florida, located on the Atlantic coast of North Florida, northeastern Florida. It is the county seat of Duval County, Florida, Duval County, with which the City of Jacksonv ...
, Russellville, Bella Vista, West Memphis, Paragould, Cabot, Searcy, Van Buren, El Dorado
El Dorado () is a mythical city of gold supposedly located somewhere in South America. The king of this city was said to be so rich that he would cover himself from head to foot in gold dust – either daily or on certain ceremonial occasions â ...
, Blytheville, Harrison, Dumas, Rison, Warren, and Mountain Home.
Demographics
Population
TheUnited States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
estimated that the population of Arkansas was 3,017,804 on July 1, 2019, a 3.49% increase since the 2010 United States census. At the 2020 U.S. census, Arkansas had a resident population of 3,011,524.
From fewer than 15,000 in 1820, Arkansas's population grew to 52,240 during a special census in 1835, far exceeding the 40,000 required to apply for statehood. Following statehood in 1836, the population doubled each decade until the 1870 census conducted following the American Civil War. The state recorded growth in each successive decade, although it gradually slowed in the 20th century.
It recorded population losses in the 1950
Events January
* January 1 – The International Police Association (IPA) – the largest police organization in the world – is formed.
* January 5 – 1950 Sverdlovsk plane crash, Sverdlovsk plane crash: ''Aeroflot'' Lisunov Li-2 ...
and 1960 censuses. This outmigration was a result of multiple factors, including farm mechanization, decreasing labor demand, and young educated people leaving the state due to a lack of non-farming industry in the state. Arkansas again began to grow, recording positive growth rates ever since and exceeding two million by the 1980 census. Arkansas's rate of change, age distributions, and gender distributions mirror national averages. Minority group
The term "minority group" has different meanings, depending on the context. According to common usage, it can be defined simply as a group in society with the least number of individuals, or less than half of a population. Usually a minority g ...
data also approximates national averages. There are fewer people in Arkansas of Hispanic or Latino origin than the national average. The center of population
In Demography, demographics, the center of population (or population center) of a region is a geographical point that describes a centerpoint of the region's population. There are several ways of defining such a "center point", leading to dif ...
of Arkansas for 2000 was located in Perry County, near Nogal.
According to HUD's 2022 Annual Homeless Assessment Report, there were an estimated 2,459 homeless
Homelessness, also known as houselessness or being unhoused or unsheltered, is the condition of lacking stable, safe, and functional housing. It includes living on the streets, moving between temporary accommodation with family or friends, liv ...
people in Arkansas.
Race and ethnicity
Per the 2019 census estimates, Arkansas was 72.0% non-Hispanic white, 15.4% Black or African American, 0.5% American Indian and Alaska Native, 1.5% Asian, 0.4% Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander, 0.1% some other race, 2.4% two or more races, and 7.7% Hispanic or Latin American of any race. In 2011, the state was 80.1% white (74.2%non-Hispanic white
Non-Hispanic Whites, also referred to as White Anglo Americans or Non-Latino Whites, are White Americans who are classified by the United States census as "White" and not of Hispanic or Latino origin. According to annual estimates from the Unit ...
), 15.6% Black or African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
, 0.9% American Indian and Alaska Native
Alaska Natives (also known as Native Alaskans, Alaskan Indians, or Indigenous Alaskans) are the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of Alaska that encompass a diverse arena of cultural and linguistic groups, including the I ...
, 1.3% Asian, and 1.8% from two or more races. Hispanics
The term Hispanic () are people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an ethnic or meta-ethnic term.
The term commonly appli ...
or Latinos of any race made up 6.6% of the population. As of 2011, 39.0% of Arkansas's population younger than age1 were minorities.

Ozarks
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, and Oklahoma, as well as a small area in the southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cover ...
and the central part of the state. African Americans live mainly in the southern and eastern parts of the state. Arkansans of Irish, English and German ancestry are mostly found in the far northwestern Ozarks near the Missouri border. Ancestors of the Irish in the Ozarks were chiefly Scots-Irish, Protestants from Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
, the Scottish lowlands and northern England part of the largest group of immigrants from Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
and Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
before the American Revolution. English and Scots-Irish immigrants settled throughout the back country of the South and in the more mountainous areas. Americans of English stock are found throughout the state.
A 2010 survey of the principal ancestries of Arkansas's residents revealed the following: 15.5% African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
, 12.3% Irish, 11.5% German, 11.0% American, 10.1% English, 4.7% Mexican, 2.1% French, 1.7% Scottish, 1.7% Dutch, 1.6% Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
, and 1.4% Scots-Irish.
Most people identifying as "American" are of English descent or Scots-Irish descent. Their families have been in the state so long, in many cases since before statehood, that they choose to identify simply as having American ancestry or do not in fact know their ancestry. Their ancestry primarily goes back to the original 13 colonies and for this reason many of them today simply claim American ancestry. Many people who identify as of Irish descent are in fact of Scots-Irish descent.
According to the American Immigration Council, in 2015, the top countries of origin for Arkansas' immigrants were Mexico, El Salvador, India, Vietnam, and Guatemala.
According to the 2006–2008 American Community Survey, 93.8% of Arkansas's population (over the age of five) spoke only English at home. About 4.5% of the state's population spoke Spanish at home. About 0.7% of the state's population spoke another Indo-European language
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia ( ...
. About 0.8% of the state's population spoke an Asian language, and 0.2% spoke other languages.
Religion
Like most other Southern states, Arkansas is part of theBible Belt
The Bible Belt is a region of the Southern United States and the Midwestern state of Missouri (which also has significant Southern influence), where evangelical Protestantism exerts a strong social and cultural influence. The region has been de ...
and predominantly Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
. The largest denominations by number of adherents in 2010 were the Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC), alternatively the Great Commission Baptists (GCB), is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist organization, the largest Protestant, and the second-largest Chr ...
with 661,382; the United Methodist Church
The United Methodist Church (UMC) is a worldwide mainline Protestant Christian denomination, denomination based in the United States, and a major part of Methodism. In the 19th century, its main predecessor, the Methodist Episcopal Church, was ...
with 158,574; non-denominational Evangelical Protestants with 129,638; the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
with 122,662; and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the ...
with 31,254. Other religions include Islam, Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, Wicca
Wicca (), also known as "The Craft", is a Modern paganism, modern pagan, syncretic, Earth religion, Earth-centred religion. Considered a new religious movement by Religious studies, scholars of religion, the path evolved from Western esote ...
/Paganism
Paganism (, later 'civilian') is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Christianity, Judaism, and Samaritanism. In the time of the ...
, Hinduism, Buddhism, and some residents have no religious affiliation.
In 2014, the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
determined that 79% of the population was Christian, dominated by evangelicals in the Southern Baptist and independent Baptist churches. In contrast with many other states, the Catholic Church as of 2014 was not the largest Christian denomination in Arkansas. Of the unaffiliated population, 2% were atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
in 2014. By 2020, the Public Religion Research Institute
The Public Religion Research Institute (PRRI) is an American nonprofit, nonpartisan research and education organization that conducts public opinion polls on a variety of topics, specializing in the quantitative and qualitative study of politic ...
determined 71% of the population was Christian. Arkansas continued to be dominated by evangelicals, followed by mainline Protestant
The mainline Protestants (sometimes also known as oldline Protestants) are a group of Protestantism in the United States, Protestant denominations in the United States and Protestantism in Canada, Canada largely of the Liberal Christianity, theolo ...
s and historically black or African American churches.
Economy
 Once a state with a cashless society in the uplands and
Once a state with a cashless society in the uplands and plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
agriculture in the lowlands, Arkansas's economy has evolved and diversified. The state's gross domestic product (GDP) was $176.24billion in 2023. Six Fortune 500
The ''Fortune'' 500 is an annual list compiled and published by ''Fortune (magazine), Fortune'' magazine that ranks 500 of the largest United States Joint-stock company#Closely held corporations and publicly traded corporations, corporations by ...
companies are based in Arkansas, including the world's #1 retailer, Walmart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores in the United States and 23 other ...
; Tyson Foods
Tyson Foods, Inc. is an American multinational corporation based in Springdale, Arkansas that operates in the food industry. The company is the world's second-largest processor and marketer of broiler industry, chicken, beef, and pork after JBS ...
, J.B. Hunt
J.B. Hunt Transport Services, Inc. is an American transportation and logistics company based in Lowell, Arkansas. It was founded by Johnnie Bryan Hunt and Johnelle Hunt in Arkansas on August 10, 1961. By 1983, J.B. Hunt had grown into the 80t ...
, Dillard's
Dillard's, Inc. is an American department store chain with approximately 267 stores in 29 states and headquartered in Little Rock, Arkansas. Currently, the largest number of stores are located in Texas with 57 and Florida with 42. The company a ...
, Murphy USA
Murphy USA is an American corporation based in El Dorado, Arkansas that operates a chain store, chain of retail gas stations that are primarily located in proximity to Walmart stores. It was founded as a spin-off of Murphy Oil in 2013.
In the f ...
, and Windstream are also headquartered in the state. The per capita personal income in 2023 was $54,347, ranking 46th in the nation, and the median household income
The median income is the income amount that divides a population into two groups, half having an income above that amount, and half having an income below that amount. It may differ from the mean (or average) income. Both of these are ways of und ...
was $55,432, which ranked 47th. The state's agriculture outputs are poultry and eggs, soybeans, sorghum, cattle, cotton, rice, hogs, and milk. Its industrial outputs are food processing, electric equipment, fabricated metal products, machinery, and paper products. Arkansas's mines produce natural gas, oil, crushed stone, bromine, and vanadium. According to CNBC
CNBC is an American List of business news channels, business news channel owned by the NBCUniversal News Group, a unit of Comcast's NBCUniversal. The network broadcasts live business news and analysis programming during the morning, Day ...
, Arkansas is the 20th-best state for business, with the 2nd-lowest cost of doing business, 5th-lowest cost of living, 11th-best workforce, 20th-best economic climate, 28th-best-educated workforce, 31st-best infrastructure and the 32nd-friendliest regulatory environment. Arkansas gained 12 spots in the best state for business rankings since 2011. As of 2014, it was the most affordable state to live in.
As of July 2023, the state's unemployment rate was 2.6%; the preliminary rate for December 2023 is 3.4%.
Industry and commerce
Arkansas's earliest industries werefur trading
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals h ...
and agriculture, with development of cotton plantations in the areas near the Mississippi River. They were dependent on slave labor through the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
.
Today only about three percent of the population are employed in the agricultural sector, it remains a major part of the state's economy, ranking 13th in the nation in the value of products sold. Arkansas is the nation's largest producer of rice, broiler
Breed broiler is any chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') that is bred and raised specifically for meat production. Most commercial broilers reach slaughter weight between four and six weeks of age, although slower growing breeds reach slaug ...
s, and turkeys, and ranks in the top three for cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
, pullets, and aquaculture (catfish). Forestry remains strong in the Arkansas Timberlands, and the state ranks fourth nationally and first in the South in softwood lumber production. Automobile parts manufacturers have opened factories in eastern Arkansas to support auto plants in other states. Bauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH) ...
was formerly a large part of the state's economy, mined mostly around Saline County.
Tourism is also very important to the Arkansas economy; the official state nickname "The Natural State" was created for state tourism advertising in the 1970s, and is still used to this day. The state maintains 52 state parks and the National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government, within the US Department of the Interior. The service manages all List ...
maintains seven properties in Arkansas. The completion of the William Jefferson Clinton Presidential Library in Little Rock has drawn many visitors to the city and revitalized the nearby River Market District. Many cities also hold festivals, which draw tourists to Arkansas culture, such as The Bradley County Pink Tomato Festival in Warren, King Biscuit Blues Festival
The King Biscuit Blues Festival is an annual, multi-day blues festival, held in Helena, Arkansas, United States.
History
The name of the festival comes from ''King Biscuit Time'', which was the longest running radio show. Sonny Boy Williamson I ...
, Ozark Folk Festival, Toad Suck Daze, and Tontitown Grape Festival.
Transportation
 Transportation in Arkansas is overseen by the
Transportation in Arkansas is overseen by the Arkansas Department of Transportation
The Arkansas Department of Transportation (ARDOT), formerly the Arkansas Highway and Transportation Department, is a government department in the U.S. state of Arkansas. Its mission is to provide a safe, efficient, aesthetically pleasing and env ...
(ArDOT), headquartered in Little Rock
Little Rock is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Arkansas, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The city's population was 202,591 as of the 2020 census. The six-county Central Arkan ...
. Several main corridors pass through Little Rock, including Interstate30 (I-30) and I-40 (the nation's 3rd-busiest trucking corridor). Arkansas first designated a state highway system in 1924, and first numbered its roads in 1926. Arkansas had one of the first paved roads, the Dollarway Road, and one of the first members of the Interstate Highway System
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, or the Eisenhower Interstate System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Hi ...
. The state maintains a large system of state highways
A state highway, state road, or state route (and the equivalent provincial highway, provincial road, or provincial route) is usually a road that is either Route number, numbered or maintained by a sub-national state or province. A road numbered ...
today, in addition to eight Interstates and 20 U.S. Routes.
In northeast Arkansas, I-55 travels north from Memphis to Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
, with a new spur to Jonesboro ( I-555). Northwest Arkansas is served by the segment of I-49
Interstate 49 (I-49) is a north–south Interstate Highway with multiple segments. The original portion is entirely within Louisiana with an additional signed portion extending from I-220 in Shreveport to the Arkansas state line, three ne ...
from Fort Smith to the beginning of the Bella Vista Bypass. This segment of I-49 currently follows mostly the same route as the former section of I-540 that extended north of I-40. The state also has the 13th largest state highway system in the nation.
 Arkansas is served by of railroad track divided among twenty-six railroad companies including three Class I railroads. Freight railroads are concentrated in southeast Arkansas to serve the industries in the region. The
Arkansas is served by of railroad track divided among twenty-six railroad companies including three Class I railroads. Freight railroads are concentrated in southeast Arkansas to serve the industries in the region. The Texas Eagle
The ''Texas Eagle'' is a long-distance passenger train operated daily by Amtrak on a route between Chicago, Illinois, and San Antonio, Texas, with major stops in St. Louis, Little Rock, Dallas, Fort Worth, and Austin. Three days per week, t ...
, an Amtrak passenger train, serves five stations in the state Walnut Ridge, Little Rock
Little Rock is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Arkansas, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The city's population was 202,591 as of the 2020 census. The six-county Central Arkan ...
, Malvern, Arkadelphia, and Texarkana
The Texarkana metropolitan statistical area (MSA), as defined by the United States Office of Management and Budget, is a two-county region anchored by the Twin cities (geographical proximity), twin cities of Texarkana, Texas (population 37,33 ...
.
Arkansas also benefits from the use of its rivers for commerce. The Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
and Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in Colorado, specifically ...
are both major rivers. The United States Army Corps of Engineers
The United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) is the military engineering branch of the United States Army. A direct reporting unit (DRU), it has three primary mission areas: Engineer Regiment, military construction, and civil wo ...
maintains the McClellan-Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System, allowing barge traffic up the Arkansas River to the Port of Catoosa in Tulsa, Oklahoma
Tulsa ( ) is the List of municipalities in Oklahoma, second-most-populous city in the U.S. state, state of Oklahoma, after Oklahoma City, and the List of United States cities by population, 48th-most-populous city in the United States. The po ...
.
There are four airports with commercial service: Clinton National Airport (formerly Little Rock National Airport or Adams Field), Northwest Arkansas Regional Airport
Northwest Arkansas National Airport in Northwest Arkansas is a public-use airport located in Benton County, Arkansas, serving the rapidly growing Northwest Arkansas region, northwest of Fayetteville and northwest of Springdale. Since its op ...
, Fort Smith Regional Airport
Fort Smith Regional Airport is a public use airport located near the Interstate 540 freeway three nautical miles (6 km) southeast of the central business district of Fort Smith, in Sebastian County, Arkansas, United States. FSM ...
, and Texarkana Regional Airport, with dozens of smaller airports in the state.
Intercity bus services across the state are provided by Flixbus
FlixBus (; styled FLiXBUS) is a German brand that offers low-cost Intercity bus service, intercity coach services in Europe, North America, South America and Asia. It is owned by , which also operates FlixTrain, FlixCar, , and Greyhound Lines. F ...
, Greyhound Lines
Greyhound Lines, Inc. is an American operator of Intercity bus service, intercity bus services. Greyhound operates the largest intercity bus network in the United States, and also operates charter and Amtrak Thruway services, as well as interci ...
, and Jefferson Lines
Jefferson Lines (JL or JLI) is a regional intercity bus company operating in 14 states in the Midwest and the West of the United States.
History
The company is operated by Jefferson Partners L.P., located in Minneapolis, Minnesota. Jefferson P ...
.
Public transit and community transport services for the elderly or those with developmental disabilities are provided by agencies such as the Central Arkansas Transit Authority and the Ozark Regional Transit
Ozark Regional Transit is the provider of mass transportation in the Northwest Arkansas region, including Fayetteville, Arkansas, Fayetteville, Springdale, Arkansas, Springdale, Rogers, Arkansas, Rogers, and Bentonville, Arkansas, Bentonville.
Hi ...
, organizations that are part of the Arkansas Transit Association.
Government
As with the federal government of the United States, political power in Arkansas is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. Each officer's term is four years long. Office holders are term-limited to two full terms plus any partial terms before the first full term.Executive
The governor of Arkansas is Sarah Huckabee Sanders. Sanders is a Republican and was inaugurated on January 10, 2023. The six other elected executive positions in Arkansas arelieutenant governor
A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-comm ...
, secretary of state, attorney general
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general (: attorneys general) or attorney-general (AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have executive responsibility for law enf ...
, treasurer
A treasurer is a person responsible for the financial operations of a government, business, or other organization.
Government
The treasury of a country is the department responsible for the country's economy, finance and revenue. The treasure ...
, auditor
An auditor is a person or a firm appointed by a company to execute an audit.Practical Auditing, Kul Narsingh Shrestha, 2012, Nabin Prakashan, Nepal To act as an auditor, a person should be certified by the regulatory authority of accounting an ...
, and land commissioner. The governor also appoints the leaders of various state boards, committees, and departments. Arkansas governors served two-year terms until a referendum lengthened the term to four years, effective with the 1986 election. Individuals elected to these offices are limited to a lifetime total of two four-year terms per office.
In Arkansas, the lieutenant governor is elected separately from the governor and thus can be from a different political party.
Legislative
TheArkansas General Assembly
The General Assembly of Arkansas is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The legislature is a bicameral body composed of the upper house Arkansas Senate with 35 members, and the lower Arkansas House of Representatives with 1 ...
is the state's bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature that is divided into two separate Deliberative assembly, assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate ...
bodies of legislators, composed of the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
and House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
. The Senate contains 35 members from districts of approximately equal population. These districts are redrawn decennially with each US census, and in election years ending in "2", the entire body is put up for reelection. Following the election, half of the seats are designated as two-year seats and are up for reelection again in two years, these "half-terms" do not count against a legislator's term limits. The remaining half serve a full four-year term. This staggers elections such that half the body is up for reelection every two years and allows for complete body turnover following redistricting. Arkansas House members can serve a maximum of three two-year terms. House districts are redistricted by the Arkansas Board of Apportionment.
In the 2012 elections, Arkansas voters elected a 21–14 Republican majority in the Senate and the Republicans gained a 51–49 majority in the House of Representatives. The 2012 elections established a Republican dominance in both bodies of legislature.
The Republican Party's majority
A majority is more than half of a total; however, the term is commonly used with other meanings, as explained in the "#Related terms, Related terms" section below.
It is a subset of a Set (mathematics), set consisting of more than half of the se ...
status in the Arkansas State House of Representatives after the 2012 elections, is the party's first since 1874. Arkansas was the last state of the old Confederacy to not have Republican control of either chamber of its house since the American Civil War.
Following the term limits changes, studies have shown that lobbyists have become less influential in state politics. Legislative staff, not subject to term limits, have acquired additional power and influence due to the high rate of elected official turnover.
Judicial
Arkansas's judicial branch has five court systems:Arkansas Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of Arkansas is the highest court in the state judiciary of Arkansas. It has ultimate and largely discretionary appellate jurisdiction over all state court cases that involve a point of state law, and original jurisdiction ...
, Arkansas Court of Appeals, Circuit Courts, District Courts and City Courts.
Most cases begin in district court, which is subdivided into state district court and local district court. State district courts exercise district-wide jurisdiction over the districts created by the General Assembly, and local district courts are presided over by part-time judges who may privately practice law. 25 state district court judges preside over 15 districts, with more districts created in 2013 and 2017. There are 28 judicial circuits of Circuit Court, with each contains five subdivisions: criminal, civil, probate, domestic relations, and juvenile court. The jurisdiction of the Arkansas Court of Appeals is determined by the Arkansas Supreme Court, and there is no right of appeal from the Court of Appeals to the high court. The Arkansas Supreme Court can review Court of Appeals cases upon application by either a party to the litigation, upon request by the Court of Appeals, or if the Arkansas Supreme Court feels the case should have been initially assigned to it. The twelve judges of the Arkansas Court of Appeals are elected from judicial districts to renewable six-year terms.
The Arkansas Supreme Court is the court of last resort in the state, composed of seven justices elected to eight-year terms. Established by the Arkansas Constitution in 1836, the court's decisions can be appealed to only the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over Stat ...
.
Federal
Both Arkansas's U.S. senators, John Boozman andTom Cotton
Thomas Bryant Cotton (born May 13, 1977) is an American politician and United States Army, Army veteran serving since 2015 as the Seniority in the United States Senate, junior United States Senate, United States senator from Arkansas. A memb ...
, are Republicans. The state has four seats in U.S. House of Representatives. All four seats are held by Republicans: Rick Crawford ( 1st district), French Hill ( 2nd district), Steve Womack
Stephen Allen Womack ( ; born February 18, 1957) is an American politician serving as the U.S. representative for since 2011. The district, which was once represented by former Senator J. William Fulbright, covers much of northwestern Arkans ...
( 3rd district), and Bruce Westerman
Bruce Eugene Westerman (born November 18, 1967) is an American forester and politician serving as the U.S. representative for Arkansas's 4th congressional district. Previously, he served as member and the majority leader of the Arkansas House ...
( 4th district).
Politics
Arkansas governorBill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
brought national attention to the state with a long speech at the 1988 Democratic National Convention endorsing Michael Dukakis
Michael Stanley Dukakis ( ; born November 3, 1933) is an American politician and lawyer who served as governor of Massachusetts from 1975 to 1979 and from 1983 to 1991. He is the longest-serving governor in Massachusetts history and only the s ...
. Some journalists suggested the speech was a threat to his ambitions; Clinton defined it "a comedy of error, just one of those fluky things".
He won the Democratic nomination for president in 1992. Clinton presented himself as a " New Democrat" and used incumbent George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushBefore the outcome of the 2000 United States presidential election, he was usually referred to simply as "George Bush" but became more commonly known as "George H. W. Bush", "Bush Senior," "Bush 41," and even "Bush th ...
's broken promise against him to win the 1992 presidential election with 43.0% of the vote to Bush's 37.5% and independent billionaire Ross Perot
Henry Ross Perot ( ; June 27, 1930 – July 9, 2019) was an American businessman, politician, and philanthropist. He was the founder and chief executive officer of Electronic Data Systems and Perot Systems. He ran an Independent politician ...
's 18.9%.
Most Republican strength traditionally lay mainly in the northwestern part of the state, particularly Fort Smith and Bentonville, as well as North Central Arkansas around the Mountain Home area. In the latter area, Republicans have been known to get 90% or more of the vote, while the rest of the state was more Democratic. After 2010, Republican strength expanded further to the Northeast and Southwest and into the Little Rock suburbs. The Democrats are mostly concentrated to central Little Rock, the Mississippi Delta, the Pine Bluff area, and the areas around the southern border with Louisiana.
Arkansas has elected only three Republicans to the U.S. Senate since Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Union ...
: Tim Hutchinson, who was defeated after one term by Mark Pryor
Mark Lunsford Pryor (born January 10, 1963) is an American attorney, politician and lobbyist who served as a United States Senate, United States Senator from Arkansas from 2003 to 2015. He previously served as Arkansas Attorney General, Attorney ...
; John Boozman, who defeated incumbent Blanche Lincoln; and Tom Cotton
Thomas Bryant Cotton (born May 13, 1977) is an American politician and United States Army, Army veteran serving since 2015 as the Seniority in the United States Senate, junior United States Senate, United States senator from Arkansas. A memb ...
, who defeated Pryor in 2014. Before 2013, the General Assembly had not been controlled by the Republican Party since Reconstruction, with the GOP holding a 51-seat majority in the state House and a 21-seat (of 35) in the state Senate following victories in 2012. Arkansas was one of the only states of the former Confederacy other than Florida and Virginia that sent two Democrats to the U.S. Senate for any period during the first decade of the 21st century.
In 2010, Republicans captured three of the state's four seats in the U.S. House of Representatives. In 2012, they won election to all four House seats. Arkansas held the distinction of having a U.S. House delegation composed entirely of military veterans ( Rick Crawford, Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
; Tim Griffin, Army Reserve; Steve Womack
Stephen Allen Womack ( ; born February 18, 1957) is an American politician serving as the U.S. representative for since 2011. The district, which was once represented by former Senator J. William Fulbright, covers much of northwestern Arkans ...
, National Guard
National guard is the name used by a wide variety of current and historical uniformed organizations in different countries. The original National Guard was formed during the French Revolution around a cadre of defectors from the French Guards.
...
; Tom Cotton
Thomas Bryant Cotton (born May 13, 1977) is an American politician and United States Army, Army veteran serving since 2015 as the Seniority in the United States Senate, junior United States Senate, United States senator from Arkansas. A memb ...
, Army). When Pryor was defeated in 2014, the entire congressional delegation was in GOP hands for the first time since Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Union ...
.
Reflecting the state's large evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of th ...
population, Arkansas has a strong social conservative bent. In the aftermath of the landmark Supreme Court decision ''Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization
''Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization'', 597 U.S. 215 (2022), is a List of landmark court decisions in the United States, landmark decision of the Supreme Court of the United States, United States Supreme Court in which the court held ...
'', Arkansas became one of nine states where abortion
Abortion is the early termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. Abortions that occur without intervention are known as miscarriages or "spontaneous abortions", and occur in roughly 30–40% of all pregnan ...
is banned. Under the Arkansas Constitution
The Constitution of Arkansas is the primary organizing law for the U.S. state of Arkansas delineating the duties, powers, structures, and functions of the state government. Arkansas' original constitution was adopted at a constitutional conv ...
, Arkansas is a right to work state. Its voters passed a ban on same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same legal Legal sex and gender, sex. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 38 countries, with a total population of 1.5 ...
in 2004, with 75% voting yes, although that ban has been inactive since the Supreme Court protected same-sex marriage in ''Obergefell v. Hodges
''Obergefell v. Hodges'', ( ), is a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court which ruled that the fundamental right to marry is guaranteed to same-sex couples by both the Due Process Clause and the Equal Protection Clause of th ...
''.
Arkansas retains the death penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in s ...
. Authorized methods of execution include the electric chair
The electric chair is a specialized device used for capital punishment through electrocution. The condemned is strapped to a custom wooden chair and electrocuted via electrodes attached to the head and leg. Alfred P. Southwick, a Buffalo, New Yo ...
.
Military
TheStrategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile compon ...
facility of Little Rock Air Force Base
Little Rock Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located approximately northeast of Little Rock, Arkansas.
The facility covers 6,217 acres (2,516 ha) with a resident population of over 3,300 and working population of approximate ...
was one of eighteen silos in the command of the 308th Strategic Missile Wing (308th SMW), specifically one of the nine silos within its 374th Strategic Missile Squadron
The 374th Strategic Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit, last assigned to the 308th Strategic Missile Wing at Little Rock Air Force Base, Arkansas. The squadron (aviation), squadron was equipped with the LGM-25C Titan I ...
(374th SMS). The squadron was responsible for Launch Complex 374–7, site of the 1980 explosion of a TitanII Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) in Damascus, Arkansas.
Taxation
Taxes are collected by the Arkansas Department of Finance and Administration.Health
Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) and informally as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by Presid ...
passed. The percentage of uninsured in Arkansas dropped from 22.5 in 2013 to 12.4 in August 2014.
The Arkansas Clean Indoor Air Act, a statewide smoking ban excluding bars and some restaurants, went into effect in 2006.
Healthcare in Arkansas is provided by a network of hospitals as members of the Arkansas Hospital Association. Major institutions with multiple branches include Baptist Health, Community Health Systems, and HealthSouth
Encompass Health Corporation, based in Birmingham, Alabama, is the nation's largest provider of inpatient rehabilitative services, offering facility-based care through its network of 166 Rehabilitation hospital, inpatient rehabilitation hospital ...
. The University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS) in Little Rock operates the UAMS Medical Center, a teaching hospital
A teaching hospital or university hospital is a hospital or medical center that provides medical education and training to future and current health professionals. Teaching hospitals are almost always affiliated with one or more universities a ...
ranked as high performing nationally in cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
and nephrology
Nephrology is a specialty for both adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function (renal physiology) and kidney disease (renal pathophysiology), the preservation of kid ...
. The pediatric division of UAMS Medical Center is known as Arkansas Children's Hospital, nationally ranked in pediatric cardiology
Cardiology () is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery di ...
and heart surgery. Together, these two institutions are the state's only Level I trauma center
A trauma center, or trauma centre, is a hospital equipped and staffed to provide care for patients suffering from major trauma, major traumatic injuries such as Falling (accident), falls, motor vehicle collisions, or gunshot wounds. The term "tra ...
s.
Education
Arkansas has 1,064 state-funded kindergartens, elementary, junior and senior high schools. The state supports a network of publicuniversities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
and colleges, including two major university systems: Arkansas State University System
The Arkansas State University System, based in Little Rock, serves almost 40,000 students annually on campuses in Arkansas and Querétaro, Queretaro, Mexico, and globally online.
The Arkansas State University System includes Arkansas State Unive ...
and University of Arkansas System
The University of Arkansas System is a state university system in the U.S. state of Arkansas. It comprises six campuses; a medical school; two law schools; a graduate school focused on public service; a historically black college, statewide rese ...
. The University of Arkansas
The University of Arkansas (U of A, UArk, or UA) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Fayetteville, Arkansas, United States. It is the Flagship campus, flagship campus of the University of Arkan ...
, flagship campus of the University of Arkansas System in Fayetteville was ranked #63 among public schools in the nation by '' U.S. News & World Report''. Other public institutions include Arkansas State University
Arkansas State University (A-State or ASU) is a public university, public research university in Jonesboro, Arkansas, United States. It is the flagship campus of the Arkansas State University System and the second-largest university in the st ...
, University of Arkansas at Pine Bluff, Arkansas Tech University, Henderson State University
Henderson State University (HSU) is a public university in Arkadelphia, Arkansas, United States. Founded in 1890 as Arkadelphia Methodist College, Henderson has an undergraduate enrollment of around 2,500 students. The campus is located on .
H ...
, Southern Arkansas University, and University of Central Arkansas across the state. It is also home to 11 private colleges and universities including Hendrix College
Hendrix College is a Private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Conway, Arkansas. Approximately 1,000 students are enrolled, mostly undergraduates. While affiliated with the United Methodist Chu ...
, one of the nation's top 100 liberal arts
Liberal arts education () is a traditional academic course in Western higher education. ''Liberal arts'' takes the term ''skill, art'' in the sense of a learned skill rather than specifically the fine arts. ''Liberal arts education'' can refe ...
colleges, according to U.S. News & World Report.
In the 1920s the state required all children to attend public schools. The school year was set at 131 days, although some areas were unable to meet that requirement.
Generally prohibited in the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and state (polity), states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also const ...
at large, school corporal punishment
Corporal punishment in schools is the deliberate infliction of physical pain as a response to undesired behavior by students. The term corporal punishment derives from , the Latin word for the body. In schools it may involve striking the student o ...
is not unusual in Arkansas, with 20,083 public school students paddled at least one time, according to government data for the 2011–12 school year. The rate of corporal punishment in public schools is higher only in Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
.
Media
As of 2010 many Arkansas local newspapers are owned byWEHCO Media
WEHCO Media, Inc., based in Little Rock, AR is a privately held media company with holdings that include newspapers, cable television systems, and internet service. Walter E. Hussman Jr. is the chairman. Hussmann is the grandson of Clyde E. Pa ...
, Alabama-based Lancaster Management, Kentucky-based Paxton Media Group
Paxton Media Group of Paducah, Kentucky, is a privately held media company with holdings that include newspapers and a TV station, WPSD-TV in Paducah. David M. Paxton is president and CEO.
The company owns 32 daily newspapers and numerous wee ...
, Missouri-based Rust Communications
Rust Communications is an American privately owned media company based in Cape Girardeau, Missouri. The '' Southeast Missourian'' is its flagship publication.
History
In 1967, Gary W. Rust purchased the ''Weekly Bulletin'', a weekly newspaper i ...
, Nevada-based Stephens Media, and New York-based GateHouse Media
GateHouse Media Inc. was an American publisher of locally based print and digital media. It published 144 daily newspapers, 684 community publications, and over 569 local-market websites in 38 states. Its parent company, New Media Investment Group ...
.
Culture
 The culture of Arkansas includes distinct cuisine, dialect, and traditional festivals. Sports are also very important to the culture, including football, baseball, basketball, hunting, and fishing. Perhaps the best-known aspect of Arkansas's culture is the stereotype that its citizens are shiftless hillbillies. The reputation began when early explorers characterized the state as a savage wilderness full of outlaws and thieves. The most enduring icon of Arkansas's hillbilly reputation is '' The Arkansas Traveller'', a painted depiction of a folk tale from the 1840s. Though intended to represent the divide between rich southeastern plantation Arkansas planters and the poor northwestern hill country, the meaning was twisted to represent a Northerner lost in the Ozarks on a white horse asking a backwoods Arkansan for directions. The state also suffers from the racial stigma common to former Confederate states, with historical events such as the
The culture of Arkansas includes distinct cuisine, dialect, and traditional festivals. Sports are also very important to the culture, including football, baseball, basketball, hunting, and fishing. Perhaps the best-known aspect of Arkansas's culture is the stereotype that its citizens are shiftless hillbillies. The reputation began when early explorers characterized the state as a savage wilderness full of outlaws and thieves. The most enduring icon of Arkansas's hillbilly reputation is '' The Arkansas Traveller'', a painted depiction of a folk tale from the 1840s. Though intended to represent the divide between rich southeastern plantation Arkansas planters and the poor northwestern hill country, the meaning was twisted to represent a Northerner lost in the Ozarks on a white horse asking a backwoods Arkansan for directions. The state also suffers from the racial stigma common to former Confederate states, with historical events such as the Little Rock Nine
The Little Rock Nine were a group of nine African American students enrolled in Little Rock Central High School in 1957. Their enrollment was followed by the Little Rock Crisis, in which the students were initially prevented from entering th ...
adding to Arkansas's enduring image.
Art and history museums display pieces of cultural value for Arkansans and tourists to enjoy. Crystal Bridges Museum of American Art in Bentonville was visited by 604,000 people in 2012, its first year. The museum includes walking trails and educational opportunities in addition to displaying over 450 works covering five centuries of American art. Several historic town sites have been restored as Arkansas state parks
State parks are parks or other protected areas managed at the sub-national level within those nations which use "state" as a political subdivision. State parks are typically established by a state to preserve a location on account of its natural ...
, including Historic Washington State Park
Historic Washington State Park (formerly Old Washington Historic State Park) is a List of Arkansas state parks, Arkansas state park in Hempstead County, Arkansas in the United States. The museum village contains a collection of pioneer artifa ...
, Powhatan Historic State Park, and Davidsonville Historic State Park
Davidsonville Historic State Park (formerly Old Davidsonville State Park) is a List of Arkansas state parks, Arkansas state park in Randolph County, Arkansas in the United States. Situated on a border between The Ozarks and the Arkansas Delta, t ...
.
Arkansas features a variety of native music across the state, ranging from the blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
heritage of West Memphis, Pine Bluff, Helena–West Helena to rockabilly
Rockabilly is one of the earliest styles of rock and roll music. It dates back to the early 1950s in the United States, especially the Southern United States, South. As a genre, it blends the sound of Western music (North America), Western musi ...
, bluegrass, and folk music from the Ozarks. Festivals such as the King Biscuit Blues Festival
The King Biscuit Blues Festival is an annual, multi-day blues festival, held in Helena, Arkansas, United States.
History
The name of the festival comes from ''King Biscuit Time'', which was the longest running radio show. Sonny Boy Williamson I ...
and Bikes, Blues, and BBQ pay homage to the history of blues in the state. The Ozark Folk Festival in Mountain View is a celebration of Ozark culture and often features folk and bluegrass musicians. Literature set in Arkansas such as ''I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings
''I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings'' is a 1969 autobiography describing the young and early years of American writer and poet Maya Angelou. The first in a Maya Angelou#Chronology of autobiographies, seven-volume series, it is a Bildungsroman, ...
'' by Maya Angelou
Maya Angelou ( ; born Marguerite Annie Johnson; April 4, 1928 – May 28, 2014) was an American memoirist, poet, and civil rights activist. She published seven autobiographies, three books of essays, several books of poetry, and is credi ...
and ''A Painted House
''A Painted House'' is a 2001 novel by American author John Grisham.
Inspired by his childhood in Arkansas, it is Grisham's first major work outside the legal thriller genre in which he established himself. Initially published in serial form, t ...
'' by John Grisham
John Ray Grisham Jr. (; born February 8, 1955) is an American novelist, lawyer, and former politician, known for his best-selling legal thrillers. According to the Academy of Achievement, American Academy of Achievement, Grisham has written 37 ...
describe the culture at various time periods.
Sports and recreation
 Team sports and especially collegiate football are important to Arkansans. College football in Arkansas began from humble beginnings, when the
Team sports and especially collegiate football are important to Arkansans. College football in Arkansas began from humble beginnings, when the University of Arkansas
The University of Arkansas (U of A, UArk, or UA) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Fayetteville, Arkansas, United States. It is the Flagship campus, flagship campus of the University of Arkan ...
first fielded a team in 1894. Over the years, many Arkansans have looked to Arkansas Razorbacks football
The Arkansas Razorbacks football program represents the University of Arkansas in the sport of American football. The Arkansas Razorbacks, Razorbacks compete in the
Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) of the National Collegiate Athletic Association ...
as the public image of the state. Although the University of Arkansas is based in Fayetteville, the Razorbacks have always played at least one game per season at War Memorial Stadium in Little Rock
Little Rock is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Arkansas, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The city's population was 202,591 as of the 2020 census. The six-county Central Arkan ...
in an effort to keep fan support in central and south Arkansas.
Arkansas State University
Arkansas State University (A-State or ASU) is a public university, public research university in Jonesboro, Arkansas, United States. It is the flagship campus of the Arkansas State University System and the second-largest university in the st ...
became the second NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision
The NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), formerly known as Division I-A, is the highest level of college football in the United States. The FBS consists of the largest schools in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). As ...
(FBS) (then known as Division I-A) team in the state in 1992 after playing in lower divisions for nearly two decades. The two schools have never played each other, due to the University of Arkansas's policy of not playing intrastate games. Two other campuses of the University of Arkansas System
The University of Arkansas System is a state university system in the U.S. state of Arkansas. It comprises six campuses; a medical school; two law schools; a graduate school focused on public service; a historically black college, statewide rese ...
are Division I members. The University of Arkansas at Pine Bluff is a member of the Southwestern Athletic Conference
The Southwestern Athletic Conference (SWAC) is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference headquartered in Birmingham, Alabama, which is made up of historically black colleges and universities (HBCUs) in the Southern United St ...
, a league whose members all play football in the second-level Football Championship Subdivision
The NCAA Division I Football Championship Subdivision (FCS), formerly known as Division I-AA, is the second-highest level of college football in the United States, after the NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision, Football Bowl Subdivision (F ...
(FCS). The University of Arkansas at Little Rock
The University of Arkansas at Little Rock (UA Little Rock, UALR) is a Public university, public research university in Little Rock, Arkansas, United States. Established as Little Rock Junior College by the Little Rock School District in 1927, the ...
, known for sports purposes as Little Rock, joined the Ohio Valley Conference
The Ohio Valley Conference (OVC) is a collegiate athletic conference which operates in the Midwestern and Southeastern United States. It participates in Division I of the NCAA; the conference's football programs compete in partnership with ...
in 2022 after playing in the Sun Belt Conference
The Sun Belt Conference (SBC) is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference that has been affiliated with the National Collegiate Athletic Association, NCAA's NCAA Division I, Division I since 1976. Originally a non-football confe ...
; unlike many other OVC members, it does not field a football program. The state's other DivisionI member is the University of Central Arkansas (UCA), which joined the ASUN Conference
The Atlantic Sun Conference (ASUN) is a collegiate athletic conference operating mostly in the Southeastern United States. The league participates at the NCAA Division I level, and began sponsoring football at the Division I FCS level in 2022. ...
in 2021 after leaving the FCS Southland Conference
The Southland Conference (SLC) is a collegiate athletic conference which operates in the South Central United States (specifically Texas and Louisiana). It participates in the NCAA's Division I for all sports; for football, it participates in ...
. Because the ASUN does not plan to start FCS football competition until at least 2022, UCA football is competing in the Western Athletic Conference
The Western Athletic Conference (WAC) is an NCAA Division I conference. The WAC covers a broad expanse of the Western United States with member institutions located in Arizona, California, Texas, Utah and Washington (state), Washington.
Due to ...
as part of a formal football partnership between the two leagues. Seven of Arkansas's smaller colleges play in NCAA Division II, with six in the Great American Conference
The Great American Conference (GAC) is a List of NCAA conferences, college athletic conference affiliated with the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) at the NCAA Division II, Division II level, with headquarters located in Russellvil ...
and one in the MIAA. Two other small Arkansas colleges compete in NCAA Division III, in which athletic scholarship
An athletic scholarship is a form of scholarship to attend a college or university or a private school, private high school awarded to an individual based predominantly on their ability to play in a sport. Athletic scholarships are common in the U ...
s are prohibited. High school football also began to grow in Arkansas in the early 20th century.
Baseball runs deep in Arkansas and was popular before the state hosted Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball league composed of 30 teams, divided equally between the National League (baseball), National League (NL) and the American League (AL), with 29 in the United States and 1 in Canada. MLB i ...
(MLB) spring training
Spring training, also called spring camp, is the preseason of the Summer Professional Baseball Leagues, such as Major League Baseball (MLB), and it is a series of practices and exhibition games preceding the start of the regular season. Spri ...
in Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a Spring (hydrology), spring produced by the emergence of Geothermal activity, geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow ...
from 1886 to the 1920s. Two minor league
Minor leagues are professional sports leagues which are not regarded as the premier leagues in those sports. Minor league teams tend to play in smaller, less elaborate venues, often competing in smaller cities/markets. This term is used in Nort ...
teams are based in the state. The Arkansas Travelers
The Arkansas Travelers, known informally as The Travs, are a Minor League Baseball team based in North Little Rock, Arkansas. The Travelers are the Double-A (baseball), Double-A affiliate of the Seattle Mariners and play in the Texas League.
Hi ...
play at Dickey–Stephens Park in North Little Rock
North Little Rock (often abbreviated "NLR") is a city in Pulaski County, Arkansas, United States. Located on the north side of the Arkansas River, it is the twin city of Little Rock. In the late nineteenth century, it was annexed by Little Ro ...
, and the Northwest Arkansas Naturals
The Northwest Arkansas Naturals are a Minor League Baseball team based in Springdale, Arkansas, Springdale, Arkansas. The team is a member of the Texas League, and serves as the Double-A (baseball), Double-A affiliate of the Kansas City Royals. T ...
play in Arvest Ballpark in Springdale. Both teams compete in Double-A Central.
Hunting continues in the state. The state created the Arkansas Game and Fish Commission
Arkansas Game and Fish Commission (AGFC) is a state agency of Arkansas, headquartered in Little Rock, Arkansas
Little Rock is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Arkansas, most populous city of t ...
in 1915 to regulate hunting. Today a significant portion of Arkansas's population participates in hunting duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family (biology), family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and goose, geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfam ...
in the Mississippi flyway
The Mississippi Flyway is a bird migration route that generally follows the Mississippi, Missouri, and Lower Ohio Rivers in the United States across the western Great Lakes to the Mackenzie River and Hudson Bay in Canada. The main endpoints of t ...
and deer
A deer (: deer) or true deer is a hoofed ruminant ungulate of the family Cervidae (informally the deer family). Cervidae is divided into subfamilies Cervinae (which includes, among others, muntjac, elk (wapiti), red deer, and fallow deer) ...
across the state.Sutherlin 1996, p. 164. Ducks Unlimited has called Stuttgart, Arkansas
Stuttgart is a city in and the county seat of the northern district of Arkansas County, Arkansas, United States. As of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census it had a population of 9,326.
Known as the "Rice and Duck Capital of the World", ...
, "the epicenter of the duck universe". Millions of acres of public land are available for both bow and modern gun hunters.
Fishing has always been popular in Arkansas, and the sport and the state have benefited from the creation of reservoirs across the state. Following the completion of Norfork Dam
Norfork Dam impounds the North Fork River (Missouri - Arkansas), North Fork River in the U.S. state of Arkansas, creating Norfork Lake. The large reservoir is maintained by the United States Army Corps of Engineers and spans Baxter County, Arkans ...
, the Norfork Tailwater
The Norfork Tailwater is the segment of the North Fork River below Norfork Dam in north central Arkansas. The Norfork Tailwater is about long and stretches from the dam below Lake Norfork to the White River at Norfork. The community of Salesv ...
and the White River have become a destination for trout
Trout (: trout) is a generic common name for numerous species of carnivorous freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', ''Salmo'' and ''Salvelinus'', all of which are members of the subfamily Salmoninae in the ...
fishers. Several smaller retirement communities such as Bull Shoals, Hot Springs Village, and Fairfield Bay have flourished due to their position on a fishing lake. The National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government, within the US Department of the Interior. The service manages all List ...
has preserved the Buffalo National River
The Buffalo National River, in Northern Arkansas, was the first National River to be designated in the United States. The Buffalo River is long. The lower flow within the boundaries of an area managed by the National Park Service, where the s ...
in its natural state and fly fishers visit it annually.
Attractions
 * Arkansas Post National Memorial at Gillett, Arkansas, Gillett
* Blanchard Springs Caverns
*
* Arkansas Post National Memorial at Gillett, Arkansas, Gillett
* Blanchard Springs Caverns
* Buffalo National River
The Buffalo National River, in Northern Arkansas, was the first National River to be designated in the United States. The Buffalo River is long. The lower flow within the boundaries of an area managed by the National Park Service, where the s ...
* Fort Smith National Historic Site
* Hot Springs National Park
* Little Rock Central High School National Historic Site
* Pea Ridge National Military Park
* President William Jefferson Clinton Birthplace Home National Historic Site
* Arkansas State Capitol Building
* List of Arkansas state parks
See also
* Index of Arkansas-related articles * Outline of Arkansas * Spanish Empire * History of Louisiana * USS Arkansas, USS ''Arkansas'', 5 ships * '''' * ''''Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Blair, Diane D. & Jay Barth ''Arkansas Politics & Government: Do the People Rule?'' (2005) * Deblack, Thomas A. ''With Fire and Sword: Arkansas, 1861–1874'' (2003) * Donovan, Timothy P. and Willard B. Gatewood Jr., eds. ''The Governors of Arkansas'' (1981) * Dougan, Michael B. ''Confederate Arkansas'' (1982), * Duvall, Leland. ed., ''Arkansas: Colony and State'' (1973)Hamilton, Peter Joseph. ''The Reconstruction Period''
(1906), full length history of era; Dunning School approach; 570 pp; ch 13 on Arkansas * Hanson, Gerald T. and Carl H. Moneyhon. ''Historical Atlas of Arkansas'' (1992) * Key, V. O. ''Southern Politics'' (1949) * Kirk, John A., ''Redefining the Color Line: Black Activism in Little Rock, Arkansas, 1940–1970'' (2002). * McMath, Sidney S. ''Promises Kept'' (2003) * Moore, Waddy W. ed., ''Arkansas in the Gilded Age, 1874–1900'' (1976). * Peirce, Neal R. ''The Deep South States of America: People, Politics, and Power in the Seven Deep South States'' (1974). * Thompson, Brock. ''The Un-Natural State: Arkansas and the Queer South'' (2010) * Thompson, George H. ''Arkansas and Reconstruction'' (1976) * Whayne, Jeannie M. ''Arkansas Biography: A Collection of Notable Lives'' (2000) * White, Lonnie J. ''Politics on the Southwestern Frontier: Arkansas Territory, 1819–1836'' (1964) * Williams, C. Fred. ed. ''A Documentary History Of Arkansas'' (2005)
External links
Arkansas.gov
€”Official State Website
Arkansas State Facts from USDA
Official State tourism website
''Encyclopedia of Arkansas''
Energy & Environmental Data for Arkansas
2000 Census of Population and Housing for Arkansas
U.S. Census Bureau
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Arkansas
Arkansas Summer Camps
Arkansas Shakespeare Theatre
* *
Arkansas State Code (the state statutes of Arkansas)
Arkansas State Databases
€”Annotated list of searchable databases produced by Arkansas state agencies and compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association. {{Coord, 35, -92, dim:300000_region:US-AR_type:adm1st, name=State of Arkansas, display=title Arkansas, 1836 establishments in the United States Contiguous United States South Central United States Southern United States States and territories established in 1836 States of the Confederate States of America States of the United States