Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar,
– ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third
Mughal emperor
The emperors of the Mughal Empire, who were all members of the Timurid dynasty (House of Babur), ruled the empire from its inception on 21 April 1526 to its dissolution on 21 September 1857. They were supreme monarchs of the Mughal Empire in ...
, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father,
Humayun
Nasir al-Din Muhammad (6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), commonly known by his regnal name Humayun (), was the second Mughal emperor, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Northern India, and Pakistan from ...
, under a regent,
Bairam Khan
Muhammad Bairam Khan (; 18 January 1501 – 31 January 1561), commonly known as Bairam Khan or Bayram Khan was an important military commander, and later commander-in-chief of the Mughal Empire, Mughal army, a powerful statesman and regent at ...
, who helped the young emperor expand and consolidate Mughal domains in the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
. He is generally considered one of the greatest emperors in Indian history and led a successful campaign to unify the various kingdoms of ''
Hindūstān'' or
India proper.
[ Quote: "Akbar, The greatest Mughal emperor of India."]
Akbar gradually enlarged the
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
to include much of the Indian subcontinent through Mughal military, political, cultural, and economic dominance. To unify the vast Mughal state, Akbar established a centralised system of administration and adopted a policy of conciliating conquered rulers through marriage and diplomacy. To preserve peace and order in a religiously and culturally diverse empire, he adopted policies that won him the support of his non-Muslim subjects, including abolishing the
sectarian tax and appointing them to high civil and military posts.
Under Akbar, Mughal India developed a strong and stable economy, which tripled in size and wealth, leading to commercial expansion and greater patronage of an
Indo-Persian culture
Indo-Persian culture refers to a cultural synthesis present on the Indian subcontinent. It is characterised by the absorption or integration of Persian aspects into the various cultures of modern-day republics of Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
. Akbar's courts at
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
,
Agra
Agra ( ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is the ...
, and
Fatehpur Sikri
Fatehpur Sikri () is a town in the Agra District of Uttar Pradesh, India. Situated from the district headquarters of Agra, Fatehpur Sikri itself was founded as the capital of the Mughal Empire in 1571 by Mughal emperors, Emperor Akbar, servin ...
attracted holy men of many faiths, poets, architects, and artisans, and became known as centres of the arts, letters, and learning.
Timurid and Perso-Islamic culture began to merge and blend with indigenous Indian elements into a distinct style of Mughal arts, including
painting
Painting is a Visual arts, visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or "Support (art), support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with ...
and
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
. Disillusioned with orthodox Islam and perhaps hoping to bring about religious unity within his empire, Akbar promulgated
Din-i Ilahi
The ''Dīn-i Ilāhī'' (, ), known during its time as ''Tawḥīd-i-Ilāhī'' (, ) or Divine Faith, was a short lived syncretic religion propounded by the Mughal emperor Akbar in 1582.
According to Iqtidar Alam Khan, it was based on the Tim ...
, a
syncretic creed derived mainly from
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
and
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
as well as elements of
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called Mazdayasnā () or Beh-dīn (), is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zoroaster, Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, ...
and
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
.
Akbar was succeeded as emperor by his son, Prince Salim, later known as
Jahangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
.
Early years
After Mughal Emperor
Humayun
Nasir al-Din Muhammad (6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), commonly known by his regnal name Humayun (), was the second Mughal emperor, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Northern India, and Pakistan from ...
was defeated at
Chausa
Chausa is a town and corresponding community development block in Buxar district, Bihar, India. It is located 11 km west of the district headquarters, Buxar, on the bank of the river Ganga. As of 2011, the population of the village of Cha ...
(1539) and
Kannauj
Kannauj (Hindustani language, Hindustani pronunciation: ) is an ancient city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar palika, Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of Ut ...
(1540) by the forces of
Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri (born Farid al-Din Khan; 1472 or 1486 – 22 May 1545), also known by his title Sultan Adil (), was the ruler of Bihar from 1530 to 1540, and Sultan of Hindustan from 1540 until his death in 1545. He defeated the Mughal Empire, ...
, Humayun fled westward to modern-day
Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
.
There, he met and married the 14-year-old
Hamida Banu Begum
Hamida Banu Begum (Persian: حمیده بانو بیگم; 1527 – 29 August 1604) was the queen consort, empress consort of the second Mughal emperor Humayun and the mother of his successor, the third Mughal emperor Akbar.[ ...]
, daughter of Shaikh Ali Akbar Jami, a
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
teacher of Humayun's younger brother
Hindal Mirza
Abu'l-Nasir Muhammad (; 4 March 1519 – 20 November 1551), better known by the sobriquet Hindal ( Chagatai for "Taker of India"), was a Mughal prince and the youngest son of Emperor Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire and the first M ...
. Jalal ud-din Muhammad Akbar was born to them the next year on 25 October 1542 (the fifth day of
Rajab
Rajab () is the seventh month of the Islamic calendar. The lexical definition of the classical Arabic verb ''rajaba'' is "to respect", which could also mean "be awe or be in fear", of which Rajab is a derivative.
This month is regarded as one ...
, 949
AH) at the
Rajput Fortress of
Amarkot
Umerkot (Urdu: ; Dhatki language, Dhatki : عمرڪوٽ; Sindhi language, Sindhi: عمرڪوٽ; International Phonetic Alphabet, IPA: Help:IPA/Hindi and Urdu, �mərkoːʈ formerly known as Amarkot) is a city in the Sindh province of Pakista ...
in
Rajputana
Rājputana (), meaning Land of the Rajputs, was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the entire present-day States of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, parts of the neighboring states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and adjo ...
(in modern-day Sindh), where his parents had been given refuge by the local Hindu ruler Rana Prasad.
During the extended period of Humayun's exile, Akbar was brought up in
Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
by his paternal uncles,
Kamran Mirza
Kamran Mirza () (1512 – 5 October 1557) was the second son of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire and the first Mughal Emperor. Kamran Mirza was born in Kabul to Babur's wife Gulrukh Begum. He was half-brother to Babur's eldest son Hu ...
and
Askari Mirza
Muhammad Askari Mirza (Persian: محمد عسکری میرزا), sometimes known simply as Askari Mirza (1518 – 5 October 1557DELHI (Mughal Empire) http://members.iinet.net.au/~royalty/ips/families/mughal.html ) was a son of Babur Mirza, the fo ...
, and aunts, in particular, Kamran Mirza's wife. He spent his youth learning to hunt, run, and fight, and although he never learned to read or write, when he retired in the evening, he would have someone read to him.
On 20 November 1551, Humayun's youngest brother, Hindal Mirza, died in a battle against Kamran Mirza's forces. Upon hearing the news of his brother's death, Humayun was overwhelmed with grief.
About the time of nine-year-old Akbar's first appointment as governor of
Ghazni
Ghazni (, ), historically known as Ghaznayn () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana (), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan with a population of around 190,000 people. The city is strategica ...
, he married Hindal's daughter,
Ruqaiya Sultan Begum
Ruqaiya Sultan Begum (alternatively spelled Ruqayya or Ruqayyah; 1542 – January 1626) was the first wife and one of the chief consorts of the third Mughal emperor, Akbar.
Ruqaiya was a first cousin of her husband and was a Mughal princess ...
, his first wife.
Humayun gave Akbar command of Hindal's troops and conferred on the imperial couple all of Hindal's wealth.
Akbar's marriage to Ruqaiya was solemnised in
Jalandhar
Jalandhar () is a city in the state of Punjab, India, Punjab in India. With a considerable population, it ranks as the List of cities in Punjab and Chandigarh by population, third most-populous city in the state and is the largest city in the ...
, Punjab, when they were both 14 years old.
Following chaos over the succession of Sher Shah Suri's son
Islam Shah
Islam Shah Suri (born Jalal Khan; 1507 – 22 November 1554) also known as Salim Shah Suri, was Sultan of Hindustan from 27 May 1545 until his death in 1554. He was the second ruler of the Sur Empire which ruled parts of India in the mid-16th ...
, Humayun reconquered Delhi in 1555, leading an army partly provided by his Persian ally
Tahmasp I
Tahmasp I ( or ; 22 February 1514 – 14 May 1576) was the second shah of Safavid Iran from 1524 until his death in 1576. He was the eldest son of Shah Ismail I and his principal consort, Tajlu Khanum.
Tahmasp ascended the throne after the ...
. A few months later, Humayun died. Akbar's guardian,
Bairam Khan
Muhammad Bairam Khan (; 18 January 1501 – 31 January 1561), commonly known as Bairam Khan or Bayram Khan was an important military commander, and later commander-in-chief of the Mughal Empire, Mughal army, a powerful statesman and regent at ...
, concealed his death to prepare for Akbar's succession. Akbar succeeded Humayun on 14 February 1556,
while in the midst of a war against
Sikandar Shah
Abul Mujāhid Sikandar Shāh (, ), commonly known as Sikandar Shah; was the second Sultan of Bengal and the Ilyas Shahi dynasty. He was the son of Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah. Sikandar Shah continued to project the imperial ambitions of his father. He ...
to reclaim the Mughal throne. In
Kalanaur, Punjab
Kalanaur is a tehsil in Gurdaspur District of Punjab state in India. It is located 25 km towards west from District headquarters Gurdaspur. This historical town is situated on newly constructed National Highway 354. The town has historical ...
, the 14-year-old Akbar was enthroned by Bairam Khan on a newly constructed platform (which still stands) and was proclaimed ''Shahanshah'' (
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
for "King of Kings").
Bairam Khan ruled on his behalf until he came of age.
Ancestry
Military campaigns
Military innovations
Akbar's military campaigns consolidated Mughal rule in the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
.
Akbar introduced organisational changes to the ''
mansabdar
The Mansabdar was a military unit within the administrative system of the Mughal Empire introduced by Akbar later used in all over in early modern India. The word ''mansab'' is of Arabic origin meaning rank or position. The system determined th ...
i'' system, establishing a hierarchical scale of military and civil ranks.
Organisational reforms were accompanied by innovations in
cannons
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during t ...
,
fortifications
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from La ...
, and the
use of elephants.
Akbar also took an interest in
matchlock
A matchlock or firelock is a historical type of firearm wherein the gunpowder is ignited by a burning piece of flammable cord or twine that is in contact with the gunpowder through a mechanism that the musketeer activates by pulling a lever or Tri ...
s and effectively employed them during various conflicts. He sought the help of the
Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
, as well as Europeans, especially the
Portuguese and Italians, in procuring advanced firearms and artillery.
Akbar's
vizier
A vizier (; ; ) is a high-ranking political advisor or Minister (government), minister in the Near East. The Abbasids, Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a help ...
Abul Fazl
Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak (14 January 1551 – 22 August 1602), also known as Abul Fazl, Abu'l Fadl and Abu'l-Fadl 'Allami, was an Indian writer, historian, and politician who served as the grand vizier of the Mughal Empire from his appointment ...
once declared that "with the exception of Turkey, there is perhaps no country in which its guns has more means of securing the Government than
ndia Ndia or NDIA may refer to:
*Ndia Constituency, Kirinyaga District, Central Province, Kenya
*Alternative name for the Southern Kirinyaga dialect of the Kikuyu language
*National Defense Industrial Association, an American trade association
*Nationa ...
"
Scholars and historians have used the term "
gunpowder empire
''Gunpowder Empire'' is a 2003 alternate history novel by Harry Turtledove. It is the first part of the Crosstime Traffic series.
Plot
In the novel, Jeremy and Amanda Solter are two teenagers living in the late 21st century. Their parents wor ...
" to analyse the success of the Mughals in India.
North India

Akbar's father Humayun had regained control of the
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
,
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
, and
Agra
Agra ( ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is the ...
with
Safavid
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the begi ...
support, but Mughal rule was still precarious when Akbar took the throne. When the Surs reconquered Agra and Delhi following the death of Humayun, Akbar's young age and the lack of military assistance from the Mughal stronghold of
Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
which was in the midst of an invasion by the ruler of
Badakhshan
Badakhshan is a historical region comprising the Wakhan Corridor in northeast Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic ...
, Prince Mirza Suleimanaggravated the situation.
When his regent,
Bairam Khan
Muhammad Bairam Khan (; 18 January 1501 – 31 January 1561), commonly known as Bairam Khan or Bayram Khan was an important military commander, and later commander-in-chief of the Mughal Empire, Mughal army, a powerful statesman and regent at ...
, called a council of war to marshall the Mughal forces, none of Akbar's chieftains approved. Bairam Khan was ultimately able to prevail over the nobles and it was decided that the Mughals would march against the strongest of the Sur rulers,
Sikandar Shah Suri
Sikandar Shah Suri (died 1559) was the last ruling Sur Empire#List of rulers of the Sur Empire, Sultan of Hindustan from the Sur Empire, Sur dynasty from February 1555 until his defeat on 22 June 1555, and the second-to-last ruler of the Sur E ...
, in Punjab. Delhi was left under the regency of
Tardi Baig Khan.
Sikandar Shah Suri, his army weakened by earlier lost battles, withdrew to avoid combat as the Mughal army approached.
Akbar also faced
Hemu
Hemu (; 1501 – 5 November 1556), also known as Hemu Vikramaditya and Hemchandra Vikramaditya, was an Indian king (maharaja) who previously served as a general and Vizier, Wazir of Muhammad Adil Shah (died 1557), Adil Shah Suri of the Sur Emp ...
, a minister and general of one of the Sur rulers, who had proclaimed himself Hindu emperor and expelled the Mughals from the
Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the Northern Plain or North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain spanning across the northern and north-eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It encompasses North India, northern and East India, easte ...
s.
Urged by Bairam Khan, who re-marshalled the Mughal army before Hemu could consolidate his position, Akbar marched on Delhi to reclaim it. His army, led by Bairam Khan, defeated Hemu and the Sur army on 5 November 1556 at the
Second Battle of Panipat
The Second Battle of Panipat was fought on 5 November 1556, between the Mughal Empire, Mughals under Akbar and emperor Hemu, titularly known as Hemu, Hemchandra Vikramaditya. Hemchandra had conquered Delhi and Agra a few weeks earlier by defeati ...
, north of Delhi.
Soon after the battle, Mughal forces occupied Delhi and then Agra. Akbar made a triumphant entry into Delhi, where he stayed for a month. Then, he and Bairam Khan returned to Punjab to deal with Sikandar Shah Suri, who had become active again.
In the next six months, the Mughals won another major battle against Sikander, who fled east to
Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
. Akbar and his forces occupied
Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
and then seized
Multan
Multan is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fifth-most populous city in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the List of cities in Pakistan by populatio ...
in the Punjab. In 1558, Akbar took possession of
Ajmer
Ajmer () is a city in the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Ajmer district and Ajmer division. It lies at the centre of Rajasthan, earning it the ...
, the aperture to
Rajputana
Rājputana (), meaning Land of the Rajputs, was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the entire present-day States of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, parts of the neighboring states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and adjo ...
, after the defeat and flight of its Muslim ruler.
The Mughals also besieged and defeated the Sur forces in control of
Gwalior Fort
The Fort of Gwalior or the Gwalior Fort is a 6th century defence hill fort in Gwalior, India. Mughal Emperor Babur called it the "pearl amongst the fortresses of Hind" because of its impregnability and magnificence and it has also been nickna ...
, a stronghold north of the
Narmada
The Narmada River, previously also known as ''Narbada'' or anglicised as ''Nerbudda'', is the 5th longest river in India and overall the longest west-flowing river in the country. It is also the largest flowing river in the state of Madhya Prade ...
river.
Royal begums (ladies), along with the families of Mughal amirs, were brought from Kabul to India at the time, "so that men might become settled and be restrained in some measure from departing to a country to which they were accustomed", according to Fazl.
Akbar made clear that he would stay in India, reintroducing the historical legacy of the
Timurid Renaissance
The Timurid Renaissance was a historical period in Asian history, Asian and Islamic history spanning the late 14th, the 15th, and the early 16th centuries. Following the Islamic Golden Age, the Timurid Empire, based in Central Asia and ruled by ...
, in contrast to his grandfather and father, who reigned as transient rulers.
Central India
By 1559, the Mughals had launched a drive to the south into Rajputana and
Malwa
Malwa () is a historical region, historical list of regions in India, region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic plateau, volcanic upland north of the ...
.
However, Akbar's disputes with his regent, Bairam Khan, temporarily put an end to the expansion.
The young emperor, at the age of eighteen, wanted to take a more active part in managing the Empire's affairs. Urged on by his foster mother,
Maham Anga
Maham Anga (died 25 June 1562) was the foster mother and chief wet nurse of the Mughal emperor Akbar. She was the political adviser of the teenage emperor and the de facto regent of the Mughal Empire from 1560 to 1562.
Biography
Maham Anga w ...
, and other relatives, Akbar dismissed Bairam Khan following a dispute at court in the spring of 1560 and ordered him to leave on
Hajj
Hajj (; ; also spelled Hadj, Haj or Haji) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for capable Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetim ...
to
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
.
Bairam Khan was prepared to comply, but people who resented him and hoped for his downfall goaded him into rebellion against Akbar.
Bairam Khan was defeated by the Mughal army in the Punjab and forced to submit. Akbar forgave him and gave him the option of either continuing in his court or resuming his pilgrimage; Bairam Khan chose the latter. Bairam Khan was assassinated on his way to Mecca, by a group of Afghans led by Mubarak Khan Lohani, whose father had been killed while fighting with the Mughals at the
Battle of Machhiwara
The Battle of Machhiwarra was fought between Mughal Empire and Suri Empire in 1555.
Background
After the death of Islam Shah Suri, the Suri Empire was in a civil war where various contenders to the throne fought each other for supremacy. Sikanda ...
in 1555.
In 1560, Akbar resumed military operations.
A Mughal army under the command of his foster brother,
Adham Khan
Adham Khan (1531 – 16 May 1562) was a general of Mughal emperor Akbar. He was the younger son of Maham Anga, and thus, was the foster brother of Akbar. In his fourth regnal year, Akbar married him to Javeda Begum, the daughter of Baqi Khan B ...
, and a Mughal commander, Pir Muhammad Khan, began the Mughal conquest of Malwa. The Afghan ruler,
Baz Bahadur
Bayazid Baz Bahadur Khan was the last Sultan of the Malwa Sultanate, who reigned from 1555 to 1562. He succeeded his father, Shuja'at Khan. He is known for his romantic liaison with Roopmati.
Baz Bahadur as sultan did not bother to look aft ...
, was defeated at the Battle of Sarangpur and fled to
Khandesh
Khandesh is a geographic region in Maharashtra, India. It was made up of present Jalgaon, Dhule and Nandurbar districts. It also said that Burhanpur District of Madhya Pradesh was also its part.
The region have seen many geographical ch ...
for refuge, leaving behind his harem, treasure, and war elephants.
Despite initial success, Akbar was ultimately displeased with the aftermath of the campaign; his foster brother retained all of the spoils and followed through with the Central Asian practice of slaughtering the surrendered garrison, their wives and children, and many Muslim theologians and Sayyids, who were descendants of
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
.
Akbar personally rode to Malwa to confront Adham Khan and relieve him of command. Pir Muhammad Khan was then sent in pursuit of Baz Bahadur, but was beaten back by the alliance of the rulers of Khandesh and
Berar
Berar may refer to:
*Vidarbha, the eastern region of Maharashtra, India, historically known as Berar
* Berar Sultanate (1490–1596), one of the Deccan sultanates
*Berar Subah (1596–1724), a subah (province) of the Mughal Empire
*Berar Province ( ...
.
Baz Bahadur temporarily regained control of Malwa until, in the next year, Akbar sent another Mughal army to invade and annexe the kingdom.
Malwa became a province of the nascent imperial administration of Akbar's regime. Baz Bahadur survived as a refugee at various courts until, eight years later in 1570, he took service under Akbar.
When Adham Khan confronted Akbar following another dispute in late 1561, the emperor threw him from a terrace into the palace courtyard at Agra. Still alive, Adham Khan was dragged up and thrown to the courtyard once again by Akbar to ensure his death.
After Adham Khan's death, Akbar distributed authority among specialised ministerial posts relating to different aspects of imperial governance to prevent any one noble from becoming too powerful.
When a powerful clan of Uzbek chiefs broke out in rebellion in 1564, Akbar routed them in Malwa and then
Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
.
He pardoned the rebellious leaders, hoping to conciliate them, but they rebelled again; Akbar quelled their second uprising. Following a third revolt, with the proclamation of
Mirza Muhammad Hakim
Shahzada Mirza Muhammad Hakim (29 April 1553 – 10 October 1585), sometimes known simply as Mirza Hakim, was the third son of the Mughal emperor Humayun. He ruled Kabul in Afghanistan, and often conflicted with his elder brother, Emperor Akbar, ...
Akbar's brother and the Mughal ruler of Kabulseveral Uzbek chieftains were slain and the rebel leaders trampled to death under elephants.
Simultaneously, the Mirzas, a group of Akbar's distant cousins who held important fiefs near Agra, rebelled and were defeated by Akbar.
In 1566, Akbar moved to meet the forces of his brother, Muhammad Hakim, who had marched into the Punjab with the intention of seizing the imperial throne. Following a brief confrontation, Muhammad Hakim accepted Akbar's supremacy and retreated back to Kabul.
In 1564, Mughal forces began the
conquest of Garha, a thinly populated, hilly area in central India that was of interest to the Mughals because of its herd of wild elephants.
The territory was ruled over by Raja Vir Narayan, a minor, and his mother,
Durgavati, a
Rajput
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
warrior queen of the Gonds.
Akbar did not personally lead the campaign because he was preoccupied with the Uzbek rebellion, leaving the expedition in the hands of Asaf Khan, the Mughal governor of Kara.
Durgavati committed suicide after her defeat at the Battle of Damoh, while Raja Vir Narayan was slain at the Fall of Chauragarh, the mountain fortress of the Gonds.
The Mughals seized immense wealth, including an uncalculated amount of gold and silver, jewels, and 1,000 elephants. Kamala Devi, a younger sister of Durgavati, was sent to the Mughal harem.
The brother of Durgavati's deceased husband was installed as the Mughal administrator of the region.
As with Malwa, Akbar entered into a dispute with his vassals over the conquest of Gondwana.
Asaf Khan was accused of keeping most of the treasures and sending back only 200 elephants to Akbar. When summoned to give accounts, he fled Gondwana. He went first to the Uzbeks, then returned to Gondwana where he was pursued by Mughal forces. Finally, he submitted and Akbar restored him to his previous position.
Assassination attempt
In January 1564, an assassin shot an arrow at Akbar, which pierced his right shoulder, as he was returning from a visit to the Dargah of Hazrat Nizamuddin near Delhi. The Emperor ordered the apprehended assassin, a slave of Mirza Sharfuddin—a noble in Akbar's court whose recent rebellion had been suppressed—to be beheaded.
Rajputana
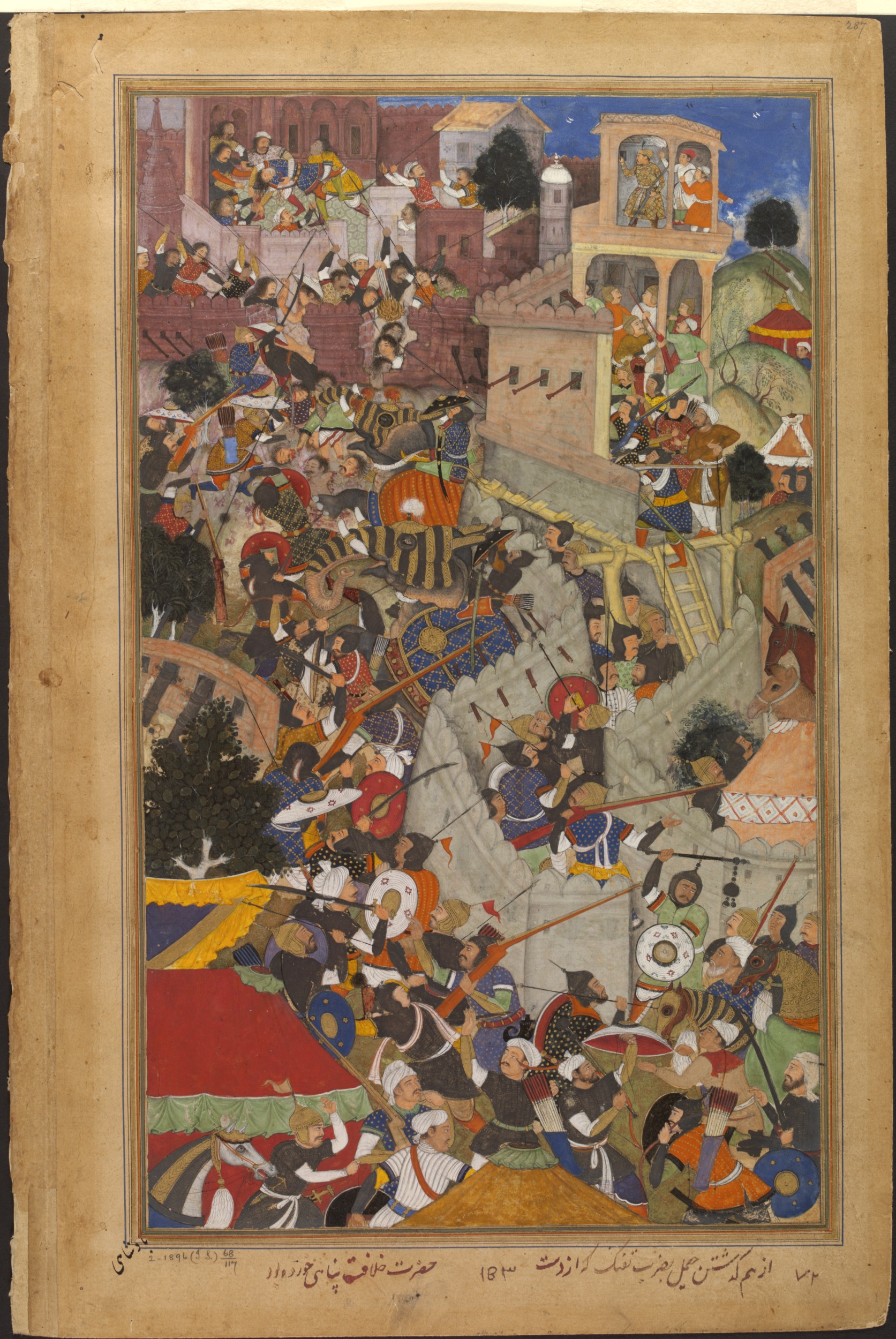


Having established Mughal rule over northern India, Akbar turned his attention to the conquest of
Rajputana
Rājputana (), meaning Land of the Rajputs, was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the entire present-day States of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, parts of the neighboring states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and adjo ...
, which was strategically important as it was a rival centre of power that flanked the Indo-Gangetic plains.
The Mughals had already established domination over parts of northern Rajputana in
Mewat
Mewat (; ) is a historical and cultural region which encompasses parts of the modern-day states of Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh in northwestern India.
Geography
The loose boundaries of the Mewat region generally include parts of th ...
,
Ajmer
Ajmer () is a city in the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Ajmer district and Ajmer division. It lies at the centre of Rajasthan, earning it the ...
, and Nagor.
Akbar sought to conquer Rajputana's heartlands, which had rarely previously submitted to the Muslim rulers of the
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries. . Beginning in 1561, the Mughals actively engaged the Rajputs in warfare and diplomacy.
Most Rajput states accepted Akbar's suzerainty; however, the rulers of Mewar and Marwar—
Udai Singh II
Udai Singh II (4 August 1522 – 28 February 1572) was the List of Ranas of Mewar, 12th Maharana of the Kingdom of Mewar and the founder of the city of Udaipur in the present-day state of Rajasthan, India. He was the fourth son of Rana SangaTo ...
and
Chandrasen Rathore
Rao Chandrasen (30 July 1541 – 11 January 1581) was a Rathore Rajput ruler of the Kingdom of Marwar. He was a younger son of Rao Maldev Rathore. He followed his father's policy and stayed hostile to the ruling foreign powers in north Indi ...
—remained outside the imperial fold.
Udai Singh was descended from the Sisodia ruler,
Rana Sanga
Sangram Singh I (12 April 1482 – 30 January 1528), most commonly known as Rana Sanga, was the Rana of Mewar, Maharana of Mewar from 1509 to 1528. A member of the List of Ranas of Mewar, Sisodia dynasty, he controlled parts of present-day Ra ...
, who had fought Babur at the
Battle of Khanwa
The Battle of Khanwa was fought at Khanwa in modern-day Rajasthan on 16 March 1527, between the Mughal Empire, led by Babur, and the Kingdom of Mewar, led by Rana Sanga for supremacy of Northern India. The battle, which ended in a Mughal vic ...
in 1527.
As the head of the
Sisodia clan, he possessed the highest ritual status of all the Rajput kings and chieftains in India. The Mughals viewed defeating Udai Singh as essential to asserting their imperial authority among the Rajputs.
During this period of his reign, Akbar was still devoted to Islam and sought to impress the superiority of his faith over what were regarded by contemporaries as the most prestigious warriors in Hinduism.
In 1567, Akbar attacked the
Chittor Fort
Chittorgarh (literally Chittor Fort), also known as Chittod Fort, is one of the largest forts in India. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The fort was the capital of Mewar and is located in the present-day city of Chittorgarh. It sprawls ove ...
in Mewar. The fortress-capital of Mewar was of strategic importance as it lay on the shortest route from Agra to
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
and was also considered a key to holding the interior parts of Rajputana. Udai Singh retreated to the hills of Mewar, leaving two Rajput warriors,
Jaimal
Jaimal Rathore (1507–1568) was the Rathore Rajput (Mertiya) ruler of Merta. He was cousin of the Hindu saint Mirabai and Great grandson of Rao Jodha Rathore and Grandson of Rao Duda Rathore (Founder of Mertiya clan of Rathore's & Establi ...
and
Patta, in charge of the defence of his capital.
Chittorgarh fell in February 1568 after a
siege of four months. The fall of Chittor was proclaimed by Akbar as "the victory of Islam over infidels
'i.e.'', non-Muslims"
In his Fathnama (dispatches announcing victory) issued on 9 March 1575 conveying his news of victory, Akbar wrote: "With the help of our blood-thirsty sword we have erased the signs of infidelity in their minds and destroyed the temples in those places and all over Hindustan."
Akbar had the surviving defenders and 30,000 non-combatants massacred and their heads displayed upon towers erected throughout the region to demonstrate his authority.
Thereafter, Udai Singh never ventured out of his mountain refuge in Mewar.
A legend, oft repeated by historians, has grown up that Akbar set up statues of Jaimal and Patta mounted on elephants at a gate of his fort in Agra to commemorate his victory. There are records from his time of two statues of elephants with their riders outside the eastern gate of his fort in Agra, but these may have had nothing to do with the Rajputs of Chittor, they may have been purely decorative. Indologist
Eugenia Vanina
Eugenia Yurevna Vanina (born 24 December 1957) is a Russian Indologist, head of the History and Culture section and a researcher in the Centre for Indian Studies at the Institute of Oriental Studies of the Russian Academy of Sciences. She is know ...
found no account that connects the statues to Jaimal and Patta until a 1629 chronicle by Dutch merchants. She believes that the narrative that the statues were monuments grew up to "provide ideological, social and psychological substantiation" of the alliance between the Mughals and the Rajputs.
The fall of Chittorgarh was followed up by a Mughal attack on the
Ranthambore Fort
Ranthambore Fort lies within the Ranthambore National Park, near the city of Sawai Madhopur in Sawai Madhopur district of Rajasthan, India. It is a formidable fort having been a focal point of the historical developments of Rajasthan. The fo ...
in 1568. Ranthambore was held by the
Hada Hada may refer to:
* Hada, or Khata, traditional ceremonial scarf used in Tibet and Mongolia
* Hada (surname), a Japanese and Romanian surname
* Hada (activist), Mongol activist advocating for the separation of Inner Mongolia from the People's Repu ...
Rajputs and reputed to be the most powerful fortress in India.
However, it fell only after a couple of months.
At that point, most of the Rajput kings had submitted to the Mughals; only the clans of Mewar continued to resist.
Udai Singh's son and successor,
Maharana Pratap
Pratap Singh I (9 May 1540 – 19 January 1597), popularly known as Maharana Pratap (), was king of the Kingdom of Mewar, in north-western India in the present-day state of Rajasthan, from 1572 until his death in 1597. He is notable for leadi ...
, was later defeated by the Mughals at the
Battle of Haldighati
The battle of Haldighati was fought on 18 June 1576 between the Mewar forces led by Maharana Pratap, and the Mughal forces led by Man Singh I of Amber. The Mughals emerged victorious after inflicting significant casualties on Mewari forces, ...
in 1576.
Akbar would celebrate his conquest of Rajputana by laying the foundation of a new capital, west-southwest of Agra, in 1569. It was called
Fatehpur Sikri
Fatehpur Sikri () is a town in the Agra District of Uttar Pradesh, India. Situated from the district headquarters of Agra, Fatehpur Sikri itself was founded as the capital of the Mughal Empire in 1571 by Mughal emperors, Emperor Akbar, servin ...
, or the "City of Victory". Pratap Singh continued to attack the Mughals and was able to retain most of his kingdom during Akbar's reign.
Western and Eastern India

Akbar's next military objectives were the conquest of Gujarat and Bengal, which connected India with the trading centres of Asia, Africa, and Europe through the
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
and the
Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
.
Gujarat had also been a haven for rebellious Mughal nobles. In Bengal, the Afghans still held considerable influence under their ruler,
Sulaiman Khan Karrani
Sulaiman Khan Karrani (, ; reigned: 1565–1572) was an Afghan Sultan of Bengal. He ascended to the throne after the death of his brother Taj Khan Karrani. According to the '' Riyaz-us-Salatin'', he shifted the seat of government from Gaur t ...
. Akbar first moved against Gujarat, which lay in the crook of the Mughal provinces of Rajputana and Malwa.
Gujarat possessed areas of rich agricultural production in its central plain, an impressive output of textiles and other industrial goods, and the busiest seaports of India.
Akbar intended to link the maritime state with the massive resources of the Indo-Gangetic plains.
Akbar's ostensible ''
casus belli
A (; ) is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A ''casus belli'' involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a ' involves offenses or threats against its ally—usually one bou ...
'' for warring with Gujarat was that the rebel Mirzas, who had previously been driven out of India, were now operating out of a base in southern Gujarat. Moreover, Akbar had received invitations from cliques in Gujarat to oust the reigning king, which further served as justification for his military expedition.
In 1572, Akbar moved to occupy
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ), also spelled Amdavad (), is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 ...
, the capital, and other northern cities, and was proclaimed the lawful sovereign of Gujarat. By 1573, he had driven out the Mirzas who, after offering token resistance, fled for refuge in the
Deccan
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound by the mount ...
.
Surat
Surat (Gujarati Language, Gujarati: ) is a city in the western Indian States and territories of India, state of Gujarat. The word Surat directly translates to ''face'' in Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of t ...
, the commercial capital of the region, and other coastal cities soon capitulated to the Mughals.
The king,
Muzaffar Shah III, was caught hiding in a corn field; he was pensioned off by Akbar with a small allowance.
Akbar then returned to Fatehpur Sikiri, where he built the
Buland Darwaza
Buland Darwaza (), or the "Door of victory", construction was started in 1573 by Mughal emperor Akbar to commemorate his victory over Gujarat. It is the main entrance to the Jama Masjid at Fatehpur Sikri, which is 43 km from Agra, India.There i ...
to commemorate his victories. But, a rebellion by Afghan nobles supported by the Rajput ruler of
Idar, as well a resurgence of the Mirzas (who retook Cambay, Broach, and Surat), forced his return to Gujarat.
Akbar crossed Rajputana and reached Ahmedabad in 11 days—a journey that normally took six weeks. The outnumbered Mughal army won a decisive victory on 2 September 1573. Akbar slew the rebel leaders and erected a tower out of their severed heads.
The conquest and subjugation of Gujarat proved highly profitable for the Mughals; after expenses, the territory yielded a revenue of more than five million rupees annually to Akbar's treasury.
After conquering Gujarat, the remaining centre of Afghan power was Bengal. In 1572, Sulaiman Khan's son,
Daud Khan, succeeded him. Daud Khan defined Mughal rule, assuming the insignia of royalty and ordering that the
khutbah
''Khutbah'' (, ''khuṭbah''; , ''khotbeh''; ) serves as the primary formal occasion for public sermon, preaching in the Islamic tradition.
Such sermons occur regularly, as prescribed by the teachings of all legal schools. The Islamic traditio ...
be proclaimed in his name, rather than Akbar's.
Munim Khan
Munʿim Khān (7 March 1525 – 23 October 1575) was a Mughal general under both emperors Humayun and Akbar. He was titled ''Khān-i-Khānān'' ('Khan of Khans') when Emperor Akbar appointed him as Prime Minister of the Mughal Empire in 1560. I ...
, the Mughal governor of Bihar, was ordered to chastise Daud Khan. Eventually, Akbar himself set out to Bengal, and in 1574, the Mughals seized
Patna
Patna (; , ISO 15919, ISO: ''Paṭanā''), historically known as Pataliputra, Pāṭaliputra, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, ...
from Daud Khan, who fled to Bengal.
Akbar then returned to Fatehpur Sikri and left his generals to finish the campaign. The Mughal army was subsequently victorious at the
Battle of Tukaroi
The Battle of Tukaroi, also known as the Battle of Bajhaura or the Battle of Mughulmari, was fought between the Mughal Empire and the Bengal Sultanate on 3 March 1575 near the village of Tukaroi in present-day Balasore District of Odisha. It r ...
in 1575, which led to the annexation of Bengal and parts of Bihar that had been under the dominion of Daud Khan. Only
Orissa
Odisha (), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is a state located in Eastern India. It is the eighth-largest state by area, and the eleventh-largest by population, with over 41 million inhabitants. The state also has the thir ...
was left in the hands of the
Karrani dynasty
The Karrani dynasty (, ) was founded in 1564 by Taj Khan Karrani, an ethnic Afghan from the Karlani tribe, hailing from Bangash district. It was the last dynasty to rule the Sultanate of Bengal, before the region became a Subah of the Mugha ...
, albeit as a fief of the Mughal Empire. A year later, however, Daud Khan rebelled and attempted to regain Bengal. He was defeated by the Mughal general
Khan Jahan Quli and fled into exile. Daud Khan was later captured and executed by Mughal forces. His severed head was sent to Akbar, while his limbs were gibbeted at Tandah, the Mughal capital in Bengal.
Afghanistan and Central Asia
Following his conquests of Gujarat and Bengal, Akbar was preoccupied with domestic concerns. He did not leave Fatehpur Sikri on a military campaign until 1581, when Punjab was again invaded by his brother, Mirza Muhammad Hakim. Akbar expelled his brother to Kabul and waged a campaign to remove him from power. At the same time, Akbar's nobles were resisting leaving India to administer the Empire's holdings in Afghanistan; they were, according to Abul Fazl "afraid of the cold of Afghanistan". Likewise, Hindu officers in the Mughal army were inhibited by the traditional
taboo against crossing the Indus. To encourage them, Akbar provided them with pay eight months in advance.
In August 1581, Akbar seized Kabul and took up residence at
Babur's old citadel. He stayed there for three weeks and his brother fled into the mountains. Akbar left Kabul in the hands of his sister,
Bakht-un-Nissa Begum
Bakht-un-Nissa Begum ( 1547 – 2 June 1608) was a Mughal princess and a daughter of the Mughal emperor Humayun.
Birth
Bakht-un-Nissa Begum was born in 1547 in Badakhshan. Her mother was Mah Chuchak Begum. On the night of her birth Humayun had a ...
, and returned to India. He then pardoned his brother, who took up de facto control of the Mughal administration in Kabul; Bakht-un-Nissa continued to be the official governor. In 1585, after Muhammad Hakim died, Kabul passed into the hands of Akbar and was officially incorporated as a province of the Mughal Empire.
The Kabul expedition was the beginning of a long period of activity over the northern frontiers of the empire.
For thirteen years, beginning in 1585, Akbar remained in the north, shifting his capital to Lahore while he dealt with challenges from
Uzbek tribes, which had driven his grandfather, Babur, out of Central Asia.
The Uzbeks were organised under
Abdullah Khan Shaybanid, a military chieftain who had seized Badakhshan and Balkh from Akbar's distant Timurid relatives, and whose troops challenged the northwestern frontiers of the Mughal Empire.
The Uzbeks also subsidised Afghan tribes on the border that were hostile to the Mughals. The tribes felt challenged by the
Yusufzai
The Yusufzai or Yousafzai (, ), also referred to as the Esapzai (, ), or Yusufzai Afghans historically, are one of the largest tribes of Pashtuns. They are natively based in the northern part of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa ( Malakand, Dir, Swat, Shangl ...
of
Bajaur
Bajaur District (, ), formerly Bajaur Agency, is a district in the Malakand Division of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. Prior to 2018, Bajaur Agency was the northernmost component of the Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA), a semi-a ...
and
Swat
A SWAT (''Special Weapons and Tactics'') team is a generic term for a police tactical unit within the United States, though the term has also been used by other nations.
SWAT units are generally trained, equipped, and deployed to res ...
and were motivated by a new religious leader, Bayazid, the founder of the
Roshaniyya sect.
In 1586, Akbar negotiated a pact with Abdullah Khan in which the Mughals agreed to remain neutral during the Uzbek invasion of Safavid-held
Khorasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West and Central Asia that encompasses western and no ...
. In return, Abdullah Khan agreed to refrain from supporting, subsidising, or offering refuge to the Afghan tribes hostile to the Mughals. Akbar, in turn, began a series of campaigns to pacify the Yusufzais and other rebels. Akbar ordered Zain Khan to lead an expedition against the Afghan tribes.
Raja Birbal, a renowned minister in Akbar's court, was also given military command. The expedition failed, and on their retreat from the mountains, Birbal and his entourage were ambushed and killed by Afghans at the Malandarai Pass in February 1586. Akbar immediately fielded new armies to reinvade the Yusufzai lands under the command of
Raja Todar Mal
Raja Todar Mal (1523-24 – 8 November 1589) was an Indian minister, economist, and military commander who served as the Finance Minister (Diwan-i-Ashraff) of the Mughal empire during the reign of Akbar I. He was also the Vakil-us-Sultanat ( ...
. Over the next six years, the Mughals contained the Yusufzai in the mountain valleys, forcing the submission of many chiefs in Swat and Bajaur. Dozens of forts were built and occupied to secure the region.
Despite his pact with the Uzbeks, Akbar nurtured a secret hope of reconquering Central Asia, but Badakshan and Balkh remained firmly part of the Uzbek dominion.
Abdullah Khan died in 1598 and the last of the rebellious Afghan tribes were subdued by 1600. The Roshaniyya movement was suppressed, its leaders were captured or driven into exile, and the
Afridi
The Afrīdī ( ''Aprīdai'', plur. ''Aprīdī''; ) are a Pashtun tribe present mostly in tribal areas in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.
The Afridis are most dominant in the Spin Ghar range west of Peshawar in Tribal areas of modern-day Khyb ...
and
Orakzai
The Orakzai (Pashto: وركزۍ) are a Pashtun tribe native to the Orakzai Agency and parts of Kurram and Khyber Agencies in Pakistan's Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province. Additionally, a sub-tribe of the Orakzai resides in Afghanistan's Maidan W ...
tribes which had risen up under them were subjugated. Jalaluddin, the son of the Roshaniyya movement's founder, Bayazid, was killed in 1601 in a fight with Mughal troops near
Ghazni
Ghazni (, ), historically known as Ghaznayn () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana (), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan with a population of around 190,000 people. The city is strategica ...
.
Indus Valley
While Akbar was in Lahore dealing with the Uzbeks, he sought to subjugate the
Indus valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the disp ...
to secure the frontier provinces.
In 1585, he sent an army to conquer
Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
in the upper Indus basin after
Yousuf Shah, the reigning king of the Shia
Chak dynasty, refused to send his son as a hostage to the Mughal court. Yousuf Shah surrendered immediately to the Mughals, but another of his sons,
Yaqub Shah, crowned himself as king, leading a resistance against the Mughal armies. In June 1589, Akbar travelled from Lahore to Srinagar to receive the surrender of Yaqub and his rebel forces.
Baltistan
Baltistan (); also known as Baltiyul or Little Tibet, is a mountainous region in the Pakistani-administered territory of Gilgit-Baltistan and constitutes a northern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a dispute bet ...
and
Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India an ...
, which were Tibetan provinces adjacent to Kashmir, pledged their allegiance to Akbar.
The Mughals also moved to conquer
Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
in the lower Indus valley.
Since 1574, the northern fortress of
Bhakkar
Bhakkar () is the principal city of Bhakkar District, Punjab, Pakistan. It lies on the left bank of the Indus River. It is the 86th most populous city in Pakistan.
Administration
Bhakkar is the administrative centre of Bhakkar Tehsil, which ...
had remained under imperial control. In 1586, the Mughal governor of Multan tried and failed to secure the capitulation of
Mirza Jani Beg, the independent ruler of
Thatta
Thatta is a city in the Pakistani province of Sindh. Thatta was the medieval capital of Sindh, and served as the seat of power for three successive dynasties. Its construction was ordered by Jam Nizamuddin II in 1495. Thatta's historic signif ...
in southern Sindh.
Akbar responded by sending a Mughal army to besiege
Sehwan
Sehwan (; ; also commonly referred to as Sehwan Sharif or ''Noble Sehwan'') is a historic city located in Jamshoro District of Sindh province in Pakistan situated on the west bank of the Indus River north-west of Hyderabad. The city is renowned ...
, the river capital of the region. Jani Beg mustered a large army to meet the Mughals.
The outnumbered Mughal forces defeated the Sindhi forces at the Battle of Sehwan. After suffering further defeats, Jani Beg surrendered to the Mughals in 1591, and in 1593, paid homage to Akbar in Lahore.
Baluchistan
As early as 1586, about half a dozen
Baluchi chiefs, under nominal Pani Afghan rule, had been persuaded to subordinate themselves to Akbar. In preparation for taking
Kandahar
Kandahar is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city, after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118 in 2015. It is the capital of Kandahar Pro ...
from the Safavids, Akbar ordered the Mughal forces to conquer the rest of the Afghan-held parts of
Baluchistan
Balochistan ( ; , ), also spelled as Baluchistan or Baluchestan, is a historical region in West and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. This arid region of de ...
in 1595.
The Mughal general
Mir Masum led an attack on the stronghold of Sibi, which was northeast of
Quetta
Quetta is the capital and largest city of the Pakistani province of Balochistan. It is the ninth largest city in Pakistan, with an estimated population of over 1.6 million in 2024. It is situated in the south-west of the country, lying in a ...
, and defeated a coalition of local chieftains in battle.
They were required to acknowledge Mughal supremacy and attend Akbar's court. As a result, the modern-day Pakistani and Afghan parts of Baluchistan, including the
Makran
Makran (), also mentioned in some sources as ''Mecran'' and ''Mokrān'', is the southern coastal region of Balochistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in the Balochistan province in Pakistan and in Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. I ...
coast, became a part of the Mughal Empire.
Safavids and Kandahar
Kandahar (also known as the ancient Indian kingdom of
Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
)
had connections with the Mughals from the time of the Empire's ancestor,
Timur
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeat ...
, the warlord who had conquered much of Western, Central, and parts of South Asia in the 14th century. However, the Safavids considered it to be an appanage of the Persian-ruled territory of
Khorasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West and Central Asia that encompasses western and no ...
, and declared its association with the Mughal emperors to be a usurpation. In 1558, while Akbar was consolidating his rule over northern India, Safavid Shah
Tahmasp I
Tahmasp I ( or ; 22 February 1514 – 14 May 1576) was the second shah of Safavid Iran from 1524 until his death in 1576. He was the eldest son of Shah Ismail I and his principal consort, Tajlu Khanum.
Tahmasp ascended the throne after the ...
seized Kandahar and expelled its Mughal governor. The recovery of Kandahar had not been a priority for Akbar, but after his military activity in the northern frontiers, he moved to restore Mughal control. At the time, the region was also under threat from the Uzbeks, but the Emperor of Persia, himself beleaguered by the Ottoman Turks, was unable to send reinforcements.
In 1593, Akbar received the exiled Safavid prince, Rostam Mirza.
Rostam Mirza pledged allegiance to the Mughals; he was granted a rank (mansab) of command over 5,000 men and received Multan as a
jagir
A jagir (), ( Hindustani: जागीर/جاگیر, ''Jāgīr''), ( Marathi: जहागीर, ''Jahāgīrá'') also spelled as jageer, was a type of feudal land grant in the Indian subcontinent at the foundation of its Jagirdar ( Zamindar ...
.
The Safavid prince and governor of Kandahar, Mozaffar Hosayn, also agreed to defect to the Mughals. Hosayn, who was in an adversary relationship with his overlord,
Shah Abbas, was granted a rank of 5,000 men, and his daughter
Kandahari Begum was married to Akbar's grandson, the Mughal prince
Khurram.
Kandahar was secured in 1595 with the arrival of a garrison headed by the Mughal general, Shah Bayg Khan.
The reconquest of Kandahar did not overtly disturb Mughal-Persian relations.
Akbar and the Persian Shah continued to exchange ambassadors and presents. However, the power equation between the two had now changed in favour of the Mughals.
Deccan Sultans
In 1593, Akbar began military operations against the Deccan Sultans, who had not submitted to his authority. He besieged
Ahmednagar Fort
The Ahmednagar Fort (''Ahmadnagar Qila'') is located close to the Bhingar Nala near Ahmednagar in Maharashtra state western India. It was the headquarters of the Ahmednagar Sultanate. In 1803, it was taken by the British during the Second Ang ...
in 1595, forcing
Chand Bibi
Sultana Chand Bibi (1550 – 18 April 1600) was the regent of the Bijapur Sultanate during the minority of Ibrahim Adil Shah II in 1580–1590, and the regent of the Ahmednagar Sultanate during the minority of her great nephew Bahadur S ...
to cede
Berar
Berar may refer to:
*Vidarbha, the eastern region of Maharashtra, India, historically known as Berar
* Berar Sultanate (1490–1596), one of the Deccan sultanates
*Berar Subah (1596–1724), a subah (province) of the Mughal Empire
*Berar Province ( ...
. A subsequent revolt forced Akbar to take the fort in August 1600. Akbar occupied
Burhanpur
Burhanpur is a historical city in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the administrative seat of Burhanpur District. It is situated on the north bank of the Tapti River and northeast of city of Mumbai , southwest of the state's capita ...
and besieged
Asirgarh Fort
Asirgarh Fort is an Indian fortress ''( qila)'' situated in the Satpura Range about north of the city of Burhanpur, in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. The fort is said to date to the early 15th-century and commands a pass through the Sa ...
in 1599, and took it on 17 January 1601, when Miran Bahadur Shah of the
Khandesh Sultanate refused to relinquish
Khandesh
Khandesh is a geographic region in Maharashtra, India. It was made up of present Jalgaon, Dhule and Nandurbar districts. It also said that Burhanpur District of Madhya Pradesh was also its part.
The region have seen many geographical ch ...
. Akbar then established the
Subah
A ''Subah'' is a term for a province or state in several South Asian languages. It was introduced by the Mughal Empire to refer to its subdivisions or provinces; and was also adopted by other polities of the Indian subcontinent. The word is derive ...
s of Ahmadnagar, Berar, and Khandesh under Prince Daniyal. "By the time of his death in 1605, Akbar controlled a broad sweep of territory from the Bay of Bengal to Qandahar and Badakshan. He touched the western sea in Sind and at
Surat
Surat (Gujarati Language, Gujarati: ) is a city in the western Indian States and territories of India, state of Gujarat. The word Surat directly translates to ''face'' in Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of t ...
and was well astride central India."
Administration
Political structure
Akbar's system of central government was based on the system that had evolved since the
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries. . Akbar reorganised the sections with a detailed set of regulations. The revenue department was headed by a ''wazir'', responsible for finances and management of ''jagir'' and ''inam'' land. The head of the military was called the ''
mir bakshi'', appointed from among the leading nobles of the court. The ''mir bakshi'' was in charge of intelligence gathering, and made recommendations to the emperor for military appointments and promotion. The ''mir saman'' was in charge of the imperial household, including the harems, and supervised the functioning of the court and royal bodyguard. The judiciary was a separate organisation headed by a chief ''
qazi
Qazi may refer to:
* Qadi
A qadi (; ) is the magistrate or judge of a Sharia court, who also exercises extrajudicial functions such as mediation, guardianship over orphans and minors, and supervision and auditing of public works.
History
...
'', who was also responsible for religious beliefs and practices.
Taxation
Akbar reformed the administration land revenues by adopting a system that had been used by
Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri (born Farid al-Din Khan; 1472 or 1486 – 22 May 1545), also known by his title Sultan Adil (), was the ruler of Bihar from 1530 to 1540, and Sultan of Hindustan from 1540 until his death in 1545. He defeated the Mughal Empire, ...
. The village continued to remain the primary unit of revenue assessment. Cultivated areas were measured and taxed through fixed rates—on the basis of prices prevailing the imperial court—based on the type of crop and productivity. This system burdened the peasantry because prices at the imperial court were often higher than those in the countryside. Akbar also introduced a decentralised system of annual assessment, which resulted in corruption among local officials. The system was abandoned in 1580 and replaced with the ' (also known as '), under which revenue was calculated as one-third of the average produce of the previous ten years, to be paid to the state in cash.
This system was later refined, taking into account local prices and grouping areas with similar productivity into assessment circles. Remission was given to peasants when the harvest failed during times of flood or drought.
The ' system was set out by
Raja Todar Mal
Raja Todar Mal (1523-24 – 8 November 1589) was an Indian minister, economist, and military commander who served as the Finance Minister (Diwan-i-Ashraff) of the Mughal empire during the reign of Akbar I. He was also the Vakil-us-Sultanat ( ...
, who also served as a revenue officer under Sher Shah Suri, in a detailed memorandum submitted to the emperor in 1582–1583.
Other local methods of assessment continued in some areas. Lands which were fallow or uncultivated were assessed at concessional rates.
Akbar also encouraged the improvement and extension of agriculture.
Zamindar
A zamindar in the Indian subcontinent was an autonomous or semi-autonomous feudal lord of a ''zamindari'' (feudal estate). The term itself came into use during the Mughal Empire, when Persian was the official language; ''zamindar'' is the ...
s were required to provide loans and agricultural implements in times of need, and to encourage farmers to plough as much land as possible and sow high-quality seeds. In turn, the zamindars were given a hereditary right to collect a share of the produce. Peasants had a hereditary right to cultivate the land as long as they paid the land revenue.
Revenue officials were guaranteed only three-quarters of their salary, with the remaining quarter dependent on their full realisation of the revenue assessed.
Military organisation
Akbar organised his army and the nobility by means of a system called the ''mansabdari''. Under this system, each officer in the army was assigned a rank (a ''mansabdar'') and assigned a number of
cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
, which he was required to supply to the imperial army.
The ''mansabdars'' were divided into 33 classes. The top three commanding ranks, ranging from 7,000 to 10,000 troops, were normally reserved for princes. Ranks between 10 and 5,000 were assigned to other members of the nobility. The empire's permanent
standing army
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars ...
was small and the imperial forces mostly consisted of contingents maintained by the ''mansabdars''. Persons were normally appointed to a low ''mansab'' and then promoted based on merit and the favour of the emperor.
Each ''mansabdar'' was required to maintain a certain number of cavalrymen and twice that number of horses. The number of horses was greater because they had to be rested and rapidly replaced in times of war. Akbar employed strict measures to ensure that the quality of the armed forces was maintained at a high level; horses were regularly inspected and usually only
Arabian horse
The Arabian or Arab horse ( , DIN 31635, DMG ''al-ḥiṣān al-ʿarabī'') is a horse breed, breed of horse with historic roots on the Arabian Peninsula. With a distinctive head shape and high tail carriage, the Arabian is one of the most easi ...
s were employed. The ''mansabdars'' were the highest paid military service in the world at the time.
Capitals

Akbar was a follower of
Salim Chishti
Sheikh Salim Chishti (, 1478–1572) also known as Sheikh al- Hind was a Sufi saint of the Chishti Order and one of the most revered Sufi saints during the Mughal Empire in India.
Biography
Sheikh Salim Chishti was a descendant of Sheik ...
, a
holy man
''Holy Man'' is a 1998 American satirical comedy-drama film directed by Stephen Herek, written by Tom Schulman, and starring Eddie Murphy, Jeff Goldblum, Kelly Preston, Robert Loggia and Jon Cryer. The film was a commercial failure and re ...
who lived in the region of Sikri near Agra. Believing the area to be lucky, Akbar had a mosque constructed there for the use of the priest. Subsequently, he celebrated the victories over Chittor and Ranthambore by laying the foundations of a new walled capital, west of Agra in 1569, which was named Fatehpur ("Town of Victory") after the conquest of Gujarat in 1573, and subsequently came to be known as
Fatehpur Sikri
Fatehpur Sikri () is a town in the Agra District of Uttar Pradesh, India. Situated from the district headquarters of Agra, Fatehpur Sikri itself was founded as the capital of the Mughal Empire in 1571 by Mughal emperors, Emperor Akbar, servin ...
to distinguish it from other similarly named towns.
The city was soon abandoned and the capital was moved to
Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
in 1585. Historians have advanced several reasons for the move, including an insufficient or poor quality water supply at Fatehpur Sikri, Akbar's campaigns in the northwest areas of the Empire or loss of interest. In 1599, Akbar moved his capital back to Agra, where he ruled until his death.
Culture
Akbar was a patron of the arts and culture. He had
Sanskrit literature
Sanskrit literature is a broad term for all literature composed in Sanskrit. This includes texts composed in the earliest attested descendant of the Proto-Indo-Aryan language known as Vedic Sanskrit, texts in Classical Sanskrit as well as some ...
translated and participated in native festivals. Akbar established the library of Fatehpur Sikri exclusively for women, and he decreed the establishment of schools for the education of both Muslims and Hindus throughout the realm. He also encouraged
bookbinding
Bookbinding is the process of building a book, usually in codex format, from an ordered stack of paper sheets with one's hands and tools, or in modern publishing, by a series of automated processes. Firstly, one binds the sheets of papers alon ...
to become a high art.
Economy
Trade
Akbar's government prioritised commercial expansion,
encouraging traders, providing protection and security for transactions, and levying a low custom duty to stimulate foreign trade. It also required that local administrators provide restitution to traders for goods stolen while in their territories. To minimise such incidents, bands of highway police called ' were enlisted to patrol roads and ensure the safety of traders. Other active measures taken included the construction and protection of routes of commerce and communications.
Akbar made concerted efforts to improve roads to facilitate the use of wheeled vehicles through the Khyber Pass, the most popular route frequented by traders and travellers journeying from
Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
into Mughal India.
He also strategically occupied the northwestern cities of Multan and Lahore in Punjab and constructed forts, such as the one at
Attock
Attock ( Punjabi, ), formerly known as Campbellpur (Punjabi, ), is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, not far from the country's capital Islamabad. It is the headquarters of the Attock District and is 36th largest city in the Punjab and 61st largest c ...
near the crossing of the
Grand Trunk Road
Grand Trunk Road (formerly known as Uttarapath, Sadak-e-Azam, Shah Rah-e-Azam, Badshahi Sadak, and Long Walk) is one of Asia's oldest and longest major roads. For at least 2,500 years it has linked Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent. It r ...
and the
Indus river
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
. He also constructed a network of smaller forts called ''thanas'' throughout the frontier to secure the overland trade route with Persia and Central Asia. He also established an international trading business for his chief consort,
Mariam-uz-Zamani
Mariam-uz-Zamani (; – 19 May 1623), commonly known by the misnomer Jodha Bai, was the Empress consort, chief consort, principal Hinduism, Hindu wife and the favourite wife of the third Mughal emperor, Akbar. She was also the longest-servi ...
, who ran an extensive trade of indigo, spices, and cotton to Gulf nations through merchant's vessels.
Coins

Akbar introduced coins with decorative features, including floral motifs, dotted borders, and
quatrefoil
A quatrefoil (anciently caterfoil) is a decorative element consisting of a symmetrical shape which forms the overall outline of four partially overlapping circles of the same diameter. It is found in art, architecture, heraldry and traditional ...
. The coins were issued in both round and square shapes, including a unique 'mehrab' (lozenge) shaped coin. Akbar's portrait type gold coin (Mohur) is generally attributed to his son, Prince Salim (later Emperor Jahangir), who had rebelled and then sought reconciliation by minting and presenting his father with gold Mohurs bearing Akbar's portrait. During the latter part of Akbar's reign, coins portrayed the concept of Akbar's newly promoted religion, with the Ilahi type and Jalla Jalal-Hu types.
Diplomacy
Matrimonial alliances
Prior to Akbar's reign, marriages between Hindu princesses and Muslim kings failed to produce stable relations between the families involved; the women were lost to their families and did not return after marriage.
Akbar departed from that practice, providing that the Hindu Rajputs who married their daughters or sisters to him would be treated equally to his Muslim fathers- and brothers-in-law, except that they would not be allowed to dine or pray with him or take Muslim wives. Akbar also made those Rajputs members of his court. Some Rajputs considered marriage to Akbar a sign of humiliation.

The
Kacchwaha Rajput, Raja
Bharmal
Raja Bharmal, also known as Bihari Mal, and Bihar Mal (1498 – 27 January 1574), was the 23rd ruler of Jaipur State, Amber, which was later known as Jaipur. He was a ruler of the Kachhwaha clan.
His daughter, Mariam-uz-Zamani was the chief ...
, of the small kingdom of
Amer
Amer may refer to:
Places
* Amer (river), a river in the Dutch province of North Brabant
* Amer, Girona, a municipality in the province of Girona in Catalonia, Spain
* Amber, India (also known as Amer, India), former city of Rajasthan state
** Am ...
, and an early member of Akbar's court, allied with Akbar by giving his daughter, Mariam-uz-Zamaniwho would go on to be Akbar's favorite wifein marriage to Akbar. Bharmal was made a noble of high rank in the imperial court, and subsequently, his son
Bhagwant Das
Raja Bhagwant Das ( – 4 December 1589) was the 23rd ruler of Amber. He also served as the Mughal Subahdar of Lahore and the Subahdar of Kabul for a few months in 1586. His step-sister, Mariam-uz-Zamani, was the chief consort of Mughal empero ...
and grandson
Man Singh
Mirza Raja Man Singh I (21 December 1550 – 6 July 1614) was the 24th Kachawaha Rajput ruler of the Kingdom of Amber from 1589 to 1614. He also served as the foremost imperial Subahdar of Bihar Subah from 1587 to 1594, then for Bengal ...
also rose to high ranks in the nobility.
Other Rajput kingdoms also established matrimonial alliances with Akbar, but Akbar did not insist upon matrimony as a precondition for forming alliances. When Akbar met with the Hada leader, Surjan Hada, to effect an alliance, Surjan accepted on the condition that Akbar could not marry any of his daughters. Consequently, no matrimonial alliance was entered into, but Surjan was made a noble and placed in charge of Garh-Katanga.
Two major Rajput clans remained aloofthe
Sisodiya
Sisodia or Sisodiya may refer to:
* Sisodia (surname), an Indian Hindu surname
* Sisodia dynasty, a Hindu dynasty
* Piplia Sisodia, a village in Madheya Pradesh, India
* Sisodiya Rani Bagh, a palace in Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
See also
*Sodhi ...
s of
Mewar
Mewar, also spelled as Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasth ...
and
Hadas of Ranthambore.
The political effect of these alliances was significant. While some Rajput women who entered Akbar's harem converted to Islam, they were generally provided full religious freedom; their relatives, who continued to remain Hindu, formed a significant part of the nobility and served to articulate the opinions of the majority of commoners in the imperial court.
The interaction between Hindu and Muslim nobles in the imperial court resulted in an exchange of thoughts and a blending of the two cultures. Newer generations of the Mughal line also represented a merger of Mughal and Rajput blood, thereby strengthening ties between the two. As a result, the Rajputs became the strongest allies of the Mughals, and Rajput soldiers and generals fought for the Mughal army under Akbar, leading it in several campaigns, including the conquest of Gujarat in 1572. Akbar's policy of religious tolerance ensured that employment in the imperial administration was open to all on merit, irrespective of creed, strengthening his imperial rule.
Akbar's daughter Meherunnissa was rumoured to be enamored of
Tansen
Rāmtanu ( – 26 April 1589), popularly referred to as Mian Tānsen (), or Sangeet Samrāt (), was a Hindustani classical musician. Born into a Hindu Gaur Brahmin family in Gwalior, he learnt and perfected his art in the northwest regio ...
and might have played a role in his coming to Akbar's court.
Tansen converted to
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
from
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
, apparently on the eve of his marriage with Akbar's daughter.
Foreign relations
Relations with the Portuguese
At the time of Akbar's ascension in 1556, the Portuguese had established several fortresses and factories on the western coast of the subcontinent, and largely controlled navigation and sea trade in that region. As a consequence, all other trading entities were subject to the terms and conditions of the Portuguese, which was resented by rulers and traders, including
Bahadur Shah of Gujarat
Qutb-ud-Din Bahadur Shah, born Bahadur Khan was a sultan of the Muzaffarid dynasty who reigned over the Gujarat Sultanate, a late medieval kingdom in India from 1526 to 1535 and again from 1536 to 1537. He ascended to the throne after competin ...
.

In 1572, the
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
annexed
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
and acquired its first access to the sea, but local officials informed Akbar that the Portuguese had begun to exert control in the Indian Ocean. Akbar obtained a ''
cartaz
The Cartaz (plural cartazes, in Portuguese) was a naval trade license or pass issued by the Portuguese empire in the Indian Ocean during the sixteenth century (circa 1502–1750). Its name derives from the Portuguese term ''cartas'', meaning letter ...
'' (permit) from the Portuguese to sail in the
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
region. At the initial meeting of the Mughals and the Portuguese during the
Siege of Surat in 1572, the Portuguese, recognising the superior strength of the Mughal army, chose to adopt diplomacy instead of war. The Portuguese Governor, upon the request of Akbar, sent him an ambassador to establish friendly relations.
Akbar accepted the offer of diplomacy, but the Portuguese continually asserted their authority and power in the Indian Ocean; Akbar expressed concern when he was required to request a permit from the Portuguese before any ships from the Mughal Empire could depart for the
Hajj
Hajj (; ; also spelled Hadj, Haj or Haji) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for capable Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetim ...
to
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
and
Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
. In 1573, Akbar issued a ''
firman
A firman (; ), at the constitutional level, was a royal mandate or decree issued by a sovereign in an Islamic state. During various periods such firmans were collected and applied as traditional bodies of law. The English word ''firman'' co ...
'' directing Mughal administrative officials in Gujarat not to provoke the Portuguese in the territory they held in
Daman. The Portuguese, in turn, issued passes for members of Akbar's family to go on Hajj to Mecca. The Portuguese made mention of the extraordinary status of the vessel and the special status to be accorded to its occupants.
Akbar was unsuccessful in purchasing compact
artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
pieces from the Portuguese, hindering his efforts to establish a Mughal navy along the Gujarat coast.
In September 1579,
Jesuits
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
from
Goa
Goa (; ; ) is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is bound by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north, and Karnataka to the ...
were invited to visit the court of Akbar. The emperor had his scribes translate the
New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
and granted the Jesuits freedom to preach the Gospel.
One of his sons,
Sultan Murad Mirza, was entrusted to
Antoni de Montserrat for his education.
While debating at court, the Jesuits denigrated Islam and Muhammad. Their comments enraged the
Imam
Imam (; , '; : , ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Salah, Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, ...
s and
Ulama
In Islam, the ''ulama'' ( ; also spelled ''ulema''; ; singular ; feminine singular , plural ) are scholars of Islamic doctrine and law. They are considered the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious knowledge in Islam.
"Ulama ...
, who objected to the remarks, but Akbar ordered their comments to be recorded. This event was followed by a rebellion of Muslim clerics in 1581 led by Mullah Muhammad Yazdi and Muiz-ul-Mulk, the chief
Qadi
A qadi (; ) is the magistrate or judge of a Sharia court, who also exercises extrajudicial functions such as mediation, guardianship over orphans and minors, and supervision and auditing of public works.
History
The term '' was in use from ...
of
Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
; the rebels sought to overthrow Akbar and put his brother Mirza Muhammad Hakim on the Mughal throne. Akbar successfully defeated the rebels, but he became more cautious about inviting guests to his court, seeking advice from his counselors.
Relations with the Ottoman Empire

In 1555, while Akbar was still a child, the
Ottoman Admiral
Seydi Ali Reis
Seydi Ali Reis (1498–1563), formerly also written Sidi Ali Reis and Sidi Ali Ben Hossein, was an Ottoman admiral and navigator. Known also as Katib-i Rumi, Galatalı or Sidi Ali Çelebi,Danışan, Gaye. 2019. “A Sixteenth-Century Otto ...
visited the
Mughal Emperor
The emperors of the Mughal Empire, who were all members of the Timurid dynasty (House of Babur), ruled the empire from its inception on 21 April 1526 to its dissolution on 21 September 1857. They were supreme monarchs of the Mughal Empire in ...
Humayun
Nasir al-Din Muhammad (6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), commonly known by his regnal name Humayun (), was the second Mughal emperor, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Northern India, and Pakistan from ...
. In 1569, during the early years of Akbar's rule, Ottoman Admiral
Kurtoğlu Hızır Reis
Kurtoğlu Hızır Reis was an Ottoman admiral who is best known for commanding the Ottoman naval expedition to Sumatra in Indonesia (1568–1569).
Background and family origins
Kurtoğlu Hızır Reis was the son of the famous Ottoman private ...
visited the Empire. These Ottoman admirals sought to end the growing threats of the Portuguese Empire during their
Indian Ocean campaigns. During his reign, Akbar six documents addressing the Ottoman
Sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ...
Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I (; , ; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the Western world and as Suleiman the Lawgiver () in his own realm, was the List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman sultan between 1520 a ...
.
In 1576, Akbar sent a contingent of pilgrims on Hajj, led by Khwaja Sultan Naqshbandi, with 600,000 rupees and 12,000 ''
khalat
A khalat (Persian: خلعت, from ) is a loose, long-sleeved outer silk or cotton robe common in Central Asia and South Asia and worn both by men and women, although in differing styles.
History
Historically, richly adorned khalats have been ...
s'' (honorific robes) for the needy of Mecca and Medina. In October 1576, Akbar sent a delegation, which included his aunt Gulbadan Begum and his consort Salima, on Hajj by two ships, including an Ottoman vessel, from
Surat
Surat (Gujarati Language, Gujarati: ) is a city in the western Indian States and territories of India, state of Gujarat. The word Surat directly translates to ''face'' in Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of t ...
, which reached the port of
Jeddah
Jeddah ( ), alternatively transliterated as Jedda, Jiddah or Jidda ( ; , ), is a List of governorates of Saudi Arabia, governorate and the largest city in Mecca Province, Saudi Arabia, and the country's second largest city after Riyadh, located ...
in 1577 and then proceeded to Mecca and Medina. Four more caravans were sent from 1577 to 1580, with gifts for the authorities of Mecca and Medina.
During this period, Akbar financed the pilgrimages of many poor
Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s from the Mughal Empire and also funded the foundations of the
Qadiriyya
The Qadiriyya () or the Qadiri order () is a Sunni Sufi order (''Tariqa'') founded by Abdul Qadir Gilani (1077–1166, also transliterated ''Jilani''), who was a Hanbali scholar from Gilan, Iran.
The order, with its many sub-orders, is widesp ...
Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are r ...
Order's dervish lodge in the Hijaz.
Akbar's attempts to build Mughal presence in Mecca and Medina reassured the local Sharifs of the Mughal Empire's ability to provide financial support, lessening their dependency upon Ottoman bounties.
Mughal-Ottoman trade also flourished during this period; merchants loyal to Akbar are known to have reached
Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
after journeying upriver through the port of
Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the Iran–Iraq bor ...
.
The imperial Mughal entourage stayed in Mecca and Medina for nearly four years and attended the Hajj four times. In 1582, the Ottoman authorities forced them to return to India. Historian Naimur Rahman Farooqi has suggested that their expulsion may explain why Akbar broke relations with the Hijaz and stopped sending Hajj caravans after 1581.
According to some accounts, Akbar expressed a desire to form an alliance with the Portuguese against the Ottomans, but nothing came of the idea.
Relations with the Safavid dynasty

Before Akbar's rule, the
Safavids
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the begi ...
and the Mughals had a long history of diplomatic relations. The Safavid ruler Tahmasp I provided refuge to Humayun when he was forced to flee the Indian subcontinent following his defeat by Sher Shah Suri. However, the Safavids differed from the Sunni Mughals and Ottomans in following the
Shia
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (imam). However, his right is understood ...
branch of Islam.
One of the longest-standing disputes between the Safavids and the Mughals pertained to control of the city of
Qandahar
Kandahar is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city, after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118 in 2015. It is the capital of Kandahar Pro ...
in the
Hindukush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and eastern Afghanistan into northwestern Pakistan and far southeastern Tajikistan. The range forms the western section of ...
region, which formed the border between the two empires.
Military strategists of the time considered the region to be militarily significant due to its geography. The city, which was administered by Bairam Khan at the time of Akbar's accession, was invaded and captured by the Persian ruler Husain Mirza, a
cousin of Tahmasp I, in 1558.
Shortly afterwards, Akbar's army completed its annexation of Kabul, and to further secure the north-western boundaries of his empire, it proceeded to Qandahar. The city capitulated without resistance on 18 April 1595, and the ruler Muzaffar Hussain joined Akbar's court. Subsequent to this, Bairam Khan sent an envoy to the court of Tahmasp I in an effort to maintain peaceful relations with the Safavids. This gesture was reciprocated and a cordial relationship prevailed between the two empires during the remainder of the first two decades of Akbar's reign. The death of Tahmasp I in 1576 resulted in civil war and instability in the Safavid empire, and diplomatic relations between the two empires ceased for more than a decade. They were restored only in 1587 following the accession of
Shah Abbas to the Safavid throne. Diplomatic relations continued to be maintained between the Safavid and Mughal courts until the end of Akbar's reign. Qandahar continued to remain in Mughal possession, and the Hindukush was the empire's western frontier for several decades until
Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan I, (Shahab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram; 5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), also called Shah Jahan the Magnificent, was the Emperor of Hindustan from 1628 until his deposition in 1658. As the fifth Mughal emperor, his reign marked the ...
's expedition into
Badakhshan
Badakhshan is a historical region comprising the Wakhan Corridor in northeast Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic ...
in 1646.
Relations with other contemporary kingdoms
Vincent Arthur Smith
Vincent Arthur Smith (3 June 1843 – 6 February 1920) was an Irish Indologist, historian, member of the Indian Civil Service, and curator. He was one of the prominent figures in Indian historiography during the British Raj.
In the 1890s, he w ...
has observed that the merchant Mildenhall was employed in 1600 to bear a letter from
Queen Elizabeth Queen Elizabeth, Queen Elisabeth or Elizabeth the Queen may refer to:
Queens regnant
* Elizabeth I (1533–1603; ), Queen of England and Ireland
* Elizabeth II (1926–2022; ), Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms
* Queen B ...
to Akbar requesting liberty to trade in his dominions on terms as good as those enjoyed by the Portuguese.
Akbar was also visited by the French explorer
Pierre Malherbe.
Religious policy

Akbar, as well as his mother and other members of his family, are believed to have been
Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
Hanafi
The Hanafi school or Hanafism is the oldest and largest Madhhab, school of Islamic jurisprudence out of the four schools within Sunni Islam. It developed from the teachings of the Faqīh, jurist and theologian Abu Hanifa (), who systemised the ...
Muslims. His early days were spent in the backdrop of an atmosphere in which liberal sentiments were encouraged and
religious narrow-mindedness was frowned upon.
From the 15th century, a number of rulers in various parts of the country adopted a more liberal policy of
religious tolerance
Religious tolerance or religious toleration may signify "no more than forbearance and the permission given by the adherents of a dominant religion for other religions to exist, even though the latter are looked on with disapproval as inferior, ...
, attempting to foster
communal harmony between Hindus and Muslims.
These sentiments were earlier encouraged by the teachings of popular saints like
Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also known as ('Father Nanak'), was an Indian spiritual teacher, mystic and poet, who is regarded as the founder of Sikhism and is t ...
,
Kabir
Kabir ( 15th century) was a well-known Indian devotional mystic poet and sant. His writings influenced Hinduism's Bhakti movement, and his verses are found in Sikhism's scripture Guru Granth Sahib, the Satguru Granth Sahib of Saint Gar ...
, and
Chaitanya
Chaitanya or Chaithanya may refer to
Philosophy
*Chaitanya (consciousness), Hindu philosophical concept
People
*Chaitanya (name)
*Chaitanya Mahaprabhu (1486–1533), founder of Gaudiya Vaishnavism
Media
*Chaitanya (film), ''Chaitanya'' (film), ...
,
and the verses of the Persian poet
Hafez
(), known by his pen name Hafez ( or 'the keeper'; 1325–1390) or Hafiz,
“Ḥāfeẓ” designates someoone who has learned the Qurʾān by heart" also known by his nickname Lisan al-Ghaib ('the tongue of the unseen'), was a Persian lyri ...
, which advocated human sympathy and a liberal outlook. The Timurid ethos of religious tolerance persisted from the times of
Timur
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeat ...
to
Humayun
Nasir al-Din Muhammad (6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), commonly known by his regnal name Humayun (), was the second Mughal emperor, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Northern India, and Pakistan from ...
, and influenced Akbar's policy of tolerance in matters of religion.
Akbar's childhood tutors, including two Irani Shias, were largely above
sectarian
Sectarianism is a debated concept. Some scholars and journalists define it as pre-existing fixed communal categories in society, and use it to explain political, cultural, or religious conflicts between groups. Others conceive of sectarianism a ...
prejudices, and made a significant contribution to Akbar's later inclination towards religious tolerance.
Akbar sponsored religious debates between different Muslim groups (
Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
,
Shia
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (imam). However, his right is understood ...
,
Ismaili
Ismailism () is a branch of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor ( imām) to Ja'far al-Sadiq, wherein they differ from the Twelver Shia, who accept ...
, and
Sufis
Sufism ( or ) is a mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic purification, spirituality, ritualism, and asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are referred to as "Sufis" (from , ), and ...
),
Parsis
The Parsis or Parsees () are a Zoroastrian ethnic group in the Indian subcontinent. They are descended from Persian refugees who migrated to the Indian subcontinent during and after the Arab-Islamic conquest of Iran in the 7th century, w ...
,
Hindus
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
(
Shaivite
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the supreme being. It is the second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million Hindus, found widely across South Asia (predominantly in ...
and
Vaishnava
Vaishnavism () ), also called Vishnuism, is one of the major Hindu traditions, that considers Vishnu as the sole supreme being leading all other Hindu deities, that is, '' Mahavishnu''. It is one of the major Hindu denominations along wit ...
),
Sikhs
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' ...
,
Jains
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and ...
, Jews,
Jesuits
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
, and
Materialists
Materialism is a form of philosophical monism according to which matter is the fundamental substance in nature, and all things, including mental states and consciousness, are results of material interactions. According to philosophical materia ...
. He was also partial to Sufism; he proclaimed that "the wisdom of Vedanta is the wisdom of Sufism".
Association with the Muslim aristocracy

During the early part of his reign, Akbar adopted an attitude of suppression towards Muslim sects that were condemned by the orthodoxy as
heretical
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, particularly the accepted beliefs or religious law of a religious organization. A heretic is a proponent of heresy.
Heresy in Christianity, Judai ...
.
In 1567, on the advice of Shaikh Abdu'n Nabi, he ordered the exhumation of Mir Murtaza Sharifi Shirazi – a
Shia
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (imam). However, his right is understood ...
buried in Delhi – because of the grave's proximity to that of
Amir Khusrau
Abu'l Hasan Yamīn ud-Dīn Khusrau (1253 – 1325 AD), better known as Amīr Khusrau, sometimes spelled as, Amir Khusrow or Amir Khusro, was an Indo-Persian Sufi singer, musician, poet and scholar, who lived during the period of the Delhi Sult ...
, arguing that a "heretic" could not be buried so close to the grave of a
Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
saint. This reflected a restrictive attitude towards the Shia, which continued to persist until the early 1570s.
He suppressed
Mahdavism in 1573 during his campaign in Gujarat, in the course of which the Mahdavi leader Bandagi Miyan Sheik Mustafa was arrested and brought in chains to the court for debate and released after eighteen months.
Akbar was reportedly angered by acts of embezzlement by many high level Muslim clerics. As Akbar increasingly came under the influence of pantheistic Sufi mysticism from the early 1570s, his outlook shifted from orthodox Islam as traditionally professed, to a new concept of Islam that transcended the limits of Islam.
Consequently, during the latter half of his reign, he adopted a policy of tolerance towards the Shias and declared a prohibition on Shia-Sunni conflict, and the empire remained neutral in matters of internal sectarian conflict. In 1579, the Mughal Emperor Akbar referred to himself as:
In 1580, a rebellion broke out in the eastern part of Akbar's empire, and a number of ''
fatwa
A fatwa (; ; ; ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (sharia) given by a qualified Islamic jurist ('' faqih'') in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist issuing fatwas is called a ''mufti'', ...
s'', declaring Akbar to be a heretic, were issued by
Qazis. Akbar suppressed the rebellion and handed out severe punishments to the Qazis. To further strengthen his position in dealing with the Qazis, Akbar issued a ''
mazhar
The mazhar (; : ''mazāhar'', مزاهر) is a large, heavy tambourine used in Arabic music. The mazhar's frame is generally made out of wood. Its single head is considerably thicker than that of the riq, its smaller cousin. Some drums have bras ...
'', or declaration, that was signed by all major ''
ulema
In Islam, the ''ulama'' ( ; also spelled ''ulema''; ; singular ; feminine singular , plural ) are scholars of Islamic doctrine and law. They are considered the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious knowledge in Islam.
"Ulama ...
s'' in 1579.
The ''mahzar'' asserted that Akbar was the ''
Khalifa
''Khalifa'' or ''Khalifah'' (; commonly "caliph" in English) is a name or title which means "successor", "ruler" or "leader". It most commonly refers to the leader of a Caliphate, but is also used as a title among various Islamic religious groups ...
'' of the age, a higher rank than that of a ''
Mujtahid
''Ijtihad'' ( ; ' , ) is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning by an expert in Islamic law, or the thorough exertion of a jurist's mental faculty in finding a solution to a legal question. It is contrasted with '' taqlid'' (i ...
''; in case of a difference of opinion among the Mujtahids, Akbar could select any one opinion and could also issue decrees that did not go against the ''
nass''. Given the prevailing Islamic sectarian conflicts in various parts of the country at that time, it is believed that the ''Mazhar'' helped stabilise the religious situation in the empire.
It also helped him eliminate the religious and political influence of the Ottoman ''Khalifa'' over his subjects, thus ensuring their loyalty to him.
Throughout his reign, Akbar was a patron of influential Muslim scholars such as
Mir Ahmed Nasrallah Thattvi
Mir Ahmed Nasrallah Thattvi (died 1588) was born in Thatta, Sindh. He was among the renowned and widely traveled Muslim scholars at the court of Mughal Emperor Akbar. He was the son of a Qazi (Kazi) in Thatta. During his early life he was in ...
and
Tahir Muhammad Thattvi
Mir Tahir Muhammad Ibn Hassan Sabzavari Tattavi was a Sindhi Muslim poet and historian during the rule of the Mughal Empire, who composed poetry under the pen-name ''Nisyani''. His family emigrated to Thatta, Sindh from Iran. His original ancestr ...
.
Din-i Ilahi
Akbar was deeply interested in religious and philosophical matters. An orthodox Muslim at the outset, he later came to be influenced by the
Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are r ...
mysticism that was being preached in the country at that time. He moved away from orthodoxy, appointing to his court several people with liberal religious philosophies, including Abul Fazl,
Faizi
Abu al-Faiz ibn Mubarak, popularly known by his pen-name, Faizi (20 September 1547 – 15 October 1595) was a poet and scholar of late medieval India whose ancestors were the ''Malik-ush-Shu'ara'' (poet laureate) of Akbar's Court. Blochmann, H. ...
, and
Birbal
Mahesh Das (; 1528 16 February 1586), popularly known by his title Rajah Birbal (), was an Indian minister and commander of the Mughal Empire. He is mostly known in the Indian subcontinent for the folk tales which focus on his wit. He was app ...
. In 1575, he built a hall called the
Ibadat Khana
The Ibādat Khāna (House of Worship) was a meeting house built in 1575 CE by the Mughal Empire, Mughal Emperor Akbar (r. 1556–1605) at Fatehpur Sikri to gather spiritual/religious leaders of different religious grounds (and beliefs) so ...
(''"House of Worship"'') at Fatehpur Sikri, to which he invited theologians, mystics, and selected courtiers renowned for their intellectual achievements to discuss matters of
spirituality
The meaning of ''spirituality'' has developed and expanded over time, and various meanings can be found alongside each other. Traditionally, spirituality referred to a religious process of re-formation which "aims to recover the original shape o ...
with them.
These discussions, initially restricted to Muslims, were acrimonious and resulted in the participants shouting at and abusing each other. Upset by this, Akbar opened the Ibadat Khana to people of all religions as well as atheists, resulting in the scope of the discussions broadening, even extending into areas such as the validity of the
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
and the nature of God. This shocked orthodox theologians, who sought to discredit Akbar by circulating rumours of his desire to forsake Islam.
Akbar's effort to evolve a meeting point among the representatives of various religions was not successful, as each of them attempted to assert the superiority of their respective religions by denouncing other religions. The debates at the Ibadat Khana grew more acrimonious and, contrary to their purpose of leading to a better understanding among religions, instead led to greater bitterness among them, resulting in the discontinuance of the debates by Akbar in 1582.
Akbar's interaction with various religious theologians had convinced him that despite their differences, all religions had several good practices, which he sought to combine into a new religious movement known as
Din-i-Ilahi. Virtues in Din-i-Ilahi included generosity, forgiveness, abstinence, prudence, wisdom, kindness, and piety. Celibacy was respected, chastity enforced, the slaughter of animals was discouraged, and there were no sacred scriptures or a priestly hierarchy. A leading noble of Akbar's court, Aziz Koka, wrote a letter to him from Mecca in 1594 arguing that the discipleship promoted by Akbar amounted to nothing more than a desire on Akbar's part to portray his superiority regarding religious matters. To commemorate Din-e-Ilahi, Akbar changed the name of
Prayag to
Allahabad
Prayagraj (, ; ISO 15919, ISO: ), formerly and colloquially known as Allahabad, is a metropolis in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.The other five cities were: Agra, Kanpur, Kanpur (Cawnpore), Lucknow, Meerut, and Varanasi, Varanasi (Benar ...
(pronounced as ''ilahabad'') in 1583.
Some modern scholars claim that Akbar did not initiate a new religion, instead introducing what
Oscar R. Gómez has called a transtheistic outlook, derived from tantric
Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism is a form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet, Bhutan and Mongolia. It also has a sizable number of adherents in the areas surrounding the Himalayas, including the Indian regions of Ladakh, Gorkhaland Territorial Administration, D ...
, and that Akbar did not use the word ''Din-i-Ilahi''.
Scholars have also argued that the theory that Din-i-Ilahi was a new religion is a misconception that arose because of erroneous translations of Abul Fazl's work by later British historians. It has been accepted that the policy of ''sulh-e-kul'', which formed the essence of Din-i-Ilahi, was adopted by Akbar not merely for religious purposes, but as a part of general imperial administrative policy. This also formed the basis for Akbar's policy of religious tolerance. At the time of Akbar's death in 1605, there were no signs of discontent among his Muslim subjects, and even theologians like Abdu'l Haq accepted that close ties remained.
Relation with Hindus
Akbar decreed that Hindus who had been forced to convert to Islam could reconvert to Hinduism without facing the death penalty. Akbar was well-liked by Hindus, who sang religious hymns to him and his eulogies.
Akbar practised several Hindu customs. He celebrated
Diwali
Diwali (), also called Deepavali (IAST: ''Dīpāvalī'') or Deepawali (IAST: ''Dīpāwalī''), is the Hindu festival of lights, with variations celebrated in other Indian religions such as Jainism and Sikhism. It symbolises the spiritual v ...
and allowed Brahman priests to tie jewelled strings around his wrists by way of blessing. Following his lead, many nobles took to wearing ''rakhi'' (protection charms).
He renounced beef and forbade the sale of all meats on certain days.
His son Jahangir and grandson Shahjahan maintained many of Akbar's concessions, such as the ban on cow slaughter, having only vegetarian dishes on certain days of the week, and drinking only Ganges water.
When Akbar was in Punjab, 200 miles away from the Ganges, water was sealed in large jars and transported to him. He referred to the Ganges water as the "water of immortality".
Relation with Jains
Akbar regularly held discussions with
Jain scholars and was impacted by their teachings. His first encounter with Jain rituals was when he saw a procession of a Jain
Shravaka named Champa after a six-month-long fast. Impressed by her power and devotion, he invited her
guru
Guru ( ; International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ''guru'') is a Sanskrit term for a "mentor, guide, expert, or master" of certain knowledge or field. In pan-Indian religions, Indian traditions, a guru is more than a teacher: tr ...
,
Hiravijaya
Hiravijaya (1526–1595), also known as Muni Hiravijayji and Hiravijay Suri, was a high priest of the Tapa Gaccha monastic order, following the Jain Śvetāmbara tradition. He is known for propounding the Jain philosophy to Mughal Emperor Ak ...
, to Fatehpur Sikri. Hiravijaya accepted the invitation and travelled to the Mughal capital from
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
.
Akbar was impressed with his scholarly approach. He held several inter-faith dialogues among philosophers of different religions. The arguments of Jains against eating meat persuaded him to become a vegetarian. Akbar also issued many imperial orders that were favourable for Jain interests, such as banning animal slaughter. Jain authors also wrote about their experience at the Mughal court in Sanskrit texts that are still largely unknown to Mughal historians.
In 1584, 1592, and 1598, Akbar declared "Amari Ghosana", which prohibited animal slaughter during
Paryushan and
Mahavira Janma Kalyanak. He removed the jizya tax from Jain pilgrim places like
Palitana
Palitana is a city in the Bhavnagar district of the Indian state of Gujarat. It is one of the most significant pilgrimage destinations for followers of Jainism, renowned for the Shatrunjaya hill temples, a sprawling complex of over 900 marble t ...
.
Santichandra, disciple of Suri, was sent to the Emperor, who in turn left his disciples Bhanuchandra and Siddhichandra in the court. Akbar invited Hiravijaya Suri's successor Vijayasena Suri to his court who visited him between 1593 and 1595. Akbar's religious tolerance was not followed by his son
Jahangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
, who later threatened Bhanuchandra.
Historical accounts
Personality

Akbar's reign was chronicled extensively by his court historian
Abul Fazl
Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak (14 January 1551 – 22 August 1602), also known as Abul Fazl, Abu'l Fadl and Abu'l-Fadl 'Allami, was an Indian writer, historian, and politician who served as the grand vizier of the Mughal Empire from his appointment ...
in the books ''
Akbarnama
The ''Akbarnama (; )'', is the official chronicle of the reign of Akbar, the third Mughal Emperor (), commissioned by Akbar himself and written by his court historian and biographer, Abul Fazl. It was written in Persian, which was the literary l ...
'' and ''Ain-i-akbari''. Other contemporary sources of Akbar's reign include the works of Badayuni, Shaikhzada Rashidi, and Shaikh Ahmed Sirhindi.
Akbar was a warrior, emperor, general,
animal trainer
Animal training is the act of teaching animals specific responses to specific conditions or stimuli. Training may be for purposes such as companionship, detection, protection, and entertainment. The type of training an animal receives will vary ...
(reputedly keeping thousands of hunting cheetahs during his reign and training many himself), and theologian.
Believed to be
dyslexic
Dyslexia (), previously known as word blindness, is a learning disability that affects either reading or writing. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, writ ...
, he was read to every day and had a remarkable memory. He created a library of over 24,000 volumes
written in
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
,
Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
,
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
,
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
,
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, Arabic, and
Kashmiri; the library was staffed by many scholars, translators, artists,
calligraphers, scribes, bookbinders, and readers, and he did much of the cataloguing himself.
Akbar was said to have been a wise emperor and a sound judge of character. His son and heir, Jahangir, wrote effusive praise of Akbar's character in his memoirs, and dozens of anecdotes to illustrate his virtues.
According to Jahangir, Akbar was "of the hue of wheat; his eyes and eyebrows were black, and his complexion rather dark than fair". Antoni de Montserrat, the
Catalan Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
who visited his court, described him as follows:
Akbar was not tall, but powerfully built and very agile. He was also noted for various acts of courage. One such incident occurred on his way back from Malwa to Agra when Akbar was 19 years old. Akbar rode alone in advance of his escort and was confronted by a tigress who, along with her cubs, came out from the shrubbery across his path. When the tigress charged the emperor, he was alleged to have dispatched the animal with his sword in a solitary blow. His approaching attendants found the emperor standing quietly by the side of the dead animal.
Abul Fazl, as well as Akbar's critic Badayuni, described him as having a commanding personality. He was notable for his command in battle, and, "like
Alexander of Macedon, was always ready to risk his life, regardless of political consequences". He often plunged on his horse into flooded rivers during the rainy seasons and safely crossed them. He rarely indulged in cruelty and is said to have been affectionate towards his relatives. He pardoned his brother Hakim, who had rebelled. On rare occasions, he dealt cruelly with offenders, such as his maternal uncle Muazzam and his foster-brother Adham Khan, who was twice
defenestrated for drawing Akbar's wrath.
He is said to have been extremely moderate in his diet. ''
Ain-e-Akbari
The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' (), or the "Administration of Akbar", is a 16th-century detailed document regarding the administration of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, written by his court historian, Abu'l Fazl, in the Persian language. It forms V ...
'' mentions that during his travels and while at home, Akbar drank water from the
Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
river, which he called "the water of immortality". Servants were stationed at Sorun, and later
Haridwar
Haridwar (; ; formerly Mayapuri) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is s ...
, to dispatch water, in sealed jars, to wherever he was stationed. According to
Jahangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
's memoirs, he was fond of fruits and had little liking for meat, which he stopped eating in his later years.
In 1570, Akbar visited
Vrindavan
Vrindavan (; ), also spelt Vrindaban and Brindaban, is a historical city in the Mathura district of Uttar Pradesh, India. It is located in the Braj, Braj Bhoomi region and holds religious importance for Hindus who believe that Krishna, one of ...
, regarded as the birthplace of
Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, c ...
, and gave permission for four temples to be built by the
Gaudiya Vaishnavas, which were Madana-mohana, Govindaji, Gopinatha, and Jugal Kisore.
To defend his stance that speech arose from hearing, he carried out a
language deprivation experiment, and had children raised in isolation, not allowed to be spoken to, and pointed out that as they grew older, they remained mute.
Hagiography
During Akbar's reign, the ongoing process of inter-religious discourse and
syncretism
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various school of thought, schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or religious assimilation, assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the ...
resulted in a series of religious attributions to him in terms of positions of assimilation, doubt, or uncertainty, which he either assisted himself or left unchallenged.
Such
hagiographical accounts of Akbar traversed a wide range of denominational and sectarian spaces, including several accounts by
Parsi
The Parsis or Parsees () are a Zoroastrian ethnic group in the Indian subcontinent. They are descended from Persian refugees who migrated to the Indian subcontinent during and after the Arab-Islamic conquest of Iran in the 7th century, w ...
s,
Jains, and Jesuit missionaries, apart from contemporary accounts by Brahminical and Muslim orthodoxy. Existing sects and denominations, as well as various religious figures who represented popular worship felt they had a claim to him. The diversity of these accounts is attributed to the fact that his reign resulted in the formation of a flexible centralised state accompanied by personal authority and cultural heterogeneity.
Akbarnāma, the ''Book of Akbar''

The (), which literally means ''Book of Akbar'', is an official biographical account of Akbar written in Persian. It includes vivid and detailed descriptions of his life and times.
The work was commissioned by Akbar, and written by
Abul Fazl
Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak (14 January 1551 – 22 August 1602), also known as Abul Fazl, Abu'l Fadl and Abu'l-Fadl 'Allami, was an Indian writer, historian, and politician who served as the grand vizier of the Mughal Empire from his appointment ...
, one of the ''Nine Jewels'' (
Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
:
Navaratnas
Navaratnāḥ (Sanskrit dvigu ''nava-ratna'', , ) refers to a distinguished assembly of nine learned and virtuous individuals who adorned the royal sabhā (court) of certain illustrious List of Indian monarchs, bhūpati-s (kings) in History of ...
) of Akbar's royal court. The book reportedly took seven years to complete and the original manuscripts contained a number of paintings supporting the texts. The paintings are in the
Mughal school of painting, and included works of masters of the imperial workshop, including
Basawan
Basāwan, or Basāvan (flourished 1580–1600), was an Indian miniature painter in the Mughal style. He was known by his contemporaries as a skilled colorist and keen observer of human nature, and for his use of portraiture in the illustrations ...
, whose use of portraiture in its illustrations was an innovation in
Indian art
Indian art consists of a variety of art forms, including painting, sculpture, pottery, and textile arts such as woven silk. Geographically, it spans the entire Indian subcontinent, including what is now India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, N ...
.
Consorts and concubines
Akbar's first wife and one of the chief consorts was his cousin, Princess
Ruqaiya Sultan Begum
Ruqaiya Sultan Begum (alternatively spelled Ruqayya or Ruqayyah; 1542 – January 1626) was the first wife and one of the chief consorts of the third Mughal emperor, Akbar.
Ruqaiya was a first cousin of her husband and was a Mughal princess ...
,
the only daughter of his paternal uncle, Prince
Hindal Mirza
Abu'l-Nasir Muhammad (; 4 March 1519 – 20 November 1551), better known by the sobriquet Hindal ( Chagatai for "Taker of India"), was a Mughal prince and the youngest son of Emperor Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire and the first M ...
, and his wife Sultanam Begum. In 1551, Hindal Mirza died fighting in a battle against Kamran Mirza's forces. Upon hearing the news of his brother's death, Humayun was overwhelmed with grief.
Hindal's daughter Ruqaiya married Akbar about the time of his first appointment, at age nine, as governor of
Ghazni Province
Ghazni (; ) is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in southeastern Afghanistan. The province contains 19 Districts of Afghanistan, districts, encompassing over a thousand villages and roughly 1.3 million people, making it the 5th most ...
.
Akbar was also given the command of his uncle's army.
Akbar's marriage with Ruqaiya was solemnised near
Jalandhar
Jalandhar () is a city in the state of Punjab, India, Punjab in India. With a considerable population, it ranks as the List of cities in Punjab and Chandigarh by population, third most-populous city in the state and is the largest city in the ...
, Punjab, when both of them were 14 years old.
She was a senior-ranking wife of Akbar. She died childless in January 1626 and was buried next to her father's grave.
His second wife was the daughter of Abdullah Khan Mughal.
The marriage took place in 1557 during the
Siege of Mankot.
Bairam Khan
Muhammad Bairam Khan (; 18 January 1501 – 31 January 1561), commonly known as Bairam Khan or Bayram Khan was an important military commander, and later commander-in-chief of the Mughal Empire, Mughal army, a powerful statesman and regent at ...
did not approve of this marriage because Abdullah's sister was married to Akbar's uncle, Prince
Kamran Mirza
Kamran Mirza () (1512 – 5 October 1557) was the second son of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire and the first Mughal Emperor. Kamran Mirza was born in Kabul to Babur's wife Gulrukh Begum. He was half-brother to Babur's eldest son Hu ...
, and so he regarded Abdullah as a partisan of Kamran. Bairam Khan opposed the match until Nasir-al-Mulk persuaded him that he could not oppose it. Nasir-al-Mulk organised a joyful gathering and a grand feast.
His third wife and one of his three chief consorts was his cousin,
Salima Sultan Begum
Salima Sultan Begum (23 February 1539 – 2 January 1613) was the third wife and chief consort of the Mughal emperor Akbar, and a granddaughter of Babur.
Salima was the daughter of Akbar's paternal aunt, Gulrukh Begum, and her husband, the Vic ...
,
the daughter of Nur-ud-din Muhammad Mirza and his wife Gulrukh Begum, also known as Gulrang, the daughter of Emperor
Babur
Babur (; 14 February 148326 December 1530; born Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad) was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also ...
. She was at first betrothed to Bairam Khan by Humayun. After Bairam Khan died in 1561, Akbar married her in the same year. She was the foster mother of Akbar's second son,
Murad Mirza. She was a poet and actively played a role in the politics of the Mughal court during Akbar's and Jahangir's reigns. She is regarded as the senior-most wife of Akbar. She died childless on 2 January 1613.
Akbar's fourth and favourite wife,
Mariam-uz-Zamani
Mariam-uz-Zamani (; – 19 May 1623), commonly known by the misnomer Jodha Bai, was the Empress consort, chief consort, principal Hinduism, Hindu wife and the favourite wife of the third Mughal emperor, Akbar. She was also the longest-servi ...
,
commonly known by the misnomer Jodha Bai, was the daughter of the ruler of Amer,
Raja Bharmal, and by birth, was of
Rajput caste. They got married on 6 February 1562 at the imperial military camp in
Sambhar, Rajasthan, near
Amer
Amer may refer to:
Places
* Amer (river), a river in the Dutch province of North Brabant
* Amer, Girona, a municipality in the province of Girona in Catalonia, Spain
* Amber, India (also known as Amer, India), former city of Rajasthan state
** Am ...
, and became one of Akbar's chief consorts.
She gradually became one of his influential wives
and was said to possess uncommon beauty. Shortly after marriage, Akbar named her 'Wali Nimat Begum' (Blessings/Gift of God). Their marriage took place when Akbar was on his way back from
Ajmer
Ajmer () is a city in the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Ajmer district and Ajmer division. It lies at the centre of Rajasthan, earning it the ...
after offering prayers to the tomb of
Moinuddin Chishti
Mu'in al-Din Hasan Chishti Sijzi (; February 1143 – March 1236), known reverentially as Khawaja Gharib Nawaz (), was a Persians, Persian Islamic scholar and Sufism, mystic from Sistan, who eventually ended up settling in the Indian subcontin ...
. Raja Bharmal had conveyed to Akbar that he was being harassed by his brother-in-law Sharif-ud-din Mirza (the Mughal ''
hakim'' of
Mewat
Mewat (; ) is a historical and cultural region which encompasses parts of the modern-day states of Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh in northwestern India.
Geography
The loose boundaries of the Mewat region generally include parts of th ...
). Akbar insisted that the Raja should submit to him personally; it was also suggested that his daughter should be married to him as a sign of complete submission. Her marriage is considered one of the most important events in the history of the Mughal Empire.
She became his first wife to have given birth to Akbar's sons. In 1564, she delivered twins named Mirza Hassan and Mirza Hussain and in 1569, she was honoured with the title of 'Mariam-uz-Zamani' after giving birth to their third and first surviving son, Prince Salim (the future emperor
Jahangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
), the heir to the throne. She was also the foster mother of Akbar's favourite son,
Daniyal Mirza
Daniyal Mirza (11 September 1572 – 19 March 1605) was a prince of the Mughal Empire who served as the Viceroy of the Deccan. He was the third son of the emperor Akbar and a half-brother of the emperor Jahangir.
Daniyal was Akbar's favouri ...
.

She commanded a high rank in the imperial harem and was a recipient of many privileges. She was an intellectual woman who held a considerable influence in Akbar's court and is known as the prime driving force for Akbar's promotion of secularism and religious neutrality.
She was also a great female patron of the architecture of her time. She died on 19 May 1623 in Agra and was buried in a grave close to her husband, Akbar, in Sikandra, Agra.
In 1562, Akbar married the former wife of Abdul Wasi, the son of Shaikh Bada, lord of Agra. Akbar was enamored with her beauty and ordered Abdul Wasi to divorce her. Another of his wives was Gauhar-un-Nissa Begum, the daughter of Shaikh Muhammad Bakhtiyar and the sister of Shaikh Jamal Bakhtiyar. Their dynasty was called Din Laqab they lived in Chandwar and Jalesar near Agra. He married the daughter of Jagmal Rathore, son of Rao Viramde of
Merta in 1562.
His next marriage took place in 1564 to the daughter of Miran Mubarak Shah, the ruler of
Khandesh
Khandesh is a geographic region in Maharashtra, India. It was made up of present Jalgaon, Dhule and Nandurbar districts. It also said that Burhanpur District of Madhya Pradesh was also its part.
The region have seen many geographical ch ...
. In 1564, he sent presents to the court with a request that his daughter be married to Akbar. Miran's request acceded and an order was issued. Itimad Khan was sent with Miran's ambassadors. Miran welcomed Itimad with honour and despatched his daughter with him. A large number of nobles accompanied her. The marriage took place in September 1564 when she reached Akbar's court. As a dowry, Mubarak Shah ceded Bijagarh and Handia to his imperial son-in-law.
He married another Rajput princess in 1570, Raj Kunwari, daughter of Kanha, the brother of Rai Kalyan Mal, the ruler of
Bikanir.
The marriage took place in 1570 when Akbar came to this part of the country. Kalyan made a homage to Akbar and requested that his brother's daughter be married to him. Akbar accepted his proposal, and the marriage was arranged.
He also married Bhanmati, daughter of Bhim Raj, another brother of Rai Kalyan Mal.
He also married Nathi Bai, daughter of Rawal Har Rai, the ruler of
Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed ''The Golden city'', is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur, in the heart of the Thar Desert. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Jaisalmer district ...
in 1570.
Rawal had sent a request that his daughter be married to Akbar. The proposal was accepted by Akbar. Raja Bhagwan Das was despatched on this service. The marriage ceremony took place after Akbar's return from
Nagor
Nagor is a village in Bhuj Taluka of Kutch at a distance of about 8 km from Bhuj town, the capital of Kachchh District of Gujarat in India.
Notable people
* Rai Bahadur Jagmal Raja Chauhan (1887–1974), railway contractor
References
...
. She was the mother of Princess Mahi Begum, who died on 8 April 1577. In 1570, Narhardas, a grandson of Rao Viramde of
Merta, married his sister, Puram Bai, to Akbar in return for Akbar's support of Keshodas's claims on Merta.
Another of his wives was Bhakkari Begum, the daughter of Sultan Mahmud of Bhakkar. On 2 July 1572, Akbar's envoy Itimad Khan reached Mahmud's court to escort his daughter to Akbar. Itimad Khan brought a dress, a bejewelled scimitar belt, a horse with a saddle and reins, and four elephants. Mahmud celebrated the occasion by holding extravagant feasts for fifteen days. On the day of the wedding, the ulema, saints, and nobles were honoured with rewards. Mahmud offered 30,000 rupees in cash and kind to Itimad Khan and sent his daughter with a grand dowry and an entourage. She came to Ajmer and waited upon Akbar. The gifts of Sultan Mahmud, carried by the delegation, were presented to the ladies of the imperial harem.
His eleventh wife was Qasima Banu Begum,
the daughter of Arab Shah. The marriage took place in 1575. A fest was held, at which the high officers and other pillars of the state were present. In 1577, the Rawal Askaran of
Dungarpur State requested that his daughter be married to Akbar. Akbar granted his request. Rai Loukaran and Rajah Birbar, servants of the Rajah, were sent from Dihalpur to do the honour of conveying his daughter. The two delivered her to Akbar's court where the marriage took place on 12 July 1577.
His twelfth wife was Bibi Daulat Shad.
She was the mother of Princess Shakr-un-Nissa Begum, and Princess
Aram Banu Begum
Aram Banu Begum (22 December 1584 - 17 June 1624) was a Mughal princess and the youngest daughter of the third Mughal Emperor Akbar.
Life
Born on 22 December 1584, Aram Banu Begum was the youngest daughter of Akbar and Bibi Daulat Shad. She ...
born on 22 December 1584. His next wife was the daughter of Shams Chak, a Kashmiri. The marriage took place on 3 November 1592. In 1593, he married the daughter of Qazi Isa and the cousin of Najib Khan. Najib told Akbar that his uncle had made his daughter a present for him. Akbar accepted his representation and on 3 July 1593, he visited Najib Khan's house and married Qazi Isa's daughter.
At some point, Akbar took into his harem Rukmavati, a daughter
Maldeo Rathore
Rao Maldeo Rathore (5 December 1511 – 7 November 1562) was a king of the Rathore dynasty, who ruled the kingdom of Marwar in present day state of Rajasthan. Maldeo ascended the throne in 1531 CE, inheriting a small ancestral principality of Ra ...
, Rao of
Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. 'Maru' is a Sanskrit word for desert. The word 'wad' literally means fence in Rajasthani languages. Engl ...
, by his mistress, Tipu Gudi. This was a ''dolo'' union as opposed to a formal marriage, representing the bride's lower status in her father's household, and serving as an expression of vassalage to an overlord. The dating of this event is not recorded.
Death
On 3 October 1605, Akbar fell ill from an attack of
dysentery
Dysentery ( , ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications may include dehyd ...
,
from which he never recovered. He is believed to have died on 26 October 1605. He was buried at
his mausoleum in Sikandra, Agra, which lies a kilometer next to the
tomb of Mariam-uz-Zamani
The Tomb of Mariam-uz-Zamani or Mariam's tomb is the mausoleum of Mariam-uz-Zamani, commonly known as Mariam-uz-Zamani#The misnomer of Jodha Bai, Jodha Bai, the favorite wife of the Akbar, Mughal Emperor Akbar. The tomb was built by her son Jah ...
, his favourite consort.
Legacy
Akbar firmly entrenched the authority of the Mughal Empire in India and beyond, after it had been threatened by the Afghans during his father's reign, establishing its military and diplomatic superiority.
Folk tales revolving around him and
Birbal
Mahesh Das (; 1528 16 February 1586), popularly known by his title Rajah Birbal (), was an Indian minister and commander of the Mughal Empire. He is mostly known in the Indian subcontinent for the folk tales which focus on his wit. He was app ...
, one of his ''navratnas'', are popular in India. He and his Hindu wife, Mariam-uz-Zamani are widely popular, as the latter is believed to have been the prime inspiration and driving force for Akbar's promotion of secularism and universal benevolence.
Citing Akbar's melding of the disparate "fiefdoms" of India into the
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
, as well as the lasting legacy of "pluralism and tolerance" that "underlies the values of the modern republic of India",
''Time'' included him in its list of top 25 world leaders.
Akbar's legacy is largely negative in
Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
. Historian
Mubarak Ali, in a study of the image of Akbar in Pakistani textbooks, has observed that Akbar "is conveniently ignored and not mentioned in any school textbook from class one to matriculation",
as opposed to the omnipresence of
emperor Aurangzeb. He quotes historian
Ishtiaq Hussain Qureshi, who said that, due to his religious tolerance, "Akbar had so weakened Islam through his policies that it could not be restored to its dominant position in the affairs".
A common thread among Pakistani historians is criticism of Akbar's
Rajput
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
policy. Ali has stated that "Akbar is criticized for bringing Muslims and Hindus together as one nation and putting the separate identity of the Muslims in danger. This policy of Akbar contradicts the
theory of Two-Nation and therefore makes him an unpopular figure in Pakistan."
Issue
Sons
Akbar's sons were:
*
Hassan Mirza (19 October 1564 – 5 November 1564) (twin with Hussain Mirza)—with
Mariam-uz-Zamani
Mariam-uz-Zamani (; – 19 May 1623), commonly known by the misnomer Jodha Bai, was the Empress consort, chief consort, principal Hinduism, Hindu wife and the favourite wife of the third Mughal emperor, Akbar. She was also the longest-servi ...
*
Hussain Mirza (19 October 1564 – 29 October 1564) (twin with Hassan Mirza)—with Mariam-uz-Zamani
*
Jahangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
(31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627)—with Mariam-uz-Zamani —Born Salim Mirza, he succeeded Akbar to the throne.
*
Murad Mirza (15 June 1570 – 12 May 1599)—with a concubine—Entrusted to
Salima Sultan Begum
Salima Sultan Begum (23 February 1539 – 2 January 1613) was the third wife and chief consort of the Mughal emperor Akbar, and a granddaughter of Babur.
Salima was the daughter of Akbar's paternal aunt, Gulrukh Begum, and her husband, the Vic ...
for the first few years, he returned to his mother's care before 1575.
*
Daniyal Mirza
Daniyal Mirza (11 September 1572 – 19 March 1605) was a prince of the Mughal Empire who served as the Viceroy of the Deccan. He was the third son of the emperor Akbar and a half-brother of the emperor Jahangir.
Daniyal was Akbar's favouri ...
(11 September 1572 – 19 March 1605)—with a concubine—Fostered by Mariam-uz-Zamani
Daughters
His daughters were:
* Fatima Banu Begum (; infancy)
*
Shahzadi Khanum
Shahzadi Khanum (born 21 November 1569) was a Mughal dynasty, Mughal princess, the second surviving child and eldest daughter of Mughal Emperor Akbar.
Family
Born on 21 November 1569, Shahzadi was the eldest daughter of the Mughal Emperor Akba ...
(born 21 November 1569)—with Bibi Salima. Fostered by
Mariam Makani. Married to Muzaffar Hussain Mirza,
Timurid Prince
* Mahi Begum (died 7 April 1577)—with Nathi Bai
*
Shakr-un-Nissa Begum (died 1 January 1653)—with Bibi Daulat Shad. Married to Shahrukh Mirza
*
Aram Banu Begum
Aram Banu Begum (22 December 1584 - 17 June 1624) was a Mughal princess and the youngest daughter of the third Mughal Emperor Akbar.
Life
Born on 22 December 1584, Aram Banu Begum was the youngest daughter of Akbar and Bibi Daulat Shad. She ...
(22 December 1584 – 17 June 1624)—with Bibi Daulat Shad
He had also adopted several children including:
* Kishnavati Bai (died August 1609)—daughter of Sekhavat Kachvahi Durjan Sal. Akbar took her as his own and had her married to
Sawai Raja Sur Singh of
Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. 'Maru' is a Sanskrit word for desert. The word 'wad' literally means fence in Rajasthani languages. Engl ...
; she became the mother of
Maharaja Gaj Singh of Marwar and Manbhavati Bai, wife of
Parviz Mirza
Parviz Mirza (31 October 1589 – 28 October 1626) was the second son of Mughal emperor Jahangir from his wife, Sahib Jamal. His daughter, Nadira Banu Begum, later became the wife of Dara Shikoh.
Early life
Born on 31 October 1589, Parviz wa ...
In popular culture
Films and television
* ''
Shahenshah Akbar
''Shahenshah Akbar'' is a Bollywood film. It was released in 1943.
Soundtrack
The music of the film was composed by Ustad Jhande Khan
Ustad, ustadh, ustaz or ustadz (abbreviated as Ust., Ut. or Ud.; from Persian ''ustād'') is an honorific ...
'' is a 1943 Indian
Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
-language film about the emperor.
* Akbar was portrayed in the award-winning 1960
Hindi movie ''
Mughal-e-Azam
''Mughal-e-Azam'' () is a 1960 Indian Epic film, epic historical drama film produced and directed by K. Asif. Starring Prithviraj Kapoor, Dilip Kumar, Madhubala, and Durga Khote, it follows the love affair between Mughal Empire, Mughal Prince ...
'' (The Great Mughal), in which his character was played by
Prithviraj Kapoor
Prithviraj Kapoor (born Prithvinath Kapoor; 3 November 1906 – 29 May 1972) was an Indian actor who is also considered to be one of the founding figures of Hindi cinema. He was associated with IPTA as one of its founding members and establish ...
.
* In the 1958 Urdu film ''
Anarkali
Anarkali () is a legendary lady said to be loved by the 16th-century Mughal Prince Salim, who later became Emperor Jahangir. According to some accounts, Anarkali was the nickname of the courtesan ( tawaif) Sharf-un-Nisa, though scholars hold ...
'', he was portrayed by Himalyawala.
* The
Government of India
The Government of India (ISO 15919, ISO: Bhārata Sarakāra, legally the Union Government or Union of India or the Central Government) is the national authority of the Republic of India, located in South Asia, consisting of States and union t ...
's
Films Division
The Films Division of India (FDI), commonly referred as Films Division, was established in 1948 following the independence of India. It was the first state film production and distribution unit, under the Ministry of Information and Broadcastin ...
produced ''Akbar'', a documentary film about the emperor, in 1967, directed by Shanti S. Varma. It won the
.
*
Om Shivpuri
Om Shivpuri (14 July 1938 – 15 October 1990) was an Indian theatre actor-director and character actor in Hindi films.
A National School of Drama, New Delhi alumnus, Shivpuri became the first chief of the National School of Drama Repertory C ...
played Akbar in the 1978 movie ''
Bhakti Mein Shakti''.
*
Akbar Saleem Anarkali is a 1979 Indian
Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of South India
** Telugu literature, is the body of works written in the Telugu language.
* Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Tel ...
-language film about the
Anarkali
Anarkali () is a legendary lady said to be loved by the 16th-century Mughal Prince Salim, who later became Emperor Jahangir. According to some accounts, Anarkali was the nickname of the courtesan ( tawaif) Sharf-un-Nisa, though scholars hold ...
legend directed by
N. T. Rama Rao
Nandamuri Taraka Rama Rao (28 May 1923 – 18 January 1996), often referred to by his initials NTR, was an Indian actor, film director, film producer, screenwriter, film editor, philanthropist, and politician who served as the Chief Minister o ...
, with Rao also portraying the role of Akbar.
* Akbar was portrayed by
Amjad Khan in the 1979 movie ''
Meera
Meera, better known as Mirabai, and venerated as Sant Meerabai, was a 16th-century Hindu mystic poet and devotee of Krishna. She is a celebrated Bhakti saint, particularly in the North Indian Hindu tradition. She is mentioned in '' Bhaktama ...
''.
* Akbar was portrayed by
Hrithik Roshan
Hrithik Roshan (; born 10 January 1974) is an Indian actor who works in Hindi cinema. He has portrayed a variety of characters and is known for his dancing skills. One of the highest-paid actors in India, he has won many awards, including si ...
in the 2008 Bollywood film ''
Jodhaa Akbar
''Jodhaa Akbar'' is a 2008 Indian Hindi-language historical drama film directed by Ashutosh Gowariker. It stars Hrithik Roshan and Aishwarya Rai Bachchan in the titular roles. Set in the 16th century, the film shows the fictional life and lo ...
''.
* Akbar and Birbal were portrayed in the Hindi series ''Akbar-Birbal'' aired on
Zee TV
ZEE TV also known as Z TV is an Indian Hindi language general entertainment pay television channel owned by Zee Entertainment Enterprises. It was launched on 1 October 1992 as the oldest privately owned television channel in India.
History ...
in the late 1990s where Akbar's role was played by
Vikram Gokhale
Vikram Gokhale (14 November 1945 – 26 November 2022) was an Indian film, television and stage actor, noted for his roles in Marathi theatre, Hindi films and television. He was the son of the Veteran Marathi theatre and film actor, Chandrakan ...
.
* A television series, called ''Akbar the Great'', directed by
Akbar Khan was aired on
DD National
DD National (formerly DD1) is an Indian state-owned entertainment television channel, founded by the Government of India, owned by the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (India), Ministry of Information and Broadcasting. It is the flagshi ...
in the 1990s.
* In 2013–2015, a television series, called ''
Jodha Akbar
''Jodha Akbar'' was an Indian historical drama television series that aired from June 18, 2013 to August 7, 2015 on Zee TV. The show was produced by Ekta Kapoor under Balaji Telefilms, and had starred Rajat Tokas and Paridhi Sharma. Critics ...
'' aired on Zee TV, in which the role of Akbar was played by actor
Rajat Tokas.
* In the Motu Patlu episode "Motu Akbar The Great", John fools Motu into believing that he is playing Akbar in a Hit Film.
* Akbar was portrayed by
Uday Tikekar
Uday Tikekar (born 4 December 1960) is an Indian film and television actor. He began his career in Marathi theatre, also putting up performances in Hindi theatre. He is married to classical singer Arati Ankalikar-Tikekar, who is a 2-time Nati ...
in
EPIC
Epic commonly refers to:
* Epic poetry, a long narrative poem celebrating heroic deeds and events significant to a culture or nation
* Epic film, a genre of film defined by the spectacular presentation of human drama on a grandiose scale
Epic(s) ...
channel's critically acclaimed historical drama ''
Siyaasat
''Siyaasat'' (English: ''Politics'') is a 2014 Indian fictional drama which aired on The EPIC Channel. The series is an adaptation of the popular 2002 award-winning fictional novel ''The Twentieth Wife'' by author Indu Sundaresan.
The series ...
'' (based on the novel ''The Twentieth Wife'').
* In
Sony TV Sony Television, Sony TV, or Sony HD may refer to any of the following television-related products from Japanese conglomerate Sony:
* Television sets designed and manufactured by Sony Corporation in Japan
** Trinitron, television hardware brand (196 ...
's historical drama ''
Bharat Ka Veer Putra – Maharana Pratap
''Bharat Ka Veer Putra – Maharana Pratap'' () is an Indian historical fiction series produced by Contiloe Entertainment. It is based on the life of Maharana Pratap, a sixteenth century ruler of Mewar kingdom. It starred Sharad Malhotra, R ...
'', Akbar was at first portrayed by
Krip Suri and later by
Avinesh Rekhi.
* Akbar is portrayed by
Kiku Sharda
Raghavendra Amarnath Sharda (born 14 February 1976), better known as Kiku Sharda, is an Indian comedian and actor who mainly works in Hindi television and Hindi films. He is best known for his role as Constable Mulayam Singh Gulgule in Sony SA ...
in
BIG Magic's sitcom ''
Akbar Birbal
'' Har Mushkil Ka Hal Akbar Birbal'' is an Indian historical comedy television series which aired on BIG Magic. It stars Kiku Sharda and Vishal Kotian. A Bhojpuri language dubbed version aired on Big Ganga.
Plot
The show's story is based o ...
''.
*
Mohammed Iqbal Khan played the role of Akbar in ABP News' documentary series,
Bharatvarsh.
* ''Akbar Rakht Se Takht Ka Safar'' is a 2017 Indian drama television series tracing Akbar's journey to the Mughal throne.
*
Shahbaz Khan played the role of Akbar in the Colors television show
Dastaan-E-Mohabbat Salim Anarkali
''Dastaan-E-Mohabbat: Salim Anarkali'' () is an Indian historical television series that aired on Colors TV. Created by Ludhiana Pathak's Writer's Galaxy Studios'','' it premiered on 1 October 2018. Starring Shaheer Sheikh and Sonarika Bhadoria ...
.
*
Ali Asgar portrayed the emperor in the 2020 Indian comedy television series, ''
Akbar Ka Bal Birbal
Akbar Ka Bal… Birbal () is an Indian Hindi historical comedy television series that aired on Star Bharat between 31 August and 27 November 2020, and was digitally available on Disney+ Hotstar. The show stars Ali Asgar and Vishal Kotian as A ...
''.
*
Naseeruddin Shah
Naseeruddin Shah (born 20 July 1950) is an Indian actor. He was notable in Indian parallel cinema and has starred in various international productions. He has won numerous awards in his career, including three National Film Awards, three Filmfa ...
portrayed him in
ZEE5
ZEE5 or Z5 is an Indian subscription video on demand and over-the-top streaming service, owned by Zee Entertainment Enterprises. It was launched in India on 14 February 2018 with content in 12 languages. The ZEE5 mobile app is available on We ...
's web series
Taj: Divided by Blood.
Fiction
* Akbar is a principal character in
Indu Sundaresan's award-winning novel ''The Twentieth Wife'' (2002) as well as in its sequel ''The Feast of Roses'' (2003).
* A fictionalised Akbar plays an important supporting role in
Kim Stanley Robinson
Kim Stanley Robinson (born March 23, 1952) is an American science fiction writer best known for his ''Mars'' trilogy. Many of his novels and stories have ecological, cultural, and political themes and feature scientists as heroes. Robinson has ...
's 2002 novel, ''
The Years of Rice and Salt
''The Years of Rice and Salt'' is an alternate history novel by American science fiction author Kim Stanley Robinson, published in 2002. The novel explores how world history might have been different if the Black Death plague had killed 99 pe ...
''.
* Akbar is also a major character in
Salman Rushdie
Sir Ahmed Salman Rushdie ( ; born 19 June 1947) is an Indian-born British and American novelist. His work often combines magic realism with historical fiction and primarily deals with connections, disruptions, and migrations between Eastern wor ...
's 2008 novel ''
The Enchantress of Florence''.
* In
Kunal Basu
''Kunal Basu'' ( Bengali: কুনাল বসু; born 4 May 1956) is an Indian author of English fiction who has written five novels – ''The Opium Clerk'' (2001), ''The Miniaturist'' (2003), '' Racists'' (2006), ''The Yellow Emperor's Cur ...
's ''
The Miniaturist'', the story revolves around a young painter during Akbar's time who paints his own version of the ''Akbarnamu''.
* Akbar is mentioned as 'Raja Baadshah' in the
Chhattisgarhi
Chhattisgarhi () is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by approximately 16.25 million people from Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra in India. It is the official language of Chhattisgarh. It is grouped within the Eastern Hindi lan ...
folktale
Oral literature, orature, or folk literature is a genre of literature that is spoken or sung in contrast to that which is written, though much oral literature has been transcribed. There is no standard definition, as anthropologists have used va ...
of "
Mohna de gori kayina".
* Akbar is the main character in ''
Empire of the Moghul
''Empire of the Moghul'' is a series of historical fiction novels written by Alex Rutherford (the pen name for Diana and Michael Preston). The series consists of six volumes covering the rise and height of the Moghul Empire in medieval India.
...
: Ruler of the World'' by
Alex Rutherford Alex Rutherford is the collective pen name of two writers, Diana Preston and her husband Michael Preston.
"Rutherford" is known for the six-book historical fiction series '' Empire of the Moghul''.
The Prestons studied at the University of Oxfor ...
, the third book in a sextet based on the six great Mughal Emperors of the Mughal Dynasty.
Video games
* Akbar is featured in the video game
Sid Meier
Sidney K. Meier ( ; born February 24, 1954) is an American businessman and computer programmer. A programmer, designer, and producer of many strategy video games and simulation video games, including the ''Civilization'' series, Meier co-found ...
's ''
Civilization IV: Beyond the Sword'' as a "great general" available in the game.
* Akbar is the AI Personality of India in ''
Age of Empires III: The Asian Dynasties''.
See also
*
Akbar II
Akbar II (; 22 April 1760 – 28 September 1837), also known as Akbar Shah II, was the nineteenth Mughal emperor from 1806 to 1837. He was the second son of Shah Alam II and the father of Bahadur Shah II, who would eventually succeed him an ...
*
Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
*
List of people known as the Great
This is a list of people known as the Great, or the equivalent, in their own language. Other languages have their own suffixes, such as Persian ''e Bozorg'' and Hindustani ''e Azam''.
In Persia, the title "the Great" at first seems to have b ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* *
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak
Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak (14 January 1551 – 22 August 1602), also known as Abul Fazl, Abu'l Fadl and Abu'l-Fadl 'Allami, was an Indian writer, historian, and politician who served as the grand vizier of the Mughal Empire from his appointment ...
''Akbar-namah'' Edited with commentary by Muhammad
Sadiq Ali
Sadiq Ali (2 May 1952 – 18 April 2011) was a senior politician of Kashmir, India, a noted poet and writer and an active environmentalist. He was an elected legislator in the Kashmir State Assembly for three consecutive terms. Mr Sadiq Ali ...
(Kanpur-Lucknow: Nawal Kishore) 1881–83 Three Vols. (
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
)
* Abu al-Fazl ibn Mubarak ''Akbarnamah'' Edited by Maulavi
Abd Al-Rahim. Bibliotheca Indica Series (Calcutta: Asiatic Society of Bengal) 1877–1887 Three Vols. (
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
)
* Haji Muhammad 'Arif Qandahari ''Tarikh-i-Akbari (Better known as Tarikh-i-Qandahari)'' edited & Annotated by Haji Mu'in'd-Din Nadwi, Dr. Azhar 'Ali Dihlawi & Imtiyaz 'Ali 'Arshi (
Rampur Raza Library
The Rampur Raza Library (''Rāmpur Razā Kitāb Khāna'') located in Rampur, Uttar Pradesh, India is a repository of Indo-Islamic cultural heritage established in the last decades of the 18th century. It was built up by successive Nawabs of ...
) 1962 (
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
)
* Martí Escayol, Maria Antònia. "Antoni de Montserrat in the Mughal Garden of good government European construction of Indian nature", ''Word, Image, Text: Studies in Literary and Visual Culture'', ed. Shormistha Panja et al., Orient Blackswan, New Delhi, 2009.
* Satyananda Giri, ''Akbar'', Trafford Publishing, 2009,
* John Correia-Afonso, ''Letters from the Mughal court'', Bombay, 1980.
*
*
*
''The Adventures of Akbar'' by Flora Annie Steel, 1847–1929 (ebook)
*
*
*
*
External links
*
''The Drama of Akbar''by
Muhammad Husain Azad
Muhammad Husain Azad ( — ; 5 May 1830 – 22 January 1910) was an Urdu writer and scholar who wrote both prose and poetry, but is mostly remembered for his prose. His best known work is Aab-e-Hayat ("Elixir of Life"). from 1922
{{Authority control
1542 births
1605 deaths
16th-century Indian monarchs
17th-century Indian monarchs
Child monarchs from Asia
Deaths from dysentery
Founders of religions
Indian people of Iranian descent
Indian Sunni Muslims
Indian warriors
Emperors of the Mughal Empire
Muslim monarchs
People from Agra
People from Umerkot
16th-century Mughal Empire people
 Akbar's father Humayun had regained control of the
Akbar's father Humayun had regained control of the 
 Having established Mughal rule over northern India, Akbar turned his attention to the conquest of
Having established Mughal rule over northern India, Akbar turned his attention to the conquest of  Akbar's next military objectives were the conquest of Gujarat and Bengal, which connected India with the trading centres of Asia, Africa, and Europe through the
Akbar's next military objectives were the conquest of Gujarat and Bengal, which connected India with the trading centres of Asia, Africa, and Europe through the  Akbar was a follower of
Akbar was a follower of  Akbar introduced coins with decorative features, including floral motifs, dotted borders, and
Akbar introduced coins with decorative features, including floral motifs, dotted borders, and  The Kacchwaha Rajput, Raja
The Kacchwaha Rajput, Raja  In 1572, the
In 1572, the  In 1555, while Akbar was still a child, the Ottoman Admiral
In 1555, while Akbar was still a child, the Ottoman Admiral  Before Akbar's rule, the
Before Akbar's rule, the  Akbar, as well as his mother and other members of his family, are believed to have been
Akbar, as well as his mother and other members of his family, are believed to have been  During the early part of his reign, Akbar adopted an attitude of suppression towards Muslim sects that were condemned by the orthodoxy as
During the early part of his reign, Akbar adopted an attitude of suppression towards Muslim sects that were condemned by the orthodoxy as  Akbar decreed that Hindus who had been forced to convert to Islam could reconvert to Hinduism without facing the death penalty. Akbar was well-liked by Hindus, who sang religious hymns to him and his eulogies.
Akbar practised several Hindu customs. He celebrated
Akbar decreed that Hindus who had been forced to convert to Islam could reconvert to Hinduism without facing the death penalty. Akbar was well-liked by Hindus, who sang religious hymns to him and his eulogies.
Akbar practised several Hindu customs. He celebrated  Akbar's reign was chronicled extensively by his court historian
Akbar's reign was chronicled extensively by his court historian  The (), which literally means ''Book of Akbar'', is an official biographical account of Akbar written in Persian. It includes vivid and detailed descriptions of his life and times. The work was commissioned by Akbar, and written by
The (), which literally means ''Book of Akbar'', is an official biographical account of Akbar written in Persian. It includes vivid and detailed descriptions of his life and times. The work was commissioned by Akbar, and written by  She commanded a high rank in the imperial harem and was a recipient of many privileges. She was an intellectual woman who held a considerable influence in Akbar's court and is known as the prime driving force for Akbar's promotion of secularism and religious neutrality. She was also a great female patron of the architecture of her time. She died on 19 May 1623 in Agra and was buried in a grave close to her husband, Akbar, in Sikandra, Agra.
In 1562, Akbar married the former wife of Abdul Wasi, the son of Shaikh Bada, lord of Agra. Akbar was enamored with her beauty and ordered Abdul Wasi to divorce her. Another of his wives was Gauhar-un-Nissa Begum, the daughter of Shaikh Muhammad Bakhtiyar and the sister of Shaikh Jamal Bakhtiyar. Their dynasty was called Din Laqab they lived in Chandwar and Jalesar near Agra. He married the daughter of Jagmal Rathore, son of Rao Viramde of Merta in 1562.
His next marriage took place in 1564 to the daughter of Miran Mubarak Shah, the ruler of
She commanded a high rank in the imperial harem and was a recipient of many privileges. She was an intellectual woman who held a considerable influence in Akbar's court and is known as the prime driving force for Akbar's promotion of secularism and religious neutrality. She was also a great female patron of the architecture of her time. She died on 19 May 1623 in Agra and was buried in a grave close to her husband, Akbar, in Sikandra, Agra.
In 1562, Akbar married the former wife of Abdul Wasi, the son of Shaikh Bada, lord of Agra. Akbar was enamored with her beauty and ordered Abdul Wasi to divorce her. Another of his wives was Gauhar-un-Nissa Begum, the daughter of Shaikh Muhammad Bakhtiyar and the sister of Shaikh Jamal Bakhtiyar. Their dynasty was called Din Laqab they lived in Chandwar and Jalesar near Agra. He married the daughter of Jagmal Rathore, son of Rao Viramde of Merta in 1562.
His next marriage took place in 1564 to the daughter of Miran Mubarak Shah, the ruler of