|
Mont Saint-Grégoire
Mont Saint-Grégoire (height: ) is a mountain in the Montérégie region of southern Quebec, Canada. It is composed of essexite and syenite, strongly contrasting with the surrounding sedimentary rocks. The area around Mont Saint-Grégoire is known for its maple syrup production, as well as some wine production. The name was changed in 1923 from Mount Johnson . Geology It is thought that Mont Saint-Grégoire might be the deep extension of a vastly eroded ancient volcanic complex, which was probably active about 125 million years ago.A Hundred-Million Year History of the Corner Rise and New England Seamounts Retrieved on 2007-08-01 The mountain was created when the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mont-Saint-Grégoire, Quebec
Mont-Saint-Grégoire () is a municipality in the province of Quebec, Canada, located in the Regional County Municipality of Le Haut-Richelieu. The population as of the Canada 2011 Census was 3,086. Residents of Mont-Saint-Grégoire are called ''Grégoriens'' (''Grégoriennes'', fem.). History Mont-Saint-Grégoire was named for Gregory the Great, pope from 590 to 604, who was succeeded by Sabinian. Saint André Bessette was born in Mont-Saint-Grégoire. Demographics Population Language See also *List of municipalities in Quebec __FORCETOC__ Quebec is the second-most populous province in Canada with 8,501,833 residents as of 2021 and is the largest in land area at . For statistical purposes, the province is divided into 1,282 census subdivisions, which are m ... References External links * Mont-Saint-Grégoire official website {{DEFAULTSORT:Mont-Saint-Gregoire, Quebec Municipalities in Quebec Incorporated places in Le Haut-Richelieu Regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syenite
Syenite is a coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock with a general composition similar to that of granite, but deficient in quartz, which, if present at all, occurs in relatively small concentrations (< 5%). Some syenites contain larger proportions of components and smaller amounts of material than most granites; those are classed as being of intermediate composition. The extrusive equivalent of syenite is trachyte. Composition of syenites The[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Quebec Under 1000 Metres
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Montérégie
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
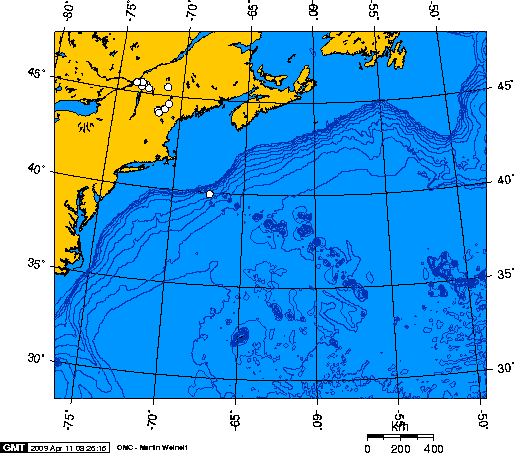
Great Meteor Hotspot Track
The New England hotspot, also referred to as the Great Meteor hotspot and sometimes the Monteregian hotspot, is a volcanic hotspot in the North Atlantic Ocean. It created the Monteregian Hills intrusions in Montreal and Montérégie, the White Mountains intrusions in New Hampshire, the New England and Corner Rise seamounts off the coast of North America, and the Seewarte Seamounts east of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge on the African Plate, the latter of which include its most recent eruptive center, the Great Meteor Seamount. The New England, Great Meteor, or Monteregian hotspot track has been used to estimate the movement of the North American Plate away from the African Plate from the early Cretaceous period to the present using the fixed hotspot reference frame. Geologic history The geologic history of the New England hotspot is the subject of much debate among geoscientists. The conventional opinion is that volcanic activity associated with the hotspot results from movement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England Hotspot
The New England hotspot, also referred to as the Great Meteor hotspot and sometimes the Monteregian hotspot, is a volcanic hotspot in the North Atlantic Ocean. It created the Monteregian Hills intrusions in Montreal and Montérégie, the White Mountains intrusions in New Hampshire, the New England and Corner Rise seamounts off the coast of North America, and the Seewarte Seamounts east of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge on the African Plate, the latter of which include its most recent eruptive center, the Great Meteor Seamount. The New England, Great Meteor, or Monteregian hotspot track has been used to estimate the movement of the North American Plate away from the African Plate from the early Cretaceous period to the present using the fixed hotspot reference frame. Geologic history The geologic history of the New England hotspot is the subject of much debate among geoscientists. The conventional opinion is that volcanic activity associated with the hotspot results from movement of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific Plate (which borders the plate to the west). It extends eastward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and westward to the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. The plate includes both continental and oceanic crust. The interior of the main continental landmass includes an extensive granitic core called a craton. Along most of the edges of this craton are fragments of crustal material called terranes, which are accreted to the craton by tectonic actions over a long span of time. It is thought that much of North America west of the Rocky Mountains is composed of such terranes. Boundaries The southern boundary with the Cocos Plate to the west and the Caribbean Plate to the east is a transform fault, represented by the Swan Islands Transform Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maple Syrup
Maple syrup is a syrup made from the sap of maple trees. In cold climates, these trees store starch in their trunks and roots before winter; the starch is then converted to sugar that rises in the sap in late winter and early spring. Maple trees are tapped by drilling holes into their trunks and collecting the sap, which is processed by heating to evaporate much of the water, leaving the concentrated syrup. Maple syrup was first made by the Indigenous peoples of North America. The practice was adopted by European settlers, who gradually changed production methods. Technological improvements in the 1970s further refined syrup processing. Virtually all of the world's maple syrup is produced in Canada and the United States. The Canadian province of Quebec is the largest producer, responsible for 70 percent of the world's output; Canadian exports of maple syrup in 2016 were C$487 million (about US$360 million), with Quebec accounting for some 90 percent of this total. Maple s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus (organic matter). The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies ( marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essexite
Essexite (), also called nepheline monzogabbro (), is a dark gray or black holocrystalline plutonic igneous rock. Its name is derived from the type locality in Essex County, Massachusetts, in the United States. Modern petrology identifies rocks according to mineralogical criteria. Utilising the IUGS QAPF diagram of Streckeisen (1974) "essexite" is more formally known as nepheline monzodiorite or nepheline monzogabbro depending on the ratio of orthoclase to plagioclase and the abundance of nepheline. Petrology In order to produce a magma composition suitable for forming essexite the partial melting of the source rocks must be restricted, generally to less than 10% partial melting. This favors producing a melt rich in large-ion lithophile elements (LILE) such as K, Ba, Rb, Cs, Sr. The source melts of essexites contain more aluminium and alkali ions than available silica tetrahedra, which is why essexites crystallise nepheline instead of plagioclase. Higher than normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu
Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu () is a city in eastern Montérégie in the Canadian province of Quebec, about southeast of Montreal. It is situated on the west bank of the Richelieu River at the northernmost navigable point of Lake Champlain. As of December 2019, the population of Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu was 98,036. History Historically, the city has been an important transportation hub. The first railway line in British North America connected it with La Prairie in 1836. It also hosts the annual International Balloon Festival of Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, a hot air balloon festival which attracts hundreds of tourists who come to see the hundreds of balloons in the sky each August. The Chambly Canal extends north along the west bank of the river and provides modern freight passage to Chambly and the St. Lawrence River. The canal has one lock near the downtown core of Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu. In the winter, the city builds a skating rink on the canal near the lock. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montérégie
Montérégie () is an administrative region in the southwest part of Quebec. It includes the cities of Boucherville, Brossard, Châteauguay, Longueuil, Saint-Hyacinthe, Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, Salaberry-de-Valleyfield and Vaudreuil-Dorion. The region had a population of 1,507,070 as of the 2016 census and a land area of , giving it a population density of 135.4 inhabitants/km2 (350 per sq. mi.). With approximately 18.5% of the province's population, it is the second most populous region of Quebec after Montreal. The majority of the population lives near the Saint Lawrence River, on the south shore of Montreal. Montérégie is known for its vineyards, orchards, panoramas, products, and the Monteregian mountains. The region is both urban (second in terms of population in Quebec) and rural. The regional economy is based on agriculture and the production of goods and services. Tourism also makes up a significant portion of the economy. History Jacques Cartier named Mont Roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)