Maple Syrup on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Maple syrup is a sweet
 Three species of maple (''Acer'') trees are predominantly used to produce maple syrup: the sugar maple (''
Three species of maple (''Acer'') trees are predominantly used to produce maple syrup: the sugar maple (''
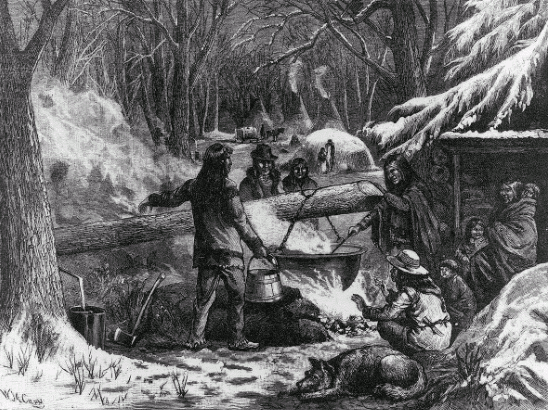
 A large number of technological changes took place during the 1970s. Plastic tubing systems that had been experimental since the early part of the century were perfected, allowing sap to flow directly from the tree to the evaporator house. Vacuum pumps were added to the tubing systems, and preheaters were developed to recycle heat lost in the steam. Producers developed reverse-osmosis machines to take a portion of water out of the sap before it was boiled, increasing processing efficiency.
Improvements in tubing and vacuum pumps, new filtering techniques, "supercharged" preheaters, and better storage containers have since been developed. Research continues on pest control and improved woodlot management. In 2009, researchers at the
A large number of technological changes took place during the 1970s. Plastic tubing systems that had been experimental since the early part of the century were perfected, allowing sap to flow directly from the tree to the evaporator house. Vacuum pumps were added to the tubing systems, and preheaters were developed to recycle heat lost in the steam. Producers developed reverse-osmosis machines to take a portion of water out of the sap before it was boiled, increasing processing efficiency.
Improvements in tubing and vacuum pumps, new filtering techniques, "supercharged" preheaters, and better storage containers have since been developed. Research continues on pest control and improved woodlot management. In 2009, researchers at the
 Maple syrup production is centred in northeastern North America; however, given the correct weather conditions, it can be made wherever suitable species of maple trees grow, such as New Zealand, where there are efforts to establish commercial production.
A maple syrup production farm is called a " sugarbush". Sap is often boiled in a " sugar house" (also known as a "sugar shack", "sugar cabin", "sugar shanty", or ''cabane à sucre''), a building
Maple syrup production is centred in northeastern North America; however, given the correct weather conditions, it can be made wherever suitable species of maple trees grow, such as New Zealand, where there are efforts to establish commercial production.
A maple syrup production farm is called a " sugarbush". Sap is often boiled in a " sugar house" (also known as a "sugar shack", "sugar cabin", "sugar shanty", or ''cabane à sucre''), a building
 In Canada, maple syrup was classified prior to 31 December 2014 by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) as one of three grades, each with several colour classes:
*Canada No. 1, including
**Extra light
**Light
**Medium
*No. 2 amber
*No. 3 dark or any other ungraded category
Producers in Ontario or Quebec may have followed either federal or provincial grading guidelines. Quebec's and Ontario's guidelines differed slightly from the federal:
*there were two "number" categories in Quebec
**Number 1, with four colour classes
**Number 2, with five colour classes
*As in Quebec, Ontario's producers had two "number" grades:
**Number 1, with three colour classes
**Number 2, with one colour class, which was typically referred to as "Ontario Amber" when produced and sold in that province only
A typical year's yield for a maple syrup producer will be about 25 to 30 per cent of each of the #1 colours, 10 per cent #2 amber, and 2 per cent #3 dark.
The United States used different grading standards — some states still do as they await state regulation. Maple syrup was divided into two major grades:
*Grade A:
**Light amber (sometimes known as fancy)
**Medium amber
**Dark amber
*Grade B.
In Massachusetts, the Grade B was renamed "Grade A Very Dark, Strong Taste"
The Vermont Agency of Agriculture Food and Markets used a similar grading system of colour, and is roughly equivalent, especially for lighter syrups, but using letters: "AA", "A", etc. The Vermont grading system differed from the US system in maintaining a slightly higher standard of product density (measured on the
In Canada, maple syrup was classified prior to 31 December 2014 by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) as one of three grades, each with several colour classes:
*Canada No. 1, including
**Extra light
**Light
**Medium
*No. 2 amber
*No. 3 dark or any other ungraded category
Producers in Ontario or Quebec may have followed either federal or provincial grading guidelines. Quebec's and Ontario's guidelines differed slightly from the federal:
*there were two "number" categories in Quebec
**Number 1, with four colour classes
**Number 2, with five colour classes
*As in Quebec, Ontario's producers had two "number" grades:
**Number 1, with three colour classes
**Number 2, with one colour class, which was typically referred to as "Ontario Amber" when produced and sold in that province only
A typical year's yield for a maple syrup producer will be about 25 to 30 per cent of each of the #1 colours, 10 per cent #2 amber, and 2 per cent #3 dark.
The United States used different grading standards — some states still do as they await state regulation. Maple syrup was divided into two major grades:
*Grade A:
**Light amber (sometimes known as fancy)
**Medium amber
**Dark amber
*Grade B.
In Massachusetts, the Grade B was renamed "Grade A Very Dark, Strong Taste"
The Vermont Agency of Agriculture Food and Markets used a similar grading system of colour, and is roughly equivalent, especially for lighter syrups, but using letters: "AA", "A", etc. The Vermont grading system differed from the US system in maintaining a slightly higher standard of product density (measured on the
Maple Syrup Quality Control Manual, University of Maine
UVM Center for Digital Initiatives: The Maple Research Collection by the Vermont Agricultural Experiment Station
US Food and Drug Administration description of table syrup
{{DEFAULTSORT:Maple syrup American cuisine Articles containing video clips Canadian cuisine Condiments Cuisine of New York (state) Cuisine of Quebec
syrup
In cooking, syrup (less commonly sirup; from ; , beverage, wine and ) is a condiment that is a thick, viscous liquid consisting primarily of a Solution (chemistry), solution of sugar in water, containing a large amount of dissolved sugars but ...
made from the sap of maple
''Acer'' is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the soapberry family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated si ...
trees. In cold climates, these trees store starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
in their trunks and roots before winter; the starch is then converted to sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecul ...
that rises in the sap in late winter and early spring. Maple trees are tapped by drilling holes into their trunks and collecting the sap, which is processed by heating to evaporate much of the water, leaving the concentrated syrup.
Maple syrup was first made by the Indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
of Northeastern North America. The practice was adopted by European settlers, who gradually changed production methods. Technological improvements in the 1970s further refined syrup processing. Almost all of the world's maple syrup is produced in Canada and the United States.
Maple syrup is graded based on its colour and taste. Sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
is the most prevalent sugar in maple syrup. In Canada, syrups must be made exclusively from maple sap to qualify as maple syrup and must also be at least 66 per cent sugar. In the United States, a syrup must be made almost entirely from maple sap to be labelled as "maple", though states such as Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
and New York have more restrictive definitions.
Maple syrup is often used as a condiment for pancakes, waffles, French toast
French toast is a Dish (food), dish of sliced bread soaked in beaten eggs as food, eggs and often milk or cream, then pan-fried. Alternative names and variants include eggy bread, Bombay toast, gypsy toast, and poor knights (of Windsor).''Oxfo ...
, oatmeal
Oatmeal is a preparation of oats that have been dehusked, steamed, and flattened, or a coarse flour of hulled oat grains ( groats) that have either been milled (ground), rolled, or steel-cut. Ground oats are also called white oats. Steel- ...
, or porridge. It is also used as an ingredient in baking and as a sweetener or flavouring agent.
Sources
 Three species of maple (''Acer'') trees are predominantly used to produce maple syrup: the sugar maple (''
Three species of maple (''Acer'') trees are predominantly used to produce maple syrup: the sugar maple (''Acer saccharum
''Acer saccharum'', the sugar maple, is a species of flowering plant in the soapberry and lychee family Sapindaceae. It is native to the hardwood forests of eastern Canada and the eastern United States. Sugar maple is best known for being the p ...
''), the black maple ('' A. nigrum''), and the red maple ('' A. rubrum''), because of the high sugar content (roughly two to five per cent) in the sap of these species. The black maple is included as a subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
or variety in a more broadly viewed concept of ''A. saccharum'', the sugar maple, by some botanists. Of these, the red maple has a shorter season because it buds earlier than sugar and black maples, which alters the flavour of the sap.
A few other species of maple are also sometimes used as sources of sap for producing maple syrup, including the box elder or Manitoba maple (''Acer negundo''), the silver maple (''A. saccharinum''), and the bigleaf maple (''A. macrophyllum''). In the Southeastern United States, Florida sugar maple ('' Acer floridanum'') is occasionally used for maple syrup production.
Similar syrups may also be produced from walnut, birch, or palm trees, among other sources.
History
Indigenous peoples
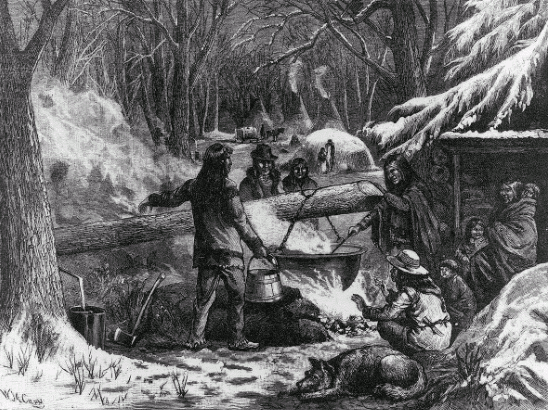
Indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
living in northeastern North America were the first groups known to have produced maple syrup and maple sugar. According to Indigenous oral traditions, as well as archaeological evidence, maple tree sap was being processed into syrup long before Europeans arrived in the region. There are no authenticated accounts of how maple syrup production and consumption began, but various legends exist; one of the most popular involves maple sap being used in place of water to cook venison served to a chief. Indigenous tribes developed rituals around syrup-making, celebrating the Sugar Moon (the first full moon of spring) with a Maple Dance. Many aboriginal dishes replaced the salt traditional in European cuisine with maple syrup.
The Algonquians recognized maple sap as a source of energy and nutrition. At the beginning of the spring thaw, they made V-shaped incisions in tree trunks; they then inserted reeds or concave pieces of bark to run the sap into clay buckets or tightly woven birch-bark baskets. The maple sap was concentrated first by leaving it exposed to the cold temperatures overnight and disposing of the layer of ice that formed on top. Following that, the sap was transported by sled to large fires where it was boiled in clay pots to produce maple syrup. Often, multiple pots were used in conjunction, with the liquid being transferred between them as it grew more concentrated. Contrary to popular belief, syrup was not typically produced by dropping heated stones into wooden bowls, especially in northeast North America where Indigenous cultures had been using clay pots for thousands of years. However, modern and historic sources contain evidence that hot stones may have occasionally been used in the upper Midwest and Canada, where hollowed out logs and birchbark containers typically replaced clay pots.
European colonists
In the early stages of European colonization in northeastern North America, local Indigenous peoples showed the arriving colonists how to tap the trunks of certain types of maples during the spring thaw to harvest the sap. André Thevet, the "Royal Cosmographer of France", wrote aboutJacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier (; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French maritime explorer from Brittany. Jacques Cartier was the first Europeans, European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, wh ...
drinking maple sap during his Canadian voyages. By 1680, European settlers and fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals h ...
rs were involved in harvesting maple products. However, rather than making incisions in the bark, the Europeans used the method of drilling tapholes in the trunks with augers. Prior to the 19th century, processed maple sap was used primarily as a source of concentrated sugar, in both liquid and crystallized-solid form, as cane sugar had to be imported from the West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
.
Maple sugaring parties typically began to operate at the start of the spring thaw in regions of woodland with sufficiently large numbers of maples. Syrup makers first bored holes in the trunks, usually more than one hole per large tree; they then inserted wooden spouts into the holes and hung a wooden bucket from the protruding end of each spout to collect the sap. The buckets were commonly made by cutting cylindrical segments from a large tree trunk and then hollowing out each segment's core from one end of the cylinder, creating a seamless, watertight container. Sap filled the buckets, and was then either transferred to larger holding vessels (barrels, large pots, or hollowed-out wooden logs), often mounted on sledges or wagons pulled by draft animals, or carried in buckets or other convenient containers. The sap-collection buckets were returned to the spouts mounted on the trees, and the process was repeated for as long as the flow of sap remained "sweet". The specific weather conditions of the thaw period were, and still are, critical in determining the length of the sugaring season. As the weather continues to warm, a maple tree's normal early spring biological process eventually alters the taste of the sap, making it unpalatable, perhaps due to an increase in amino acids.
The boiling process was very time-consuming. The harvested sap was transported back to the party's base camp, where it was then poured into large vessels (usually made from metal) and boiled down to achieve the desired concentration. The sap was usually transported using large barrels pulled by horses or oxen to a central collection point, where it was processed either over a fire built out in the open or inside a shelter built for that purpose (the "sugar shack").
Since 1850
Around the time of theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
(1861–1865), syrup makers started using large, flat sheet metal pans as they were more efficient for boiling than heavy, rounded iron kettles, because of a greater surface area for evaporation. Around this time, cane sugar replaced maple sugar as the dominant sweetener in the US; as a result, producers focused marketing efforts on maple syrup. The first evaporator, used to heat and concentrate sap, was patented in 1858. In 1872, an evaporator was developed that featured two pans and a metal arch or firebox, which greatly decreased boiling time. Around 1900, producers bent the tin that formed the bottom of a pan into a series of flues, which increased the heated surface area of the pan and again decreased boiling time. Some producers also added a finishing pan, a separate batch evaporator, as a final stage in the evaporation process.
Buckets began to be replaced with plastic bags, which allowed people to see at a distance how much sap had been collected. Syrup producers also began using tractors to haul vats of sap from the trees being tapped (the sugar bush) to the evaporator. Some producers adopted motor-powered tappers and metal tubing systems to convey sap from the tree to a central collection container, but these techniques were not widely used. Heating methods also diversified: modern producers use wood, oil, natural gas, propane, or steam to evaporate sap. Modern filtration methods were perfected to prevent contamination of the syrup.
 A large number of technological changes took place during the 1970s. Plastic tubing systems that had been experimental since the early part of the century were perfected, allowing sap to flow directly from the tree to the evaporator house. Vacuum pumps were added to the tubing systems, and preheaters were developed to recycle heat lost in the steam. Producers developed reverse-osmosis machines to take a portion of water out of the sap before it was boiled, increasing processing efficiency.
Improvements in tubing and vacuum pumps, new filtering techniques, "supercharged" preheaters, and better storage containers have since been developed. Research continues on pest control and improved woodlot management. In 2009, researchers at the
A large number of technological changes took place during the 1970s. Plastic tubing systems that had been experimental since the early part of the century were perfected, allowing sap to flow directly from the tree to the evaporator house. Vacuum pumps were added to the tubing systems, and preheaters were developed to recycle heat lost in the steam. Producers developed reverse-osmosis machines to take a portion of water out of the sap before it was boiled, increasing processing efficiency.
Improvements in tubing and vacuum pumps, new filtering techniques, "supercharged" preheaters, and better storage containers have since been developed. Research continues on pest control and improved woodlot management. In 2009, researchers at the University of Vermont
The University of Vermont and State Agricultural College, commonly referred to as the University of Vermont (UVM), is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Burlington, Vermont, United States. Foun ...
unveiled a new type of tap that prevents backflow of sap into the tree, reducing bacterial contamination and preventing the tree from attempting to heal the bore hole. Experiments show that it may be possible to use saplings in a plantation instead of mature trees, dramatically boosting productivity per acre. As a result of the smaller tree diameter, milder diurnal temperature swings are needed for the tree to freeze and thaw, which enables sap production in milder climatic conditions outside of northeastern North America.
Processing
Open pan evaporation methods have been streamlined since colonial days, but remain basically unchanged. Sap must first be collected and boiled down to obtain syrup. Maple syrup is made by boiling between 20 and 50 volumes of sap (depending on its concentration) over an open fire until 1 volume of syrup is obtained, usually at a temperature over the boiling point of water. As the boiling point of water varies with changes in air pressure, the correct value for pure water is determined at the place where the syrup is being produced each time evaporation is begun and periodically throughout the day. Syrup can be boiled entirely over one heat source or can be drawn off into smaller batches and boiled at a more controlled temperature. Defoamers are often added during boiling. Boiling the syrup is a tightly controlled process, which ensures appropriate sugar content. Syrup boiled too long will eventually crystallize, whereas under-boiled syrup will be watery, and will quickly spoil. The finished syrup has a density of 66° on theBrix scale
Degrees Brix (symbol °Bx) is a measure of the dissolved solids in a liquid, based on its specific gravity, and is commonly used to measure dissolved sugar content of a solution. One degree Brix is 1 gram of sucrose solute dissolved in 100 grams ...
(a hydrometric scale used to measure sugar solutions). The syrup is then filtered to remove precipitated "sugar sand", crystals made up largely of sugar and calcium malate. These crystals are not toxic, but create a "gritty" texture in the syrup if not filtered out.
In addition to open pan evaporation methods, many large producers use the more fuel efficient reverse osmosis procedure to separate the water from the sap. Smaller producers can also use batchwise recirculating reverse osmosis, with the most energy-efficient operation taking the sugar concentration to 25% prior to boiling.
The higher the sugar content of the sap, the smaller the volume of sap is needed to obtain the same amount of syrup. To yield 1 unit of syrup, sap at 1.5 per cent sugar content will require 57 units, while sap at 3.5 per cent sugar content only needs 25 units of sap. The sap's sugar content is highly variable and will fluctuate even within the same tree.
The filtered syrup is graded and packaged while still hot, usually at a temperature of or greater. The containers are turned over after being sealed to sterilize the cap with the hot syrup. Packages can be made of metal, glass, or coated plastic, depending on volume and target market. The syrup can also be heated longer and further processed to create a variety of other maple products, including maple sugar, maple butter or cream, and maple candy or taffy.
Off-flavours
Off-flavours can sometimes develop during the production of maple syrup, resulting from contaminants in the boiling apparatus (such asdisinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than ...
s), microorganisms
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from antiquity, with an early attestation in ...
, fermentation
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduce ...
products, metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
lic can flavours, and "buddy sap", an off-flavour occurring late in the syrup season when tree budding has begun. In some circumstances, it is possible to remove off-flavours through processing.
Production
louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is a national art museum in Paris, France, and one of the most famous museums in the world. It is located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement of Paris, 1st arron ...
d at the top to vent the steam from the boiling sap.
Maples are usually tapped beginning at 30 to 40 years of age. Each tree can support between one and three taps, depending on its trunk diameter. The average maple tree will produce of sap per season, up to per day. This is roughly equal to seven per cent of its total sap. Tap seasons typically happen during late winter and spring and usually last for four to eight weeks, though the exact dates depend on the weather, location, and climate.
During the day, sucrose stored in the roots for the winter rises through the trunk as sugary sap. A hole is bored into the trunk of the tree to allow the sap to flow out of a spile that is tapped in the hole. The taps are left in place for the season, and the sap flows during the day when the temperature is above freezing. Some producers also tap in autumn, though this practice is less common than spring tapping. Maples can continue to be tapped for sap until they are over 100 years old.
Climate change is dramatically impacting the production of maple syrup. Increased temperatures in late winter/early spring causes the season for maple sap collection to shift earlier in the year, with increased summer temperatures causing a decrease in sugar content in sap, and drought/heavy rainfall impacting forest ecosystems.
Commerce
Until the 1930s, the United States produced most of the world's maple syrup. Today, after rapid growth in the 1990s, Canada produces more than 80 per cent of the world's maple syrup, producing about in 2016. Within Canada,Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
is the largest producer, responsible for 72 per cent of the world's output; Canadian exports of maple syrup in 2016 were C$487 million (about US$
The United States dollar (Currency symbol, symbol: Dollar sign, $; ISO 4217, currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and International use of the U.S. dollar, several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introdu ...
360 million), with Quebec accounting for some 90 per cent of this total. In 2023, Canada exported $376 million of maple syrup to the United States, $47.8 million to Germany, $31.6 million to France, and $30.2 million to the UK, exporting to 68 countries in total.
, Quebec accounts for 91.6 per cent of maple syrup produced in Canada, followed by New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
at 4.7 per cent and Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
at 3.4 per cent. However, 96.8 per cent of exported Canadian maple syrup originated from Quebec, whereas 2.6 per cent of exported syrup originated from New Brunswick, and the remaining 0.6 per cent from all other provinces. Ontario holds the most maple syrup farms in Canada outside of Quebec, with 389 maple syrup producers in 2021. This is followed by New Brunswick, with 114 maple syrup producers; and Nova Scotia, with 39 maple syrup producers.
As of 2016, Quebec had some 7,300 producers working with 13,500 farmers, collectively making over of syrup. Production in Quebec is controlled through a supply management system, with producers receiving quota allotments from the government sanctioned Quebec Maple Syrup Producers (QMSP; ), which also maintains reserves of syrup, although there is a black-market trade in Quebec product. In 2017, the QMSP mandated increased output of maple syrup production, attempting to establish Quebec's dominance in the world market.
The Canadian provinces of Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
and Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
produce maple syrup using the sap of the box elder or Manitoba maple (''Acer negundo''). In 2011, there were 67 maple syrup producers in Manitoba and 24 in Saskatchewan. A Manitoba maple tree's yield is usually less than half that of a similar sugar maple tree. Manitoba maple syrup has a slightly different flavour from sugar-maple syrup, because it contains less sugar and the tree's sap flows more slowly. British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
is home to a growing maple sugar industry using sap from the bigleaf maple, which is native to the West Coast of the United States and Canada. In 2011, there were 82 maple syrup producers in British Columbia.
Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
has long been the largest US producer, with a record produced in 2022. In 2019 it led with over , followed by New York with and Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
with . Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
, Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
, New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
, Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
and Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
all produced marketable quantities of maple syrup.
Maple syrup has been produced on a small scale in some other countries, notably Japan and South Korea. However, in South Korea in particular, it is traditional to consume maple sap, called ''gorosoe'', instead of processing it into syrup.
Markings
Under Canadian maple product regulations, containers of maple syrup must include the words "maple syrup", its grade name and net quantity inlitre
The litre ( Commonwealth spelling) or liter ( American spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metres (m3). A ...
s or millilitres, on the main display panel with a minimum font size of 1.6 mm. If the maple syrup is of Canada Grade A level, the name of the colour class must appear on the label in both English and French. Also, the lot number or production code, and either: (1) the name and address of the sugar bush establishment, packing or shipper establishment, or (2) the first dealer and the registration number of the packing establishment, must be labelled on any display panel other than the bottom.
Grades
Following an effort from the International Maple Syrup Institute (IMSI) and many maple syrup producer associations, both Canada and the United States have altered their laws regarding the classification of maple syrup to be uniform. Whereas in the past each state or province had their own laws on the classification of maple syrup, now those laws define a unified grading system. This had been a work in progress for several years, and most of the finalization of the new grading system was made in 2014. The Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) announced in the '' Canada Gazette'' on 28 June 2014 that rules for the sale of maple syrup would be amended to include new descriptors, at the request of the IMSI. As of 31 December 2014, the CFIA and as of 2 March 2015, theUnited States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an executive department of the United States federal government that aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and producti ...
(USDA) Agricultural Marketing Service issued revised standards intended to harmonize Canadian and United States regulations on the classification of maple syrup as follows:
*Grade A
**Golden colour and delicate taste
**Amber colour and rich taste
**Dark colour and robust taste
**Very dark colour and strong taste
*Processing grade
*Substandard
As long as maple syrup does not have an off-flavour, is of a uniform colour, and is free from turbidity and sediment, it can be labelled as one of the A grades. If it exhibits any problems, it does not meet Grade A requirements, and then must be labelled as "processing grade" maple syrup and may not be sold in containers smaller than . If maple syrup does not meet the requirements of processing-grade maple syrup (including a fairly characteristic maple taste), it is classified as substandard.
This grading system was accepted and made law by most maple-producing states and provinces, and became compulsory in Canada as of 13 December 2016. Vermont, in an effort to "jump-start" the new grading regulations, adopted the new grading system as of 1 January 2014, after the grade changes passed the US Senate and House in 2013. Maine passed a bill to take effect as soon as both Canada and the United States adopted the new grades. In New York, the new grade changes became law on 1 January 2015. New Hampshire did not require legislative approval and so the new grade laws became effective as of 16 December 2014, and producer compliance was required as of 1 January 2016.
Golden and amber grades typically have a milder flavour than dark and very dark, which are both dark and have an intense maple flavour. The darker grades of syrup are used primarily for cooking and baking, although some specialty dark syrups are produced for table use. Syrup harvested earlier in the season tends to yield a lighter colour. With the new grading system, the classification of maple syrup depends ultimately on its internal transmittance at 560 nm wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
through a 10 mm sample. Golden must have 75 per cent or more transmittance, amber must have 50.0 to 74.9 per cent transmittance, dark must have 25.0 to 49.9 per cent transmittance, and very dark is any product having less than 25.0 per cent transmittance.
Old grading system
Baumé scale
The Baumé scale is a pair of hydrometer scales developed by French pharmacist Antoine Baumé in 1768 to measure density of various liquids. The unit of the Baumé scale has been notated variously as ''degrees Baumé'', ''B°'', ''Bé°'' and simp ...
). New Hampshire maintained a similar standard, but not a separate state grading scale. The Vermont-graded product had 0.9 per cent more sugar and less water in its composition than US-graded. One grade of syrup not for table use, called commercial or Grade C, was also produced under the Vermont system.
Packing regulations
In Canada, the packing of maple syrup must follow the "Packing" conditions stated in the maple products regulations, or utilize the equivalent Canadian or imported grading system. As stated in the maple products regulations, Canadian maple syrup can be classified as "Canadian Grade A" and "Canadian Processing Grade". Any maple syrup container under these classifications should be filled to at least 90% of the bottle size while still containing the net quantity of syrup product as stated on the label. Every container of maple syrup must be new if it has a capacity of 5 litres or less or is marked with a grade name. Every container of maple sugar must also be new if it has a capacity of less than 5 kg or is either exported out of Canada or conveyed from one province to another. Each maple syrup product must be verified clean if it follows a grade name or if it is exported out of the province in which it was originally manufactured.Nutrition
The basic ingredient in maple syrup is the sap from thexylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue (biology), tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem; both of these are part of the vascular bundle. The basic function of the xylem is to transport water upward from the roots to parts o ...
of sugar maple or various other species of maple trees. It consists primarily of sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
and water, with small amounts of the monosaccharides glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
and fructose
Fructose (), or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and gal ...
from the inverted sugar created in the boiling process.
In a 100g amount, maple syrup provides 260 calorie
The calorie is a unit of energy that originated from the caloric theory of heat. The large calorie, food calorie, dietary calorie, kilocalorie, or kilogram calorie is defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one liter o ...
s and is composed of 32 per cent water by weight, 67 per cent carbohydrates
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ma ...
(90 per cent of which are sugars), and no appreciable protein or fat (table). Maple syrup is generally low in overall micronutrient content, although manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
and riboflavin
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is a vitamin found in food and sold as a dietary supplement. It is essential to the formation of two major coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide. These coenzymes are involved in ...
are at high levels along with moderate amounts of zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
and calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
(right table). It also contains trace amounts of amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s which increase in content as sap flow occurs.
Maple syrup contains a wide variety of polyphenol
Polyphenols () are a large family of naturally occurring phenols. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include phenolic acids, flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as ...
s and volatile organic compound
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic compounds that have a high vapor pressure at room temperature. They are common and exist in a variety of settings and products, not limited to Indoor mold, house mold, Upholstery, upholstered furnitur ...
s, including vanillin, hydroxybutanone, lignans, propionaldehyde
Propionaldehyde or propanal is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CHO. It is the 3-carbon aldehyde. It is a colourless, flammable liquid with a pungent and fruity odour. It is produced on a large scale industrially.
Production
Propiona ...
, and numerous organic acids. It is not yet known exactly all compounds responsible for the distinctive flavour of maple syrup, although primary flavour-contributing compounds are maple furanone (5-ethyl-3-hydroxy-4-methyl-2(5H)-furanone), strawberry furanone, and maltol. New compounds have been identified in maple syrup, one of which is quebecol, a natural phenolic compound created when the maple sap is boiled to create syrup. Its sweetness derives from a high content of sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
(99% of total sugars). Its brown colour – a significant factor in the appeal and quality grading of maple syrup – develops during thermal evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
.
One author described maple syrup as "a unique ingredient, smooth- and silky-textured, with a sweet, distinctive flavour – hints of caramel with overtones of toffee will not do – and a rare colour, amber set alight. Maple flavour is, well, maple flavour, uniquely different from any other." Agriculture Canada has developed a "flavour wheel" that details 91 unique flavours that can be present in maple syrup. These flavours are divided into 13 families: vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus ''Vanilla (genus), Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the flat-leaved vanilla (''Vanilla planifolia, V. planifolia'').
''Vanilla'' is not Autogamy, autogamous, so pollination ...
, burnt, milky, fruity, floral, spicy, foreign (deterioration or fermentation), foreign (environment), maple, confectionery, plant (herbaceous), plant (forest, humus or cereals), and plant (ligneous). These flavours are evaluated using a procedure similar to wine tasting. Other culinary experts praise its unique flavour. Environmental factors, including weather and soil type
A soil type is a taxonomic unit in soil science. All soils that share a certain set of well-defined properties form a distinctive soil type. Soil type is a technical term of soil classification, the science that deals with the systematic categ ...
, impact flavor.
Maple syrup and its various artificial imitations are widely used as toppings for pancakes, waffles, and French toast
French toast is a Dish (food), dish of sliced bread soaked in beaten eggs as food, eggs and often milk or cream, then pan-fried. Alternative names and variants include eggy bread, Bombay toast, gypsy toast, and poor knights (of Windsor).''Oxfo ...
in North America. They can also be used to flavour a variety of foods, including fritter
A fritter is a portion of meat, seafood, fruit, vegetables, or other ingredients which have been Batter (cooking), battered or breading, breaded, or just a portion of dough without further ingredients, that is deep-frying, deep-fried. Fritters ar ...
s, ice cream, hot cereal, fresh fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
, bacon
Bacon is a type of Curing (food preservation), salt-cured pork made from various cuts of meat, cuts, typically the pork belly, belly or less fatty parts of the back. It is eaten as a side dish (particularly in breakfasts), used as a central in ...
, and sausages. It is also used as sweetener for granola
Granola is a food consisting of rolled oats, nuts, seeds, honey or other sweeteners such as brown sugar, and sometimes puffed rice, that is usually baked until crisp, toasted and golden brown. The mixture is stirred while baking to avoid b ...
, applesauce
Apple sauce is a purée (not necessarily served as a true sauce) made of apples. It can be made with peeled or unpeeled apples and can be spiced or sweetened. Apple sauce is inexpensive and is widely consumed in North America and some parts of E ...
, baked beans
Baked beans is a Dish (food), dish traditionally containing white Phaseolus vulgaris, common beans that are parboiling, parboiled and then baking, baked in sauce at low temperature for a lengthy period. Canned baked beans are not baked, but ar ...
, candied sweet potatoes, winter squash, cakes, pies, breads, tea, coffee, and hot toddies.
Imitations
In Canada, maple syrup must be made entirely from maple sap, and syrup must have a density of 66° on the Brix scale to be marketed as maple syrup. In the United States, maple syrup must be made almost entirely from maple sap, although small amounts of substances such as salt may be added. Labelling laws prohibit imitation syrups from having "maple" in their names unless the finished product contains 10 per cent or more of natural maple syrup. Table syrup, also known as pancake syrup and waffle syrup, is often used as a substitute for maple syrup. Table syrups are mostly made usingcorn syrup
Corn syrup is a food syrup that is made from the starch of corn/maize and contains varying amounts of sugars: glucose, maltose and higher oligosaccharides, depending on the grade. Corn syrup is used in foods to soften Mouthfeel, texture, add vol ...
and high-fructose corn syrup, giving them a less complex and more artificial flavour compared to maple syrup. In the United States, consumers generally prefer imitation syrups, likely because of the significantly lower cost and sweeter flavour; they typically cost about , whereas authentic maple syrup costs as of 2015.
In 2016, maple syrup producers from nine US states petitioned the Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) to regulate labelling of products containing maple syrup or using the word "maple" in manufactured products, indicating that imitation maple products contained insignificant amounts of natural maple syrup. In September 2016, the FDA published a consumer advisory to carefully inspect the ingredient list of products labelled as "maple".
Cultural significance
Maple products are considered emblematic of Canada, and are frequently sold in tourist shops and airports as souvenirs from Canada. The sugar maple's leaf has come to symbolize Canada, and is depicted on the country's flag. Several US states, including West Virginia, New York, Vermont, and Wisconsin, have the sugar maple as their state tree. A scene of sap collection is depicted on the Vermont state quarter, issued in 2001. Maple syrup and maple sugar were used during the American Civil War and by abolitionists in the years before the war because most cane sugar and molasses were produced by Southernslaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
. Because of food rationing during the Second World War, people in the northeastern United States were encouraged to stretch their sugar rations by sweetening foods with maple syrup and maple sugar, and recipe books were printed to help housewives employ this alternative source.
See also
* Canadian cuisine * Great Canadian Maple Syrup Heist * List of foods made from maple * List of syrups * Mapleine * TreacleReferences
Notes
Cited works
* * * *Further reading
* * *External links
Maple Syrup Quality Control Manual, University of Maine
UVM Center for Digital Initiatives: The Maple Research Collection by the Vermont Agricultural Experiment Station
US Food and Drug Administration description of table syrup
{{DEFAULTSORT:Maple syrup American cuisine Articles containing video clips Canadian cuisine Condiments Cuisine of New York (state) Cuisine of Quebec
Syrup
In cooking, syrup (less commonly sirup; from ; , beverage, wine and ) is a condiment that is a thick, viscous liquid consisting primarily of a Solution (chemistry), solution of sugar in water, containing a large amount of dissolved sugars but ...
Forestry in Canada
Forestry in the United States
Indigenous cuisine in Canada
Maritime culture
New England cuisine
Non-timber forest products
Syrup
Tree tapping
Native American cuisine