|
Bárðarbunga
Bárðarbunga (, alternative name Veiðivötn), is an active and productive stratovolcano located under Vatnajökull in Vatnajökull National Park which is Iceland's most extensive glacier. The second highest mountain in Iceland, above sea level, Bárðarbunga is also part of the Bárðarbunga-Veiðivötn volcanic system that is approximately long and wide. Bárðarbunga erupted in late August 2014, the eruption style effusive, which is common in Iceland, but had not been seen for a few years. Lava covered the surrounding landscape northwest of the Vatnajökull glacier. Description Bárðarbunga is a subglacial stratovolcano and central volcano under the ice cap of Vatnajökull glacier in the Vatnajökull National Park in Iceland. It is one of the six volcanic systems under Vatnajökull. The central volcano has a rim that rises to about above sea level, making it the second highest mountain in Iceland, being lower than Hvannadalshnjúkur. The caldera is about , u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2014–2015 Eruption Of Bárðarbunga
The 2014–2015 eruption of Bárðarbunga was a Hawaiian eruption in the Bárðarbunga volcanic system in Iceland, that began on 29 August 2014, and ended on 27 February 2015. The eruption emitted large volumes of sulphur dioxide and impacted air quality in Iceland. There was no effect on flights outside of the immediate vicinity due to a lack of a significant emission of volcanic ash. The eruption took place in the lava field of Holuhraun northeast of the Bárðarbunga caldera proper. Overview Seismic activity surrounding the Bárðarbunga volcano gradually increased from 2007 to 2014, with a brief pause during the nearby eruption at Grímsvötn in 2011. By the summer of 2014 activity reached a level similar to that just before the Grímsvötn eruption. In May 2014 there was a small earthquake sequence of about 200 events. GPS data recorded a displacement of 14 cm in the region since the beginning of the phase of unrest, compared to a figure of 2 cm over the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1996 Eruption Of Gjálp
Gjálp () is a hyaloclastite ridge (tindar) in Iceland under the Vatnajökull glacier shield. Its present form resulted from an eruption series in 1996 and it is probably part of the Grímsvötn volcanic system.Snæbjörn Guðmundsson: ''Vegavísir um jarðfræði Íslands.'' Reykjavík 2015, p. 280-281 However, not all the scientists were of this opinion, as seismic studies are consistent with a lateral dike intrusion at about depth from Bárðarbunga being the trigger event. This does not exclude a shallower secondary intrusion from Grímsvötn being important in the subaerial eruption itself. Importance The eruption was of importance, because it was for the first time that a subglacial eruption under a thick ice cover as well as the connected jökulhlaup could be observed and analyzed by modern technique. Geography Eruption location The subglacial eruption fissure is to be found in the northwest corner of Vatnajökull ice cap more or less halfway between the central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loki-Fögrufjöll
The Loki-Fögrufjöll ( volcanic system; also known as Hamarinn after its central volcano or Lokahryggur ) is a subglacial volcano under the Vatnajökull glacier. The subglacial volcano is found within the Bárðarbunga fissure volcanic system, but is outside the caldera of Bárðarbunga itself. Earthquake swarms associated with the volcano are separate in time and place from other swarms in the Bárðarbunga system. The fissure swarm extending south-west towards Torfajökull has not had recent earthquakes or erupted in the Holocene. A geothermally and seismically active ridge called Lokahryggur or the Loki Ridge, extends eastward from Hamarinn under the ice to where in 1996 the 1996 eruption of Gjálp, Gjálp volcanic fissure erupted between Bárðarbunga and Grímsvötn and produced a large jökulhlaup. The last confirmed eruption was in 1910 when tephra was erupted, but the system may also have had subglacial eruptions in 1986, 1991, 2006, 2008 and 2011. See also * Volcan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torfajökull
Torfajökull ( Icelandic for "Torfi's glacier"; ) is a rhyolitic stratovolcano, with a large caldera (central volcano) capped by a glacier of the same name and associated with a complex of subglacial volcanoes. Torfajökull last erupted in 1477 and consists of the largest area of silicic extrusive rocks in Iceland. This is now known to be due to a VEI 5 eruption 55,000 years ago. Geography The volcano is located north of Mýrdalsjökull and south of Þórisvatn Lake, Iceland. To its south-west is the volcano and glacier of Tindfjallajökull and almost directly to its west is the volcano of Hekla. Adjacent to the southern edge of its glacier of Torfajökull it has a peak of but the south-eastern caldera margin also extends to the glacier of Kaldaklofsjökull which is on the western slopes of a peak called Háskerðingur that is high. Laufafell dome at is at the north-western edge of the Torfajökull volcanic system and almost halfway between Hekla and the glacier of Torfajö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grímsvötn
Grímsvötn (; ''vötn'' = "waters", singular: ) is an active volcano with a (partially subglacial) fissure system located in Vatnajökull National Park, Iceland. The central volcano is completely subglacial and located under the northwestern side of the Vatnajökull ice cap. The subglacial caldera is at , at an elevation of . Beneath the caldera is the magma chamber of the Grímsvötn volcano. Grímsvötn is a basaltic volcano which has the highest eruption frequency of all the volcanoes in Iceland. It has a southwest-northeast-trending fissure system. The massive climate-impacting Laki fissure eruption of 1783–1784 took place in a part of the same Grímsvötn-Laki volcanic system. Grímsvötn was erupting at the same time as Laki during 1783, but continued to erupt until 1785. Because most of the volcanic system lies underneath Vatnajökull, most of its eruptions have been subglacial and the interaction of magma and meltwater from the ice causes phreatomagmatic explosive acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungnafellsjökull
Tungnafellsjökull (, "''Tungna-fells glacier''" or "tongue-fells glacier") is a icecap glacier upon a volcano of the same name in Iceland. The volcano is also known as Vonarskarð. Geography It has an elevation of and is located north–west of the area of the Vatnajökull glacier under the Bárðarbunga central volcano. To its west is the volcano of Hofsjökull. The Tungnafellsjökull volcanic system is located in a desert area that is fairly inaccessible, with little vegetation, and large areas of sand and sandy ridges. Three glacial rivers drain the Tungnafellsjökull glacier. Geology It is the eastern most part of the Mid-Iceland belt and thus at the north–eastern corner of the Hreppar microplate. There are two central volcanoes, with the most southern being called Hágöngur and the most northern called here Tungnafellsjökull. Tungnafellsjökull has two calderas, with the western most Tungnafellsjökull caldera being topped by a glacier and the eastern most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Þjórsá Lava
The Great Þjórsá Lava ( Icelandic: ''Þjórsárhraunið mikla'' ) is the largest lava flow in Iceland (by both area and volume) and the largest lava flow that is known to have erupted in a single eruption in the Holocene. Þjórsá Lava has a total volume of more than , covering approximately . The Þjórsá Lava does not appear on the surface until downstream of its identified eruptive area. Geography In the lowlands of South Iceland the lava has overflown wide areas, covering the districts Landsveit, Gnúpverjahreppur, Skeið and Flói. The main rivers of South Iceland, Þjórsá and Hvítá/Ölfusá, stream along the borders of the lava to the east and west and the long beach between the river mouths is formed by the lava. The sea level seems to have been around lower than today when the lava was erupted. Along with the rising sea level the ocean has transgressed the lava front so its border line is submerged several hundreds of metres off-shore and its littoral zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the structural integrity of such a chamber, greatly diminishing its capacity to support its own roof and any substrate or rock resting above. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a Volcanic crater, crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur over the course of a century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times within a given window of 100 years. Only eight caldera-forming collapses are known to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
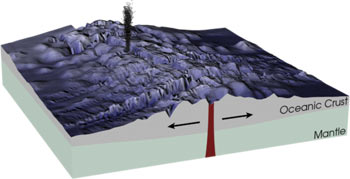
Fissure Vent
A fissure vent, also known as a volcanic fissure, eruption fissure or simply a fissure, is a linear volcanic vent through which lava erupts, usually without any explosive activity. The vent is often a few metres wide and may be many kilometres long. Fissure vents can cause large flood basalts which run first in lava channels and later in lava tubes. After some time, the eruption tends to become focused at one or more spatter cones. Volcanic cones and their craters that are aligned along a fissure form a crater row. Small fissure vents may not be easily discernible from the air, but the crater rows (see Laki) or the canyons (see Eldgjá) built up by some of them are. The dikes that feed fissures reach the surface from depths of a few kilometers and connect them to deeper magma reservoirs, often under volcanic centers. Fissures are usually found in or along rifts and rift zones, such as Iceland and the East African Rift. Fissure vents are often part of the structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vatnajökull National Park
Vatnajökull National Park ( ) is one of three national parks in Iceland, and is the largest one. It encompasses all of Vatnajökull glacier and extensive surrounding areas. These include the national parks previously existing at Skaftafell in the southwest and Jökulsárgljúfur in the north. The unique qualities of Vatnajökull National Park are primarily its great variety of landscape features, created by the combined forces of rivers, glacial ice, and volcanic and geothermal activity. The park spans 14% of the country's area and is Europe's second largest national park in terms of area after Yugyd Va in the Ural Mountains of Russia. The glacier itself is the largest in Europe at . In 2019 the park was enlarged to the north. On 5 July 2019 Vatnajökull National Park was inscribed as a World Heritage Site. History Vatnajökull National Park was established on 7 June 2008. When established, the park covered an area of 12,000 km2, but with later additions of Lakagíga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Settlement Of Iceland
The settlement of Iceland ( ) is generally believed to have begun in the second half of the ninth century, when Norsemen, Norse settlers migrated across the North Atlantic. The reasons for the migration are uncertain: later in the Middle Ages Icelanders themselves tended to cite civil strife brought about by the ambitions of the Norway, Norwegian king Harald I of Norway, but modern historians focus on deeper factors, such as a shortage of arable land in Scandinavia. Unlike Great Britain and Ireland, Iceland was unsettled land and could be claimed without conflict with existing inhabitants. On the basis of by Ari Þorgilsson, and , histories dating from the twelfth and thirteenth centuries and providing a wealth of detail about the settlement, the years 870 and 874 have traditionally been considered the first years of settlement. However, these sources are largely unreliable in the details they provide about the settlement, and recent research focuses more heavily on archaeological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitive Case
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can also serve purposes indicating other relationships. For example, some verbs may feature arguments in the genitive case; and the genitive case may also have adverbial uses (see adverbial genitive). The genitive construction includes the genitive case, but is a broader category. Placing a modifying noun in the genitive case is one way of indicating that it is related to a head noun, in a genitive construction. However, there are other ways to indicate a genitive construction. For example, many Afroasiatic languages place the head noun (rather than the modifying noun) in the construct state. Possessive grammatical constructions, including the possessive case, may be regarded as subsets of the genitive construction. For example, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |