|
Grímsvötn
Grímsvötn (; ''vötn'' = "waters", singular: ) is an active volcano with a (partially subglacial) fissure system located in Vatnajökull National Park, Iceland. The central volcano is completely subglacial and located under the northwestern side of the Vatnajökull ice cap. The subglacial caldera is at , at an elevation of . Beneath the caldera is the magma chamber of the Grímsvötn volcano. Grímsvötn is a basaltic volcano which has the highest eruption frequency of all the volcanoes in Iceland. It has a southwest-northeast-trending fissure system. The massive climate-impacting Laki fissure eruption of 1783–1784 took place in a part of the same Grímsvötn-Laki volcanic system. Grímsvötn was erupting at the same time as Laki during 1783, but continued to erupt until 1785. Because most of the volcanic system lies underneath Vatnajökull, most of its eruptions have been subglacial and the interaction of magma and meltwater from the ice causes phreatomagmatic explosive acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vatnajökull
Vatnajökull ( Icelandic pronunciation: , literally "Glacier of Lakes"; sometimes translated as Vatna Glacier in English) is the largest and most voluminous ice cap in Iceland, and the second largest in area in Europe after the Severny Island ice cap of Novaya Zemlya. It is in the south-east of the island, covering approximately 10% of the country. Size With an area of 7,700 km2, Vatnajökull is the second largest ice cap in Europe by volume (about 3,000 km3) and area (after the still larger Severny Island ice cap of Novaya Zemlya, Russia, which is in the extreme northeast of Europe). On 7 June 2008, it became a part of the Vatnajökull National Park. The average thickness of the ice is , with a maximum thickness of . Iceland's highest peak, Hvannadalshnúkur (), as part of the Öræfajökull, is in the southern periphery of Vatnajökull, near Skaftafell. Peaks Hrútsfjallstindar is a series of Icelandic peaks rising from Vatnajökull between Svínafellsjök ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hringvegur
Route 1 or the Ring Road ( or ) is a national road in Iceland that circles the entire country. As a major trunk route, it is considered to be the most important piece of transport infrastructure in Iceland as it connects the majority of towns together in the most densely populated areas of the country. Economically, it carries a large proportion of goods traffic as well as tourist traffic. The total length of the road is , making it the longest ring road in Europe. The road was completed in 1974, coinciding with the 1,100th anniversary of the country's settlement when the longest bridge in Iceland, crossing the Skeiðará river in the southeast, was opened. Previously, vehicles intending to travel between southern settlements, e.g. Vík to Höfn, had to travel north of the country through Akureyri, making the opening a major transport improvement to the country. Many popular tourist attractions in Iceland, such as the Seljalandsfoss and Skógafoss waterfalls, Dyrhólaey cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grímsvötn Volcano Showing Plume - May 22
Grímsvötn (; ''vötn'' = "waters", singular: ) is an active volcano with a (partially subglacial) fissure system located in Vatnajökull National Park, Iceland. The central volcano is completely subglacial and located under the northwestern side of the Vatnajökull ice cap. The subglacial caldera is at , at an elevation of . Beneath the caldera is the magma chamber of the Grímsvötn volcano. Grímsvötn is a basaltic volcano which has the highest eruption frequency of all the volcanoes in Iceland. It has a southwest-northeast-trending fissure system. The massive climate-impacting Laki fissure eruption of 1783–1784 took place in a part of the same Grímsvötn-Laki volcanic system. Grímsvötn was erupting at the same time as Laki during 1783, but continued to erupt until 1785. Because most of the volcanic system lies underneath Vatnajökull, most of its eruptions have been Subglacial eruption, subglacial and the interaction of magma and meltwater from the ice causes phreatomagm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
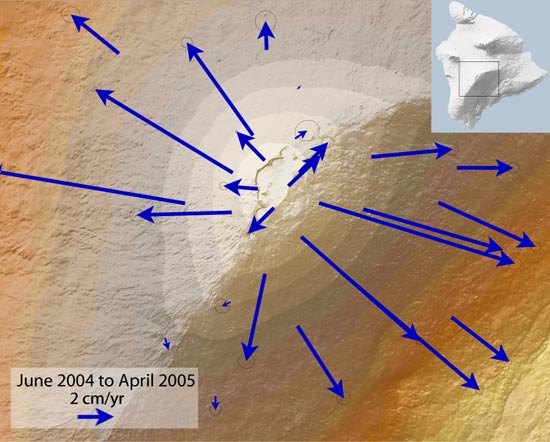
Deformation (volcanology)
In volcanology, deformation refers to the change in the shape of a volcano or the surrounding landscape due to the movement of magma. This can be in the form of inflation, which is a response to pressurization, or deflation, which is a response to depressurization. Inflation is represented by swelling of the ground surface, a volcanic edifice, or a subsurface magma body. It can be caused by magma accumulation, exsolution of Volatile (astrogeology), volatiles, Geothermal energy, geothermal processes, heating, and tectonic Compression (geology), compression. Deflation is represented by shrinking of the ground surface, a volcanic edifice, or a subsurface magma body. It can be caused by magma withdrawal (related to intrusion or Types of volcanic eruptions, eruption), volatile escape, thermal contraction, phase changes during crystallization, and Extensional tectonics, tectonic extension. Deformation is a key indicator of pre-eruptive unrest at many active volcanoes, but deformation si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Tremor
A harmonic tremor is a sustained release of seismic and infrasonic energy typically associated with the underground movement of magma, the venting of volcanic gases from magma, or both in volcanoes, and with repetitive stick-slip or other impulsive activity in non-volcanic systems. It is a long-duration release of seismic energy, often containing distinct spectral lines. Volcanic tremor often precedes or accompanies a volcanic eruption. Being a long-duration continuous signal from a temporally extended source tremor contrasts distinctly with transient and often impulsive sources of seismic radiation typically associated with earthquakes and explosions. Nonvolcanic, episodic tremor at plate boundaries (particularly in subduction zones) has been attributed to swarms of long-period earthquakes and is distinguished by the term episodic tremor and slip (ETS) and may occur during slow earthquakes. Iceberg impacts with the seafloor or other icebergs can also generate distinct iceberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, produced during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer to all explosive eruption products (correctly referred to as '' tephra''), including particles larger than 2 mm. Volcanic ash is formed during explosive volcanic eruptions when dissolved gases in magma expand and escape violently into the atmosphere. The force of the gases shatters the magma and propels it into the atmosphere where it solidifies into fragments of volcanic rock and glass. Ash is also produced when magma comes into contact with water during phreatomagmatic eruptions, causing the water to explosively flash to steam leading to shattering of magma. Once in the air, ash is transported by wind up to thousands of kilometres away. Due to its wide dispersal, ash can have a number of impacts on society, including animal a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Photo Grímsvötn Nov
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the United States's civil space program, aeronautics research and space research. Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the lunar Artemis program. NASA's science division is focused on better understanding Earth through the Earth Observing System; advancing heliophysics through the efforts of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |