pubic symphysis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the
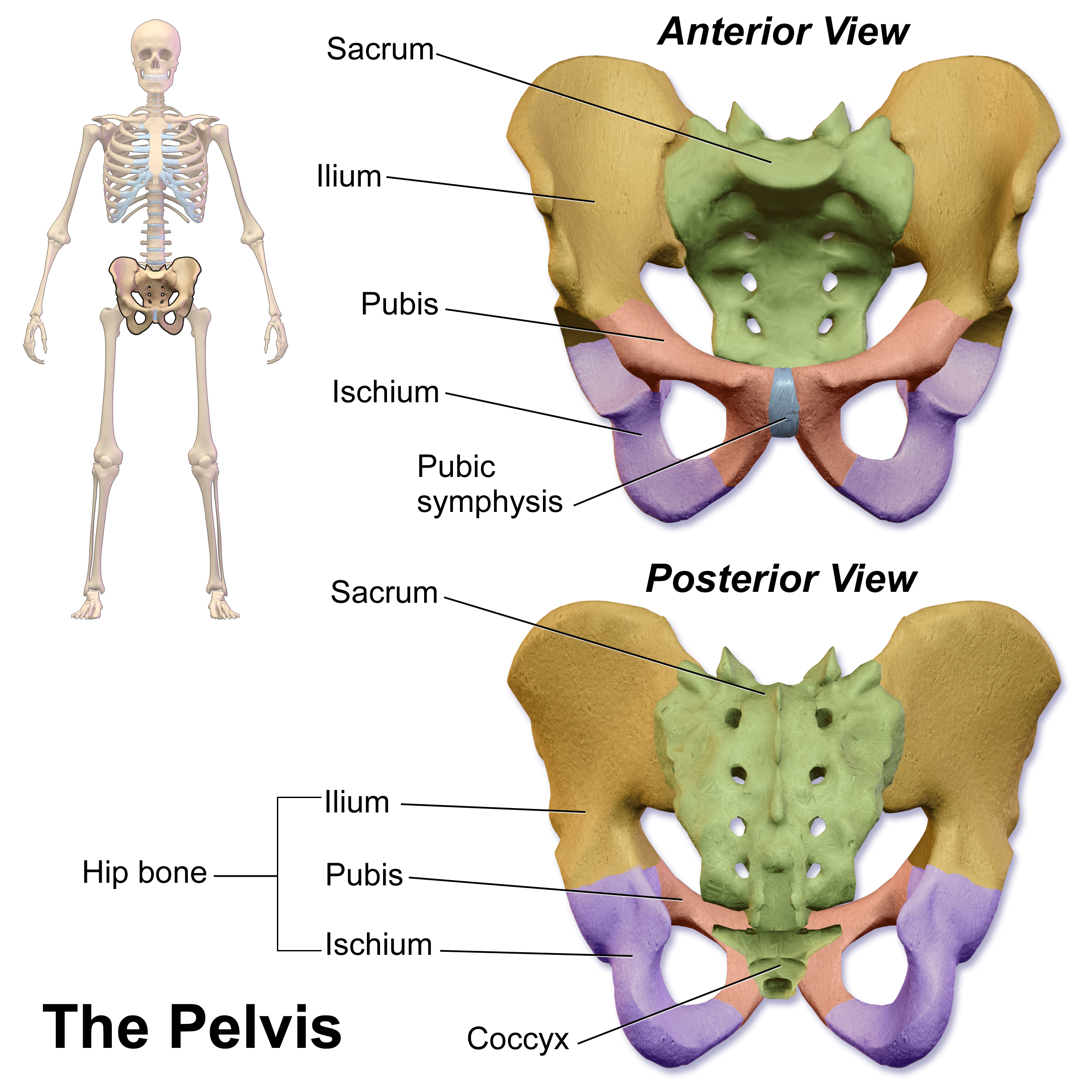 The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by
The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by
File:Gray1228.png, Median sagittal section of male pelvis
File:Gray1230.png, Median sagittal section of female pelvis
File:Slide3ADA.JPG, Anterior view of the body pelvis from a dissection. Pubic symphysis anteriorly.
Pelvic Instability Network Support (PINS)
* – "Major Joints of the Lower Extremity – hip and sacrum (anterior view)" * – "The Male Pelvis: Hemisection of the Male Pelvis" * {{DEFAULTSORT:Pubic Symphysis Pelvis Joints
urinary bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters ...
. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is close to the clitoris
The clitoris ( or ) is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the o ...
. In most adults it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth.
The name comes from the Greek word ''symphysis'', meaning 'growing together'.
Structure
 The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by
The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of ...
and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is avascular, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disease. The ends of both pubic bones are covered by a thin layer of hyaline cartilage attached to the fibrocartilage. The fibrocartilaginous disk is reinforced by a series of ligaments. These ligaments cling to the fibrocartilaginous disk to the point that fibers intermix with it.
Two such ligaments are the superior pubic ligament and the inferior pubic ligament, which provide the most stability; the anterior and posterior ligaments are weaker. The strong and thicker superior ligament is reinforced by the tendons of the rectus abdominis muscle, the abdominal external oblique muscle, the gracilis muscle, and by muscles of the hip. The superior pubic ligament connects together the two pubic bones superiorly, extending laterally as far as the pubic tubercles. The inferior ligament in the pubic arch is also known as the arcuate pubic ligament or subpubic ligament; it is a thick, triangular arch of ligamentous fibers, connecting together the two pubic bones below, and forming the upper boundary of the pubic arch. Above, it is blended with the interpubic fibrocartilaginous lamina; laterally, it is attached to the inferior rami of the pubic bones; below, it is free, and is separated from the fascia of the urogenital diaphragm by an opening through which the deep dorsal vein of the penis passes into the pelvis.
Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of ...
is composed of small, chained bundles of thick, clearly defined, type I collagen fibers. This fibrous connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue ...
bundles have cartilage cells between them; these cells to a certain extent resemble tendon cells. The collagenous fibers are usually placed in an orderly arrangement parallel to tension on the tissue. It has a low content of glycosaminoglycans (2% of dry weight). Glycosaminoglycans are long, unbranched polysaccharides
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with w ...
(relatively complex carbohydrates) consisting of repeating disaccharide
A disaccharide (also called a double sugar or ''biose'') is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides are joined by glycosidic linkage. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides are simple sugars soluble in water. Three common examples are sucrose, ...
units. Fibrocartilage does not have a surrounding perichondrium. Perichondrium surrounds the cartilage of developing bone; it has a layer of dense, irregular connective tissue and functions in the growth and repair of cartilage.
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is the white, shiny gristle at the end of long bones. This cartilage has poor healing potential, and efforts to induce it to repair itself frequently end up with a similar, but poorer fibrocartilage.Development
In the newborn, the symphysis pubis is 9–10 mm in width, with thick cartilaginous end-plates. By mid-adolescence the adult size is achieved. During adulthood the end-plates decrease in width to a thinner layer. Degeneration of the symphysis pubis accompanies aging and postpartum. Women have a greater thickness of this pubic disc which allows more mobility of the pelvic bones, hence providing a greater diameter of pelvic cavity duringchildbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births glo ...
.
Function
Analysis of the pelvis shows the skinny regions function as arches, transferring the weight of the upright trunk from the sacrum to the hips. The symphysis pubis connects these two weight-bearing arches, and the ligaments that surround this pelvic region maintain the mechanical integrity. The main motions of the symphysis pubis are superior/inferior glide and separation/compression. The functions of the joint are to absorb shock during walking and allow delivery of a baby.Clinical significance
Injury
The pubic symphysis widens slightly when the legs are stretched far apart. In sports where these movements are often performed, the risk of a pubic symphysis blockage is high, in which case, after completion of the movement, the bones at the symphysis do not realign correctly and can get jammed in a dislocated position. The resulting pain can be severe, especially when further strain is put upon the affected joint. In most cases, the joint can only be successfully reduced into its normal position by a trained medical professional.Disease
Metabolic diseases, such as renal osteodystrophy, produce widening, while ochronosis results in calcific deposits in the symphysis. Inflammatory diseases, such asankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hi ...
, result in bony fusion of the symphysis. Osteitis pubis, the most common inflammatory disease in this area, is treated with anti-inflammatory medication and rest. Degenerative joint disease of the symphysis, which can cause groin pain, results from instability or from abnormal pelvic mechanics.
'' Symphysiolysis'' is separation or slipping of the symphysis. It has been estimated to occur in 0.2% of pregnancies.
Pregnancy
Duringpregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
in the human, hormones such as relaxin remodel this ligamentous capsule allowing the pelvic bones to be more flexible for delivery. The gap of the symphysis pubis, normally is 4–5 mm but during pregnancy there will be an increase of at least 2–3 mm, therefore, it is considered that a total width of up to 9 mm between the two bones is normal for a pregnant woman. The symphysis pubis separates to some degree during childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births glo ...
. In some women this separation can become a diastasis of the symphysis pubis. The diastasis could be the result of a rapid birth, or a forceps delivery, or may be a prenatal condition. A diastasis of the symphysis pubis is a cause of pelvic girdle pain (PGP). Overall, about 45% of all pregnant women and 25% of all women postpartum suffer from PGP.
Symphysiotomy
Symphysiotomy is a surgical procedure in which the cartilage of the pubic symphysis is divided to widen the pelvis allowing childbirth when there is a mechanical problem. It allows the safe delivery of the fetus where Caesarean section is not an option. Symphysiotomy is suggested for woman in isolated areas experiencing obstructed labor where other medical intervention is unavailable. This practice was carried out in Europe before the introduction of the Caesarean section. Historically, during obstructed labor, the skull of the fetus was also, at least occasionally, crushed in order to further facilitate the delivery.Society and culture
Use in forensic anthropology
Pubic symphyses have importance in the field of forensic anthropology, as they can be used to estimate the age of adult skeletons. Throughout life, the surfaces are worn at a fairly predictable rate. By examining the wear of the pubic symphysis, it is possible to estimate the age of the person at death.Additional images
See also
References
External links
Pelvic Instability Network Support (PINS)
* – "Major Joints of the Lower Extremity – hip and sacrum (anterior view)" * – "The Male Pelvis: Hemisection of the Male Pelvis" * {{DEFAULTSORT:Pubic Symphysis Pelvis Joints