|
Synovium
The synovial membrane (also known as the synovial stratum, synovium or stratum synoviale) is a specialized connective tissue that lines the inner surface of capsules of synovial joints and tendon sheath. It makes direct contact with the fibrous membrane on the outside surface and with the synovial fluid lubricant on the inside surface. In contact with the synovial fluid at the tissue surface are many rounded macrophage-like synovial cells (type A) and also type B cells, which are also known as fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS). Type A cells maintain the synovial fluid by removing wear-and-tear debris. As for the FLS, they produce hyaluronan, as well as other extracellular components in the synovial fluid. Structure The synovial membrane is variable but often has two layers: * The outer layer, or subintima, can be of almost any type of connective tissue – fibrous (dense collagenous type), adipose (fatty; e.g. in intra-articular fat pads) or areolar (loose collagenous t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast-like Synoviocyte
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) represent a specialised cell type located inside joints in the synovium. These cells play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes in normal tissues The inner lining of the joint consists of the synovium (also called the synovial membrane), a thin layer located between the joint capsule and the joint cavity. The word "synovium" is derived from the word "synovia" (or synovial fluid), which is a clear, viscous fluid produced by the synovium, and its main purpose is to reduce friction between the joint cartilages during movement. Synovium is also important to maintain proper joint function by providing the structural support and supply of the necessary nutrients to the surrounding cartilage. Synovial membrane is divided into two compartments – the outer layer (subintima) and the inner layer (intima). The inner layer is mainly composed of two cell types, specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synovial Fluid
Synovial fluid, also called synovia, elp 1/sup> is a viscous, non-Newtonian fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints. With its egg white–like consistency, the principal role of synovial fluid is to reduce friction between the articular cartilage of synovial joints during movement. Synovial fluid is a small component of the transcellular fluid component of extracellular fluid. Structure The inner membrane of synovial joints is called the synovial membrane and secretes synovial fluid into the joint cavity. Synovial fluid is an ultrafiltrate from plasma, and contains proteins derived from the blood plasma and proteins that are produced by cells within the joint tissues. The fluid contains hyaluronan secreted by fibroblast-like cells in the synovial membrane, lubricin (proteoglycan 4; PRG4) secreted by the surface chondrocytes of the articular cartilage and interstitial fluid filtered from the blood plasma. This fluid forms a thin layer (roughly 50 μm) at the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligament
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the: * Peritoneal ligament: a fold of peritoneum or other membranes. * Fetal remnant ligament: the remnants of a fetal tubular structure. * Periodontal ligament: a group of fibers that attach the cementum of teeth to the surrounding alveolar bone. Ligaments are similar to tendons and fasciae as they are all made of connective tissue. The differences among them are in the connections that they make: ligaments connect one bone to another bone, tendons connect muscle to bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. These are all found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments cannot usually be regenerated naturally; however, there are periodontal ligament stem cells located near the periodontal ligament which are involved in the adult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Badger
Badgers are short-legged omnivores in the family Mustelidae (which also includes the otters, wolverines, martens, minks, polecats, weasels, and ferrets). Badgers are a polyphyletic rather than a natural taxonomic grouping, being united by their squat bodies and adaptions for fossorial activity. All belong to the caniform suborder of carnivoran mammals. The fifteen species of mustelid badgers are grouped in four subfamilies: four species of Melinae (genera ''Meles'' and ''Arctonyx'') including the European badger, five species of Helictidinae (genus ''Melogale'') or ferret-badger, the honey badger or ratel Mellivorinae (genus ''Mellivora''), and the American badger Taxideinae (genus ''Taxidae''). Badgers include the most basal mustelids; the American badger is the most basal of all, followed successively by the ratel and the Melinae; the estimated split dates are about 17.8, 15.5 and 14.8 million years ago, respectively. The two species of Asiatic stink badge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ball And Socket
The ball-and-socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of axes, which have one common center. This enables the joint to move in many directions. An enarthrosis is a special kind of spheroidal joint in which the socket covers the sphere beyond its equator.Platzer, Werner (2008) ''Color Atlas of Human Anatomy'', Volume 1p.28/ref> Examples Examples of this form of articulation are found in the hip, where the round head of the femur (ball) rests in the cup-like acetabulum (socket) of the pelvis; and in the shoulder joint, where the rounded upper extremity of the humerus (ball) rests in the cup-like glenoid fossa (socket) of the shoulder blade.And the phalanges (toes, fingers)Introduction to Joints: Synovial Joints - Ball and Socket Joints (The shoulder also includes a sternoclavicular joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinge
A hinge is a mechanical bearing that connects two solid objects, typically allowing only a limited angle of rotation between them. Two objects connected by an ideal hinge rotate relative to each other about a fixed axis of rotation: all other translations or rotations being prevented, and thus a hinge has one degree of freedom. Hinges may be made of flexible material or of moving components. In biology, many joints function as hinges, like the elbow joint. History Ancient remains of stone, marble, wood, and bronze hinges have been found. Some date back to at least Ancient Egypt. In Ancient Rome, hinges were called cardō and gave name to the goddess Cardea and the main street Cardo. This name cardō lives on figuratively today as "the chief thing (on which something turns or depends)" in words such as ''cardinal''. According to the OED, the English word hinge is related to '' hang''. Door hinges ; Barrel hinge: A barrel hinge consists of a sectional barrel (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replacement Joint
Replacement arthroplasty (from Greek ''arthron'', joint, limb, articulate, + ''plassein'', to form, mould, forge, feign, make an image of), or joint replacement surgery, is a procedure of orthopedic surgery in which an arthritic or dysfunctional joint surface is replaced with an orthopedic prosthesis. Joint replacement is considered as a treatment when severe joint pain or dysfunction is not alleviated by less-invasive therapies. It is a form of arthroplasty, and is often indicated from various joint diseases, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Joint replacement surgery has become more common, with knees and hips replaced most often. About 773,000 Americans had a hip or knee replaced in 2009.Joint Replacement Surgery and You. (April, 2009) In ''Arthritis, Musculoskeletal and Skin Disease online''. Retrieved from http://www.niams.nih.gov/#. Uses Shoulder For shoulder replacement, there are a few major approaches to access the shoulder joint. The first is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
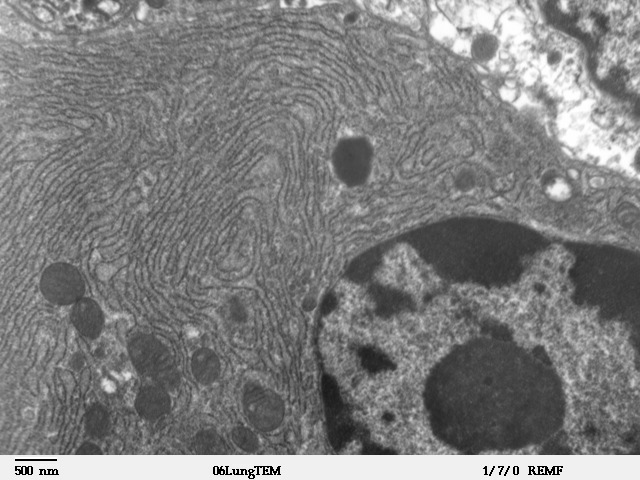
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus. It was identified in 1897 by the Italian scientist Camillo Golgi and was named after him in 1898. Discovery Owing to its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was discovered in 1898 by Italian physician Camillo Golgi during an investigation of the nervous system. After first observing it under h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubricin
Proteoglycan 4 or lubricin is a proteoglycan that in humans is encoded by the ''PRG4'' gene. It acts as a joint/ boundary lubricant. Function Lubricin is present in synovial fluid and on the surface (superficial layer) of articular cartilage and therefore plays an important role in joint lubrication and synovial homeostasis. When first isolated, cartilage lubricin was called "superficial zone protein" (SZP). Due to the discovery that the 32-kDa amino terminal fragment of lubricin could stimulate in-vitro megakaryocyte growth, the gene responsible for the expression of lubricin was initially called "megakaryocyte-stimulating factor" (MSF). However, Lubricin, MSF, and SZP are now collectively known as Proteoglycan 4 (hence PRG4 for the gene nomenclature). The evidence that lubricin is actually a proteoglycan is not solid. The expression of lubricin has also been detected and the protein localized in tendon, meniscus, lung, liver, heart, bone, ligament, muscle, and skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |