Nanotechnology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an
 The term "nano-technology" was first used by
The term "nano-technology" was first used by  Second, fullerenes were discovered in 1985 by Harry Kroto, Richard Smalley, and Robert Curl, who together won the 1996
Second, fullerenes were discovered in 1985 by Harry Kroto, Richard Smalley, and Robert Curl, who together won the 1996
 Several phenomena become pronounced as the size of the system decreases. These include statistical mechanical effects, as well as quantum mechanical effects, for example the "
Several phenomena become pronounced as the size of the system decreases. These include statistical mechanical effects, as well as quantum mechanical effects, for example the "
They have constructed at least three distinct molecular devices whose motion is controlled from the desktop with changing voltage: a nanotube nanomotor, a molecular actuator, and a nanoelectromechanical relaxation oscillator. See nanotube nanomotor for more examples. An experiment indicating that positional molecular assembly is possible was performed by Ho and Lee at


 There are several important modern developments. The
There are several important modern developments. The

 As of August 21, 2008, the
As of August 21, 2008, the
"People in the US and the UK show strong similarities in their attitudes toward nanotechnologies"
. Nanotechnology Today. Experts, including director of the Woodrow Wilson Center's Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies David Rejeski, have testified that successful commercialization depends on adequate oversight, risk research strategy, and public engagement.
. BBC. 2012-08-24
What is Nanotechnology?
(A Vega/BBC/OU Video Discussion). {{Authority control 1960 introductions 1985 introductions Articles containing video clips Emerging technologies 1986 neologisms 1970s neologisms
 Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, a ...
ic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. A more generalized description of nanotechnology was subsequently established by the National Nanotechnology Initiative, which defined nanotechnology as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers
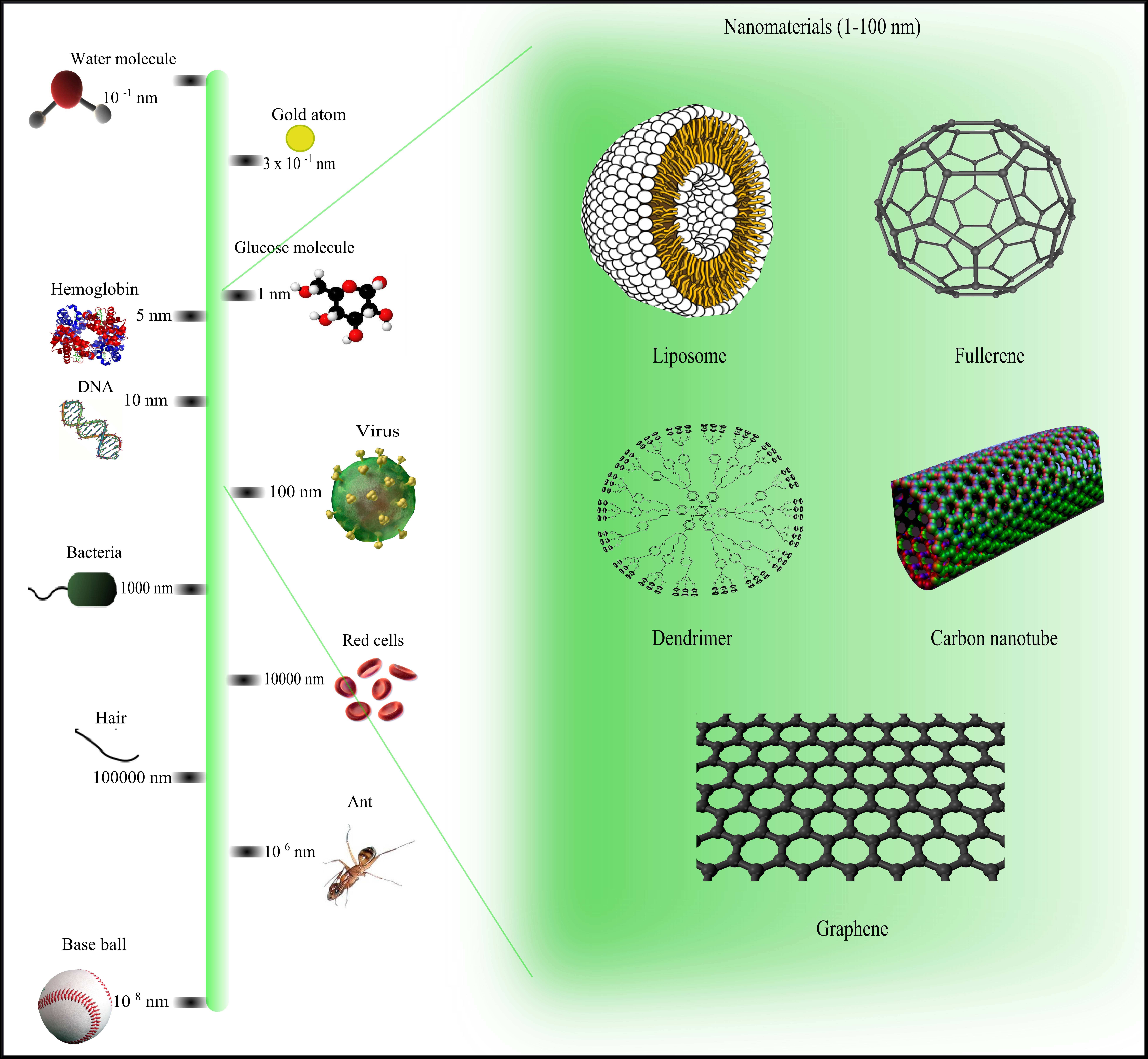
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re ...
(nm). This definition reflects the fact that quantum mechanical effects are important at this quantum-realm scale, and so the definition shifted from a particular technological goal to a research category inclusive of all types of research and technologies that deal with the special properties of matter which occur below the given size threshold. It is therefore common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as " nanoscale technologies" to refer to the broad range of research and applications whose common trait is size.
Nanotechnology as defined by size is naturally broad, including fields of science as diverse as surface science
Surface science is the study of physical and chemical phenomena that occur at the interface of two phases, including solid– liquid interfaces, solid– gas interfaces, solid–vacuum interfaces, and liquid– gas interfaces. It includes th ...
, organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J ...
, molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and phys ...
, semiconductor physics
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. ...
, energy storage, engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
, microfabrication
Microfabrication is the process of fabricating miniature structures of micrometre scales and smaller. Historically, the earliest microfabrication processes were used for integrated circuit fabrication, also known as " semiconductor manufacturing ...
, and molecular engineering. The associated research and applications are equally diverse, ranging from extensions of conventional device physics to completely new approaches based upon molecular self-assembly, from developing new materials with dimensions on the nanoscale to direct control of matter on the atomic scale.
Scientists currently debate the future implications of nanotechnology. Nanotechnology may be able to create many new materials and devices with a vast range of applications, such as in nanomedicine, nanoelectronics, biomaterial
A biomaterial is a substance that has been engineered to interact with biological systems for a medical purpose, either a therapeutic (treat, augment, repair, or replace a tissue function of the body) or a diagnostic one. As a science, biomateria ...
s energy production, and consumer products. On the other hand, nanotechnology raises many of the same issues as any new technology, including concerns about the toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subs ...
and environmental impact of nanomaterials, and their potential effects on global economics, as well as speculation about various doomsday scenarios
A global catastrophic risk or a doomsday scenario is a hypothetical future event that could damage human well-being on a global scale, even endangering or destroying modern civilization. An event that could cause human extinction or permanen ...
. These concerns have led to a debate among advocacy groups and governments on whether special regulation of nanotechnology is warranted.
Origins
The concepts that seeded nanotechnology were first discussed in 1959 by renowned physicist Richard Feynman in his talk '' There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom'', in which he described the possibility of synthesis via direct manipulation of atoms. The term "nano-technology" was first used by
The term "nano-technology" was first used by Norio Taniguchi
was a professor of Tokyo University of Science. He coined the term '' nano-technology'' in 1974
N. Taniguchi, "On the Basic Concept of 'Nano-Technology'," Proc. Intl. Conf. Prod. Eng.
Tokyo, Part II, Japan Society of Precision Engineering, 1974. ...
in 1974, though it was not widely known. Inspired by Feynman's concepts, K. Eric Drexler
Kim Eric Drexler (born April 25, 1955) is an American engineer best known for studies of the potential of molecular nanotechnology (MNT), from the 1970s and 1980s. His 1991 doctoral thesis at Massachusetts Institute of Technology was revised and ...
used the term "nanotechnology" in his 1986 book '' Engines of Creation: The Coming Era of Nanotechnology'', which proposed the idea of a nanoscale "assembler" which would be able to build a copy of itself and of other items of arbitrary complexity with atomic control. Also in 1986, Drexler co-founded The Foresight Institute (with which he is no longer affiliated) to help increase public awareness and understanding of nanotechnology concepts and implications.
The emergence of nanotechnology as a field in the 1980s occurred through convergence of Drexler's theoretical and public work, which developed and popularized a conceptual framework for nanotechnology, and high-visibility experimental advances that drew additional wide-scale attention to the prospects of atomic control of matter. In the 1980s, two major breakthroughs sparked the growth of nanotechnology in the modern era. First, the invention of the scanning tunneling microscope in 1981 which provided unprecedented visualization of individual atoms and bonds, and was successfully used to manipulate individual atoms in 1989. The microscope's developers Gerd Binnig
Gerd Binnig (; born 20 July 1947) is a German physicist. He is most famous for having won the Nobel Prize in Physics jointly with Heinrich Rohrer in 1986 for the invention of the scanning tunneling microscope.
Early life and education
Binnig wa ...
and Heinrich Rohrer
Heinrich Rohrer (6 June 1933 – 16 May 2013) was a Swiss physicist who shared half of the 1986 Nobel Prize in Physics with Gerd Binnig for the design of the scanning tunneling microscope (STM). The other half of the Prize was awarded to Ernst ...
at IBM Zurich Research Laboratory
IBM Research is the research and development division for IBM, an American multinational information technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, with operations in over 170 countries. IBM Research is the largest industrial research org ...
received a Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
in 1986. Binnig, Quate and Gerber also invented the analogous atomic force microscope
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the op ...
that year.
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
. C60 was not initially described as nanotechnology; the term was used regarding subsequent work with related carbon nanotubes (sometimes called graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure.
tubes or Bucky tubes) which suggested potential applications for nanoscale electronics and devices. The discovery of carbon nanotubes
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube
Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers.
''Single-wall carbon na ...
is largely attributed to Sumio Iijima of NEC
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. The company was known as the Nippon Electric Company, Limited, before rebranding in 1983 as NEC. It provides IT and network soluti ...
in 1991, for which Iijima won the inaugural 2008 Kavli Prize
The Kavli Prize was established in 2005 as a joint venture of the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters, the Norwegian Ministry of Education and Research, and the Kavli Foundation. It honors, supports, and recognizes scientists for outstan ...
in Nanoscience.
A nanolayer-base metal–semiconductor junction (M–S junction) transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
was initially proposed by A. Rose in 1960, and fabricated by L. Geppert, Mohamed Atalla and Dawon Kahng in 1962. Decades later, advances in multi-gate
A multigate device, multi-gate MOSFET or multi-gate field-effect transistor (MuGFET) refers to a metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) that has more than one gate on a single transistor. The multiple gates may be control ...
technology enabled the scaling of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) devices down to nano-scale
The nanoscopic scale (or nanoscale) usually refers to structures with a length scale applicable to nanotechnology, usually cited as 1–100 nanometers (nm). A nanometer is a billionth of a meter. The nanoscopic scale is (roughly speaking) a ...
levels smaller than 20 nm gate length, starting with the FinFET
A fin field-effect transistor (FinFET) is a multigate device, a MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor) built on a substrate where the gate is placed on two, three, or four sides of the channel or wrapped around the channel, ...
(fin field-effect transistor), a three-dimensional, non-planar, double-gate MOSFET. At UC Berkeley, a team of researchers including Digh Hisamoto, Chenming Hu, Tsu-Jae King Liu, Jeffrey Bokor and others fabricated FinFET devices down to a 17nm process in 1998, then 15nm in 2001, and then 10nm in 2002.
In the early 2000s, the field garnered increased scientific, political, and commercial attention that led to both controversy and progress. Controversies emerged regarding the definitions and potential implications of nanotechnologies, exemplified by the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
's report on nanotechnology. Challenges were raised regarding the feasibility of applications envisioned by advocates of molecular nanotechnology, which culminated in a public debate between Drexler and Smalley in 2001 and 2003.
Meanwhile, commercialization of products based on advancements in nanoscale technologies began emerging. These products are limited to bulk applications of nanomaterials
*
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale).
Nanomaterials research takes a materials science-based approach to n ...
and do not involve atomic control of matter. Some examples include the Silver Nano platform for using silver nanoparticles as an antibacterial agent, nanoparticle-based transparent sunscreens, carbon fiber
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers (Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon compo ...
strengthening using silica nanoparticles, and carbon nanotubes for stain-resistant textiles.
Governments moved to promote and fund research into nanotechnology, such as in the U.S. with the National Nanotechnology Initiative, which formalized a size-based definition of nanotechnology and established funding for research on the nanoscale, and in Europe via the European Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development.
By the mid-2000s new and serious scientific attention began to flourish. Projects emerged to produce nanotechnology roadmaps which center on atomically precise manipulation of matter and discuss existing and projected capabilities, goals, and applications.
In 2006, a team of Korean researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and the National Nano Fab Center developed a 3 nm MOSFET, the world's smallest nanoelectronic device. It was based on gate-all-around (GAA) FinFET technology.
Over sixty countries created nanotechnology research and development (R&D) government programs between 2001 and 2004. Government funding was exceeded by corporate spending on nanotechnology R&D, with most of the funding coming from corporations based in the United States, Japan and Germany. The top five organizations that filed the most intellectual patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
s on nanotechnology R&D between 1970 and 2011 were Samsung Electronics
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (, sometimes shortened to SEC and stylized as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean multinational electronics corporation headquartered in Yeongtong-gu, Suwon, South Korea. It is the pinnacle of the Samsung chaebol, acc ...
(2,578 first patents), Nippon Steel
was formed in 2012 by the merger of the old Nippon Steel and Sumitomo Metal. was established in 1970 by the merger of Fuji Iron & Steel and Yawata Iron & Steel. Nippon Steel is the world's third largest steel producer by volume as of 2019.
...
(1,490 first patents), IBM (1,360 first patents), Toshiba
, commonly known as Toshiba and stylized as TOSHIBA, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, ...
(1,298 first patents) and Canon (1,162 first patents). The top five organizations that published the most scientific papers on nanotechnology research between 1970 and 2012 were the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Russian Academy of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across t ...
, Centre national de la recherche scientifique, University of Tokyo and Osaka University.
Fundamental concepts
Nanotechnology is the engineering of functional systems at the molecular scale. This covers both current work and concepts that are more advanced. In its original sense, nanotechnology refers to the projected ability to construct items from the bottom up, using techniques and tools being developed today to make complete, high-performance products. One nanometer (nm) is one billionth, or 10−9, of a meter. By comparison, typical carbon-carbon bond lengths, or the spacing between theseatom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, a ...
s in a molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and b ...
, are in the range , and a DNA double-helix has a diameter around 2 nm. On the other hand, the smallest cellular life-forms, the bacteria of the genus '' Mycoplasma'', are around 200 nm in length. By convention, nanotechnology is taken as the scale range following the definition used by the National Nanotechnology Initiative in the US. The lower limit is set by the size of atoms (hydrogen has the smallest atoms, which are approximately a quarter of a nm kinetic diameter Kinetic diameter is a measure applied to atoms and molecules that expresses the likelihood that a molecule in a gas will collide with another molecule. It is an indication of the size of the molecule as a target. The kinetic diameter is not the s ...
) since nanotechnology must build its devices from atoms and molecules. The upper limit is more or less arbitrary but is around the size below which the phenomena not observed in larger structures start to become apparent and can be made use of in the nano device. These new phenomena make nanotechnology distinct from devices which are merely miniaturised versions of an equivalent macroscopic device; such devices are on a larger scale and come under the description of microtechnology.
To put that scale in another context, the comparative size of a nanometer to a meter is the same as that of a marble to the size of the earth. Or another way of putting it: a nanometer is the amount an average man's beard grows in the time it takes him to raise the razor to his face.
Two main approaches are used in nanotechnology. In the "bottom-up" approach, materials and devices are built from molecular components which assemble themselves chemically by principles of molecular recognition. In the "top-down" approach, nano-objects are constructed from larger entities without atomic-level control.
Areas of physics such as nanoelectronics, nanomechanics
Nanomechanics is a branch of '' nanoscience'' studying fundamental ''mechanical'' (elastic, thermal and kinetic) properties of physical systems at the nanometer scale. Nanomechanics has emerged on the crossroads of biophysics, classical mechanics, ...
, nanophotonics
Nanophotonics or nano-optics is the study of the behavior of light on the nanometer scale, and of the interaction of nanometer-scale objects with light. It is a branch of optics, optical engineering, electrical engineering, and nanotechnolog ...
and nanoionics
Nanoionics is the study and application of phenomena, properties, effects, methods and mechanisms of processes connected with fast ion transport (FIT) in all-solid-state nanoscale systems. The topics of interest include fundamental properties of ...
have evolved during the last few decades to provide a basic scientific foundation of nanotechnology.
Larger to smaller: a materials perspective
quantum
In physics, a quantum (plural quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity ( physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a physical property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantizat ...
size effect" where the electronic properties of solids are altered with great reductions in particle size. This effect does not come into play by going from macro to micro dimensions. However, quantum effects can become significant when the nanometer size range is reached, typically at distances of 100 nanometers or less, the so-called quantum realm. Additionally, a number of physical (mechanical, electrical, optical, etc.) properties change when compared to macroscopic systems. One example is the increase in surface area to volume ratio altering mechanical, thermal and catalytic properties of materials. Diffusion and reactions at nanoscale, nanostructures materials and nanodevices with fast ion transport are generally referred to nanoionics. ''Mechanical'' properties of nanosystems are of interest in the nanomechanics research. The catalytic activity of nanomaterials also opens potential risks in their interaction with biomaterial
A biomaterial is a substance that has been engineered to interact with biological systems for a medical purpose, either a therapeutic (treat, augment, repair, or replace a tissue function of the body) or a diagnostic one. As a science, biomateria ...
s.
Materials reduced to the nanoscale can show different properties compared to what they exhibit on a macroscale, enabling unique applications. For instance, opaque substances can become transparent (copper); stable materials can turn combustible (aluminium); insoluble materials may become soluble (gold). A material such as gold, which is chemically inert at normal scales, can serve as a potent chemical catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
at nanoscales. Much of the fascination with nanotechnology stems from these quantum and surface phenomena that matter exhibits at the nanoscale.
Simple to complex: a molecular perspective
Modern synthetic chemistry has reached the point where it is possible to prepare small molecules to almost any structure. These methods are used today to manufacture a wide variety of useful chemicals such as pharmaceuticals or commercialpolymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
s. This ability raises the question of extending this kind of control to the next-larger level, seeking methods to assemble these single molecules into supramolecular assemblies
In chemistry, a supramolecular assembly is a complex of molecules held together by noncovalent bonds. While a supramolecular assembly can be simply composed of two molecules (e.g., a DNA double helix or an inclusion compound), or a defined nu ...
consisting of many molecules arranged in a well defined manner.
These approaches utilize the concepts of molecular self-assembly and/or supramolecular chemistry to automatically arrange themselves into some useful conformation through a bottom-up approach. The concept of molecular recognition is especially important: molecules can be designed so that a specific configuration or arrangement is favored due to non-covalent
In chemistry, a non-covalent interaction differs from a covalent bond in that it does not involve the sharing of electrons, but rather involves more dispersed variations of electromagnetic interactions between molecules or within a molecule. Th ...
intermolecular forces. The Watson–Crick basepairing rules are a direct result of this, as is the specificity of an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
being targeted to a single substrate, or the specific folding of the protein itself. Thus, two or more components can be designed to be complementary and mutually attractive so that they make a more complex and useful whole.
Such bottom-up approaches should be capable of producing devices in parallel and be much cheaper than top-down methods, but could potentially be overwhelmed as the size and complexity of the desired assembly increases. Most useful structures require complex and thermodynamically unlikely arrangements of atoms. Nevertheless, there are many examples of self-assembly based on molecular recognition in biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary ...
, most notably Watson–Crick basepairing and enzyme-substrate interactions. The challenge for nanotechnology is whether these principles can be used to engineer new constructs in addition to natural ones.
Molecular nanotechnology: a long-term view
Molecular nanotechnology, sometimes called molecular manufacturing, describes engineered nanosystems (nanoscale machines) operating on the molecular scale. Molecular nanotechnology is especially associated with the molecular assembler, a machine that can produce a desired structure or device atom-by-atom using the principles of mechanosynthesis. Manufacturing in the context of productive nanosystems is not related to, and should be clearly distinguished from, the conventional technologies used to manufacture nanomaterials such as carbon nanotubes and nanoparticles. When the term "nanotechnology" was independently coined and popularized by Eric Drexler (who at the time was unaware of an earlier usage by Norio Taniguchi) it referred to a future manufacturing technology based on molecular machine systems. The premise was that molecular-scale biological analogies of traditional machine components demonstrated molecular machines were possible: by the countless examples found in biology, it is known that sophisticated,stochastic
Stochastic (, ) refers to the property of being well described by a random probability distribution. Although stochasticity and randomness are distinct in that the former refers to a modeling approach and the latter refers to phenomena themselv ...
ally optimized biological machines can be produced.
It is hoped that developments in nanotechnology will make possible their construction by some other means, perhaps using biomimetic principles. However, Drexler and other researchers have proposed that advanced nanotechnology, although perhaps initially implemented by biomimetic means, ultimately could be based on mechanical engineering principles, namely, a manufacturing technology based on the mechanical functionality of these components (such as gears, bearings, motors, and structural members) that would enable programmable, positional assembly to atomic specification. The physics and engineering performance of exemplar designs were analyzed in Drexler's book ''Nanosystems''.
In general it is very difficult to assemble devices on the atomic scale, as one has to position atoms on other atoms of comparable size and stickiness. Another view, put forth by Carlo Montemagno
Carlo Montemagno (August 7, 1956 – October 11, 2018) was an American engineer and expert in nanotechnology and biomedical engineering, focusing on futuristic technologies to create interdisciplinary solutions for the grand challenges in health ...
, is that future nanosystems will be hybrids of silicon technology and biological molecular machines. Richard Smalley argued that mechanosynthesis are impossible due to the difficulties in mechanically manipulating individual molecules.
This led to an exchange of letters in the ACS publication Chemical & Engineering News in 2003. Though biology clearly demonstrates that molecular machine systems are possible, non-biological molecular machines are today only in their infancy. Leaders in research on non-biological molecular machines are Dr. Alex Zettl
Alex Zettl is an American professor of experimental condensed-matter physics. His research involving the properties of novel materials has produced significant advances in the field.
Biography
Zettl received a B.A. degree from the University of ...
and his colleagues at Lawrence Berkeley Laboratories and UC BerkeleThey have constructed at least three distinct molecular devices whose motion is controlled from the desktop with changing voltage: a nanotube nanomotor, a molecular actuator, and a nanoelectromechanical relaxation oscillator. See nanotube nanomotor for more examples. An experiment indicating that positional molecular assembly is possible was performed by Ho and Lee at
Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to tea ...
in 1999. They used a scanning tunneling microscope to move an individual carbon monoxide molecule (CO) to an individual iron atom (Fe) sitting on a flat silver crystal, and chemically bound the CO to the Fe by applying a voltage.
Current research


Nanomaterials
The nanomaterials field includes subfields which develop or study materials having unique properties arising from their nanoscale dimensions. * Interface and colloid science has given rise to many materials which may be useful in nanotechnology, such as carbon nanotubes and other fullerenes, and various nanoparticles and nanorods. Nanomaterials with fast ion transport are related also to nanoionics and nanoelectronics. *Nanoscale materials can also be used for bulk applications; most present commercial applications of nanotechnology are of this flavor. *Progress has been made in using these materials for medical applications; see Nanomedicine. *Nanoscale materials such asnanopillar
Nanopillars is an emerging technology within the field of nanostructures. Nanopillars are pillar shaped nanostructures approximately 10 nanometers in diameter that can be grouped together in lattice like arrays. They are a type of metamaterial, whi ...
s are sometimes used in solar cell
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
s which combats the cost of traditional silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
solar cells.
*Development of applications incorporating semiconductor nanoparticles to be used in the next generation of products, such as display technology, lighting, solar cells and biological imaging; see quantum dots.
*Recent application of nanomaterials
*
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale).
Nanomaterials research takes a materials science-based approach to n ...
include a range of biomedical applications, such as tissue engineering, drug delivery, antibacterials and biosensors.
Bottom-up approaches
These seek to arrange smaller components into more complex assemblies. *DNA nanotechnology utilizes the specificity of Watson–Crick basepairing to construct well-defined structures out of DNA and other nucleic acids. *Approaches from the field of "classical" chemical synthesis (Inorganic and organic synthesis) also aim at designing molecules with well-defined shape (e.g. bis-peptides). *More generally, molecular self-assembly seeks to use concepts of supramolecular chemistry, and molecular recognition in particular, to cause single-molecule components to automatically arrange themselves into some useful conformation. *Atomic force microscope
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the op ...
tips can be used as a nanoscale "write head" to deposit a chemical upon a surface in a desired pattern in a process called dip pen nanolithography. This technique fits into the larger subfield of nanolithography
Nanolithography (NL) is a growing field of techniques within nanotechnology dealing with the engineering (patterning e.g. etching, depositing, writing, printing etc) of nanometer-scale structures on various materials.
The modern term reflects on ...
.
*Molecular Beam Epitaxy
Molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE) is an epitaxy method for thin-film deposition of single crystals. MBE is widely used in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, including transistors, and it is considered one of the fundamental tools for the dev ...
allows for bottom up assemblies of materials, most notably semiconductor materials commonly used in chip and computing applications, stacks, gating, and nanowire lasers.
Top-down approaches
These seek to create smaller devices by using larger ones to direct their assembly. *Many technologies that descended from conventional solid-state silicon methods for fabricatingmicroprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circ ...
s are now capable of creating features smaller than 100 nm, falling under the definition of nanotechnology. Giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in multilayers composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter G ...
-based hard drives already on the market fit this description, as do atomic layer deposition
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a thin-film deposition technique based on the sequential use of a gas-phase chemical process; it is a subclass of chemical vapour deposition. The majority of ALD reactions use two chemicals called precursors (a ...
(ALD) techniques. Peter Grünberg and Albert Fert received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2007 for their discovery of Giant magnetoresistance and contributions to the field of spintronics.
*Solid-state techniques can also be used to create devices known as nanoelectromechanical systems or NEMS, which are related to microelectromechanical systems or MEMS.
* Focused ion beams can directly remove material, or even deposit material when suitable precursor gasses are applied at the same time. For example, this technique is used routinely to create sub-100 nm sections of material for analysis in Transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a ...
.
*Atomic force microscope tips can be used as a nanoscale "write head" to deposit a resist, which is then followed by an etching process to remove material in a top-down method.
Functional approaches
These seek to develop components of a desired functionality without regard to how they might be assembled. *Magnetic assembly for the synthesis of anisotropic superparamagnetic materials such as recently presented magnetic nano chains. * Molecular scale electronics seeks to develop molecules with useful electronic properties. These could then be used as single-molecule components in a nanoelectronic device. For an example see rotaxane. *Synthetic chemical methods can also be used to create synthetic molecular motors, such as in a so-called nanocar.Biomimetic approaches
* Bionics or biomimicry seeks to apply biological methods and systems found in nature, to the study and design of engineering systems and modern technology.Biomineralization
Biomineralization, also written biomineralisation, is the process by which living organisms produce minerals, often to harden or stiffen existing tissues. Such tissues are called mineralized tissues. It is an extremely widespread phenomenon; ...
is one example of the systems studied.
* Bionanotechnology is the use of biomolecules for applications in nanotechnology, including use of viruses and lipid assemblies. Nanocellulose
Nanocellulose is a term referring to nano-structured cellulose. This may be either cellulose nanocrystal (CNC or NCC), cellulose nanofibers (CNF) also called nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC), or bacterial nanocellulose, which refers to nano-struc ...
is a potential bulk-scale application.
Speculative
These subfields seek to anticipate what inventions nanotechnology might yield, or attempt to propose an agenda along which inquiry might progress. These often take a big-picture view of nanotechnology, with more emphasis on its societal implications than the details of how such inventions could actually be created. *Molecular nanotechnology is a proposed approach which involves manipulating single molecules in finely controlled, deterministic ways. This is more theoretical than the other subfields, and many of its proposed techniques are beyond current capabilities. * Nanorobotics centers on self-sufficient machines of some functionality operating at the nanoscale. There are hopes for applying nanorobots in medicine. Nevertheless, progress on innovative materials and methodologies has been demonstrated with some patents granted about new nanomanufacturing devices for future commercial applications, which also progressively helps in the development towards nanorobots with the use of embedded nanobioelectronics concepts. *Productive nanosystems are "systems of nanosystems" which will be complex nanosystems that produce atomically precise parts for other nanosystems, not necessarily using novel nanoscale-emergent properties, but well-understood fundamentals of manufacturing. Because of the discrete (i.e. atomic) nature of matter and the possibility of exponential growth, this stage is seen as the basis of another industrial revolution. Mihail Roco, one of the architects of the USA's National Nanotechnology Initiative, has proposed four states of nanotechnology that seem to parallel the technical progress of the Industrial Revolution, progressing from passive nanostructures to active nanodevices to complex nanomachines and ultimately to productive nanosystems. * Programmable matter seeks to design materials whose properties can be easily, reversibly and externally controlled though a fusion ofinformation science
Information science (also known as information studies) is an academic field which is primarily concerned with analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval, movement, dissemination, and protection of information. ...
and materials science.
*Due to the popularity and media exposure of the term nanotechnology, the words picotechnology
The term picotechnology is a portmanteau of picometre and technology, intended to parallel the term nanotechnology. It is a hypothetical future level of technological manipulation of matter, on the scale of trillionths of a metre or picoscale ...
and femtotechnology have been coined in analogy to it, although these are only used rarely and informally.
Dimensionality in nanomaterials
Nanomaterials can be classified in 0D, 1D, 2D and 3Dnanomaterials
*
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale).
Nanomaterials research takes a materials science-based approach to n ...
. The dimensionality play a major role in determining the characteristic of nanomaterials including physical
Physical may refer to:
* Physical examination, a regular overall check-up with a doctor
* ''Physical'' (Olivia Newton-John album), 1981
** "Physical" (Olivia Newton-John song)
* ''Physical'' (Gabe Gurnsey album)
* "Physical" (Alcazar song) (2004)
* ...
, chemical and biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
characteristics. With the decrease in dimensionality, an increase in surface-to-volume ratio is observed. This indicate that smaller dimensional nanomaterials
*
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale).
Nanomaterials research takes a materials science-based approach to n ...
have higher surface area compared to 3D nanomaterials. Recently, two dimensional (2D) nanomaterials are extensively investigated for electronic, biomedical, drug delivery and biosensor applications.
Tools and techniques
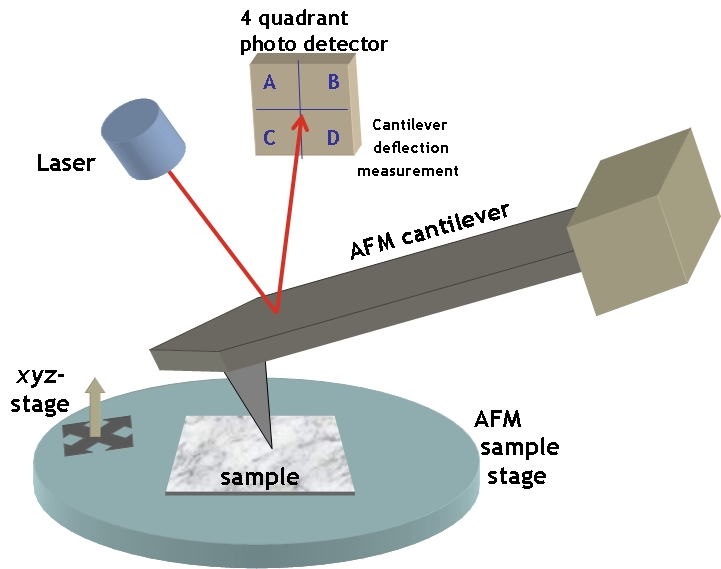
 There are several important modern developments. The
There are several important modern developments. The atomic force microscope
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the op ...
(AFM) and the Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) are two early versions of scanning probes that launched nanotechnology. There are other types of scanning probe microscopy. Although conceptually similar to the scanning confocal microscope developed by Marvin Minsky
Marvin Lee Minsky (August 9, 1927 – January 24, 2016) was an American cognitive and computer scientist concerned largely with research of artificial intelligence (AI), co-founder of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's AI laboratory ...
in 1961 and the scanning acoustic microscope
A scanning acoustic microscope (SAM) is a device which uses focused sound to investigate, measure, or image an object (a process called scanning acoustic tomography). It is commonly used in failure analysis and non-destructive evaluation. It al ...
(SAM) developed by Calvin Quate and coworkers in the 1970s, newer scanning probe microscopes have much higher resolution, since they are not limited by the wavelength of sound or light.
The tip of a scanning probe can also be used to manipulate nanostructures (a process called positional assembly). Feature-oriented scanning
Feature-oriented scanning (FOS) is a method of precision measurement of surface topography with a scanning probe microscope in which surface features (objects) are used as reference points for microscope probe attachment. With FOS method, by passi ...
methodology may be a promising way to implement these nanomanipulations in automatic mode. However, this is still a slow process because of low scanning velocity of the microscope.
Various techniques of nanolithography such as optical lithography, X-ray lithography
X-ray lithography is a process used in semiconductor device fabrication industry to selectively remove parts of a thin film of photoresist. It uses X-rays to transfer a geometric pattern from a mask to a light-sensitive chemical photoresist, o ...
, dip pen nanolithography, electron beam lithography or nanoimprint lithography
Nanoimprint lithography (NIL) is a method of fabricating nanometer scale patterns. It is a simple nanolithography process with low cost, high throughput and high resolution. It creates patterns by mechanical deformation of imprint resist and subse ...
were also developed. Lithography is a top-down fabrication technique where a bulk material is reduced in size to nanoscale pattern.
Another group of nanotechnological techniques include those used for fabrication of nanotubes and nanowires, those used in semiconductor fabrication such as deep ultraviolet lithography, electron beam lithography, focused ion beam machining, nanoimprint lithography, atomic layer deposition, and molecular vapor deposition, and further including molecular self-assembly techniques such as those employing di-block copolymers. The precursors of these techniques preceded the nanotech era, and are extensions in the development of scientific advancements rather than techniques which were devised with the sole purpose of creating nanotechnology and which were results of nanotechnology research.
The top-down approach anticipates nanodevices that must be built piece by piece in stages, much as manufactured items are made. Scanning probe microscopy is an important technique both for characterization and synthesis of nanomaterials. Atomic force microscopes and scanning tunneling microscopes can be used to look at surfaces and to move atoms around. By designing different tips for these microscopes, they can be used for carving out structures on surfaces and to help guide self-assembling structures. By using, for example, feature-oriented scanning approach, atoms or molecules can be moved around on a surface with scanning probe microscopy techniques. At present, it is expensive and time-consuming for mass production but very suitable for laboratory experimentation.
In contrast, bottom-up techniques build or grow larger structures atom by atom or molecule by molecule. These techniques include chemical synthesis, self-assembly and positional assembly. Dual polarisation interferometry is one tool suitable for characterisation of self assembled thin films. Another variation of the bottom-up approach is molecular beam epitaxy
Molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE) is an epitaxy method for thin-film deposition of single crystals. MBE is widely used in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, including transistors, and it is considered one of the fundamental tools for the dev ...
or MBE. Researchers at Bell Telephone Laboratories like John R. Arthur. Alfred Y. Cho, and Art C. Gossard developed and implemented MBE as a research tool in the late 1960s and 1970s. Samples made by MBE were key to the discovery of the fractional quantum Hall effect for which the 1998 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded. MBE allows scientists to lay down atomically precise layers of atoms and, in the process, build up complex structures. Important for research on semiconductors, MBE is also widely used to make samples and devices for the newly emerging field of spintronics
Spintronics (a portmanteau meaning spin transport electronics), also known as spin electronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid- ...
.
However, new therapeutic products, based on responsive nanomaterials, such as the ultradeformable, stress-sensitive Transfersome vesicles, are under development and already approved for human use in some countries.
Research and development
Because of the variety of potential applications (including industrial and military), governments have invested billions of dollars in nanotechnology research. Prior to 2012, the USA invested $3.7 billion using its National Nanotechnology Initiative, the European Union invested $1.2 billion, and Japan invested $750 million. Over sixty countries created nanotechnology research and development (R&D) programs between 2001 and 2004. In 2012, the US and EU each invested on nanotechnology research, followed by Japan with . Global investment reached in 2012. Government funding was exceeded by corporate R&D spending on nanotechnology research, which was in 2012. The largest corporate R&D spenders were from the US, Japan and Germany which accounted for a combined .Applications

 As of August 21, 2008, the
As of August 21, 2008, the Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies
The Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies was established in 2005 as a partnership between the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars and the Pew Charitable Trusts. The Project was intended to address the social, political, and public sa ...
estimates that over 800 manufacturer-identified nanotech products are publicly available, with new ones hitting the market at a pace of 3–4 per week. The project lists all of the products in a publicly accessible online database. Most applications are limited to the use of "first generation" passive nanomaterials which includes titanium dioxide in sunscreen, cosmetics, surface coatings, and some food products; Carbon allotropes used to produce gecko tape; silver in food packaging, clothing, disinfectants and household appliances; zinc oxide in sunscreens and cosmetics, surface coatings, paints and outdoor furniture varnishes; and cerium oxide as a fuel catalyst.
Further applications allow tennis balls to last longer, golf balls to fly straighter, and even bowling ball
A bowling ball is a hard spherical ball used to knock down bowling pins in the sport of bowling.
Balls used in ten-pin bowling and American nine-pin bowling traditionally have holes for two fingers and the thumb. Balls used in five-pin bowl ...
s to become more durable and have a harder surface. Trousers and socks have been infused with nanotechnology so that they will last longer and keep people cool in the summer. Bandages are being infused with silver nanoparticles to heal cuts faster. Video game consoles and personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or te ...
s may become cheaper, faster, and contain more memory thanks to nanotechnology. Also, to build structures for on chip computing with light, for example on chip optical quantum information processing, and picosecond transmission of information.
Nanotechnology may have the ability to make existing medical applications cheaper and easier to use in places like the general practitioner's office and at home. Cars are being manufactured with nanomaterials so they may need fewer metal
A metal (from ancient Greek, Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, e ...
s and less fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy b ...
to operate in the future.
Scientists are now turning to nanotechnology in an attempt to develop diesel engines with cleaner exhaust fumes. Platinum is currently used as the diesel engine catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
in these engines. The catalyst is what cleans the exhaust fume particles. First a reduction catalyst is employed to take nitrogen atoms from NOx molecules in order to free oxygen. Next the oxidation catalyst oxidizes the hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide to form carbon dioxide and water. Platinum is used in both the reduction and the oxidation catalysts. Using platinum though, is inefficient in that it is expensive and unsustainable. Danish company InnovationsFonden invested DKK 15 million in a search for new catalyst substitutes using nanotechnology. The goal of the project, launched in the autumn of 2014, is to maximize surface area and minimize the amount of material required. Objects tend to minimize their surface energy; two drops of water, for example, will join to form one drop and decrease surface area. If the catalyst's surface area that is exposed to the exhaust fumes is maximized, efficiency of the catalyst is maximized. The team working on this project aims to create nanoparticles that will not merge. Every time the surface is optimized, material is saved. Thus, creating these nanoparticles will increase the effectiveness of the resulting diesel engine catalyst—in turn leading to cleaner exhaust fumes—and will decrease cost. If successful, the team hopes to reduce platinum use by 25%.
Nanotechnology also has a prominent role in the fast developing field of Tissue Engineering. When designing scaffolds, researchers attempt to mimic the nanoscale features of a cell's microenvironment to direct its differentiation down a suitable lineage. For example, when creating scaffolds to support the growth of bone, researchers may mimic osteoclast resorption pits.
Researchers have successfully used DNA origami
DNA origami is the nanoscale folding of DNA to create arbitrary two- and three-dimensional shapes at the nanoscale. The specificity of the interactions between complementary base pairs make DNA a useful construction material, through design of ...
-based nanobots capable of carrying out logic functions to achieve targeted drug delivery in cockroaches. It is said that the computational power of these nanobots can be scaled up to that of a Commodore 64.
Nanoelectronics
Commercial nanoelectronicsemiconductor device fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are ...
began in the 2010s. In 2013, SK Hynix
SK hynix Inc. is a South Korean supplier of dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) chips and flash memory chips. Hynix is the world's second-largest memory chipmaker (after Samsung Electronics) and the world's third-largest semiconductor company. ...
began commercial mass-production of a 16nm process, TSMC began production of a 16nm FinFET
A fin field-effect transistor (FinFET) is a multigate device, a MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor) built on a substrate where the gate is placed on two, three, or four sides of the channel or wrapped around the channel, ...
process, and Samsung Electronics
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (, sometimes shortened to SEC and stylized as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean multinational electronics corporation headquartered in Yeongtong-gu, Suwon, South Korea. It is the pinnacle of the Samsung chaebol, acc ...
began production of a 10nm process. TSMC began production of a 7 nm process in 2017, and Samsung began production of a 5 nm process in 2018. In 2019, Samsung announced plans for the commercial production of a 3nm GAAFET process by 2021.
Commercial production of nanoelectronic semiconductor memory
Semiconductor memory is a digital electronic semiconductor device used for digital data storage, such as computer memory. It typically refers to devices in which data is stored within metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) memory cells on a si ...
also began in the 2010s. In 2013, SK Hynix
SK hynix Inc. is a South Korean supplier of dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) chips and flash memory chips. Hynix is the world's second-largest memory chipmaker (after Samsung Electronics) and the world's third-largest semiconductor company. ...
began mass-production of 16nm NAND flash
Flash memory is an Integrated circuit, electronic Non-volatile memory, non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for t ...
memory, and Samsung
The Samsung Group (or simply Samsung) ( ko, 삼성 ) is a South Korean multinational manufacturing conglomerate headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea. It comprises numerous affiliated businesses, most of them united under the ...
began production of 10nm multi-level cell
In electronics, a multi-level cell (MLC) is a memory cell capable of storing more than a single bit of information, compared to a single-level cell (SLC), which can store only one bit per memory cell. A memory cell typically consists of a single ...
(MLC) NAND flash memory. In 2017, TSMC began production of SRAM memory using a 7 nm process.
Implications
An area of concern is the effect that industrial-scale manufacturing and use of nanomaterials would have on human health and the environment, as suggested by nanotoxicology research. For these reasons, some groups advocate that nanotechnology be regulated by governments. Others counter that overregulation would stifle scientific research and the development of beneficial innovations.Public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
research agencies, such as the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health are actively conducting research on potential health effects stemming from exposures to nanoparticles.
Some nanoparticle products may have unintended consequences. Researchers have discovered that bacteriostatic silver nanoparticles used in socks to reduce foot odor are being released in the wash. These particles are then flushed into the waste water stream and may destroy bacteria which are critical components of natural ecosystems, farms, and waste treatment processes.
Public deliberations on risk perception in the US and UK carried out by the Center for Nanotechnology in Society found that participants were more positive about nanotechnologies for energy applications than for health applications, with health applications raising moral and ethical dilemmas such as cost and availability.Harthorn, Barbara Herr (January 23, 2009"People in the US and the UK show strong similarities in their attitudes toward nanotechnologies"
. Nanotechnology Today. Experts, including director of the Woodrow Wilson Center's Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies David Rejeski, have testified that successful commercialization depends on adequate oversight, risk research strategy, and public engagement.
Berkeley, California
Berkeley ( ) is a city on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay in northern Alameda County, California, United States. It is named after the 18th-century Irish bishop and philosopher George Berkeley. It borders the cities of Oakland and E ...
is currently the only city in the United States to regulate nanotechnology; Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. As part of the Boston metropolitan area, the cities population of the 2020 U.S. census was 118,403, making it the fourth most populous city in the state, behind Boston, ...
in 2008 considered enacting a similar law, but ultimately rejected it.
Health and environmental concerns
Nanofibers are used in several areas and in different products, in everything from aircraft wings to tennis rackets. Inhaling airborne nanoparticles and nanofibers may lead to a number of pulmonary diseases, e.g. fibrosis. Researchers have found that when rats breathed in nanoparticles, the particles settled in the brain and lungs, which led to significant increases in biomarkers for inflammation and stress response and that nanoparticles induce skin aging through oxidative stress in hairless mice. A two-year study at UCLA's School of Public Health found lab mice consuming nano-titanium dioxide showed DNA and chromosome damage to a degree "linked to all the big killers of man, namely cancer, heart disease, neurological disease and aging". A Nature Nanotechnology study suggests some forms ofcarbon nanotubes
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube
Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers.
''Single-wall carbon na ...
– a poster child for the "nanotechnology revolution" – could be as harmful as asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
if inhaled in sufficient quantities. Anthony Seaton
Anthony Seaton (born 1938) qualified in medicine from Cambridge University in 1962, and after training in Liverpool was appointed assistant professor of medicine at the University of West Virginia, USA in 1969. He became consulting chest physicia ...
of the Institute of Occupational Medicine in Edinburgh, Scotland, who contributed to the article on carbon nanotubes said "We know that some of them probably have the potential to cause mesothelioma. So those sorts of materials need to be handled very carefully." In the absence of specific regulation forthcoming from governments, Paull and Lyons (2008) have called for an exclusion of engineered nanoparticles in food. A newspaper article reports that workers in a paint factory developed serious lung disease and nanoparticles were found in their lungs.Nanofibres 'may pose health risk'. BBC. 2012-08-24
Regulation
Calls for tighter regulation of nanotechnology have occurred alongside a growing debate related to the human health and safety risks of nanotechnology. There is significant debate about who is responsible for the regulation of nanotechnology. Some regulatory agencies currently cover some nanotechnology products and processes (to varying degrees) – by "bolting on" nanotechnology to existing regulations – there are clear gaps in these regimes. Davies (2008) has proposed a regulatory road map describing steps to deal with these shortcomings. Stakeholders concerned by the lack of a regulatory framework to assess and control risks associated with the release of nanoparticles and nanotubes have drawn parallels with bovine spongiform encephalopathy ("mad cow" disease), thalidomide, genetically modified food, nuclear energy, reproductive technologies, biotechnology, andasbestosis
Asbestosis is long-term inflammation and scarring of the lungs due to asbestos fibers. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, and chest tightness. Complications may include lung cancer, mesothelioma, and pulmonary heart ...
. Dr. Andrew Maynard, chief science advisor to the Woodrow Wilson Center's Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies, concludes that there is insufficient funding for human health and safety research, and as a result there is currently limited understanding of the human health and safety risks associated with nanotechnology. As a result, some academics have called for stricter application of the precautionary principle, with delayed marketing approval, enhanced labelling and additional safety data development requirements in relation to certain forms of nanotechnology.
The Royal Society report identified a risk of nanoparticles or nanotubes being released during disposal, destruction and recycling, and recommended that "manufacturers of products that fall under extended producer responsibility regimes such as end-of-life regulations publish procedures outlining how these materials will be managed to minimize possible human and environmental exposure" (p. xiii).
The Center for Nanotechnology in Society has found that people respond to nanotechnologies differently, depending on application – with participants in public deliberations more positive about nanotechnologies for energy than health applications – suggesting that any public calls for nano regulations may differ by technology sector.
See also
* Carbon nanotube * Electrostatic deflection (molecular physics/nanotechnology) * Energy applications of nanotechnology *Ethics of nanotechnologies Ethics of nanotechnology is the study of the ethical issues emerging from advances in nanotechnology and its impacts.
According to Andrew Chen, ethical concerns about nanotechnologies should include the possibility of their military applications, ...
* Ion implantation-induced nanoparticle formation
* Gold nanoparticle
* List of emerging technologies
* List of nanotechnology organizations
* List of software for nanostructures modeling
* Magnetic nanochains
* Materiomics
* Nano-thermite
* Molecular design software
* Molecular mechanics
* Nanobiotechnology
* Nanoelectromechanical relay A nanoelectromechanical (NEM) relay is an electrically actuated switch that is built on the nanometer scale using semiconductor fabrication techniques. They are designed to operate in replacement of, or in conjunction with, traditional semiconductor ...
* Nanoengineering
* Nanofluidics
* NanoHUB
* Nanometrology
* Nanoneuronics
* Nanoparticle
* Nanoscale networks
* Nanotechnology education
Nanotechnology education involves a multidisciplinary natural science education with courses such as physics, chemistry, mathematics and molecular biology. It is being offered by many universities around the world. The first program involving ...
* Nanotechnology in fiction
The use of nanotechnology in fiction has attracted scholarly attention. The first use of the distinguishing concepts of nanotechnology was "There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom", a talk given by physicist Richard Feynman in 1959. K. Eric Drexle ...
* Nanotechnology in water treatment
Green nanotechnology refers to the use of nanotechnology to enhance the environmental sustainability of processes producing negative externalities. It also refers to the use of the products of nanotechnology to enhance sustainability. It includes ...
* Nanoweapons
* National Nanotechnology Initiative
* Self-assembly of nanoparticles
* Top-down and bottom-up
* Translational research
* Wet nanotechnology
References
External links
*What is Nanotechnology?
(A Vega/BBC/OU Video Discussion). {{Authority control 1960 introductions 1985 introductions Articles containing video clips Emerging technologies 1986 neologisms 1970s neologisms