Kellett Fellowship on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a
 Discussions regarding the founding of a college in the
Discussions regarding the founding of a college in the
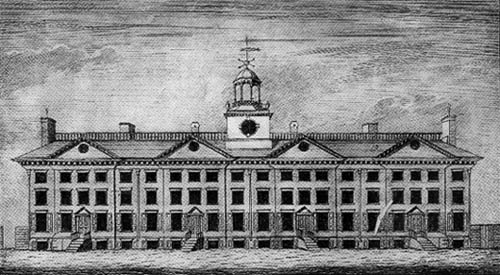 After the Revolution, the college turned to the State of New York in order to restore its vitality, promising to make whatever changes to the school's charter the state might demand. The legislature agreed to assist the college, and on May 1, 1784, it passed "an Act for granting certain privileges to the College heretofore called King's College". The Act created a board of regents to oversee the resuscitation of King's College, and, in an effort to demonstrate its support for the new Republic, the legislature stipulated that "the College within the City of New York heretofore called King's College be forever hereafter called and known by the name of Columbia College", a reference to
After the Revolution, the college turned to the State of New York in order to restore its vitality, promising to make whatever changes to the school's charter the state might demand. The legislature agreed to assist the college, and on May 1, 1784, it passed "an Act for granting certain privileges to the College heretofore called King's College". The Act created a board of regents to oversee the resuscitation of King's College, and, in an effort to demonstrate its support for the new Republic, the legislature stipulated that "the College within the City of New York heretofore called King's College be forever hereafter called and known by the name of Columbia College", a reference to  On May 21, 1787,
On May 21, 1787,

 In November 1813, the college agreed to incorporate its medical school with The College of Physicians and Surgeons, a new school created by the Regents of New York, forming Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons. The college's enrollment, structure, and academics stagnated for the majority of the 19th century, with many of the college presidents doing little to change the way that the college functioned. In 1857, the college moved from the King's College campus at Park Place to a primarily
In November 1813, the college agreed to incorporate its medical school with The College of Physicians and Surgeons, a new school created by the Regents of New York, forming Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons. The college's enrollment, structure, and academics stagnated for the majority of the 19th century, with many of the college presidents doing little to change the way that the college functioned. In 1857, the college moved from the King's College campus at Park Place to a primarily
 The majority of Columbia's graduate and undergraduate studies are conducted in Morningside Heights on
The majority of Columbia's graduate and undergraduate studies are conducted in Morningside Heights on  The Nicholas Murray Butler Library, known simply as
The Nicholas Murray Butler Library, known simply as  A statue by sculptor
A statue by sculptor

 In April 2007, the university purchased more than two-thirds of a site for a new campus in
In April 2007, the university purchased more than two-thirds of a site for a new campus in
 According to the
According to the
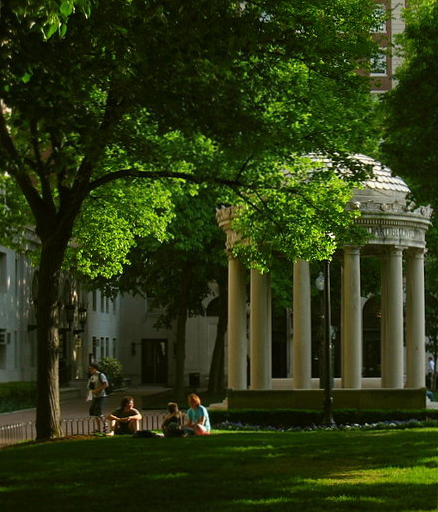 Columbia University received 60,551 applications for the class of 2025 (entering 2021) and a total of around 2,218 were admitted to the two schools for an overall acceptance rate of 3.66%. Columbia is a racially diverse school, with approximately 52% of all students identifying themselves as persons of color. Additionally, 50% of all undergraduates received grants from Columbia. The average grant size awarded to these students is $46,516. In 2015–2016, annual undergraduate tuition at Columbia was $50,526 with a total cost of attendance of $65,860 (including room and board).
Annual gifts, fund-raising, and an increase in spending from the university's endowment have allowed Columbia to extend generous financial aid packages to qualifying students. On April 11, 2007, Columbia University announced a $400 million donation from media billionaire alumnus John Kluge to be used exclusively for undergraduate financial aid. The donation is among the largest single gifts to higher education. , undergraduates from families with incomes as high as $60,000 a year will have the projected cost of attending the university, including room, board, and academic fees, fully paid for by the university. That same year, the university ended loans for incoming and then-current students who were on financial aid, replacing loans that were traditionally part of aid packages with grants from the university. However, this does not apply to international students, transfer students, visiting students, or students in the School of General Studies. In the fall of 2010, admission to Columbia's undergraduate colleges Columbia College and the Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science (also known as SEAS or Columbia Engineering) began accepting the Common Application. The policy change made Columbia one of the last major academic institutions and the last
Columbia University received 60,551 applications for the class of 2025 (entering 2021) and a total of around 2,218 were admitted to the two schools for an overall acceptance rate of 3.66%. Columbia is a racially diverse school, with approximately 52% of all students identifying themselves as persons of color. Additionally, 50% of all undergraduates received grants from Columbia. The average grant size awarded to these students is $46,516. In 2015–2016, annual undergraduate tuition at Columbia was $50,526 with a total cost of attendance of $65,860 (including room and board).
Annual gifts, fund-raising, and an increase in spending from the university's endowment have allowed Columbia to extend generous financial aid packages to qualifying students. On April 11, 2007, Columbia University announced a $400 million donation from media billionaire alumnus John Kluge to be used exclusively for undergraduate financial aid. The donation is among the largest single gifts to higher education. , undergraduates from families with incomes as high as $60,000 a year will have the projected cost of attending the university, including room, board, and academic fees, fully paid for by the university. That same year, the university ended loans for incoming and then-current students who were on financial aid, replacing loans that were traditionally part of aid packages with grants from the university. However, this does not apply to international students, transfer students, visiting students, or students in the School of General Studies. In the fall of 2010, admission to Columbia's undergraduate colleges Columbia College and the Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science (also known as SEAS or Columbia Engineering) began accepting the Common Application. The policy change made Columbia one of the last major academic institutions and the last
 The University Senate was established by the trustees after a university-wide referendum in 1969. It succeeded to the powers of the University Council, which was created in 1890 as a body of faculty, deans, and other administrators to regulate inter-Faculty affairs and consider issues of university-wide concern. The University Senate is a unicameral body consisting of 107 members drawn from all constituencies of the university. These include the president of the university, the provost, the deans of Columbia College and the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, all of whom serve ''ex officio'', and five additional representatives, appointed by the president, from the university's administration. The president serves as the Senate's presiding officer. The Senate is charged with reviewing the educational policies, physical development, budget, and external relations of the university. It oversees the welfare and academic freedom of the faculty and the welfare of students.
The president of Columbia University, who is selected by the trustees in consultation with the executive committee of the University Senate and who serves at the trustees' pleasure, is the chief executive officer of the university. Assisting the president in administering the university are the provost, the senior executive vice president, the executive vice president for health and biomedical sciences, several other vice presidents, the general counsel, the secretary of the university, and the deans of the faculties, all of whom are appointed by the trustees on the nomination of the president and serve at their pleasure. Lee C. Bollinger became the 19th president of Columbia University on June 1, 2002. As
The University Senate was established by the trustees after a university-wide referendum in 1969. It succeeded to the powers of the University Council, which was created in 1890 as a body of faculty, deans, and other administrators to regulate inter-Faculty affairs and consider issues of university-wide concern. The University Senate is a unicameral body consisting of 107 members drawn from all constituencies of the university. These include the president of the university, the provost, the deans of Columbia College and the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, all of whom serve ''ex officio'', and five additional representatives, appointed by the president, from the university's administration. The president serves as the Senate's presiding officer. The Senate is charged with reviewing the educational policies, physical development, budget, and external relations of the university. It oversees the welfare and academic freedom of the faculty and the welfare of students.
The president of Columbia University, who is selected by the trustees in consultation with the executive committee of the University Senate and who serves at the trustees' pleasure, is the chief executive officer of the university. Assisting the president in administering the university are the provost, the senior executive vice president, the executive vice president for health and biomedical sciences, several other vice presidents, the general counsel, the secretary of the university, and the deans of the faculties, all of whom are appointed by the trustees on the nomination of the president and serve at their pleasure. Lee C. Bollinger became the 19th president of Columbia University on June 1, 2002. As  Columbia has four official undergraduate colleges: Columbia College, the liberal arts college offering the Bachelor of Arts degree; the Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science (also known as SEAS or Columbia Engineering), the engineering and applied science school offering the Bachelor of Science degree; the School of General Studies, the liberal arts college offering the Bachelor of Arts degree to non-traditional students undertaking full- or part-time study; and
Columbia has four official undergraduate colleges: Columbia College, the liberal arts college offering the Bachelor of Arts degree; the Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science (also known as SEAS or Columbia Engineering), the engineering and applied science school offering the Bachelor of Science degree; the School of General Studies, the liberal arts college offering the Bachelor of Arts degree to non-traditional students undertaking full- or part-time study; and
 Columbia is
Columbia is
 Several prestigious awards are administered by Columbia University, most notably the
Several prestigious awards are administered by Columbia University, most notably the

 The '' Columbia Daily Spectator'' is the nation's second-oldest continuously operating daily student newspaper. '' The Blue and White'' is a monthly literary magazine established in 1890 that discusses campus life and local politics. '' Bwog'', originally an offshoot of ''The Blue and White'' but now fully independent, is an online campus news and entertainment source. '' The Morningside Post'' is a student-run multimedia news publication.
Political publications include '' The Current'', a journal of politics, culture and Jewish Affairs; the '' Columbia Political Review'', the multi-partisan political magazine of the Columbia Political Union; and ''AdHoc'', which denotes itself as the "progressive" campus magazine and deals largely with local political issues and arts events.
''Columbia Magazine'' is the alumni magazine of Columbia, serving all 340,000+ of the university's alumni. Arts and literary publications include ''The Columbia Review'', the nation's oldest college literary magazine; ''Surgam'', the literary magazine of
The '' Columbia Daily Spectator'' is the nation's second-oldest continuously operating daily student newspaper. '' The Blue and White'' is a monthly literary magazine established in 1890 that discusses campus life and local politics. '' Bwog'', originally an offshoot of ''The Blue and White'' but now fully independent, is an online campus news and entertainment source. '' The Morningside Post'' is a student-run multimedia news publication.
Political publications include '' The Current'', a journal of politics, culture and Jewish Affairs; the '' Columbia Political Review'', the multi-partisan political magazine of the Columbia Political Union; and ''AdHoc'', which denotes itself as the "progressive" campus magazine and deals largely with local political issues and arts events.
''Columbia Magazine'' is the alumni magazine of Columbia, serving all 340,000+ of the university's alumni. Arts and literary publications include ''The Columbia Review'', the nation's oldest college literary magazine; ''Surgam'', the literary magazine of
 Columbia is a top supplier of young engineering entrepreneurs for New York City. Over the past 20 years, graduates of Columbia established over 100 technology companies.
The Columbia University Organization of Rising Entrepreneurs (CORE) was founded in 1999. The student-run group aims to foster entrepreneurship on campus. Each year CORE hosts dozens of events, including talks, #StartupColumbia, a conference and venture competition for $250,000, and Ignite@CU, a weekend for undergrads interested in design, engineering, and entrepreneurship. Notable speakers include Peter Thiel, Jack Dorsey, Alexis Ohanian, Drew Houston, and Mark Cuban. As of 2006, CORE had awarded graduate and undergraduate students over $100,000 in seed capital.
CampusNetwork, an on-campus social networking site called Campus Network that preceded Facebook, was created and popularized by Columbia engineering student Adam Goldberg in 2003.
Columbia is a top supplier of young engineering entrepreneurs for New York City. Over the past 20 years, graduates of Columbia established over 100 technology companies.
The Columbia University Organization of Rising Entrepreneurs (CORE) was founded in 1999. The student-run group aims to foster entrepreneurship on campus. Each year CORE hosts dozens of events, including talks, #StartupColumbia, a conference and venture competition for $250,000, and Ignite@CU, a weekend for undergrads interested in design, engineering, and entrepreneurship. Notable speakers include Peter Thiel, Jack Dorsey, Alexis Ohanian, Drew Houston, and Mark Cuban. As of 2006, CORE had awarded graduate and undergraduate students over $100,000 in seed capital.
CampusNetwork, an on-campus social networking site called Campus Network that preceded Facebook, was created and popularized by Columbia engineering student Adam Goldberg in 2003.
 A member institution of the
A member institution of the  Former students include
Former students include
 Established in 2003 by university president Lee C. Bollinger, the World Leaders Forum at Columbia University provides the opportunity for undergraduate and graduate students alike to listen to world leaders in government, religion, industry, finance, and academia. The World Leaders Forum is a year-around event series that strives to provide a platform for uninhibited speech among nations and cultures, while educating students about problems and progress around the globe.
Past forum speakers include former president of the United States
Established in 2003 by university president Lee C. Bollinger, the World Leaders Forum at Columbia University provides the opportunity for undergraduate and graduate students alike to listen to world leaders in government, religion, industry, finance, and academia. The World Leaders Forum is a year-around event series that strives to provide a platform for uninhibited speech among nations and cultures, while educating students about problems and progress around the globe.
Past forum speakers include former president of the United States
 The Columbia University Orchestra was founded by composer
The Columbia University Orchestra was founded by composer
 In one of the school's longest-lasting traditions, begun in 1975, at midnight before the
In one of the school's longest-lasting traditions, begun in 1975, at midnight before the
File:Alexander Hamilton portrait by John Trumbull 1806.jpg, Alexander Hamilton: Founding Father of the United States; author of '' The Federalist Papers''; first
File:Zbigniew Brzezinski, 1977.jpg, Zbigniew Brzezinski
File:Sonia Sotomayor in SCOTUS robe.jpg, Sonia Sotomayor
File:Kimberlé Crenshaw (40901215153).jpg, Kimberlé Crenshaw
File:Lee Bollinger - Daniella Zalcman less noise.jpg, Lee Bollinger
File:FranzBoas.jpg, Franz Boas
File:Margaret Mead (1901-1978).jpg,
private
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* " In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorde ...
research university
A research university or a research-intensive university is a university that is committed to research as a central part of its mission. They are the most important sites at which knowledge production occurs, along with "intergenerational kn ...
in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
, Columbia is the oldest institution of higher education in New York and the fifth-oldest institution of higher learning in the United States. It is one of nine colonial colleges founded prior to the Declaration of Independence. It is a member of the Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight school ...
. Columbia is ranked among the top universities in the world.
Columbia was established by royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, b ...
under George II of Great Britain
George II (George Augustus; german: link=no, Georg August; 30 October / 9 November 1683 – 25 October 1760) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (Electorate of Hanover, Hanover) and a prince-ele ...
. It was renamed Columbia College in 1784 following the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
, and in 1787 was placed under a private board of trustees headed by former students Alexander Hamilton and John Jay
John Jay (December 12, 1745 – May 17, 1829) was an American statesman, patriot, diplomat, abolitionist, signatory of the Treaty of Paris, and a Founding Father of the United States. He served as the second governor of New York and the f ...
. In 1896, the campus was moved to its current location in Morningside Heights and renamed Columbia University.
Columbia scientists and scholars have played a pivotal role in scientific breakthroughs including brain-computer interface; the laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The ...
and maser
A maser (, an acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation) is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves through amplification by stimulated emission. The first maser was built by Charles H. Townes, James ...
; nuclear magnetic resonance; the first nuclear pile
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from ...
; the first nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
reaction in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
; the first evidence for plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label= Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of larg ...
and continental drift; and much of the initial research and planning for the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
Columbia is organized into twenty schools, including four undergraduate schools and 16 graduate schools. The university's research efforts include the Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory
The Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory (LDEO) is the scientific research center of the Columbia Climate School, and a unit of The Earth Institute at Columbia University. It focuses on climate and earth sciences and is located on a 189-acre ( ...
, the Goddard Institute for Space Studies
The Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) is a laboratory in the Earth Sciences Division of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center affiliated with the Columbia University Earth Institute.
The institute is located at Columbia University in ...
, and accelerator laboratories with Big Tech
Big Tech, also known as the Tech Giants, refers to the most dominant companies in the information technology industry, mostly located in the United States. The term also refers to the four or five largest American tech companies, called the Big ...
firms such as Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...
and IBM. Columbia is a founding member of the Association of American Universities and was the first school in the United States to grant the MD degree
Doctor of Medicine (abbreviated M.D., from the Latin ''Medicinae Doctor'') is a medical degree, the meaning of which varies between different jurisdictions. In the United States, and some other countries, the M.D. denotes a professional degree. T ...
. The university also annually administers the Pulitzer Prize
The Pulitzer Prize () is an award for achievements in newspaper, magazine, online journalism, literature, and musical composition within the United States. It was established in 1917 by provisions in the will of Joseph Pulitzer, who had made ...
. With over 15 million volumes, Columbia University Library
Columbia University Libraries is the library system of Columbia University and one of the largest academic library systems in North America. With 15.0 million volumes and over 160,000 journals and serials, as well as extensive electronic resource ...
is the third-largest private research library in the United States.
The university's endowment stands at $13.3 billion in 2022, among the largest of any academic institution. , its alumni, faculty, and staff have included: seven Founding Fathers of the United States; four U.S. presidents; 33 foreign heads of state; two secretaries-general of the United Nations; ten justices of the United States Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
, one of whom currently serves; 101 Nobel laureates; 125 National Academy of Sciences members; 53 living billionaires; 22 Olympic medalists; 33 Academy Award winners; and 125 Pulitzer Prize recipients.
History
Colonial period
Province of New York
The Province of New York (1664–1776) was a British proprietary colony and later royal colony on the northeast coast of North America. As one of the Middle Colonies, New York achieved independence and worked with the others to found the U ...
began as early as 1704, at which time Colonel Lewis Morris wrote to the Society for the Propagation of the Gospel in Foreign Parts, the missionary arm of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Brit ...
, persuading the society that New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
was an ideal community in which to establish a college. However, it was not until the founding of the College of New Jersey (renamed Princeton
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the nin ...
) across the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between Ne ...
in New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delawa ...
that the City of New York seriously considered founding a college. In 1746, an act was passed by the general assembly of New York to raise funds for the foundation of a new college. In 1751, the assembly appointed a commission of ten New York residents, seven of whom were members of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Brit ...
, to direct the funds accrued by the state lottery towards the foundation of a college.
Classes were initially held in July 1754 and were presided over by the college's first president, Dr. Samuel Johnson. Dr. Johnson was the only instructor of the college's first class, which consisted of a mere eight students. Instruction was held in a new schoolhouse adjoining Trinity Church, located on what is now lower Broadway in Manhattan. The college was officially founded on October 31, 1754, as King's College by royal charter of George II, making it the oldest institution of higher learning in the State of New York and the fifth oldest in the United States.
In 1763, Dr. Johnson was succeeded in the presidency by Myles Cooper
Myles Cooper (1735 – May 1, 1785) was a figure in colonial New York. An Anglican priest, he served as the President of King's College (predecessor of today's Columbia University) from 1763 to 1775, and was a public opponent of the American Rev ...
, a graduate of The Queen's College, Oxford
The Queen's College is a constituent college of the University of Oxford, England. The college was founded in 1341 by Robert de Eglesfield in honour of Philippa of Hainault. It is distinguished by its predominantly neoclassical architecture, ...
, and an ardent Tory. In the charged political climate of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
, his chief opponent in discussions at the college was an undergraduate of the class of 1777, Alexander Hamilton. The Irish anatomist, Samuel Clossy
Samuel Clossy MB MD (''c.'' 1724 – 22 August 1786) was a pioneering Irish anatomist and the first college professor of a medical subject in North America.
Early life and education
Samuel Clossy was born around 1724 in Dublin, Ireland. His pa ...
, was appointed professor of natural philosophy in October 1765 and later the college's first professor of anatomy in 1767. The American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
broke out in 1776, and was catastrophic for the operation of King's College, which suspended instruction for eight years beginning in 1776 with the arrival of the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
. The suspension continued through the military occupation of New York City by British troops until their departure in 1783. The college's library was looted and its sole building requisitioned for use as a military hospital first by American and then British forces.
18th century
 After the Revolution, the college turned to the State of New York in order to restore its vitality, promising to make whatever changes to the school's charter the state might demand. The legislature agreed to assist the college, and on May 1, 1784, it passed "an Act for granting certain privileges to the College heretofore called King's College". The Act created a board of regents to oversee the resuscitation of King's College, and, in an effort to demonstrate its support for the new Republic, the legislature stipulated that "the College within the City of New York heretofore called King's College be forever hereafter called and known by the name of Columbia College", a reference to
After the Revolution, the college turned to the State of New York in order to restore its vitality, promising to make whatever changes to the school's charter the state might demand. The legislature agreed to assist the college, and on May 1, 1784, it passed "an Act for granting certain privileges to the College heretofore called King's College". The Act created a board of regents to oversee the resuscitation of King's College, and, in an effort to demonstrate its support for the new Republic, the legislature stipulated that "the College within the City of New York heretofore called King's College be forever hereafter called and known by the name of Columbia College", a reference to Columbia
Columbia may refer to:
* Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America
Places North America Natural features
* Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region i ...
, an alternative name for America which in turn comes from the name of Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
. The Regents finally became aware of the college's defective constitution in February 1787 and appointed a revision committee, which was headed by John Jay
John Jay (December 12, 1745 – May 17, 1829) was an American statesman, patriot, diplomat, abolitionist, signatory of the Treaty of Paris, and a Founding Father of the United States. He served as the second governor of New York and the f ...
and Alexander Hamilton. In April of that same year, a new charter was adopted for the college granted the power to a separate board of 24 trustees.Moore, Nathanal Fischer (1846). ''A Historical Sketch of Columbia''. New York, New York: Columbia University Press.
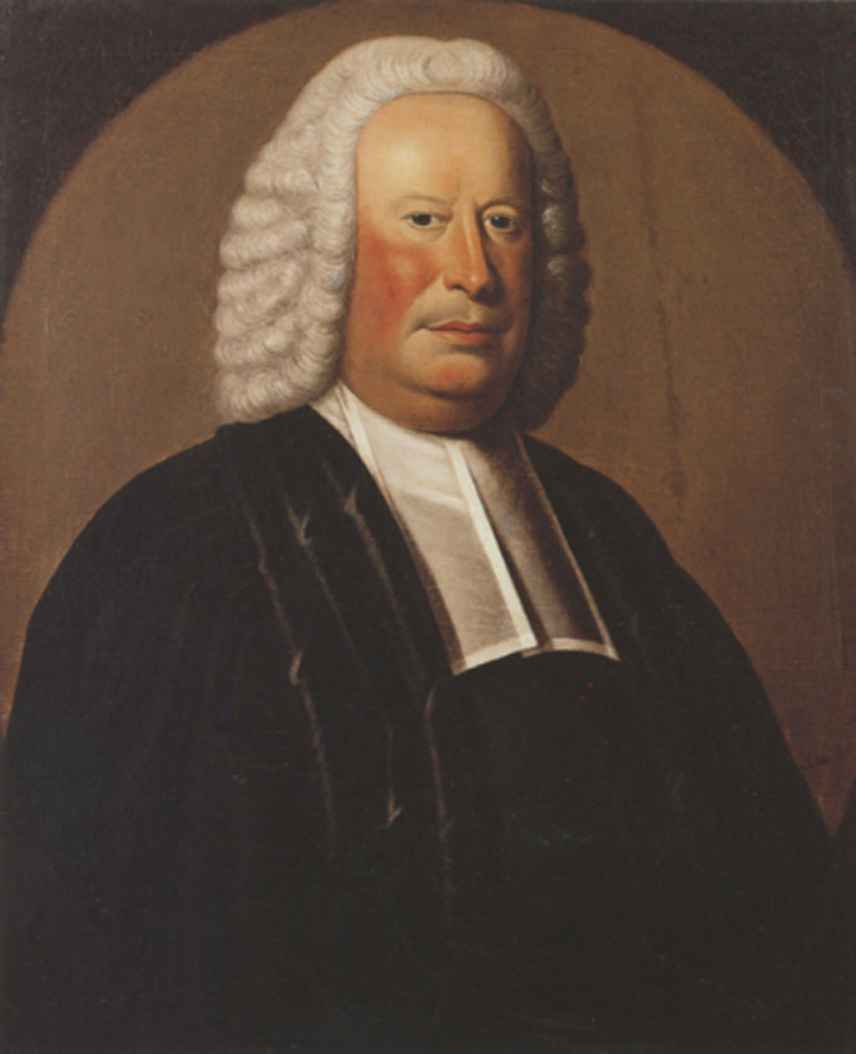
 On May 21, 1787,
On May 21, 1787, William Samuel Johnson
William Samuel Johnson (October 7, 1727 – November 14, 1819) was an American Founding Father and statesman. Before the Revolutionary War, he served as a militia lieutenant before being relieved following his rejection of his election to the Fi ...
, the son of Dr. Samuel Johnson, was unanimously elected president of Columbia College. Prior to serving at the university, Johnson had participated in the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Nav ...
and been chosen as a delegate to the Constitutional Convention. For a period in the 1790s, with New York City as the federal and state capital and the country under successive Federalist governments, a revived Columbia thrived under the auspices of Federalists such as Hamilton and Jay. Both President George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
and Vice President John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
attended the college's commencement on May 6, 1789, as a tribute of honor to the many alumni of the school who had been involved in the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
.
19th century to present
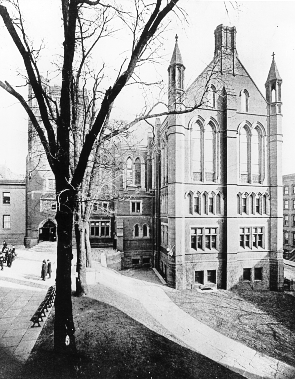

 In November 1813, the college agreed to incorporate its medical school with The College of Physicians and Surgeons, a new school created by the Regents of New York, forming Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons. The college's enrollment, structure, and academics stagnated for the majority of the 19th century, with many of the college presidents doing little to change the way that the college functioned. In 1857, the college moved from the King's College campus at Park Place to a primarily
In November 1813, the college agreed to incorporate its medical school with The College of Physicians and Surgeons, a new school created by the Regents of New York, forming Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons. The college's enrollment, structure, and academics stagnated for the majority of the 19th century, with many of the college presidents doing little to change the way that the college functioned. In 1857, the college moved from the King's College campus at Park Place to a primarily Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
campus on 49th Street and Madison Avenue, where it remained for the next forty years. During the last half of the 19th century, under the leadership of President F.A.P. Barnard, the president that Barnard College
Barnard College of Columbia University is a private women's liberal arts college in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It was founded in 1889 by a group of women led by young student activist Annie Nathan Meyer, who petitioned Columbia ...
is named after, the institution rapidly assumed the shape of a modern university. Barnard College was created in 1889 as a response to the university's refusal to accept women. By this time, the college's investments in New York real estate became a primary source of steady income for the school, mainly owing to the city's expanding population. In 1896, university president Seth Low
Seth Low (January 18, 1850 – September 17, 1916) was an American educator and political figure who served as the mayor of Brooklyn from 1881 to 1885, the president of Columbia University from 1890 to 1901, a diplomatic representative of ...
moved the campus from 49th Street to its present location, a more spacious campus in the developing neighborhood of Morningside Heights. Under the leadership of Low's successor, Nicholas Murray Butler, who served for over four decades, Columbia rapidly became the nation's major institution for research, setting the "multiversity" model that later universities would adopt. Prior to becoming the president of Columbia University, Butler founded Teachers College, as a school to prepare home economists and manual art teachers for the children of the poor, with philanthropist Grace Hoadley Dodge. Teachers College is currently affiliated as the university's Graduate School of Education.
Research into the atom by faculty members John R. Dunning
John Ray Dunning (September 24, 1907 – August 25, 1975) was an American physicist who played key roles in the Manhattan Project that developed the first atomic bombs. He specialized in neutron physics, and did pioneering work in gaseous diffusio ...
, I. I. Rabi, Enrico Fermi and Polykarp Kusch placed Columbia's physics department in the international spotlight in the 1940s after the first nuclear pile was built to start what became the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
. In 1928, Seth Low
Seth Low (January 18, 1850 – September 17, 1916) was an American educator and political figure who served as the mayor of Brooklyn from 1881 to 1885, the president of Columbia University from 1890 to 1901, a diplomatic representative of ...
Junior College was established by Columbia University in order to mitigate the number of Jewish applicants to Columbia College. The college was closed in 1936 due to the adverse effects of the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
and its students were subsequently taught at Morningside Heights, although they did not belong to any college but to the university at large.
There was an evening school called University Extension, which taught night classes, for a fee, to anyone willing to attend. In 1947, the program was reorganized as an undergraduate college and designated the School of General Studies in response to the return of GIs after World War II. In 1995, the School of General Studies was again reorganized as a full-fledged liberal arts college for non-traditional students (those who have had an academic break of one year or more, or are pursuing dual-degrees) and was fully integrated into Columbia's traditional undergraduate curriculum. Within the same year, the Division of Special Programs—later the School of Continuing Education, and now the School of Professional Studies—was established to reprise the former role of University Extension. While the School of Professional Studies only offered non-degree programs for lifelong learners and high school students in its earliest stages, it now offers degree programs in a diverse range of professional and inter-disciplinary fields.
In the aftermath of World War II, the discipline of international relations became a major scholarly focus of the university, and in response, the School of International and Public Affairs was founded in 1946, drawing upon the resources of the faculties of political science, economics, and history. The Columbia University Bicentennial was celebrated in 1954.
During the 1960s Columbia experienced large-scale student activism, which reached a climax in the spring of 1968 when hundreds of students occupied buildings on campus. The incident forced the resignation of Columbia's president, Grayson Kirk
Grayson Louis Kirk (October 12, 1903 – November 21, 1997) was an American political scientist who served as president of Columbia University during the Columbia University protests of 1968. He was also an advisor to the State Department and ...
, and the establishment of the University Senate.
Though several schools within the university had admitted women for years, Columbia College first admitted women in the fall of 1983, after a decade of failed negotiations with Barnard College
Barnard College of Columbia University is a private women's liberal arts college in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It was founded in 1889 by a group of women led by young student activist Annie Nathan Meyer, who petitioned Columbia ...
, the all-female institution affiliated with the university, to merge the two schools. Barnard College still remains affiliated with Columbia, and all Barnard graduates are issued diplomas signed by the presidents of Columbia University
The president of Columbia University is the chief officer of Columbia University in New York City. The position was first created in 1754 by the original royal charter for the university, issued by George II, and the power to appoint the preside ...
and Barnard College.
During the late 20th century, the university underwent significant academic, structural, and administrative changes as it developed into a major research university. For much of the 19th century, the university consisted of decentralized and separate faculties specializing in Political Science, Philosophy, and Pure Science. In 1979, these faculties were merged into the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences. In 1991, the faculties of Columbia College, the School of General Studies, the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the School of the Arts, and the School of Professional Studies were merged into the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, leading to the academic integration and centralized governance of these schools. In 2010, the School of International and Public Affairs, which was previously a part of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, became an independent faculty.
Campus
Morningside Heights
 The majority of Columbia's graduate and undergraduate studies are conducted in Morningside Heights on
The majority of Columbia's graduate and undergraduate studies are conducted in Morningside Heights on Seth Low
Seth Low (January 18, 1850 – September 17, 1916) was an American educator and political figure who served as the mayor of Brooklyn from 1881 to 1885, the president of Columbia University from 1890 to 1901, a diplomatic representative of ...
's late-19th century vision of a university campus where all disciplines could be taught at one location. The campus was designed along Beaux-Arts planning principles by the architects McKim, Mead & White
McKim, Mead & White was an American architectural firm that came to define architectural practice, urbanism, and the ideals of the American Renaissance in fin de siècle New York. The firm's founding partners Charles Follen McKim (1847–1909), Wil ...
. Columbia's main campus occupies more than six city blocks, or , in Morningside Heights, New York City, a neighborhood that contains a number of academic institutions. The university owns over 7,800 apartments in Morningside Heights, housing faculty, graduate students, and staff. Almost two dozen undergraduate dormitories (purpose-built or converted) are located on campus or in Morningside Heights. Columbia University has an extensive tunnel system, more than a century old, with the oldest portions predating the present campus. Some of these remain accessible to the public, while others have been cordoned off.
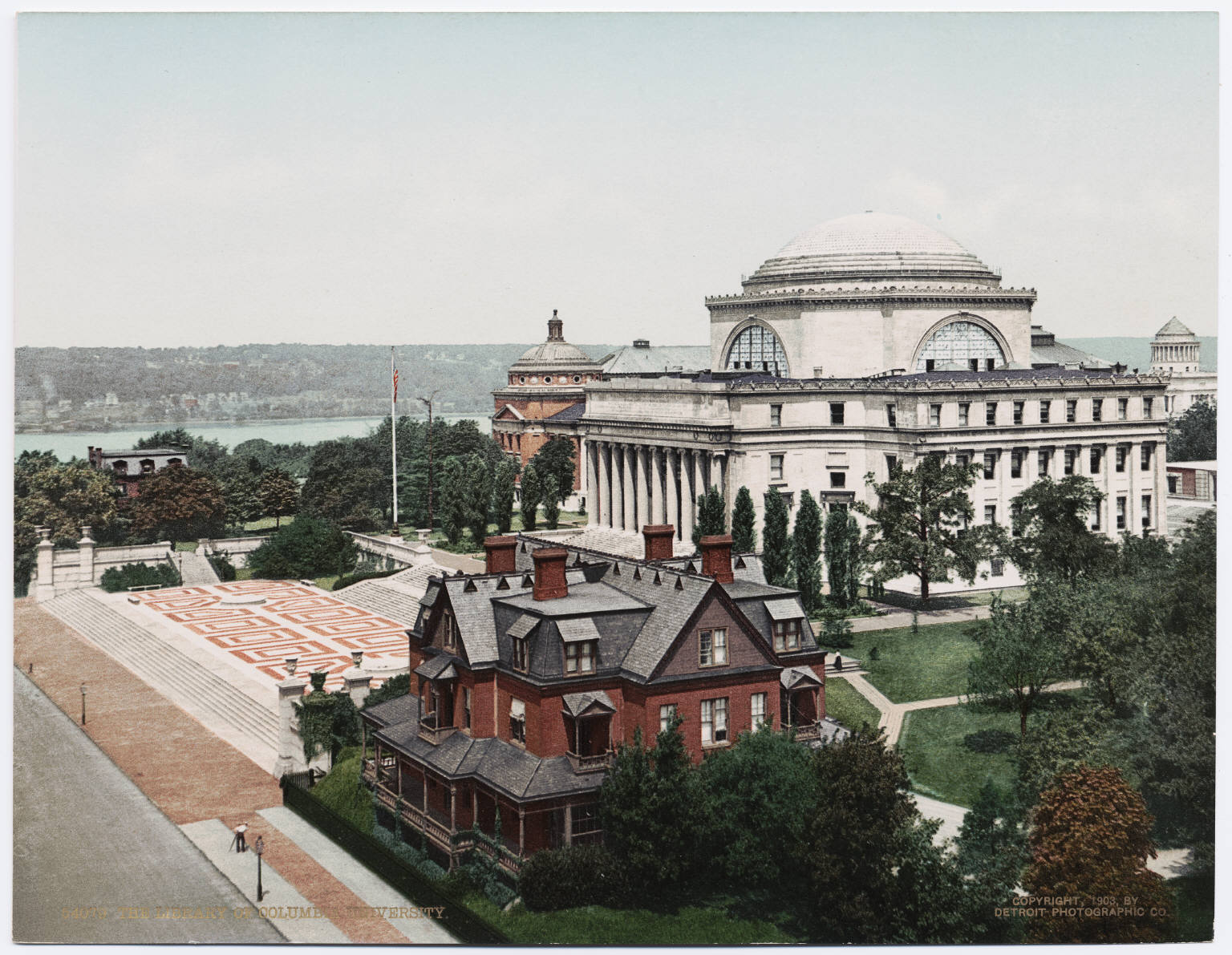
 The Nicholas Murray Butler Library, known simply as
The Nicholas Murray Butler Library, known simply as Butler Library
Butler Library is located on the Morningside Heights campus of Columbia University at 535 West 114th Street, in Manhattan, New York City. It is the university's largest single library with over 2 million volumes, as well as one of the larges ...
, is the largest single library in the Columbia University Library System, and is one of the largest buildings on the campus. Proposed as "South Hall" by the university's former president Nicholas Murray Butler as expansion plans for Low Memorial Library stalled, the new library was funded by Edward Harkness, benefactor of Yale's residential college system, and designed by his favorite architect, James Gamble Rogers. It was completed in 1934 and renamed for Butler in 1946. The library design is neo-classical in style. Its facade features a row of columns in the Ionic order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite ...
above which are inscribed the names of great writers, philosophers, and thinkers, most of whom are read by students engaged in the Core Curriculum of Columbia College. , Columbia's library system includes over 15.0 million volumes, making it the eighth largest library system and fifth largest collegiate library system in the United States.
Several buildings on the Morningside Heights campus are listed on the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic ...
. Low Memorial Library, a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places liste ...
and the centerpiece of the campus, is listed for its architectural significance. Philosophy Hall
Philosophy Hall is a building on the campus of Columbia University in New York City. It houses the English, Philosophy, and French departments, along with the university's writing center, part of its registrar's office, and the student lounge of it ...
is listed as the site of the invention of FM radio
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting using frequency modulation (FM). Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to provide high fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting is cap ...
. Also listed is Pupin Hall, another National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places liste ...
, which houses the physics and astronomy departments. Here the first experiments on the fission of uranium were conducted by Enrico Fermi. The uranium atom was split there ten days after the world's first atom-splitting in Copenhagen, Denmark. Other buildings listed include Casa Italiana, the Delta Psi, Alpha Chapter building of St. Anthony Hall, Earl Hall
Earl Hall is a building on the campus of Columbia University. Built in 1900–1902 and designed by McKim, Mead & White, the building serves as a center for student religious life. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places
The ...
, and the buildings of the affiliated Union Theological Seminary.
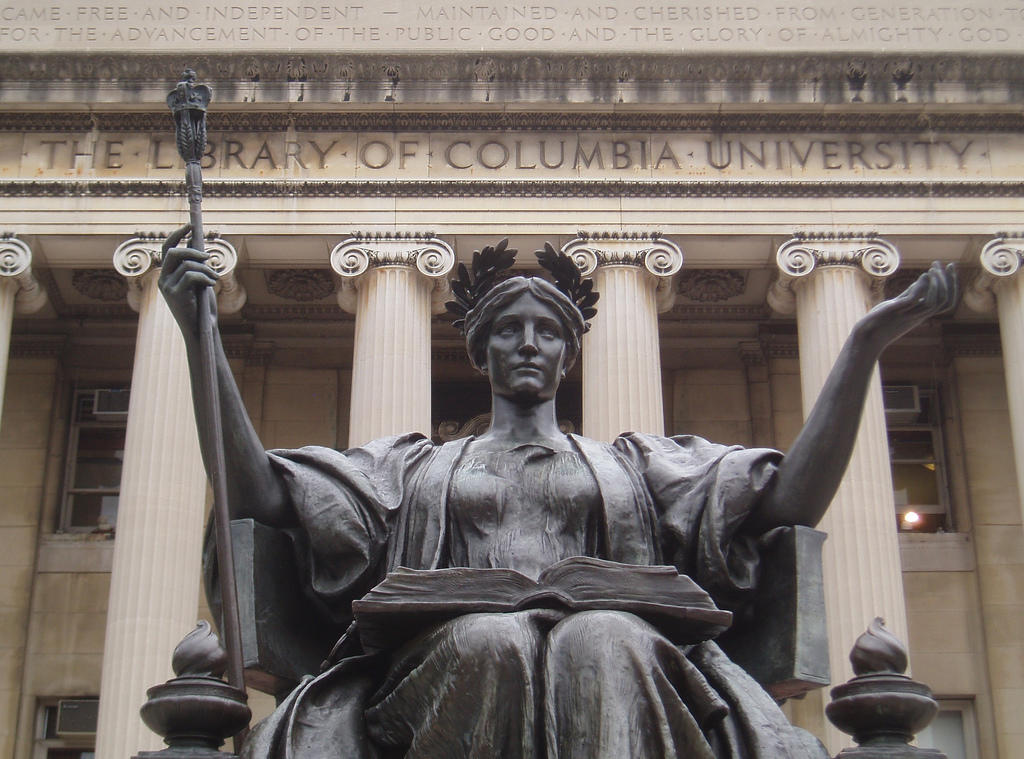
 A statue by sculptor
A statue by sculptor Daniel Chester French
Daniel Chester French (April 20, 1850 – October 7, 1931) was an American sculptor of the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, best known for his 1874 sculpture '' The Minute Man'' in Concord, Massachusetts, and his 1920 monum ...
called '' Alma Mater'' is centered on the front steps of Low Memorial Library. McKim, Mead & White invited French to build the sculpture in order to harmonize with the larger composition of the court and library in the center of the campus. Draped in an academic gown, the female figure of Alma Mater wears a crown of laurels and sits on a throne. The scroll-like arms of the throne end in lamps, representing sapientia and doctrina. A book signifying knowledge, balances on her lap, and an owl, the attribute of wisdom, is hidden in the folds of her gown. Her right hand holds a scepter composed of four sprays of wheat, terminating with a crown of King's College which refers to Columbia's origin as a royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, b ...
institution in 1754. A local actress named Mary Lawton was said to have posed for parts of the sculpture. The statue was dedicated on September 23, 1903, as a gift of Mr. & Mrs. Robert Goelet, and was originally covered in golden leaf. During the Columbia University protests of 1968 a bomb damaged the sculpture, but it has since been repaired. The small hidden owl on the sculpture is also the subject of many Columbia legends, the main legend being that the first student in the freshmen class to find the hidden owl on the statue will be valedictorian, and that any subsequent Columbia male who finds it will marry a Barnard student, given that Barnard is a women's college.
"The Steps", alternatively known as "Low Steps" or the "Urban Beach", are a popular meeting area for Columbia students. The term refers to the long series of granite steps leading from the lower part of campus (South Field) to its upper terrace. With a design inspired by the City Beautiful movement, the steps of Low Library provides Columbia University and Barnard College students, faculty, and staff with a comfortable outdoor platform and space for informal gatherings, events, and ceremonies. McKim's classical facade epitomizes late 19th-century new-classical designs, with its columns and portico marking the entrance to an important structure.
Other campuses

 In April 2007, the university purchased more than two-thirds of a site for a new campus in
In April 2007, the university purchased more than two-thirds of a site for a new campus in Manhattanville
Manhattanville (also known as West Harlem or West Central Harlem) is a neighborhood in the New York City borough of Manhattan bordered on the north by 135th Street; on the south by 122nd and 125th Streets; on the west by Hudson River; and ...
, an industrial neighborhood to the north of the Morningside Heights campus. Stretching from 125th Street to 133rd Street
133rd Street is a street in Manhattan and the Bronx, New York City. In Harlem, Manhattan, it begins at Riverside Drive on its western side and crosses Broadway, Amsterdam Avenue, and ends at Convent Avenue, before resuming on the eastern side ...
, Columbia Manhattanville houses buildings for Columbia's Business School, School of International and Public Affairs, Columbia School of the Arts, and the Jerome L. Greene Center for Mind, Brain, and Behavior, where research will occur on neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. The $7 billion expansion plan included demolishing all buildings, except three that are historically significant (the Studebaker Building, Prentis Hall
Prentis Hall is a historic building located on the Manhattanville campus of Columbia University at 632 West 125th Street. It houses the university's department of music and the Computer Music Center, as well as facilities for the School of the ...
, and the Nash Building), eliminating the existing light industry and storage warehouses, and relocating tenants in 132 apartments. Replacing these buildings created of space for the university. Community activist groups in West Harlem fought the expansion for reasons ranging from property protection and fair exchange for land, to residents' rights. Subsequent public hearings drew neighborhood opposition. , the State of New York's Empire State Development Corporation approved use of eminent domain, which, through declaration of Manhattanville's "blighted" status, gives governmental bodies the right to appropriate private property for public use. On May 20, 2009, the New York State Public Authorities Control Board approved the Manhanttanville expansion plan.
NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital is affiliated with the medical schools of both Columbia University and Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to tea ...
. According to ''U.S. News & World Report''s "2020–21 Best Hospitals Honor Roll and Medical Specialties Rankings", it is ranked fourth overall and second among university hospitals. Columbia's medical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, ...
has a strategic partnership with New York State Psychiatric Institute, and is affiliated with 19 other hospitals in the U.S. and four hospitals overseas. Health-related schools are located at the Columbia University Medical Center
NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center (NYP/CUIMC), also known as the Columbia University Irving Medical Center (CUIMC), is an academic medical center and the largest campus of NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital. It includes Co ...
, a campus located in the neighborhood of Washington Heights, fifty blocks uptown. Other teaching hospitals affiliated with Columbia through the NewYork-Presbyterian network include the Payne Whitney Clinic in Manhattan, and the Payne Whitney Westchester, a psychiatric institute located in White Plains, New York. On the northern tip of Manhattan island (in the neighborhood of Inwood), Columbia owns the Baker Field, which includes the Lawrence A. Wien Stadium
Robert K. Kraft Field at Lawrence A. Wien Stadium, officially known as Robert K. Kraft Field at Lawrence A. Wien Stadium at Baker Athletics Complex, is a stadium in the Inwood neighborhood at the northern tip of the island of Manhattan, New Y ...
as well as facilities for field sports, outdoor track, and tennis. There is a third campus on the west bank of the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between Ne ...
, the Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory
The Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory (LDEO) is the scientific research center of the Columbia Climate School, and a unit of The Earth Institute at Columbia University. It focuses on climate and earth sciences and is located on a 189-acre ( ...
and Earth Institute in Palisades, New York. A fourth is the Nevis Laboratories in Irvington, New York for the study of particle and motion physics. A satellite site in Paris, France holds classes at Reid Hall
Reid Hall is a complex of academic facilities owned and operated by Columbia University that is located in the Montparnasse quartier of Paris, France. It houses the Columbia University Institute for Scholars at Reid Hall in addition to various ...
.
Sustainability
In 2006, the university established the Office of Environmental Stewardship to initiate, coordinate and implement programs to reduce the university's environmental footprint. The U.S. Green Building Council selected the university's Manhattanville plan for the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) Neighborhood Design pilot program. The plan commits to incorporating smart growth, new urbanism and "green" building design principles. Columbia is one of the 2030 Challenge Partners, a group of nine universities in the city of New York that have pledged to reduce theirgreenhouse emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
by 30% within the next ten years. Columbia University adopts LEED standards for all new construction and major renovations. The university requires a minimum of Silver, but through its design and review process seeks to achieve higher levels. This is especially challenging for lab and research buildings with their intensive energy use; however, the university also uses lab design guidelines that seek to maximize energy efficiency while protecting the safety of researchers.
Every Thursday and Sunday of the month, Columbia hosts a greenmarket
A farmers' market (or farmers market according to the AP stylebook, also farmer's market in the Cambridge Dictionary) is a physical retail marketplace intended to sell foods directly by farmers to consumers. Farmers' markets may be indoors or o ...
where local farmers can sell their produce to residents of the city. In addition, from April to November Hodgson's farm, a local New York gardening center, joins the market bringing a large selection of plants and blooming flowers. The market is one of the many operated at different points throughout the city by the non-profit group GrowNYC. Dining services at Columbia spends 36 percent of its food budget on local products, in addition to serving sustainably harvested seafood and fair trade coffee on campus. Columbia has been rated "B+" by the 2011 College Sustainability Report Card for its environmental and sustainability initiatives.A. W. Kuchler August William Kuchler (born ''August Wilhelm Küchler''; 1907–1999) was a German-born American geographer and naturalist who is noted for developing a plant association system in widespread use in the United States. Some of this database has bec ...
U.S. potential natural vegetation
In ecology, potential natural vegetation (PNV), also known as Kuchler potential vegetation, is the vegetation that would be expected given environmental constraints (climate, geomorphology, geology) without human intervention or a hazard event ...
types, Columbia University would have a dominant vegetation type of Appalachian Oak (''104'') with a dominant vegetation form of Eastern Hardwood Forest (''25'').
Transportation
Columbia Transportation
Columbia Transportation is a fare-free bus network providing service to Columbia University campuses. It is operated by Academy Bus Lines and Luxury Transportation to serve employees and students. The buses are open to all Columbia faculty, st ...
is the bus service of the university, operated by Academy Bus Lines
Academy Bus Lines is a bus company in New Jersey providing local bus services in northern New Jersey, line-run services to/from New York City from points in southern and central New Jersey, and contract and charter service in the eastern United ...
. The buses are open to all Columbia faculty, students, Dodge Fitness Center members, and anyone else who holds a Columbia ID card. In addition, all TSC students can ride the buses.
Academics
Undergraduate admissions and financial aid
Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight school ...
university to switch to the Common Application.
Scholarships are also given to undergraduate students by the admissions committee. Designations include John W. Kluge Scholars, John Jay Scholars, C. Prescott Davis Scholars, Global Scholars, Egleston Scholars, and Science Research Fellows. Named scholars are selected by the admission committee from first-year applicants. According to Columbia, the first four designated scholars "distinguish themselves for their remarkable academic and personal achievements, dynamism, intellectual curiosity, the originality and independence of their thinking, and the diversity that stems from their different cultures and their varied educational experiences".
In 1919, Columbia established a student application process characterized by ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' as "the first modern college application". The application required a photograph of the applicant, the maiden name of the applicant's mother, and the applicant's religious background.
Organization
Columbia University is an independent, privately supported, nonsectarian institution of higher education. Its official corporate name is " The Trustees of Columbia University in the City of New York". The university's first charter was granted in 1754 by King George II; however, its modern charter was first enacted in 1787 and last amended in 1810 by the New York State Legislature. The university is governed by 24 trustees, customarily including the president, who serves '' ex officio''. The trustees themselves are responsible for choosing their successors. Six of the 24 are nominated from a pool of candidates recommended by the Columbia Alumni Association. Another six are nominated by the board in consultation with the executive committee of the University Senate. The remaining 12, including the president, are nominated by the trustees themselves through their internal processes. The term of office for trustees is six years. Generally, they serve for no more than two consecutive terms. The trustees appoint the president and other senior administrative officers of the university, and review and confirm faculty appointments as required. They determine the university's financial and investment policies, authorize the budget, supervise the endowment, direct the management of the university's real estate and other assets, and otherwise oversee the administration and management of the university. The University Senate was established by the trustees after a university-wide referendum in 1969. It succeeded to the powers of the University Council, which was created in 1890 as a body of faculty, deans, and other administrators to regulate inter-Faculty affairs and consider issues of university-wide concern. The University Senate is a unicameral body consisting of 107 members drawn from all constituencies of the university. These include the president of the university, the provost, the deans of Columbia College and the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, all of whom serve ''ex officio'', and five additional representatives, appointed by the president, from the university's administration. The president serves as the Senate's presiding officer. The Senate is charged with reviewing the educational policies, physical development, budget, and external relations of the university. It oversees the welfare and academic freedom of the faculty and the welfare of students.
The president of Columbia University, who is selected by the trustees in consultation with the executive committee of the University Senate and who serves at the trustees' pleasure, is the chief executive officer of the university. Assisting the president in administering the university are the provost, the senior executive vice president, the executive vice president for health and biomedical sciences, several other vice presidents, the general counsel, the secretary of the university, and the deans of the faculties, all of whom are appointed by the trustees on the nomination of the president and serve at their pleasure. Lee C. Bollinger became the 19th president of Columbia University on June 1, 2002. As
The University Senate was established by the trustees after a university-wide referendum in 1969. It succeeded to the powers of the University Council, which was created in 1890 as a body of faculty, deans, and other administrators to regulate inter-Faculty affairs and consider issues of university-wide concern. The University Senate is a unicameral body consisting of 107 members drawn from all constituencies of the university. These include the president of the university, the provost, the deans of Columbia College and the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, all of whom serve ''ex officio'', and five additional representatives, appointed by the president, from the university's administration. The president serves as the Senate's presiding officer. The Senate is charged with reviewing the educational policies, physical development, budget, and external relations of the university. It oversees the welfare and academic freedom of the faculty and the welfare of students.
The president of Columbia University, who is selected by the trustees in consultation with the executive committee of the University Senate and who serves at the trustees' pleasure, is the chief executive officer of the university. Assisting the president in administering the university are the provost, the senior executive vice president, the executive vice president for health and biomedical sciences, several other vice presidents, the general counsel, the secretary of the university, and the deans of the faculties, all of whom are appointed by the trustees on the nomination of the president and serve at their pleasure. Lee C. Bollinger became the 19th president of Columbia University on June 1, 2002. As president of the University of Michigan
The president of the University of Michigan is a constitutional officer who serves as the principal executive officer of the University of Michigan. The president is chosen by the Board of Regents of the University of Michigan, as provided for ...
, he played a leading role in the twin Supreme Court cases Grutter v. Bollinger and Gratz v. Bollinger
''Gratz v. Bollinger'', 539 U.S. 244 (2003), was a United States Supreme Court case regarding the University of Michigan undergraduate affirmative action admissions policy. In a 6–3 decision announced on June 23, 2003, Chief Justice Rehnq ...
, which upheld the use of student diversity as a compelling justification for affirmative action in higher education.
 Columbia has four official undergraduate colleges: Columbia College, the liberal arts college offering the Bachelor of Arts degree; the Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science (also known as SEAS or Columbia Engineering), the engineering and applied science school offering the Bachelor of Science degree; the School of General Studies, the liberal arts college offering the Bachelor of Arts degree to non-traditional students undertaking full- or part-time study; and
Columbia has four official undergraduate colleges: Columbia College, the liberal arts college offering the Bachelor of Arts degree; the Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science (also known as SEAS or Columbia Engineering), the engineering and applied science school offering the Bachelor of Science degree; the School of General Studies, the liberal arts college offering the Bachelor of Arts degree to non-traditional students undertaking full- or part-time study; and Barnard College
Barnard College of Columbia University is a private women's liberal arts college in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It was founded in 1889 by a group of women led by young student activist Annie Nathan Meyer, who petitioned Columbia ...
. Barnard College
Barnard College of Columbia University is a private women's liberal arts college in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It was founded in 1889 by a group of women led by young student activist Annie Nathan Meyer, who petitioned Columbia ...
is a women's liberal arts college and an academic affiliate in which students receive a Bachelor of Arts degree from Columbia University. Their degrees are signed by the presidents of Columbia University and Barnard College. Barnard students are also eligible to cross-register classes that are available through the Barnard Catalogue and alumnae can join the Columbia Alumni Association.
Joint degree programs are available through Union Theological Seminary, the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
The Jewish Theological Seminary (JTS) is a Conservative Jewish education organization in New York City, New York. It is one of the academic and spiritual centers of Conservative Judaism and a major center for academic scholarship in Jewish studie ...
, as well as through the Juilliard School
The Juilliard School ( ) is a Private university, private performing arts music school, conservatory in New York City. Established in 1905, the school trains about 850 undergraduate and graduate students in dance, drama, and music. It is widely ...
. Teachers College and Barnard College
Barnard College of Columbia University is a private women's liberal arts college in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It was founded in 1889 by a group of women led by young student activist Annie Nathan Meyer, who petitioned Columbia ...
are official faculties of the university; both colleges' presidents are deans under the university governance structure. The Columbia University Senate includes faculty and student representatives from Teachers College and Barnard College who serve two-year terms; all senators are accorded full voting privileges regarding matters impacting the entire university. Teachers College is an affiliated, financially independent graduate school with their own Board of Trustees. Pursuant to an affiliation agreement, Columbia is given the authority to confer "degrees and diplomas" to the graduates of Teachers College. The degrees are signed by presidents of Teachers College and Columbia University in a manner analogous to the university's other graduate schools. Columbia's General Studies school also has joint undergraduate programs available through University College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £143 million (2020)
, budget = ...
, Sciences Po, City University of Hong Kong, Trinity College Dublin, and the Juilliard School
The Juilliard School ( ) is a Private university, private performing arts music school, conservatory in New York City. Established in 1905, the school trains about 850 undergraduate and graduate students in dance, drama, and music. It is widely ...
.
The university also has several Columbia Global Centers Columbia Global Centers are research outposts established by Columbia University in different locations around the world, as part of its initiative to further establish an international research university. The first of these centers opened in Marc ...
, in Amman, Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the Capital city, capital of the China, People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's Li ...
, Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
, Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the secon ...
, Nairobi
Nairobi ( ) is the capital and largest city of Kenya. The name is derived from the Maasai phrase ''Enkare Nairobi'', which translates to "place of cool waters", a reference to the Nairobi River which flows through the city. The city proper ...
, Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
, Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
, Santiago
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile, is the capital and largest city of Chile as well as one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is the center of Chile's most densely populated region, the Santiago Metropolitan Region, whos ...
, and Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
.
International partnerships
Columbia students can study abroad for a semester or a year at partner institutions such as Sciences Po,École des hautes études en sciences sociales
The School for Advanced Studies in the Social Sciences (french: École des hautes études en sciences sociales; EHESS) is a graduate ''grande école'' and '' grand établissement'' in Paris focused on academic research in the social sciences. The ...
(EHESS), École normale supérieure
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France
* École, S ...
(ENS), Panthéon-Sorbonne University, King's College London, London School of Economics
, mottoeng = To understand the causes of things
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £240.8 million (2021)
, budget = £391.1 milli ...
, University College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £143 million (2020)
, budget = ...
and the University of Warwick
, mottoeng = Mind moves matter
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £7.0 million (2021)
, budget = £698.2 million (2020 ...
. Select students can study at either the University of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light
, established =
, endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019)
, budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20)
, chancellor ...
or the University of Cambridge
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts.
Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge.
, established =
, other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Schola ...
for a year if approved by both Columbia and either Oxford or Cambridge. Columbia also has a dual MA program with the Aga Khan University
Aga Khan University is a non-profit institution and an agency of the Aga Khan Development Network. It was Founded in 1983 as Pakistan's first private university. Starting in 2000, the university expanded to Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, the United Ki ...
in London.
Rankings
Columbia University is ranked 18th in the United States and seventh globally for 2022–2023 by '' U.S. News & World Report''. In the previous year, Columbia was ranked sixth in the United States, although this was later found to have partly resulted from inaccurate statistics submitted by the university, resulting in its temporary delisting from the rankings. QS University Rankings listed Columbia as fifth in the United States. Ranked 15th among U.S. colleges for 2020 by ''The Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' is an American business-focused, international daily newspaper based in New York City, with international editions also available in Chinese and Japanese. The ''Journal'', along with its Asian editions, is published ...
'' and ''Times Higher Education
''Times Higher Education'' (''THE''), formerly ''The Times Higher Education Supplement'' (''The Thes''), is a British magazine reporting specifically on news and issues related to higher education.
Ownership
TPG Capital acquired TSL Education ...
'', in recent years it has been ranked as high as second. Individual colleges and schools were also nationally ranked by ''U.S. News & World Report'' for its 2021 edition. Columbia Law School was ranked fourth, the Mailman School of Public Health fourth, the School of Social Work
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compuls ...
tied for third, Columbia Business School
Columbia Business School (CBS) is the business school of Columbia University, a private research university in New York City. Established in 1916, Columbia Business School is one of six Ivy League business schools and is one of the oldest bus ...
eighth, the College of Physicians and Surgeons tied for sixth for research (and tied for 31st for primary care), the School of Nursing
Nurse education consists of the theoretical and practical training provided to nurses with the purpose to prepare them for their duties as nursing care professionals. This education is provided to student nurses by experienced nurses and other med ...
tied for 11th in the master's program and tied for first in the doctorate nursing program, and the Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science (graduate) was ranked tied for 14th.
In 2021, Columbia was ranked seventh in the world (sixth in the United States) by '' Academic Ranking of World Universities'', sixth in the world by ''U.S. News & World Report'', 19th in the world by ''QS World University Rankings
''QS World University Rankings'' is an annual publication of university rankings by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS). The QS system comprises three parts: the global overall ranking, the subject rankings (which name the world's top universities for th ...
'', and 11th globally by ''Times Higher Education World University Rankings''. It was ranked in the first tier of American research universities, along with Harvard, MIT, and Stanford, in the 2019 report from the Center for Measuring University Performance
The Center for Measuring University Performance is a research center at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. ''The Center'' is best known for an annual report it produces, The Top American Research Universities, that ranks American univers ...
. In 2022, Columbia's reporting of metrics used for university ranking was criticized by Professor of Mathematics Michael Thaddeus, who argued key data supporting the ranking was "inaccurate, dubious or highly misleading." Subsequently, U.S. News & World Report "unranked" Columbia from its 2022 list of Best Colleges saying that it could not verify the data submitted by the university.
Columbia's Graduate School of Architecture, Planning and Preservation
Graduate School of Architecture, Planning and Preservation (GSAPP) is the architecture school of Columbia University, a private research university in New York City. It is regarded as an important and highly prestigious architecture school.
was ranked the second most admired graduate program by Architectural Record in 2020.
In 2015, Columbia University was ranked the first in the state by average professor salaries. In 2011, the Mines ParisTech: Professional Ranking of World Universities ranked Columbia third best university for forming CEOs in the US and 12th worldwide.
Research
 Columbia is
Columbia is classified
Classified may refer to:
General
*Classified information, material that a government body deems to be sensitive
*Classified advertising or "classifieds"
Music
*Classified (rapper) (born 1977), Canadian rapper
* The Classified, a 1980s American ro ...
among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". Columbia was the first North American site where the uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
atom was split. The College of Physicians and Surgeons played a central role in developing the modern understanding of neuroscience with the publication of '' Principles of Neural Science'', described by historian of science Katja Huenther as the "neuroscience 'bible' ". The book was written by a team of Columbia researchers that included Nobel Prize winner Eric Kandel, James H. Schwartz, and Thomas Jessell
Thomas Michael Jessell (2 August 1951 – 28 April 2019) was the Claire Tow Professor of biochemistry and molecular biophysics at Columbia University in New York and a prominent developmental neuroscientist. In 2018, Columbia University announce ...
. Columbia was the birthplace of FM radio
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting using frequency modulation (FM). Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to provide high fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting is cap ...
and the laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The ...
. The first brain-computer interface capable of translating brain signals into speech was developed by neuroengineers at Columbia. The MPEG-2 algorithm of transmitting high quality audio and video over limited bandwidth was developed by Dimitris Anastassiou, a Columbia professor of electrical engineering. Biologist Martin Chalfie was the first to introduce the use of Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) in labeling cells in intact organisms. Other inventions and products related to Columbia include Sequential Lateral Solidification (SLS) technology for making LCDs, System Management Arts (SMARTS), Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) (which is used for audio, video, chat, instant messaging and whiteboarding), pharmacopeia
A pharmacopoeia, pharmacopeia, or pharmacopoea (from the obsolete typography ''pharmacopœia'', meaning "drug-making"), in its modern technical sense, is a book containing directions for the identification of compound medicines, and published by ...
, Macromodel (software for computational chemistry), a new and better recipe for glass concrete, Blue LEDs, and Beamprop (used in photonics).
Columbia scientists have been credited with about 175 new inventions in the health sciences each year. More than 30 pharmaceutical products based on discoveries and inventions made at Columbia reached the market. These include Remicade (for arthritis), Reopro (for blood clot complications), Xalatan
Latanoprost, sold under the brand name Xalatan among others, is a medication used to treat increased pressure inside the eye. This includes ocular hypertension and open angle glaucoma. It is applied as eye drops to the eyes. Onset of effects is ...
(for glaucoma), Benefix, Latanoprost
Latanoprost, sold under the brand name Xalatan among others, is a medication used to treat increased pressure inside the eye. This includes ocular hypertension and open angle glaucoma. It is applied as eye drops to the eyes. Onset of effects is ...
(a glaucoma treatment), shoulder prosthesis, homocysteine (testing for cardiovascular disease), and Zolinza
Vorinostat ( rINN) also known as Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid ( suberoyl+ anilide+hydroxamic acid abbreviated as SAHA) is a member of a larger class of compounds that inhibit histone deacetylases (HDAC). Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDI) ...
(for cancer therapy). Columbia Technology Ventures (formerly Science and Technology Ventures), , manages some 600 patents and more than 250 active license agreements. Patent-related deals earned Columbia more than $230 million in the 2006 fiscal year, according to the university, more than any university in the world. Columbia owns many unique research facilities, such as the Columbia Institute for Tele-Information dedicated to telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that ...
s and the Goddard Institute for Space Studies
The Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) is a laboratory in the Earth Sciences Division of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center affiliated with the Columbia University Earth Institute.
The institute is located at Columbia University in ...
, which is an astronomical observatory affiliated with NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
.
Military and veteran enrollment
Columbia is a long-standing participant of theUnited States Department of Veterans Affairs
The United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is a Cabinet-level executive branch department of the federal government charged with providing life-long healthcare services to eligible military veterans at the 170 VA medical centers a ...
Yellow Ribbon Program, allowing eligible veterans to pursue a Columbia undergraduate degree regardless of socioeconomic status for over 70 years. As a part of the Eisenhower Leader Development Program (ELDP) in partnership with the United States Military Academy
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known Metonymy, metonymically as West Point or simply as Army, is a United States service academies, United States service academy in West Point, New York. It was originally established as a f ...
at West Point, Columbia is the only school in the Ivy League to offer a graduate degree program in organizational psychology to aid military officers in tactical decision making and strategic management.
Awards
 Several prestigious awards are administered by Columbia University, most notably the
Several prestigious awards are administered by Columbia University, most notably the Pulitzer Prize
The Pulitzer Prize () is an award for achievements in newspaper, magazine, online journalism, literature, and musical composition within the United States. It was established in 1917 by provisions in the will of Joseph Pulitzer, who had made ...
and the Bancroft Prize in history. Updated 2013 by Sig Gissler. Other prizes, which are awarded by the Graduate School of Journalism, include the Alfred I. duPont–Columbia University Award
The Alfred I. duPont–Columbia University Award honors excellence in broadcast and digital journalism in the public service and is considered one of the most prestigious awards in journalism. The awards were established in 1942 and administered ...
, the National Magazine Awards
The National Magazine Awards, also known as the Ellie Awards, honor print and digital publications that consistently demonstrate superior execution of editorial objectives, innovative techniques, noteworthy enterprise and imaginative design. Or ...
, the Maria Moors Cabot Prizes, the John Chancellor Award, and the Lukas Prizes, which include the J. Anthony Lukas Book Prize and Mark Lynton History Prize. The university also administers the Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize
The Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize for Biology or Biochemistry is an annual prize awarded by Columbia University to a researcher or group of researchers who have made an outstanding contribution in basic research in the fields of biology or biochemis ...
, which is considered an important precursor to the Nobel Prize, 51 of its 101 recipients having gone on to win either a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordi ...
or Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
as of October 2018; the W. Alden Spencer Award; the Vetlesen Prize, which is known as the Nobel Prize of geology; the Japan-U.S. Friendship Commission Prize for the Translation of Japanese Literature, the oldest such award; the Edwin Howard Armstrong award
The Major Armstrong award, named after the inventor of FM radio, Edwin Howard Armstrong, is presented "to AM and FM stations for excellence and originality in radio broadcasting" by the Armstrong Memorial Research Foundation at Columbia Universi ...
; the Calderone Prize in public health; and the Ditson Conductor's Award.
Student life
Students
In 2020, Columbia University's student population was 31,455 (8,842 students in undergraduate programs and 22,613 in postgraduate programs), with 45% of the student population identifying themselves as a minority. Twenty-six percent of students at Columbia have family incomes below $60,000. 16% of students at Columbia receive Federal Pell Grants, which mostly go to students whose family incomes are below $40,000. Seventeen percent of students are the first member of their family to attend a four-year college. On-campus housing is guaranteed for all four years as an undergraduate. Columbia College and the Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science (also known as SEAS or Columbia Engineering) share housing in the on-campus residence halls. First-year students usually live in one of the large residence halls situated around South Lawn: Carman Hall, Furnald Hall, Hartley Hall, John Jay Hall, or Wallach Hall (originally Livingston Hall). Upperclassmen participate in a room selection process, wherein students can pick to live in a mix of either corridor- or apartment-style housing with their friends. The Columbia University School of General Studies,Barnard College
Barnard College of Columbia University is a private women's liberal arts college in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It was founded in 1889 by a group of women led by young student activist Annie Nathan Meyer, who petitioned Columbia ...
and graduate schools have their own apartment-style housing in the surrounding neighborhood.
Columbia University is home to many fraternities, sororities, and co-educational Greek organizations. Approximately 10–15% of undergraduate students are associated with Greek life. Many Barnard women also join Columbia sororities. There has been a Greek presence on campus since the establishment in 1836 of the Delta chapter of Alpha Delta Phi. The InterGreek Council is the self-governing student organization that provides guidelines and support to its member organizations within each of the three councils at Columbia, the Interfraternity Council, Panhellenic Council, and Multicultural Greek Council. The three council presidents bring their affiliated chapters together once a month to meet as one Greek community. The InterGreek Council meetings provide opportunity for member organizations to learn from each other, work together and advocate for community needs.
Publications

 The '' Columbia Daily Spectator'' is the nation's second-oldest continuously operating daily student newspaper. '' The Blue and White'' is a monthly literary magazine established in 1890 that discusses campus life and local politics. '' Bwog'', originally an offshoot of ''The Blue and White'' but now fully independent, is an online campus news and entertainment source. '' The Morningside Post'' is a student-run multimedia news publication.
Political publications include '' The Current'', a journal of politics, culture and Jewish Affairs; the '' Columbia Political Review'', the multi-partisan political magazine of the Columbia Political Union; and ''AdHoc'', which denotes itself as the "progressive" campus magazine and deals largely with local political issues and arts events.
''Columbia Magazine'' is the alumni magazine of Columbia, serving all 340,000+ of the university's alumni. Arts and literary publications include ''The Columbia Review'', the nation's oldest college literary magazine; ''Surgam'', the literary magazine of
The '' Columbia Daily Spectator'' is the nation's second-oldest continuously operating daily student newspaper. '' The Blue and White'' is a monthly literary magazine established in 1890 that discusses campus life and local politics. '' Bwog'', originally an offshoot of ''The Blue and White'' but now fully independent, is an online campus news and entertainment source. '' The Morningside Post'' is a student-run multimedia news publication.
Political publications include '' The Current'', a journal of politics, culture and Jewish Affairs; the '' Columbia Political Review'', the multi-partisan political magazine of the Columbia Political Union; and ''AdHoc'', which denotes itself as the "progressive" campus magazine and deals largely with local political issues and arts events.
''Columbia Magazine'' is the alumni magazine of Columbia, serving all 340,000+ of the university's alumni. Arts and literary publications include ''The Columbia Review'', the nation's oldest college literary magazine; ''Surgam'', the literary magazine of The Philolexian Society
The Philolexian Society of Columbia University is one of the oldest college literary and debate societies in the United States, and the oldest student group at Columbia. Founded in 1802, the Society aims to "improve its members in Oratory, Comp ...
; ''Quarto'', Columbia University's official undergraduate literary magazine; ''4x4'', a student-run alternative to ''Quarto''; ''Columbia'', a nationally regarded literary journal; the ''Columbia Journal of Literary Criticism''; and ''The Mobius Strip'', an online arts and literary magazine. ''Inside New York
''Inside New York'' is a New York City guidebook written and published annually by students of several universities, including Columbia University, New York University, The New School and other New York City universities. Founded in 1978 as the '' ...
'' is an annual guidebook to New York City, written, edited, and published by Columbia undergraduates. Through a distribution agreement with Columbia University Press
Columbia University Press is a university press based in New York City, and affiliated with Columbia University. It is currently directed by Jennifer Crewe (2014–present) and publishes titles in the humanities and sciences, including the fie ...
, the book is sold at major retailers and independent bookstores.
Columbia is home to numerous undergraduate academic publications. The ''Columbia Undergraduate Science Journal'' prints original science research in its two annual publications. The '' Journal of Politics & Society'' is a journal of undergraduate research in the social sciences; ''Publius'' is an undergraduate journal of politics established in 2008 and published biannually; the ''Columbia East Asia Review'' allows undergraduates throughout the world to publish original work on China, Japan, Korea, Tibet, and Vietnam and is supported by the Weatherhead East Asian Institute; ''The Birch
''The Birch'' is a national biannual undergraduate journal of Eastern European and Eurasian culture.
History and profile
''The Birch'' was established in 2004. The journal, which is run by undergraduates at Columbia University, is the first exclu ...
'' is an undergraduate journal of Eastern European and Eurasian culture that is the first national student-run journal of its kind; the ''Columbia Economics Review'' is the undergraduate economic journal on research and policy supported by the Columbia Economics Department; and the ''Columbia Science Review'' is a science magazine that prints general interest articles and faculty profiles.
Humor publications on Columbia's campus include '' The Fed'', a triweekly satire and investigative newspaper, and the ''Jester of Columbia
The ''Jester of Columbia'', or simply the ''Jester'', is a humor magazine at Columbia University in New York City. Founded on April Fool's Day, 1901, it is one of the oldest such publications in the United States. Printed continuously at least ...
.'' Other publications include ''The Columbian'', the undergraduate colleges' annually published yearbook; the ''Gadfly'', a biannual journal of popular philosophy produced by undergraduates; and ''Rhapsody in Blue'', an undergraduate urban studies magazine. Professional journals published by academic departments at Columbia University include ''Current Musicology'' and ''The Journal of Philosophy
''The Journal of Philosophy'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal on philosophy, founded in 1904 at Columbia University. Its stated purpose is "To publish philosophical articles of current interest and encourage the interchange of ideas, ...
''. During the spring semester, graduate students in the Journalism School publish ''The Bronx Beat'', a bi-weekly newspaper covering the South Bronx.
Founded in 1961 under the auspices of Columbia University's Graduate School of Journalism, the ''Columbia Journalism Review
The ''Columbia Journalism Review'' (''CJR'') is a biannual magazine for professional journalists that has been published by the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism since 1961. Its contents include news and media industry trends, ana ...
'' (CJR) examines day-to-day press performance as well as the forces that affect that performance. The magazine is published six times a year.
Broadcasting
Columbia is home to two pioneers in undergraduate campus radio broadcasting, WKCR-FM and CTV. Many undergraduates are also involved with Barnard's radio station, WBAR. WKCR, the student run radio station that broadcasts to the Tri-state area, claims to be the oldest FM radio station in the world, owing to the university's affiliation with Major Edwin Armstrong. The station went operational on July 18, 1939, from a 400-foot antenna tower in Alpine, New Jersey, broadcasting the first FM transmission in the world. Initially, WKCR was not a radio station, but an organization concerned with the technology of radio communications. As membership grew, however, the nascent club turned its efforts to broadcasting. Armstrong helped the students in their early efforts, donating a microphone and turntables when they designed their first makeshift studio in a dorm room. The station has its studios on the second floor of Alfred Lerner Hall on the Morningside campus with its main transmitter tower at4 Times Square
4 Times Square (also known as 151 West 42nd Street or One Five One; formerly the Condé Nast Building) is a 52-story skyscraper at Times Square in the Midtown Manhattan neighborhood of New York City. Located at 1472 Broadway, between 42nd ...
in Midtown Manhattan
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan and serves as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Buildi ...
. Columbia Television (CTV) is the nation's second oldest student television station
A student television station is a television station run by university, high or middle school students that primarily airs school/university news and in many cases, student-produced soap operas, entertainment shows, and other programming.
At the ...
and the home of CTV News, a weekly live news program produced by undergraduate students.
Debate and Model UN
The Philolexian Society is a literary and debating club founded in 1802, making it the oldest student group at Columbia, as well as the third oldest collegiate literary society in the country. The society annually administers the Joyce Kilmer Memorial Bad Poetry Contest. The Columbia Parliamentary Debate Team competes in tournaments around the country as part of theAmerican Parliamentary Debate Association
The American Parliamentary Debate Association (APDA) is the oldest intercollegiate parliamentary debating association in the United States. APDA sponsors over 50 tournaments a year, all in a parliamentary format, as well as a national champi ...
, and hosts both high school and college tournaments on Columbia's campus, as well as public debates on issues affecting the university.
The Columbia International Relations Council and Association (CIRCA), oversees Columbia's Model United Nations activities. CIRCA hosts college and high school Model UN conferences, hosts speakers influential in international politics to speak on campus, and trains students from underprivileged schools in New York in Model UN.
Technology and entrepreneurship
 Columbia is a top supplier of young engineering entrepreneurs for New York City. Over the past 20 years, graduates of Columbia established over 100 technology companies.
The Columbia University Organization of Rising Entrepreneurs (CORE) was founded in 1999. The student-run group aims to foster entrepreneurship on campus. Each year CORE hosts dozens of events, including talks, #StartupColumbia, a conference and venture competition for $250,000, and Ignite@CU, a weekend for undergrads interested in design, engineering, and entrepreneurship. Notable speakers include Peter Thiel, Jack Dorsey, Alexis Ohanian, Drew Houston, and Mark Cuban. As of 2006, CORE had awarded graduate and undergraduate students over $100,000 in seed capital.
CampusNetwork, an on-campus social networking site called Campus Network that preceded Facebook, was created and popularized by Columbia engineering student Adam Goldberg in 2003.
Columbia is a top supplier of young engineering entrepreneurs for New York City. Over the past 20 years, graduates of Columbia established over 100 technology companies.
The Columbia University Organization of Rising Entrepreneurs (CORE) was founded in 1999. The student-run group aims to foster entrepreneurship on campus. Each year CORE hosts dozens of events, including talks, #StartupColumbia, a conference and venture competition for $250,000, and Ignite@CU, a weekend for undergrads interested in design, engineering, and entrepreneurship. Notable speakers include Peter Thiel, Jack Dorsey, Alexis Ohanian, Drew Houston, and Mark Cuban. As of 2006, CORE had awarded graduate and undergraduate students over $100,000 in seed capital.
CampusNetwork, an on-campus social networking site called Campus Network that preceded Facebook, was created and popularized by Columbia engineering student Adam Goldberg in 2003. Mark Zuckerberg
Mark Elliot Zuckerberg (; born ) is an American business magnate, internet entrepreneur, and philanthropist. He is known for co-founding the social media website Facebook and its parent company Meta Platforms (formerly Facebook, Inc.), of ...
later asked Goldberg to join him in Palo Alto to work on Facebook, but Goldberg declined the offer. The Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science offers a minor in Technical Entrepreneurship through its Center for Technology, Innovation, and Community Engagement. SEAS' entrepreneurship activities focus on community building initiatives in New York and worldwide, made possible through partners such as Microsoft Corporation.
On June 14, 2010, Mayor Michael R. Bloomberg
Michael Rubens Bloomberg (born February 14, 1942) is an American businessman, politician, philanthropist, and author. He is the majority owner, co-founder and CEO of Bloomberg L.P. He was Mayor of New York City from 2002 to 2013, and was a ca ...
launched the NYC Media Lab to promote innovations in New York's media industry. Situated at the New York University Tandon School of Engineering, the lab is a consortium of Columbia University, New York University
New York University (NYU) is a private research university in New York City. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded by a group of New Yorkers led by then- Secretary of the Treasury Albert Gallatin.
In 1832, th ...
, and New York City Economic Development Corporation
New York City Economic Development Corporation (NYCEDC) is a nonprofit corporation whose stated mission is to "leverage the city’s assets to create beneficial jobs that drive growth. This ensures equitable and sustainable development across al ...
acting to connect companies with universities in new technology research. The Lab is modeled after similar ones at MIT and Stanford, and was established with a $250,000 grant from the New York City Economic Development Corporation.
Athletics
 A member institution of the
A member institution of the National Collegiate Athletic Association
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges ...
(NCAA) in Division I FCS, Columbia fields varsity teams in 29 sports and is a member of the Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight school ...
. The football Lions play home games at the 17,000-seat Robert K. Kraft Field at Lawrence A. Wien Stadium
Robert K. Kraft Field at Lawrence A. Wien Stadium, officially known as Robert K. Kraft Field at Lawrence A. Wien Stadium at Baker Athletics Complex, is a stadium in the Inwood neighborhood at the northern tip of the island of Manhattan, New Y ...
. The Baker Athletics Complex also includes facilities for baseball, softball, soccer, lacrosse, field hockey, tennis, track, and rowing, as well as the new Campbell Sports Center, which opened in January 2013. The basketball, fencing, swimming & diving, volleyball, and wrestling programs are based at the Dodge Physical Fitness Center on the main campus.
 Former students include
Former students include Baseball Hall of Famers
The National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum is a history museum and hall of fame in Cooperstown, New York, operated by private interests. It serves as the central point of the history of baseball in the United States and displays baseball-re ...
Lou Gehrig
Henry Louis Gehrig (born Heinrich Ludwig Gehrig ; June 19, 1903June 2, 1941) was an American professional baseball first baseman who played 17 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the New York Yankees (1923–1939). Gehrig was renowned f ...
and Eddie Collins, football Hall of Famer Sid Luckman, Marcellus Wiley
Marcellus Vernon Wiley Sr. (born November 30, 1974) is an American sportscaster and former American football defensive end who played 10 seasons in the National Football League (NFL). He played for the Buffalo Bills, San Diego Chargers, Dallas ...
, and world champion women's weightlifter Karyn Marshall. On May 17, 1939, fledgling NBC broadcast a doubleheader between the Columbia Lions and the Princeton Tigers
The Princeton Tigers are the athletic teams of Princeton University. The school sponsors 35 varsity teams in 20 sports. The school has won several NCAA national championships, including one in men's fencing, three in women's lacrosse, six in m ...
at Columbia's Baker Field, making it the first televised regular athletic event in history.
Columbia University athletics has a long history, with many accomplishments in athletic fields. In 1870, Columbia played against Rutgers University
Rutgers University (; RU), officially Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, is a public land-grant research university consisting of four campuses in New Jersey. Chartered in 1766, Rutgers was originally called Queen's College, and was ...
in the second intercollegiate rugby football game in the history of the sport. Eight years later, Columbia crew won the famed Henley Royal Regatta
Henley Royal Regatta (or Henley Regatta, its original name pre-dating Royal patronage) is a rowing event held annually on the River Thames by the town of Henley-on-Thames, England. It was established on 26 March 1839. It differs from the thr ...
in the first-ever defeat for an English crew rowing in English waters. In 1900, Olympian and Columbia College student Maxie Long
Maxwell Warburn Long (October 16, 1878 – March 4, 1959) was an American athlete, winner of 400 m at the 1900 Summer Olympics.
Having won three AAU titles from 1898 to 1900 and IC4A title in 1899 in 440 yd (402 m), 1899 an AAU title in 220 yd ...
set the first official world record in the 400 meters with a time of 47.8 seconds. In 1983, Columbia men's soccer went 18–0 and was ranked first in the nation, but lost to Indiana 1–0 in double overtime in the NCAA championship game; nevertheless, the team went further toward the NCAA title than any Ivy League soccer team in history. The football program unfortunately is best known for its record of futility set during the 1980s: between 1983 and 1988, the team lost 44 games in a row, which is still the record for the NCAA Football Championship Subdivision. The streak was broken on October 8, 1988, with a 16–13 victory over arch-rival Princeton University
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the ...
. That was the Lions' first victory at Wien Stadium, which had been opened during the losing streak and was already four years old. A new tradition has developed with the Liberty Cup. The Liberty Cup is awarded annually to the winner of the football game between Fordham and Columbia Universities, two of the only three NCAA Division I football teams in New York City.
World Leaders Forum
 Established in 2003 by university president Lee C. Bollinger, the World Leaders Forum at Columbia University provides the opportunity for undergraduate and graduate students alike to listen to world leaders in government, religion, industry, finance, and academia. The World Leaders Forum is a year-around event series that strives to provide a platform for uninhibited speech among nations and cultures, while educating students about problems and progress around the globe.
Past forum speakers include former president of the United States
Established in 2003 by university president Lee C. Bollinger, the World Leaders Forum at Columbia University provides the opportunity for undergraduate and graduate students alike to listen to world leaders in government, religion, industry, finance, and academia. The World Leaders Forum is a year-around event series that strives to provide a platform for uninhibited speech among nations and cultures, while educating students about problems and progress around the globe.
Past forum speakers include former president of the United States Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and again ...
, the prime minister of India Atal Bihari Vajpayee, former president of Ghana John Agyekum Kufuor
John Kofi Agyekum Kufuor (born 8 December 1938) is a Ghanaian politician who served as the President of Ghana from 7 January 2001 to 7 January 2009. He was also Chairperson of the African Union from 2007 to 2008.
Kufuor's career has been spe ...
, president of Afghanistan Hamid Karzai
Hamid Karzai (; Pashto/ fa, حامد کرزی, , ; born 24 December 1957) is an Afghan statesman who served as the fourth president of Afghanistan from July 2002 to September 2014, including as the first elected president of the Islamic Repub ...
, prime minister of Russia Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime min ...
, president of the Republic of Mozambique Joaquim Alberto Chissano, president of the Republic of Bolivia Carlos Diego Mesa Gisbert, president of the Republic of Romania Ion Iliescu, president of the Republic of Latvia Vaira Vīķe-Freiberga
Vaira Vīķe-Freiberga (born 1 December 1937) is a Latvian politician who served as the sixth President of Latvia from 1999 to 2007. She is the first woman to hold the post. She was elected President of Latvia in 1999 and re-elected for the seco ...
, the first female president of Finland Tarja Halonen, President Yudhoyono of Indonesia, President Pervez Musharraf
General Pervez Musharraf ( ur, , Parvez Muśharraf; born 11 August 1943) is a former Pakistani politician and four-star general of the Pakistan Army who became the tenth president of Pakistan after the successful military takeover of t ...
of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, Iraq President Jalal Talabani, the 14th Dalai Lama
The 14th Dalai Lama (spiritual name Jetsun Jamphel Ngawang Lobsang Yeshe Tenzin Gyatso, known as Tenzin Gyatso (Tibetan: བསྟན་འཛིན་རྒྱ་མཚོ་, Wylie: ''bsTan-'dzin rgya-mtsho''); né Lhamo Thondup), known as ...
, president of the Islamic Republic of Iran Mahmoud Ahmadinejad
Mahmoud Ahmadinejad ( fa, محمود احمدینژاد, Mahmūd Ahmadīnežād ), born Mahmoud Sabbaghian ( fa, محمود صباغیان, Mahmoud Sabbāghyān, 28 October 1956),
, financier George Soros, Mayor of New York City Michael R. Bloomberg
Michael Rubens Bloomberg (born February 14, 1942) is an American businessman, politician, philanthropist, and author. He is the majority owner, co-founder and CEO of Bloomberg L.P. He was Mayor of New York City from 2002 to 2013, and was a ca ...
, President Václav Klaus of the Czech Republic, President Cristina Fernández de Kirchner of Argentina, former Secretary-General of the United Nations Kofi Annan, and Al Gore
Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic ...
.
Other
 The Columbia University Orchestra was founded by composer
The Columbia University Orchestra was founded by composer Edward MacDowell
Edward Alexander MacDowell (December 18, 1860January 23, 1908) was an American composer and pianist of the late Romantic period. He was best known for his second piano concerto and his piano suites '' Woodland Sketches'', ''Sea Pieces'' and '' ...
in 1896, and is the oldest continually operating university orchestra in the United States. Undergraduate student composers at Columbia may choose to become involved with Columbia New Music, which sponsors concerts of music written by undergraduate students from all of Columbia's schools. The Notes and Keys, the oldest a cappella
''A cappella'' (, also , ; ) music is a performance by a singer or a singing group without instrumental accompaniment, or a piece intended to be performed in this way. The term ''a cappella'' was originally intended to differentiate between Ren ...
group at Columbia, was founded in 1909. There are a number of performing arts groups at Columbia dedicated to producing student theater, including the Columbia Players, King's Crown Shakespeare Troupe (KCST), Columbia Musical Theater Society (CMTS), NOMADS (New and Original Material Authored and Directed by Students), LateNite Theatre, Columbia University Performing Arts League (CUPAL), Black Theatre Ensemble (BTE), sketch comedy group Chowdah, and improvisational troupes Alfred and Fruit Paunch.
The Columbia Queer Alliance
Columbia Queer Alliance (CQA) is the central Columbia University student organization that represents lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and questioning LGBTQ students. It is the oldest such student organization in the world, originally called ...
is the central Columbia student organization that represents the bisexual, lesbian, gay, transgender, and questioning student population. It is the oldest gay student organization in the world, founded as the Student Homophile
Terms used to describe homosexuality have gone through many changes since the emergence of the first terms in the mid-19th century. In English, some terms in widespread use have been sodomite, Achillean, Sapphic, Uranian, homophile, lesbian, ...
League in 1967 by students including lifelong activist Stephen Donaldson.
Columbia University campus military groups include the U.S. Military Veterans of Columbia University and Advocates for Columbia ROTC. In the 2005–06 academic year, the Columbia Military Society, Columbia's student group for ROTC cadets and Marine officer candidates, was renamed the Hamilton Society for "students who aspire to serve their nation through the military in the tradition of Alexander Hamilton".
The largest student service organization at Columbia is Community Impact (CI). Founded in 1981, CI provides food, clothing, shelter, education, job training, and companionship for residents in its surrounding communities. CI consists of about 950 Columbia University student volunteers participating in 25 community service programs, which serve more than 8,000 people each year.
Columbia has several secret societies, including St. Anthony Hall, which was founded at the university in 1847, and two senior societies, the Nacoms and Sachems.
Traditions
Orgo Night
 In one of the school's longest-lasting traditions, begun in 1975, at midnight before the
In one of the school's longest-lasting traditions, begun in 1975, at midnight before the Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J ...
exam—often the first day of final exams—the Columbia University Marching Band invaded and briefly occupied the main undergraduate reading room in Butler Library
Butler Library is located on the Morningside Heights campus of Columbia University at 535 West 114th Street, in Manhattan, New York City. It is the university's largest single library with over 2 million volumes, as well as one of the larges ...
to distract and entertain studying students with some forty-five minutes of raucous jokes and music, beginning and ending with the singing of the school's fight song, "Roar, Lion, Roar
"Roar, Lion, Roar" is the primary fight song of Columbia University. It was originally titled "Bold Buccaneers" and was written with different lyrics for the 1923 Varsity Show ''Half Moon Inn'' by Columbia undergraduates Corey Ford and Morris W. ...
". After the main show before a crowd that routinely began filling the room well before the announced midnight start time, the Band led a procession to several campus locations, including the residential quadrangle of Barnard College
Barnard College of Columbia University is a private women's liberal arts college in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It was founded in 1889 by a group of women led by young student activist Annie Nathan Meyer, who petitioned Columbia ...
for more music and temporary relief from the stress of last-minute studying.
In December 2016, following several years of complaints from students who said that some Orgo Night scripts and advertising posters were offensive to minority groups, as well as a ''The New York Times'' article on the Band's crass treatment of sexual assault on campus, University administrators banned the Marching Band from performing its Orgo Night show in the traditional Butler Library location. Protests and allegations of censorship followed, but University President Lee Bollinger said that complaints and publicity about the shows had "nothing to do with" the prohibition. The Band instead performed—at midnight, as usual—outside the main entrance of Butler Library.
The Band's official alumni organization, the Columbia University Band Alumni Association, registered protests with the administration, and an ad hoc group of alumni writing under the name "A. Hamiltonius" published a series of pamphlets addressing their dissatisfaction with the ban, but at the end of the spring 2017 semester the university administration held firm, prompting the Marching Band to again stage its show outside the building. For Orgo Night December 2017, Band members quietly infiltrated the library with their musical instruments during the evening and popped up at midnight to perform the show inside despite the ban. Prior to the spring 2018 exam period, the administration warned the group's leaders against a repeat and restated the injunction, warning of sanctions; the Band again staged its Orgo Night show in front of the library.
Tree Lighting and Yule Log ceremonies
The campus Tree Lighting ceremony was inaugurated in 1998. It celebrates the illumination of the medium-sized trees lining College Walk in front of Kent Hall and Hamilton Hall on the east end and Dodge Hall and Pulitzer Hall on the west, just before finals week in early December. The lights remain on until February 28. Students meet at the sundial for free hot chocolate, performances by ''a cappella'' groups, and speeches by the university president and a guest. Immediately following the College Walk festivities is one of Columbia's older holiday traditions, the lighting of the Yule Log. The Christmas ceremony dates to a period prior to theAmerican Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, but lapsed before being revived by President Nicholas Murray Butler in 1910. A troop of students dressed as Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
soldiers carry the eponymous log from the sundial to the lounge of John Jay Hall, where it is lit amid the singing of seasonal carols. The Christmas ceremony is accompanied by a reading of '' A Visit From St. Nicholas'' by Clement Clarke Moore
Clement Clarke Moore (July 15, 1779 – July 10, 1863) was an American writer, scholar and real estate developer. He is best known as author of the Christmas poem "A Visit from St. Nicholas."
Moore was Professor of Oriental and Greek Literature ...
and '' Yes, Virginia, There is a Santa Claus'' by Francis Pharcellus Church
Francis Pharcellus Church (February 22, 1839 – April 11, 1906) was an American publisher and editor. Born in Rochester, New York, he graduated from Columbia University and embarked on a career in journalism. With his brother, William Cona ...
.
The Varsity Show
The Varsity Show is an annual musical written by and for students and was established in 1894, making it one of Columbia's oldest traditions. Past writers and directors have included Columbians Richard Rodgers and Oscar Hammerstein, Lorenz Hart, I.A.L. Diamond,Herman Wouk
Herman Wouk ( ; May 27, 1915 – May 17, 2019) was an American author best known for historical fiction such as ''The Caine Mutiny'' (1951) for which he won the Pulitzer Prize in fiction.
His other major works include ''The Winds of War'' and ...
and Eric Garcetti
Eric Michael Garcetti (born February 4, 1971) is an American politician who served as the 42nd mayor of Los Angeles from 2013 until 2022. A member of the Democratic Party, he was first elected in the 2013 election, and reelected in 2017. A f ...
. The show has one of the largest operating budgets of all university events.
Notable people
Alumni
The university has graduated many notable alumni, including fiveFounding Fathers of the United States
The Founding Fathers of the United States, known simply as the Founding Fathers or Founders, were a group of late-18th-century American revolutionary leaders who united the Thirteen Colonies, oversaw the war for independence from Great Britai ...
, an author of the United States Constitution and a member of the Committee of Five. Three United States presidents have attended Columbia, as well as ten Justices of the Supreme Court of the United States, including three Chief Justices. , 125 Pulitzer Prize winners and 39 Oscar winners have attended Columbia. , there were 101 National Academy members who were alumni.
In a 2016 ranking of universities worldwide with respect to living graduates who are billionaires, Columbia ranked second, after Harvard.
Former U.S. Presidents Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
and Franklin Delano Roosevelt attended the law school. Other political figures educated at Columbia include former U.S. President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, Obama was the first Af ...
, Associate Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court Ruth Bader Ginsburg
Joan Ruth Bader Ginsburg ( ; ; March 15, 1933September 18, 2020) was an American lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1993 until her death in 2020. She was nominated by Presiden ...
, former U.S. Secretary of State Madeleine Albright
Madeleine Jana Korbel Albright (born Marie Jana Korbelová; May 15, 1937 – March 23, 2022) was an American diplomat and political scientist who served as the 64th United States secretary of state from 1997 to 2001. A member of the Democrat ...
, former chairman of the U.S. Federal Reserve Bank Alan Greenspan
Alan Greenspan (born March 6, 1926) is an American economist who served as the 13th chairman of the Federal Reserve from 1987 to 2006. He works as a private adviser and provides consulting for firms through his company, Greenspan Associates LLC. ...
, U.S. Attorney General Eric Holder, and U.S. Solicitor General Donald Verrilli Jr. The university has also educated 29 foreign heads of state, including president of Georgia Mikheil Saakashvili, president of East Timor Jose Ramos Horta
Jose is the English transliteration of the Hebrew and Aramaic name ''Yose'', which is etymologically linked to ''Yosef'' or Joseph. The name was popular during the Mishnaic and Talmudic periods.
* Jose ben Abin
* Jose ben Akabya
*Jose the Galil ...
, president of Estonia Toomas Hendrik Ilves and other historical figures such as Wellington Koo, Radovan Karadžić, Gaston Eyskens, and T. V. Soong. One of the architects of the Constitution of India, Dr. B. R. Ambedkar was also an alumnus of Columbia.
Alumni of Columbia have occupied top positions in Wall Street and the rest of the business world. Notable members of the Astor family attended Columbia, while other business graduates include investor Warren Buffett, former CEO of PBS and NBC Larry Grossman, chairman of Wal-Mart S. Robson Walton, Bain Capital Co-Managing Partner, Jonathan Lavine, Thomson Reuters
Thomson Reuters Corporation ( ) is a Canadian multinational media conglomerate. The company was founded in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, where it is headquartered at the Bay Adelaide Centre.
Thomson Reuters was created by the Thomson Corp ...
CEO Tom Glocer, New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is by far the world's largest stock exchange by market capitalization of its liste ...
president Lynn Martin, and AllianceBernstein Chairman and CEO Lewis A. Sanders. CEO's of top Fortune 500 companies include James P. Gorman of Morgan Stanley
Morgan Stanley is an American multinational investment management and financial services company headquartered at 1585 Broadway in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. With offices in more than 41 countries and more than 75,000 employees, the fir ...
, Robert J. Stevens of Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It ...
, Philippe Dauman of Viacom, Robert Bakish of Paramount Global
Paramount Global ( doing business as Paramount) is an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate owned and operated by National Amusements (79.4%) and headquartered at One Astor Plaza in Midtown Manhattan, New York. ...
, Ursula Burns of Xerox
Xerox Holdings Corporation (; also known simply as Xerox) is an American corporation that sells print and digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox is headquartered in Norwalk, Connecticut (having moved from St ...
, Devin Wenig of EBay
eBay Inc. ( ) is an American multinational e-commerce company based in San Jose, California, that facilitates consumer-to-consumer and business-to-consumer sales through its website. eBay was founded by Pierre Omidyar in 1995 and became ...
, Vikram Pandit of Citigroup
Citigroup Inc. or Citi ( stylized as citi) is an American multinational investment bank and financial services corporation headquartered in New York City. The company was formed by the merger of banking giant Citicorp and financial conglomera ...
, Ralph Izzo of Public Service Enterprise Group, Gail Koziara Boudreaux of Anthem, and Frank Blake of The Home Depot
The Home Depot, Inc., is an American multinational home improvement retail corporation that sells tools, construction products, appliances, and services, including fuel and transportation rentals. Home Depot is the largest home improvement re ...
. Notable labor organizer and women's educator Louise Leonard McLaren received her degree of Master of Arts from Columbia.
In science and technology, Columbia alumni include: founder of IBM Herman Hollerith; inventor of FM radio
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting using frequency modulation (FM). Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to provide high fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting is cap ...
Edwin Armstrong; Francis Mechner; integral in development of the nuclear submarine Hyman Rickover; founder of Google China Kai-Fu Lee; scientists Stephen Jay Gould
Stephen Jay Gould (; September 10, 1941 – May 20, 2002) was an American paleontologist, evolutionary biologist, and historian of science. He was one of the most influential and widely read authors of popular science of his generation. Goul ...
, Robert Millikan, Helium–neon laser inventor Ali Javan and Mihajlo Pupin; chief-engineer of the New York City Subway
The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system owned by the government of New York City and leased to the New York City Transit Authority, an affiliate agency of the state-run Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA). Opened on October ...
, William Barclay Parsons; philosophers Irwin Edman
Irwin Edman (November 28, 1896 – September 4, 1954) was an American philosopher and professor of philosophy.
Biography
Irwin Edman was born in New York City to Jewish parents. He grew up in the Morningside Heights neighborhood of Manhatta ...
and Robert Nozick; economist Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and the ...
; psychologist Harriet Babcock
Harriet Babcock (1877–1952) was an American psychologist who specialized in abnormal psychology research in addition to developing measures and theories of intelligence. After her doctoral work at Columbia University, she worked primarily in t ...
; archaeologist Josephine Platner Shear
Josephine Platner Shear (3 July 1901 - 11 February 1967) was an American classical archaeologist and numismatist, who was excavation and numismatic lead for the Agora excavations.
Biography
Josephine Platner was born on 3 July 1901 in Omaha, Ne ...
; and sociologists Lewis A. Coser
Lewis Alfred Coser (27 November 1913 in Berlin – 8 July 2003 in Cambridge, Massachusetts) was a German-American sociologist, serving as the 66th president of the American Sociological Association in 1975.
Biography
Born in Berlin as Ludwig ...
and Rose Laub Coser.
Many Columbia alumni have gone on to renowned careers in the arts, including composers Richard Rodgers, Oscar Hammerstein II, Lorenz Hart, and Art Garfunkel; and painter Georgia O'Keeffe. Five United States Poet Laureate
A poet laureate (plural: poets laureate) is a poet officially appointed by a government or conferring institution, typically expected to compose poems for special events and occasions. Albertino Mussato of Padua and Francesco Petrarca (Petrarch ...
s received their degrees from Columbia. Columbia alumni have made an indelible mark in the field of American poetry and literature, with such people as Jack Kerouac and Allen Ginsberg
Irwin Allen Ginsberg (; June 3, 1926 – April 5, 1997) was an American poet and writer. As a student at Columbia University in the 1940s, he began friendships with William S. Burroughs and Jack Kerouac, forming the core of the Beat Gener ...
, pioneers of the Beat Generation; and Langston Hughes
James Mercer Langston Hughes (February 1, 1901 – May 22, 1967) was an American poet, social activist, novelist, playwright, and columnist from Joplin, Missouri. One of the earliest innovators of the literary art form called jazz poetry, H ...
and Zora Neale Hurston, seminal figures in the Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the t ...
, all having attended the university. Other notable writers who attended Columbia include authors Isaac Asimov
yi, יצחק אזימאװ
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Petrovichi, Russian SFSR
, spouse =
, relatives =
, children = 2
, death_date =
, death_place = Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
, nationality = Russian (1920–1922)Soviet (192 ...
, J.D. Salinger, Upton Sinclair, Ursula K. Le Guin
Ursula Kroeber Le Guin (; October 21, 1929 – January 22, 2018) was an American author best known for her works of speculative fiction, including science fiction works set in her Hainish universe, and the '' Earthsea'' fantasy series. She was ...
, Danielle Valore Evans
Danielle Evans (born Danielle Valore Evans) is an American fiction writer. She is a graduate of Columbia University and the University of Iowa.
In 2011, she was honored by the National Book Foundation as one of its "5 Under 35" fiction writers.
' ...
, and Hunter S. Thompson.
University alumni have also been very prominent in the film industry, with 33 alumni and former students winning a combined 43 Academy Awards
The Academy Awards, better known as the Oscars, are awards for artistic and technical merit for the American and international film industry. The awards are regarded by many as the most prestigious, significant awards in the entertainment ind ...
(). Some notable Columbia alumni that have gone on to work in film include directors Sidney Lumet (''12 Angry Men
''Twelve Angry Men'' is an American courtroom drama written by Reginald Rose concerning the jury of a homicide trial. It was broadcast initially as a television play in 1954. The following year it was adapted for the stage. It was adapted for a ...
'') and Kathryn Bigelow (''The Hurt Locker
''The Hurt Locker'' is a 2008 American war thriller film directed by Kathryn Bigelow and written by Mark Boal. It stars Jeremy Renner, Anthony Mackie, Brian Geraghty, Christian Camargo, Ralph Fiennes, David Morse, and Guy Pearce. The film follow ...
''), screenwriters Howard Koch ('' Casablanca'') and Joseph L. Mankiewicz ('' All About Eve''), and actors James Cagney
James Francis Cagney Jr. (; July 17, 1899March 30, 1986) was an American actor, dancer and film director. On stage and in film, Cagney was known for his consistently energetic performances, distinctive vocal style, and deadpan comic timing. He ...
, Ed Harris and Timothée Chalamet.United States Secretary of the Treasury
The United States secretary of the treasury is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, and is the chief financial officer of the federal government of the United States. The secretary of the treasury serves as the principal a ...
— King's College
File:John Jay (Gilbert Stuart portrait).jpg, John Jay
John Jay (December 12, 1745 – May 17, 1829) was an American statesman, patriot, diplomat, abolitionist, signatory of the Treaty of Paris, and a Founding Father of the United States. He served as the second governor of New York and the f ...
: Founding Father of the United States; author of ''The Federalist Papers''; first Chief Justice of the United States; second Governor of New York — King's College
File:Robert R Livingston, attributed to Gilbert Stuart (1755-1828).jpg, Robert R. Livingston: Founding Father of the United States; drafter of the Declaration of Independence; first United States Secretary of Foreign Affairs — King's College
File:Gouverneur Morris.jpg, Gouverneur Morris: Founding Father of the United States; author of the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
; United States Senator
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and po ...
from New York — King's College
File:DeWitt Clinton by Rembrandt Peale.jpg, DeWitt Clinton
DeWitt Clinton (March 2, 1769February 11, 1828) was an American politician and naturalist. He served as a United States senator, as the mayor of New York City, and as the seventh governor of New York. In this last capacity, he was largely re ...
: United States Senator
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and po ...
from New York; sixth Governor of New York; responsible for construction of Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing ...
— Columbia College
File:President Barack Obama.jpg, Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, Obama was the first Af ...
: 44th President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal gove ...
; United States Senator from Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rock ...
; Nobel laureate — Columbia College
File:FDR in 1933.jpg, Franklin D. Roosevelt: 32nd President of the United States; 44th Governor of New York — Columbia Law School
File:President Theodore Roosevelt, 1904.jpg, Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
: 26th President of the United States; 25th Vice President of the United States; 33rd Governor of New York; Nobel laureate – Columbia Law School
File:Wellington Koo 1945.jpg, Wellington Koo: acting President of the Republic of China
The president of the Republic of China, now often referred to as the president of Taiwan, is the head of state of the Republic of China (ROC), as well as the commander-in-chief of the Republic of China Armed Forces. The position once had ...
; judge of the International Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice (ICJ; french: Cour internationale de justice, links=no; ), sometimes known as the World Court, is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN). It settles disputes between states in accordan ...
— Columbia College, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar.jpg, B. R. Ambedkar: Founding Father of India; architect of the Constitution of India
The Constitution of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme law of India. The document lays down the framework that demarcates fundamental political code, structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions and sets out fundamental ...
; First Minister of Law and Justice
The Minister of Law and Justice is the head of the Ministry of Law and Justice and one of the cabinet ministers of the Government of India. The first Law and Justice Minister of independent India was B. R. Ambedkar, who served in first Nehru min ...
— Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:Ruth Bader Ginsburg official SCOTUS portrait.jpg, Ruth Bader Ginsburg
Joan Ruth Bader Ginsburg ( ; ; March 15, 1933September 18, 2020) was an American lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1993 until her death in 2020. She was nominated by Presiden ...
: Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States — Columbia Law School
File:Associate Justice Neil Gorsuch Official Portrait.jpg, Neil Gorsuch: Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States — Columbia College
File:Charles Evans Hughes cph.3b15401.jpg, Charles Evans Hughes: 11th Chief Justice of the United States; 44th United States Secretary of State; 35th Governor of New York — Columbia Law School
File:Chief Justice Harlan Fiske Stone photograph circa 1927-1932 (cropped).jpg, Harlan Fiske Stone: 12th Chief Justice of the United States; 52nd United States Attorney General
The United States attorney general (AG) is the head of the United States Department of Justice, and is the chief law enforcement officer of the federal government of the United States. The attorney general serves as the principal advisor to the p ...
— Columbia Law School
File:William Barr.jpg, William Barr: 77th and 85th United States Attorney General – Columbia College, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:Hamilton Fish Brady Edited.jpg, Hamilton Fish
Hamilton Fish (August 3, 1808September 7, 1893) was an American politician who served as the 16th Governor of New York from 1849 to 1850, a United States Senator from New York from 1851 to 1857 and the 26th United States Secretary of State fro ...
: 26th United States Secretary of State; United States Senator from New York; 16th Governor of New York — Columbia College
File:Secalbright.jpg, Madeleine Albright
Madeleine Jana Korbel Albright (born Marie Jana Korbelová; May 15, 1937 – March 23, 2022) was an American diplomat and political scientist who served as the 64th United States secretary of state from 1997 to 2001. A member of the Democrat ...
: 64th United States Secretary of State; first female Secretary of State — School of International and Public Affairs
File:Frances Perkins cph.3a04983.jpg, Frances Perkins: fourth United States Secretary of Labor; first female member of any U.S. Cabinet
The Cabinet of the United States is a body consisting of the vice president of the United States and the heads of the executive branch's departments in the federal government of the United States. It is the principal official advisory body to t ...
— Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:Robert Andrews Millikan 1920s.jpg, Robert A. Millikan: Nobel laureate; measured the elementary electric charge — Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:II Rabi.jpg, Isidor Isaac Rabi: Nobel Laureate; discovered nuclear magnetic resonance — Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:Schwinger.jpg, Julian S. Schwinger
Julian Seymour Schwinger (; February 12, 1918 – July 16, 1994) was a Nobel Prize winning American theoretical physicist. He is best known for his work on quantum electrodynamics (QED), in particular for developing a relativistically invaria ...
: Nobel laureate; pioneer of quantum field theory — Columbia College, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:Portrait of Milton Friedman.jpg, Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and the ...
: Nobel laureate, leading member of the Chicago school of economics — Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:Simon Kuznets 1971b.jpg, Simon Kuznets: Nobel laureate; invented concept of GDP; Milton Friedman's doctoral advisor — School of General Studies, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:Alan Greenspan color photo portrait.jpg, Alan Greenspan
Alan Greenspan (born March 6, 1926) is an American economist who served as the 13th chairman of the Federal Reserve from 1987 to 2006. He works as a private adviser and provides consulting for firms through his company, Greenspan Associates LLC. ...
: 13th Chair of the Federal Reserve — Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:Warren Buffett KU Visit.jpg, Warren Buffett: CEO of Berkshire Hathaway; one of the world's wealthiest people — Columbia Business School
File:Hollerith.jpg, Herman Hollerith: inventor; co-founder of IBM – School of Engineering and Applied Sciences
File:Robert Kraft at Patriots at Raiders 12-14-08.JPG, Robert Kraft: billionaire; owner of the New England Patriots
The New England Patriots are a professional American football team based in the Greater Boston area. They compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the league's American Football Conference (AFC) AFC East, East divisio ...
; chairman and CEO of the Kraft Group — Columbia College
File:Rodgers.jpg, Richard Rodgers: legendary Emmy, Grammy, Oscar, and Tony award-winning composer; Pulitzer Prize
The Pulitzer Prize () is an award for achievements in newspaper, magazine, online journalism, literature, and musical composition within the United States. It was established in 1917 by provisions in the will of Joseph Pulitzer, who had made ...
winner — Columbia College
File:LangstonHughes crop.jpg, Langston Hughes
James Mercer Langston Hughes (February 1, 1901 – May 22, 1967) was an American poet, social activist, novelist, playwright, and columnist from Joplin, Missouri. One of the earliest innovators of the literary art form called jazz poetry, H ...
: Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the t ...
poet, novelist, and playwright — School of Engineering and Applied Science
File:Zora Neale Hurston.jpg, Zora Neale Hurston: Harlem Renaissance author, anthropologist, and filmmaker — Barnard College, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:Allen Ginsberg 1979 - cropped.jpg, Allen Ginsberg
Irwin Allen Ginsberg (; June 3, 1926 – April 5, 1997) was an American poet and writer. As a student at Columbia University in the 1940s, he began friendships with William S. Burroughs and Jack Kerouac, forming the core of the Beat Gener ...
: poet; founder of the Beat Generation — Columbia College
File:Kerouac by Palumbo 2 (cropped).png, Jack Kerouac: poet; founder of the Beat Generation — Columbia College
File:Isaac.Asimov01.jpg, Isaac Asimov
yi, יצחק אזימאװ
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Petrovichi, Russian SFSR
, spouse =
, relatives =
, children = 2
, death_date =
, death_place = Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
, nationality = Russian (1920–1922)Soviet (192 ...
: science fiction writer; biochemist — School of General Studies, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
File:J. D. Salinger (Catcher in the Rye portrait).jpg, J. D. Salinger: novelist, '' The Catcher in the Rye'' — School of General Studies
File:Amelia Earhart 1935.jpg, Amelia Earhart: first female aviator to fly solo across the Atlantic Ocean — School of General Studies
File:Jake Gyllenhaal (22373266462) (cropped 2).jpg, Jake Gyllenhaal: actor and film producer — Columbia College
Faculty
As of 2021, Columbia employs 4,381 faculty, including 70 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 178 members of theAmerican Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, a ...
, and 65 members of the National Academy of Medicine. In total, the Columbia faculty has included 52 Nobel laureates, 12 National Medal of Science recipients, and 32 National Academy of Engineering members.
Columbia University faculty played particularly important roles during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and the creation of the New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Con ...
under President Franklin D. Roosevelt, who attended Columbia Law School. The three core members of Roosevelt's Brain Trust: Adolf A. Berle
Adolf Augustus Berle Jr. (; January 29, 1895 – February 17, 1971) was an American lawyer, educator, writer, and diplomat. He was the author of ''The Modern Corporation and Private Property'', a groundbreaking work on corporate governance, a pro ...
, Raymond Moley, and Rexford Tugwell
Rexford Guy Tugwell (July 10, 1891 – July 21, 1979) was an American economist who became part of Franklin D. Roosevelt's first "Brain Trust", a group of Columbia University academics who helped develop policy recommendations leading up to ...
, were law professors at Columbia. The Statistical Research Group The Statistical Research Group (SRG) was a research group at Columbia University focused on military problems during World War II. Abraham Wald, Allen Wallis, Herbert Solomon, Frederick Mosteller, George Stigler and Milton Friedman were all part ...
, which used statistics to analyze military problems during World War II, was composed of Columbia researchers and faculty including George Stigler and Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and the ...
. Columbia faculty and researchers, including Enrico Fermi, Leo Szilard, Eugene T. Booth, John R. Dunning
John Ray Dunning (September 24, 1907 – August 25, 1975) was an American physicist who played key roles in the Manhattan Project that developed the first atomic bombs. He specialized in neutron physics, and did pioneering work in gaseous diffusio ...
, George B. Pegram
George Braxton Pegram (October 24, 1876 – August 12, 1958) was an American physicist who played a key role in the technical administration of the Manhattan Project. He graduated from Trinity College (now Duke University) in 1895, and taught hig ...
, Walter Zinn
Walter Henry Zinn (December 10, 1906 – February 14, 2000) was an American nuclear physicist who was the first director of the Argonne National Laboratory from 1946 to 1956. He worked at the Manhattan Project's Metallurgical Laboratory during W ...
, Chien-Shiung Wu
)
, spouse =
, residence =
, nationality = ChineseAmerican
, field = Physics
, work_institutions = Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica University of California at Berkeley Smith College Princeton University Columbia UniversityZhejiang ...
, Francis G. Slack, Harold Urey
Harold Clayton Urey ( ; April 29, 1893 – January 5, 1981) was an American physical chemist whose pioneering work on isotopes earned him the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1934 for the discovery of deuterium. He played a significant role in th ...
, Herbert L. Anderson
Herbert Lawrence Anderson (May 24, 1914 – July 16, 1988) was an American nuclear physicist who was Professor of Physics at the University of Chicago.
He contributed to the Manhattan Project. He was also a member of the team which made the first ...
, and Isidor Isaac Rabi, also played a significant role during the early phases of the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
.
Following the rise of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, the exiled Institute for Social Research
The Institute for Social Research (german: Institut für Sozialforschung, IfS) is a research organization for sociology and continental philosophy, best known as the institutional home of the Frankfurt School and critical theory. Currently a pa ...
at Goethe University Frankfurt would affiliate itself with Columbia from 1934 to 1950. It was during this period that thinkers including Theodor Adorno, Max Horkheimer, and Herbert Marcuse wrote and published some of the most seminal works of the Frankfurt School
The Frankfurt School (german: Frankfurter Schule) is a school of social theory and critical philosophy associated with the Institute for Social Research, at Goethe University Frankfurt in 1929. Founded in the Weimar Republic (1918–1933), dur ...
, including '' Reason and Revolution'', ''Dialectic of Enlightenment
''Dialectic of Enlightenment'' (german: Dialektik der Aufklärung) is a work of philosophy and social criticism written by Frankfurt School philosophers Max Horkheimer and Theodor W. Adorno. The text, published in 1947, is a revised version of ...
'', and ''Eclipse of Reason''. Professors Edward Said, author of ''Orientalism'', and Gayatri Spivak are generally considered as founders of the field of postcolonialism; other professors that have significantly contributed to the field include Hamid Dabashi and Joseph Massad
Joseph Andoni Massad ( ar, جوزيف مسعد; born 1963) is a Jordanian academic specializing in Middle Eastern studies, who serves as Professor of Modern Arab Politics and Intellectual History in the Department of Middle Eastern, South Asian, ...
. The works of professors Kimberlé Crenshaw, Patricia J. Williams
Patricia J. Williams (born August 28, 1951) is an American legal scholar and a proponent of critical race theory, a school of legal thought that emphasizes race as a fundamental determinant of the American legal system.
Early life
Williams rece ...
, and Kendall Thomas were foundational to the field of critical race theory.
Columbia and its affiliated faculty have also made significant contributions to the study of religion. The affiliated Union Theological Seminary is a center of liberal Christianity
Liberal Christianity, also known as Liberal Theology and historically as Christian Modernism (see Catholic modernism and Fundamentalist–Modernist controversy), is a movement that interprets Christian teaching by taking into consideration ...
in the United States, having served as the birthplace of Black theology through the efforts of faculty including James H. Cone and Cornel West, and Womanist theology, through the works of Katie Cannon, Emilie Townes, and Delores S. Williams. Likewise, the Jewish Theological Seminary of America was the birthplace of Conservative Judaism
Conservative Judaism, known as Masorti Judaism outside North America, is a Jewish religious movement which regards the authority of ''halakha'' (Jewish law) and traditions as coming primarily from its people and community through the generati ...
movement in the United States, which was founded and led by faculty members including Solomon Schechter, Alexander Kohut, and Louis Ginzberg
Louis Ginzberg ( he, לוי גינצבורג, ''Levy Gintzburg''; russian: Леви Гинцберг, ''Levy Ginzberg''; November 28, 1873 – November 11, 1953) was a Russian-born American rabbi and Talmudic scholar of Lithuanian-Jewish desc ...
in the early 20th century, and is a major center for Jewish studies in general.
Other schools of thought in the humanities Columbia professors made significant contributions toward include the Dunning School, founded by William Archibald Dunning
William Archibald Dunning (12 May 1857 – 25 August 1922) was an American historian and political scientist at Columbia University noted for his work on the Reconstruction era of the United States. He founded the informal Dunning School of inte ...
; the anthropological schools of historical particularism and cultural relativism
Cultural relativism is the idea that a person's beliefs and practices should be understood based on that person's own culture. Proponents of cultural relativism also tend to argue that the norms and values of one culture should not be evaluated ...
, founded by Franz Boas; and functional psychology, whose founders and proponents include John Dewey, James McKeen Cattell, Edward L. Thorndike, and Robert S. Woodworth
Robert Sessions Woodworth (October 17, 1869 – July 4, 1962) was an American academic psychologist and the creator of the personality test which bears his name. A graduate of Harvard and Columbia, he studied under William James along with othe ...
.Leahey, Thomas Hardy (2004). ''A History of Psychology: Main Currents in psychological thought''. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall. .
Notable figures that have served as the president of Columbia University include 34th President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal gove ...
Dwight D. Eisenhower, 4th Vice President of the United States
The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice p ...
George Clinton, Founding Father and U.S. Senator
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and power ...
from Connecticut William Samuel Johnson
William Samuel Johnson (October 7, 1727 – November 14, 1819) was an American Founding Father and statesman. Before the Revolutionary War, he served as a militia lieutenant before being relieved following his rejection of his election to the Fi ...
, Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiolo ...
laureate Nicholas Murray Butler, and First Amendment
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and reco ...
scholar Lee Bollinger.Margaret Mead
Margaret Mead (December 16, 1901 – November 15, 1978) was an American cultural anthropologist who featured frequently as an author and speaker in the mass media during the 1960s and the 1970s.
She earned her bachelor's degree at Barnard C ...
File:Edward Sapir.jpg, Edward Sapir
File:John Dewey cph.3a51565.jpg, John Dewey
File:Charles Beard.jpg, Charles A. Beard
File:Max Horkheimer.jpg, Max Horkheimer
File:Herbert Marcuse in Newton, Massachusetts 1955 (cropped).jpg, Herbert Marcuse
File:Edward Said and Daniel Barenboim in Sevilla, 2002 (Said).jpg, Edward Said
File:Gayatri Spivak on Subversive Festival.jpg, Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak
File:Orhan Pamuk 2009 Shankbone.jpg, Orhan Pamuk
File:Edwin H. Armstrong portrait by Florian Bachrach, with autographed dedication to Charles R. Underhill, August 18, 1950 - New England Wireless & Steam Museum - East Greenwich, RI - DSC06641 (cropped).jpg, Edwin Howard Armstrong
File:Enrico Fermi 1943-49.jpg, Enrico Fermi
File:Chien-Shiung Wu (1912-1997) in 1958.jpg, Chien-Shiung Wu
)
, spouse =
, residence =
, nationality = ChineseAmerican
, field = Physics
, work_institutions = Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica University of California at Berkeley Smith College Princeton University Columbia UniversityZhejiang ...
File:TD Lee.jpg, Tsung-Dao Lee
Tsung-Dao Lee (; born November 24, 1926) is a Chinese-American physicist, known for his work on parity violation, the Lee–Yang theorem, particle physics, relativistic heavy ion (RHIC) physics, nontopological solitons, and soliton stars ...
File:Jack-Steinberger-2008.JPG, Jack Steinberger
File:Joachim Frank.jpg, Joachim Frank
File:Joseph E. Stiglitz, 2019 (cropped).jpg, Joseph Stiglitz
File:FMSTAN & SPIDER Global meeting in Austrian Foreign Ministries in Vienna (49120446508) (cropped).jpg, Jeffrey Sachs
File:Robert Mundell (cropped).jpg, Robert Mundell
File:Thomas Hunt Morgan.jpg, Thomas Hunt Morgan
File:Eric Kandel 01.JPG, Eric Kandel
File:Professor Richard Axel ForMemRS.jpg, Richard Axel
Richard Axel (born July 2, 1946) is an American molecular biologist and university professor in the Department of Neuroscience at Columbia University and investigator at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. His work on the olfactory system won ...
File:Andrei Okounkov 2018.jpg, Andrei Okounkov
See also
* Columbia Glacier, aglacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such a ...
in Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U ...
, U.S., named for Columbia University
* Columbia MM, a text-based mail client developed at Columbia University
* Columbia Non-neutral Torus
The Columbia Non-neutral Torus (CNT) is a small stellarator at the Columbia University Plasma Physics Laboratory designed by Thomas Sunn Pedersen with the aid of Wayne Reiersen and Fred Dahlgren of the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory to co ...
, a small stellarator at the Columbia University Plasma Physics Laboratory
* '' Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center'', an album of electronic music released in 1961
* '' Columbia Revolt'', a black-and-white 1968 documentary film
* Columbia Scholastic Press Association
* Columbia School of Linguistics
* Columbia Spelling Board
The Simplified Spelling Board was an American organization created in 1906 to reform the spelling of the English language, making it simpler and easier to learn, and eliminating many of what were considered to be its inconsistencies. The board op ...
, a historic etymological organization
* Columbia University Partnership for International Development
* Columbia Encyclopedia
The ''Columbia Encyclopedia'' is a one-volume encyclopedia produced by Columbia University Press and, in the last edition, sold by the Gale Group. First published in 1935, and continuing its relationship with Columbia University
Columbi ...
* Mount Columbia, a mountain in Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the ...
, U.S., named for Columbia University
* Nutellagate, a controversy surrounding high Nutella consumption at Columbia University
* ''The Strawberry Statement
''The Strawberry Statement'' is a non-fiction book by James Simon Kunen, written when he was 19, which chronicled his experiences at Columbia University from 1966–1968, particularly the April 1968 protests and takeover of the office of the dea ...
'', a non-fiction account of the 1968 protests
* Columbia University in popular culture
Notes
Notes
References
Further reading
* Robert A. McCaughey: ''Stand, Columbia: A History of Columbia University in the City of New York, 1754–2004'', Columbia University Press, 2003, . * ''Living Legacies at Columbia'', ed. by Wm Theodore De Bary, Columbia University Press, 2006, .External links
* {{Authority control 1754 establishments in the Province of New York Colonial colleges Educational institutions established in 1754 McKim, Mead & White buildings New York (state) in the American Revolution Private universities and colleges in New York City Universities and colleges in Manhattan