|
Thomas Jessell
Thomas Michael Jessell (2 August 1951 – 28 April 2019) was the Claire Tow Professor of biochemistry and molecular biophysics at Columbia University in New York and a prominent developmental neuroscientist. In 2018, Columbia University announced his termination from his administrative positions after an internal investigation uncovered violations of university policies. He died shortly after from a rapidly neurodegenerative condition diagnosed as progressive supranuclear palsy. Education Jessell received his PhD in neuroscience from the University of Cambridge PhD in 1977 with Leslie Iversen at the MRC Neurochemical Pharmacology Unit. Career and research After his PhD, he worked as a postdoctoral fellow at Harvard Medical School with Gerald Fischbach. In 1981 he became an assistant professor in the Department of Neurobiology at Harvard Medical School. In 1985 he joined the Columbia University faculty where he worked for the remainder of his career and became Claire Tow Prof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city#National capitals, Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national Government of the United Kingdom, government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the Counties of England, counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kavli Prize
The Kavli Prize was established in 2005 as a joint venture of the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters, the Norwegian Ministry of Education and Research, and the Kavli Foundation. It honors, supports, and recognizes scientists for outstanding work in the fields of astrophysics, nanoscience and neuroscience. Three prizes are awarded every second year. Each of the three Kavli Prizes consists of a gold medal, a scroll, and a cash award of US$1,000,000. The medal has a diameter of , a thickness of , and weighs . The first Kavli Prizes were awarded on 9 September 2008 in Oslo, presented by Haakon, Crown Prince of Norway. Selection committees The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters appoints three prize committees consisting of leading international scientists after receiving recommendations made from the following organisations: *Chinese Academy of Sciences * French Academy of Sciences * Max Planck Society * United States National Academy of Sciences *Norwegian Aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NAS Award For Scientific Reviewing
The NAS Award for Scientific Reviewing is awarded by the U.S. National Academy of Sciences "to recognize authors whose reviews have synthesized extensive and difficult material, rendering a significant service to science and influencing the course of scientific thought." It has been awarded annually in specific fields since 1979. List of NAS Award for Scientific Reviewing winners *Christina Maslach (2020, social sciences) : For her insightful, integrative reviews discovering and developing the rigorous research and multidimensional theory of worker or job burnout and interventions to mitigate it, thereby advancing science and improving human wellbeing. *Robert Kennicutt (2019, astronomy) : For the highly cited review "Star Formation in Galaxies Along the Hubble Sequence" and related work synthesizing the broad field of stellar formation, which provided a critical intellectual foundation for the field. *Ad Bax (2018, structural biology) : For lucid, revelatory reviews and pionee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
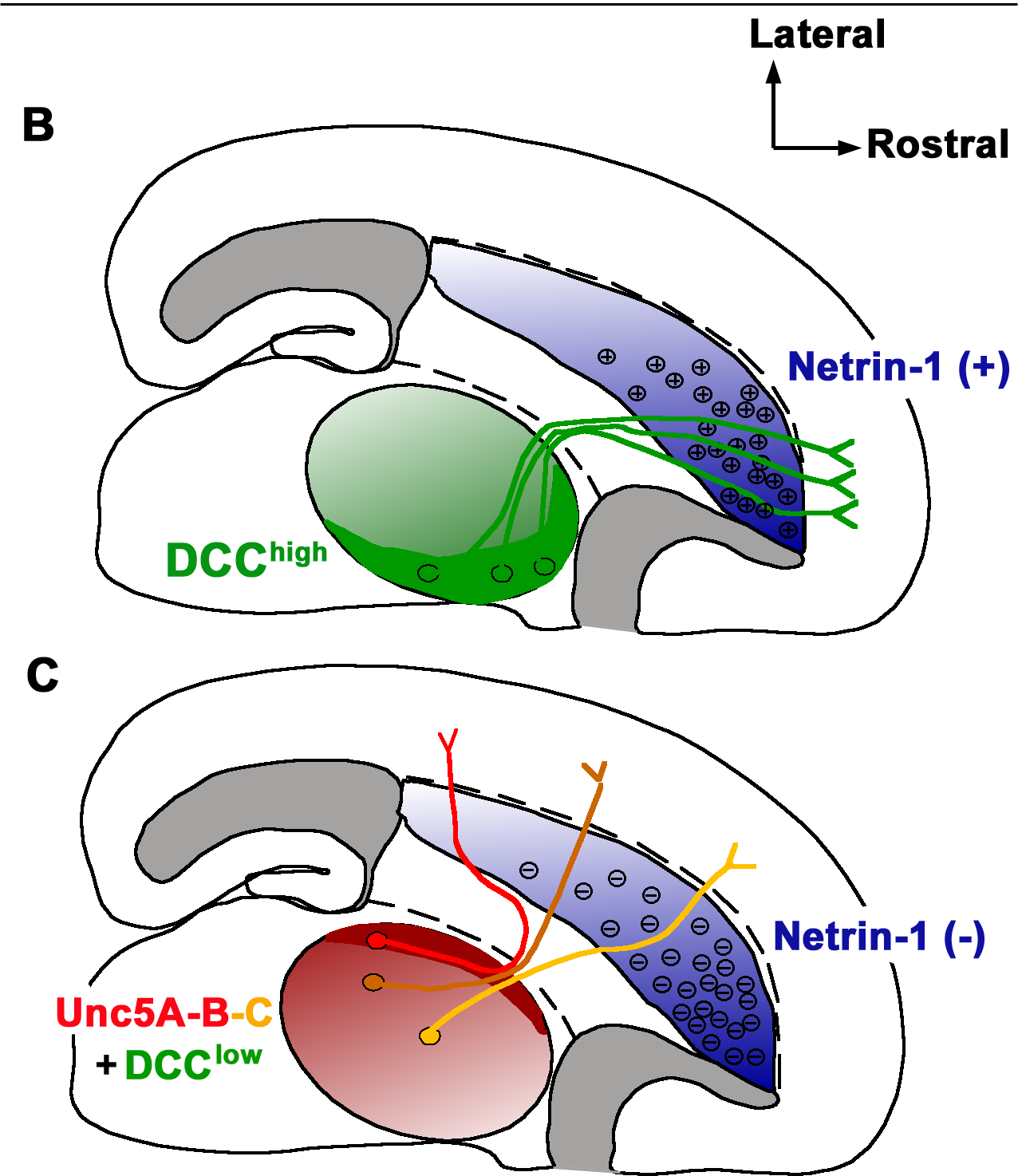
Netrin
Netrins are a class of proteins involved in axon guidance. They are named after the Sanskrit word "netr", which means "one who guides". Netrins are genetically conserved across nematode worms, fruit flies, frogs, mice, and humans. Structurally, netrin resembles the extracellular matrix protein laminin. Netrins are chemotropic; a growing axon will either move towards or away from a higher concentration of netrin. Though the detailed mechanism of axon guidance is not fully understood, it is known that netrin attraction is mediated through UNC-40/DCC cell surface receptors and repulsion is mediated through UNC-5 receptors. Netrins also act as growth factors, encouraging cell growth activities in target cells. Mice deficient in netrin fail to form the hippocampal comissure or the corpus callosum. A proposed model for netrin activity in the spinal column of developing human embryos is that netrins are released by the floor plate and then are picked up by receptor proteins embed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Development (biology)
Development of the human body is the process of growth to maturity. The process begins with fertilization, where an egg released from the ovary of a female is penetrated by a sperm cell from a male. The resulting zygote develops through mitosis and cell differentiation, and the resulting embryo then implants in the uterus, where the embryo continues development through a fetal stage until birth. Further growth and development continues after birth, and includes both physical and psychological development, influenced by genetic, hormonal, environmental and other factors. This continues throughout life: through childhood and adolescence into adulthood. Before birth Development before birth, or prenatal development () is the process in which a zygote, and later an embryo and then a fetus develops during gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization and the formation of the zygote, the first stage in embryonic development which continues in fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Cell
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dendri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
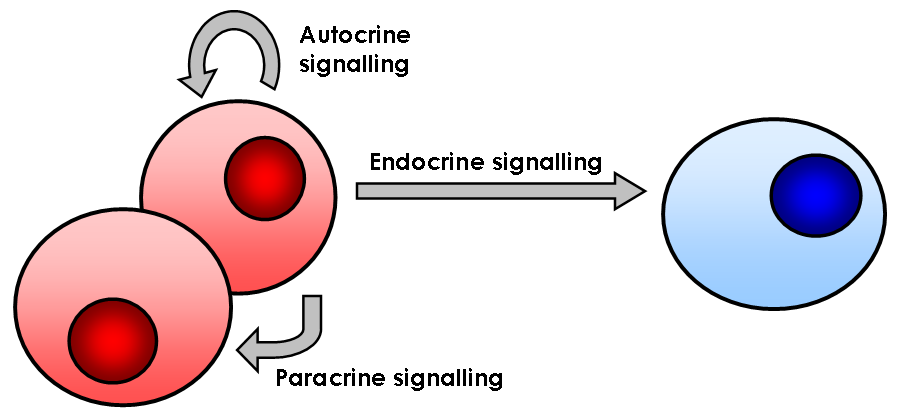
Signal (biology)
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Medical School
Harvard Medical School (HMS) is the graduate medical school of Harvard University and is located in the Longwood Medical Area of Boston, Massachusetts. Founded in 1782, HMS is one of the oldest medical schools in the United States and is consistently ranked first for research among medical schools by '' U.S. News & World Report''. Unlike most other leading medical schools, HMS does not operate in conjunction with a single hospital but is directly affiliated with several teaching hospitals in the Boston area. Affiliated teaching hospitals and research institutes include Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston Children's Hospital, McLean Hospital, Cambridge Health Alliance, The Baker Center for Children and Families, and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital. History Harvard Medical School was founded on September 19, 1782, after President Joseph Willard presented a report wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postdoctoral
A postdoctoral fellow, postdoctoral researcher, or simply postdoc, is a person professionally conducting research after the completion of their doctoral studies (typically a PhD). The ultimate goal of a postdoctoral research position is to pursue additional research, training, or teaching in order to have better skills to pursue a career in academia, research, or any other field. Postdocs often, but not always, have a temporary academic appointment, sometimes in preparation for an academic faculty position. They continue their studies or carry out research and further increase expertise in a specialist subject, including integrating a team and acquiring novel skills and research methods. Postdoctoral research is often considered essential while advancing the scholarly mission of the host institution; it is expected to produce relevant publications in peer-reviewed academic journals or conferences. In some countries, postdoctoral research may lead to further formal qualification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslie Iversen
Leslie Lars Iversen (31 October 1937 – 30 July 2020), was a British pharmacologist, known for his work on the neurochemistry of neurotransmission. Career and research From 1971 to 1982, Iversen was Director of the MRC Neurochemical Pharmacology Unit in Cambridge. Between 1982 and 1995 he worked as Director of the Merck, Sharp & Dohme Neuroscience Research Centre. In 1995 he became Visiting Professor of Pharmacology at the University of Oxford. In 2010 he was accused of plagiarism. Consequently one of his books now credits the original author of the plagiarized work. Awards and honours He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society (FRS) in 1980 and gave the Society's Ferrier Lecture in 1983. He was appointed a Commander of the Order of the British Empire (CBE) in the 2013 New Year Honours, "for services to pharmacology". He died on 30 July 2020, survived by his wife of over 60 years, Susan Iversen Susan Diana Iversen (born 28 February 1940) is a British experiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a late-onset degenerative disease involving the gradual deterioration and death of specific volumes of the brain. The condition leads to symptoms including loss of balance, slowing of movement, difficulty moving the eyes, and cognitive impairment. PSP may be mistaken for other neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's, frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's. The cause of the condition is uncertain, but involves accumulation of tau protein within the brain. Medications such as levodopa and amantadine may be useful in some cases. PSP affects about six people per 100,000. The first symptoms typically occur at 60–70 years of age. Males are slightly more likely to be affected than females. No association has been found between PSP and any particular race, location, or occupation. Signs and symptoms The initial symptoms in two-thirds of cases are loss of balance, lunging forward when mobilizing, fast walking, bumping into objects or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)