Art of Spain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Spanish art has been an important contributor to
 The early
The early
File:Tesoro de Villena.jpg, The
Western art
The art of Europe, or Western art, encompasses the history of visual art in Europe. European prehistoric art started as mobile Upper Paleolithic rock and cave painting and petroglyph art and was characteristic of the period between the Paleol ...
and Spain has produced many famous and influential artists including Velázquez, Goya and Picasso
Pablo Ruiz Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist and Scenic design, theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th ce ...
. Spanish art was particularly influenced by France and Italy during the Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
and Neoclassical periods, but Spanish art has often had very distinctive characteristics, partly explained by the Moorish
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or se ...
heritage in Spain (especially in Andalusia
Andalusia (, ; es, Andalucía ) is the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Peninsular Spain. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognised as a ...
), and through the political and cultural climate in Spain during the Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
and the subsequent eclipse of Spanish power under the Bourbon Bourbon may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bourbon whiskey, an American whiskey made using a corn-based mash
* Bourbon barrel aged beer, a type of beer aged in bourbon barrels
* Bourbon biscuit, a chocolate sandwich biscuit
* A beer produced by Bras ...
dynasty.
The prehistoric art
In the history of art, prehistoric art is all art produced in preliterate, prehistorical cultures beginning somewhere in very late geological history, and generally continuing until that culture either develops writing or other methods of rec ...
of Spain had many important periods-it was one of the main centres of European Upper Paleolithic art
The art of the Upper Paleolithic represents the oldest form of prehistoric art. Figurative art is present in prehistoric Europe, Europe and Prehistoric Indonesia, Southeast Asia, beginning between about 40,000 to 35,000 years ago.
Non-figura ...
and the rock art of the Spanish Levant in the subsequent periods. In the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
large parts of Spain were a centre for Celtic art, and Iberian sculpture
Iberian sculpture, a subset of Iberian art, describes the various sculptural styles developed by the Iberians from the Bronze Age up to the Roman conquest. For this reason it is sometimes described as Pre-Roman Iberian sculpture.
Almost all ext ...
has a distinct style, partly influenced by coastal Greek settlements. Spain was conquered by the Romans by 200 BC and Rome was rather smoothly replaced by the Germanic Visigoth
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is kno ...
s in the 5th century AD, who soon Christianized. The relatively few remains of Visigothic art and architecture show an attractive and distinct version of wider European trends. With the Umayyad conquest of Hispania
The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania (in the Iberian Peninsula) from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of t ...
in the 8th century there was a notable Moorish
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or se ...
presence in art specially in Southern Iberia. Over the following centuries the wealthy courts of Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus DIN 31635, translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label=Berber languages, Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, ...
produced many works of exceptional quality, culminating in the Alhambra
The Alhambra (, ; ar, الْحَمْرَاء, Al-Ḥamrāʾ, , ) is a palace and fortress complex located in Granada, Andalusia, Spain. It is one of the most famous monuments of Islamic architecture and one of the best-preserved palaces of the ...
in Granada
Granada (,, DIN 31635, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the fo ...
, right at the end of Muslim Spain.
Meanwhile, the parts of Spain remaining Christian, or that were re-conquered, were prominent in Pre-Romanesque
Pre-Romanesque art and architecture is the period in European art from either the emergence of the Merovingian kingdom in about 500 AD or from the Carolingian Renaissance in the late 8th century, to the beginning of the 11th century Romanesqu ...
and Romanesque art
Romanesque art is the art of Europe from approximately 1000 AD to the rise of the Gothic Art, Gothic style in the 12th century, or later depending on region. The preceding period is known as the Pre-Romanesque period. The term was invented by 1 ...
. Late Gothic Spanish art flourished under the unified monarchy in the Isabelline Gothic and Plateresque styles, and the already strong traditions in painting and sculpture began to benefit from the influence of imported Italian artists. The enormous wealth that followed the flood of American gold saw lavish spending on the arts in Spain, much of it directed at religious art in the Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
. Spanish control of the leading centre of North European art, Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
, from 1483 and also of the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
from 1548, both ending in 1714, had a great influence on Spanish art, and the level of spending attracted artists from other areas, such as El Greco
Domḗnikos Theotokópoulos ( el, Δομήνικος Θεοτοκόπουλος ; 1 October 1541 7 April 1614), most widely known as El Greco ("The Greek"), was a Greek painter, sculptor and architect of the Spanish Renaissance. "El G ...
, Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Duchy of Brabant in the Southern Netherlands (modern-day Belgium). He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque traditio ...
and (from a safe distance) Titian
Tiziano Vecelli or Vecellio (; 27 August 1576), known in English as Titian ( ), was an Italians, Italian (Republic of Venice, Venetian) painter of the Renaissance, considered the most important member of the 16th-century Venetian school (art), ...
in the Spanish Golden Age
The Spanish Golden Age ( es, Siglo de Oro, links=no , "Golden Century") is a period of flourishing in arts and literature in Spain, coinciding with the political rise of the Spanish Empire under the Catholic Monarchs of Spain and the Spanish H ...
, as well as great native painters such as Diego Velázquez
Diego Rodríguez de Silva y Velázquez (baptized June 6, 1599August 6, 1660) was a Spanish painter, the leading artist in the court of King Philip IV of Spain and Portugal, and of the Spanish Golden Age. He was an individualistic artist of th ...
, José de Ribera
Jusepe de Ribera (1591 – 1652) was a painter and printmaker, who along with Francisco de Zurbarán, Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, and the singular Diego Velázquez, are regarded as the major artists of Spanish Baroque painting. Referring to ...
, Francisco de Zurbarán and Bartolomé Esteban Murillo
Bartolomé Esteban Murillo ( , ; late December 1617, baptized January 1, 1618April 3, 1682) was a Spanish Baroque painter. Although he is best known for his religious works, Murillo also produced a considerable number of paintings of contemporar ...
.
Spanish Baroque architecture
Spanish Baroque is a strand of Baroque architecture that evolved in Spain, its provinces, and former colonies.
History
As Italian Baroque influences penetrated across the Pyrenees, they gradually superseded in popularity the restrained classici ...
has survived in large quantity, and has both strains marked by exuberant extravagance, as in the Churrigueresque style, and a rather severe classicism, as in the work of Juan de Herrera
Juan de Herrera (1530 – 15 January 1597) was a Spanish architect, mathematician and geometrician.
One of the most outstanding Spanish architects in the 16th century, Herrera represents the peak of the Renaissance in Spain. His sober style reac ...
. It was generally the former which marked the emerging art and Spanish Colonial architecture of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
outside Europe, as in Latin America ( New Spanish Baroque and Andean Baroque
Andean Baroque (Spanish: ''Barroco andino'' or ''arquitectura mestiza'') is an artistic movement that appeared in colonial Peru between 1680 and 1780. It is located geographically between Arequipa and Lake Titicaca in what is now Peru, where rul ...
), while the Baroque Churches of the Philippines
The Baroque Churches of the Philippines are a collection of four Spanish Colonial-era baroque churches in the Philippines, which were included in UNESCO's World Heritage List in 1993. The churches are also considered as national cultural treas ...
are simpler.
The decline of the Habsburg monarchy brought this period to an end, and Spanish art in the 18th and early-19th century was generally less exciting, with the huge exception of Francisco Goya
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes (; ; 30 March 174616 April 1828) was a Spanish romantic painter and printmaker. He is considered the most important Spanish artist of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. His paintings, drawings, and ...
. The rest of 19th-century Spanish art followed European trends, generally at a conservative pace, until the Catalan movement of Modernisme
''Modernisme'' (, Catalan for "modernism"), also known as Catalan modernism and Catalan art nouveau, is the historiographic denomination given to an art and literature movement associated with the search of a new entitlement of Catalan culture ...
, which initially was more a form of Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
. Picasso dominates Spanish Modernism
Modernism is both a philosophy, philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western world, Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new fo ...
in the usual English sense, but Juan Gris, Salvador Dalí
Salvador Domingo Felipe Jacinto Dalí i Domènech, Marquess of Dalí of Púbol (; ; ; 11 May 190423 January 1989) was a Spanish Surrealism, surrealist artist renowned for his technical skill, precise draftsmanship, and the striking and bizarr ...
and Joan Miró
Joan Miró i Ferrà ( , , ; 20 April 1893 – 25 December 1983) was a Catalan painter, sculptor and ceramicist born in Barcelona. A museum dedicated to his work, the Fundació Joan Miró, was established in his native city of Barcelona i ...
are other leading figures.
Ancient Iberia
 The early
The early Iberians
The Iberians ( la, Hibērī, from el, Ἴβηρες, ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (among ...
have left many remains; northern-western Spain shares with south-western France the region where the richest Upper Paleolithic art
The art of the Upper Paleolithic represents the oldest form of prehistoric art. Figurative art is present in prehistoric Europe, Europe and Prehistoric Indonesia, Southeast Asia, beginning between about 40,000 to 35,000 years ago.
Non-figura ...
in Europe is found in the Cave of Altamira and other sites where there are cave painting
In archaeology, Cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric origin, and the oldest known are more than 40,000 ye ...
s made between 35,000 and 11,000 BC. The Rock art of the Iberian Mediterranean Basin
The group of over 700 sites of prehistoric Rock art of the Iberian Mediterranean Basin, also known as Levantine art, were collectively declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1998. The sites are in the eastern part of Spain and contain rock ...
(as UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
term it) is from the eastern side of Spain, probably dating from about 8000–3500 BC, and shows animal and hunting scenes often developed with a growing feeling for the whole composition of a large scene. Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
in particular is rich in megalithic
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
monuments, including the Almendres Cromlech
The Cromlech of the Almendres ( pt, Cromeleque dos Almendres/Cromeleque na Herdade dos Almendres) is a megalithic complex (commonly known as the ''Almendres Cromlech''), located 4.5 road km WSW of the village of Nossa Senhora de Guadalupe, in th ...
, and Iberian schematic art
Iberian schematic art is the name given to a series of prehistoric representations (almost always cave paintings) that appear in the Iberian peninsula, which are associated with the first metallurgical cultures (the Copper Age, the Bronze Age ...
is stone sculpture, petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions ...
s and cave painting
In archaeology, Cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric origin, and the oldest known are more than 40,000 ye ...
s from the early metal ages, found all over the Iberian peninsula, with both geometric patterns, but also a higher usage of simple pictogram
A pictogram, also called a pictogramme, pictograph, or simply picto, and in computer usage an icon, is a graphic symbol that conveys its meaning through its pictorial resemblance to a physical object. Pictographs are often used in writing and ...
-like human figures than is typical of comparable art from other areas. The Casco de Leiro
The gold Casco de Leiro ("Helmet of Leiro") is a ritual hemispherical cap probably dating to the end of the Late Bronze Age (''circa'' 1,000 to 800 BC) in the town of Leiro (municipality of Rianxo, Galicia, Spain). The circumstances of its disc ...
, a late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
gold ritual helmet, may relate to other golden hats
Golden hats (or gold hats) (german: Goldhüte, singular: ) are a very specific and rare type of archaeological artifact from Bronze Age Europe. So far, four such objects ("cone-shaped gold hats of the Schifferstadt type") are known. The objects ...
found in Germany, and the Treasure of Villena
The Treasure of Villena ( es, Tesoro de Villena) is one of the greatest hoard finds of gold of the European Bronze Age. It comprises 59 objects made of gold, silver, iron and amber with a total weight of almost 10 kilograms, 9 of them of 23.5 ka ...
is a huge hoard of geometrically decorated vessels and jewellery, perhaps from the 10th century BC, including 10 kilos of gold.
Iberian sculpture
Iberian sculpture, a subset of Iberian art, describes the various sculptural styles developed by the Iberians from the Bronze Age up to the Roman conquest. For this reason it is sometimes described as Pre-Roman Iberian sculpture.
Almost all ext ...
before the Roman occupation reflects the contacts with other advanced ancient cultures who set up small coastal colonies, including the Greeks and Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient thalassocracy, thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-st ...
; the Sa Caleta Phoenician Settlement on Ibiza
Ibiza (natively and officially in ca, Eivissa, ) is a Spanish island in the Mediterranean Sea off the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. It is from the city of Valencia. It is the third largest of the Balearic Islands, in Spain. Its l ...
has survived to be excavated, where most now lie under large towns, and the Lady of Guardamar Lady of Guardamar (''Dama de Guardamar''), is a limestone female bust, 50 cm high, dated circa 400 BCE, that was discovered in fragments in the Phoenician archaeological site of Cabezo Lucero in Guardamar del Segura in Alicante province, Spain, on ...
was excavated from another Phoenician site. The Lady of Elche (probably 4th century BC) possibly represents Tanit, but also shows Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
influence, as do the 6th century Sphinx of Agost and Biche of Balazote
The Bicha of Balazote is an Iberian sculpture that was found in the borough of Balazote in Albacete province ( Castile-La Mancha), Spain. Carlos Fuentes has called it the "Beast of Balazote." The sculpture has been dated to the 6th century BCE, ...
. The Bulls of Guisando are the most impressive examples of ''verraco
The ''verracos'' ( es, verraco; pt, berrão; literally 'boar'), in the Iberian Peninsula, are the Vettones's granite megalithic monuments, sculptures of animals as found in the west of the Iberian '' meseta'' – the high central plain of the ...
s'', which are large Celtiberian animal sculptures in stone; the 5th century BC Bull of Osuna
The Bull of Osuna is a limestone high relief Iberian sculpture, 82 cm high, dated from the end of the 5th century BCE, that is on display at the National Archaeological Museum of Spain in Madrid.
It was found in the archeological site of the ancien ...
is a more developed single example. Some decorated ''falcata
The falcata is a type of sword typical of pre-Roman Iberia. The falcata was used to great effect for warfare in the ancient Iberian peninsula, and is firmly associated with the southern Iberian tribes, among other ancient peoples of Hispania. ...
'', the distinctive curving Iberian sword, have survived, and large numbers of bronze statuettes used as votive offerings. The Romans gradually conquered all of Iberia between 218 BC and 19 AD.
As elsewhere in the Western Empire, the Roman occupation largely overwhelmed native styles; Iberia was an important agricultural area for the Romans, and the elite acquired vast estates producing wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
s and wine, with some later emperors coming from the Iberian provinces; many huge villas have been excavated. The Aqueduct of Segovia, Roman Walls of Lugo
The Roman walls of Lugo (Spanish, Galician: ''Muralla Romana de Lugo'') are the ancient Roman defensive walls stretching around the Old Town of Lugo, Spain. They were built in the third century AD to defend the ancient Roman town of ''Lucus Au ...
, Alcántara Bridge
The Alcántara Bridge (also known as Trajan's Bridge at Alcantara) is a Roman bridge at Alcántara, in Extremadura, Spain. Alcántara is from the Arabic word ''al-Qantarah'' (القنطرة) meaning "the arch". The stone arch bridge was buil ...
(104–106 AD), and the Tower of Hercules
The Tower of Hercules ( es, Torre de Hércules) is the oldest existent lighthouse known. It has an ancient Rome, ancient Roman origin on a peninsula about from the centre of A Coruña, Galicia (Spain), Galicia, in north-western Spain. Until the ...
lighthouse are among a number of well-preserved major monuments, impressive remains of Roman engineering
The ancient Romans were famous for their advanced engineering accomplishments. Technology for bringing running water into cities was developed in the east, but transformed by the Romans into a technology inconceivable in Greece. The architecture ...
if not always art. Roman temples survive fairly complete at Vic
Vic (; es, Vic or Pancracio Celdrán (2004). Diccionario de topónimos españoles y sus gentilicios (5ª edición). Madrid: Espasa Calpe. p. 843. ISBN 978-84-670-3054-9. «Vic o Vich (viquense, vigitano, vigatán, ausense, ausetano, ausonense): ...
, Évora
Évora ( , ) is a city and a municipality in Portugal. It has 53,591 inhabitants (2021), in an area of 1307.08 km2. It is the historic capital of the Alentejo and serves as the seat of the Évora District.
Due to its well-preserved old to ...
(now in Portugal), and Alcántara
Alcántara is a municipality in the province of Cáceres, Extremadura, Spain, on the Tagus, near Portugal. The toponym is from the Arabic word ''al-Qanṭarah'' (القنطرة) meaning "the bridge".
History
Archaeological findings have atteste ...
, as well as elements in Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
and Córdoba. There must have been local workshops producing the high-quality mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
s found, though most of the better free-standing sculpture was probably imported. The Missorium of Theodosius I
The Missorium of Theodosius I is a large ceremonial silver dish preserved in the Real Academia de la Historia, in Madrid, Spain. It was probably made in Constantinople for the tenth anniversary (decennalia) in 388 AD of the reign of the Emperor ...
is an important Late Antique
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English has ...
silver dish that was found in Spain but was probably made in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
.
Treasure of Villena
The Treasure of Villena ( es, Tesoro de Villena) is one of the greatest hoard finds of gold of the European Bronze Age. It comprises 59 objects made of gold, silver, iron and amber with a total weight of almost 10 kilograms, 9 of them of 23.5 ka ...
, perhaps 10th century BC
The Lady of Elche, once polychrome stone bust discovered by chance in 1897 at L'Alcúdia, believed to be a piece of Iberian sculpture from the 4th century BC, National Archaeological Museum of Spain, Madrid (20098349590).jpg, Lady of Elche from Elx
Elche ( ca-valencia, Elx) is a city and municipality of Spain, belonging to the province of Alicante, in the Valencian Community. According to 2014 data, Elche has a population of 228,647 inhabitants,Bulls of Guisando a Vettones
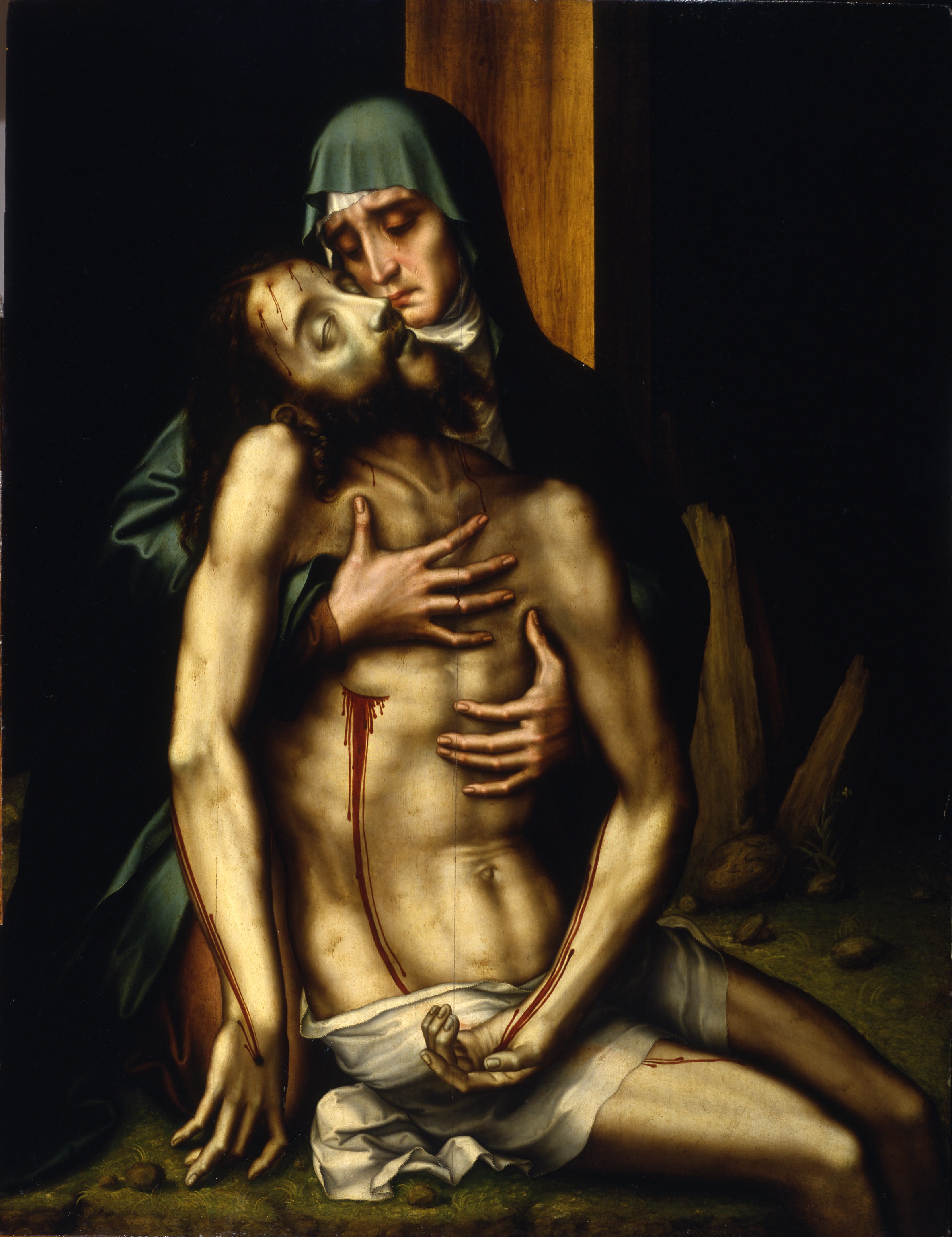
 The Christianized
The Christianized
File:Pyxid Al Mughira OA 4068.jpg, Ivory
 In Spain, the art of the Romanesque period represented a smooth transition from the preceding Pre-Romanesque and Mozarabic styles. Many of the best surviving Romanesque church
In Spain, the art of the Romanesque period represented a smooth transition from the preceding Pre-Romanesque and Mozarabic styles. Many of the best surviving Romanesque church
 Overall the Renaissance and subsequent Mannerist styles are hard to categorise in Spain, due to the mix of Flemish and Italian influences, and regional variations.
The main centre for Italian Renaissance influence entering Spain was
Overall the Renaissance and subsequent Mannerist styles are hard to categorise in Spain, due to the mix of Flemish and Italian influences, and regional variations.
The main centre for Italian Renaissance influence entering Spain was
 The
The 
 The beginning of the
The beginning of the
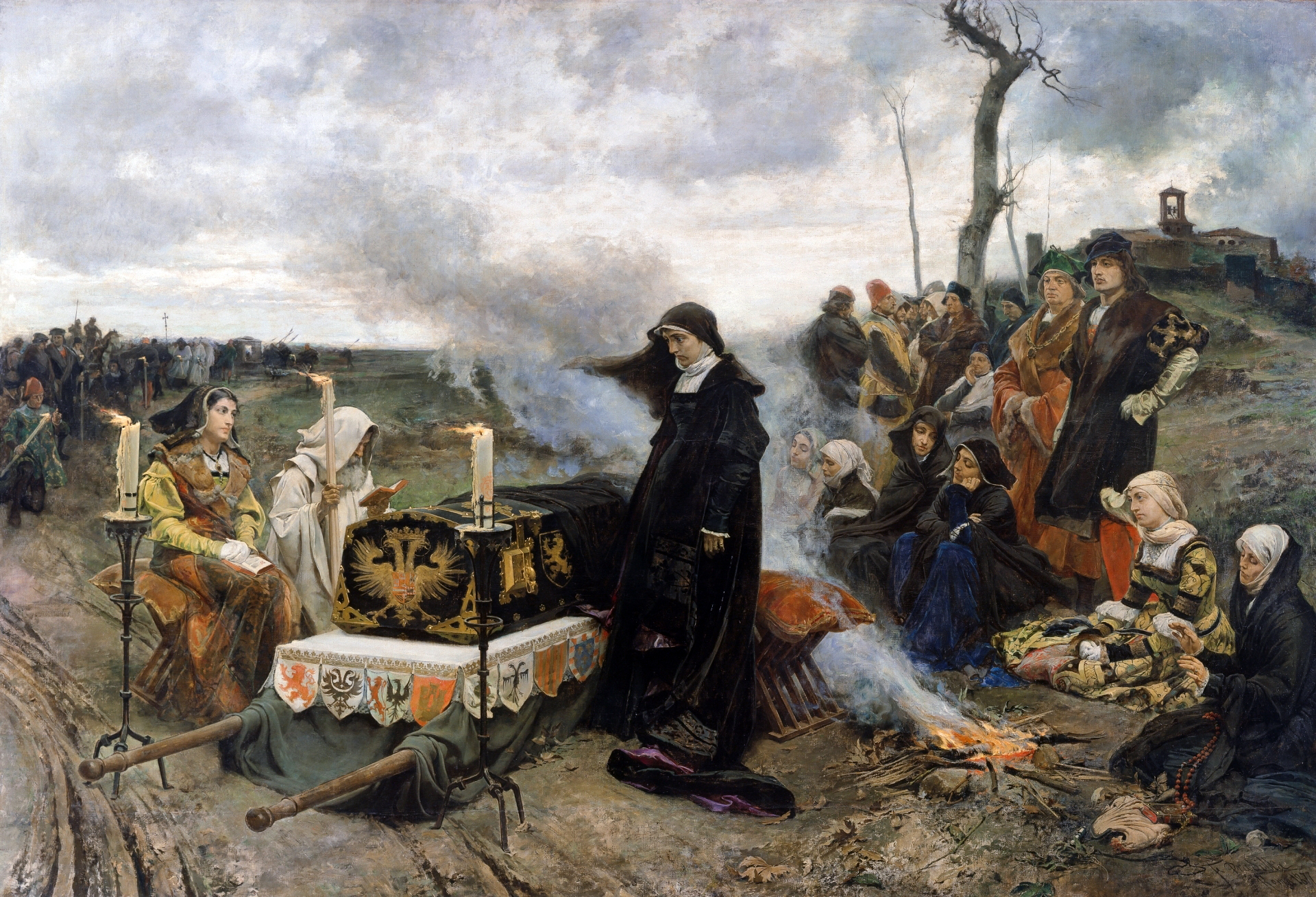
 Various art movements of the 19th Century influenced Spanish artists, largely through them undertaking training in foreign capitals, particularly in Paris and Rome. In this way Neo-classicism,
Various art movements of the 19th Century influenced Spanish artists, largely through them undertaking training in foreign capitals, particularly in Paris and Rome. In this way Neo-classicism,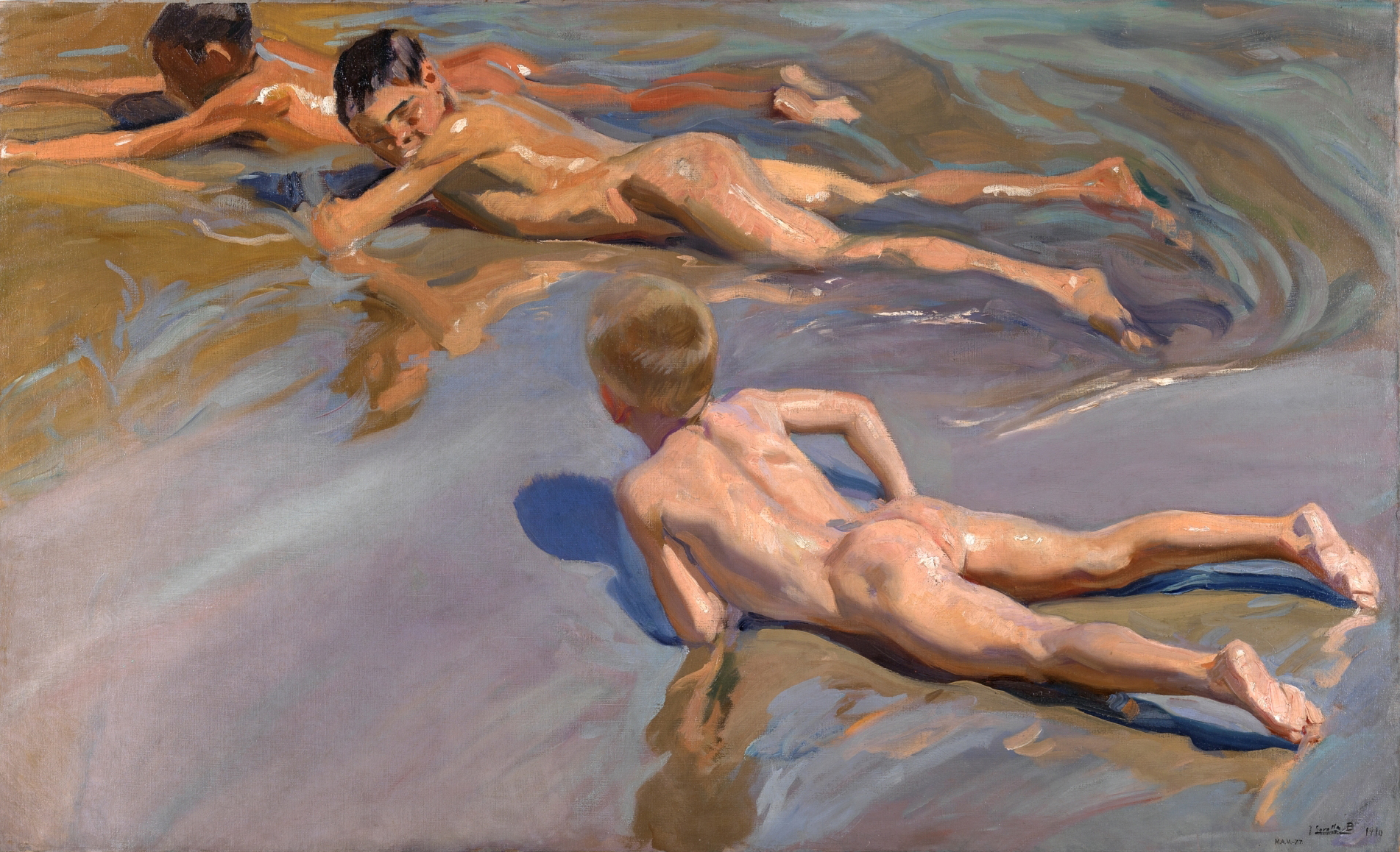  The later part of the century saw a strong period of Romanticism represented in history paintings, as in the works of
The later part of the century saw a strong period of Romanticism represented in history paintings, as in the works of

 During the first half of 20th century many leading Spanish artists were working in Paris, where they contributed to – and sometimes led – developments in the
During the first half of 20th century many leading Spanish artists were working in Paris, where they contributed to – and sometimes led – developments in the
verraco
The ''verracos'' ( es, verraco; pt, berrão; literally 'boar'), in the Iberian Peninsula, are the Vettones's granite megalithic monuments, sculptures of animals as found in the west of the Iberian '' meseta'' – the high central plain of the ...
s in El Tiemblo
El Tiemblo is a municipality located in the province of Ávila, Castile and León, Spain. According to the 2012 census (INE), the municipality has a population of 4,461 inhabitants, and covers an area of about 75 km2.
Location
El Tiemblo ...
, province of Ávila
Early Medieval
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
ruled Iberia after the collapse of the Empire, and the rich 7th century Treasure of Guarrazar
The Treasure of Guarrazar, Guadamur, Province of Toledo, Castile-La Mancha, Spain, is an archeological find composed of twenty-six votive crowns and gold crosses that had originally been offered to the Roman Catholic Church by the Kings of ...
, probably deposited to avoid looting in the Muslim Conquest of Spain
The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania (in the Iberian Peninsula) from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of t ...
, is now a unique survival of Christian votive crown
A votive crown is a votive offering in the form of a crown, normally in precious metals and often adorned with jewels. Especially in the Early Middle Ages, they are of a special form, designed to be suspended by chains at an altar, shrine or imag ...
s in gold; though Spanish in style, the form was probably then used by elites across Europe. Other Visigothic art
The Visigoths entered Hispania (modern Spain and Portugal) in 415 and they rose to be the dominant people there until the Umayyad conquest of Hispania of 711 brought their kingdom to an end.
This period in Iberian art is dominated by their st ...
in the form of metalwork, mostly jewellery and buckles, and stone relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the ...
s, survives to give an idea of the culture of this originally barbarian Germanic people, who kept themselves very largely separate from their Iberian subjects, and whose rule crumbled when the Muslims arrived in 711.
The jewelled ''crux gemmata
A ''crux gemmata'' (Latin for jewelled cross) is a form of cross typical of Early Christian and Early Medieval art, where the cross, or at least its front side, is principally decorated with jewels. In an actual cross, rather than a painted imag ...
'' Victory Cross
The Victory Cross ( Asturian and Spanish: ''Cruz de la Victoria'') is an early 10th century Asturian crux gemmata or jewelled cross, given by King Alfonso III of Asturias, who reigned from 866 to 910, to the Cathedral of San Salvador of Ovied ...
, La Cava Bible and the Agate Casket of Oviedo
The Agate Casket of Oviedo ( es, Caja de las Ágatas, sometimes in English Agate Box, "Box of Agates") is an elaborately decorated box, casket or small chest given by King Fruela II of Asturias and his wife Nunila to the Cathedral of San Salvador, ...
are survivals from the 9-10th century of the rich Pre-Romanesque
Pre-Romanesque art and architecture is the period in European art from either the emergence of the Merovingian kingdom in about 500 AD or from the Carolingian Renaissance in the late 8th century, to the beginning of the 11th century Romanesqu ...
culture of the Asturias region in north-western Spain, which remained under Christian rule; the Santa María del Naranco
The church of St Mary at Mount Naranco ( es, Iglesia de Santa María del Naranco; ast, Ilesia de Santa María'l Narancu) is a pre-Romanesque Asturian building on the slope of Mount Naranco situated from Oviedo, northern Spain.
Ramiro I of Ast ...
banqueting house overlooking Oviedo
Oviedo (; ast, Uviéu ) is the capital city of the Principality of Asturias in northern Spain and the administrative and commercial centre of the region. It is also the name of the municipality that contains the city. Oviedo is located ap ...
, completed in 848 and later surviving as a church, is a unique survival in Europe. The Codex Vigilanus
The ''Codex Vigilanus'' or ''Codex Albeldensis'' (Spanish: ''Códice Vigilano'' or ''Albeldense'') is an illuminated compilation of various historical documents accounting for a period extending from antiquity to the 10th century in Hispania. ...
, completed in 976 in the region of Rioja, shows a complex mixture of several styles.
Muslim and Mozarab Spain
The extraordinary palace-city of Medina Azahara near Córdoba was built in the 10th century for theUmmayad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
Caliphs of Córdoba
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
, intended as the capital of Islamic Andaluz
The Andalusian dialects of Spanish ( es, andaluz, , ) are spoken in Andalusia, Ceuta, Melilla, and Gibraltar. They include perhaps the most distinct of the southern variants of peninsular Spanish, differing in many respects from northern varietie ...
, and is still being excavated. A considerable amount of the highly sophisticated decoration of the main buildings has survived, showing the enormous wealth of this very centralized state. The palace at Aljafería
The Aljafería Palace ( es, Palacio de la Aljafería; ar, قصر الجعفرية, tr. ''Qaṣr al-Jaʿfariyah'') is a fortified medieval palace built during the second half of the 11th century in the Taifa of Zaragoza in Al-Andalus, present d ...
is later, from after Islamic Spain split into a number of kingdoms. Famous examples of Islamic architecture
Islamic architecture comprises the architectural styles of buildings associated with Islam. It encompasses both secular and religious styles from the early history of Islam to the present day. The Islamic world encompasses a wide geographic ar ...
and its decoration are the Cathedral–Mosque of Córdoba, whose Islamic elements were added in stages between 784 and 987, and the Alhambra
The Alhambra (, ; ar, الْحَمْرَاء, Al-Ḥamrāʾ, , ) is a palace and fortress complex located in Granada, Andalusia, Spain. It is one of the most famous monuments of Islamic architecture and one of the best-preserved palaces of the ...
and Generalife
The Generalife (; ar, جَنَّة الْعَرِيف, translit=Jannat al-‘Arīf) was a summer palace and country estate of the Nasrid rulers of the Emirate of Granada in Al-Andalus. It is located directly east of and uphill from the Alhambra ...
palaces in Granada
Granada (,, DIN 31635, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the fo ...
from the final periods of Muslim Spain.
The Pisa Griffin
The Pisa Griffin is a large bronze sculpture of a griffin, a mythical beast, that has remained in Pisa, Italy since the Middle Ages despite its Islamic origin, specifically 11th century Al-Andalus (Islamic Spain). The Pisa Griffin is the largest ...
is the largest known Islamic sculpture of an animal, and the most spectacular of a group of such figures from Al-Andalus, many made to hold up the basins of fountains (as at the Alhambra), or in smaller cases as perfume-burners and the like.
The Christian population of Muslim Spain (the Mozarabs) developed a style of Mozarabic art
Mozarabic art refers to art of Mozarabs (from ''musta'rab'' meaning “Arabized”), Iberian Christians living in Al-Andalus, the Muslim conquered territories in the period that comprises from the Arab invasion of the Iberian Peninsula (711) to ...
whose best known survivals are a series of illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is often supplemented with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers, liturgical services and psalms, the ...
s, several of the commentaries on the Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament (and consequently the final book of the Christian Bible). Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: , meaning "unveiling" or "revelation". The Book of R ...
by the Asturian Saint Beatus of Liébana (c. 730 – c. 800), which gave subject matter that allowed the brightly coloured primitivist style full scope to demonstrate its qualities in manuscripts of the 10th century like the Morgan Beatus
The Morgan Beatus (New York, Morgan Library & Museum, MS 644) is an illuminated manuscript with miniatures by the artist Magius of the Commentary on the Book of the Apocalypse by the eighth-century Spanish monk Beatus, which described the en ...
, probably the earliest, the Gerona Beatus (illuminated by a female artist Ende), Escorial Beatus The Escorial Beatus (Escorial, Biblioteca Monasterio, Cod. & II. 5) is a 10th-century illuminated manuscript of the Commentary on the Apocalypse by Beatus of Liébana. The illuminations of the manuscript show similarities in style to those produce ...
and the Saint-Sever Beatus
The Saint-Sever Beatus, also known as the Apocalypse of Saint-Sever (Paris, Bibliothèque Nationale, MS lat. 8878), is a Romanesque Illuminated manuscript from the 11th century. It was made at Saint-Sever Abbey, then in the Duchy of Gascony, un ...
, which was actually produced some distance from Muslim rule in France. Mozarabic elements, including a background of brightly coloured strips, can be seen in some later Romanesque frescos.
Hispano-Moresque ware
Hispano-Moresque ware is a style of initially Islamic pottery created in Al-Andalus, which continued to be produced under Christian rule in styles blending Islamic and European elements. It was the most elaborate and luxurious pottery being pr ...
pottery began in the south, presumably mainly for local markets, but Muslim potters were later encouraged to migrate to the Valencia
Valencia ( va, València) is the capital of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, Valencia and the Municipalities of Spain, third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is ...
region, where the Christian lords marketed their luxury lustreware
Lustreware or lusterware (respectively the spellings for British English and American English) is a type of pottery or porcelain with a Metal, metallic glaze that gives the effect of iridescence. It is produced by metallic Oxide, oxides in an Cer ...
s to elites all over Christian Europe in the 14th and 15th centuries, including the Popes and the English court. Spanish Islamic ivory carving
Ivory carving is the carving of ivory, that is to say animal tooth or tusk, generally by using sharp cutting tools, either mechanically or manually. Objects carved in ivory are often called "ivories".
Humans have ornamentally carved ivory since ...
and textiles were also very fine; the continuing industries producing tiles and carpets in the peninsula owe their origins largely to the Islamic kingdoms.
After the expulsion of the Islamic rulers during the Reconquista
The ' (Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Nasrid ...
, considerable Muslim populations, and Christian craftsmen trained in Muslim styles, remained in Spain, and Mudéjar
Mudéjar ( , also , , ca, mudèjar , ; from ar, مدجن, mudajjan, subjugated; tamed; domesticated) refers to the group of Muslims who remained in Iberia in the late medieval period despite the Christian reconquest. It is also a term for ...
is the term for work in art and architecture produced by such people. The Mudéjar Architecture of Aragon
Mudéjar architecture of Aragon is an aesthetic trend in Mudéjar style in Aragon, (Spain) and has been recognized in some representative buildings as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.
The chronology of the Aragonese Mudéjar occupies 12th to the ...
is recognised as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, and the 14th century ''Patio de las Doncellas'' built for Peter of Castile in the Alcázar of Seville
The Royal Alcázars of Seville ( es, Reales Alcázares de Sevilla), historically known as al-Qasr al-Muriq (, ''The Verdant Palace'') and commonly known as the Alcázar of Seville (), is a royal palace in Seville, Spain, built for the Christian ...
is another outstanding example. The style could harmonize well with Christian European medieval and Renaissance styles, for example in elaborate wood and stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and a ...
ceilings, and Mudéjar work often continued to be produced for some centuries after an area passed to Christian rule.
pyxis of al-Mughira The pyxis made in 968 CE/357AH for Prince al-Mughira (15 cm x 8 cm) is a portable ivory carved container that dates from Medieval Islam's Spanish Umayyad period. It is in the collection of the Louvre in Paris. The container was made in on ...
, Medina Azahara, 968
File:B Pierpont 154v.jpg, Page from the Morgan Beatus
The Morgan Beatus (New York, Morgan Library & Museum, MS 644) is an illuminated manuscript with miniatures by the artist Magius of the Commentary on the Book of the Apocalypse by the eighth-century Spanish monk Beatus, which described the en ...
File:Majolika-Kanne mit Medici-Wappen KGM K1692.jpg, Hispano-Moresque ware
Hispano-Moresque ware is a style of initially Islamic pottery created in Al-Andalus, which continued to be produced under Christian rule in styles blending Islamic and European elements. It was the most elaborate and luxurious pottery being pr ...
jug with the Medici
The House of Medici ( , ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici, in the Republic of Florence during the first half of the 15th century. The family originated in the Muge ...
arms, 1450–1460
Painting
Romanesque
 In Spain, the art of the Romanesque period represented a smooth transition from the preceding Pre-Romanesque and Mozarabic styles. Many of the best surviving Romanesque church
In Spain, the art of the Romanesque period represented a smooth transition from the preceding Pre-Romanesque and Mozarabic styles. Many of the best surviving Romanesque church frescos
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaste ...
that were at the time found all over Europe come from Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the north ...
with good examples in the churches of the Vall de Boí
The Vall de Boí () is a narrow, steep-sided valley and a small municipality in the province of Lleida, in the autonomous community of Catalonia, northern Spain. It lies in the northeastern corner of the comarca of Alta Ribagorça, on the edges ...
area; many of these were only uncovered during the 20th Century. Some of the best examples have been moved to museums, especially the Museu Nacional d’Art de Catalunya in Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
, which has the famous Central Apse from Sant Climent in Taüll and the frescos from Sigena
Villanueva de Sigena or Villanueva de Sijena is a town in the county of Los Monegros, in the northern province of Huesca, in Aragon (Spain). Located near the Alcanadre river, the local economy is primarily agricultural-based.
The Royal Monastery ...
. The finest examples of Castillian Romanesque frescoes are considered to be those in the San Isidoro in Leon
Leon, Léon (French) or León (Spanish) may refer to:
Places
Europe
* León, Spain, capital city of the Province of León
* Province of León, Spain
* Kingdom of León, an independent state in the Iberian Peninsula from 910 to 1230 and again fro ...
, the paintings from San Baudelio de Berlanga, now mostly in various museums including the Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
in New York, and those from Santa Cruz de Maderuelo
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring children gifts during the late evening and overnight ...
in Segovia. There are also a number of altar frontal
An ''antependium'' (from Latin ''ante-'' and ''pendēre'' "to hang before"; pl: ''antependia''), also known as a ''parament'' or ''hanging'', or, when speaking specifically of the hanging for the altar, an altar frontal (Latin: ''pallium altaris ...
s painted on wood and other early panel paintings.
Gothic
The Gothic art of Spain represented a gradual development from previous Romanesque styles, being led by external models, first from France, and then later from Italy. Another distinctive aspect was the incorporation of Mudejar elements. Eventually the Italian influence, which transmitted Byzantine stylistic techniques andiconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct fro ...
, entirely displaced the initial Franco-Gothic style Catalonia continued to be a prosperous area which has left many fine altarpiece
An altarpiece is an artwork such as a painting, sculpture or relief representing a religious subject made for placing at the back of or behind the altar of a Christian church. Though most commonly used for a single work of art such as a painting o ...
s; however the region went into decline after the emphasis of trade moved to the Atlantic after the American colonies opened up, which partly accounts for so many medieval survivals there, as there was not the money for Renaissance and Baroque renovations to churches.
Early Renaissance
Due to important economic and political links between Spain and Flanders from the mid-15th century onwards, the early Renaissance in Spain was heavily influenced by Netherlandish painting, leading to the identification of a Hispano-Flemish school of painters. Leading exponents included Fernando Gallego,Bartolomé Bermejo
Bartolomé Bermejo ( 1440 – c.1501) was a Spanish painter who adopted Flemish painting techniques and conventions. Born in Cordoba, he is known for his work in the Crown of Aragon, including the Principality of Catalonia and the Kingdom of ...
, Pedro Berruguete and Juan de Flandes.
Renaissance and Mannerism
 Overall the Renaissance and subsequent Mannerist styles are hard to categorise in Spain, due to the mix of Flemish and Italian influences, and regional variations.
The main centre for Italian Renaissance influence entering Spain was
Overall the Renaissance and subsequent Mannerist styles are hard to categorise in Spain, due to the mix of Flemish and Italian influences, and regional variations.
The main centre for Italian Renaissance influence entering Spain was Valencia
Valencia ( va, València) is the capital of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, Valencia and the Municipalities of Spain, third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is ...
due to its proximity and close links with Italy. This influence was felt via then import of artworks, including four paintings by Piombo
Sebastiano del Piombo (; c. 1485 – 21 June 1547) was an Italian painter of the High Renaissance and early Mannerist periods famous as the only major artist of the period to combine the colouring of the Venetian school in which he was trained w ...
and many prints by Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. List of works by Raphael, His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of ...
, the arrival of the Italian Renaissance artist Paolo de San Leocadio, and also by Spanish artists who spent time working and training there. Such artists included Fernando Yáñez de la Almedina
Fernando (or Hernando) Yáñez de la Almedina, born in Almedina, Spain in ''c''. 1475 and died in Valencia, Kingdom of Spain in 1536, was a Spanish painter. He was one of the most important early Renaissance painters in Spain. Of supposed ...
(1475–1540) and Fernando Llanos, who displayed Leonadesque features in their works, such as delicate, melancholic expressions, and sfumato
Sfumato (, ) is a painting technique for softening the transition between colours, mimicking an area beyond what the human eye is focusing on, or the out-of-focus plane. It is one of the canonical painting modes of the Renaissance. Leonardo da V ...
modelling of features.
Elsewhere in Spain, the influence of the Italian Renaissance was less pure, with a relatively superficial use of techniques that were combined with preceding Flemish practices and incorporated Mannerist features, due to the relatively late examples from Italy, once Italian art was already strongly Mannerist. Apart from technical aspects, the themes and spirit of the Renaissance were modified to the Spanish culture and religious environment. Consequently, very few classical subjects or female nudes were depicted, and the works frequently exhibited a sense of pious devotion and religious intensity – attributes that would remain dominant in much art of Counter Reformation Spain throughout the 17th century, and beyond.
artists included Vicente Juan Masip
Vicente Juan Masip (also known as Joan de Joanes) (15071579) was a Spanish painter of the Renaissance period. He is commonly considered the foremost member of the Valencian school of painters.
Masip was born in La Font de la Figuera. His fathe ...
(1475–1550) and his son Juan de Juanes
Vicente Juan Masip (also known as Joan de Joanes) (15071579) was a Spanish painter of the Renaissance period. He is commonly considered the foremost member of the Valencian school of painters.
Masip was born in La Font de la Figuera. His fathe ...
(1510–1579), the painter and architect Pedro Machuca
Pedro Machuca (c. 1490 in Toledo, Spain – 1550 in Granada) is mainly remembered as the Spanish architect responsible for the design of the Palace of Charles V (begun 1528) adjacent to the Alcazar in Granada. The significance of this work is tha ...
(1490–1550), and Juan Correa de Vivar
Juan Correa de Vivar (c. 1510 – 16 April 1566) was a Spanish painter.
Life
Correa was born in Mascaraque; his date of birth has been determined to be around 1510. Records show he grew up wealthy. When Juan was 17 or 18 years old he joined t ...
(1510–1566).
However, the most popular Spanish painter of the early 17th Century was Luis de Morales
Luis de Morales (1509 – 9 May 1586) was a Spanish painter active during the Spanish Renaissance in the 16th century. Known as "El Divino", most of his work was of religious subjects, including many representations of the Madonna and Child and ...
(1510?–1586), called by his contemporaries "The Divine", because of the religious intensity of his paintings. From the Renaissance he also frequently used sfumato modeling, and simple compositions, but combined them with Flemish style precision of details. His subjects included many devotional images, including the ''Virgin and Child''.
Golden Age
 The
The Spanish Golden Age
The Spanish Golden Age ( es, Siglo de Oro, links=no , "Golden Century") is a period of flourishing in arts and literature in Spain, coinciding with the political rise of the Spanish Empire under the Catholic Monarchs of Spain and the Spanish H ...
, a period of Spanish political ascendancy and subsequent decline, saw a great development of art in Spain. The period is generally considered to have begun at some point after 1492 and ended by or with the Treaty of the Pyrenees
The Treaty of the Pyrenees (french: Traité des Pyrénées; es, Tratado de los Pirineos; ca, Tractat dels Pirineus) was signed on 7 November 1659 on Pheasant Island, and ended the Franco-Spanish War that had begun in 1635.
Negotiations were ...
in 1659, though in art the start is delayed until the reign of Philip III (1598–1621), or just before, and the end also delayed until the 1660s or later. The style thus forms a part of the wider Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
period in art, although as well as considerable influence from great Baroque masters such as Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of hi ...
and later Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Duchy of Brabant in the Southern Netherlands (modern-day Belgium). He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque traditio ...
, the distinctive nature of the art of the period also included influences that modified typical Baroque characteristics. These included influence from contemporary Dutch Golden Age painting and the native Spanish tradition which give much of the art of the period an interest in naturalism, and an avoidance of the grandiosity of much Baroque art. Important early contributors included Juan Bautista Maíno
Friar Juan Bautista Maíno, or Mayno (October 1581, Pastrana – 1 April 1649, Madrid) was a Spanish Baroque painter.
Biography
His father was a merchant who sold Milanese fabrics and his mother was a Portuguese noblewoman. Both were at th ...
(1569–1649), who brought a new naturalistic style into Spain, Francisco Ribalta
Francesc Ribalta (2 June 1565 – 12 January 1628), also known as ''Francisco Ribaltá'' or ''de Ribalta'', was a Spanish painter of the Baroque period, mostly of religious subjects.
Biography
He was born in Solsona, Lleida. Although his fi ...
(1565–1628), and the influential still life
A still life (plural: still lifes) is a work of art depicting mostly wikt:inanimate, inanimate subject matter, typically commonplace objects which are either natural (food, flowers, dead animals, plants, rocks, shells, etc.) or artificiality, m ...
painter, Sánchez Cotán (1560–1627).

El Greco
Domḗnikos Theotokópoulos ( el, Δομήνικος Θεοτοκόπουλος ; 1 October 1541 7 April 1614), most widely known as El Greco ("The Greek"), was a Greek painter, sculptor and architect of the Spanish Renaissance. "El G ...
(1541–1614) was one of the most individualistic of the painters of the period, developing a strongly Mannerist style based on his origins in the post Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
Cretan school, in contrast to the naturalist approaches then predominant in Seville, Madrid and elsewhere in Spain. Many of his works reflect the silvery-greys and strong colours of Venetian painters such as Titian
Tiziano Vecelli or Vecellio (; 27 August 1576), known in English as Titian ( ), was an Italians, Italian (Republic of Venice, Venetian) painter of the Renaissance, considered the most important member of the 16th-century Venetian school (art), ...
, but combined with strange elongations of figures, unusual lighting, disposing of perspective space, and filling the surface with very visible and expressive brushwork.
Although mostly active in Italy, particularly in Naples, José de Ribera
Jusepe de Ribera (1591 – 1652) was a painter and printmaker, who along with Francisco de Zurbarán, Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, and the singular Diego Velázquez, are regarded as the major artists of Spanish Baroque painting. Referring to ...
(1591–1652) considered himself Spanish, and his style is sometimes used as an example of the extremes of Counter-Reformation Spanish art. His work was very influential (largely through the circulation of his drawing and prints throughout Europe) and developed significantly through his career.
Being the gateway to the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
, Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula ...
became the cultural centre of Spain in the 16th Century, and attracted artists from across Europe, drawn by lure of commissions for the growing empire, and for the numerous religious houses of the wealthy city. Starting from a strongly Flemish tradition of detailed and smooth brushwork, as revealed in the works of Francisco Pacheco
Francisco Pacheco del Río (bap. 3 November 1564 – 27 November 1644) was a Spanish painter, best known as the teacher and father-in-law of Diego Velázquez and Alonzo Cano, and for his textbook on painting, entitled ''Art of Painting'', ...
(1564–1642), over time a more naturalistic approach developed, with the influence of Juan de Roelas
Juan de Roelas, de las Roelas or Ruela (c. 1570, in Flanders – 1625, in Olivares) was a Flemish painter whose entire documented career took place in Spain. He played a major role in the transition from Mannerist to Baroque painting in S ...
(c. 1560–1624) and Francisco Herrera the Elder
Francisco Herrera (1576–1656) was a distinguished Spanish painter, born in Seville. He was the founder of the Seville school.
Biography
Francisco Herrera was born in Seville in 1576. Francisco Pacheco was his teacher, but Herrera soon broke ...
(1590–1654). This more naturalistic approach, influenced by Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of hi ...
, became predominant in Seville, and formed the training background of three Golden Age masters: Cano, Zurbarán and Velázquez.
Francisco de Zurbarán (1598–1664) is known for the forceful, realistic use of chiaroscuro
Chiaroscuro ( , ; ), in art, is the use of strong contrasts between light and dark, usually bold contrasts affecting a whole composition. It is also a technical term used by artists and art historians for the use of contrasts of light to achi ...
in his religious paintings and still life
A still life (plural: still lifes) is a work of art depicting mostly wikt:inanimate, inanimate subject matter, typically commonplace objects which are either natural (food, flowers, dead animals, plants, rocks, shells, etc.) or artificiality, m ...
s. Although seen as limited in his development, and struggling to handle complex scenes. Zurbarán's great ability to evoke religious feelings made him very successful in receiving commissions in conservative Counter-Reformation Seville.
Sharing the same painting master – Francisco Pacheco – as Velázquez, Alonso Cano (16601–1667) was also active in sculpture and architecture. His style moved from the naturalism of his early period, to a more delicate, idealistic approach, revealing Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
and van Dyck influences.
Velázquez
Diego Velázquez
Diego Rodríguez de Silva y Velázquez (baptized June 6, 1599August 6, 1660) was a Spanish painter, the leading artist in the court of King Philip IV of Spain and Portugal, and of the Spanish Golden Age. He was an individualistic artist of th ...
(1599–1660) was the leading artist in the court of King Philip IV Philip IV may refer to:
* Philip IV of Macedon (died 297 BC)
* Philip IV of France (1268–1314), Avignon Papacy
* Philip IV of Burgundy or Philip I of Castile (1478–1506)
* Philip IV, Count of Nassau-Weilburg (1542–1602)
* Philip IV of Spain ...
. In addition to numerous renditions of scenes of historical and cultural significance, he created scores of portraits of the Spanish royal family, other notable European figures, and commoners. In many portraits, Velázquez gave a dignified quality to less fortunate members of society like beggars and dwarfs. In contrast to these portraits, the gods and goddesses of Velázquez tend to be portrayed as common people, without divine characteristics. Besides the forty portraits of Philip by Velázquez, he painted portraits of other members of the royal family, including princes, infantas (princesses), and queens.
Later Baroque
Later Baroque elements were introduced as a foreign influence, through visits to Spain byRubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Duchy of Brabant in the Southern Netherlands (modern-day Belgium). He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque traditio ...
, and the circulation of artists and patrons between Spain and the Spanish possessions of Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
and the Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the Ha ...
. Significant Spanish painters taking up the new style were Juan Carreño de Miranda
Juan Carreño de Miranda (25 March 1614 — 3 October 1685) was a Spanish painter of the Baroque period.
Biography
Born in Avilés in Asturias, son of a painter with the same name, Juan Carreño de Miranda. His family moved to Madrid in 1623, ...
(1614–1685), Francisco Rizi (1614–1685) and Francisco de Herrera the Younger (1627–1685), son of Francisco de Herrera
Francisco Herrera (1576–1656) was a distinguished Spanish painter, born in Seville. He was the founder of the Seville school.
Biography
Francisco Herrera was born in Seville in 1576. Francisco Pacheco was his teacher, but Herrera soon broke ...
the Elder an initiator of the naturalist emphasis of the Seville School
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. ...
. Other notable Baroque painters were Claudio Coello
Claudio Coello (2 March 1642 – 20 April 1693) was a Spanish Baroque painter. Coello is considered the last great Spanish painter of the 17th century.
The son of Faustino Coello, a famous Portuguese sculptor, he was a court painter for Char ...
(1642–1693), Antonio de Pereda
Antonio de Pereda y Salgado ( – January 30, 1678) was a Spanish Baroque-era painter, best known for his still lifes.
Biography
Pereda was born in Valladolid, the eldest of three brothers from an artistic family. His father, mother and two b ...
(1611–1678), Mateo Cerezo (1637–1666) and Juan de Valdés Leal
Juan de Valdés Leal (4 May 1622 – 15 October 1690) was a Spanish painter and etcher of the Baroque era.
Career
Valdés was born in Seville in 1622. He became a painter, sculptor, and architect. By his twenties, he was studying under Antoni ...
(1622–1690).
The pre-eminent painter of the period – and most famous Spanish painter prior to the 19th century appreciation of Velázquez, Zurbarán and El Greco – was Bartolomé Esteban Murillo
Bartolomé Esteban Murillo ( , ; late December 1617, baptized January 1, 1618April 3, 1682) was a Spanish Baroque painter. Although he is best known for his religious works, Murillo also produced a considerable number of paintings of contemporar ...
(1617–1682). Working for most of his career in Seville, his early work reflected the naturalism of Caravaggio, using a subdued, brown palette, simple but not harsh lighting, and religious themes that are portrayed in a natural or domestic setting, as in his ''Holy Family with a Little Bird '' (c. 1650). Later he incorporated elements of the Flemish Baroque
Flemish Baroque painting refers to the art produced in the Southern Netherlands during Spanish control in the 16th and 17th centuries. The period roughly begins when the Dutch Republic was split from the Habsburg Spain regions to the south with ...
from Rubens and Van Dyck. In the ''Soult Immaculate Conception'', a brighter and more radiant colour range is used, the swirling cherubs bringing all the focus upon the Virgin, whose heavenward gaze and diffuse and warmly glowing halo make it an effective devotional image, an important component of his output; the Immaculate Conception of the Virgin theme alone was represented about twenty times by Murillo.
18th century
 The beginning of the
The beginning of the Bourbon dynasty
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spanis ...
in Spain under Philip V Philip V may refer to:
* Philip V of Macedon (221–179 BC)
* Philip V of France (1293–1322)
* Philip II of Spain, also Philip V, Duke of Burgundy (1526–1598)
* Philip V of Spain
Philip V ( es, Felipe; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was ...
led to great changes in art patronage, with the new French-oriented court favoring the styles and artists of Bourbon France. Few Spanish painters were employed by the court – a rare exception being Miguel Jacinto Meléndez (1679–1734) – and it took some time before Spanish painters adapted to the new Rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, ...
and Neoclassical styles. Leading European painters, including Giovanni Battista Tiepolo
Giovanni Battista Tiepolo ( , ; March 5, 1696 – March 27, 1770), also known as Giambattista (or Gianbattista) Tiepolo, was an Italian painter and printmaker from the Republic of Venice who painted in the Rococo style, considered an impo ...
and Anton Raphael Mengs, were active and influential.
Restricted from royal sponsorship, many Spanish painters continued the Baroque style in religious compositions. This was true of Francisco Bayeu y Subias (1734–1795), a skilled fresco painter, and of Mariano Salvador Maella (1739–1819) who both developed in the direction of the severe Neoclassicism of Mengs. Another important avenue for Spanish artists was portraiture, which was an active sphere for Antonio González Velázquez
Antonio González Velázquez (1723–1793) was a Spanish late-Baroque painter.
Biography
Velázquez was born in Madrid into a family of artists; his father Pablo González Velázquez and brothers Alejandro and Luis were all painters. He received ...
(1723–1794), Joaquín Inza (1736–1811) and Agustín Esteve
Agustín Esteve y Marqués (May 12, 1753 – 1830) was a Spanish painter, mainly active in the Royal household in Madrid.
Biography
Agustín Esteve was a portraitist to the Spanish Crown, who was influenced by Francisco Goya, including nu ...
(1753–1820). But it is in the genre of the still life that royal patronage was also successfully found, in the works by artists such as the court painter Bartolomé Montalvo
Bartolomé Montalvo (1769 – 11 August 1846) was a Spanish painter born in Sangarcía near Segovia. He was a pupil of Zacarías Velazquez. He was admitted to the Real Academia de Bellas Artes de San Fernando on 6 April 1814. In 1816 became ''pint ...
(1769–1846) and Luis Egidio Meléndez
Luis Egidio Meléndez (1716–1780) was a Spanish painter. Though he received little acclaim during his lifetime and died in poverty, Meléndez is recognized as the greatest Spanish still-life painter of the 18th century. His mastery of compos ...
(1716–1780).
Continuing in the Spanish still life tradition of Sánchez Cotán and Zurbarán, Meléndez produced a series of cabinet paintings, commissioned by the Prince of Asturias, the future King Charles IV, intended to show the full range of edible foods from Spain. Rather than being merely formal studies in Natural History, he used stark lighting, low viewpoints and severe compositions to dramatise the subjects. He showed great interest and attention to the details of reflections, textures and highlights (such the highlight on the patterned vase in ''Still Life with Oranges, Jars, and Boxes of Sweets'') reflecting the new spirit of the age of Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
.
Goya
Francisco Goya
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes (; ; 30 March 174616 April 1828) was a Spanish romantic painter and printmaker. He is considered the most important Spanish artist of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. His paintings, drawings, and ...
was a portraitist and court painter to the Spanish Crown, a chronicler of history, and, in his unofficial work, a revolutionary and a visionary. Goya painted the Spanish royal family, including Charles IV of Spain
, house = Bourbon-Anjou
, father = Charles III of Spain
, mother =Maria Amalia of Saxony
, birth_date =11 November 1748
, birth_place =Palace of Portici, Portici, Naples
, death_date =
, death_place = ...
and Ferdinand VII
, house = Bourbon-Anjou
, father = Charles IV of Spain
, mother = Maria Luisa of Parma
, birth_date = 14 October 1784
, birth_place = El Escorial, Spain
, death_date =
, death_place = Madrid, Spain
, burial_plac ...
. His themes range from merry festivals for tapestry, draft cartoons, to scenes of war, fighting and corpses. In his early stage, he painted draft cartoons as templates for tapestries and focused on scenes from everyday life with vivid colors. During his lifetime, Goya also made several series of ''grabados'', etchings which depicted the decadence of society and the horrors of war. His most famous painting series are the ''Black Paintings
The ''Black Paintings'' (Spanish: ''Pinturas negras'') is the name given to a group of 14 paintings by Francisco Goya from the later years of his life, likely between 1819 and 1823. They portray intense, haunting themes, reflective of both his ...
'', painted at the end of his life. This series features works that are obscure in both color and meaning, producing uneasiness and shock.
He is considered the most important Spanish artist of late 18th and early 19th centuries and throughout his long career was a commentator and chronicler of his era. Immensely successful in his lifetime, Goya is often referred to as both the last of the Old Masters and the first of the moderns.
19th century
 Various art movements of the 19th Century influenced Spanish artists, largely through them undertaking training in foreign capitals, particularly in Paris and Rome. In this way Neo-classicism,
Various art movements of the 19th Century influenced Spanish artists, largely through them undertaking training in foreign capitals, particularly in Paris and Rome. In this way Neo-classicism, Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
, Realism
Realism, Realistic, or Realists may refer to:
In the arts
*Realism (arts), the general attempt to depict subjects truthfully in different forms of the arts
Arts movements related to realism include:
*Classical Realism
*Literary realism, a move ...
and Impressionism
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open Composition (visual arts), composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating ...
became important strands. However, they were often delayed or transformed by local conditions, including repressive governments, and by the tragedies of the Carlist Wars
The Carlist Wars () were a series of civil wars that took place in Spain during the 19th century. The contenders fought over claims to the throne, although some political differences also existed. Several times during the period from 1833 to 187 ...
. Portraits and historical subjects were popular, and the art of the past - particularly the styles and techniques of Velázquez - were significant.
Early years were still dominated by the academicism of Vincente López (1772–1850) and then the Neoclassicism of the French painter, Jacques-Louis David
Jacques-Louis David (; 30 August 1748 – 29 December 1825) was a French painter in the Neoclassicism, Neoclassical style, considered to be the preeminent painter of the era. In the 1780s, his cerebral brand of history painting marked a change in ...
, as in the works by José de Madrazo (1781–1859), the founder of an influential line of artists and gallery directors. His son, Federico de Madrazo
Federico de Madrazo y Kuntz (9 February 181510 June 1894) was a Spanish painter.
Biography
Born in Rome, he was the son of José de Madrazo y Agudo, the painter and former Director of the Prado Museum. Federico's grandfather on his mother side ...
(1781–1859), was a leading figure in Spanish Romanticism, together with Leonardo Alenza (1807–1845), Valeriano Bécquer
Valeriano Domínguez Bécquer, (15 December 1833 – 23 September 1870) was a Spanish painter and graphic artist, who often worked in the costumbrismo style.Antonio María Esquivel
Antonio María Esquivel y Suárez de Urbina (8 March 1806 – 9 April 1857) was a Spanish painter in the Romantic style who specialized in portraits.''Arte Español'': Journal of the "Sociedad Española de Amigos del Arte''Estudio y catálogo de ...
.
 The later part of the century saw a strong period of Romanticism represented in history paintings, as in the works of
The later part of the century saw a strong period of Romanticism represented in history paintings, as in the works of Antonio Gisbert
Antonio Gisbert Pérez (19 December 1834 – 27 November 1901) was a Spanish artist situated on the cusp between the realist and romantic movements in art. He was known for painting pictures of important events in a country's history in a re ...
(1834–1901), Eduardo Rosales
Eduardo Rosales Gallinas (4 November 1836 – 13 September 1873) was a Spanish painter. He was an adherent of the Italian-based art movement known as " Purismo" and specialized in historical scenes.
Biography
He was born in Madrid. The second ...
(1836–1873) and Francisco Pradilla (1848–1921). In these works the techniques of Realism were frequently used with Romantic subjects. This can clearly be seen in ''Joan the Mad'', a famed early work by Pradilla. The composition, facial expressions, and stormy sky reflect the dramatic emotion of the scene; yet the precise clothing, the texture of the mud, and other details, show great realism in the artist's attitude and style. Mariano Fortuny(1838–1874) also developed a strong Realist style, after earlier being influenced by the French Romantic Eugène Delacroix
Ferdinand Victor Eugène Delacroix ( , ; 26 April 1798 – 13 August 1863) was a French Romantic artist regarded from the outset of his career as the leader of the French Romantic school.Noon, Patrick, et al., ''Crossing the Channel: Britis ...
, and became Spain's famous artist of the century
Joaquín Sorolla (1863–1923) excelled in the dexterous representation of the people and landscape under the sunlight of his native land, thus reflecting the spirit of Impressionism
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open Composition (visual arts), composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating ...
in many paintings, particularly his famous seaside paintings. In ''Children on the beach'' he makes the reflections, shadows and gloss of the water and skin his true subject. The composition is very daring, with the horizon omitted, one of the boys cut off, and strong diagonals leading to the contrasts and increased saturation of the upper-left of the work.
20th century

Modernist art
Modern art includes artistic work produced during the period extending roughly from the 1860s to the 1970s, and denotes the styles and philosophies of the art produced during that era. The term is usually associated with art in which the trad ...
movement. As perhaps the most important example of this, Picasso
Pablo Ruiz Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist and Scenic design, theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th ce ...
, working together with the French artist Braque
Georges Braque ( , ; 13 May 1882 – 31 August 1963) was a major 20th-century List of French artists, French painter, Collage, collagist, Drawing, draughtsman, printmaker and sculpture, sculptor. His most notable contributions were in his all ...
, created the concepts of Cubism
Cubism is an early-20th-century avant-garde art movement that revolutionized European painting and sculpture, and inspired related movements in music, literature and architecture. In Cubist artwork, objects are analyzed, broken up and reassemble ...
; and the sub-movement of Synthetic Cubism
Cubism is an early-20th-century avant-garde art movement that revolutionized European painting and sculpture, and inspired related movements in music, literature and architecture. In Cubist artwork, objects are analyzed, broken up and reassemble ...
has been judged to have found its purest expression in the paintings and collages of Madrid-born Juan Gris. In a similar way, Salvador Dalí
Salvador Domingo Felipe Jacinto Dalí i Domènech, Marquess of Dalí of Púbol (; ; ; 11 May 190423 January 1989) was a Spanish Surrealism, surrealist artist renowned for his technical skill, precise draftsmanship, and the striking and bizarr ...
became a central figure of the Surrealist movement in Paris; and Joan Miró
Joan Miró i Ferrà ( , , ; 20 April 1893 – 25 December 1983) was a Catalan painter, sculptor and ceramicist born in Barcelona. A museum dedicated to his work, the Fundació Joan Miró, was established in his native city of Barcelona i ...
was influential in abstract art.
Picasso
Pablo Ruiz Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist and Scenic design, theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th ce ...
's Blue Period (1901–1904), which consisted of somber, blue-tinted paintings was influenced by a trip through Spain. The Museu Picasso
The Museu Picasso (, "Picasso Museum") is an art museum in Barcelona, in Catalonia, Spain. It houses an extensive collection of artworks by the twentieth-century Spanish artist Pablo Picasso, with a total of 4251 of his works. It is housed in f ...
in Barcelona features many of Picasso's early works, created while he was living in Spain, as well as the extensive collection of Jaime Sabartés, Picasso's close friend from his Barcelona days who, for many years, was Picasso's personal secretary. There are many precise and detailed figure studies done in his youth under his father's tutelage, as well as rarely seen works from his old age that clearly demonstrate Picasso's firm grounding in classical techniques. Picasso presented the most durable homage to Velázquez in 1957 when he recreated '' Las Meninas'' in his characteristically cubist form. While Picasso was worried that if he copied Velázquez's painting, it would be seen only as a copy and not as any sort of unique representation, he proceeded to do so, and the enormous work—the largest he had produced since ''Guernica'' in 1937—earned a position of relevance in the Spanish canon of art. Málaga
Málaga (, ) is a municipality of Spain, capital of the Province of Málaga, in the autonomous community of Andalusia. With a population of 578,460 in 2020, it is the second-most populous city in Andalusia after Seville and the sixth most pop ...
, Picasso's birthplace, houses two museums with significant collections, the Museo Picasso Málaga
The Museo Picasso Málaga is a museum in Málaga, Andalusia, Spain, the city where artist Pablo Ruiz Picasso was born.Birthplace Museum.
 The Plateresque style extended from beginnings of the 16th century until the last third of the century and its stylistic influence pervaded the works of all great Spanish artists of the time.
The Plateresque style extended from beginnings of the 16th century until the last third of the century and its stylistic influence pervaded the works of all great Spanish artists of the time.
 Another period of Spanish Renaissance sculpture, the Baroque, encompassed the last years of the 16th century and extended into the 17th century until reaching its final flowering the 18th, developing a truly Spanish school and style, of sculpture, more realistic, intimate and independently creative than that of the previous one which was tied to European trends, especially those of the Netherlands and Italy. There were two Schools of special flair and talent: the
Another period of Spanish Renaissance sculpture, the Baroque, encompassed the last years of the 16th century and extended into the 17th century until reaching its final flowering the 18th, developing a truly Spanish school and style, of sculpture, more realistic, intimate and independently creative than that of the previous one which was tied to European trends, especially those of the Netherlands and Italy. There were two Schools of special flair and talent: the
Salvador Dalí
Salvador Domingo Felipe Jacinto Dalí i Domènech, Marquess of Dalí of Púbol (; ; ; 11 May 190423 January 1989) was a Spanish Surrealism, surrealist artist renowned for his technical skill, precise draftsmanship, and the striking and bizarr ...
was a central artist within the Surrealist movement in Paris. Although Dalí was criticized for accommodating Franco's regime, André Breton
André Robert Breton (; 19 February 1896 – 28 September 1966) was a French writer and poet, the co-founder, leader, and principal theorist of surrealism. His writings include the first ''Surrealist Manifesto'' (''Manifeste du surréalisme'') o ...
, the Surrealist leader and poet, asked him to represent Spain at the 1959 Homage to Surrealism Exhibition which celebrated the fortieth anniversary of Surrealism. In line with the Surrealist movement's objectives, Dalí stated that his artistic aim was that "the world of imagination and of concrete irrationality may be as objectively evident ... as that of the exterior world", and this goal can be seen in one of his most familiar paintings, '' The Persistence of Memory''. Here he paints with a precise, realistic style, based on studies of Dutch and Spanish masters, but with a subject that dissolves the boundaries between organic and mechanical and is more akin to the nightmarish scenes of the Netherlandish painter Hieronymus Bosch, whose ''Garden of Earthly Delights
"Garden of Earthly Delights" is a song written by Andy Partridge of the English rock band XTC, released as the opening track on their 1989 album '' Oranges & Lemons''. Partridge wrote the song as a children's guide to the world dedicated to his so ...
'' provided the model for the central, sleeping figure of Dalí's work.
Joan Miró
Joan Miró i Ferrà ( , , ; 20 April 1893 – 25 December 1983) was a Catalan painter, sculptor and ceramicist born in Barcelona. A museum dedicated to his work, the Fundació Joan Miró, was established in his native city of Barcelona i ...
was also closely associated with the Surrealists in Paris, who particularly approved of his use of automatism in composition and execution, designed to expose the subconscious mind. Although his later and more popular paintings are refined, whimsical and apparently effortless, his influential period in the 1920s and 1930s produced works that were provocative in their sexual symbolism and imagery, and employing rough, experimental materials, including sandpaper, unsized canvases, and collage. In mature period painting, ''La Leçon de Ski'', his characteristic language of signs, figures and black linear forms against more textured and painterly background is evident.
Ignacio Zuloaga
Ignacio Zuloaga y Zabaleta (July 26, 1870October 31, 1945) was a Spanish painter, born in Eibar (Guipuzcoa), near the monastery of Loyola.
Family
He was the son of metalworker and damascener Plácido Zuloaga and grandson of the organizer and d ...
and José Gutiérrez Solana
José Romano Gutiérrez-Solana y Gutiérrez-Solana (28 February 1886, Madrid – 24 June 1945, Madrid) was a Spanish painter, engraver and author. He usually signed his paintings as "J. Solana". Generally, he is considered to be an Expression ...
were other significant painters of the first half of 20th century.
Post WW2
In the post-War period, the Catalan artistAntoni Tàpies
Antoni Tàpies i Puig, 1st Marquess of Tápies (; 13 December 1923 – 6 February 2012) was a Catalan People, Catalan painter, sculptor and art theorist, who became one of the most famous European artists of his generation.
Life
The son of Jo ...
became famous for his abstract works, many of which use very thick textures and the incorporation of non-standard materials and objects. Tàpies has won several international awards for his works.
Sculpture
 The Plateresque style extended from beginnings of the 16th century until the last third of the century and its stylistic influence pervaded the works of all great Spanish artists of the time.
The Plateresque style extended from beginnings of the 16th century until the last third of the century and its stylistic influence pervaded the works of all great Spanish artists of the time.
Alonso Berruguete
Alonso González de Berruguete (Alonso Berruguete) (c. 1488 – 1561) was a Spanish painter, sculptor and architect. He is considered to be the most important sculptor of the Spanish Renaissance, and is known for his emotive sculptures depict ...
(sculptor, painter and architect) is called the "Prince of Spanish sculpture" because of the grandeur, originality, and expressiveness achieved in his works.
His main works were the upper stalls of the choir of the Cathedral of Toledo
, native_name_lang =
, image = Toledo Cathedral, from Plaza del Ayuntamiento.jpg
, imagesize = 300px
, imagelink =
, imagealt =
, landscape =
, caption ...
, the tomb of Cardinal Tavera in the same Cathedral, and the altarpiece of the Visitation in the church of Santa Úrsula in the same locality.
Other notable sculptors were Bartolomé Ordóñez Bartolomé Ordóñez (Burgos, c. 1480 – Carrara, 6 December 1520) was a Spanish Renaissance sculptor.
Life and work
Little is known about Ordóñez before the last five years of his life. His will indicates that he was an ''hidalgo'' born in Bur ...
, Diego de Siloé, Juan de Juni and Damián Forment.
 Another period of Spanish Renaissance sculpture, the Baroque, encompassed the last years of the 16th century and extended into the 17th century until reaching its final flowering the 18th, developing a truly Spanish school and style, of sculpture, more realistic, intimate and independently creative than that of the previous one which was tied to European trends, especially those of the Netherlands and Italy. There were two Schools of special flair and talent: the
Another period of Spanish Renaissance sculpture, the Baroque, encompassed the last years of the 16th century and extended into the 17th century until reaching its final flowering the 18th, developing a truly Spanish school and style, of sculpture, more realistic, intimate and independently creative than that of the previous one which was tied to European trends, especially those of the Netherlands and Italy. There were two Schools of special flair and talent: the Seville School
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. ...
, to which Juan Martínez Montañés belonged (called the Sevillian Fidias), whose most celebrated works are the Crucifix in the Cathedral of Seville, another in Vergara, and a Saint John; and the Granada School, to which Alonso Cano belonged, to whom an Immaculate Conception and a Virgin of Rosary, are attributed.
Another notable Andalusian Baroque sculptors were Pedro de Mena, Pedro Roldán
Pedro Roldán (1624–1699) was a Baroque sculptor from Seville, Andalusia, Spain. His daughter Luisa Roldán, known as ''La Roldana'', was also a major figure of Spanish Baroque sculpture.
Life
Pedro Roldán was born in Seville in 1624, w ...
and his daughter Luisa Roldán
Luisa Ignacia Roldán (8 September 1652 – 10 January 1706), known also as La Roldana, was a Spanish sculptor of the Baroque Era. She is the earliest woman sculptor documented in Spain. Roldán is recognized in the Hispanic Society Museu ...
, Juan de Mesa and Pedro Duque Cornejo
Pedro Duque y Cornejo (1677–1757) was a Spanish Baroque painter and sculptor of the Sevillian school of sculpture, a disciple of his grandfather Pedro Roldán.
He was born in Seville and worked mostly in his home city (church of the Sagrario, ...
.
The Valladolid school of the 17th century ( Gregorio Fernández, Francisco del Rincón) was succeeded in the 18th century, although with less brilliance, by the Madrid School, and it was soon transformed into a purely academic style by the middle of the century. In turn, the Andalusian school was replaced by that of Murcia, epitomised in the person of Francisco Salzillo, during the first half of the century. This last sculptor is distinguished by the originality, fluidity, and dynamic treatment of his works, even in those representations of great tragedy. More than 1,800 works are attributed to him, the most famous products of his hand being the Holy Week floats (pasos) in Murcia, most notable amongst which are those of the Agony in the Garden and the Kiss of Judas.
In the 20th century the most important Spanish sculptors were Julio González, Pablo Gargallo, Eduardo Chillida
Eduardo Chillida Juantegui, or Eduardo Txillida Juantegi in Basque (10 January 1924 – 19 August 2002), was a Spanish Basque sculptor notable for his monumental abstract works.
Early life and career
Born in San Sebastián (Donostia) to Ped ...
and Pablo Serrano
Pablo Serrano Aguilar, (8 March 1908, Crivillén, Teruel – 26 November 1985, Madrid) was a Spanish abstract sculptor.
Personal life
1920–1925. Pablo Serrano studied as a boarder in the Escuelas Profesionales Salesianas in Sarriá (Barcel ...
.
Spanish collectors and museums of art
The Spanish royal collection was accumulated by Spanish monarchs beginning with Isabel the Catholic, Queen of Castile (1451–1504), who accumulated large and impressive collections of objets d'art, 370 tapestries, and 350 paintings, a number by important artists including Rogier van der Weyden, Hans Memling, Hieronymus Bosch, Juan de Flandes, and Sandro Botticelli. However many of these were dispersed by auction after her death in 1504. Isabel's grandson,Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, the first Habsburg king of Spain, was a patron and collector of art, as was his sister, Mary of Hungary. Both admired works by Titian
Tiziano Vecelli or Vecellio (; 27 August 1576), known in English as Titian ( ), was an Italians, Italian (Republic of Venice, Venetian) painter of the Renaissance, considered the most important member of the 16th-century Venetian school (art), ...
. When the siblings died, the art passed to Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from ...
, Charles's son, an even keener collector. Philip IV (1605–1665) followed in the family tradition as a passionate art collector and patron. During his reign, Velázquez, Zurbarán and others produced many works of art. Philip commissioned works and purchased others, sending his representatives to acquire works for the monarch's collection. One of Philip IV's major contributions to art in Spain was to entail his collection, preventing their sale or other dispersal. Under the Spanish Bourbon monarch, Charles IV, the notion of bringing together major works from other repositories in Spain took shape, probably not for the public to view but for artists to study.Alcolea Blanch, ''The Prado'', p. 15. The Prado Museum
The Prado Museum ( ; ), officially known as Museo Nacional del Prado, is the main Spanish national art museum, located in central Madrid. It is widely considered to house one of the world's finest collections of European art, dating from the ...
in Madrid became the main repository for that art.
The Royal Academy of Fine Arts of San Francisco, founded in 1744, now functions also as a museum in Madrid. The Museum of the Americas in Madrid has a collection of casta
() is a term which means "lineage" in Spanish and Portuguese and has historically been used as a racial and social identifier. In the context of the Spanish America, Spanish Empire in the Americas it also refers to a now-discredited 20th-centu ...
paintings and other art brought back to Spain from the Americas, as well as sculpture and archeological artifacts.
Other artistic disciplines
*Architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
* Cinematography
Cinematography (from ancient Greek κίνημα, ''kìnema'' "movement" and γράφειν, ''gràphein'' "to write") is the art of motion picture (and more recently, electronic video camera) photography.
Cinematographers use a lens to focu ...
* Music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
References
Further reading
* Alcolea Blanch, Santiago. ''The Prado''. Translated from the Spanish by Richard-Lewis Rees and Angela Patricia Hall. New York: Harry N. Abrams, Inc. Publishers 1991. * * Berg Sobré, Judith. ''Behind the Altar Table: The Development of the Painted Retablo in Spain, 1350-1500''. Columbia, Miss. 1989. * Brown, Jonathan, ''Painting in Spain, 1500-1700'' (Pelican History of Art), Yale University Press, 1998, * Dodds, Jerrilynn D. (ed.) ''Al-Andalus: The Art of Islamic Spain''. New York 1992. * Gardner's: ''Art Through The Ages - International Edition'', Brace Harcourt Jovanovich, 9th Edn. 1991 * Gudiol, José, ''The Arts of Spain'', 1964, Thames and Hudson * Jiménez Blanco, María Dolores, ed. ''The Prado Guide'', Madrid: Museo National del Prado, English 2nd Revised Edition, 2009 * * Moffitt, John F. ''The Arts in Spain''. London: Thames & Hudson 1999. * O'Neill, John P. (ed.), ''The Art of Medieval Spain, AD 500-1200''. New York 1993. * Palol, Pedro and Max Hirmer. ''Early Medieval Art in Spain''. New York 1966. * (full text resource that contains information on Ribera as well as a number of other Spanish artists) * Tomlinson, Janis, ''From El Greco to Goya: Painting in Spain 1561–1828'', Abrams Art History, 1997 * Williams, John. ''Early Spanish Manuscript Illumination''. New York 1977. * Young, Eric. '' Bartolomé Bermejo: The Great Hispano-Flemish Master''. London 1975.External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Spanish Art Art by country