|
Xiaolongbao
''Xiaolongbao'' () refers to a type of small Chinese steamed bun (''baozi'') traditionally prepared in a ''xiaolong'', a small bamboo steaming basket, hence the name. '' Xiaolongbao'' are often referred to as a kind of "dumpling", but should not be confused with Chinese ''jiaozi'' or ''wonton''. In some parts of China and overseas, xiaolongbao may specifically refer to a kind of soup dumpling, the tangbao (Chinese 汤包) of Jiangnan cuisine, which are strongly associated with Shanghai and Wuxi. In Shanghainese, these are also known as ' or ''xiaolong''-style mantous, as Wu Chinese-speaking peoples use the traditional definition of "mantou", which refers to both filled and unfilled buns. Shengjianbao are very similar to tangbao but are pan-fried instead of steamed. Origins "Xiaolongbao" originated in Changzhou, Jiangsu province, by Wan Hua Tea House in the years of Daoguang Emperor (1820 to 1850). Xiaolongbao evolved from the guantangbao (soup-filled dumplings/buns) from Kaif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiaolongbao
''Xiaolongbao'' () refers to a type of small Chinese steamed bun (''baozi'') traditionally prepared in a ''xiaolong'', a small bamboo steaming basket, hence the name. '' Xiaolongbao'' are often referred to as a kind of "dumpling", but should not be confused with Chinese ''jiaozi'' or ''wonton''. In some parts of China and overseas, xiaolongbao may specifically refer to a kind of soup dumpling, the tangbao (Chinese 汤包) of Jiangnan cuisine, which are strongly associated with Shanghai and Wuxi. In Shanghainese, these are also known as ' or ''xiaolong''-style mantous, as Wu Chinese-speaking peoples use the traditional definition of "mantou", which refers to both filled and unfilled buns. Shengjianbao are very similar to tangbao but are pan-fried instead of steamed. Origins "Xiaolongbao" originated in Changzhou, Jiangsu province, by Wan Hua Tea House in the years of Daoguang Emperor (1820 to 1850). Xiaolongbao evolved from the guantangbao (soup-filled dumplings/buns) from Kaif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangbao
Tangbao or soup buns are a large, soup-filled type of steamed buns (''baozi'') in Chinese cuisine. They are also sometimes known as ''guantang bao'' or soup-filled buns. Various varieties are found, with some name variations in various parts of the country. All of these buns are made by wrapping a gelatinous filling in dough, which is then steamed to melt the filling into soup. Types Some examples of tangbao include: * ''Tangbao'' from Kaifeng, in Henan province: The traditional ''tang bao'' in Kaifeng is a large bun, similar to other baozi, which is bitten open to release the soup filling, which is then drunk with a spoon. However, the traditional form has all but disappeared, with most eateries choosing to serve a Jiangsu-style ''tangbao'' where the soup is drunk with a straw. * ''Tangbao'' from Yangzhou, Jingjiang and elsewhere in Jiangsu province: This variety is found throughout the Jiangnan region. Often served in its own individual steaming basket, the large steamed bun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baozi
Baozi (), Pao-tsih or bao, is a type of yeast-leavened filled bun in various Chinese cuisines. There are many variations in fillings (meat or vegetarian) and preparations, though the buns are most often steamed. They are a variation of '' mantou'' from Northern China. Two types are found in most parts of China and Indonesia: ''Dàbāo'' (大包, "big bun"), measuring about across, served individually, and usually purchased for take-away. The other type, ''Xiǎobāo'' (小包, "small bun"), measure approximately wide, and are most commonly eaten in restaurants, but may also be purchased for take-away. Each order consists of a steamer containing between three and ten pieces. A small ceramic dish for dipping the baozi is provided for vinegar or soy sauce, both of which are available in bottles at the table, along with various types of chili and garlic pastes, oils or infusions, fresh coriander and leeks, sesame oil, and other flavorings. They are popular throughout China and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowing through it. With a population of 24.89 million as of 2021, Shanghai is the most populous urban area in China with 39,300,000 inhabitants living in the Shanghai metropolitan area, the second most populous city proper in the world (after Chongqing) and the only city in East Asia with a GDP greater than its corresponding capital. Shanghai ranks second among the administrative divisions of Mainland China in human development index (after Beijing). As of 2018, the Greater Shanghai metropolitan area was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product ( nominal) of nearly 9.1 trillion RMB ($1.33 trillion), exceeding that of Mexico with GDP of $1.22 trillion, the 15th largest in the world. Shanghai is one of the world's major centers for f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanxiang
Nanxiang () is a town in the Jiading District of Shanghai. Sights The town is home to Guyi Garden, a large Ming dynasty Suzhou-style park. One of the biggest temples in Shanghai, Yun Xiang Si (), is located in the middle of the town, attracting a large number of tourists from all around the world. Food Nanxiang is home to the original Nanxiang Xiaolongbao (Nanxiang xiaolong mantou) that eventually became known as Shanghai-style xiaolongbao. Nanxiang Bun Shop is well known across China. The dish was also made more widely known after featuring in the film ''Leaving Me, Loving You'', which was set in Shanghai and starred the Hong Kong pop singers Leon Lai and Faye Wong. Transportation It is connected to downtown Shanghai by the Hujia Expressway (coded A12 in the Shanghai expressway system; A12 is now S5), which was the first expressway in China. It is about away from downtown. The Nanxiang station on Line 11 of the Shanghai Metro The Shanghai Metro (; Shanghainese: '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaifeng
Kaifeng () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Henan province, China. It is one of the Eight Ancient Capitals of China, having been the capital eight times in history, and is best known for having been the Chinese capital during the Northern Song dynasty. As of 31 December 2018, around 4,465,000 people lived in Kaifeng's Prefecture, of whom 1,652,000 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of Xiangfu, Longting, Shunhe Hui, Gulou and Yuwantai Districts. Located along the Yellow River's southern bank, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the west, Xinxiang to the northwest, Shangqiu to the east, Zhoukou to the southeast, Xuchang to the southwest, and Heze of Shandong to the northeast. Kaifeng is also a major city in the world by scientific research outputs as tracked by the Nature Index. The city is home to a campus of Henan University, one of the national key universities in the Double First Class University Plan. Names The postal romanization f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
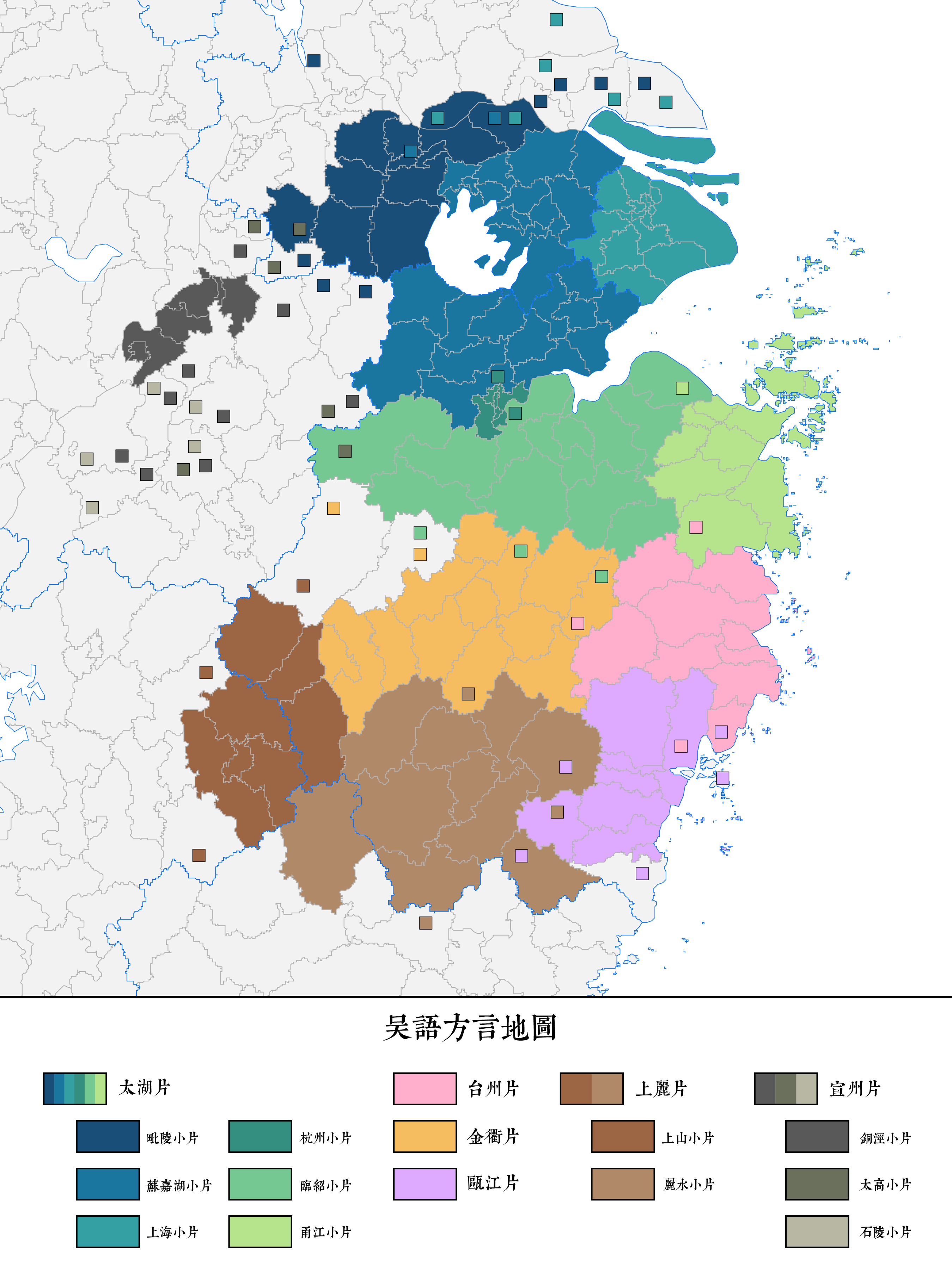
Wu Chinese
The Wu languages (; Wu romanization and IPA: ''wu6 gniu6'' [] ( Shanghainese), ''ng2 gniu6'' [] (Suzhounese), Mandarin pinyin and IPA: ''Wúyǔ'' []) is a major group of Sinitic languages spoken primarily in Shanghai, Zhejiang, Zhejiang Province, and the part of Jiangsu, Jiangsu Province south of the Yangtze River, which makes up the cultural region of Wu. The Suzhou dialect was the prestige dialect of Wu as of the 19th century, and formed the basis of Wu's koiné dialect, Shanghainese, at the turn of the 20th century. Speakers of various Wu languages sometimes inaccurately labelled their mother tongue as "Shanghainese" when introduced to foreigners. The languages of Northern Wu are mutually intelligible with each other, while those of Southern Wu are not. Historical linguists view Wu of great significance because it distinguished itself from other varieties of Chinese by preserving the voiced initials of the ancient Middle Chinese and by preserving the checked ton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shengjianbao
Shengjian mantou (Wu Chinese: ssanji mhoedhou), shengjian bao, or shengjian for short, is a type of small, pan-fried ''baozi'' (steamed buns) which is a specialty of Suzhou and Shanghai. It is typically filled with pork and gelatin that melts into soup/liquid when cooked. Within Shanghai, shengjian mantou typically have thin, crispy skins while those sold elsewhere usually have thicker, bread-like skins. It first originated and became popular in Suzhou at the beginning of the 20th century. Then, its popularity spread to the Yangtze River Delta. It has been one of the most common breakfast items in Shanghai since the early 1920s. As a ubiquitous breakfast item, it has a significant place in Shanghai cuisine. Naming In Modern Chinese, a filled bun is usually called ''baozi'' or ''bao'', while an unfilled (plain) bun is usually called a ''mantou''. However, in the Jiangnan region where Wu Chinese is spoken, the word ''mantou'' refers to both filled and unfilled buns, as in Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daoguang Emperor
The Daoguang Emperor (; 16 September 1782 – 26 February 1850), also known by his temple name Emperor Xuanxong of Qing, born Mianning, was the seventh Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the sixth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1820 to 1850. His reign was marked by "external disaster and internal rebellion." These included the First Opium War and the beginning of the Taiping Rebellion which nearly brought down the dynasty. The historian Jonathan Spence characterizes the Daoguang Emperor as a "well meaning but ineffective man" who promoted officials who "presented a purist view even if they had nothing to say about the domestic and foreign problems surrounding the dynasty." Early years The Daoguang Emperor was born in the Forbidden City, Beijing, in 1782, and was given the name Mianning (). It was later changed to Minning () when he became emperor. The first character of his private name was changed from ''Mian'' to ''Min'' to avoid the relatively common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is also applied to the entirety of China proper. Henan is a birthplace of Han Chinese civilization, with over 3,200 years of recorded history and remained China's cultural, economic and political center until approximately 1,000 years ago. Henan Province is home to many heritage sites, including the ruins of Shang dynasty capital city Yin and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the Eight Great Ancient Capitals of China, Luoyang, Anyang, Kaifeng and Zhengzhou, are in Henan. The practice of tai chi also began here in Chen Jia Gou Village (Chen style), as did the later Yang and Wu styles. Although the name of the province () means "south of the ellowriver.", approximately a quarter of the province lies north of the Yellow River, also known as the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghainese Language
The Shanghainese language, also known as the Shanghai dialect, or Hu language, is a variety of Wu Chinese spoken in the central districts of the City of Shanghai and its surrounding areas. It is classified as part of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Shanghainese, like the rest of the Wu language group, is mutually unintelligible with other varieties of Chinese, such as Mandarin. Shanghainese belongs a separate group of the Taihu Wu subgroup. With nearly 14 million speakers, Shanghainese is also the largest single form of Wu Chinese. Since the late 19th century it has served as the lingua franca of the entire Yangtze River Delta region, but in recent decades its status has declined relative to Mandarin, which most Shanghainese speakers can also speak. Like other Wu varieties, Shanghainese is rich in vowels and consonants, with around twenty unique vowel qualities, twelve of which are phonemic. Similarly, Shanghainese also has voiced obstruent initials, which is rare ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |