geology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with
 A rock is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloids. Most research in geology is associated with the study of rocks, as they provide the primary record of the majority of the geological history of the Earth. There are three major types of rock:
A rock is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloids. Most research in geology is associated with the study of rocks, as they provide the primary record of the majority of the geological history of the Earth. There are three major types of rock: 
 To study all three types of rock, geologists evaluate the minerals of which they are composed and their other physical properties, such as
To study all three types of rock, geologists evaluate the minerals of which they are composed and their other physical properties, such as

 In the 1960s, it was discovered that the Earth's lithosphere, which includes the crust and rigid uppermost portion of the
In the 1960s, it was discovered that the Earth's lithosphere, which includes the crust and rigid uppermost portion of the  The development of plate tectonics has provided a physical basis for many observations of the solid Earth. Long linear regions of geological features are explained as plate boundaries.
For example:
*
The development of plate tectonics has provided a physical basis for many observations of the solid Earth. Long linear regions of geological features are explained as plate boundaries.
For example:
*

 Advances in
Advances in
 * 4.567 Ga (gigaannum: billion years ago): Solar system formation
* 4.54 Ga: Accretion, or formation, of Earth
* c. 4 Ga: End of
* 4.567 Ga (gigaannum: billion years ago): Solar system formation
* 4.54 Ga: Accretion, or formation, of Earth
* c. 4 Ga: End of
 Methods for
Methods for  The ''
The ''
 Geologists also use methods to determine the absolute age of rock samples and geological events. These dates are useful on their own and may also be used in conjunction with relative dating methods or to calibrate relative methods.
At the beginning of the 20th century, advancement in geological science was facilitated by the ability to obtain accurate absolute dates to geological events using
Geologists also use methods to determine the absolute age of rock samples and geological events. These dates are useful on their own and may also be used in conjunction with relative dating methods or to calibrate relative methods.
At the beginning of the 20th century, advancement in geological science was facilitated by the ability to obtain accurate absolute dates to geological events using
 The geology of an area changes through time as rock units are deposited and inserted, and deformational processes change their shapes and locations.
Rock units are first emplaced either by deposition onto the surface or intrusion into the
The geology of an area changes through time as rock units are deposited and inserted, and deformational processes change their shapes and locations.
Rock units are first emplaced either by deposition onto the surface or intrusion into the 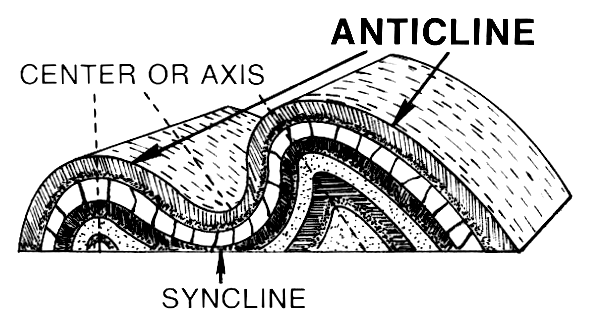 Even higher pressures and temperatures during horizontal shortening can cause both folding and
Even higher pressures and temperatures during horizontal shortening can cause both folding and  The addition of new rock units, both depositionally and intrusively, often occurs during deformation. Faulting and other deformational processes result in the creation of topographic gradients, causing material on the rock unit that is increasing in elevation to be eroded by hillslopes and channels. These sediments are deposited on the rock unit that is going down. Continual motion along the fault maintains the topographic gradient in spite of the movement of sediment and continues to create
The addition of new rock units, both depositionally and intrusively, often occurs during deformation. Faulting and other deformational processes result in the creation of topographic gradients, causing material on the rock unit that is increasing in elevation to be eroded by hillslopes and channels. These sediments are deposited on the rock unit that is going down. Continual motion along the fault maintains the topographic gradient in spite of the movement of sediment and continues to create
 Geologists use a number of fields, laboratory, and numerical modeling methods to decipher Earth history and to understand the processes that occur on and inside the Earth. In typical geological investigations, geologists use primary information related to petrology (the study of rocks), stratigraphy (the study of sedimentary layers), and structural geology (the study of positions of rock units and their deformation). In many cases, geologists also study modern soils,
Geologists use a number of fields, laboratory, and numerical modeling methods to decipher Earth history and to understand the processes that occur on and inside the Earth. In typical geological investigations, geologists use primary information related to petrology (the study of rocks), stratigraphy (the study of sedimentary layers), and structural geology (the study of positions of rock units and their deformation). In many cases, geologists also study modern soils,

 Geological
Geological

 Structural geologists use microscopic analysis of oriented thin sections of geological samples to observe the
Structural geologists use microscopic analysis of oriented thin sections of geological samples to observe the
 In the laboratory, stratigraphers analyze samples of stratigraphic sections that can be returned from the field, such as those from
In the laboratory, stratigraphers analyze samples of stratigraphic sections that can be returned from the field, such as those from
 With the advent of space exploration in the twentieth century, geologists have begun to look at other planetary bodies in the same ways that have been developed to study the
With the advent of space exploration in the twentieth century, geologists have begun to look at other planetary bodies in the same ways that have been developed to study the

 In the field of
In the field of
 Geologists and geophysicists study natural hazards in order to enact safe
Geologists and geophysicists study natural hazards in order to enact safe
 The study of the physical material of the Earth dates back at least to
The study of the physical material of the Earth dates back at least to
File:M.V. Lomonosov by L.Miropolskiy after G.C.Prenner (1787, RAN).jpg, Mikhail Lomonosov, Russian
1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens
One Geology: This interactive geological map of the world is an international initiative of the geological surveys around the globe. This groundbreaking project was launched in 2007 and contributed to the 'International Year of Planet Earth', becoming one of their flagship projects.
''Earth Science News, Maps, Dictionary, Articles, Jobs''
American Geophysical Union
American Geosciences Institute
European Geosciences Union
Geological Society of America
Geological Society of London
Video-interviews with famous geologists
Geology OpenTextbook
Chronostratigraphy benchmarks
{{Authority control
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
and other astronomical objects
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often us ...
, the features or rocks
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's ...
of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres ...
, including hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is call ...
, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science
Earth system science (ESS) is the application of systems science to the Earth. In particular, it considers interactions and 'feedbacks', through material and energy fluxes, between the Earth's sub-systems' cycles, processes and "spheres"— atmo ...
and planetary science.
Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, althoug ...
s are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geologi ...
as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
, the evolutionary history of life
The history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms evolved, from the earliest emergence of life to present day. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago (abbreviated as ''Ga'', for ''gigaannum'') and evide ...
, and the Earth's past climates
Paleoclimatology ( British spelling, palaeoclimatology) is the study of climates for which direct measurements were not taken. As instrumental records only span a tiny part of Earth's history, the reconstruction of ancient climate is important t ...
.
Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of Earth and other terrestrial planets and predominantly solid planetary bodies. Geologists use a wide variety of methods to understand the Earth's structure and evolution, including field work
Field research, field studies, or fieldwork is the collection of raw data outside a laboratory, library, or workplace setting. The approaches and methods used in field research vary across disciplines. For example, biologists who conduct f ...
, rock description, geophysical techniques, chemical analysis
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separati ...
, physical experiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a ...
s, and numerical modelling
Computer simulation is the process of mathematical modelling, performed on a computer, which is designed to predict the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be dete ...
. In practical terms, geology is important for mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
and hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources
Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. 97% of the water on the Earth is salt water and only three percent is fresh water; slight ...
, understanding natural hazards, the remediation of environmental
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
problems, and providing insights into past climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
. Geology is a major academic discipline
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, ...
, and it is central to geological engineering
Geological engineering is a discipline of engineering concerned with the application of geological science and engineering principles to fields, such as civil engineering, mining, environmental engineering, and forestry, among others.M. Diederichs, ...
and plays an important role in geotechnical engineering.
Geological material
The majority of geological data comes from research on solid Earth materials. Meteorites and other extraterrestrial natural materials are also studied by geological methods.Mineral
Minerals are natural occurring elements and compounds with a definite homogeneous chemical composition and ordered atomic composition. Each mineral has distinct physical properties, and there are many tests to determine each of them. The specimens can be tested for: * '' Luster'': Quality of light reflected from the surface of a mineral. Examples are metallic, pearly, waxy, dull. * ''Color'': Minerals are grouped by their color. Mostly diagnostic but impurities can change a mineral's color. * Streak: Performed by scratching the sample on aporcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
plate. The color of the streak can help name the mineral.
* Hardness: The resistance of a mineral to scratching.
* Breakage pattern: A mineral can either show fracture or cleavage, the former being breakage of uneven surfaces, and the latter a breakage along closely spaced parallel planes.
* Specific gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its densest ...
: the weight of a specific volume of a mineral.
* Effervescence: Involves dripping hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
on the mineral to test for fizzing.
* Magnetism: Involves using a magnet to test for magnetism.
* Taste: Minerals can have a distinctive taste, such as halite
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, p ...
(which tastes like table salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantitie ...
).
Rock
 A rock is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloids. Most research in geology is associated with the study of rocks, as they provide the primary record of the majority of the geological history of the Earth. There are three major types of rock:
A rock is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloids. Most research in geology is associated with the study of rocks, as they provide the primary record of the majority of the geological history of the Earth. There are three major types of rock: igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
, sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
, and metamorphic
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causi ...
. The rock cycle
The rock cycle is a basic concept in geology that describes transitions through geologic time among the three main rock types: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. Each rock type is altered when it is forced out of its equilibrium conditi ...
illustrates the relationships among them (see diagram).
When a rock solidifies
Freezing is a phase transition where a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. In accordance with the internationally established definition, freezing means the solidification phase change of a liquid ...
or crystallizes
Crystallization is the process by which solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely dep ...
from melt (magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural sa ...
or lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
), it is an igneous rock. This rock can be weathered
''Weathered'' is the third studio album by American rock band Creed, released on November 20, 2001. It was the last Creed album to be released until '' Full Circle'' came out in October 2009, with Creed disbanding in June 2004. It is the only Cr ...
and eroded
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is disti ...
, then redeposited and lithified
Lithification (from the Ancient Greek word ''lithos'' meaning 'rock' and the Latin-derived suffix ''-ific'') is the process in which sediments compact under pressure, expel connate fluids, and gradually become solid rock. Essentially, lithificatio ...
into a sedimentary rock. It can then be turned into a metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
by heat and pressure that change its mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
content, resulting in a characteristic fabric. All three types may melt again, and when this happens, new magma is formed, from which an igneous rock may once more solidify.
Organic matter, such as coal, bitumen, oil and natural gas, is linked mainly to organic-rich sedimentary rocks.

 To study all three types of rock, geologists evaluate the minerals of which they are composed and their other physical properties, such as
To study all three types of rock, geologists evaluate the minerals of which they are composed and their other physical properties, such as texture
Texture may refer to:
Science and technology
* Surface texture, the texture means smoothness, roughness, or bumpiness of the surface of an object
* Texture (roads), road surface characteristics with waves shorter than road roughness
* Texture ...
and fabric
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not th ...
.
Unlithified material
Geologists also study unlithified materials (referred to as ''superficial deposits
Superficial deposits (or surficial deposits) refer to geological deposits typically of Quaternary age (less than 2.6 million years old). These geologically recent unconsolidated sediments may include stream channel and floodplain deposits, beach ...
'') that lie above the bedrock. This study is often known as Quaternary geology
Quaternary geology is the branch of geology that study developments from 2.6 million years ago onwards. In particular, Quaternary geology study the process and deposits that developed during the Quaternary, a period characterized by glacial-intergl ...
, after the Quaternary period
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
of geologic history, which is the most recent period of geologic time.
Magma
Magma is the original unlithified source of all igneous rocks. The active flow of molten rock is closely studied involcanology
Volcanology (also spelled vulcanology) is the study of volcanoes, lava, magma and related geological, geophysical and geochemical phenomena (volcanism). The term ''volcanology'' is derived from the Latin word '' vulcan''. Vulcan was the an ...
, and igneous petrology
Igneous petrology is the study of igneous rocks—those that are formed from magma. As a branch of geology, igneous petrology is closely related to volcanology, tectonophysics, and petrology in general. The modern study of igneous rocks utilizes a ...
aims to determine the history of igneous rocks from their original molten source to their final crystallization.
Whole-Earth structure
Plate tectonics
upper mantle
The upper mantle of Earth is a very thick layer of rock inside the planet, which begins just beneath the crust (at about under the oceans and about under the continents) and ends at the top of the lower mantle at . Temperatures range from appr ...
, is separated into tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
s that move across the plastically deforming, solid, upper mantle, which is called the asthenosphere. This theory is supported by several types of observations, including seafloor spreading and the global distribution of mountain terrain and seismicity.
There is an intimate coupling between the movement of the plates on the surface and the convection of the mantle (that is, the heat transfer caused by the slow movement of ductile mantle rock). Thus, oceanic plates and the adjoining mantle convection currents
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
always move in the same direction – because the oceanic lithosphere is actually the rigid upper thermal boundary layer
In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is the thin layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a bounding surface formed by the fluid flowing along the surface. The fluid's interaction with the wall induces a no-slip boundary cond ...
of the convecting mantle. This coupling between rigid plates moving on the surface of the Earth and the convecting mantle is called plate tectonics.
 The development of plate tectonics has provided a physical basis for many observations of the solid Earth. Long linear regions of geological features are explained as plate boundaries.
For example:
*
The development of plate tectonics has provided a physical basis for many observations of the solid Earth. Long linear regions of geological features are explained as plate boundaries.
For example:
* Mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a diver ...
s, high regions on the seafloor where hydrothermal vents and volcanoes exist, are seen as divergent boundaries, where two plates move apart.
* Arcs of volcanoes and earthquakes are theorized as convergent boundaries
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a ...
, where one plate subducts, or moves, under another.
Transform boundaries, such as the San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly through California. It forms the tectonic boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, and its motion is right-lateral strike-slip (horizonta ...
system, resulted in widespread powerful earthquakes. Plate tectonics also has provided a mechanism for Alfred Wegener
Alfred Lothar Wegener (; ; 1 November 1880 – November 1930) was a German climatologist, geologist, geophysicist, meteorologist, and polar researcher.
During his lifetime he was primarily known for his achievements in meteorology and ...
's theory of continental drift
Continental drift is the hypothesis that the Earth's continents have moved over geologic time relative to each other, thus appearing to have "drifted" across the ocean bed. The idea of continental drift has been subsumed into the science of pl ...
, in which the continents
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
move across the surface of the Earth over geological time. They also provided a driving force for crustal deformation, and a new setting for the observations of structural geology. The power of the theory of plate tectonics lies in its ability to combine all of these observations into a single theory of how the lithosphere moves over the convecting mantle.
Earth structure
seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other ...
, computer modeling
Computer simulation is the process of mathematical modelling, performed on a computer, which is designed to predict the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be dete ...
, and mineralogy and crystallography at high temperatures and pressures give insights into the internal composition and structure of the Earth.
Seismologists can use the arrival times of seismic wave
A seismic wave is a wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth. It can result from an earthquake, volcanic eruption, magma movement, a large landslide, and a large man-made explosion that produces low-frequency acoustic energy ...
s to image the interior of the Earth. Early advances in this field showed the existence of a liquid outer core
Earth's outer core is a fluid layer about thick, composed of mostly iron and nickel that lies above Earth's solid inner core and below its mantle. The outer core begins approximately beneath Earth's surface at the core-mantle boundary and e ...
(where shear waves
In physics, a transverse wave is a wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave's advance. This is in contrast to a longitudinal wave which travels in the direction of its oscillations. Water waves are an example of t ...
were not able to propagate) and a dense solid inner core
Earth's inner core is the innermost geologic layer of planet Earth. It is primarily a solid ball with a radius of about , which is about 20% of Earth's radius or 70% of the Moon's radius.
There are no samples of Earth's core accessible for d ...
. These advances led to the development of a layered model of the Earth, with a crust and lithosphere on top, the mantle below (separated within itself by seismic discontinuities at 410 and 660 kilometers), and the outer core and inner core below that. More recently, seismologists have been able to create detailed images of wave speeds inside the earth in the same way a doctor images a body in a CT scan. These images have led to a much more detailed view of the interior of the Earth, and have replaced the simplified layered model with a much more dynamic model.
Mineralogists have been able to use the pressure and temperature data from the seismic and modeling studies alongside knowledge of the elemental composition of the Earth to reproduce these conditions in experimental settings and measure changes in crystal structure. These studies explain the chemical changes associated with the major seismic discontinuities in the mantle and show the crystallographic structures expected in the inner core of the Earth.
Geological time
The geological time scale encompasses the history of the Earth. It is bracketed at the earliest by the dates of the firstSolar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
material at 4.567 Ga (or 4.567 billion years ago) and the formation of the Earth at
4.54 Ga
(4.54 billion years), which is the beginning of the informally recognized Hadean eon
The Hadean ( ) is a geologic eon of Earth history preceding the Archean. On Earth, the Hadean began with the planet's formation about 4.54 billion years ago (although the start of the Hadean is defined as the age of the oldest solid material ...
a division of geological time. At the later end of the scale, it is marked by the present day (in the Holocene epoch
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
).
Timescale of the Earth
Important milestones on Earth
Late Heavy Bombardment
The Late Heavy Bombardment (LHB), or lunar cataclysm, is a hypothesized event thought to have occurred approximately 4.1 to 3.8 billion years (Ga) ago, at a time corresponding to the Neohadean and Eoarchean eras on Earth. According to the hypot ...
, the first life
* c. 3.5 Ga: Start of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
* c. 2.3 Ga: Oxygenated atmosphere, first snowball Earth
* 730–635 Ma (megaannum: million years ago): second snowball Earth
* 541 ± 0.3 Ma: Cambrian explosion – vast multiplication of hard-bodied life; first abundant fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s; start of the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
* c. 380 Ma: First vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
land animals
* 250 Ma: Permian-Triassic extinction – 90% of all land animals die; end of Paleozoic and beginning of Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
* 66 Ma: Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction – Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s die; end of Mesozoic and beginning of Cenozoic
* c. 7 Ma: First hominin
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The ...
s appear
* 3.9 Ma: First Australopithecus
''Australopithecus'' (, ; ) is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genus ''Homo'' (which includes modern humans) emerged within ''Australopithecus'', as sister to e.g. ''Austral ...
, direct ancestor to modern Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
, appear
* 200 ka (kiloannum: thousand years ago): First modern Homo sapiens appear in East Africa
Timescale of the Moon
Timescale of Mars
Dating methods
Relative dating
relative dating
Relative dating is the science of determining the relative order of past events (i.e., the age of an object in comparison to another), without necessarily determining their absolute age (i.e., estimated age). In geology, rock or superficial dep ...
were developed when geology first emerged as a natural science. Geologists still use the following principles today as a means to provide information about geological history and the timing of geological events.
The ''principle of uniformitarianism
Uniformitarianism, also known as the Doctrine of Uniformity or the Uniformitarian Principle, is the assumption that the same natural laws and processes that operate in our present-day scientific observations have always operated in the universe in ...
'' states that the geological processes observed in operation that modify the Earth's crust at present have worked in much the same way over geological time. A fundamental principle of geology advanced by the 18th-century Scottish physician and geologist James Hutton is that "the present is the key to the past." In Hutton's words: "the past history of our globe must be explained by what can be seen to be happening now."
The '' principle of intrusive relationships'' concerns crosscutting intrusions. In geology, when an igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
intrusion cuts across a formation of sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
, it can be determined that the igneous intrusion is younger than the sedimentary rock. Different types of intrusions include stocks, laccolith
A laccolith is a body of intrusive rock with a dome-shaped upper surface and a level base, fed by a conduit from below. A laccolith forms when magma (molten rock) rising through the Earth's crust begins to spread out horizontally, prying apar ...
s, batholiths, sills and dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes ...
.
The ''principle of cross-cutting relationships
Cross-cutting relationships is a principle of geology that states that the geologic feature which cuts another is the younger of the two features. It is a relative dating technique in geology. It was first developed by Danish geological pioneer ...
'' pertains to the formation of faults and the age of the sequences through which they cut. Faults are younger than the rocks they cut; accordingly, if a fault is found that penetrates some formations but not those on top of it, then the formations that were cut are older than the fault, and the ones that are not cut must be younger than the fault. Finding the key bed in these situations may help determine whether the fault is a normal fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tecton ...
or a thrust fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks.
Thrust geometry and nomenclature
Reverse faults
A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less.
If ...
.
The '' principle of inclusions and components'' states that, with sedimentary rocks, if inclusions (or ''clasts
Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus,Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p. G-3 chunks, and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks ...
'') are found in a formation, then the inclusions must be older than the formation that contains them. For example, in sedimentary rocks, it is common for gravel from an older formation to be ripped up and included in a newer layer. A similar situation with igneous rocks occurs when xenolith
A xenolith ("foreign rock") is a rock fragment ( country rock) that becomes enveloped in a larger rock during the latter's development and solidification. In geology, the term ''xenolith'' is almost exclusively used to describe inclusions in ig ...
s are found. These foreign bodies are picked up as magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural sa ...
or lava flows, and are incorporated, later to cool in the matrix. As a result, xenoliths are older than the rock that contains them.
principle of original horizontality
The principle of original horizontality states that layers of sediment are originally deposited horizontally under the action of gravity. It is a relative dating technique. The principle is important to the analysis of folded and tilted strata. I ...
'' states that the deposition of sediments occurs as essentially horizontal beds. Observation of modern marine and non-marine sediments in a wide variety of environments supports this generalization (although cross-bedding
In geology, cross-bedding, also known as cross-stratification, is layering within a stratum and at an angle to the main bedding plane. The sedimentary structures which result are roughly horizontal units composed of inclined layers. The origina ...
is inclined, the overall orientation of cross-bedded units is horizontal).
The '' principle of superposition'' states that a sedimentary rock layer in a tectonically
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents ...
undisturbed sequence is younger than the one beneath it and older than the one above it. Logically a younger layer cannot slip beneath a layer previously deposited. This principle allows sedimentary layers to be viewed as a form of the vertical timeline, a partial or complete record of the time elapsed from deposition of the lowest layer to deposition of the highest bed.
The ''principle of faunal succession
The principle of faunal succession, also known as the law of faunal succession, is based on the observation that sedimentary rock strata contain fossilized flora and fauna, and that these fossils succeed each other vertically in a specific, reli ...
'' is based on the appearance of fossils in sedimentary rocks. As organisms exist during the same period throughout the world, their presence or (sometimes) absence provides a relative age of the formations where they appear. Based on principles that William Smith laid out almost a hundred years before the publication of Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
's theory of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
, the principles of succession developed independently of evolutionary thought. The principle becomes quite complex, however, given the uncertainties of fossilization, localization of fossil types due to lateral changes in habitat ( facies change in sedimentary strata), and that not all fossils formed globally at the same time.
Absolute dating
 Geologists also use methods to determine the absolute age of rock samples and geological events. These dates are useful on their own and may also be used in conjunction with relative dating methods or to calibrate relative methods.
At the beginning of the 20th century, advancement in geological science was facilitated by the ability to obtain accurate absolute dates to geological events using
Geologists also use methods to determine the absolute age of rock samples and geological events. These dates are useful on their own and may also be used in conjunction with relative dating methods or to calibrate relative methods.
At the beginning of the 20th century, advancement in geological science was facilitated by the ability to obtain accurate absolute dates to geological events using radioactive isotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
s and other methods. This changed the understanding of geological time. Previously, geologists could only use fossils and stratigraphic correlation to date sections of rock relative to one another. With isotopic dates, it became possible to assign absolute ages to rock units, and these absolute dates could be applied to fossil sequences in which there was datable material, converting the old relative ages into new absolute ages.
For many geological applications, isotope ratio
The term stable isotope has a meaning similar to stable nuclide, but is preferably used when speaking of nuclides of a specific element. Hence, the plural form stable isotopes usually refers to isotopes of the same element. The relative abundanc ...
s of radioactive elements are measured in minerals that give the amount of time that has passed since a rock passed through its particular closure temperature
In radiometric dating, closure temperature or blocking temperature refers to the temperature of a system, such as a mineral, at the time given by its radiometric date. In physical terms, the closure temperature is the temperature at which a syste ...
, the point at which different radiometric isotopes stop diffusing into and out of the crystal lattice. These are used in geochronologic
Geochronology is the science of determining the age of rocks, fossils, and sediments using signatures inherent in the rocks themselves. Absolute geochronology can be accomplished through radioactive isotopes, whereas relative geochronology is pr ...
and thermochronologic studies. Common methods include uranium–lead dating
Uranium–lead dating, abbreviated U–Pb dating, is one of the oldest and most refined of the radiometric dating schemes. It can be used to date rocks that formed and crystallised from about 1 million years to over 4.5 billion years ago with routi ...
, potassium–argon dating, argon–argon dating
Argon–argon (or 40Ar/39Ar) dating is a radiometric dating method invented to supersede potassiumargon (K/Ar) dating in accuracy. The older method required splitting samples into two for separate potassium and argon measurements, while the newer ...
and uranium–thorium dating
Uranium–thorium dating, also called thorium-230 dating, uranium-series disequilibrium dating or uranium-series dating, is a radiometric dating technique established in the 1960s which has been used since the 1970s to determine the age of calciu ...
. These methods are used for a variety of applications. Dating of lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
and volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, created during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer ...
layers found within a stratigraphic sequence can provide absolute age data for sedimentary rock units that do not contain radioactive isotopes and calibrate relative dating techniques. These methods can also be used to determine ages of pluton emplacement.
Thermochemical techniques can be used to determine temperature profiles within the crust, the uplift of mountain ranges, and paleo-topography.
Fractionation of the lanthanide series
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–71, from lanthanum through lutetium. These elements, along with the chemically similar elements scandium and yttr ...
elements is used to compute ages since rocks were removed from the mantle.
Other methods are used for more recent events. Optically stimulated luminescence
In physics, optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) is a method for measuring doses from ionizing radiation. It is used in at least two applications:
* Luminescence dating of ancient materials: mainly geological sediments and sometimes fired pott ...
and cosmogenic radionuclide dating are used to date surfaces and/or erosion rates. Dendrochronology can also be used for the dating of landscapes. Radiocarbon dating is used for geologically young materials containing organic carbon
Total organic carbon (TOC) is the amount of carbon found in an organic compound and is often used as a non-specific indicator of water quality or cleanliness of pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment. TOC may also refer to the amount of organic c ...
.
Geological development of an area
overlying rock
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the l ...
. Deposition can occur when sediments settle onto the surface of the Earth and later lithify
Diagenesis () is the process that describes physical change, physical and chemical changes in sediments first caused by water-rock interactions, microbial activity, and compaction after their deposition (geology), deposition. Increased pressure ...
into sedimentary rock, or when as volcanic material
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Ear ...
such as volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, created during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer ...
or lava flows blanket the surface. Igneous intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
s such as batholiths, laccolith
A laccolith is a body of intrusive rock with a dome-shaped upper surface and a level base, fed by a conduit from below. A laccolith forms when magma (molten rock) rising through the Earth's crust begins to spread out horizontally, prying apar ...
s, dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes ...
, and sills, push upwards into the overlying rock, and crystallize as they intrude.
After the initial sequence of rocks has been deposited, the rock units can be deformed and/or metamorphosed
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causi ...
. Deformation typically occurs as a result of horizontal shortening, horizontal extension, or side-to-side ( strike-slip) motion. These structural regimes broadly relate to convergent boundaries
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a ...
, divergent boundaries, and transform boundaries, respectively, between tectonic plates.
When rock units are placed under horizontal compression
Compression may refer to:
Physical science
*Compression (physics), size reduction due to forces
*Compression member, a structural element such as a column
*Compressibility, susceptibility to compression
* Gas compression
*Compression ratio, of a ...
, they shorten and become thicker. Because rock units, other than muds, do not significantly change in volume, this is accomplished in two primary ways: through faulting
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
and folding
Fold, folding or foldable may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Fold'' (album), the debut release by Australian rock band Epicure
* Fold (poker), in the game of poker, to discard one's hand and forfeit interest in the current pot
*Abov ...
. In the shallow crust, where brittle deformation
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
can occur, thrust faults form, which causes the deeper rock to move on top of the shallower rock. Because deeper rock is often older, as noted by the principle of superposition, this can result in older rocks moving on top of younger ones. Movement along faults can result in folding, either because the faults are not planar or because rock layers are dragged along, forming drag folds as slip occurs along the fault. Deeper in the Earth, rocks behave plastically and fold instead of faulting. These folds can either be those where the material in the center of the fold buckles upwards, creating "antiform
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the ...
s", or where it buckles downwards, creating " synforms". If the tops of the rock units within the folds remain pointing upwards, they are called anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the ...
s and synclines, respectively. If some of the units in the fold are facing downward, the structure is called an overturned anticline or syncline, and if all of the rock units are overturned or the correct up-direction is unknown, they are simply called by the most general terms, antiforms, and synforms.
 Even higher pressures and temperatures during horizontal shortening can cause both folding and
Even higher pressures and temperatures during horizontal shortening can cause both folding and metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of ch ...
of the rocks. This metamorphism causes changes in the mineral composition
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
of the rocks; creates a foliation
In mathematics (differential geometry), a foliation is an equivalence relation on an ''n''-manifold, the equivalence classes being connected, injectively immersed submanifolds, all of the same dimension ''p'', modeled on the decomposition of ...
, or planar surface, that is related to mineral growth under stress. This can remove signs of the original textures of the rocks, such as bedding
Bedding, also known as bedclothes or bed linen, is the materials laid above the mattress of a bed for hygiene, warmth, protection of the mattress, and decorative effect. Bedding is the removable and washable portion of a human sleeping environm ...
in sedimentary rocks, flow features of lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
s, and crystal patterns in crystalline rock
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
s.
Extension causes the rock units as a whole to become longer and thinner. This is primarily accomplished through normal fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tecton ...
ing and through the ductile stretching and thinning. Normal faults drop rock units that are higher below those that are lower. This typically results in younger units ending up below older units. Stretching of units can result in their thinning. In fact, at one location within the Maria Fold and Thrust Belt, the entire sedimentary sequence of the Grand Canyon appears over a length of less than a meter. Rocks at the depth to be ductilely stretched are often also metamorphosed. These stretched rocks can also pinch into lenses, known as '' boudins'', after the French word for "sausage" because of their visual similarity.
Where rock units slide past one another, strike-slip faults develop in shallow regions, and become shear zones at deeper depths where the rocks deform ductilely.
 The addition of new rock units, both depositionally and intrusively, often occurs during deformation. Faulting and other deformational processes result in the creation of topographic gradients, causing material on the rock unit that is increasing in elevation to be eroded by hillslopes and channels. These sediments are deposited on the rock unit that is going down. Continual motion along the fault maintains the topographic gradient in spite of the movement of sediment and continues to create
The addition of new rock units, both depositionally and intrusively, often occurs during deformation. Faulting and other deformational processes result in the creation of topographic gradients, causing material on the rock unit that is increasing in elevation to be eroded by hillslopes and channels. These sediments are deposited on the rock unit that is going down. Continual motion along the fault maintains the topographic gradient in spite of the movement of sediment and continues to create accommodation space
Accommodation is a fundamental concept in sequence stratigraphy, a subdiscipline of geology. It is defined as the space that is available for the Deposition (geology), deposition of sediments. Accommodation space can be pictured as the volume b ...
for the material to deposit. Deformational events are often also associated with volcanism and igneous activity. Volcanic ashes and lavas accumulate on the surface, and igneous intrusions enter from below. Dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes ...
, long, planar igneous intrusions, enter along cracks, and therefore often form in large numbers in areas that are being actively deformed. This can result in the emplacement of dike swarm
A dike swarm (American spelling) or dyke swarm (British spelling) is a large geological structure consisting of a major group of parallel, linear, or radially oriented magmatic dikes intruded within continental crust or central volcanoes ...
s, such as those that are observable across the Canadian shield, or rings of dikes around the lava tube of a volcano.
All of these processes do not necessarily occur in a single environment and do not necessarily occur in a single order. The Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
, for example, consist almost entirely of layered basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
ic lava flows. The sedimentary sequences of the mid-continental United States and the Grand Canyon in the southwestern United States contain almost-undeformed stacks of sedimentary rocks that have remained in place since Cambrian time. Other areas are much more geologically complex. In the southwestern United States, sedimentary, volcanic, and intrusive rocks have been metamorphosed, faulted, foliated, and folded. Even older rocks, such as the Acasta gneiss of the Slave craton
The Slave Craton is an Archaean craton in the north-western Canadian Shield, in Northwest Territories and Nunavut. The Slave Craton includes the 4.03 Ga-old Acasta Gneiss which is one of the oldest dated rocks on Earth.
Covering about , ...
in northwestern Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, the oldest known rock in the world have been metamorphosed to the point where their origin is indiscernible without laboratory analysis. In addition, these processes can occur in stages. In many places, the Grand Canyon in the southwestern United States being a very visible example, the lower rock units were metamorphosed and deformed, and then deformation ended and the upper, undeformed units were deposited. Although any amount of rock emplacement and rock deformation can occur, and they can occur any number of times, these concepts provide a guide to understanding the geological history of an area.
Methods of geology
river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of w ...
s, landscapes, and glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s; investigate past and current life and biogeochemical
Biogeochemistry is the scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natural environment (including the biosphere, the cryosphere, th ...
pathways, and use geophysical methods to investigate the subsurface. Sub-specialities of geology may distinguish endogenous and exogenous geology.
Field methods

 Geological
Geological field work
Field research, field studies, or fieldwork is the collection of raw data outside a laboratory, library, or workplace setting. The approaches and methods used in field research vary across disciplines. For example, biologists who conduct f ...
varies depending on the task at hand. Typical fieldwork could consist of:
* Geological map
A geologic map or geological map is a special-purpose map made to show various geological features. Rock (geology), Rock units or stratum, geologic strata are shown by color or symbols. Bed (geology), Bedding planes and structural features such ...
ping
** Structural mapping: identifying the locations of major rock units and the faults and folds that led to their placement there.
** Stratigraphic mapping: pinpointing the locations of sedimentary facies
In geology, a facies ( , ; same pronunciation and spelling in the plural) is a body of rock with specified characteristics, which can be any observable attribute of rocks (such as their overall appearance, composition, or condition of formatio ...
( lithofacies and biofacies) or the mapping of isopach
An isopach map () illustrates thickness variations within a tabular unit, layer or stratum. Isopachs are contour lines of equal thickness over an area. Isopach maps are utilized in hydrographic survey, stratigraphy, sedimentology, structural geolo ...
s of equal thickness of sedimentary rock
** Surficial mapping: recording the locations of soils and surficial deposits
* Surveying of topographic features
** compilation of topographic map
In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large- scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines (connecting points of equal elevation), but histori ...
s
** Work to understand change across landscapes, including:
*** Patterns of erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
and deposition
*** River-channel change through migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
and avulsion
*** Hillslope processes
* Subsurface mapping through geophysical methods
** These methods include:
*** Shallow seismic
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other ...
surveys
*** Ground-penetrating radar
Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is a Geophysics, geophysical method that uses radar pulses to Geophysical imaging, image the subsurface. It is a non-intrusive method of surveying the sub-surface to investigate underground utilities such as concrete, ...
*** Aeromagnetic survey
An aeromagnetic survey is a common type of geophysical survey carried out using a magnetometer aboard or towed behind an aircraft. The principle is similar to a magnetic survey carried out with a hand-held magnetometer, but allows much larger ar ...
s
*** Electrical resistivity tomography
Electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) or electrical resistivity imaging (ERI) is a geophysical technique for imaging sub-surface structures from electrical resistivity measurements made at the surface, or by electrodes in one or more borehole ...
** They aid in:
*** Hydrocarbon exploration
Hydrocarbon exploration (or oil and gas exploration) is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for deposits of hydrocarbons, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth using petroleum geology.
Exploration methods
Vis ...
*** Finding groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated ...
*** Locating buried archaeological artifacts
* High-resolution stratigraphy
** Measuring and describing stratigraphic sections on the surface
** Well drilling
Well drilling is the process of drilling a hole in the ground for the extraction of a natural resource such as ground water, brine, natural gas, or petroleum, for the injection of a fluid from surface to a subsurface reservoir or for subsurf ...
and logging
* Biogeochemistry
Biogeochemistry is the scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natural environment (including the biosphere, the cryosphere, ...
and geomicrobiology
Geomicrobiology is the scientific field at the intersection of geology and microbiology and is a major subfield of geobiology. It concerns the role of microbes on geological and geochemical processes and effects of minerals and metals to microb ...
** Collecting samples to:
*** determine biochemical pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reac ...
s
*** identify new species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of organisms
*** identify new chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
s
** and to use these discoveries to:
*** understand early life on Earth and how it functioned and metabolized
*** find important compounds for use in pharmaceuticals
* Paleontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
: excavation of fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
material
** For research into past life and evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
** For museum
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make thes ...
s and education
* Collection of samples for geochronology
Geochronology is the science of determining the age of rocks, fossils, and sediments using signatures inherent in the rocks themselves. Absolute geochronology can be accomplished through radioactive isotopes, whereas relative geochronology is ...
and thermochronology
Thermochronology is the study of the thermal evolution of a region of a planet. Thermochronologists use radiometric dating along with the closure temperatures that represent the temperature of the mineral being studied at the time given by the dat ...
* Glaciology
Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice.
Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, c ...
: measurement of characteristics of glaciers and their motion
Petrology
In addition to identifying rocks in the field ( lithology), petrologists identify rock samples in the laboratory. Two of the primary methods for identifying rocks in the laboratory are throughoptical microscopy
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ...
and by using an electron microprobe
An electron microprobe (EMP), also known as an electron probe microanalyzer (EPMA) or electron micro probe analyzer (EMPA), is an analytical tool used to non-destructively determine the chemical composition of small volumes of solid materials. It ...
. In an optical mineralogy
Optical mineralogy is the study of minerals and rocks by measuring their optical properties. Most commonly, rock and mineral samples are prepared as thin sections or grain mounts for study in the laboratory with a petrographic microscope. Opti ...
analysis, petrologists analyze thin section
In optical mineralogy and petrography, a thin section (or petrographic thin section) is a thin slice of a rock or mineral sample, prepared in a laboratory, for use with a polarizing petrographic microscope, electron microscope and electron ...
s of rock samples using a petrographic microscope
A petrographic microscope is a type of optical microscope used in petrology and optical mineralogy to identify rocks and minerals in thin sections. The microscope is used in optical mineralogy and petrography, a branch of petrology whi ...
, where the minerals can be identified through their different properties in plane-polarized and cross-polarized light, including their birefringence, pleochroism
Pleochroism (from Greek πλέων, ''pléōn'', "more" and χρῶμα, ''khrôma'', "color") is an optical phenomenon in which a substance has different colors when observed at different angles, especially with polarized light.
Backgrou ...
, twinning, and interference properties with a conoscopic lens. In the electron microprobe, individual locations are analyzed for their exact chemical compositions and variation in composition within individual crystals. Stable and radioactive isotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
studies provide insight into the geochemical evolution of rock units.
Petrologists can also use fluid inclusion data and perform high temperature and pressure physical experiments to understand the temperatures and pressures at which different mineral phases appear, and how they change through igneous and metamorphic processes. This research can be extrapolated to the field to understand metamorphic processes and the conditions of crystallization of igneous rocks. This work can also help to explain processes that occur within the Earth, such as subduction and magma chamber
A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it up ...
evolution.
Structural geology
 Structural geologists use microscopic analysis of oriented thin sections of geological samples to observe the
Structural geologists use microscopic analysis of oriented thin sections of geological samples to observe the fabric
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not th ...
within the rocks, which gives information about strain within the crystalline structure of the rocks. They also plot and combine measurements of geological structures to better understand the orientations of faults and folds to reconstruct the history of rock deformation in the area. In addition, they perform analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analog ...
and numerical experiments of rock deformation in large and small settings.
The analysis of structures is often accomplished by plotting the orientations of various features onto stereonets. A stereonet is a stereographic projection of a sphere onto a plane, in which planes are projected as lines and lines are projected as points. These can be used to find the locations of fold axes, relationships between faults, and relationships between other geological structures.
Among the most well-known experiments in structural geology are those involving orogenic wedges, which are zones in which mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually highe ...
s are built along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. In the analog versions of these experiments, horizontal layers of sand are pulled along a lower surface into a back stop, which results in realistic-looking patterns of faulting and the growth of a critically tapered (all angles remain the same) orogenic wedge. Numerical models work in the same way as these analog models, though they are often more sophisticated and can include patterns of erosion and uplift in the mountain belt. This helps to show the relationship between erosion and the shape of a mountain range. These studies can also give useful information about pathways for metamorphism through pressure, temperature, space, and time.
Stratigraphy
drill core
A modern core drill is a drill specifically designed to remove a cylinder of material, much like a hole saw. The material left inside the drill bit is referred to as the ''core''.
Core drills used in metal are called annular cutters. Core dr ...
s. Stratigraphers also analyze data from geophysical surveys that show the locations of stratigraphic units in the subsurface. Geophysical data and well log
Well logging, also known as borehole logging is the practice of making a detailed record (a ''well log'') of the geologic formations penetrated by a borehole. The log may be based either on visual inspection of samples brought to the surface (' ...
s can be combined to produce a better view of the subsurface, and stratigraphers often use computer programs to do this in three dimensions. Stratigraphers can then use these data to reconstruct ancient processes occurring on the surface of the Earth, interpret past environments, and locate areas for water, coal, and hydrocarbon extraction.
In the laboratory, biostratigraphers analyze rock samples from outcrop and drill cores for the fossils found in them. These fossils help scientists to date the core and to understand the depositional environment
In geology, depositional environment or sedimentary environment describes the combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment and, therefore, the rock types that will be ...
in which the rock units formed. Geochronologists precisely date rocks within the stratigraphic section to provide better absolute bounds on the timing and rates of deposition.
Magnetic stratigraphers look for signs of magnetic reversals in igneous rock units within the drill cores. Other scientists perform stable-isotope studies on the rocks to gain information about past climate.
Planetary geology
 With the advent of space exploration in the twentieth century, geologists have begun to look at other planetary bodies in the same ways that have been developed to study the
With the advent of space exploration in the twentieth century, geologists have begun to look at other planetary bodies in the same ways that have been developed to study the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
. This new field of study is called planetary geology (sometimes known as astrogeology) and relies on known geological principles to study other bodies of the solar system. This is a major aspect of planetary science, and largely focuses on the terrestrial planets
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, ...
, icy moon Icy commonly refers to conditions involving ice, a frozen state, usually referring to frozen water.
Icy or Icey may also refer to:
People
* Icy Spicy Leoncie, an Icelandic-Indian musician
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* ICY (band), a voca ...
s, asteroids, comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
s, and meteorites. However, some planetary geophysicists study the giant planet
The giant planets constitute a diverse type of planet much larger than Earth. They are usually primarily composed of low-boiling-point materials (volatiles), rather than rock or other solid matter, but massive solid planets can also exist. The ...
s and exoplanets.
Although the Greek-language-origin prefix ''geo
Geo- is a prefix derived from the Greek word ''γη'' or ''γαια'', meaning "earth", usually in the sense of "ground or land”.
GEO or Geo may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''GEO'' (magazine), a popular scientific magazine ...
'' refers to Earth, "geology" is often used in conjunction with the names of other planetary bodies when describing their composition and internal processes: examples are "the geology of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geo ...
" and "Lunar geology
The geology of the Moon (sometimes called selenology, although the latter term can refer more generally to " lunar science") is quite different from that of Earth. The Moon lacks a true atmosphere, which eliminates erosion due to weather. It does ...
". Specialized terms such as ''selenology'' (studies of the Moon), ''areology'' (of Mars), etc., are also in use.
Although planetary geologists are interested in studying all aspects of other planets, a significant focus is to search for evidence of past or present life on other worlds. This has led to many missions whose primary or ancillary purpose is to examine planetary bodies for evidence of life. One of these is the Phoenix lander
''Phoenix'' was an uncrewed space probe that landed on the surface of Mars on May 25, 2008, and operated until November 2, 2008. ''Phoenix'' was operational on Mars for sols ( days). Its instruments were used to assess the local habitabilit ...
, which analyzed Martian
Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun, has appeared as a setting in works of fiction since at least the mid-1600s. It became the most popular celestial object in fiction in the late 1800s as the Moon was evidently lifeless. At the time, the pr ...
polar soil for water, chemical, and mineralogical constituents related to biological processes.
Applied geology

Economic geology
Economic geology is a branch of geology that deals with aspects of economic minerals that humankind uses to fulfill various needs. Economic minerals are those extracted profitably for various practical uses. Economic geologists help locate and manage the Earth'snatural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. ...
s, such as petroleum and coal, as well as mineral resources, which include metals such as iron, copper, and uranium.
Mining geology
Mining geology
Mining geology is an applied science which combines the principles of economic geology and mining engineering to the development of a defined mineral resource. Mining geologists and engineers work to develop an identified ore deposit to economica ...
consists of the extractions of mineral resources from the Earth. Some resources of economic interests include gemstones, metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
s such as gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, and many minerals such as asbestos, perlite
Perlite is an amorphous volcanic glass that has a relatively high water content, typically formed by the hydration of obsidian. It occurs naturally and has the unusual property of greatly expanding when heated sufficiently. It is an industrial ...
, mica, phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
s, zeolites
Zeolites are microporous, crystalline aluminosilicate materials commonly used as commercial adsorbents and catalysts. They mainly consist of silicon, aluminium, oxygen, and have the general formula ・y where is either a metal ion or H+. These p ...
, clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
, pumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular v ...
, quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
, and silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
, as well as elements such as sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
, chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
, and helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
.
Petroleum geology
Petroleum geologist
A petroleum geologist is an earth scientist who works in the field of petroleum geology, which involves all aspects of oil discovery and production. Petroleum geologists are usually linked to the actual discovery of oil and the identification of ...
s study the locations of the subsurface of the Earth that can contain extractable hydrocarbons, especially petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
. Because many of these reservoirs are found in sedimentary basin
Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock. They form when long-term subside ...
s, they study the formation of these basins, as well as their sedimentary and tectonic evolution and the present-day positions of the rock units.
Engineering geology
Engineering geology is the application of geological principles to engineering practice for the purpose of assuring that the geological factors affecting the location, design, construction, operation, and maintenance of engineering works are properly addressed. Engineering geology is distinct fromgeological engineering
Geological engineering is a discipline of engineering concerned with the application of geological science and engineering principles to fields, such as civil engineering, mining, environmental engineering, and forestry, among others.M. Diederichs, ...
, particularly in North America.
 In the field of
In the field of civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewage ...
, geological principles and analyses are used in order to ascertain the mechanical principles of the material on which structures are built. This allows tunnels to be built without collapsing, bridges and skyscrapers to be built with sturdy foundations, and buildings to be built that will not settle in clay and mud.
Hydrology
Geology and geological principles can be applied to various environmental problems such as stream restoration, the restoration ofbrownfields
In urban planning, brownfield land is any previously developed land that is not currently in use. It may be potentially contaminated, but this is not required for the area to be considered brownfield. The term is also used to describe land pre ...
, and the understanding of the interaction between natural habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
and the geological environment. Groundwater hydrology, or hydrogeology
Hydrogeology (''hydro-'' meaning water, and ''-geology'' meaning the study of the Earth) is the area of geology that deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rocks of the Earth's crust (commonly in aqui ...
, is used to locate groundwater, which can often provide a ready supply of uncontaminated water and is especially important in arid regions, and to monitor the spread of contaminants in groundwater wells.
Paleoclimatology
Geologists also obtain data through stratigraphy,boreholes
A borehole is a narrow shaft bored in the ground, either vertically or horizontally. A borehole may be constructed for many different purposes, including the extraction of water ( drilled water well and tube well), other liquids (such as petrol ...
, core sample
A core sample is a cylindrical section of (usually) a naturally-occurring substance. Most core samples are obtained by drilling with special drills into the substance, such as sediment or rock, with a hollow steel tube, called a core drill. The ...
s, and ice cores. Ice cores and sediment cores are used for paleoclimate reconstructions, which tell geologists about past and present temperature, precipitation, and sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
across the globe. These datasets are our primary source of information on global climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
outside of instrumental data.
Natural hazards
building code
A building code (also building control or building regulations) is a set of rules that specify the standards for constructed objects such as buildings and non-building structures. Buildings must conform to the code to obtain planning permiss ...
s and warning systems that are used to prevent loss of property and life. Examples of important natural hazards that are pertinent to geology (as opposed those that are mainly or only pertinent to meteorology) are:
History
 The study of the physical material of the Earth dates back at least to
The study of the physical material of the Earth dates back at least to ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of Classical Antiquity, classical antiquity ( AD 600), th ...
when Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, Θεόφραστος ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routle ...
(372–287 BCE) wrote the work '' Peri Lithon'' (''On Stones''). During the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
period, Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
wrote in detail of the many minerals and metals, then in practical use – even correctly noting the origin of amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In ...
. Additionally, in the 4th century BCE Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
made critical observations of the slow rate of geological change. He observed the composition of the land and formulated a theory where the Earth changes at a slow rate and that these changes cannot be observed during one person's lifetime. Aristotle developed one of the first evidence-based concepts connected to the geological realm regarding the rate at which the Earth physically changes.
Abu al-Rayhan al-Biruni (973–1048 CE) was one of the earliest Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
geologists, whose works included the earliest writings on the geology of India
The geology of India is diverse. Different regions of India contain rocks belonging to different geologic periods, dating as far back as the Eoarchean Era. Some of the rocks are very deformed and altered. Other deposits include recently ...
, hypothesizing that the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
was once a sea. Drawing from Greek and Indian scientific literature that were not destroyed by the Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
, the Persian scholar Ibn Sina (Avicenna, 981–1037) proposed detailed explanations for the formation of mountains, the origin of earthquakes, and other topics central to modern geology, which provided an essential foundation for the later development of the science. In China, the polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
Shen Kuo (1031–1095) formulated a hypothesis for the process of land formation: based on his observation of fossil animal shells in a geological stratum in a mountain hundreds of miles from the ocean, he inferred that the land was formed by the erosion of the mountains and by deposition of silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel ...
.
Nicolas Steno
Niels Steensen ( da, Niels Steensen; Latinized to ''Nicolaus Steno'' or ''Nicolaus Stenonius''; 1 January 1638 – 25 November 1686law of superposition
The law of superposition is an axiom that forms one of the bases of the sciences of geology, archaeology, and other fields pertaining to geological stratigraphy. In its plainest form, it states that in undeformed stratigraphic sequences, the ...
, the principle of original horizontality
The principle of original horizontality states that layers of sediment are originally deposited horizontally under the action of gravity. It is a relative dating technique. The principle is important to the analysis of folded and tilted strata. I ...
, and the principle of lateral continuity
The principle of lateral continuity states that layers of sediment initially extend laterally in all directions; in other words, they are laterally continuous. As a result, rocks that are otherwise similar, but are now separated by a valley or oth ...
: three defining principles of stratigraphy.
The word ''geology'' was first used by Ulisse Aldrovandi
Ulisse Aldrovandi (11 September 1522 – 4 May 1605) was an Italian naturalist, the moving force behind Bologna's botanical garden, one of the first in Europe. Carl Linnaeus and the comte de Buffon reckoned him the father of natural history st ...
in 1603, then by Jean-André Deluc
Jean-André Deluc or de Luc (8 February 1727 – 7 November 1817) was a Swiss geologist, natural philosopher and meteorologist. He also devised measuring instruments.
Biography
Jean-André Deluc was born in Geneva. His family had come to the ...
in 1778 and introduced as a fixed term by Horace-Bénédict de Saussure in 1779. The word is derived from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
γῆ, ''gê'', meaning "earth" and λόγος, ''logos
''Logos'' (, ; grc, λόγος, lógos, lit=word, discourse, or reason) is a term used in Western philosophy, psychology and rhetoric and refers to the appeal to reason that relies on logic or reason, inductive and deductive reasoning. Ari ...
'', meaning "speech". But according to another source, the word "geology" comes from a Norwegian, Mikkel Pedersøn Escholt Mikkel Peders �n Escholt (c. 1600 – 1669) was a Norwegian priest and natural theologian, best known for his book ''Geologia Norvegica'' written in Danish in 1657 where he is considered as among the first to use the word "geology".
Very little is ...
(1600–1699), who was a priest and scholar. Escholt first used the definition in his book titled, ''Geologia Norvegica'' (1657).
William Smith (1769–1839) drew some of the first geological maps and began the process of ordering rock strata (layers) by examining the fossils contained in them.
In 1763, Mikhail Lomonosov published his treatise ''On the Strata of Earth''. His work was the first narrative of modern geology, based on the unity of processes in time and explanation of the Earth's past from the present.
James Hutton (1726-1797) is often viewed as the first modern geologist. In 1785 he presented a paper entitled ''Theory of the Earth'' to the Royal Society of Edinburgh. In his paper, he explained his theory that the Earth must be much older than had previously been supposed to allow enough time for mountains to be eroded and for sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sa ...
s to form new rocks at the bottom of the sea, which in turn were raised up to become dry land. Hutton published a two-volume version of his ideas in 1795.
Followers of Hutton were known as '' Plutonists'' because they believed that some rocks were formed by ''vulcanism'', which is the deposition of lava from volcanoes, as opposed to the '' Neptunists'', led by Abraham Werner
Abraham Gottlob Werner (; 25 September 174930 June 1817) was a German geologist who set out an early theory about the stratification of the Earth's crust and propounded a history of the Earth that came to be known as Neptunism. While most tenet ...
, who believed that all rocks had settled out of a large ocean whose level gradually dropped over time.
The first geological map of the U.S. was produced in 1809 by William Maclure
William Maclure (27 October 176323 March 1840) was an Americanized Scottish geologist, cartographer and philanthropist. He is known as the 'father of American geology'. As a social experimenter on new types of community life, he collaborated ...
. In 1807, Maclure commenced the self-imposed task of making a geological survey of the United States. Almost every state in the Union was traversed and mapped by him, the Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range (; also spelled Alleghany or Allegany), informally the Alleghenies, is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada and posed a significant barrier to land travel in less devel ...
being crossed and recrossed some 50 times. The results of his unaided labours were submitted to the American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS), founded in 1743 in Philadelphia, is a scholarly organization that promotes knowledge in the sciences and humanities through research, professional meetings, publications, library resources, and communit ...
in a memoir entitled ''Observations on the Geology of the United States explanatory of a Geological Map'', and published in the ''Society's Transactions'', together with the nation's first geological map. This antedates William Smith's geological map of England by six years, although it was constructed using a different classification of rocks.
Sir Charles Lyell
Sir Charles Lyell, 1st Baronet, (14 November 1797 – 22 February 1875) was a Scottish geologist who demonstrated the power of known natural causes in explaining the earth's history. He is best known as the author of ''Principles of Geolo ...
(1797-1875) first published his famous book, ''Principles of Geology
''Principles of Geology: Being an Attempt to Explain the Former Changes of the Earth's Surface, by Reference to Causes Now in Operation'' is a book by the Scottish geologist Charles Lyell that was first published in 3 volumes from 1830–1833. Ly ...
'', in 1830. This book, which influenced the thought of Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
, successfully promoted the doctrine of uniformitarianism
Uniformitarianism, also known as the Doctrine of Uniformity or the Uniformitarian Principle, is the assumption that the same natural laws and processes that operate in our present-day scientific observations have always operated in the universe in ...
. This theory states that slow geological processes have occurred throughout the Earth's history
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geologic ...
and are still occurring today. In contrast, catastrophism is the theory that Earth's features formed in single, catastrophic events and remained unchanged thereafter. Though Hutton believed in uniformitarianism, the idea was not widely accepted at the time.
Much of 19th-century geology revolved around the question of the Earth's exact age. Estimates varied from a few hundred thousand to billions of years. By the early 20th century, radiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares ...
allowed the Earth's age to be estimated at two billion years. The awareness of this vast amount of time opened the door to new theories about the processes that shaped the planet.
Some of the most significant advances in 20th-century geology have been the development of the theory of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
in the 1960s and the refinement of estimates of the planet's age. Plate tectonics theory arose from two separate geological observations: seafloor spreading
Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.
History of study
Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener a ...
and continental drift
Continental drift is the hypothesis that the Earth's continents have moved over geologic time relative to each other, thus appearing to have "drifted" across the ocean bed. The idea of continental drift has been subsumed into the science of pl ...
. The theory revolutionized the Earth sciences
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres ...
. Today the Earth is known to be approximately 4.5 billion years old.
polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
, author of the first systematic treatise in scientific geology ( 1763)
File:Hutton James portrait Raeburn.jpg, James Hutton, Scottish geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, althoug ...
and father of modern geology
File:John Tuzo Wilson in 1992.jpg, John Tuzo Wilson
John Tuzo Wilson (October 24, 1908 – April 15, 1993) was a Canadian geophysicist and geologist who achieved worldwide acclaim for his contributions to the theory of plate tectonics.
''Plate tectonics'' is the scientific theory that the rigi ...
, Canadian geophysicist and father of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
File:MSH80 david johnston at camp 05-17-80 med (cropped).jpg, The volcanologist
A volcanologist, or volcano scientist, is a geologist who focuses on understanding the formation and eruptive activity of volcanoes. Volcanologists frequently visit volcanoes, sometimes active ones, to observe and monitor volcanic eruptions, col ...
David A. Johnston
David Alexander Johnston (December 18, 1949 – May 18, 1980) was an American United States Geological Survey (USGS) volcanologist who was killed by the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in the U.S. state of Washington. A principal scientist on ...
13 hours before his death at the1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens
Fields or related disciplines
*Earth system science
Earth system science (ESS) is the application of systems science to the Earth. In particular, it considers interactions and 'feedbacks', through material and energy fluxes, between the Earth's sub-systems' cycles, processes and "spheres"— atmo ...
* Economic geology
** Mining geology
Mining geology is an applied science which combines the principles of economic geology and mining engineering to the development of a defined mineral resource. Mining geologists and engineers work to develop an identified ore deposit to economica ...
** Petroleum geology
* Engineering geology
Engineering geology is the application of geology to engineering study for the purpose of assuring that the geological factors regarding the location, design, construction, operation and maintenance of engineering works are recognized and accou ...
* Environmental geology
* Environmental science
* Geoarchaeology
* Geochemistry
Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the ...
** Biogeochemistry
Biogeochemistry is the scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natural environment (including the biosphere, the cryosphere, ...
** Isotope geochemistry
Isotope geochemistry is an aspect of geology based upon the study of natural variations in the relative abundances of isotopes of various elements. Variations in isotopic abundance are measured by isotope ratio mass spectrometry, and can reveal ...
* Geochronology
Geochronology is the science of determining the age of rocks, fossils, and sediments using signatures inherent in the rocks themselves. Absolute geochronology can be accomplished through radioactive isotopes, whereas relative geochronology is ...
* Geodetics
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure ( geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equiva ...
* Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
* Geological engineering
Geological engineering is a discipline of engineering concerned with the application of geological science and engineering principles to fields, such as civil engineering, mining, environmental engineering, and forestry, among others.M. Diederichs, ...
* Geological modelling
* Geometallurgy Geometallurgy relates to the practice of combining geology or geostatistics with metallurgy, or, more specifically, extractive metallurgy, to create a spatially or geologically based predictive model for mineral processing plants. It is used in t ...
* Geomicrobiology
Geomicrobiology is the scientific field at the intersection of geology and microbiology and is a major subfield of geobiology. It concerns the role of microbes on geological and geochemical processes and effects of minerals and metals to microb ...
* Geomorphology
* Geomythology
Geomythology (also called “legends of the earth," "landscape mythology," “myths of observation,” “natural knowledge") is the study of oral and written traditions created
by pre-scientific cultures to account for, often in poetic or mytholog ...
* Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' so ...
* Glaciology
Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice.
Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, c ...
* Historical geology
Historical geology or palaeogeology is a discipline that uses the principles and methods of geology to reconstruct the geological history of Earth. Historical geology examines the vastness of geologic time, measured in billions of years, and inve ...
* Hydrogeology
Hydrogeology (''hydro-'' meaning water, and ''-geology'' meaning the study of the Earth) is the area of geology that deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rocks of the Earth's crust (commonly in aqui ...
* Meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did no ...
* Mineralogy
* Oceanography
** Marine geology
Marine geology or geological oceanography is the study of the history and structure of the ocean floor. It involves geophysical, geochemical, sedimentological and paleontological investigations of the ocean floor and coastal zone. Marine geolog ...
* Paleoclimatology
Paleoclimatology (American and British English spelling differences, British spelling, palaeoclimatology) is the study of climates for which direct measurements were not taken. As instrumental records only span a tiny part of Earth's history, the ...
* Paleontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
** Micropaleontology
Micropaleontology (American spelling; spelled micropalaeontology in European usage) is the branch of paleontology (palaeontology) that studies microfossils, or fossils that require the use of a microscope to see the organism, its morphology and it ...
** Palynology
Palynology is the "study of dust" (from grc-gre, παλύνω, palynō, "strew, sprinkle" and ''-logy'') or of "particles that are strewn". A classic palynologist analyses particulate samples collected from the air, from water, or from deposit ...
* Petrology
* Petrophysics
Petrophysics (from the Greek πέτρα, ''petra'', "rock" and φύσις, ''physis'', "nature") is the study of physical and chemical rock properties and their interactions with fluids.
A major application of petrophysics is in studying reservo ...
* Physical geography
Physical geography (also known as physiography) is one of the three main branches of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere, ...
* Planetary geology
* Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
* Regional geology
Regional geology is the geological study of large-scale regions. Usually, it encompasses multiple geological disciplines to piece together the history of an area. It is the geologic equivalent of regional geography. The size and the borders of e ...
* Sedimentology
* Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other ...
* Soil science
Soil science is the study of soil as a natural resource on the surface of the Earth including soil formation, classification and mapping; physical, chemical, biological, and fertility properties of soils; and these properties in relation to th ...
** Pedology (soil study)
Pedology (from Greek: πέδον, ''pedon'', "soil"; and λόγος, ''logos'', "study") is a discipline within soil science which focuses on understanding and characterizing soil formation, evolution, and the theoretical frameworks for modeling ...
* Speleology
Speleology is the scientific study of caves and other karst features, as well as their make-up, structure, physical properties, history, life forms, and the processes by which they form ( speleogenesis) and change over time (speleomorphology) ...
* Stratigraphy
** Biostratigraphy
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of B ...
** Chronostratigraphy
Chronostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy that studies the ages of rock strata in relation to time.
The ultimate aim of chronostratigraphy is to arrange the sequence of deposition and the time of deposition of all rocks within a geologic ...
** Lithostratigraphy
Lithostratigraphy is a sub-discipline of stratigraphy, the geological science associated with the study of strata or rock layers. Major focuses include geochronology, comparative geology, and petrology.
In general, strata are primarily igneous ...
* Structural geology
* Systems geology
* Tectonics
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents k ...
* Volcanology
Volcanology (also spelled vulcanology) is the study of volcanoes, lava, magma and related geological, geophysical and geochemical phenomena (volcanism). The term ''volcanology'' is derived from the Latin word '' vulcan''. Vulcan was the an ...
See also
*Glossary of geology
This glossary of geology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to geology, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. For other terms related to the Earth sciences
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural scienc ...
* Geoprofessions
Geoprofessions is a term coined by the Geoprofessional Business Association to connote various technical disciplines that involve engineering, earth and environmental services applied to below-ground (“subsurface”), ground-surface, and ground-s ...
* Geotourism
Geotourism is tourism associated with geological attractions and destinations.Dowling, R. & Newsome, D. (Eds.)(2006) ''Geotourism'' ; Elsevier, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford Geotourism deals with the abiotic natural and built environments.Sadry ...
* Glossary of geology terms
This glossary of geology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to geology, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. For other terms related to the Earth sciences
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural scienc ...
* Index of geology articles
This is a list of all articles related to geology that cannot be readily placed on the following subtopic pages:
* Geologic time scale
* List of compounds
* Lists of earthquakes
* List of elements by name
* Geology of the English counties
* ...
* International Union of Geological Sciences ( IUGS)
* Outline of geology
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geology:
Geology – one of the Earth sciences – is the study of the Earth, with the general exclusion of present-day life, flow within the ocean, and the atmosphere. ...
* Timeline of geology
Timeline of geology
Early works
* c. 1025 – Al-Biruni publishes the ''Kitāb fī Taḥqīq mā li-l-Hind'' (''Researches on India''), in which he discusses the geology of India and hypothesizes that it was once a sea.
* 1027 – Avicenna publ ...
References
External links
One Geology: This interactive geological map of the world is an international initiative of the geological surveys around the globe. This groundbreaking project was launched in 2007 and contributed to the 'International Year of Planet Earth', becoming one of their flagship projects.
''Earth Science News, Maps, Dictionary, Articles, Jobs''
American Geophysical Union
American Geosciences Institute
European Geosciences Union
Geological Society of America
Geological Society of London
Video-interviews with famous geologists
Geology OpenTextbook
Chronostratigraphy benchmarks
{{Authority control