|
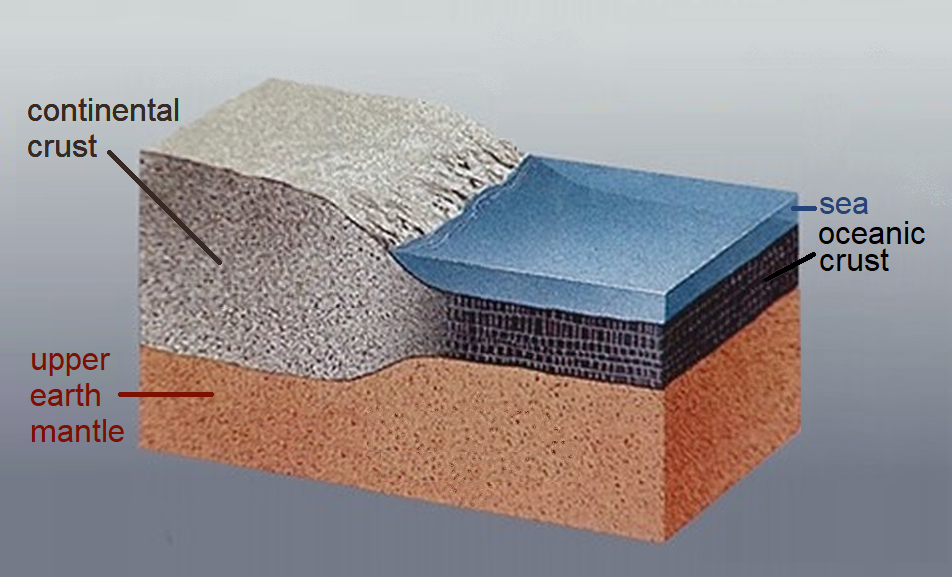
Lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy. Earth's lithosphere Earth's lithosphere, which constitutes the hard and rigid outer vertical layer of the Earth, includes the crust and the lithospheric mantle (or mantle lithosphere), the uppermost part of the mantle that is not convecting. The layer below the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere, which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle that is able to convect. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress. The lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lithosphere–asthenosphere Boundary
The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary (referred to as the LAB by geophysicists) represents a Mechanics, mechanical difference between layers in Structure of the Earth, Earth's inner structure. Earth's inner structure can be described both Chemical substance, chemically (Crust (geology), crust, Mantle (geology), mantle, and Core (geology), core) and mechanically. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary lies between Earth's cooler, rigid lithosphere and the warmer, ductile asthenosphere. The actual depth of the boundary is still a topic of debate and study, although it is known to vary according to the environment. The following overview follows the chapters in the research monograph by Irina Artemieva on "The Lithosphere". Definition The LAB is determined from the differences in the lithosphere and asthenosphere including, but not limited to, differences in grain size, chemical composition, thermal properties, and extent of Partial melting, partial melt; these are factors that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Asthenosphere
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between c. below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere is not well defined. The asthenosphere is almost solid, but a slight amount of melting (less than 0.1% of the rock) contributes to its mechanical weakness. More extensive decompression melting of the asthenosphere takes place where it wells upwards, and this is the most important source of magma on Earth. It is the source of mid-ocean ridge basalt (MORB) and of some magmas that erupt above subduction zones or in regions of continental rifting. Characteristics The asthenosphere is a part of the upper mantle just below the lithosphere that is involved in plate tectonic movement and isostatic adjustments. It is composed of peridotite, a rock containing mostly the minerals olivine and pyroxene. The lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Earth Cutaway Schematic-en
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large sheets of ice at Earth's polar deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a magnetosphere capable of deflecting most of the destructive solar winds and cosmic radiation. Earth has a dynamic atmosphere, which sustains Earth' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
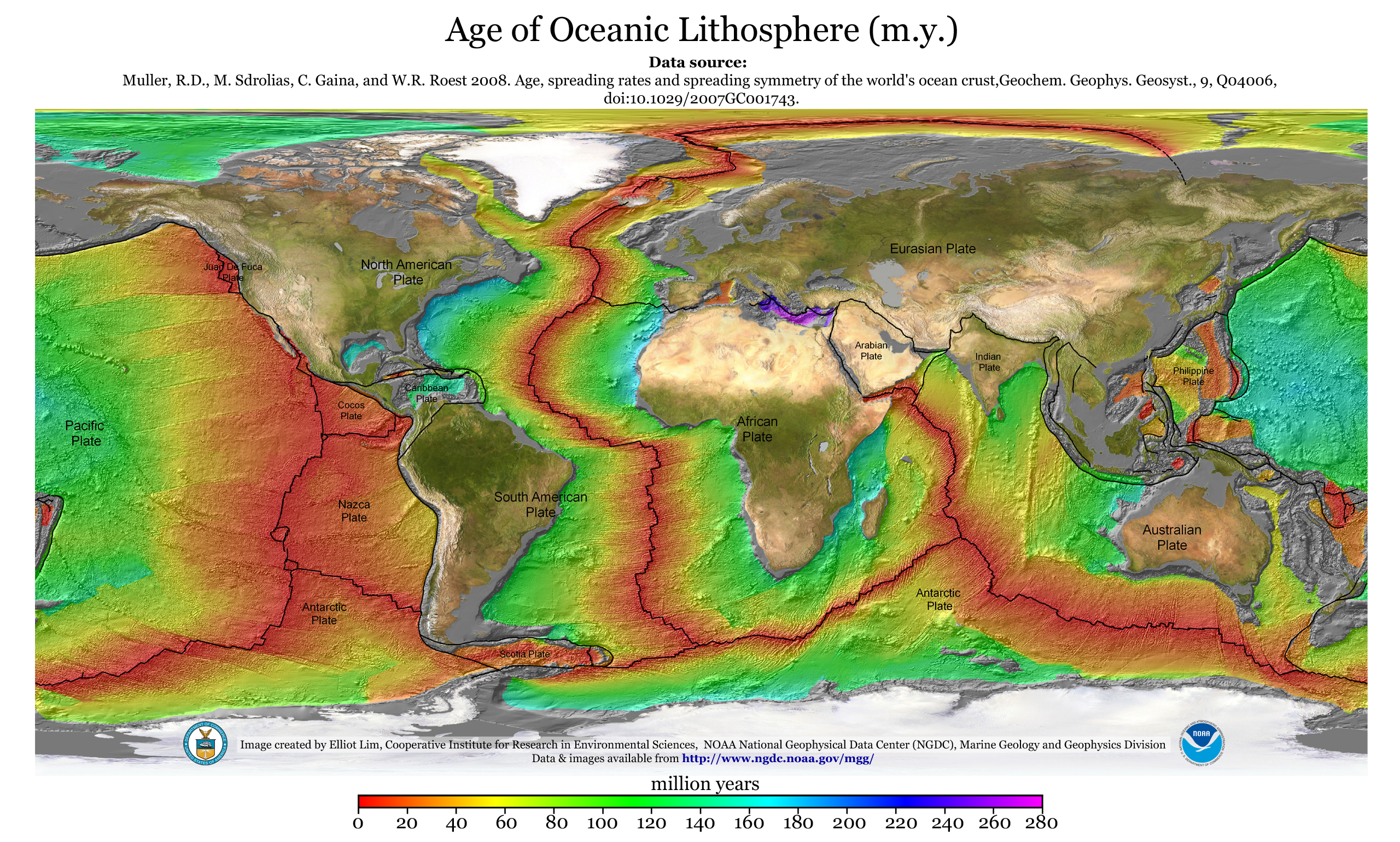
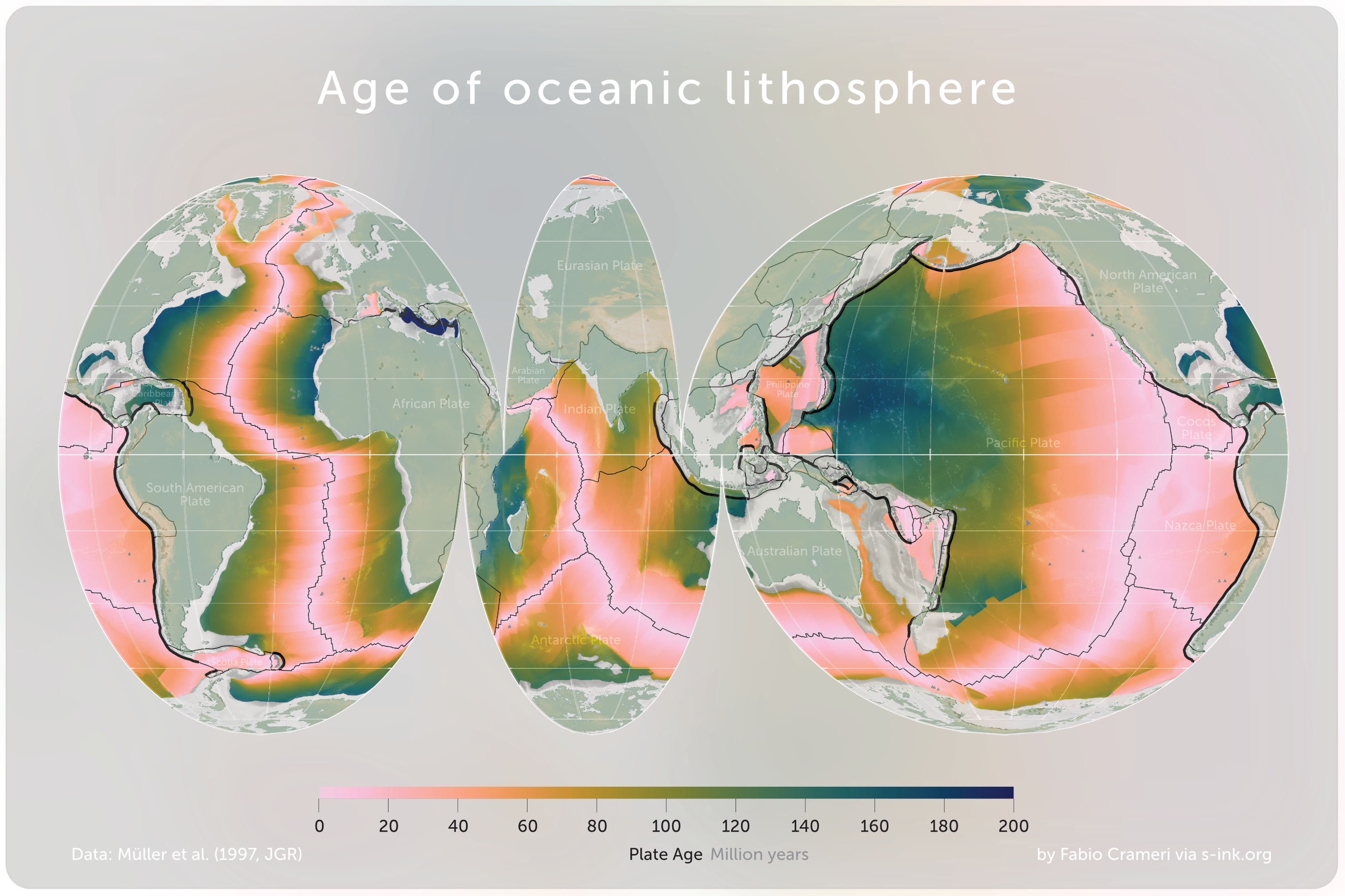
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust lies above the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however, it is denser, having a mean density of about 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. The crust uppermost is the result of the cooling of magma derived from mantle material below the plate. The magma is injected into the spreading center, which consists mainly of a partly solidified crystal mush derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by Earth science, geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s. The processes that result in plates and shape Earth's crust are called ''tectonics''. Tectonic plates also occur in other planets and moons. Earth's lithosphere, the rigid outer shell of the planet including the crust (geology), crust and upper mantle, is fractured into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary (or fault (geology), fault): , , or . The relative movement of the plates typically ranges from zero to 10 cm annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mantle (geology)
A mantle is a layer inside a planetary body bounded below by a Planetary core, core and above by a Crust (geology), crust. Mantles are made of Rock (geology), rock or Volatile (astrogeology), ices, and are generally the largest and most massive layer of the planetary body. Mantles are characteristic of planetary bodies that have undergone planetary differentiation, differentiation by density. All Terrestrial planet, terrestrial planets (including Earth), half of the giant planets, specifically ice giants, a number of Asteroid, asteroids, and some planetary Natural satellite, moons have mantles. Examples Earth The Earth's mantle is a layer of Silicate minerals, silicate rock between the Crust (geology), crust and the Earth's outer core, outer core. Its mass of 4.01 × 1024 kg is 67% the mass of the Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly solid, but in Geologic time scale, geological time it behaves as a Viscosity, visc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called '' sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. Most continental crust is dry land above sea level. However, 94% of the Zealandia continental crust region is submerged beneath the Pacific Ocean, with New Zealand constituting 93% of the above-water portion. Thickness and density The continental crust consists of various layers, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Augustus Edward Hough Love
Augustus Edward Hough Love FRS (17 April 1863, Weston-super-Mare – 5 June 1940, Oxford), often known as A. E. H. Love, was a mathematician famous for his work on the mathematical theory of elasticity. He also worked on wave propagation and his work on the structure of the Earth in ''Some Problems of Geodynamics'' won for him the Adams prize in 1911 when he developed a mathematical model of surface waves known as Love waves. Love also contributed to the theory of tidal locking and introduced the parameters known as Love numbers, used in problems related to Earth tides, the tidal deformation of the solid Earth due to the gravitational attraction of the Moon and Sun. Life and career He was educated at Wolverhampton Grammar School and in 1881 won a scholarship to St John's College, Cambridge, where he was at first undecided whether to study classics or mathematics. His successful progress (he was placed Second Wrangler) vindicated his choice of mathematics, and in 1886 he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its distinctive geologic history, which is different from the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton. There is also an older usage of the term ''terrane'', which described a series of related rock formations or an area with a preponderance of a particular rock or rock group. Overview A tectonostratigraphic terrane did not necessarily originate as an independent microplate, since it may not contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Plates Tect2 En
Plate may refer to: Cooking * Plate (dishware), broad, mainly flat vessel commonly used to serve food * Plates, tableware, dishes or dishware used for setting a table, serving food and dining * Plate, the content of such a plate (for example: rice plate) * Plate, to present food, on a plate * Plate, forequarter cut of beef Places * Plate, Germany, municipality in Parchim, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany * Plate, borough of Lüchow, Lower Saxony, Germany * River Plate (other) * Tourelle de la Plate, lighthouse in France Science and technology Biology and medicine * Plate (anatomy), several meanings * Dental plate, also known as dentures * Dynamic compression plate, metallic plate used in orthopedics to fix bone * Microtiter plate (or microplate or microwell plate), flat plate with multiple "wells" used as small test tubes * Orthopedic plate, internal fixation used in orthopaedic surgery * Petri dish or Petri plate, shallow dish on which biological cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Joseph Barrell
Joseph Barrell (December 15, 1869 – May 4, 1919) was an American geologist who developed many ideas on the origins of the Earth, isostasy and ideas on the origins of sedimentary rocks. He suggested that they were produced by the action of rivers, winds, and ice (continental), as well as by marine sedimentation. He also independently arrived at the theory of stoping as a mechanism for igneous intrusion. He was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1915. Life and career The Barrell family originated from a family that migrated from Suffolk in Britain to Boston in 1637. Joseph was born at New Providence on December 15, 1869. His father Henry Ferdinand and his mother Elizabeth née Wisner, of Swiss descent, had owned a farm in Warwick, Orange County, New York before moving to a new farm in New Jersey. Henry Ferdinand was a trustee at the local public library and for the public school and Joseph, the fifth of nine children, grew up in a home surrounded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |