|
Accommodation Space
Accommodation is a fundamental concept in sequence stratigraphy, a subdiscipline of geology. It is defined as the space that is available for the deposition of sediments. Accommodation space can be pictured as the volume between the actual surface and the theoretical equilibrium surface where deposition and erosion are in balance at every point. In marine environments, this equilibrium level is sea level. In marine environments, changes in accommodation on long temporal scales is mainly determined by tectonics or by changes in eustatic sea level. In fluvial environments, changes in accommodation are controlled by the gradient, discharge and sediment supply. In the lower parts of river systems, the change of accommodation in the fluvial system is controlled by the changes in marine accommodation. The term is also sometimes used to described processes by which room is made for plutons to intrude country rock Country rock is a genre of music which fuses rock and country. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Stratigraphy
Sequence stratigraphy is a branch of geology, specifically a branch of stratigraphy, that attempts to discern and understand historic geology through time by subdividing and linking sedimentary deposits into unconformity bounded units on a variety of scales. The essence of the method is mapping of strata based on identification of surfaces which are assumed to represent time lines (e.g. subaerial unconformities, maximum flooding surfaces), thereby placing stratigraphy in chronostratigraphic framework allowing understanding of the evolution of the earth's surface in a particular region through time. Sequence stratigraphy is a useful alternative to a purely lithostratigraphic approach, which emphasizes solely based on the compositional similarity of the lithology of rock units rather than time significance. Unconformities are particularly important in understanding geologic history because they represent erosional surfaces where there is a clear gap in the record. Conversely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deposition (geology)
Deposition is the geological process in which sediments, soil and rocks are added to a landform or landmass. Wind, ice, water, and gravity transport previously weathered surface material, which, at the loss of enough kinetic energy in the fluid, is deposited, building up layers of sediment. Deposition occurs when the forces responsible for sediment transportation are no longer sufficient to overcome the forces of gravity and friction, creating a resistance to motion; this is known as the null-point hypothesis. Deposition can also refer to the buildup of sediment from organically derived matter or chemical processes. For example, chalk is made up partly of the microscopic calcium carbonate skeletons of marine plankton, the deposition of which has induced chemical processes (diagenesis) to deposit further calcium carbonate. Similarly, the formation of coal begins with the deposition of organic material, mainly from plants, in anaerobic conditions. Null-point hypothesis The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone (sedimentary rocks) through lithification. Sediments are most often transported by water ( fluvial processes), but also wind ( aeolian processes) and glaciers. Beach sands and river channel deposits are examples of fluvial transport and deposition, though sediment also often settles out of slow-moving or standing water in lakes and oceans. Desert sand dunes and loess are examples of aeolian transport and deposition. Glacial moraine deposits and till are ice-transported sediments. Classification Sediment can be classified based on its grain size, grain sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonics
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles is essential to geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonics is associated with the stretching and thinning of the crust or the lithosphere. This type of tectonics is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustatic Sea Level
The eustatic sea level is the distance from the center of the earth to the sea surface. An increase of the eustatic sea level can be generated by decreasing glaciation, increasing spreading rates of the mid-ocean ridges or more mid-oceanic ridges. Conversely, increasing glaciation, decreasing spreading rates or fewer mid-ocean ridges lead to a fall of the eustatic sea level. Changes in the eustatic sea level lead to changes in accommodation and therefore affect the deposition of sediments in marine environments. Eustatic (global) sea level refers to the volume of Earth’s oceans. This is not a physical level but instead represents the sea level if all of the water in the oceans were contained in a single basin. Eustatic sea level is not relative to local surfaces, because relative sea level is dependent on many factors including tectonics, continental rise and subsidence. Eustatic sea level follows the ‘bathtub approach’ which describes the ocean as a single bathtub. One can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluvial
In geography and geology, fluvial processes are associated with rivers and streams and the deposits and landforms created by them. When the stream or rivers are associated with glaciers, ice sheets, or ice caps, the term glaciofluvial or fluvioglacial is used. Fluvial processes Fluvial processes include the motion of sediment and erosion or deposition on the river bed. The movement of water across the stream bed exerts a shear stress directly onto the bed. If the cohesive strength of the substrate is lower than the shear exerted, or the bed is composed of loose sediment which can be mobilized by such stresses, then the bed will be lowered purely by clearwater flow. In addition, if the river carries significant quantities of sediment, this material can act as tools to enhance wear of the bed ( abrasion). At the same time the fragments themselves are ground down, becoming smaller and more rounded ( attrition). Sediment in rivers is transported as either bedload (the coar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stream Gradient
Stream gradient (or stream slope) is the grade (slope), grade (or slope) of a stream measured by the ratio of drop in elevation per unit horizontal distance, usually expressed as metre, meters per kilometre, kilometer or Foot (length), feet per mile. Hydrology and geology A high gradient indicates a steep slope and rapid volumetric flow rate, flow of water (i.e. more ability to erode); where as a low gradient indicates a more nearly level stream bed and sluggishly moving water, that may be able to carry only small amounts of very fine sediment. High gradient streams tend to have steep, narrow V-shaped valleys, and are referred to as young streams. Low gradient streams have wider and less rugged valleys, with a tendency for the stream to meander. Many rivers involve, to some extent, a flattening of the river gradient as approach the terminus at sea level. Fluvial erosion A stream that flows upon a uniformly erosion, erodible substrate will tend to have a steep gradient near its sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
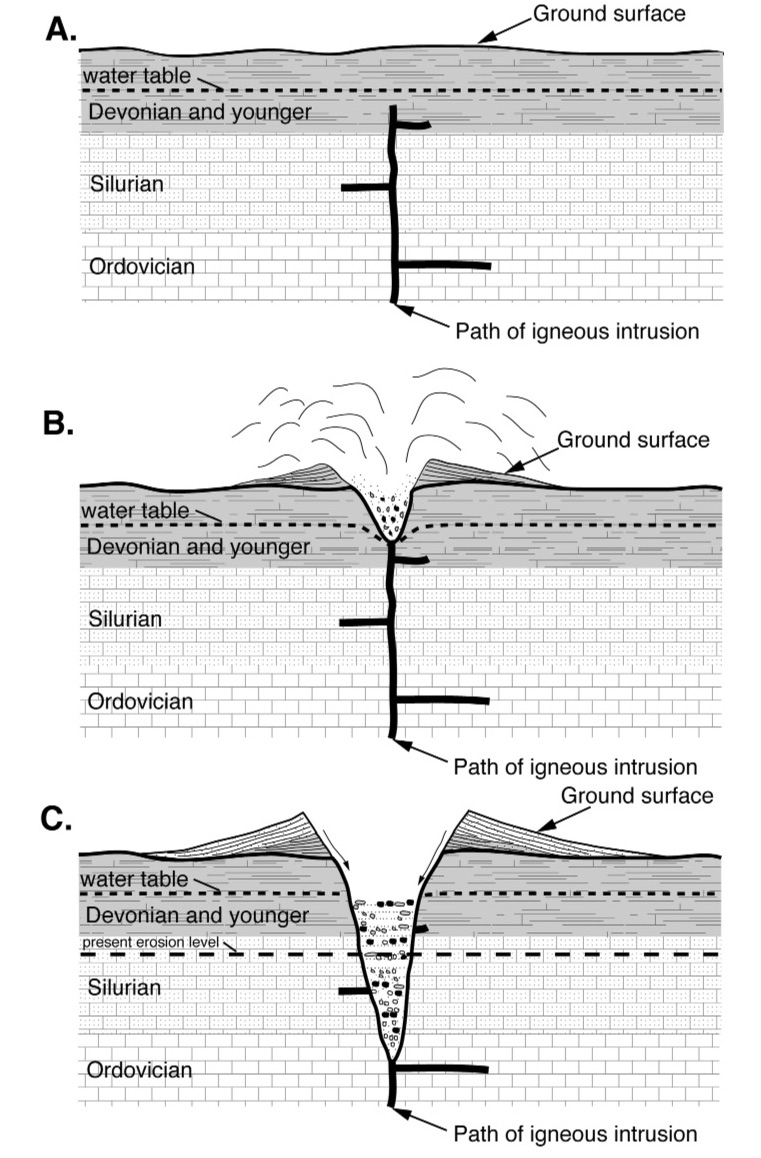
Pluton
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and compositions, illustrated by examples like the Palisades Sill of New York and New Jersey; the Henry Mountains of Utah; the Bushveld Igneous Complex of South Africa; Shiprock in New Mexico; the Ardnamurchan intrusion in Scotland; and the Sierra Nevada Batholith of California. Because the solid country rock into which magma intrudes is an excellent insulator, cooling of the magma is extremely slow, and intrusive igneous rock is coarse-grained ( phaneritic). Intrusive igneous rocks are classified separately from extrusive igneous rocks, generally on the basis of their mineral content. The relative amounts of quartz, alkali feldspar, plagioclase, and feldspathoid is particularly important in classifying intrusive igneous rocks. Intrusio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Country Rock (geology)
In geology, country rock is the rock native to an area, in contrast to any intrusion of viscous geologic material, commonly magma, or perhaps rock salt (in salt domes) or unconsolidated sediments. Magma is typically less dense than the rock it intrudes, widening and filling existing cracks, sometimes melting the already-existing country rock. The term "country rock" is similar to, and in many cases interchangeable with, the terms basement and wall rocks. Country rock can denote the widespread lithology of a region in relation to the rock which is being discussed or observed. Geologic settings Settings in geology when the term ''country rock'' is used include: Igneous intrusions When describing a pluton or dike, the igneous rock can be described as intruding the surrounding ''country rock'', the rock into which the pluton has intruded.Newfoundland and LabradorGlossary of Geological Terms Accessed June 2018. When country rock is intruded by a dike, perpendicula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |