Washington (), officially the State of Washington, is a
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* '' Our ...
in the
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
region of the
Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the Wes ...
. Named for
George Washington—the first
U.S. president—the state was formed from the western part of the
Washington Territory
The Territory of Washington was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington. It was created from th ...
, which was ceded by the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading post ...
in 1846, by the
Oregon Treaty in the settlement of the
Oregon boundary dispute. The state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean,
Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idah ...
to the south,
Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and W ...
to the east, and the
Canadian province of
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include ...
to the north. It was admitted to the Union as the 42nd state in 1889.
Olympia is the
state capital; the state's largest city is
Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a port, seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the county seat, seat of King County, Washington, King County, Washington (state), Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in bo ...
. Washington is often referred to as Washington state to distinguish it from the nation's capital,
Washington, D.C.
Washington is the
18th-largest state, with an area of , and the
13th-most populous state, with more than 7.7 million people. The majority of Washington's residents live in the
Seattle metropolitan area, the center of transportation, business, and industry on
Puget Sound, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean consisting of numerous islands, deep
fjords, and bays carved out by glaciers. The remainder of the state consists of deep
temperate rainforests in the west;
mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
s in the west, central, northeast, and far southeast; and a semi-arid basin region in the east, central, and south, given over to intensive agriculture. Washington is the second most populous state on the
West Coast and in the Western United States, after
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
.
Mount Rainier, an active
stratovolcano, is the state's highest elevation at , and is the most
topographically prominent mountain in the
contiguous U.S.
Washington is a leading
lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, w ...
producer; its rugged surface is rich in stands of
Douglas fir,
hemlock,
ponderosa pine,
white pine,
spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ( taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the sub ...
,
larch
Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus ''Larix'', of the family Pinaceae (subfamily Laricoideae). Growing from tall, they are native to much of the cooler temperate northern hemisphere, on lowlands in the north and high on mountains furt ...
, and
cedar. The state is the largest producer of apples, hops, pears, blueberries, spearmint oil, and sweet cherries in the U.S., and ranks high in the production of apricots, asparagus, dry edible peas, grapes, lentils, peppermint oil, and potatoes. Livestock, livestock products, and commercial fishing—particularly of salmon, halibut, and bottomfish—are also significant contributors to the state's economy.
Washington ranks second only to California in
wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are ...
production.
Manufacturing industries in Washington include aircraft, missiles, shipbuilding, and other transportation equipment, food processing, metals, and metal products, chemicals, and machinery. Washington has more than a thousand dams, including the
Grand Coulee Dam
Grand Coulee Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, built to produce hydroelectric power and provide irrigation water. Constructed between 1933 and 1942, Grand Coulee originally had two powerho ...
, built for a variety of purposes including irrigation, electricity generation, flood control, and water storage.
Washington is one of the
wealthiest as well as most socially liberal states in the country. The state consistently ranks among the best for
life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
and low
unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refer ...
. Along with
Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
, Washington was one of the
first to legalize medicinal and recreational cannabis, was among the first states to legalize
same-sex marriage in 2012, and was one of only four U.S. states to have been providing legal
abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pregn ...
s
on request before the 1973
Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
decision in ''
Roe v. Wade'' loosened abortion laws nationwide.
Similarly, Washington voters approved a
2008 referendum on legalization of
physician-assisted suicide, and Washington is currently one of ten states—along with Washington, D.C.—to have legalized the practice.
Etymology
Washington was named after
President George Washington by an act of the
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washi ...
during the creation of
Washington Territory
The Territory of Washington was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington. It was created from th ...
in 1853; the territory was to be named "Columbia", for the
Columbia River and the
Columbia District, but Kentucky representative
Richard H. Stanton found the name too similar to the
District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan ...
(the national capital, itself containing the city of Washington), and proposed naming the new territory after President Washington.
Washington is the only U.S. state named after a president.
Confusion over the state of Washington and the city of Washington, D.C., led to renaming proposals during the statehood process for Washington in 1889, including
David Dudley Field II's suggestion to name the new state "Tacoma"; these proposals failed to garner support. Washington, D.C.'s, own
statehood movement in the 21st century has included a proposal to use the name "State of Washington, Douglass Commonwealth", which would conflict with the current state of Washington.
Residents of Washington (known as "Washingtonians") and the
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
simply refer to the state as "Washington", and the nation's capital "Washington, D.C.", "the other Washington", or simply "D.C."
History
Early history

The 9,300-year-old skeletal remains of
Kennewick Man, one of the oldest and most complete human remains found in North America, were discovered in Washington in the 1990s.
The area has been known to host
megathrust earthquakes in the past, the last being the
Cascadia earthquake of 1700. Before the arrival of Europeans, the region had many established tribes of indigenous peoples, notable for their
totem poles and their ornately carved canoes and masks. Prominent among their industries were
salmon
Salmon () is the common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of ...
fishing and, notably among the
Makah, whale hunting. The peoples of the Interior had a different subsistence-based culture based on hunting, food-gathering and some forms of agriculture, as well as a dependency on salmon from the Columbia and its tributaries. The
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) ce ...
epidemic of the 1770s devastated the Native American population.
European exploration
The first recorded European landing on the Washington coast was by Spanish Captain Don
Bruno de Heceta in 1775, on board the ''Santiago'', part of a two-ship
flotilla with the ''Sonora''. He claimed the coastal lands up to
Prince William Sound for Spain as part of their claimed rights under the
Treaty of Tordesillas, which they maintained made the Pacific a "Spanish lake" and all its shores part of the Spanish Empire.
In 1778,
British explorer Captain
James Cook sighted
Cape Flattery, at the entrance to the
Strait of Juan de Fuca, but Cook did not realize the strait existed. It was not discovered until
Charles William Barkley, captain of the ''
Imperial Eagle'', sighted it in 1787. The straits were further explored by
Spanish explorers Manuel Quimper in 1790 and Francisco de Eliza in 1791, and British explorer
George Vancouver
Post-captain, Captain George Vancouver (22 June 1757 – 10 May 1798) was a British Royal Navy officer best known for his Vancouver Expedition, 1791–1795 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern West Coast of the Un ...
in 1792.
European settlement
The British–Spanish
Nootka Convention of 1790 ended Spanish claims of exclusivity and opened the Northwest Coast to explorers and traders from other nations, most notably Britain and Russia as well as the fledgling United States. American captain
Robert Gray (for whom
Grays Harbor County
Grays Harbor County is a county in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, the population was 75,636. Its county seat is Montesano, and its largest city is Aberdeen. Grays Harbor County is included in the Aberdeen Micropolitan ...
is named) then discovered the mouth of the Columbia River. He named the river after his ship, the
''Columbia''. Beginning in 1792, Gray established trade in
sea otter pelts. The
Lewis and Clark Expedition entered the state on October 10, 1805.
Explorer
David Thompson, on his voyage down the Columbia River, camped at the confluence with the Snake River on July 9, 1811, and erected a pole and a notice claiming the territory for Great Britain and stating the intention of the
North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great we ...
to build a trading post at the site.

Britain and the United States agreed to what has since been described as "joint occupancy" of lands west of the
Continental Divide
A continental divide is a drainage divide on a continent such that the drainage basin on one side of the divide feeds into one ocean or sea, and the basin on the other side either feeds into a different ocean or sea, or else is endorheic, no ...
to the Pacific Ocean as part of the
Anglo–American Convention of 1818, which established the 49th Parallel as the international boundary west from
Lake of the Woods to the
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
. Resolution of the territorial and treaty issues west to the Pacific was deferred until a later time. In 1819, Spain ceded their rights north of the 42nd Parallel to the United States.
Negotiations with Great Britain over the next few decades failed to settle upon a compromise boundary and the
Oregon boundary dispute was highly contested between Britain and the United States. Disputed joint occupancy by Britain and the U.S. lasted for several decades. With American settlers pouring into
Oregon Country,
Hudson's Bay Company, which had previously discouraged settlement because it conflicted with the fur trade, reversed its position in an attempt to maintain British control of the
Columbia District.
Fur trapper
James Sinclair, on orders from
Sir George Simpson, Governor of the Hudson's Bay Company, led some 200 settlers from the
Red River Colony
The Red River Colony (or Selkirk Settlement), also known as Assinboia, was a colonization project set up in 1811 by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk, on of land in British North America. This land was granted to Douglas by the Hudson's Ba ...
west in 1841 to settle on Hudson Bay Company farms near
Fort Vancouver. The party crossed the Rockies into the
Columbia Valley, near present-day
Radium Hot Springs, British Columbia, then traveled south-west down the
Kootenai River and Columbia River. Despite such efforts, Britain eventually ceded all claims to land south of the 49th parallel to the United States in the
Oregon Treaty on June 15, 1846.
In 1836, a group of missionaries, including
Marcus Whitman, established several missions and Whitman's own settlement Waiilatpu, in what is now southeastern Washington state, near present-day
Walla Walla County, in the territory of both the
Cayuse Cayuse may refer to:
*Cayuse people, a people native to Oregon, United States
*Cayuse language, an extinct language of the Cayuse people
*Cayuse, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the United States
*Cayuse horse, an archaic term for a feral or ...
and the
Nez Perce Indian tribes. Whitman's settlement would in 1843 help the
Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what is now the state of Kans ...
, the overland emigration route to the west, get established for thousands of emigrants in the following decades. Marcus provided medical care for the Native Americans, but when Indian patients—lacking immunity to new, "European" diseases—died in striking numbers, while at the same time many white patients recovered, they held "medicine man" Marcus Whitman personally responsible, and murdered Whitman and twelve other white settlers in the
Whitman massacre in 1847. This event triggered the
Cayuse War between settlers and Indians.
Fort Nisqually, a farm and trading post of the Hudson's Bay Company and the first European settlement in the
Puget Sound area, was founded in 1833. Black pioneer
George Washington Bush and his Caucasian wife, Isabella James Bush, from
Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
and
Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to ...
, respectively, led four white families into the territory and founded New Market, now
Tumwater, in 1846. They settled in Washington to avoid
Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idah ...
's
Black Exclusion Law, which prohibited African Americans from entering the territory while simultaneously prohibiting
slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. After them, many more settlers, migrating overland along the Oregon Trail, wandered north to settle in the Puget Sound area.
Spanish and Russian claims to the region were ceded in the early 19th century through a series of treaties. The Spanish signed the
Adams–Onís Treaty of 1819, and the Russians the
Russo-American Treaty of 1824 and
1825.
The
Oregon Question remained contested between the United Kingdom and the United States until the 1846
Oregon Treaty established the border between
British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English overseas possessions, English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland (island), Newfound ...
and the United States along the 49th parallel until the
Strait of Georgia.
Vague wording in the treaty left the ownership of the
San Juan Islands in doubt; during the so-called
Pig War, both nations agreed to a joint military occupation of the islands.
Kaiser
Wilhelm I of the
German Empire was selected as an arbitrator to end the dispute, with a three-man commission ruling in favor of the United States in 1872. The border established by the Oregon Treaty and finalized by the arbitration in 1872 remains the boundary between Washington and
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include ...
.
Statehood

The growing population of Oregon Territory north of the Columbia River formally requested a new territory. As a result of the
Monticello Convention, held in present-day
Cowlitz County
Cowlitz County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, its population was 110,730. The county seat is Kelso, and its largest city is Longview. The county was formed in April 1854. Its name derives from the ...
,
U.S. Congress passed legislation and
President Millard Fillmore signed into law on March 2, 1853, the creation of a new
Washington Territory
The Territory of Washington was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington. It was created from th ...
.
The boundary of Washington Territory initially extended farther east than the present state, including what is now the
Idaho Panhandle and parts of western Montana, and picked up more land to the southeast that was left behind when Oregon was admitted as a state; the creation of
Idaho Territory in 1863 established the final eastern border. A
Washington state constitution
The Constitution of the State of Washington is the document that describes the structure and function of the government of the U.S. State of Washington. The constitution was adopted as part of Washington Territory's path to statehood in 1889. An e ...
was drafted and ratified in 1878, but it was never officially adopted. Although never approved by the United States Congress, the 1878 constitution is an important historical document that shows the political thinking of the time; it was used extensively during the drafting of Washington state's 1889 constitution, the one and only official Constitution of the State of Washington. Washington became the
42nd state of the United States on November 11, 1889.
Early prominent industries in the new state included agriculture and lumber. In Eastern Washington, the
Yakima River Valley became known for its apple orchards, while the growth of wheat using
dry farming techniques became particularly productive. Heavy rainfall to the west of the Cascade Range produced dense forests, and the ports along Puget Sound prospered from the manufacturing and shipping of lumber products, particularly the
Douglas fir. Other industries that developed in the state included fishing, salmon canning and mining.
Post–statehood
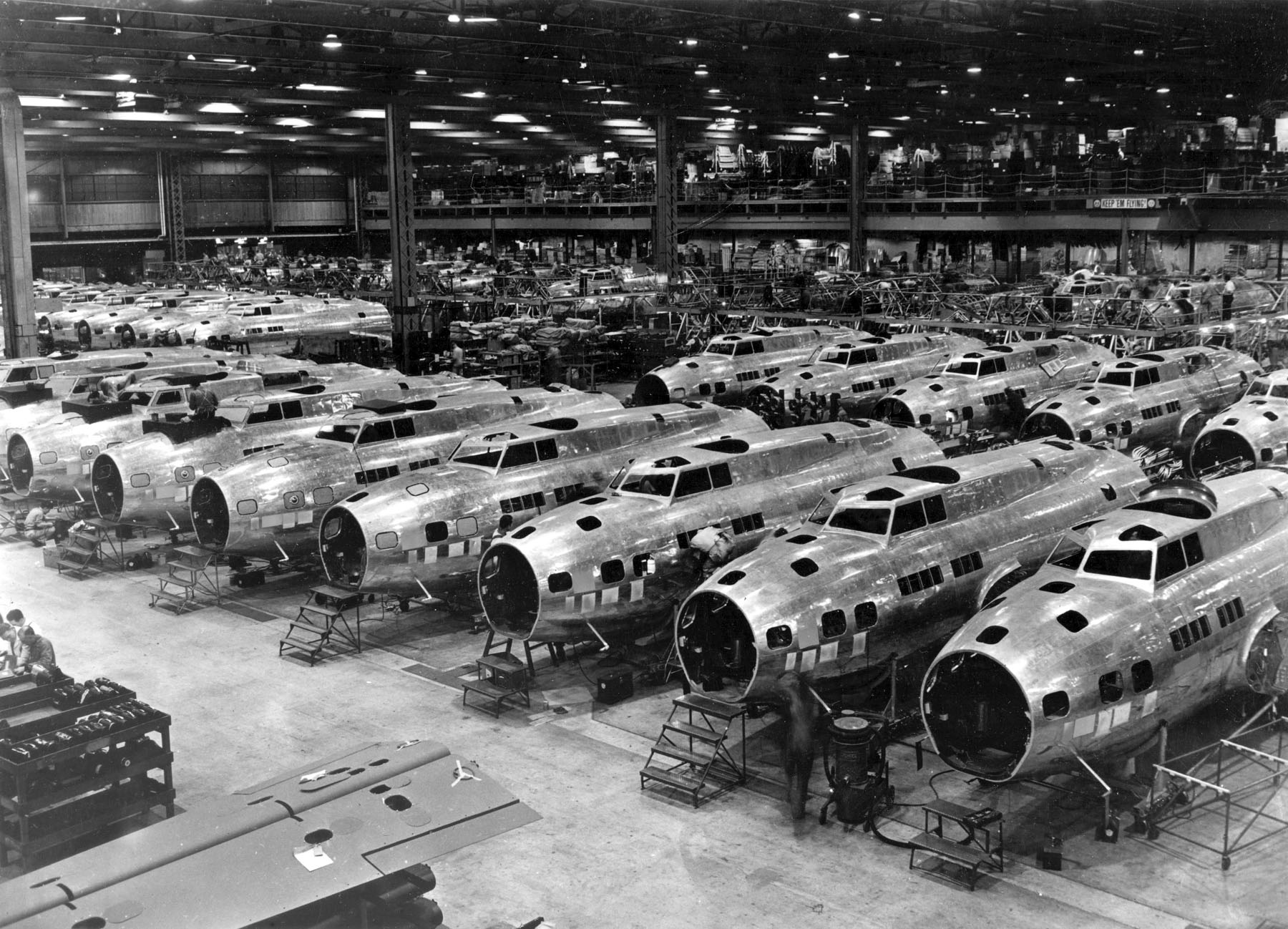


For a long period,
Tacoma had large smelters where gold, silver, copper, and lead ores were treated.
Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a port, seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the county seat, seat of King County, Washington, King County, Washington (state), Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in bo ...
was the primary port for trade with Alaska and the rest of the country, and for a time, it possessed a large shipbuilding industry. The region around eastern Puget Sound developed heavy industry during the period including
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, and the
Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and ...
company became an established icon in the area.
During the
Great Depression, a series of
hydroelectric dams were constructed along the Columbia River as part of a project to increase the production of electricity. This culminated in 1941 with the completion of the
Grand Coulee Dam
Grand Coulee Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, built to produce hydroelectric power and provide irrigation water. Constructed between 1933 and 1942, Grand Coulee originally had two powerho ...
, the largest concrete structure in the United States and the largest dam in the world at its construction.
During World War II, the state became a focus for war industries. While the Boeing Company produced many
heavy bomber
Heavy bombers are bomber aircraft capable of delivering the largest payload of air-to-ground weaponry (usually bombs) and longest range (takeoff to landing) of their era. Archetypal heavy bombers have therefore usually been among the large ...
s, ports in Seattle,
Bremerton,
Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. Th ...
, and Tacoma were available for the manufacture of warships. Seattle was the point of departure for many soldiers in the Pacific, several of whom were quartered at Fort Lawton, which later became
Discovery Park. In Eastern Washington, the
Hanford Works atomic energy Atomic energy or energy of atoms is energy carried by atoms. The term originated in 1903 when Ernest Rutherford began to speak of the possibility of atomic energy.Isaac Asimov, ''Atom: Journey Across the Sub-Atomic Cosmos'', New York:1992 Plume, ...
plant was opened in 1943 and played a major role in the construction of
atomic bombs.
After the end of World War II, and with the beginning of the
civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
, the state's growing
Black or African American population's wages were 53% above the national average. The early diversification of Washington through the
Great Migration led to successful efforts at reducing discrimination in the workplace. In 1950, Seattle's first black representative for the
state's legislature was elected. At the
1970 U.S. census, the black population grew to 7.13% of the total population.
In 1970, the state was one of only four U.S. states to have been providing legal abortions before the 1973
Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
decision in ''
Roe v. Wade'' which loosened abortion laws nationwide.
On May 18, 1980, following a period of heavy tremors and small eruptions, the north face of
Mount St. Helens slid off in the largest landslide in recorded history before erupting violently, destroying a large part of the top of the volcano. The eruption flattened the forest
up to 20 km north of the volcano, killed 57 people, flooded the Columbia River and its tributaries with ash and mud, and blanketed large parts of Washington eastward and other surrounding states in ash, making day look like night.
Geography

Washington is the northwesternmost state of the
contiguous United States. It borders
Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and W ...
to the east, bounded mostly by the meridian running north from the confluence of the
Snake River
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snak ...
and
Clearwater River (about 117°02'23" west), except for the southernmost section where the border follows the Snake River. Oregon is to the south, with the Columbia River forming the western part and the 46th parallel forming the eastern part of the Oregon–Washington border. During Washington's partition from Oregon, the original plan for the border followed the Columbia River east until the confluence with the Snake, and then would have followed the Snake River east; this was changed to keep
Walla Walla's fertile farmland in Washington.
To the west of Washington lies the Pacific Ocean.
Its northern border lies mostly along the
49th parallel, and then via marine boundaries through the
Strait of Georgia,
Haro Strait, and
Strait of Juan de Fuca, with the
Canadian province of
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include ...
to the north.
Washington is part of a region known as the
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
, a term which always refers to at least Washington and Oregon, and may or may not include some or all the following, depending on the user's intent: Idaho, western
Montana
Montana () is a U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West List of regions of the United States#Census Bureau-designated regions and divisions, division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North ...
,
northern California
Northern California (colloquially known as NorCal) is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the northern portion of the U.S. state of California. Spanning the state's northernmost 48 counties, its main population centers incl ...
, British Columbia, and
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S ...
.
The high mountains of the
Cascade Range run north-south, bisecting the state. In addition to
Western Washington and
Eastern Washington, residents call the two parts of the state the "Westside" and the "Eastside", "Wet side" and "Dry side", or "Timberland" and "Wheatland", the latter pair more commonly in the names of region-specific businesses and institutions. These terms reflect the geography, climate, and industry of the land on both sides of the Cascades.
Western Washington

From the
Cascade Mountains westward,
Western Washington has a mostly
Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
, with mild temperatures and wet winters, autumns and springs, and relatively dry summers. The Cascade Range has several
volcanoes, which reach altitudes significantly higher than the rest of the mountains. From north to south, these major volcanoes are
Mount Baker,
Glacier Peak,
Mount Rainier,
Mount St. Helens, and
Mount Adams. All are active volcanoes.
Mount Rainier—the tallest mountain in the state—
is south of the city of Seattle, from which it is prominently visible. The
U.S. Geological Survey considers Mount Rainier the most dangerous volcano in the Cascade Range, due to its proximity to the
Seattle metropolitan area, and most dangerous in the continental U.S. according to the
Decade Volcanoes list.
It is also covered with more
glacial ice than any other peak in the contiguous 48 states.
Western Washington also is home of the
Olympic Mountains, far west on the
Olympic Peninsula
The Olympic Peninsula is a large arm of land in western Washington that lies across Puget Sound from Seattle, and contains Olympic National Park. It is bounded on the west by the Pacific Ocean, the north by the Strait of Juan de Fuca, an ...
, which support dense forests of conifers and areas of
temperate rainforest. These deep forests, such as the
Hoh Rainforest, are among the only rainforests in the continental United States. While Western Washington does not always experience a high amount of rainfall as measured in total inches of rain per year, it does consistently have more rainy days per year than most other places in the country.
Eastern Washington
Eastern Washington—the part of the state east of the Cascades—has a relatively dry climate, in distinct contrast to the west side. It includes large areas of semiarid
steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslan ...
and a few truly arid
deserts in the
rain shadow of the Cascades; the Hanford reservation receives an average annual precipitation of . Despite the limited amount of rainfall,
agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peop ...
is an extremely important business throughout much of Eastern Washington, as the soil is highly productive and
irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been dev ...
, aided by dams along the Columbia River, is fairly widespread. The spread of population in Eastern Washington is dominated by access to water, especially rivers. The main cities are all located alongside rivers or lakes; most of them are named after the river or lake they adjoin.
Farther east, the climate becomes less arid, with annual rainfall increasing as one goes east to in Pullman, near the Washington–Idaho border. The
Okanogan Highlands and the rugged
Kettle River Range and
Selkirk Mountains cover much of the state's northeastern quadrant. The
Palouse southeast region of Washington was grassland that has been mostly converted into farmland, and extends to the
Blue Mountains.
Climate
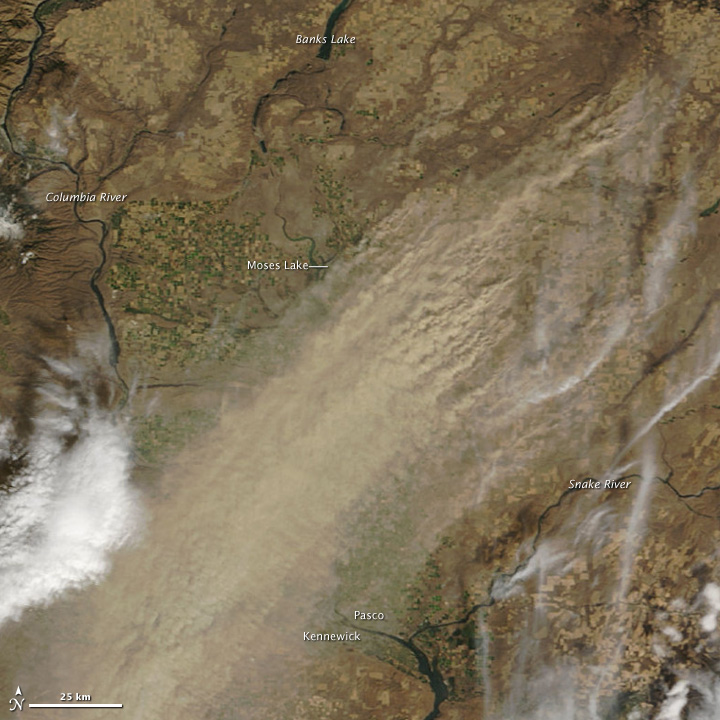


The state of Washington has a temperate climate. The eastern half of Washington has a semi-arid climate, while the western side of Washington as well as the coastal areas of the state have a cool oceanic climate. Major factors determining Washington's climate include the large semi-permanent
low pressure and
high pressure systems of the north Pacific Ocean, the continental air masses of North America, and the Olympic and Cascade mountains. In the spring and summer, a high-pressure
anticyclone system dominates the north Pacific Ocean, causing air to spiral out in a clockwise fashion. For Washington, this means
prevailing winds from the northwest bring relatively cool air and a predictably
dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The ...
.
In the autumn and winter, a low-pressure
cyclone system takes over in the north Pacific Ocean. The air spiraling inward in a counter-clockwise fashion causes Washington's prevailing winds to come from the southwest, and bring relatively cool and overcast weather and a predictably
wet season
The wet season (sometimes called the Rainy season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. It is the time of year where the majority of a country's or region's annual precipitation occurs. Generally, the se ...
. The term "
Pineapple Express" is used colloquially to describe
atmospheric river events, where repeated storm systems are directed by this persistent cyclone from the tropical Pacific regions a great distance into the Pacific Northwest.
Despite Western Washington's marine climate similar to many coastal cities of Europe, there are exceptions such as the "Big Snow" events of 1880, 1881, 1893, and 1916,
and the "deep freeze" winters of 1883–1884, 1915–1916, 1949–1950, and 1955–1956, among others. During these events, Western Washington experienced up to of snow, sub-zero (−18 °C) temperatures, three months with snow on the ground, and lakes and rivers frozen over for weeks.
Seattle's lowest officially recorded temperature is set on January 31, 1950, but low-altitude areas approximately three hours away from Seattle have recorded lows as cold as .
The Southern Oscillation greatly influences weather during the cold season. During the El Niño phase, the jet stream enters the U.S. farther south through California, therefore late fall and winter are drier than normal with less snowpack. The La Niña phase reinforces the jet stream through the Pacific Northwest, causing Washington to have more rain and snow than average.
In 2006, the Climate Impacts Group at the
University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington.
Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seat ...
published ''The Impacts of Climate change in Washington's Economy'', a preliminary assessment of the risks and opportunities presented given the possibility of a rise in global temperatures and their effects on Washington state.
Rain shadow effects

Rainfall in Washington varies dramatically going from east to west. The Olympic Peninsula's western side receives as much as of precipitation annually, making it the wettest area of the 48 conterminous states and a
temperate rainforest. Weeks may pass without a clear day. The western slopes of the Cascade Range receive some of the heaviest annual snowfall (in some places more than water equivalent) in the country. In the rain shadow area east of the Cascades, the annual precipitation is only . Precipitation then increases again eastward toward the Rocky Mountains (about east of the Idaho border).
The Olympic mountains and Cascades compound this climatic pattern by causing
orographic lift of the air masses blown inland from the Pacific Ocean, resulting in the windward side of the mountains receiving high levels of precipitation and the leeward side receiving low levels. This occurs most dramatically around the Olympic Mountains and the Cascade Range. In both cases, the windward slopes facing southwest receive high precipitation and mild, cool temperatures. While the Puget Sound lowlands are known for clouds and rain in the winter, the western slopes of the Cascades receive larger amounts of precipitation, often falling as snow at higher elevations.
Mount Baker, near the state's northern border, is one of the snowiest places in the world. In 1999, it set the world record for snowfall in a single season—.
East of the Cascades, a large region experiences strong rain shadow effects. Semi-arid conditions occur in much of Eastern Washington with the strongest rain shadow effects at the relatively low elevations of the central
Columbia Plateau—especially the region just east of the Columbia River from about the Snake River to the
Okanagan Highland. Thus, instead of rain forests, much of Eastern Washington is covered with dry
grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natur ...
,
shrub-steppe, and
dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, fl ...
s.
Temperatures
The average annual temperature ranges from on the Pacific coast to in the northeast. The lowest temperature recorded in the state was in
Winthrop and
Mazama. The highest recorded temperature in the state was at
Hanford on June 29, 2021. Both records were set east of the Cascades. Western Washington is known for its mild climate, considerable fog, frequent cloud cover, long-lasting drizzles in the winter and warm, temperate summers. The eastern region, which does not benefit from the general moderating effect of the Pacific Ocean, occasionally experiences extreme climate. Arctic cold fronts in the winter and heat waves in the summer are not uncommon. In the Western region, temperatures have reached as high as in
Maple Valley during the
June 2021 heat wave, and as low as in
Longview.
Flora and fauna


Forests cover about half the state's land area, mostly west of the northern Cascades. Approximately two-thirds of Washington's forested area is publicly owned, including 64 percent of federal land. Common trees and plants in the region are
camassia
''Camassia'' is a genus of plants in the asparagus family native to North America. Common names include camas, quamash, Indian hyacinth, camash, and wild hyacinth.
It grows in the wild in great numbers in moist meadows. They are perennial p ...
, Douglas fir, hemlock,
penstemon, ponderosa pine,
western red cedar, and many species of ferns. The state's various areas of wilderness offer sanctuary, with substantially large populations of shorebirds and marine mammals. The Pacific shore surrounding the
San Juan Islands is heavily inhabited by
killer, gray, and humpback whales.
In Eastern Washington, the flora is vastly different.
Tumbleweeds and
sagebrush dominate the landscape throughout large parts of the countryside.
Russian olives and other trees are common alongside riverbanks; however, apart from the riversides, large swaths of Eastern Washington have no naturally existing trees at all (though many trees have been planted and are irrigated by people, of course). A wider variety of flora can be found in both the
Blue Mountains and the eastern sides of the Cascades.
Mammals native to the state include the
bat,
black bear,
bobcat,
cougar
The cougar (''Puma concolor'') is a large cat native to the Americas. Its range spans from the Canadian Yukon to the southern Andes in South America and is the most widespread of any large wild terrestrial mammal in the Western Hemisphere. I ...
,
coyote,
deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the ...
,
elk,
gray wolf,
hare,
moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
,
mountain beaver,
muskrat,
opossum
Opossums () are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia () endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 93 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered Nort ...
,
pocket gopher,
rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit s ...
,
raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight o ...
,
river otter,
skunk
Skunks are mammals in the family Mephitidae. They are known for their ability to spray a liquid with a strong, unpleasant scent from their anal glands. Different species of skunk vary in appearance from black-and-white to brown, cream or gi ...
, and
tree squirrel. Because of the wide range of geography, the State of Washington is home to several different ecoregions, which allow for a varied range of bird species. This range includes raptors, shorebirds, woodland birds, grassland birds, ducks, and others. There have also been a large number of species introduced to Washington, dating back to the early 18th century, including horses and burros. The
channel catfish
The channel catfish (''Ictalurus punctatus'') is North America's most numerous catfish species. It is the official fish of Kansas, Missouri, Iowa, Nebraska, and Tennessee, and is informally referred to as a "channel cat". In the United States, th ...
,
lamprey, and
sturgeon are among the 400 known
freshwater fishes.
Along with the Cascades frog, there are several forms of snakes that define the most prominent
reptiles and amphibians. Coastal bays and islands are often inhabited by plentiful amounts of shellfish and whales. There are five species of
salmon
Salmon () is the common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of ...
that ascend the Western Washington area, from streams to spawn.
Washington has a variety of
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government within the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of ...
units. Among these are the
Alta Lake State Park,
Lake Roosevelt National Recreation Area,
San Juan Islands National Wildlife Refuge
The San Juan Islands National Wildlife Refuge is in the San Juan Islands of the Salish Sea, north of Puget Sound, in the State of Washington. Created in 1976, it comprises 83 small, uninhabited islands, scattered throughout the San Juans, with ...
, as well as three national parks—the
Olympic National Park,
North Cascades National Park, and
Mount Rainier National Park. The three national parks were established between 1899 and 1968. Almost 95 percent (876,517 acres, 354,714 hectares, 3,547.14 square kilometers) of Olympic National Park's area has been designated as wilderness under the
National Wilderness Preservation System. Additionally, there are 143
state parks and9
national forests
A state forest or national forest is a forest that is administered or protected by some agency of a sovereign state, sovereign or federated state, or territory (country subdivision), territory.
Background
The precise application of the terms va ...
, run by the
Washington State Park System and the
United States Forest Service
The United States Forest Service (USFS) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Agriculture that administers the nation's 154 national forests and 20 national grasslands. The Forest Service manages of land. Major divisions of the agency inc ...
. The
Okanogan National Forest is the largest national forest on the
West Coast, encompassing . It is managed together as the Okanogan–
Wenatchee National Forest, encompassing a considerably larger area of around .
Administrative divisions
There are 39 counties within the state, and 281 incorporated municipalities which are divided into cities and towns. The majority of the state's population lives within Western Washington, in the Seattle metropolitan area; the city of Seattle is the principal city of the metropolitan area, and Western Washington, with a 2020 census population of 737,015.
Demographics
Population
Washington's population was 7,705,281 in the
2020 census,
a 14.6 percent increase since the
2010 census.
In 2018, the state ranked 13th overall in population, and was the third most populous, after California and Texas, west of the Mississippi River. Washington has the largest Pacific Northwest population, followed by Oregon, then Idaho. The Washington State Office of Financial Management reported the state population at 7,656,200 as of April 1, 2020.
As of the 2010 census, the population of Washington was 6,724,540. The Seattle-Tacoma-Bellevue Metropolitan Area population was 3,439,809 in the 2010 census, half the state total.
The
center of population of Washington in 2010 was at , in an unpopulated part of the
Cascade Mountains in rural eastern
King County, southeast of
North Bend, northeast of
Enumclaw
Enumclaw ( ) is a city in King County, Washington, United States. The population was 12,543 at the 2020 census.
The Enumclaw Plateau, on which the city resides, was formed by a volcanic mudflow (lahar) from Mount Rainier approximately 5,700 ye ...
, and west of
Snoqualmie Pass.
Washington's proportion of residents under the age of five was 6.7%, 25.7% under 18, and 11.2% 65 or older.
The racial composition of Washington's population as of 2016 was:
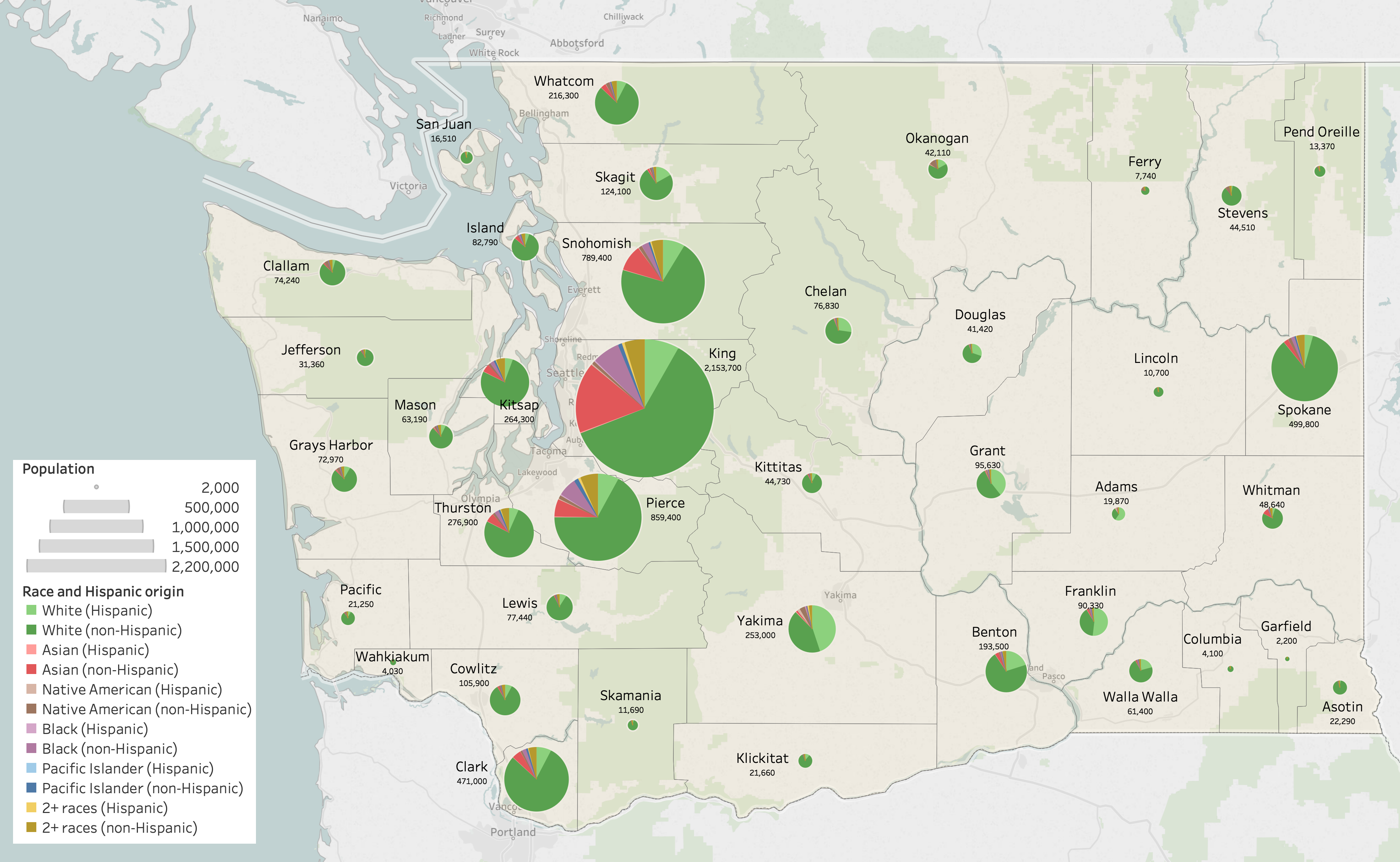
According to the 2016
American Community Survey, 12.1% of Washington's population were of
Hispanic or Latino origin (of any race):
Mexican (9.7%),
Puerto Rican (0.4%),
Cuban (0.1%), and other Hispanic or Latino origin (1.8%).
The five largest ancestry groups were:
German (17.8%),
Irish (10.8%),
English (10.4%),
Norwegian (5.4%), and
American (4.6%).
; Birth data
In 2011, 44.3 percent of Washington's population younger than age1 were minorities.
''Note: Births in table don't add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
* Since 2016, data for births of
White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
Areas of concentration

While the population of African Americans in the Pacific Northwest is relatively scarce overall, they are mostly concentrated in the
South End and
Central District areas of Seattle, and in inner Tacoma. The black community of Seattle consisted of one individual in 1858,
Manuel Lopes Manuel Lopes may refer to:
* Manuel Lopes Rodrigues (1860-1917), Brazilian painter
* Manuel Lopes (barber) (died 1895), Cape Verdean-American barber
* Manuel Lopes (writer)
Manuel António de Sousa Lopes (December 23, 1907 – January 25, 2005) w ...
, and grew to a population of 406 by 1900. It developed substantially during and after World War II when wartime industries and the
U.S. Armed Forces employed and recruited tens of thousands of African Americans from the
Southeastern United States
The Southeastern United States, also referred to as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical region of the United States. It is located broadly on the eastern portion of the southern United States and the southern po ...
. They moved west in the second wave of the
Great Migration, leaving a high influence on West Coast
rock music
Rock music is a broad genre of popular music that originated as "rock and roll" in the United States in the late 1940s and early 1950s, developing into a range of different styles in the mid-1960s and later, particularly in the United States and ...
and
R&B and
soul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun '':wikt:soul, soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The ea ...
in the 1960s, including Seattle native
Jimi Hendrix, a pioneer in hard rock, who was of African American and
Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, th ...
Indian descent.
Native Americans lived on Indian reservations or jurisdiction lands such as the
Colville Indian Reservation,
Makah,
Muckleshoot Indian Reservation,
Quinault,
Salish people,
Spokane Indian Reservation, and
Yakama Indian Reservation. The westernmost and Pacific coasts have primarily American Indian communities, such as the
Chinook,
Lummi, and
Salish.
Urban Indian
Urban Indians are American Indians and Canadian First Nations peoples who live in urban areas. Urban Indians represent a growing proportion of the Native population in the United States. The National Urban Indian Family Coalition (NUIFC) consi ...
communities formed by the U.S.
Bureau of Indian Affairs relocation programs in Seattle since the end of World War II brought a variety of Native American peoples to this diverse metropolis. The city was named for
Chief Seattle in the very early 1850s when European Americans settled the sound.

Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders are mostly concentrated in the Seattle−Tacoma metropolitan area of the state. Seattle,
Bellevue, and
Redmond, which are all within King County, have sizable Chinese communities (including
Taiwanese), as well as significant
Indian and
Japanese communities. The
Chinatown-International District in Seattle has a historical Chinese population dating back to the 1860s, who mainly emigrated from
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020 ...
Province in southern China, and is home to a diverse East and Southeast Asian community.
Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
are heavily concentrated in the suburban cities of
Federal Way and
Auburn to the south, and in
Lynnwood to the north. Tacoma is home to thousands of
Cambodians, and has one of the largest Cambodian-American communities in the United States, along with
Long Beach, California
Long Beach is a city in Los Angeles County, California. It is the 42nd-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 466,742 as of 2020. A charter city, Long Beach is the seventh-most populous city in California.
Incorporate ...
, and
Lowell, Massachusetts
Lowell () is a city in Massachusetts, in the United States. Alongside Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, It is one of two traditional county seat, seats of Middlesex County, Massachusetts, Middlesex County. With an estimated population of 115,5 ...
. The
Vietnamese and
Filipino populations of Washington are mostly concentrated within the Seattle metropolitan area. Washington state has the second highest percentage of Pacific Islander people in the mainland U.S. (behind
Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its ...
); the Seattle-Tacoma area is home to more than 15,000 people of
Samoan ancestry, who mainly reside in southeast Seattle, Tacoma, Federal Way, and in
SeaTac.
[Race, Hispanic or Latino, Age, and Housing Occupancy: 2010 more information 2010 Census Redistricting Data (Public Law 94-171) Summary File](_blank)
. Factfinder2census.gov. (2010). Retrieved December 30, 2011.
The most numerous (ethnic, not racial, group) are Latinos at 11%, as
Mexican Americans formed a large ethnic group in the
Chehalis Valley Chehalis may refer to:
People
* Chehalis people, a Native American people of Washington state
**Lower Chehalis language
**Upper Chehalis language
* Sts'Ailes people (Chehalis people), a First Nation in British Columbia
* Chehalis First Nation, Brit ...
,
Skagit Valley, farming areas of
Yakima Valley, and
Eastern Washington. They were reported to at least date as far back as the 1800s. But it was in the late 20th century, that large-scale Mexican immigration and other Latinos settled in the southern suburbs of Seattle, with limited concentrations in King,
Pierce, and
Snohomish Counties during the region's real estate construction booms in the 1980s and 1990s.
Additionally, Washington has a large
Ethiopian
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of ...
community, with many
Eritrean residents as well.
Both emerged in the late 1960s, and developed since 1980. An estimated 30,000
Somali
Somali may refer to:
Horn of Africa
* Somalis, an inhabitant or ethnicity associated with Greater Somali Region
** Proto-Somali, the ancestors of modern Somalis
** Somali culture
** Somali cuisine
** Somali language, a Cushitic language
** Soma ...
immigrants reside in the Seattle area.
Languages
In 2010, 82.51% (5,060,313) of Washington residents age5 and older spoke English at home as a
primary language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother to ...
, while 7.79% (477,566) spoke Spanish, 1.19% (72,552) Chinese (which includes
Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
and
Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern standa ...
), 0.94% (57,895) Vietnamese, 0.84% (51,301)
Tagalog
Tagalog may refer to:
Language
* Tagalog language, a language spoken in the Philippines
** Old Tagalog, an archaic form of the language
** Batangas Tagalog, a dialect of the language
* Tagalog script, the writing system historically used for Tagal ...
, 0.83% (50,757) Korean, 0.80% (49,282) Russian, and 0.55% (33,744) German. In total, 17.49% (1,073,002) of Washington's population age5 and older spoke a
mother language other than English.
Religion
Major religious affiliations of the people of Washington are:
*
Christian: 60%
**
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
: 40%
***
Evangelical Protestant
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual exp ...
: 25%
***
Mainline Protestant: 13%
***
Black church: 2%
**
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
: 17%
**
Latter-day Saint: 4%
*
Unaffiliated: 32%
*
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
: 1%
*
Hindu: 1%
*
Muslim: 0.5%
*
Other religions 3%
The largest denominations by number of adherents in 2010 were the
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, with 784,332;
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a nontrinitarian Christian church that considers itself to be the restoration of the original church founded by Jesus Christ. The ...
, with 282,356; and the
Assemblies of God
The Assemblies of God (AG), officially the World Assemblies of God Fellowship, is a group of over 144 autonomous self-governing national groupings of churches that together form the world's largest Pentecostal denomination."Assemblies of God". ...
, with 125,005.
is the largest
Wiccan church in the country.
Like other West Coast states, the percentage of Washington's population identifying themselves as "
non-religious" is higher than the national average.
Economy

Washington has a relatively strong economy, with a total
gross state product of $612,996.5 million in 2019, placing it fifth in the nation and growing by 6.5 percent per year—the fastest rate in the United States. The
minimum wage
A minimum wage is the lowest remuneration that employers can legally pay their employees—the price floor below which employees may not sell their labor. Most countries had introduced minimum wage legislation by the end of the 20th century. B ...
as of January 1, 2021, was $13.69 an hour, the second highest of any state or district in the country behind Washington D.C at $14.00 an hour. Significant business within the state include the design and manufacture of aircraft (
Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and ...
),
automotive (
Paccar), computer software development (
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation, multinational technology company, technology corporation producing Software, computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at th ...
,
Bungie,
Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...
,
Nintendo of America,
Valve,
ArenaNet),
telecom (
T-Mobile US),
electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
,
biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
,
aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It h ...
production, lumber and wood products (
Weyerhaeuser), mining, beverages (
Starbucks
Starbucks Corporation is an American multinational chain of coffeehouses and roastery reserves headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It is the world's largest coffeehouse chain.
As of November 2021, the company had 33,833 stores in 80 ...
,
Jones Soda), real estate (
John L. Scott
John L. Scott Real Estate is headquartered in Bellevue, WA. It currently has over 110 offices with over 3,000 brokers in Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Northern California.
Current
John L. Scott is owned and operated by a third-generation Scott ...
,
Colliers International
Colliers is a Canada-based diversified professional services and investment management company with approximately 18,000 employees in more than 400 offices in 63 countries.
The firm provides services to commercial real estate users, owners, inv ...
,
Windermere Real Estate
Windermere Real Estate is a real estate company founded in 1972 and based in Seattle, Washington. It is a privately held company and is the largest regional real estate company in the Western U.S., with over 300 offices and 6,500 agents.
History ...
, Kidder Mathews), retail (
Nordstrom,
Eddie Bauer,
Car Toys,
Costco
Costco Wholesale Corporation ( doing business as Costco Wholesale and also known simply as Costco) is an American multinational corporation which operates a chain of membership-only big-box retail stores ( warehouse club). As of 2022, Cost ...
,
R.E.I.), and tourism (
Alaska Airlines
Alaska Airlines is a major American airline headquartered in SeaTac, Washington, within the Seattle metropolitan area. It is the sixth largest airline in North America when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and the nu ...
,
Expedia, Inc.
Expedia Group, Inc. is an American online travel shopping company for consumer and small business travel. Its websites, which are primarily travel fare aggregators and travel metasearch engines, include Expedia.com, Hotels.com, Vrbo (previousl ...
). A ''
Fortune'' magazine survey of the top 20 Most Admired Companies in the U.S. has four Washington-based companies: Amazon, Starbucks, Microsoft, and Costco. At over 80 percent the state has significant amounts of hydroelectric power generation. Also, significant amounts of trade with Asia pass through the ports of the Puget Sound, leading to a number six ranking of U.S. ports (ranking combines twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs) moved and infrastructure index).
With the passage of Initiative 1183, the Washington State Liquor Control Board (WSLCB) ended its monopoly of all-state liquor store and liquor distribution operations on June 1, 2012.
, the state's unemployment rate was 3.7 percent.
Taxes

The state of Washington is one of seven states that do not levy a personal
income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
. The state does not collect a
corporate income tax or
franchise tax either. Washington businesses are responsible for various other state levies, including the
business and occupation tax The business and occupation tax (often abbreviated as B&O tax or B/O tax) is a type of tax levied by the U.S. states of Washington, West Virginia, and, as of 2010, Ohio, and by municipal governments in West Virginia and Kentucky.
It is a type of gr ...
(B & O), a
gross receipts tax which charges varying rates for different types of businesses.
Washington's state base
sales tax is 6.5%, which is combined with a local sales tax that varies by locality. The combined state and local retail sales tax rates increase the taxes paid by consumers, depending on the variable local sales tax rates, generally between 7.5% and 10%.
As of March 2017, the combined sales tax rate in Seattle and Tacoma was 10.1%.
The cities of Lynnwood and Mill Creek have the highest sale tax rate in the state at 10.5%. These taxes apply to services as well as products. Most foods are exempt from sales tax. However, prepared foods,
dietary supplements, and
soft drinks remain taxable.
An
excise tax
file:Lincoln Beer Stamp 1871.JPG, upright=1.2, 1871 U.S. Revenue stamp for 1/6 barrel of beer. Brewers would receive the stamp sheets, cut them into individual stamps, cancel them, and paste them over the Bunghole, bung of the beer barrel so when ...
applies to certain products such as gasoline, cigarettes, and alcoholic beverages.
Property tax was the first tax levied in the state of Washington, and its collection accounts for about 30% of Washington's total state and local revenue. It continues to be the most important revenue source for
public schools
Public school may refer to:
*State school (known as a public school in many countries), a no-fee school, publicly funded and operated by the government
*Public school (United Kingdom), certain elite fee-charging independent schools in England and ...
, fire protection,
libraries, parks and recreation, and other special-purpose districts.
All
real property and
personal property are subject to tax unless specifically exempted by law. Most personal property owned by individuals is exempt from tax.
Personal property tax
A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inherit ...
applies to personal property used when conducting business, or to other personal property not exempt by law. All property taxes are paid to the county treasurer's office where the property is located. Neither does the state assess any tax on retirement income earned and received from another state. Washington does not collect
inheritance tax
An inheritance tax is a tax paid by a person who inherits money or property of a person who has died, whereas an estate tax is a levy on the estate (money and property) of a person who has died.
International tax law distinguishes between an e ...
es. However, the
estate tax is de-coupled from the federal estate tax laws, and therefore, the state imposes its estate tax.
Washington state has the 18th highest per capita
effective tax rate in the United States, as of 2017. Their tax policy differs from neighboring Oregon's, which levies no sales tax, but does levy a personal income tax. This leads to
border economic anomalies in the
Portland-Vancouver metropolitan area. Additional border economies exist with neighboring British Columbia and Idaho.
Agriculture

Washington is a leading agricultural state. The following figures are from th
Washington State Department of Agricultureand the USDA, National Agricultural Statistics Service, Washington Field Office. For 2018, the total value of Washington's agricultural products was $10.6 billion.
In 2014, Washington ranked first in the nation in production of red
raspberries (90.5 percent of total U.S. production),
hops (79.3 percent),
spearmint oil (75 percent), wrinkled seed
peas (70.4 percent),
apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ances ...
s (71.1 percent), sweet
cherries (62.3 percent), pears (45.6 percent),
Concord grapes (55.1 percent),
carrots for processing (30.6 percent), and green peas for processing (32.4 percent).
Washington also ranked second in the nation in the production of fall potatoes (a quarter of the nation's production),
nectarines,
apricots, asparagus, all raspberries, grapes (all varieties taken together), sweet corn for processing (a quarter of the nation's production), and summer onions (a fifth of the nation's production). Washington also ranked third in the nation in the production of dried peas, lentils, onions, and peppermint oil.
The apple industry is of particular importance to Washington. Because of the favorable climate of dry, warm summers and cold winters of central Washington, the state has led the U.S. in apple production since the 1920s. Two areas account for the vast majority of the state's apple crop: the Wenatchee–Okanogan region (comprising
Chelan,
Okanogan,
Douglas, and
Grant counties), and the Yakima region (comprising
Yakima,
Benton Benton may refer to:
Places
Canada
*Benton, a local service district south of Woodstock, New Brunswick
*Benton, Newfoundland and Labrador
United Kingdom
* Benton, Devon, near Bratton Fleming
* Benton, Tyne and Wear
United States
*Benton, Alabam ...
, and
Kittitas counties). Washington produces seven principal varieties of apples which are exported to more than sixty countries.
Wine

Washington ranks second
in the United States in the production of wine, behind only
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
.
[A. Domine (ed) ''Wine'' pg 798–800 Ullmann Publishing 2008 ] By 2006, the state had over of
vineyards, a
harvest of of grapes, and exports going to more than forty countries around the world from the state's 600
wineries. By 2021, that number had grown to 1050 wineries. While there are some
viticultural activities in the cooler, wetter
western half of the state, almost all (99%) of wine grape production takes place in the desert-like
eastern half.
[J. Robinson (ed) ''The Oxford Companion to Wine'', Third Edition, pg. 761–762 Oxford University Press 2006 ] The
rain shadow of the Cascade Range leaves the
Columbia River Basin with around of annual rain fall, making
irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been dev ...
and
water rights of paramount interest to the Washington wine industry. Viticulture in the state is also influenced by long sunlight hours (on average, two more hours a day than in California during the
growing season) and consistent temperatures.
[C. Fallis, editor ''The Encyclopedic Atlas of Wine'', p. 50 Global Book Publishing 2006 ]
Internet access
As of December 2014, there are 124 broadband providers offering service to Washington state; 93 percent of consumers have access to broadband speeds of 25/3Mbit/s or more.
From 2009–2014, the Washington State Broadband Project was awarded $7.3 million in federal grants, but the program was discontinued in 2014. For infrastructure, another $166 million has been awarded since 2011 for broadband infrastructure projects in Washington state.
''
U.S. News & World Report'' ranked Washington second nationally for household internet access, and sixth for online download speed, based on data from 2014 and 2015.
Transportation


Washington's state transportation system comprises several modes that are maintained by various government entities. The
state highway system, called
State Routes, includes over of roads and the
Washington State Ferries system, the largest of its kind in the nation and the third largest in the world. There are also of local roads maintained by cities and counties, as well as several ferries operated by local governments.
There are 140
public airfields in Washington, including 16
state airports owned by the
Washington State Department of Transportation.
Seattle-Tacoma International Airport (Sea-Tac) is the major commercial airport of greater Seattle.
Boeing Field in Seattle is one of the busiest primary non-hub airports in the U.S.
There are extensive waterways around Washington's largest cities, including Seattle,
Bellevue, Tacoma, and
Olympia. The state highways incorporate an extensive network of bridges and the largest ferry system in the United States to serve transportation needs in the Puget Sound area. Washington's marine highway constitutes a fleet of twenty-eight ferries that navigate
Puget Sound and its inland waterways to 20 different ports of call, completing close to 147,000 sailings each year. Washington is home to four of the five longest
floating bridges in the world: the
Evergreen Point Floating Bridge,
Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge and
Homer M. Hadley Memorial Bridge over
Lake Washington, and the
Hood Canal Bridge
The Hood Canal Bridge (officially William A. Bugge Bridge) is a floating bridge in the northwest United States, located in western Washington. It carries State Route 104 across Hood Canal of Puget Sound and connects the Olympic and Kitsap P ...
which connects the Olympic Peninsula and
Kitsap Peninsula. Among its most famous bridges is the
Tacoma Narrows Bridge, which collapsed in 1940 and was rebuilt. Washington has 75 port districts,
including several major
seaports on the Pacific Ocean. Among these are ports in
Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a port, seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the county seat, seat of King County, Washington, King County, Washington (state), Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in bo ...
,
Tacoma,
Kalama,
Anacortes
Anacortes ( ) is a city in Skagit County, Washington, United States. The name "Anacortes" is an adaptation of the name of Anne Curtis Bowman, who was the wife of early Fidalgo Island settler Amos Bowman.[Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. Th ...]
,
Everett,
Longview, Grays Harbor, Olympia, and
Port Angeles. The Columbia and Snake rivers also provide of inland waterways that are navigable by barges as far east as
Lewiston, Idaho.
The Cascade Mountain Range also impedes transportation. Washington operates and maintains roads over seven major
mountain passes and eight minor passes. During the winter months, some of these passes are plowed, sanded, and kept safe with avalanche control. Not all stay open through the winter. The North Cascades Highway,
State Route 20
Route 20, or Highway 20, may refer to:
International
* European route E20
Australia
* Sturt Highway (NSW/VIC/SA)
* Yarra Bank Highway
Brazil
* BR-020
Canada
* Alberta Highway 20
* British Columbia Highway 20
* Manitoba Highway 20
*Ne ...
, closes every year due to snowfall and avalanches in the area of
Washington Pass. The
Cayuse Cayuse may refer to:
*Cayuse people, a people native to Oregon, United States
*Cayuse language, an extinct language of the Cayuse people
*Cayuse, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the United States
*Cayuse horse, an archaic term for a feral or ...
and
Chinook passes east of Mount Rainier also close in winter.
Washington is crossed by several
freight railroads, and Amtrak's passenger
Cascade route between Eugene, Oregon, and Vancouver, BC is the eighth busiest Amtrak service in the U.S. Seattle's
King Street Station, the busiest station in Washington, and 15th busiest in the U.S., serves as the terminus for the two long-distance Amtrak routes in Washington, the
Empire Builder to Chicago and the
Coast Starlight to Los Angeles. The
Sounder commuter rail service operates in Seattle and its surrounding cities, between
Everett and
Lakewood Lakewood may refer to:
Places Australia
* Lakewood, Western Australia, an abandoned town in Western Australia
Canada
* Lakewood, Edmonton, Alberta
* Lakewood Suburban Centre, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan
Philippines
* Lakewood, Zamboanga del S ...
. The intercity network includes the
Cascade Tunnel, the longest railroad tunnel in the United States, which is part of the
Stevens Pass route on the BNSF Northern Transcom.
Sound Transit
Link light rail currently operates in the Seattle area at a length of , and in
Tacoma at a length of . The entire system has a funded expansion plan that will expand light rail to a total of 116 miles by 2041. Seattle also has a
streetcar network
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport ...
with two lines and plans to expand further by 2025. 32 local bus transit systems exist across the state,
the busiest being
King County Metro, located in Seattle and King County, with just above 122 million riders in 2017. Residents of Vancouver have resisted proposals to extend Portland's mass transit system into Washington.
Environment
Hanford Nuclear Reservation is currently the most
contaminated nuclear site in the United States and is the focus of the nation's largest
environmental cleanup. The radioactive materials are known to be leaking from Hanford into the environment.
In 2007, Washington became the first state in the nation to target all forms of highly toxic
brominated flame retardants known as
PBDEs for elimination from the many common household products in which they are being used. A 2004 study of 40 mothers from Oregon, Washington, British Columbia, and Montana found PBDEs in the breast milk of every woman tested.
Three recent studies by the
Washington State Department of Ecology showed toxic chemicals banned decades ago linger in the environment and concentrate in the food chain. In one of the studies, state government scientists found unacceptable levels of toxic substances in 93 samples of freshwater fish from 45 sites. The toxic substances included
PCBs,
dioxins, two chlorinated pesticides,
DDE,
dieldrin and PBDEs. As a result of the study, the department will investigate the sources of PCBs in the Wenatchee River, where unhealthy levels of PCBs were found in mountain whitefish. Based on the 2007 information and a previous 2004 Ecology study, the
Washington State Department of Health advises the public not to eat
mountain whitefish from the
Wenatchee River from
Leavenworth downstream to where the river joins the Columbia, due to unhealthy levels of PCBs. Study results also showed high levels of contaminants in fish tissue that scientists collected from Lake Washington and the Spokane River, where fish consumption advisories are already in effect.
On March 27, 2006, Governor
Christine Gregoire signed into law the recently approved House Bill 2322. This bill would limit
phosphorus content in dishwashing detergents statewide to 0.5 percent over the next six years. Though the ban would be effective statewide in 2010, it would take place in
Whatcom County,
Spokane County, and
Clark County in 2008. A recent discovery had linked high contents of phosphorus in water to a boom in
algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from ...
population. An invasive amount of algae in bodies of water would lead to a variety of excess ecological and technological issues.
Government and politics
State government

Washington's
executive branch
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a state.
In political systems b ...
is headed by a governor elected for a four-year term. The current statewide elected officials are:
*
Jay Inslee
Jay Robert Inslee (; born February 9, 1951) is an American politician, lawyer, and economist who has served as the 23rd List of governors of Washington, governor of Washington since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democ ...
,
Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
(D)
*
Denny Heck,
Lieutenant Governor (D)
*
Steve Hobbs,
Secretary of State (D)
*
Mike Pellicciotti,
State Treasurer (D)
*
Patrice McCarthy,
State Auditor (D)
*
Bob Ferguson,
Attorney General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general or attorney-general (sometimes abbreviated AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. The plural is attorneys general.
In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have exec ...
(D)
*
Chris Reykdal,
Superintendent of Public Instruction
A state education agency or state department of education is the state-level government organization within each U.S. state or territory responsible for education, including providing information, resources, and technical assistance on educationa ...
(D)
*
Hilary Franz,
Commissioner of Public Lands (D)
*
Mike Kreidler,
Insurance Commissioner (D)
The
bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single gro ...
Washington State Legislature is the state's
legislative branch. The
state legislature
A state legislature is a legislative branch or body of a political subdivision in a federal system.
Two federations literally use the term "state legislature":
* The legislative branches of each of the fifty state governments of the United Sta ...
is composed of a
lower House of Representatives and an
upper
Upper may refer to:
* Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot
* Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both
* ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found fo ...
State Senate. The state is divided into 49 legislative districts of equal population, each of which elects two representatives and one senator. Representatives serve two-year terms, while senators serve for four years. There are no
term limits. The
Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
has a majority in the House and Senate.
The
Washington Supreme Court is the highest court in the state. Nine justices serve on the bench and are elected statewide.
Federal representation
The two current
United States senators from Washington are
Patty Murray and
Maria Cantwell, both Democrats. Murray has represented the state since 1993, while Cantwell was first elected in 2001. The state is one of four with two female senators.
Washington's ten representatives in the United States House of Representatives (
''see map of districts'') as of the 2020 election are
Suzan DelBene (D-1),
Rick Larsen (D-2),
Jaime Herrera Beutler (R-3),
Dan Newhouse (R-4),
Cathy McMorris Rodgers (R-5),
Derek Kilmer (D-6),
Pramila Jayapal (D-7),
Kim Schrier (D-8),
Adam Smith (D-9), and
Marilyn Strickland
Marilyn Strickland (born September 25, 1962) is an American politician who is the U.S. representative from Washington's 10th congressional district. The district is based in the state capital of Olympia, and also includes much of eastern Tacom ...
(D-10).
Due to
Congressional redistricting as a result of the
2010 Census, Washington gained one seat in the
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together the ...
. With the extra seat, Washington also gained one electoral vote, raising its total to 12.
Politics

The state is typically thought of as politically divided by the Cascade Mountains, with Western Washington being
liberal (particularly the ) and Eastern Washington being
conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
. Washington has voted for the
Democratic
Democrat, Democrats, or Democratic may refer to:
Politics
*A proponent of democracy, or democratic government; a form of government involving rule by the people.
*A member of a Democratic Party:
**Democratic Party (United States) (D)
**Democratic ...
presidential nominee in every election since
1988.
Although the Eastern half of the state votes heavily
Republican, the overwhelming
Democratic
Democrat, Democrats, or Democratic may refer to:
Politics
*A proponent of democracy, or democratic government; a form of government involving rule by the people.
*A member of a Democratic Party:
**Democratic Party (United States) (D)
**Democratic ...
dominance in the
Seattle metropolitan area has turned Washington into a reliably
blue state.
Michael Dukakis
Michael Stanley Dukakis (; born November 3, 1933) is an American retired lawyer and politician who served as governor of Massachusetts from 1975 to 1979 and again from 1983 to 1991. He is the longest-serving governor in Massachusetts history a ...
narrowly won Washington in 1988, and Democrats have won the state in every presidential election since, and by safe margins since
2008.
Washington was considered a key swing state in 1968, and it was the only western state to give its electoral votes to Democratic nominee
Hubert Humphrey
Hubert Horatio Humphrey Jr. (May 27, 1911 – January 13, 1978) was an American pharmacist and politician who served as the 38th vice president of the United States from 1965 to 1969. He twice served in the United States Senate, representing M ...
over his Republican opponent
Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was t ...
. Washington was considered a part of the 1994
Republican Revolution
The "Republican Revolution", "Revolution of '94", or "Gingrich Revolution" are political slogans that refer to the Republican Party (GOP) success in the 1994 U.S. mid-term elections, which resulted in a net gain of 54 seats in the House of ...
, and had the biggest pick-up in the house for Republicans, who picked up seven of Washington's nine House seats. However, this dominance did not last for long, as Democrats picked up one seat in the 1996 election, and two more in 1998, giving the Democrats a 5–4 majority.
The
governorship is held by Democrat
Jay Inslee
Jay Robert Inslee (; born February 9, 1951) is an American politician, lawyer, and economist who has served as the 23rd List of governors of Washington, governor of Washington since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democ ...
, who was elected to his first term in the
2012 gubernatorial election and, after the 2020 election, became the first incumbent in more than 40 years to be elected for a third term. In 2013 and 2014, both houses of the
Washington State Legislature (the
Washington Senate and the
Washington House of Representatives) were controlled by Democrats. The state senate was under Republican control, due to two Democrats' joining Republicans to form the
Majority Coalition Caucus. After the 2014 elections, the Democrats retained control of the House, while Republicans took a majority in the Senate without the need for a coalition. In November 2017, a special election gave Democrats a one-seat majority in the Senate and complete control over state government. Since then, in the 2018 election, the Democrats have only expanded their majorities.
No state has gone longer without a Republican governor than
Washington. Democrats have controlled the
Washington Governor's Mansion for years; the last Republican Governor was
John Spellman, who left office in 1985. Washington has not voted for a Republican senator, governor, or presidential candidate since 1994, tying Delaware for the longest streak in the country.
Washington uses the
non-partisan blanket primary system after the approval of
Initiative 872 in 2004. All candidates run on the same ballot during primary elections and the top two candidates advance to the general election in November, regardless of party affiliation. This has resulted in several same-party general election match-ups.
In a 2020 study, Washington was ranked as the second easiest state for citizens to vote in.
Notable legislation

Washington is one of the ten states to have legalized
assisted suicide. In 2008 the
Washington Death with Dignity Act ballot initiative passed and became law.
In November 2009, Washington voters approved full domestic partnerships via
Referendum 71, marking the first time voters in any state expanded recognition of same-sex relationships at the ballot box. Three years later, in November 2012,
same-sex marriage was affirmed via
Referendum 74, making Washington one of only three states to have approved same-sex marriage by popular vote.
Also in November 2012, Washington was one of the first two states to approve the legal sale and possession of
cannabis for both recreational and medical use with
Initiative 502. Although marijuana is still illegal under U.S. federal law, persons 21 and older in Washington state can possess up to one ounce of marijuana, 16 ounces of marijuana-infused product in solid form, 72 ounces of marijuana-infused product in liquid form, or any combination of all three, and can legally consume marijuana and marijuana-infused products.
In November 2016, voters approved Initiative 1433, which among other things requires employers to guarantee paid
sick leave to most workers. On January 1, 2018, the law went into effect, with Washington becoming the seventh state with paid sick leave requirements.
With the passage of
Initiative 1639 in the 2018 elections, Washington adopted stricter gun laws.
Washington enacted a measure in May 2019 in favor of
sanctuary cities, similar to California and Oregon laws which are among the strongest statewide mandates in the nation.
In 2019 the legislature passed the Clean Energy Transformation Act, which requires all electricity sales to be from zero-carbon sources by 2045 and net-zero by 2030.
Education
Elementary and secondary education
As of the 2020–2021 school year, 1,094,330 students were enrolled in elementary and secondary schools in Washington, with 67,841 teachers employed to educate them. As of August 2009, there were 295
school district
A school district is a special-purpose district that operates local public primary and secondary schools in various nations.
North America United States
In the U.S, most K–12 public schools function as units of local school districts, whi ...
s in the state, serviced by nine
Educational Service Districts.
Washington School Information Processing Cooperative (a non-profit opt-in state agency) provides information management systems for fiscal & human resources and student data. Elementary and secondary schools are under the jurisdiction of the
Washington State Office of Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI).
High school
juniors
Junior or Juniors may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Junior'' (Junior Mance album), 1959
* ''Junior'' (Röyksopp album), 2009
* ''Junior'' (Kaki King album), 2010
* ''Junior'' (LaFontaines album), 2019
Films
* ''Junior'' (1994 ...
and
seniors in Washington have the option of using the state's
Running Start program. Begun by the
state legislature
A state legislature is a legislative branch or body of a political subdivision in a federal system.
Two federations literally use the term "state legislature":
* The legislative branches of each of the fifty state governments of the United Sta ...
in 1990, it allows students to attend institutions of higher education at public expense, simultaneously earning high school and college credit.
The state also has several public arts-focused high schools including
Tacoma School of the Arts, the
Vancouver School of Arts and Academics
The Vancouver School of Arts and Academics (VSAA) is a public arts magnet school for grades 6 to 12 in Vancouver, Washington, United States. It is part of the Vancouver Public Schools and in addition to traditional academic studies, the school's ...
, and
The Center School. There are also four Science and Math based high schools: one in the
Tri-Cities Tri-Cities most often refers to:
*Tri-Cities, Tennessee, United States
*Tri-Cities, Washington, United States
Tri-City, Tricity or Tri-Cities may also refer to:
Populated places
Americas
Canada
*Tri-Cities (British Columbia), consisting of Co ...
known as Delta, one in Tacoma known as SAMI, another in Seattle known as
Raisbeck Aviation High School
Raisbeck Aviation High School (or RAHS), part of the Highline School District, is located in Tukwila, Washington. The school is an aviation- and aerospace-themed STEM school and one of the Highline School District's small schools. It is focused o ...
, and one in Redmond known as
Tesla STEM High School.
Higher education
There are more than 40 institutions of higher education in Washington. The state has major research universities, technical schools, religious schools, and private career colleges. Colleges and universities include the
University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington.
Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seat ...
,
Seattle University,
Washington State University,
Western Washington University,
Eastern Washington University,
Central Washington University,
Seattle Pacific University,
Saint Martin's University,
Pacific Lutheran University,
Gonzaga University,
University of Puget Sound,
The Evergreen State College,
Whitman College, and
Walla Walla University.
Health care
Insurance
The top two health insurers as of 2017 were
Premera Blue Cross, with 24 percent market share, followed by
Kaiser Permanente
Kaiser Permanente (; KP), commonly known simply as Kaiser, is an American integrated managed care consortium, based in Oakland, California, United States, founded in 1945 by industrialist Henry J. Kaiser and physician Sidney Garfield. Kaiser ...
at 21 percent. For the individual market,
Molina Healthcare had the top share at 23%.
The state adopted the
Washington Healthplanfinder system in 2014 after the passage of the federal
Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and colloquially known as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by Pres ...
(also known as "ObamaCare").
The state of Washington reformed its health care system in 1993 through the Washington Health Services Act. The legislation required individuals to obtain health insurance or face penalties, and required employers to provide insurance to employees. In addition, health insurance companies were required to sell policies to all individuals, regardless of pre-existing conditions, and cover basic benefits. The act was mostly repealed in 1995 before it could go into full effect.
Facilities
Hospitals exist across the state, but many of Washington's best-known medical facilities are located
in and around Seattle. The Seattle–Tacoma area has six major hospitals:
Harborview Medical Center,
University of Washington Medical Center,
Seattle Children’s
Seattle Children's, formerly Children's Hospital and Regional Medical Center, formerly Children's Orthopedic Hospital, is a children's hospital in the Laurelhurst neighborhood of Seattle, Washington. The hospital specializes in the care of inf ...
,
Swedish Medical Center,
MultiCare Tacoma General Hospital
MultiCare Health System's Tacoma General Hospital is the largest hospital in Tacoma, Washington. It is a level II trauma center with 437 beds and the second largest obstetrical care center in the state of Washington. Tacoma General began ser ...
, and
St. Joseph Medical Center. The Seattle-area hospitals are concentrated on
First Hill, which is home to
Virginia Mason Medical Center (the neighborhood has received the nickname "Pill Hill" owing to the high concentration of healthcare facilities).
Culture
Sports
Pickleball, a racquet sport invented on
Bainbridge Island
Bainbridge Island is a city and island in Kitsap County, Washington. It is located in Puget Sound. The population was 23,025 at the 2010 census and an estimated 25,298 in 2019, making Bainbridge Island the second largest city in Kitsap County ...
in 1965, was designated as Washington's official
state sport
This is a list of official U.S. state sports as recognized by state legislatures.
Table
See also
* List of U.S. state, district, and territorial insignia
* National sport
A national sport is considered to be an intrinsic part of the culture o ...
in 2022.
For two years in a row, 2021 and 2022, the sport was named the fastest growing sport in the United States by the Sports and Fitness Industry Association (SFIA).
Major professional teams
Minor professional and amateur teams
College sports teams
;
NCAA Division I
NCAA Division I (D-I) is the highest level of intercollegiate athletics sanctioned by the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) in the United States, which accepts players globally. D-I schools include the major collegiate athleti ...
*
Washington Huskies (
Pac-12 Conference
The Pac-12 Conference is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference, that operates in the Western United States, participating in 24 sports at the NCAA Division I level. Its College football, football teams compete in the NCAA D ...
;
Football Bowl Subdivision)
*
Washington State Cougars (
Pac-12 Conference
The Pac-12 Conference is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference, that operates in the Western United States, participating in 24 sports at the NCAA Division I level. Its College football, football teams compete in the NCAA D ...
;
Football Bowl Subdivision)
*
Gonzaga Bulldogs (
West Coast Conference)
*
Seattle Redhawks (
Western Athletic Conference
The Western Athletic Conference (WAC) is an NCAA Division I conference. The WAC covers a broad expanse of the western United States with member institutions located in Arizona, California, New Mexico, Utah, Washington, and Texas.
Due to most of ...
)
*
Eastern Washington Eagles
The Eastern Washington Eagles are the intercollegiate varsity athletic teams that represent Eastern Washington University, located in Cheney, southwest of Spokane. A member of the Big Sky Conference, EWU's athletic program comprises five men's ...
(
Big Sky Conference
The Big Sky Conference (BSC) is a collegiate athletic conference affiliated with the NCAA's Division I with football competing in the Football Championship Subdivision. Member institutions are located in the western United States in the eigh ...
;
Football Championship Subdivision)
;
NCAA Division II
*
Central Washington Wildcats
*
Saint Martin's Saints
*
Seattle Pacific Falcons
*
Western Washington Vikings
The Western Washington Vikings represent Western Washington University in intercollegiate sports in the Great Northwest Athletic Conference of the NCAA Division II with the exception of the women's rowing team which is a member of the Northwes ...
;
NCAA Division III
*
Pacific Lutheran Lutes
*
Puget Sound Loggers
*
Whitman Blues
Whitman College is a private liberal arts college in Walla Walla, Washington. The school offers 53 majors and 33 minors in the liberal arts and sciences, and it has a student-to-faculty ratio of 9:1. Whitman was the first college in the Pacific ...
*
Whitworth Pirates
Individual sports
The
Seattle Open Invitational golf tournament was part of the
PGA Tour
The PGA Tour (stylized in all capital letters as PGA TOUR by its officials) is the organizer of professional golf tours in the United States and North America. It organizes most of the events on the flagship annual series of tournaments also k ...
from the 1930s to the 1960s. The
GTE Northwest Classic was part of the
Senior PGA Tour
PGA Tour Champions (formerly the Senior PGA Tour and the Champions Tour) is a men's professional senior golf tour, administered as a branch of the PGA Tour.
History and format
The Senior PGA Championship, founded in 1937, was for many year ...
from 1986 to 1995, and the
Boeing Classic since 2005. In addition, the
2015 U.S. Open was held at
Chambers Bay, and several major tournaments were held at
Sahalee Country Club.
Pacific Raceways is a motorsports venue that has hosted the Northwest Nationals of the
NHRA Mello Yello Drag Racing Series and a round of the
Trans-Am Series.
The
WTA Seattle tennis tournament was part of the
WTA Tour from 1977 to 1982.
Symbols, honors, and names
Four ships of the
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
, including two battleships, have been named
USS ''Washington'' in honor of the state. Previous ships had held that name in honor of George Washington.
The Evergreen State
The state's nickname, "The Evergreen State",
[ was proposed in 1890 by Charles T. Conover of Seattle. The name proved popular as the forests were full of ]evergreen
In botany, an evergreen is a plant which has foliage that remains green and functional through more than one growing season. This also pertains to plants that retain their foliage only in warm climates, and contrasts with deciduous plants, which ...
trees and the abundance of rain keeps the shrubbery and grasses green throughout the year. Although the nickname is widely used by the state, appearing on vehicle license plates for instance, it has not been officially adopted.[ The Evergreen State College, a state-funded institution in Olympia, also takes its name from this nickname.
]
State symbols
The state song is " Washington, My Home", the state bird A state bird is the insignia of a nation or a state (sub-national entity).
For lists of these animals, see:
* List of national birds, national birds on country level
* List of Australian bird emblems, for the Australian states
* List of Brazilian ...
is the American goldfinch, the state fruit is the apple, and the state vegetable is the Walla Walla sweet onion. The state dance, adopted in 1979, is the square dance. The state tree is the western hemlock. The state flower is the coast rhododendron. The state fish is the steelhead.[ The state folk song is "]Roll On, Columbia, Roll On
"Roll On, Columbia, Roll On" is an American folk song written in 1941 by American folk singer Woody Guthrie, who popularized the song through his own recording of it. The song glamorized the harnessing of the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwes ...
" by Woody Guthrie
Woodrow Wilson Guthrie (; July 14, 1912 – October 3, 1967) was an American singer-songwriter, one of the most significant figures in American folk music. His work focused on themes of American Left, American socialism and anti-fascism. He ...
. The unofficial, but popularly accepted, state rock song is Louie Louie. The state grass is bluebunch wheatgrass. The state insect
State insects are designated by 48 individual states of the fifty United States. Some states have more than one designated insect, or have multiple categories (e.g., state insect and state butterfly, etc.). Iowa and Michigan are the two states with ...
is the green darner dragonfly. The state gem is petrified wood. The state fossil is the Columbian mammoth. The state marine mammal is the orca
The orca or killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') is a toothed whale belonging to the oceanic dolphin family, of which it is the largest member. It is the only extant species in the genus '' Orcinus'' and is recognizable by its black-and-white ...
. The state soil is Tokul soil. The state land mammal is the Olympic marmot.[ The state seal (featured in the state flag as well) was inspired by the unfinished portrait of President George Washington by Gilbert Stuart. The ]state sport
This is a list of official U.S. state sports as recognized by state legislatures.
Table
See also
* List of U.S. state, district, and territorial insignia
* National sport
A national sport is considered to be an intrinsic part of the culture o ...
is pickleball.
Friendship partners
Washington has relationships with many provinces, states, and other entities worldwide.
* Jalisco
Jalisco (, , ; Nahuatl: Xalixco), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Jalisco ; Nahuatl: Tlahtohcayotl Xalixco), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal ...
, Mexico (1996)
See also
* Index of Washington-related articles
The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the U.S. state of Washington.
0–9
* .wa.us – Internet second-level domain for the state of Washington
* 42nd state to join the United States of America
A
*Adjacent states an ...
* Outline of Washington Outline of Washington may refer to:
* Outline of Washington (state)
* Outline of Washington, D.C.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to District of Columbia:
Washington, D.C., legally named the District of ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* .
*
Volume 2
* Edmond S. Meany
''History of the State of Washington''
New York: Macmillan, 1909.
* . Reprinted from the ''Washington Historical Quarterly'', 1918–1919.
External links
*
The official tourism site of the State of Washington
Washington State Databases
Secretary of State's Washington History website
Constitution of the State of Washington
Washington Administrative Code (State Administrative Rules)
State Code Search Tool
Energy Profile for Washington
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Washington
Washington State Facts from USDA
U.S. Census Bureau Quick Facts: Washington
Online Encyclopedia of Washington State History
Police Scanner Information for Washington state
CWU Brooks Library Edward W. Nolan Photograph Collection
*
*
{{coord, 47, -120, dim:300000_region:US-WA_type:adm1st, name=State of Washington, display=title
1889 establishments in the United States
Geography of the Pacific Northwest
States and territories established in 1889
States of the United States
States of the West Coast of the United States
Contiguous United States
 The 9,300-year-old skeletal remains of Kennewick Man, one of the oldest and most complete human remains found in North America, were discovered in Washington in the 1990s. The area has been known to host megathrust earthquakes in the past, the last being the Cascadia earthquake of 1700. Before the arrival of Europeans, the region had many established tribes of indigenous peoples, notable for their totem poles and their ornately carved canoes and masks. Prominent among their industries were
The 9,300-year-old skeletal remains of Kennewick Man, one of the oldest and most complete human remains found in North America, were discovered in Washington in the 1990s. The area has been known to host megathrust earthquakes in the past, the last being the Cascadia earthquake of 1700. Before the arrival of Europeans, the region had many established tribes of indigenous peoples, notable for their totem poles and their ornately carved canoes and masks. Prominent among their industries were  Britain and the United States agreed to what has since been described as "joint occupancy" of lands west of the
Britain and the United States agreed to what has since been described as "joint occupancy" of lands west of the  The growing population of Oregon Territory north of the Columbia River formally requested a new territory. As a result of the Monticello Convention, held in present-day
The growing population of Oregon Territory north of the Columbia River formally requested a new territory. As a result of the Monticello Convention, held in present-day 
 For a long period, Tacoma had large smelters where gold, silver, copper, and lead ores were treated.
For a long period, Tacoma had large smelters where gold, silver, copper, and lead ores were treated.  Washington is the northwesternmost state of the contiguous United States. It borders
Washington is the northwesternmost state of the contiguous United States. It borders  From the Cascade Mountains westward, Western Washington has a mostly
From the Cascade Mountains westward, Western Washington has a mostly 
 The state of Washington has a temperate climate. The eastern half of Washington has a semi-arid climate, while the western side of Washington as well as the coastal areas of the state have a cool oceanic climate. Major factors determining Washington's climate include the large semi-permanent low pressure and high pressure systems of the north Pacific Ocean, the continental air masses of North America, and the Olympic and Cascade mountains. In the spring and summer, a high-pressure anticyclone system dominates the north Pacific Ocean, causing air to spiral out in a clockwise fashion. For Washington, this means prevailing winds from the northwest bring relatively cool air and a predictably
The state of Washington has a temperate climate. The eastern half of Washington has a semi-arid climate, while the western side of Washington as well as the coastal areas of the state have a cool oceanic climate. Major factors determining Washington's climate include the large semi-permanent low pressure and high pressure systems of the north Pacific Ocean, the continental air masses of North America, and the Olympic and Cascade mountains. In the spring and summer, a high-pressure anticyclone system dominates the north Pacific Ocean, causing air to spiral out in a clockwise fashion. For Washington, this means prevailing winds from the northwest bring relatively cool air and a predictably 
 According to the 2016 American Community Survey, 12.1% of Washington's population were of Hispanic or Latino origin (of any race): Mexican (9.7%), Puerto Rican (0.4%), Cuban (0.1%), and other Hispanic or Latino origin (1.8%). The five largest ancestry groups were: German (17.8%),
Irish (10.8%), English (10.4%), Norwegian (5.4%), and American (4.6%).
; Birth data
In 2011, 44.3 percent of Washington's population younger than age1 were minorities.
''Note: Births in table don't add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
* Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
According to the 2016 American Community Survey, 12.1% of Washington's population were of Hispanic or Latino origin (of any race): Mexican (9.7%), Puerto Rican (0.4%), Cuban (0.1%), and other Hispanic or Latino origin (1.8%). The five largest ancestry groups were: German (17.8%),
Irish (10.8%), English (10.4%), Norwegian (5.4%), and American (4.6%).
; Birth data
In 2011, 44.3 percent of Washington's population younger than age1 were minorities.
''Note: Births in table don't add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
* Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
 While the population of African Americans in the Pacific Northwest is relatively scarce overall, they are mostly concentrated in the South End and Central District areas of Seattle, and in inner Tacoma. The black community of Seattle consisted of one individual in 1858,
While the population of African Americans in the Pacific Northwest is relatively scarce overall, they are mostly concentrated in the South End and Central District areas of Seattle, and in inner Tacoma. The black community of Seattle consisted of one individual in 1858,  Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders are mostly concentrated in the Seattle−Tacoma metropolitan area of the state. Seattle, Bellevue, and Redmond, which are all within King County, have sizable Chinese communities (including Taiwanese), as well as significant Indian and Japanese communities. The Chinatown-International District in Seattle has a historical Chinese population dating back to the 1860s, who mainly emigrated from
Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders are mostly concentrated in the Seattle−Tacoma metropolitan area of the state. Seattle, Bellevue, and Redmond, which are all within King County, have sizable Chinese communities (including Taiwanese), as well as significant Indian and Japanese communities. The Chinatown-International District in Seattle has a historical Chinese population dating back to the 1860s, who mainly emigrated from  Washington has a relatively strong economy, with a total gross state product of $612,996.5 million in 2019, placing it fifth in the nation and growing by 6.5 percent per year—the fastest rate in the United States. The
Washington has a relatively strong economy, with a total gross state product of $612,996.5 million in 2019, placing it fifth in the nation and growing by 6.5 percent per year—the fastest rate in the United States. The  The state of Washington is one of seven states that do not levy a personal
The state of Washington is one of seven states that do not levy a personal  Washington is a leading agricultural state. The following figures are from th
Washington is a leading agricultural state. The following figures are from th Washington ranks second in the United States in the production of wine, behind only
Washington ranks second in the United States in the production of wine, behind only 
 Washington's
Washington's  Washington is one of the ten states to have legalized assisted suicide. In 2008 the Washington Death with Dignity Act ballot initiative passed and became law.
In November 2009, Washington voters approved full domestic partnerships via Referendum 71, marking the first time voters in any state expanded recognition of same-sex relationships at the ballot box. Three years later, in November 2012, same-sex marriage was affirmed via Referendum 74, making Washington one of only three states to have approved same-sex marriage by popular vote.
Also in November 2012, Washington was one of the first two states to approve the legal sale and possession of cannabis for both recreational and medical use with Initiative 502. Although marijuana is still illegal under U.S. federal law, persons 21 and older in Washington state can possess up to one ounce of marijuana, 16 ounces of marijuana-infused product in solid form, 72 ounces of marijuana-infused product in liquid form, or any combination of all three, and can legally consume marijuana and marijuana-infused products.
In November 2016, voters approved Initiative 1433, which among other things requires employers to guarantee paid sick leave to most workers. On January 1, 2018, the law went into effect, with Washington becoming the seventh state with paid sick leave requirements.
With the passage of Initiative 1639 in the 2018 elections, Washington adopted stricter gun laws.
Washington enacted a measure in May 2019 in favor of sanctuary cities, similar to California and Oregon laws which are among the strongest statewide mandates in the nation.
In 2019 the legislature passed the Clean Energy Transformation Act, which requires all electricity sales to be from zero-carbon sources by 2045 and net-zero by 2030.
Washington is one of the ten states to have legalized assisted suicide. In 2008 the Washington Death with Dignity Act ballot initiative passed and became law.
In November 2009, Washington voters approved full domestic partnerships via Referendum 71, marking the first time voters in any state expanded recognition of same-sex relationships at the ballot box. Three years later, in November 2012, same-sex marriage was affirmed via Referendum 74, making Washington one of only three states to have approved same-sex marriage by popular vote.
Also in November 2012, Washington was one of the first two states to approve the legal sale and possession of cannabis for both recreational and medical use with Initiative 502. Although marijuana is still illegal under U.S. federal law, persons 21 and older in Washington state can possess up to one ounce of marijuana, 16 ounces of marijuana-infused product in solid form, 72 ounces of marijuana-infused product in liquid form, or any combination of all three, and can legally consume marijuana and marijuana-infused products.
In November 2016, voters approved Initiative 1433, which among other things requires employers to guarantee paid sick leave to most workers. On January 1, 2018, the law went into effect, with Washington becoming the seventh state with paid sick leave requirements.
With the passage of Initiative 1639 in the 2018 elections, Washington adopted stricter gun laws.
Washington enacted a measure in May 2019 in favor of sanctuary cities, similar to California and Oregon laws which are among the strongest statewide mandates in the nation.
In 2019 the legislature passed the Clean Energy Transformation Act, which requires all electricity sales to be from zero-carbon sources by 2045 and net-zero by 2030.