|
George Simpson (administrator)
Sir George Simpson ( – 7 September 1860) was a Scottish explorer and colonial governor of the Hudson's Bay Company during the period of its greatest power. From 1820 to 1860, he was in practice, if not in law, the British viceroy for the whole of Rupert's Land, an enormous territory of 3.9 millions square kilometers in northern North America. His efficient administration of the west was a precondition for the confederation of western and eastern Canada. He was noted for his grasp of administrative detail and his physical stamina in traveling through the wilderness. Excepting voyageurs and their Siberian equivalents, few men have spent as much time traveling in the wilderness. Simpson was the first person known to have circumnavigated the world by land. Early life Born at Dingwall, Ross-Shire, Scotland, as the illegitimate son of George Simpson, Writer to the Signet, he was raised by two aunts and his paternal grandmother, Isobel Simpson (1731–1821), daughter of Georg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Pearce
Stephen Pearce (16 November 1819 – 31 January 1904) was an English portrait and equestrian painter. Forty-four portraits which he painted are in the National Portrait Gallery, London, which also contains two self-portraits. Life He was born on 16 November 1819 at the King's Mews, Charing Cross, was only child of Stephen Pearce, clerk in the department of the master of horse, and Ann Whittington. He was trained at Sass's Academy in Charlotte Street, and at the Royal Academy schools, 1840, and in 1841 became a pupil of Sir Martin Archer Shee. From 1842 to 1846, he acted as amanuensis to Charles Lever, and he afterwards visited Italy. Paintings by him of favourite horses in the royal mews (transferred in 1825 to Buckingham Palace) were exhibited at the Royal Academy in 1839 and 1841, and from 1849, on his return from Italy, till 1885 he contributed numerous portraits and equestrian paintings to Burlington House. Early friendship with Sir John Barrow, 1st Baronet, Sir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberian Fur Trade
The Siberian fur trade is an exchange concerned with the gathering, buying and selling of valuable animal furs that originate from Siberia. The Siberian fur trade expanded from localized trade, and Siberian fur is now traded around the world. The Siberian fur trade had a significant impact on the development of Siberia through exploration and colonization. The fur trade also precipitated a decline in the number of fur-bearing animals and resulted in Siberia being conquered by Russia. Beginnings Traditionally, Siberians hunted as a means of sustenance and only used the fur from animals they hunted and consumed for gloves and hats. The practice of hunting animals solely for fur began after the Russians came to Siberia. Sable quickly became the most valuable and popular type of Siberian fur, and still maintains the distinction to this day. The Siberian fur trade began in the sixteenth century, peaked in the seventeenth century, and continues to the present day.Fur Trade: Russia. Answe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-peaked hill around which the early city of Ville-Marie is built. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which obtained its name from the same origin as the city, and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. The city is east of the national capital Ottawa, and southwest of the provincial capital, Quebec City. As of 2021, the city had a population of 1,762,949, and a metropolitan population of 4,291,732, making it the second-largest city, and second-largest metropolitan area in Canada. French is the city's official language. In 2021, it was spoken at home by 59.1% of the population and 69.2% in the Montreal Census Metropolitan Area. Overall, 85.7% of the population of the city of Montreal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaver Club
The Beaver Club was a gentleman's dining club founded in 1785 by the predominantly English-speaking men who had gained control of the fur trade of Montreal. According to the club's rules, the object of their meeting was "to bring together, at stated periods during the winter season, a set of men highly respectable in society, who had passed their best days in a savage country and had encountered the difficulties and dangers incident to a pursuit of the fur trade of Canada". Only fragmentary records remain of their meetings, but from these it is clear that the Beaver Club was "an animated expression of the ''esprit de corps'' of the North West Company". The men of the Beaver Club were the predecessors of Montreal's Square Milers. Origins In 18th century North America, the fur 'barons' of Montreal might only have been compared to the tobacco 'lords' of Virginia for their wealth and grand style of living. The members of the Beaver Club were '' bon vivants'', renowned for the Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great wealth at stake, tensions between the companies increased to the point where several minor armed skirmishes broke out, and the two companies were forced by the British government to merge. Before the Company After the French landed in Quebec in 1608, spread out and built a fur trade empire in the St. Lawrence basin. The French competed with the Dutch (from 1614) and English (1664) in New York and the English in Hudson Bay (1670). Unlike the French who travelled into the northern interior and traded with First Nations in their camps and villages, the English made bases at trading posts on Hudson Bay, inviting the indigenous people to trade. After 1731, pushed trade west beyond Lake Winnipeg. After the British conquest of New France in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl Of Selkirk
Thomas may refer to: People * List of people with given name Thomas * Thomas (name) * Thomas (surname) * Saint Thomas (other) * Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church * Thomas the Apostle * Thomas (bishop of the East Angles) (fl. 640s–650s), medieval Bishop of the East Angles * Thomas (Archdeacon of Barnstaple) (fl. 1203), Archdeacon of Barnstaple * Thomas, Count of Perche (1195–1217), Count of Perche * Thomas (bishop of Finland) (1248), first known Bishop of Finland * Thomas, Earl of Mar (1330–1377), 14th-century Earl, Aberdeen, Scotland Geography Places in the United States * Thomas, Illinois * Thomas, Indiana * Thomas, Oklahoma * Thomas, Oregon * Thomas, South Dakota * Thomas, Virginia * Thomas, Washington * Thomas, West Virginia * Thomas County (other) * Thomas Township (other) Elsewhere * Thomas Glacier (Greenland) Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Thomas'' (Burto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Colvile-Wedderburn
Andrew Colvile (born Andrew Wedderburn; 6 November 1779 – 3 February 1856) was a Scottish businessman, notable as the governor of the Hudson's Bay Company, a huge organisation set up for the North American fur trade but also instrumental in the early history of Canada. He was also chairman of the West India Docks. Early life and family background Andrew was born Andrew Wedderburn in 1779. His grandfather, Sir John Wedderburn, 5th Baronet of Blackness, was involved with the Jacobite rising of 1745, and was convicted of treason. The punishment for this was threefold: the death penalty, the confiscation of all his estates (he had property at Inveresk), and the attainting of his family, including the baronetcy. At least two of his sons moved to Jamaica, including Andrew's uncle and father. The former, John Wedderburn of Ballendean, is notable for the civil case brought under Scots law by his former slave Joseph Knight. Andrew's father, James Wedderburn, set up as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
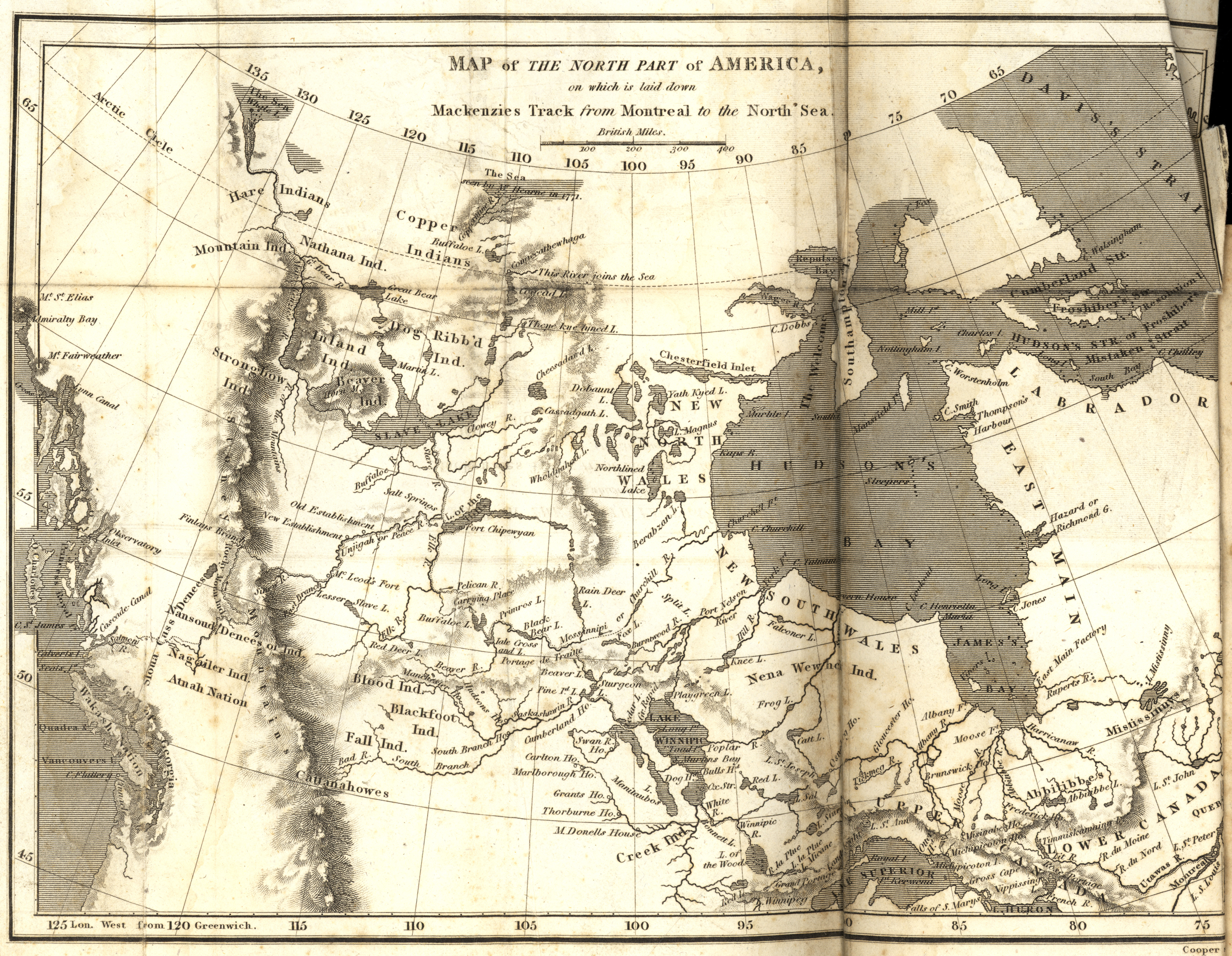
Alexander Mackenzie (explorer)
Sir Alexander Mackenzie (or MacKenzie, gd, Alasdair MacCoinnich; – 12 March 1820) was a Scottish explorer known for accomplishing the first crossing of America north of Mexico in 1793. The Mackenzie River is named after him. Early life Mackenzie was born in House in Stornoway in Lewis. He was the third of the four children born to Kenneth 'Corc' Mackenzie (1731–1780) and his wife Isabella MacIver, from another prominent mercantile family in Stornoway. When only 14 years old, Mackenzie's father served as an ensign to protect Stornoway during the Jacobite rising of 1745. He later became a merchant and held the tack of Melbost; his grandfather being a younger brother of Murdoch Mackenzie, 6th Laird of Fairburn. Educated at the same school as Colin Mackenzie, the army officer and first Surveyor General of India, he sailed to New York City with his father to join an uncle, John Mackenzie, in 1774, after his mother died in Scotland. In 1776, during the American War of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duncan Forbes, Lord Culloden
Duncan Forbes of Culloden (10 November 1685 – 10 December 1747) was a Scottish lawyer and Whig politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1721 to 1737. As Lord President and senior Scottish legal officer, he played a major role in helping the government suppress the 1745 Jacobite Rising. Life Duncan Forbes was born on 10 November 1685, in Culloden House near Inverness, second son of Duncan Forbes (1644-1704) and his wife Mary Innes (ca 1650–1716). The fifth of nine children, he had seven sisters; Jean (ca 1678-?) and Margaret both married, while little is known of the others. His elder brother, John (1673-1734), was 12 years older; despite the age difference, the two were close friends all their lives. Forbes was educated at the local grammar school before progressing to Marischal College, Aberdeen in 1699. After briefly attending the University of Edinburgh in 1705, he completed his legal studies at Leyden University in the Netherlands. He returned home in 1707 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Mackenzie, 2nd Earl Of Seaforth
George Mackenzie, 2nd Earl of Seaforth (died 1651) was a Highland clan chief and Scottish nobleman, who played an equivocating role in Scotland in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Origins Mackenzie was the son of Kenneth Mackenzie, 1st Lord Mackenzie of Kintail (died 1611), and Isobel, the daughter of Sir Gilbert Ogilvie of Powrie. The Mackenzies were a clan from Ross-shire that had risen to prominence in the 15th century during the disintegration of the Lordship of the Isles. On the death in 1633 of his elder half-brother Colin without male heirs, Mackenzie inherited his estates and the title of Earl of Seaforth. Prior to that point, he was known as George Mackenzie of Kildun. Estates As a result of the acquisitive proclivities of Seaforth's ancestors, his estates were very extensive. In 1633 he was "served heir male to his brother … in the lands and barony of Ellandonnan, including the barony of Lochalsh, in which was included the barony of the lands and towns of Loch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gruinard Island
Gruinard Island ( ; gd, Eilean Ghruinneard) is a small, oval-shaped Scottish island approximately long by wide, located in Gruinard Bay, about halfway between Gairloch and Ullapool. At its closest point to the mainland, it is about offshore. The island was dangerous for all mammals after experiments with the anthrax bacterium in 1942, until it was decontaminated in the late 20th century. Early history The island was mentioned by Dean Munro who travelled the area in the mid-16th century. He wrote that it was Clan MacKenzie territory, "full of woods" (it is treeless today), and that it was "''guid for fostering of thieves and rebellis''" (good for fostering thieves and rebels). The island was historically split between the counties of Ross-shire and Cromartyshire. The population was recorded as six in 1881. Gruinard has been uninhabited since the 1920s.Haswell-Smith (2004) p. 187 Biological warfare testing In 1942, during the Second World War, a biological warfare test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laird
Laird () is the owner of a large, long-established Scottish estate. In the traditional Scottish order of precedence, a laird ranked below a baron and above a gentleman. This rank was held only by those lairds holding official recognition in a territorial designation by the Lord Lyon King of Arms. They are usually styled 'name'' 'surname''of 'lairdship'' However, since "laird" is a courtesy title, it has no formal status in law. Historically, the term bonnet laird was applied to rural, petty landowners, as they wore a bonnet like the non-landowning classes. Bonnet lairds filled a position in society below lairds and above husbandmen (farmers), similar to the yeomen of England. An Internet fad is the selling of tiny souvenir plots of Scottish land and a claim of a "laird" title to go along with it, but the Lord Lyon has decreed these meaningless for several reasons. Etymology ''Laird'' (earlier ''lard'') is the now-standard Scots pronunciation (and spelling, which is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)