Wnt signalling pathway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In cellular biology, the Wnt signaling pathways are a group of
 Wnt comprises a diverse family of secreted
Wnt comprises a diverse family of secreted

 The noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway also does not involve
The noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway also does not involve
signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), rece ...
pathways which begin with proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, re ...
that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptor
Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. They are specialized integra ...
s. The name Wnt, pronounced "wint", is a portmanteau
In linguistics, a blend—also known as a blend word, lexical blend, or portmanteau—is a word formed by combining the meanings, and parts of the sounds, of two or more words together.
created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine
In cellular biology, paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication (biology), cellular communication in which a Cell (biology), cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of ...
) or same-cell communication (autocrine
Autocrine signaling is a form of cell signaling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger (called the autocrine agent) that binds to autocrine receptors on that same cell, leading to changes in the cell. This can be contrasted with ...
). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans.
Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. All three pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
to a Frizzled
Frizzled is a family of atypical G protein-coupled receptor, G protein-coupled receptors that serve as receptors in the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. When activated, Frizzled leads to activation of Dishevelled in the cytosol ...
family receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
, which passes the biological signal to the Dishevelled protein inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
transcription, and is thought to be negatively regulated in part by the SPATS1 gene. The noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway regulates the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is compos ...
that is responsible for the shape of the cell. The noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway regulates calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
inside the cell.
Wnt signaling was first identified for its role in carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cell (biology), cells are malignant transformation, transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, G ...
, then for its function in embryonic development
In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm, sperm cell (spermat ...
. The embryonic processes it controls include body axis patterning, cell fate specification, cell proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation ...
and cell migration
Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryogenesis, embryonic development, wound healing and immune system, immune responses all require the orchestrated movemen ...
. These processes are necessary for proper formation of important tissues including bone, heart and muscle. Its role in embryonic development
In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm, sperm cell (spermat ...
was discovered when genetic mutations in Wnt pathway proteins produced abnormal fruit fly embryos. Later research found that the genes responsible for these abnormalities also influenced breast cancer development in mice. Wnt signaling also controls tissue regeneration in adult bone marrow, skin and intestine.
This pathway's clinical importance was demonstrated by mutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosi ...
that lead to various diseases, including breast
The breasts are two prominences located on the upper ventral region of the torso among humans and other primates. Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryology, embryological tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is ...
and prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, ...
, glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nons ...
, type II diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
and others. In recent years, researchers reported first successful use of Wnt pathway inhibitors in mouse models of disease.
History and etymology
The discovery of Wnt signaling was influenced by research on oncogenic (cancer-causing)retroviruses
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. After invading a host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
. In 1982, Roel Nusse and Harold Varmus
Harold Eliot Varmus (born December 18, 1939) is an American Nobel Prize-winning scientist. He is currently the Lewis Thomas University Professor of Medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine and a senior associate at the New York Genome Center.
He was ...
infected mice with mouse mammary tumor virus in order to mutate mouse genes to see which mutated genes could cause breast tumors. They identified a new mouse proto-oncogene that they named int1 (integration 1).
Int1 is highly conserved across multiple species, including humans and ''Drosophila
''Drosophila'' (), from Ancient Greek δρόσος (''drósos''), meaning "dew", and φίλος (''phílos''), meaning "loving", is a genus of fly, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or p ...
''. Its presence in '' D. melanogaster'' led researchers to discover in 1987 that the int1 gene in ''Drosophila'' was actually the already known and characterized ''Drosophila'' gene known as Wingless (Wg). Since previous research by Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard
Christiane (Janni) Nüsslein-Volhard (; born 20 October 1942) is a German developmental biologist and a 1995 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine laureate. She is the only woman from Germany to have received a Nobel Prize in the sciences.
N� ...
and Eric Wieschaus
Eric Francis Wieschaus (born June 8, 1947 in South Bend, Indiana) is an American Evolutionary developmental biology, evolutionary developmental biologist and 1995 Nobel Prize-winner.
Early life
Born in South Bend, Indiana, he attended John Carro ...
(which won them the Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred N ...
in Physiology or Medicine in 1995) had already established the function of Wg as a segment polarity gene involved in the formation of the body axis during embryonic development
In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm, sperm cell (spermat ...
, researchers determined that the mammalian int1 discovered in mice is also involved in embryonic development.
Continued research led to the discovery of further int1-related genes; however, because those genes were not identified in the same manner as int1, the int gene nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. (The theoretical field studying nomenclature is sometimes referred to as ''onymology'' or ''taxonymy'' ). The principl ...
was inadequate. Thus, the int/Wingless family became the Wnt family and int1 became Wnt1. The name Wnt is a portmanteau
In linguistics, a blend—also known as a blend word, lexical blend, or portmanteau—is a word formed by combining the meanings, and parts of the sounds, of two or more words together.
of int and Wg and stands for "Wingless-related integration site".
Proteins
 Wnt comprises a diverse family of secreted
Wnt comprises a diverse family of secreted lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
-modified signaling glycoproteins
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
that are 350–400 amino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into p ...
in length. The lipid modification of all Wnts is palmitoleoylation of a single totally conserved cysteine residue. Palmitoleoylation is necessary because it is required for Wnt to bind to its carrier protein Wntless (WLS) so it can be transported to the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
for secretion and it allows the Wnt protein to bind its receptor Frizzled Wnt proteins also undergo glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not ...
, which attaches a carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ...
in order to ensure proper secretion. In Wnt signaling, these proteins act as ligands
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's ...
to activate the different Wnt pathways via paracrine and autocrine routes.
These proteins are highly conserved across species. They can be found in mice, humans, ''Xenopus'', zebrafish
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Danionidae of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (an ...
, ''Drosophila'' and many others.
Mechanism

Foundation
Wnt signaling begins when a Wnt protein binds to the N-terminal extra-cellular cysteine-rich domain of aFrizzled
Frizzled is a family of atypical G protein-coupled receptor, G protein-coupled receptors that serve as receptors in the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. When activated, Frizzled leads to activation of Dishevelled in the cytosol ...
(Fz) family receptor. These receptors span the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
seven times and constitute a distinct family of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). However, to facilitate Wnt signaling, co-receptors may be required alongside the interaction between the Wnt protein and Fz receptor. Examples include lipoprotein receptor-related protein ( LRP)-5/6, receptor tyrosine kinase
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are the high-affinity cell surface receptors for many polypeptide growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. Of the 90 unique tyrosine kinase genes identified in the human genome, 58 encode receptor tyrosine kinas ...
(RTK), and ROR2
Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2, also known as neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor-related 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ROR2'' gene located on position 9 of the long arm of chromosome 9 (human), chrom ...
. Upon activation of the receptor, a signal is sent to the phosphoprotein
A phosphoprotein is a protein that is posttranslationally modified by the attachment of either a single phosphate group, or a complex molecule such as 5'-phospho-DNA, through a phosphate group. The target amino acid is most often serine, threonin ...
Dishevelled
Dishevelled (Dsh) is a family of proteins involved in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways. Dsh (Dvl in mammals) is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that acts directly downstream of frizzled receptors. It takes its name from its initi ...
(Dsh), which is located in the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
. This signal is transmitted via a direct interaction between Fz and Dsh. Dsh proteins are present in all organisms and they all share the following highly conserved protein domains
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of se ...
: an amino-terminal DIX domain, a central PDZ domain
The PDZ domain is a common structural domain of 80-90 Amino acid, amino-acids found in the Signal transduction, signaling proteins of bacteria, yeast, plants, viruses and animals. Proteins containing PDZ domains play a key role in anchoring recept ...
, and a carboxy-terminal DEP domain. These different domains are important because after Dsh, the Wnt signal can branch off into multiple pathways and each pathway interacts with a different combination of the three domains.
Canonical and noncanonical pathways
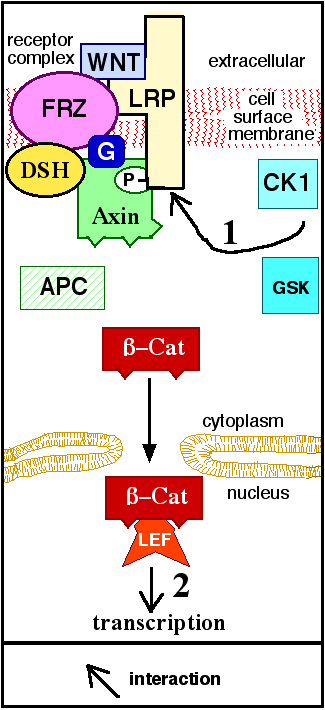
The three best characterized Wnt signaling pathways are the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. As their names suggest, these pathways belong to one of two categories: canonical or noncanonical. The difference between the categories is that a canonical pathway involves the proteinbeta-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcrip ...
(β-catenin) while a noncanonical pathway operates independently of it.

Canonical pathway
The canonical Wnt pathway (or Wnt/β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
pathway) is the Wnt pathway that causes an accumulation of β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
in the cytoplasm and its eventual translocation into the nucleus to act as a transcriptional coactivator of transcription factors
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The fun ...
that belong to the TCF/LEF family. Without Wnt, β-catenin would not accumulate in the cytoplasm since a destruction complex would normally degrade it. This destruction complex includes the following proteins: Axin, adenomatosis polyposis coli (APC), protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) and casein kinase 1
The Casein kinase 1 family () of protein kinases are serine/threonine-selective enzymes that function as regulators of signal transduction pathways in most eukaryotic cell types. CK1 isoforms are involved in Wnt signaling pathway, Wnt signaling, ci ...
α (CK1α). It degrades β-catenin by targeting it for ubiquitination
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 19 ...
, which subsequently sends it to the proteasome
Proteasomes are essential protein complexes responsible for the degradation of proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are found inside all e ...
to be digested. However, as soon as Wnt binds Fz and LRP5/ 6, the destruction complex function becomes disrupted. This is due to Wnt causing the translocation of the negative Wnt regulator, Axin, and the destruction complex to the plasma membrane. Phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
by other proteins in the destruction complex subsequently binds Axin to the cytoplasmic tail of LRP5/6. Axin becomes de-phosphorylated and its stability and levels decrease. Dsh then becomes activated via phosphorylation and its DIX and PDZ domains inhibit the GSK3 activity of the destruction complex. This allows β-catenin to accumulate and localize to the nucleus and subsequently induce a cellular response via gene transduction alongside the TCF/LEF (T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancing factor) transcription factors. β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
recruits other transcriptional coactivators, such as BCL9
B-cell CLL/lymphoma 9 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BCL9'' gene.
Function
BCL9, together with its paralogue gene BCL9L (BCL9 like or BCL9.2), have been extensively studied for their role as transcriptional beta-caten ...
, Pygopus and Parafibromin/Hyrax. The complexity of the transcriptional complex assembled by β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
is beginning to emerge thanks to new high-throughput proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital macromolecules of all living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replicatio ...
studies. However, a unified theory of how β‐catenin drives target gene expression is still missing, and tissue-specific players might assist β‐catenin to define its target genes. The extensivity of the β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
interacting proteins complicates our understanding: β-catenin may be directly phosphorylated at Ser552 by Akt, which causes its disassociation from cell-cell contacts and accumulation in cytosol, thereafter 14-3-3ζ interacts with β-catenin (pSer552) and enhances its nuclear translocation. BCL9
B-cell CLL/lymphoma 9 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BCL9'' gene.
Function
BCL9, together with its paralogue gene BCL9L (BCL9 like or BCL9.2), have been extensively studied for their role as transcriptional beta-caten ...
and Pygopus have been reported, in fact, to possess several β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
-independent functions (therefore, likely, Wnt signaling-independent).

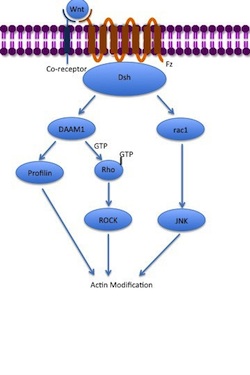
Noncanonical pathways
The noncanonical planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway does not involve β-catenin. It does not use LRP-5/6 as its co-receptor and is thought to use NRH1, Ryk, PTK7 orROR2
Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2, also known as neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor-related 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ROR2'' gene located on position 9 of the long arm of chromosome 9 (human), chrom ...
. The PCP pathway is activated via the binding of Wnt to Fz and its co-receptor. The receptor then recruits Dsh, which uses its PDZ and DIX domains to form a complex with Dishevelled-associated activator of morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
1 ( DAAM1). Daam1 then activates the small G-protein Rho
Rho (; uppercase Ρ, lowercase ρ or ; or ) is the seventeenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 100. It is derived from Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter resh . Its uppercase form uses the same ...
through a guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside ...
exchange factor. Rho activates Rho-associated kinase (ROCK), which is one of the major regulators of the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is compos ...
. Dsh also forms a complex with rac1 and mediates profilin binding to actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
. Rac1 activates JNK and can also lead to actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many fo ...
. Profilin binding to actin can result in restructuring of the cytoskeleton and gastrulation
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals, the blastocyst, is reorganized into a two-layered or three-layered embryo known as ...
.
 The noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway also does not involve
The noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway also does not involve β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
. Its role is to help regulate calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for ...
(ER) in order to control intracellular calcium levels. Like other Wnt pathways, upon ligand binding, the activated Fz receptor directly interacts with Dsh and activates specific Dsh-protein domains. The domains involved in Wnt/calcium signaling are the PDZ and DEP domains. However, unlike other Wnt pathways, the Fz receptor directly interfaces with a trimeric G-protein. This co-stimulation of Dsh and the G-protein can lead to the activation of either PLC or cGMP-specific PDE. If PLC is activated, the plasma membrane component PIP2
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)''P''2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)''P''2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of ...
is cleaved into DAG and IP3. When IP3 binds its receptor on the ER, calcium is released. Increased concentrations of calcium and DAG can activate Cdc42
Cell division control protein 42 homolog (Cdc42 or CDC42) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDC42'' gene. Cdc42 is involved in regulation of the cell cycle. It was originally identified in ''S. cerevisiae'' (yeast) as a mediator of ...
through PKC. Cdc42 is an important regulator of ventral patterning. Increased calcium also activates calcineurin
Calcineurin (CaN) is a calcium and calmodulin dependent serine/threonine protein phosphatase (also known as protein phosphatase 3, and calcium-dependent serine-threonine phosphatase). It activates the T cells of the immune system and can be block ...
and CaMKII
/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaM kinase II or CaMKII) is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that is regulated by the /calmodulin complex. CaMKII is involved in many signaling cascades and is thought to be an important mediat ...
. Calcineurin induces activation of the transcription factor NFAT
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) is a family of transcription factors shown to be important in immune response. One or more members of the NFAT family is expressed in most cells of the immune system. NFAT is also involved in the developme ...
, which regulates cell adhesion, migration and tissue separation. CaMKII activates TAK1 and NLK kinase, which can interfere with TCF/β-Catenin signaling in the canonical Wnt pathway. However, if PDE is activated, calcium release from the ER is inhibited. PDE mediates this through the inhibition of PKG, which subsequently causes the inhibition of calcium release.
Integrated Wnt Pathway
The binary distinction of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways has come under scrutiny and an integrated, convergent Wnt pathway has been proposed. Some evidence for this was found for one Wnt ligand (Wnt5A). Evidence for a convergent Wnt signaling pathway that shows integrated activation of Wnt/Ca2+ and Wnt/β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
signaling, for multiple Wnt ligands, was described in mammalian cell lines.
Other pathways
Wnt signaling also regulates a number of other signaling pathways that have not been as extensively elucidated. One such pathway includes the interaction between Wnt andGSK3
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase that mediates the addition of phosphate molecules onto serine and threonine amino acid residues. First discovered in 1980 as a regulatory kinase for its namesake, glycogen ...
. During cell growth, Wnt can inhibit GSK3 in order to activate mTOR in the absence of β-catenin. However, Wnt can also serve as a negative regulator of mTOR via activation of the tumor suppressor
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell (biology), cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results ...
TSC2, which is upregulated via Dsh and GSK3 interaction. During myogenesis
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscle, skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development.
Skeletal muscle#Skeletal muscle cells, Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor cell, precursor myoblasts in ...
, Wnt uses PA and CREB
CREB-TF (CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein) is a cellular transcription factor. It binds to certain DNA sequences called cAMP response elements (CRE), thereby increasing or decreasing the transcription of the genes. CREB was first des ...
to activate MyoD
MyoD, also known as myoblast determination protein 1, is a protein in animals that plays a major role in regulating muscle differentiation. MyoD, which was discovered in the laboratory of Harold M. Weintraub, belongs to a family of proteins kn ...
and Myf5 genes. Wnt also acts in conjunction with Ryk and Src to allow for regulation of neuron repulsion during axonal guidance. Wnt regulates gastrulation
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals, the blastocyst, is reorganized into a two-layered or three-layered embryo known as ...
when CK1 serves as an inhibitor of Rap1-ATPase in order to modulate the cytoskeleton during gastrulation. Further regulation of gastrulation is achieved when Wnt uses ROR2 along with the CDC42
Cell division control protein 42 homolog (Cdc42 or CDC42) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDC42'' gene. Cdc42 is involved in regulation of the cell cycle. It was originally identified in ''S. cerevisiae'' (yeast) as a mediator of ...
and JNK pathway to regulate the expression of PAPC. Dsh can also interact with aPKC, Pa3, Par6 and LGl in order to control cell polarity and microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter bet ...
cytoskeleton development. While these pathways overlap with components associated with PCP and Wnt/Calcium signaling, they are considered distinct pathways because they produce different responses.
Regulation
In order to ensure proper functioning, Wnt signaling is constantly regulated at several points along its signaling pathways. For example, Wnt proteins are palmitoylated. The protein ''porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp Spine (zoology), spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two Family (biology), families of animals: the Old World porcupines of the family Hystricidae, and the New ...
'' mediates this process, which means that it helps regulate when the Wnt ligand is secreted by determining when it is fully formed. Secretion is further controlled with proteins such as GPR177 (wntless) and evenness interrupted and complexes such as the retromer complex.
Upon secretion
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mec ...
, the ligand can be prevented from reaching its receptor through the binding of proteins such as the stabilizers Dally and glypican 3 (GPC3), which inhibit diffusion. In cancer cells, both the heparan sulfate chains and the core protein of GPC3 are involved in regulating Wnt binding and activation for cell proliferation. Wnt recognizes a heparan sulfate structure on GPC3, which contains IdoA2S and GlcNS6S, and the 3-O-sulfation in GlcNS6S3S enhances the binding of Wnt to the heparan sulfate glypican. A cysteine-rich domain at the N-lobe of GPC3 has been identified to form a Wnt-binding hydrophobic groove including phenylalanine-41 that interacts with Wnt. Blocking the Wnt binding domain using a nanobody called HN3 can inhibit Wnt activation.
At the Fz receptor, the binding of proteins other than Wnt can antagonize signaling. Specific antagonists
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the main enemy or rival of the protagonist and is often depicted as a villain.Dickkopf (Dkk), Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF-1), secreted Frizzled-related proteins (SFRP),
Cerberus
In Greek mythology, Cerberus ( or ; ''Kérberos'' ), often referred to as the hound of Hades, is a polycephaly, multi-headed dog that guards the gates of the Greek underworld, underworld to prevent the dead from leaving. He was the offspring o ...
, Frzb, Wise, SOST
Sclerostin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOST'' gene. It is a secreted glycoprotein with a C-terminus, C-terminal cysteine knot-like (CTCK) domain and sequence similarity to the PARN, DAN (differential screening-selected gene a ...
, and Naked cuticle
Naked cuticle (Nkd) is a conserved family of intracellular proteins encoded in most animal genomes. The original mutants were discovered by 1995 Nobel laureates Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard and Eric F. Wieschaus and colleagues in their genetic scr ...
. These constitute inhibitors of Wnt signaling. However, other molecules also act as activators. Norrin and R-Spondin2 activate Wnt signaling in the absence of Wnt ligand.
Interactions between Wnt signaling pathways also regulate Wnt signaling. As previously mentioned, the Wnt/calcium pathway can inhibit TCF/β-catenin, preventing canonical Wnt pathway signaling. Prostaglandin E2
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), also known as dinoprostone, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin with oxytocic properties that is used as a medication. Dinoprostone is used in labor induction, bleeding after delivery, termination of pregnanc ...
(PGE2) is an essential activator of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Interaction of PGE2 with its receptors E2/E4 stabilizes β-catenin through cAMP/PKA mediated phosphorylation. The synthesis of PGE2 is necessary for Wnt signaling mediated processes such as tissue regeneration and control of stem cell population in zebrafish and mouse. Intriguingly, the unstructured regions of several oversized intrinsically disordered proteins
In molecular biology, an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered protein tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure, typically in the absence of its macromolecular interaction partners, such as other ...
play crucial roles in regulating Wnt signaling.
Induced cell responses
Embryonic development
Wnt signaling plays a critical role in embryonic development. It operates in bothvertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
and invertebrates
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordate subphylum ...
, including humans, frogs, zebrafish, '' C. elegans'', ''Drosophila'' and others. It was first found in the segment polarity of Drosophila, where it helps to establish anterior and posterior polarities. It is implicated in other developmental processes. As its function in ''Drosophila'' suggests, it plays a key role in body axis formation, particularly the formation of the anteroposterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provi ...
and dorsoventral axes. It is involved in the induction of cell differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell changes from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular ...
to prompt formation of important organs such as lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
and ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
. Wnt further ensures the development of these tissues through proper regulation of cell proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation ...
and migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
. Wnt signaling functions can be divided into axis patterning, cell fate specification, cell proliferation and cell migration.
Axis patterning
In early embryo development, the formation of the primary body axes is a crucial step in establishing the organism's overall body plan. The axes include the anteroposterior axis, dorsoventral axis, and right-left axis. Wnt signaling is implicated in the formation of the anteroposterior and dorsoventral (DV) axes. Wnt signaling activity in anterior-posterior development can be seen in mammals, fish and frogs. In mammals, theprimitive streak
The primitive streak is a structure that forms in the early embryo in amniotes. In amphibians, the equivalent structure is the blastopore. During early embryonic development, the embryonic disc becomes oval shaped, and then pear-shaped with the ...
and other surrounding tissues produce the morphogenic compounds Wnts, BMPs, FGFs, Nodal and retinoic acid
Retinoic acid (simplified nomenclature for all-''trans''-retinoic acid) is a metabolite of vitamin A1 (all-''trans''-retinol) that is required for embryonic development, male fertility, regulation of bone growth and immune function. All-''trans ...
to establish the posterior region during late gastrula
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells), or in mammals, the blastocyst, is reorganized into a two-layered or three-layered e ...
. These proteins form concentration gradients. Areas of highest concentration establish the posterior region while areas of lowest concentration indicate the anterior region. In fish and frogs, β-catenin produced by canonical Wnt signaling causes the formation of organizing centers, which, alongside BMPs, elicit posterior formation. Wnt involvement in DV axis formation can be seen in the activity of the formation of the Spemann organizer, which establishes the dorsal region. Canonical Wnt signaling β-catenin production induces the formation of this organizer via the activation of the genes twin and siamois. Similarly, in avian gastrulation, cells of the Koller's sickle
In avian gastrulation, Koller's sickle is a local thickening of cells at the posterior edge of the upper layer of the area pellucida called the epiblast. Koller's sickle is crucial for avian development, due to its critical role in inducing the d ...
express different mesodermal marker genes that allow for the differential movement of cells during the formation of the primitive streak. Wnt signaling activated by FGFs is responsible for this movement.
Wnt signaling is also involved in the axis formation of specific body parts and organ systems later in development. In vertebrates, sonic hedgehog
Sonic hedgehog protein (SHH) is a major signaling molecule of embryonic development in humans and animals, encoded by the ''SHH'' gene.
This signaling molecule is key in regulating embryonic morphogenesis in all animals. SHH controls organoge ...
(Shh) and Wnt morphogenetic signaling gradients establish the dorsoventral axis of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
during neural tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural folds become elevated, ...
axial patterning. High Wnt signaling establishes the dorsal region while high Shh signaling indicates the ventral region. Wnt is involved in the DV formation of the central nervous system through its involvement in axon guidance. Wnt proteins guide the axons of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
in an anterior-posterior direction. Wnt is also involved in the formation of the limb DV axis. Specifically, Wnt7a helps produce the dorsal patterning of the developing limb.
In the embryonic differentiation waves
A mechanochemistry, mechanochemical based model for Neurulation#Primary neural induction, primary neural induction was first proposed in 1985 by Brodland and Richard Gordon (theoretical biologist), Gordon. They proposed that there is a mecha ...
model of development Wnt plays a critical role as part a signalling complex in competent cells ready to differentiate. Wnt reacts to the activity of the cytoskeleton, stabilizing the initial change created by a passing wave of contraction or expansion and simultaneously signals the nucleus through the use of its different signalling pathways as to which wave the individual cell has participated in. Wnt activity thereby amplifies mechanical signalling that occurs during development.
Cell fate specification
Cell fate specification orcell differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell changes from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular ...
is a process where undifferentiated cells can become a more specialized cell type. Wnt signaling induces differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical ...
and endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gastr ...
progenitor cells
A progenitor cell is a Cell (biology), biological cell that can Cellular differentiation, differentiate into a specific cell type. Stem cell, Stem cells and progenitor cells have this ability in common. However, stem cells are less specified than ...
. These progenitor cells further differentiate into cell types such as endothelial, cardiac and vascular smooth muscle lineages. Wnt signaling induces blood formation from stem cells. Specifically, Wnt3 leads to mesoderm committed cells with hematopoietic
Haematopoiesis (; ; also hematopoiesis in American English, sometimes h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult human, roughly ten ...
potential. Wnt1 antagonizes neural differentiation and is a major factor in self-renewal of neural stem cells. This allows for regeneration of nervous system cells, which is further evidence of a role in promoting neural stem cell proliferation. Wnt signaling is involved in germ cell
A germ cell is any cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they unde ...
determination, gut tissue specification, hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction betwee ...
development, lung tissue development, trunk neural crest cell
The neural crest is a ridge-like structure that is formed transiently between the epidermal ectoderm and neural plate during vertebrate development. Neural crest cells originate from this structure through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, an ...
differentiation, nephron
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structu ...
development, ovary development and sex determination. Wnt signaling also antagonizes heart formation, and Wnt inhibition was shown to be a critical inducer of heart tissue during development, and small molecule Wnt inhibitors are routinely used to produce cardiomyocytes from pluripotent stem cells.
Cell proliferation
In order to have the mass differentiation of cells needed to form the specified cell tissues of different organisms, proliferation and growth ofembryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are Cell potency#Pluripotency, pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-Implantation (human embryo), implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4� ...
s must take place. This process is mediated through canonical Wnt signaling, which increases nuclear and cytoplasmic β-catenin. Increased β-catenin can initiate transcriptional activation of proteins such as cyclin D1 and ''c-myc
''Myc'' is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The ''Myc'' family consists of three related human genes: ''c-myc'' ( MYC), ''l-myc'' ( MYCL), and ''n-myc'' ( MYCN). ''c-myc'' (also sometimes ...
'', which control the G1 to S phase
S phase (Synthesis phase) is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated, occurring between G1 phase and G2 phase. Since accurate duplication of the genome is critical to successful cell division, the processes that occur during S ...
transition in the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
. Entry into the S phase causes DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biolog ...
and ultimately mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
, which are responsible for cell proliferation. This proliferation increase is directly paired with cell differentiation because as the stem cells proliferate, they also differentiate. This allows for overall growth and development of specific tissue systems during embryonic development. This is apparent in systems such as the circulatory system where Wnt3a leads to proliferation and expansion of hematopoietic stem cells needed for red blood cell formation.
The biochemistry of cancer stem cells is subtly different from that of other tumor cells. These so-called Wnt-addicted cells hijack and depend on constant stimulation of the Wnt pathway to promote their uncontrolled growth, survival and migration. In cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, Wnt signaling can become independent of regular stimuli, through mutations in downstream oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes that become permanently activated even though the normal receptor has not received a signal. β-catenin binds to transcription factors such as the protein '' TCF4'' and in combination the molecules activate the necessary genes. LF3 strongly inhibits this binding ''in vitro,'' in cell lines and reduced tumor growth in mouse models. It prevented replication and reduced their ability to migrate, all without affecting healthy cells. No cancer stem cells remained after treatment. The discovery was the product of "rational drug design
Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the invention, inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic compound, organi ...
", involving AlphaScreens and ELISA technologies.
Cell migration
Cell migration during embryonic development allows for the establishment of body axes, tissue formation, limb induction and several other processes. Wnt signaling helps mediate this process, particularly during convergent extension. Signaling from both the Wnt PCP pathway and canonical Wnt pathway is required for proper convergent extension during gastrulation. Convergent extension is further regulated by the Wnt/calcium pathway, which blocks convergent extension when activated. Wnt signaling also induces cell migration in later stages of development through the control of the migration behavior of neuroblasts,neural crest
The neural crest is a ridge-like structure that is formed transiently between the epidermal ectoderm and neural plate during vertebrate development. Neural crest cells originate from this structure through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, ...
cells, myocyte
A muscle cell, also known as a myocyte, is a mature contractile Cell (biology), cell in the muscle of an animal. In humans and other vertebrates there are three types: skeletal muscle, skeletal, smooth muscle, smooth, and Cardiac muscle, cardiac ...
s, and tracheal cells.
Wnt signaling is involved in another key migration process known as the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This process allows epithelial cells to transform into mesenchymal cells so that they are no longer held in place at the laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major constituents of the basement membrane, namely the basal lamina (the protein network foundation for most cells and organs). Laminins are vital to bi ...
. It involves cadherin down-regulation so that cells can detach from laminin and migrate. Wnt signaling is an inducer of EMT, particularly in mammary development.
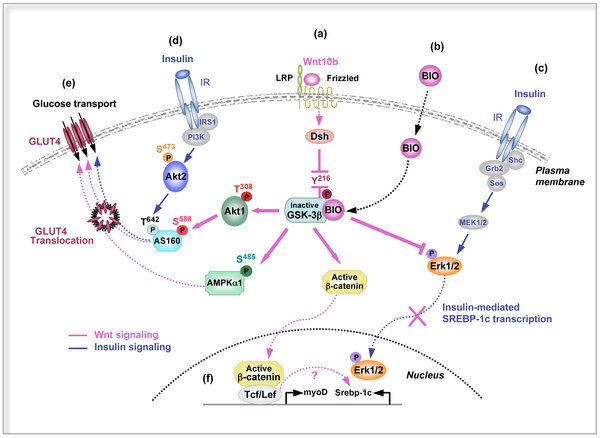
Insulin sensitivity

Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
is a peptide hormone
Peptide hormones are hormones composed of peptide molecules. These hormones influence the endocrine system of animals, including humans. Most hormones are classified as either amino-acid-based hormones (amines, peptides, or proteins) or steroid h ...
involved in glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning fo ...
within certain organisms. Specifically, it leads to upregulation of glucose transporter
Glucose transporters are a wide group of membrane proteins that facilitate the transport of glucose across the plasma membrane, a process known as facilitated diffusion. Because glucose is a vital source of energy for all life, these transporte ...
s in the cell membrane in order to increase glucose uptake from the bloodstream
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart an ...
. This process is partially mediated by activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which can increase a cell's insulin sensitivity. In particular, Wnt10b is a Wnt protein that increases this sensitivity in skeletal muscle cells.
Clinical implications
Cancer
Since its initial discovery, Wnt signaling has had an association withcancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
. When Wnt1 was discovered, it was first identified as a proto-oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.
in a mouse model for breast cancer. The fact that Wnt1 is a homolog
In biology, homology is similarity in anatomical structures or genes between organisms of different taxa due to shared ancestry, ''regardless'' of current functional differences. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures as retained her ...
of Wg shows that it is involved in embryonic development, which often calls for rapid cell division and migration. Misregulation of these processes can lead to tumor development via excess cell proliferation.
Canonical Wnt pathway activity is involved in the development of benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
and malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
breast tumors. The role of Wnt pathway in tumor chemoresistance has been also well documented, as well as its role in the maintenance of a distinct subpopulation of cancer-initiating cells. Its presence is revealed by elevated levels of β-catenin in the nucleus and/or cytoplasm, which can be detected with immunohistochemical staining
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Hewett ...
and Western blotting
The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot), or western blotting, is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. Besides detec ...
. Increased β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
expression is correlated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. This accumulation may be due to factors such as mutations in β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
, deficiencies in the β-catenin destruction complex, most frequently by mutations in structurally disordered regions of ''APC'', overexpression of Wnt ligands, loss of inhibitors and/or decreased activity of regulatory pathways (such as the Wnt/calcium pathway). Breast tumors can metastasize
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
due to Wnt involvement in EMT. Research looking at metastasis of basal-like breast cancer to the lungs showed that repression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling can prevent EMT, which can inhibit metastasis.
Wnt signaling has been implicated in the development of other cancers as well as in desmoid fibromatosis. Changes in ''CTNNB1
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
'' expression, which is the gene that encodes β-catenin, can be measured in breast, colorectal, melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare case ...
, prostate
The prostate is an male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemica ...
, lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
, and other cancers. Increased expression of Wnt ligand-proteins such as Wnt1, Wnt2 and Wnt7A were observed in the development of glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nons ...
, oesophageal cancer and ovarian cancer respectively. Other proteins that cause multiple cancer types in the absence of proper functioning include ROR1, ROR2, SFRP4, Wnt5A, WIF1 and those of the TCF/LEF family. Wnt signaling is further implicated in the pathogenesis of bone metastasis from breast and prostate cancer with studies suggesting discrete on and off states. Wnt is down-regulated during the dormancy stage by autocrine '' DKK1'' to avoid immune surveillance, as well as during the dissemination stages by intracellular Dact1. Meanwhile Wnt is activated during the early outgrowth phase by E-selectin.
The link between PGE2 and Wnt suggests that a chronic inflammation-related increase of PGE2 may lead to activation of the Wnt pathway in different tissues, resulting in carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cell (biology), cells are malignant transformation, transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, G ...
.
Type II diabetes
Diabetes mellitus type 2
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
is a common disease that causes reduced insulin secretion and increased insulin resistance in the periphery. It results in increased blood glucose levels, or hyperglycemia, which can be fatal if untreated. Since Wnt signaling is involved in insulin sensitivity, malfunctioning of its pathway could be involved. Overexpression of Wnt5b, for instance, may increase susceptibility due to its role in adipogenesis, since obesity and type II diabetes have high comorbidity. Wnt signaling is a strong activator of mitochondrial biogenesis. This leads to increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) known to cause DNA and cellular damage. This ROS-induced damage is significant because it can cause acute hepatic insulin resistance, or injury-induced insulin resistance. Mutations in Wnt signaling-associated transcription factors, such as TCF7L2, are linked to increased susceptibility.
See also
*AXIN1 *GSK-3 *Management of hair loss *Wingless localisation element 3 (WLE3) *WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 1 (WISP1) *WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 2 (WISP2) *WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 3 (WISP3)References
Further reading
* *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Wnt Signaling Pathway Signal transduction Genes Evolutionary developmental biology