|
Retromer
Retromer is a complex of proteins that has been shown to be important in recycling transmembrane receptors from endosomes to the ''trans''-Golgi network (TGN) and directly back to the plasma membrane. Mutations in retromer and its associated proteins have been linked to Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Retromer is a heteropentameric complex, which in humans is composed of a less defined membrane-associated sorting nexin dimer ( SNX1, SNX2, SNX5, SNX6), and a vacuolar protein sorting (Vps) heterotrimer containing Vps26, Vps29, and Vps35. Although the SNX dimer is required for the recruitment of retromer to the endosomal membrane, the cargo binding function of this complex is contributed by the core heterotrimer through the binding of Vps26 and Vps35 subunits to various cargo molecules including M6PR, wntless, SORL1 (which is also a receptor for other cargo proteins such as APP), and sortilin. Early study on sorting of acid hydrolases such as carboxypeptidase Y (C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retromer And SORL1 On Tubular Endosome
Retromer is a complex of proteins that has been shown to be important in recycling transmembrane receptors from endosomes to the Golgi apparatus, ''trans''-Golgi network (TGN) and directly back to the plasma membrane. Mutations in retromer and its associated proteins have been linked to Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Retromer is a heteropentameric complex, which in humans is composed of a less defined membrane-associated sorting nexin dimer (SNX1, SNX2, SNX5, SNX6), and a vacuolar protein sorting (Vps) heterotrimer containing VPS26A, Vps26, VPS29, Vps29, VPS35, and Vps35. Although the SNX dimer is required for the recruitment of retromer to the endosomal membrane, the cargo binding function of this complex is contributed by the core heterotrimer through the binding of Vps26 and Vps35 subunits to various cargo molecules including cation-dependent mannose-6-phosphate receptor, M6PR, GPR177, wntless, SORL1 (which is also a receptor for other cargo proteins such as Amyloid-beta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retromer 6H7W
Retromer is a complex of proteins that has been shown to be important in recycling transmembrane receptors from endosomes to the ''trans''-Golgi network (TGN) and directly back to the plasma membrane. Mutations in retromer and its associated proteins have been linked to Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Retromer is a heteropentameric complex, which in humans is composed of a less defined membrane-associated sorting nexin dimer ( SNX1, SNX2, SNX5, SNX6), and a vacuolar protein sorting (Vps) heterotrimer containing Vps26, Vps29, and Vps35. Although the SNX dimer is required for the recruitment of retromer to the endosomal membrane, the cargo binding function of this complex is contributed by the core heterotrimer through the binding of Vps26 and Vps35 subunits to various cargo molecules including M6PR, wntless, SORL1 (which is also a receptor for other cargo proteins such as APP), and sortilin. Early study on sorting of acid hydrolases such as carboxypeptidase Y (CPY ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VPS35
Vacuolar protein sorting ortholog 35 (VPS35) is a protein involved in autophagy and is implicated in Neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's disease (PD) and Alzheimer's disease (AD). VPS35 is part of a complex called the retromer, which is responsible for transporting select cargo proteins between vesicular structures (e.g., endosomes, lysosomes, vacuoles) and the Golgi apparatus. Mutations in the VPS35 gene (''VPS35'') cause aberrant autophagy, where cargo proteins fail to be transported and dysfunctional or unnecessary proteins fail to be degraded. There are numerous pathways affected by altered ''VPS35'' levels and activity, which have clinical significance in neurodegeneration. There is therapeutic relevance for VPS35, as interventions aimed at correcting VPS35 function are in speculation. Gene In humans, ''VPS35'' is Transcription (biology), transcribed on chromosome 16q11.2 where is spans about 29.6 kilobases and contains 17 exons. It is Conserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
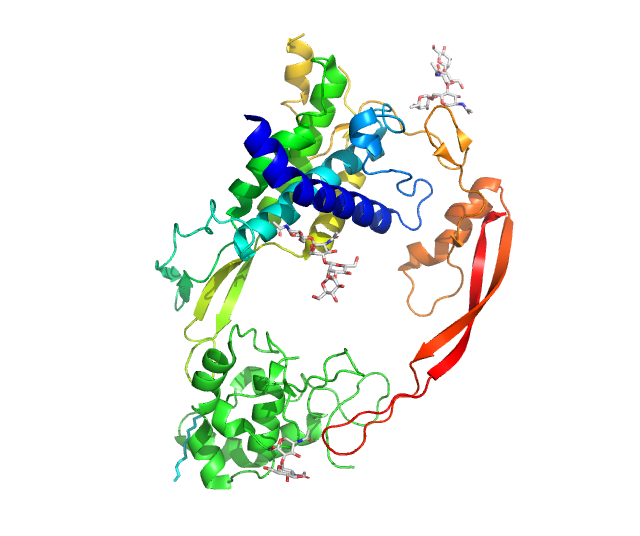
SORL1
Sortilin-related receptor, L(DLR class) A repeats containing is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SORL1 gene. SORL1 (also known as SORLA, SORLA1, or LR11; SORLA or SORL1 are used, often interchangeably, for the protein product of the SORL1 gene) is a 2214 residue type I transmembrane protein receptor that binds certain peptides and integral membrane protein cargo in the endolysosomal pathway and delivers them for sorting to the retromer multi protein complex; the gene is predominantly expressed in the central nervous system. Endosomal traffic jams linked to SORL1 retromer dysfunction are the earliest cellular pathology in both familial and the more common sporadic Alzheimer’s patients. Retromer regulates protein trafficking from the early endosome either back to the trans-Golgi (retrograde) or back to the plasma membrane (direct recycling). Two forms of retromer are known: the VPS26A retromer and the VPS26B retromer, the latter being dedicated to direct recycling in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VPS26A
Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 26A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VPS26A'' gene. This gene belongs to a group of vacuolar protein sorting (VPS) genes. The encoded protein is a component of a large multimeric complex, termed the retromer complex, involved in retrograde transport of proteins from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. The close structural similarity between the yeast and human proteins that make up this complex suggests a similarity in function. Expression studies in yeast and mammalian cells indicate that this protein interacts directly with VPS35, which serves as the core of the retromer complex. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Structure Vps26 is a 38-kDa subunit that has a two-lobed structure with a polar core that resembles the arrestin family of trafficking adaptor. This fold consist of two related β-sandwich subdomains with a fibronectin type III domain topology. The tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNX1
Sorting nexin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX1 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a sorting nexin. SNX1 is a component of the retromer complex. Function This gene encodes a member of the sorting nexin family. Members of this family contain a phox ( PX) domain, which is a phosphoinositide binding domain, and are involved in intracellular trafficking. This endosomal protein regulates the cell-surface expression of epidermal growth factor receptor. This protein also has a role in sorting protease-activated receptor-1 from early endosomes to lysosome A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...s. This protein may form oligomeric complexes with other family members. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Externa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VPS29
VPS29 is a human gene coding for the vacuolar protein sorting protein Vps29, a component of the retromer complex. Yeast homolog The homologous protein (one that performs the same function) in yeast is Vacuolar protein sorting 29 homolog (S. cerevisiae). Function VPS29 belongs to a group of genes coding for vacuolar protein sorting (VPS) proteins that, when functionally impaired, disrupt the efficient delivery of vacuolar hydrolases. The protein encoded by this gene, Vps29, is a component of a large multimeric complex, termed the retromer complex, which is involved in retrograde transport of proteins from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. Vps29 may be involved in the formation of the inner shell of the retromer coat for retrograde vesicles leaving the prevacuolar compartment. Alternative splice variants encoding different isoforms, and usage of multiple polyadenylation Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPR177
Protein wntless homolog, commonly known as Wntless, is encoded in humans by the ''WLS'' gene. Wntless is a receptor for Wnt proteins in Wnt-secreting cells. Wntless was shown to be a cargo for the retromer complex. It has been found essential for hair follicle induction. A homozygous missense mutation In genetics, a missense mutation is a point mutation in which a single nucleotide change results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid. It is a type of nonsynonymous substitution. Missense mutations change amino acids, which in turn alt ... in the ''WLS'' gene was identified in Zaki syndrome. References Further reading * * * * See also * {{G protein-coupled receptors G protein-coupled receptors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endosome
Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of the endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membrane can follow this pathway all the way to lysosomes for degradation or can be recycled back to the cell membrane in the endocytic cycle. Molecules are also transported to endosomes from the trans Golgi network and either continue to lysosomes or recycle back to the Golgi apparatus. Endosomes can be classified as early, sorting, or late depending on their stage post internalization. Endosomes represent a major sorting compartment of the endomembrane system in cells. Function Endosomes provide an environment for material to be sorted before it reaches the degradative lysosome. For example, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is taken into the cell by binding to the LDL receptor at the cell surface. Upon reaching early endosomes, the LDL dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wnt Signaling Pathway
In cellular biology, the Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt, pronounced "wint", is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans. Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. All three pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand to a Frizzled family receptor, which passes the biological signal to the Dishevelled protein inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene transcription, and is thought to be negatively regulated in part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 Receptor
Insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (IGF2R), also called the cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor (CI-MPR) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IGF2R'' gene. IGF2R is a multifunctional protein receptor that binds insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) at the cell surface and mannose-6-phosphate (M6P)-tagged proteins in the ''trans''- Golgi network. Structure The structure of the IGF2R is a type I transmembrane protein (that is, it has a single transmembrane domain with its C-terminus on the cytoplasmic side of lipid membranes) with a large extracellular/lumenal domain and a relatively short cytoplasmic tail. The extracellular domain consists of a small region homologous to the collagen-binding domain of fibronectin and of fifteen repeats of approximately 147 amino acid residues. Each of these repeats is homologous to the 157-residue extracytoplasmic domain of the mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Binding to IGF2 is mediated through one of the repeats, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |