Volpar Super Turbo 18 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Beechcraft Model 18 (or "Twin Beech", as it is also known) is a 6- to 11-seat, twin-engined, low-wing, tailwheel light aircraft manufactured by the Beech Aircraft Corporation of Wichita, Kansas. Continuously produced from 1937 to November 1969 (over 32 years, a world record at the time), over 9,000 were built, making it one of the world's most widely used light aircraft. Sold worldwide as a civilian executive, utility, cargo aircraft, and passenger
''
'' National Museum of the U.S. Air Force'', Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio. Retrieved: August 5, 2017."Twin Beech: The 1930s airplane that set Beech Aircraft Corporation on a course towards 50 years of success"
''
'' National Museum of the U.S. Air Force'', Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio. Retrieved: August 5, 2017. In the early postwar era, the Beech 18 was the pre-eminent "business aircraft" and "feeder airliner". Besides carrying passengers, its civilian uses have included aerial spraying, sterile insect release, fish stocking, dry-ice
"Research and Technology Program Perspectives for General Aviation and Commuter Aircraft"
NASA Contract NASW-3554 for NASA, Sept. 1982, N83-17454#. Retrieved: Dec. 18, 2014. (In particular, see: Table 2.4 "COMMUTER CARGO FLEET IN 1981 - TOP TEN AIRCRAFT MODELS - NUMBER IN FLEET," which notes Beech 18 units are more than the next two aircraft ''combined'' (Convair 500/680 and Douglas DC-3), and more than the next three general aviation aircraft combined."Beech 18" FAA Aircraft Registry.
'' Federal Aviation Administration''. Retrieved: August 5, 2017.
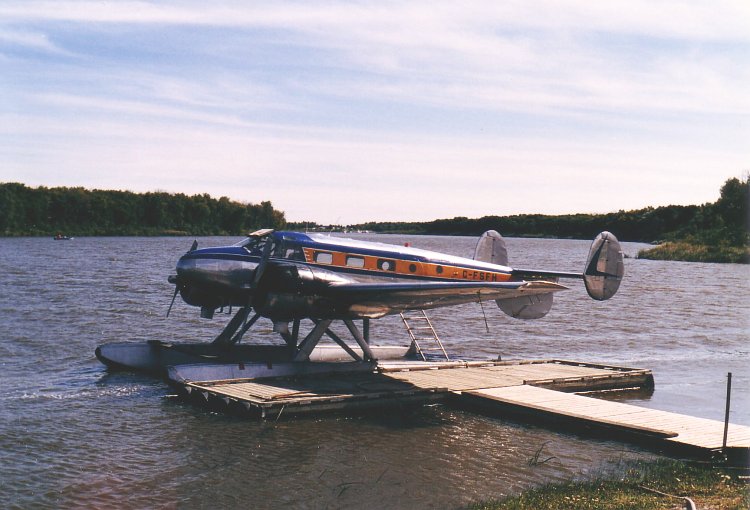
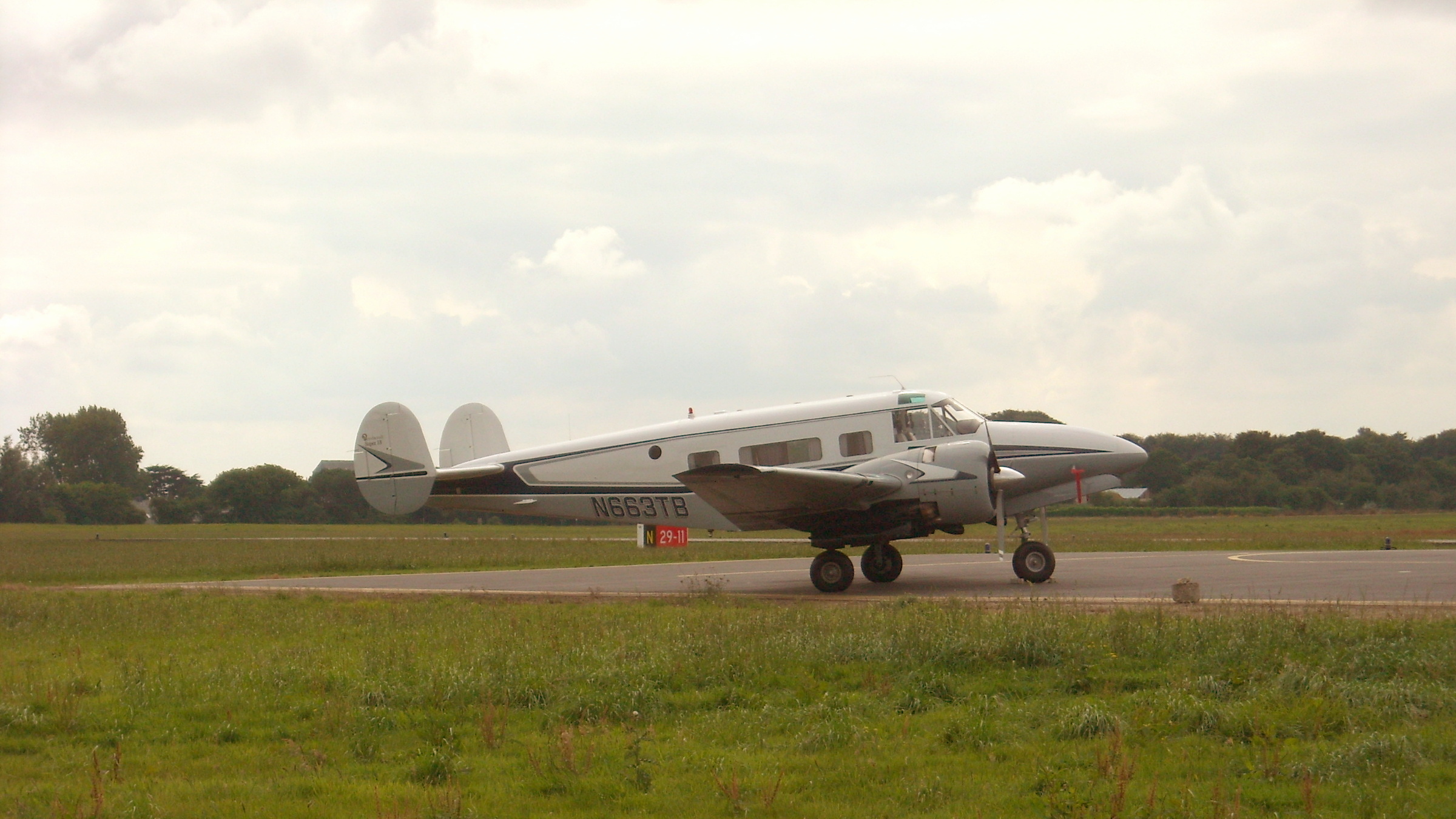

 By the late 1930s, Beechcraft management speculated that a demand would exist for a new design dubbed the Model 18, which would have a military application, and increased the main production facilities. The design was mainly conventional for the time, including twin radial engines, all-metal semimonocoque construction with fabric-covered control surfaces, and tailwheel
By the late 1930s, Beechcraft management speculated that a demand would exist for a new design dubbed the Model 18, which would have a military application, and increased the main production facilities. The design was mainly conventional for the time, including twin radial engines, all-metal semimonocoque construction with fabric-covered control surfaces, and tailwheel
''Beechcraft Heritage Museum''. Retrieved: August 24, 2008. Construction of the Beechcraft Model 18 ended in 1970 with a final Model H18 going to Japan Airlines. Through the years, 32 variations of the basic design had flown, over 200 improvement modification kits were developed, and almost 8,000 aircraft were built. In one case, the aircraft was modified to a triple tail, trigear, humpbacked configuration and appeared similar to a miniature Lockheed Constellation. Another distinctive conversion was carried out by Pacific Airmotive as the PacAero Tradewind. This featured a lengthened nose to accommodate the tricycle nosewheel, and the Model 18's twin tailfins were replaced by a single fin."Beechcraft 3NMT Expeditor."
''Canadian Museum of Flight.'' Retrieved: August 13, 2012.
 Production got an early boost when Nationalist China paid the company US$750,000 for six M18R light bombers,"Beechcraft page."
Production got an early boost when Nationalist China paid the company US$750,000 for six M18R light bombers,"Beechcraft page."
''Aerofiles.'' Retrieved: August 12, 2008. but by the time of the U.S. entry into World War II, only 39 Model 18s had been sold, of which 29 were for civilian customers. Work began in earnest on a variant specifically for training United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) military pilots, bombardiers, and navigators. The effort resulted in the Army AT-7. Further development led to the AT-11 navigation trainer, C-45 military transport, and F-2 (the "F" standing for "Fotorecon", short for "photographic reconnaissance"). The United States Navy first adopted the Beech 18 as the JRB-1, equivalent to the F-2, followed by the JRB-2 transport; the JRB was initially named the Voyager, but this name did not enter common use, and JRBs were generally called Expeditors like their USAAF counterparts. The first JRB-1 obtained by the Navy, bureau number (BuNo) ''09771'', was converted from the last civil Model 18 built before production was earmarked solely for the military for the duration of the war. The Navy subsequently obtained more Model 18s as the JRB-3 (C-45B), JRB-4 (UC-45F), SNB-1 Kansan (AT-11), SNB-2 (AT-7), and SNB-2C (AT-7C). Existing naval Twin Beeches were subsequently modified into the SNB-2H air ambulance, SNB-2P reconnaissance trainer, and SNB-3Q electronic countermeasures trainer. The United States Coast Guard acquired seven JRB-4 and JRB-5 aircraft from the Navy between 1943 and 1947; they were primarily used as utility transports, with one aircraft later converted for aerial mapping, and another used for proficiency flying. After the war, the USAAF became the United States Air Force (USAF), and the USAF
''Beechcraft Heritage Museum''. Retrieved: August 24, 2008. The USN had many of its surviving aircraft remanufactured as well, resulting in the JRB-6, the SNB-5, and SNB-5P. The Coast Guard retired its JRBs in 1956 and sold most of them as surplus in 1959, but one was retained by the United States Coast Guard Reserve until at least 1972. With the adoption of the
''University of Texas at Dallas'', 2006. Retrieved: August 5, 2017.
"Beech JRB Expedition (sic), Beech SNB Kansan and Navigator".
''microworks.ne.'' Retrieved: August 28, 2008. *Model S18B :Version of Model 18B capable of being fitted with skis or floats. ;Model 18D :Variant with seating for two pilots and nine passengers, fitted with
''Beechcraft Heritage Museum.'' Retrieved: August 12, 2008. ;Model A18D :Variant of 18D with MTOW increased by to . *Model SA18D :Seaplane version of Model A18D, but same MTOW as S18D. ;Model 18R :Model with
''Federal Aviation Administration''. Retrieved: August 12, 2008. ;Model D18S :First post-World War II variant introduced in 1945, with seating for eight passengers and MTOW of , 1,035 built"Aircraft Serial Number Lists 1945–2008."
''Hawker Beechcraft''. Retrieved: August 8, 2008. ;Model D18C :Variant with Continental R9-A engines of and MTOW of , introduced in 1947, 31 built.FAA Beech D18/E18/G18/H18 Series Type Certificate.
Retrieved 8 August 2008."Beech 18".
''Airliners.net''. Retrieved: August 8, 2008. ;Model E18S :Variant with redesigned wing and MTOW of ; 403 built ;Model E18S-9700 :Variant of E18S with MTOW of ; 57 built ;Model G18S :Superseded E18S, MTOW of ; 155 built
;Model G18S-9150
:Lightweight version of G18, MTOW of ; one built
;Model H18
:Last production version, fitted with optional tricycle undercarriage developed by Volpar and MTOW of ; 149 built, of which 109 were manufactured with tricycle undercarriage
:Superseded E18S, MTOW of ; 155 built
;Model G18S-9150
:Lightweight version of G18, MTOW of ; one built
;Model H18
:Last production version, fitted with optional tricycle undercarriage developed by Volpar and MTOW of ; 149 built, of which 109 were manufactured with tricycle undercarriage
''uswarplanes.net''. Retrieved 24 August 2008.Baugher, Joe
''USAAS-USAAC-USAAF-USAF Aircraft Serial Numbers–1908 to Present''. Retrieved: June 11, 2011. ;C-45D :Designation given to two AT-7 aircraft converted as passenger transports during manufacture, redesignated UC-45D in January 1943Baugher, Joe
''USAAS-USAAC-USAAF-USAF Aircraft Serial Numbers–1908 to Present''. Retrieved: June 11, 2011. ;C-45E :Designation given to two AT-7 and four AT-7B aircraft converted as passenger transports during manufacture, redesignated UC-45E in January 1943 ;C-45F :Standardized seven-seat version based on C18S, with longer nose than preceding models; 1,137 ordered, redesignated UC-45F ;C-45G :AT-7s and AT-11s remanufactured in the early 1950s for the USAF to similar standard as civil D18S with autopilot and R-985-AN-3 engines; 372 aircraft rebuilt ;TC-45G :Multiengine crew trainer variant of C-45G; AT-7s and AT-11s remanufactured in the early 1950s for the USAF to similar standard as civil D18S, 96 aircraft rebuiltBaugher, Joe
"USAF 1951 Serial Number List."
''USAAS-USAAC-USAAF-USAF Aircraft Serial Numbers–1908 to Present''. Retrieved 11 June 2011. ;C-45H :AT-7s and AT-11s remanufactured in the early 1950s for the USAF to similar standard as civil D18S, with no autopilot and R-985-AN-14B engines; 432 aircraft rebuiltBaugher, Joe
''USAAS-USAAC-USAAF-USAF Aircraft Serial Numbers–1908 to Present''. Retrieved: August 24, 2008. ;TC-45H ;RC-45J :In 1962, all surviving U.S. Navy SNB-5Ps were redesignated RC-45J ;TC-45J :In 1962 all surviving U.S. Navy SNB-5s were redesignated TC-45J ;UC-45J :Subsequent redesignation of RC-45J and TC-45J ;AT-7 Navigator :Navigation trainer based on C18S, with an astrodome and positions for three students, powered by 450-hp ;F-2
:Photo-reconnaissance version based on B18
;F-2A
:Improved version
;F-2B
;F-2
:Photo-reconnaissance version based on B18
;F-2A
:Improved version
;F-2B

 ;JRB-1
:Photographic aircraft, based on the C18S, fitted with fairing over cockpit for improved visibility, 11 obtained,Swanborough and Bowers 1976, p. 41. at least one conversion from impressed civil B18S
;JRB-2
:Light transport, based on the C18S; 15 obtained, at least one conversion from JRB-1, some transferred from USAAF C-45A stocks
;JRB-3
:Photographic version, similar to C-45B; 23 obtained, some transferred from USAAF C-45B stocks
;JRB-4
:Utility transport version, equivalent to UC-45F; 328 obtained from USAAF
;JRB-6
:Remanufactured JRB
;SNB-1
:Similar to AT-11; 110 built
;SNB-2
:Navigation trainer similar to AT-7, 299 built
;SNB-2C
:Navigation trainer similar to AT-7C, 375 built
;SNB-2H
:Ambulance conversion
;SNB-2P
:Photo-reconnaissance trainer conversion
;SNB-3Q
:Electronic countermeasures trainer conversion
;SNB-5
:Remanufactured SNB or JRB
;SNB-5P
:Remanufactured SNB-2P
;JRB-1
:Photographic aircraft, based on the C18S, fitted with fairing over cockpit for improved visibility, 11 obtained,Swanborough and Bowers 1976, p. 41. at least one conversion from impressed civil B18S
;JRB-2
:Light transport, based on the C18S; 15 obtained, at least one conversion from JRB-1, some transferred from USAAF C-45A stocks
;JRB-3
:Photographic version, similar to C-45B; 23 obtained, some transferred from USAAF C-45B stocks
;JRB-4
:Utility transport version, equivalent to UC-45F; 328 obtained from USAAF
;JRB-6
:Remanufactured JRB
;SNB-1
:Similar to AT-11; 110 built
;SNB-2
:Navigation trainer similar to AT-7, 299 built
;SNB-2C
:Navigation trainer similar to AT-7C, 375 built
;SNB-2H
:Ambulance conversion
;SNB-2P
:Photo-reconnaissance trainer conversion
;SNB-3Q
:Electronic countermeasures trainer conversion
;SNB-5
:Remanufactured SNB or JRB
;SNB-5P
:Remanufactured SNB-2P
 ;Conrad 9800
:Modification increasing the gross weight to 9,800 pounds with a single piece windshield
;Dumod I
: Executive conversion with Volpar tricycle landing gear, new wing tips, enlarged fight deck and refurbished 6–7 seat cabin with larger windows. Originally named Infinité I. 37 converted by 1966.Taylor 1967, p. 250.
;Dumod Liner
:Stretched airliner conversion. Similar to Dumod I but with forward fuselage stretched by , allowing up to 15 passengers to be carried. Originally named Infinité II.
;Hamilton HA-1
:conversion of a TC-45J aircraft
;Hamilton Little Liner
:Modification of D18S with aerodynamic improvements and new, retractable tailwheel, capable of carrying 11 seatsTaylor 1965, p. 280.
;Hamilton Westwind
:Turboprop conversions with various engines
;Conrad 9800
:Modification increasing the gross weight to 9,800 pounds with a single piece windshield
;Dumod I
: Executive conversion with Volpar tricycle landing gear, new wing tips, enlarged fight deck and refurbished 6–7 seat cabin with larger windows. Originally named Infinité I. 37 converted by 1966.Taylor 1967, p. 250.
;Dumod Liner
:Stretched airliner conversion. Similar to Dumod I but with forward fuselage stretched by , allowing up to 15 passengers to be carried. Originally named Infinité II.
;Hamilton HA-1
:conversion of a TC-45J aircraft
;Hamilton Little Liner
:Modification of D18S with aerodynamic improvements and new, retractable tailwheel, capable of carrying 11 seatsTaylor 1965, p. 280.
;Hamilton Westwind
:Turboprop conversions with various engines
 ;Hamilton Westwind II STD: Stretched conversion powered by two 840-hp
;Hamilton Westwind II STD: Stretched conversion powered by two 840-hp
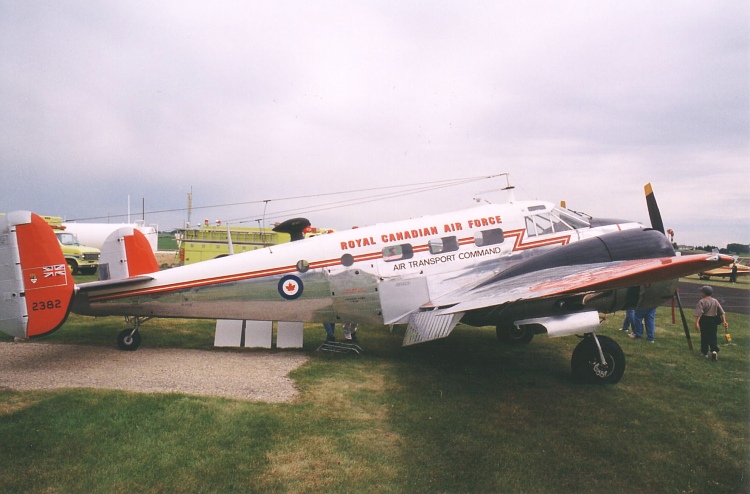



 ;
* Argentine Air ForceBridgman 1951, p. 3a.
* Argentine Naval Aviation
;
* Bolivian Air ForceBridgman 1951, p. 4a.
;
*
;
* Argentine Air ForceBridgman 1951, p. 3a.
* Argentine Naval Aviation
;
* Bolivian Air ForceBridgman 1951, p. 4a.
;
*

Experimental Aircraft Association (Chapter 1000) Beech E18S overview and pictorial tour
{{Authority control 0018 1930s United States military trainer aircraft C-45, Beechcraft 1930s United States civil utility aircraft World War II trainer aircraft of the United States Aircraft first flown in 1937 Twin piston-engined tractor aircraft Low-wing aircraft Twin-tail aircraft
airliner
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an ...
on tailwheels, nosewheels, skis, or floats, it was also used as a military aircraft."Beechcraft D18S Twin Beech."''
National Air and Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum of the Smithsonian Institution, also called the Air and Space Museum, is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States.
Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, it opened its main building on the Nat ...
'' of the Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C. Retrieved: December 17, 2014."Fact Sheet: Beech C-45H Expeditor."'' National Museum of the U.S. Air Force'', Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio. Retrieved: August 5, 2017."Twin Beech: The 1930s airplane that set Beech Aircraft Corporation on a course towards 50 years of success"
''
Flying Magazine
''Flying'', sometimes styled ''FLYING'', is an aviation magazine published since 1927 and called Ziff Davis#Popular Aviation, ''Popular Aviation'' prior to 1942, as well as ''Aeronautics'' for a brief period. It is read by pilots, aircraft owners ...
'', February 1982, pp. 26-30, Retrieved: August 5, 2017
During and after World War II, over 4,500 Beech 18s were used in military service—as light transport, light bomber (for China), aircrew trainer (for bombing, navigation, and gunnery), photo-reconnaissance, and "mother ship" for target drones
Drone most commonly refers to:
* Drone (bee), a male bee, from an unfertilized egg
* Unmanned aerial vehicle
* Unmanned surface vehicle, watercraft
* Unmanned underwater vehicle or underwater drone
Drone, drones or The Drones may also refer to:
...
—including United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) C-45 Expeditor, AT-7 Navigator, and AT-11 Kansan; and United States Navy (USN) UC-45J Navigator, SNB-1 Kansan, and others. In World War II, over 90% of USAAF bombardiers and navigators trained in these aircraft."Fact Sheet: Beech AT-11 Kansan."'' National Museum of the U.S. Air Force'', Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio. Retrieved: August 5, 2017. In the early postwar era, the Beech 18 was the pre-eminent "business aircraft" and "feeder airliner". Besides carrying passengers, its civilian uses have included aerial spraying, sterile insect release, fish stocking, dry-ice
cloud seeding
Cloud seeding is a type of weather modification that aims to change the amount or type of precipitation that falls from clouds by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei, which alter the microphysical p ...
, aerial firefighting, air-mail delivery, ambulance service, numerous movie productions, skydiving, freight, weapon- and drug-smuggling
Smuggling is the illegal transportation of objects, substances, information or people, such as out of a house or buildings, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations.
There are various ...
, engine testbed, skywriting, banner towing, and stunt aircraft. Many are privately owned, around the world, with 240 in the U.S. still on the FAA Aircraft Registry in August 2017.Bauschspies, James S. and William E. Simpson"Research and Technology Program Perspectives for General Aviation and Commuter Aircraft"
NASA Contract NASW-3554 for NASA, Sept. 1982, N83-17454#. Retrieved: Dec. 18, 2014. (In particular, see: Table 2.4 "COMMUTER CARGO FLEET IN 1981 - TOP TEN AIRCRAFT MODELS - NUMBER IN FLEET," which notes Beech 18 units are more than the next two aircraft ''combined'' (Convair 500/680 and Douglas DC-3), and more than the next three general aviation aircraft combined."Beech 18" FAA Aircraft Registry.
'' Federal Aviation Administration''. Retrieved: August 5, 2017.
Design and development

 By the late 1930s, Beechcraft management speculated that a demand would exist for a new design dubbed the Model 18, which would have a military application, and increased the main production facilities. The design was mainly conventional for the time, including twin radial engines, all-metal semimonocoque construction with fabric-covered control surfaces, and tailwheel
By the late 1930s, Beechcraft management speculated that a demand would exist for a new design dubbed the Model 18, which would have a military application, and increased the main production facilities. The design was mainly conventional for the time, including twin radial engines, all-metal semimonocoque construction with fabric-covered control surfaces, and tailwheel undercarriage
Undercarriage is the part of a moving vehicle that is underneath the main body of the vehicle. The term originally applied to this part of a horse-drawn carriage, and usage has since broadened to include:
*The landing gear of an aircraft.
*The ch ...
. Less conventional was the twin-tailfin configuration. The Model 18 can be mistaken for the larger Lockheed Electra Lockheed Electra refers to two distinct aircraft designs:
* Lockheed Model 10 Electra, a ten-passenger piston engine aircraft of the 1930s, which had two immediate variants:
** Lockheed Model 12 Electra Junior, a six-passenger scaled-down version o ...
series of airliners, which closely resemble it. Early production aircraft were powered either by two 330-hp (250-kW) Jacobs L-6s or 350-hp (260-kW) Wright R-760Es. The 450-hp (336-kW) Pratt & Whitney R-985
The Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior is a series of nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engines built by the Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Company from the 1930s to the 1950s. These engines have a displacement of ; initial versions produced , ...
became the definitive engine from the prewar C18S onwards. The Beech 18 prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototyp ...
first flew on January 15, 1937.
The aircraft has used a variety of engines and has had a number of airframe modifications to increase gross weight and speed. At least one aircraft was modified to a 600-hp (447-kW) Pratt & Whitney R-1340 powerplant configuration. With the added weight of about 200 lb (91 kg) per engine, the concept of a Model 18 fitted with R-1340 engines was deemed unsatisfactory due to the weakest structural area of the aircraft being the engine mounts. Nearly every airframe component has been modified.
In 1955, deliveries of the Model E18S commenced; the E18S featured a fuselage that was extended higher for more headroom in the passenger cabin. All later Beech 18s (sometimes called Super 18s) featured this taller fuselage, and some earlier models (including one AT-11) have been modified to this larger fuselage. The Model H18, introduced in 1963, featured optional tricycle undercarriage. Unusually, the undercarriage was developed for earlier-model aircraft under an STC STC may refer to:
Education
* Saint Theresa's College (disambiguation), any of several institutions
* St. Thomas' College, Matale, Sri Lanka
* S. Thomas' College, Mount Lavinia, Sri Lanka
* Scott Theological College, Kenya
* Sha Tin College, H ...
by Volpar, and installed in H18s at the factory during manufacture. A total of 109 H18s was built with tricycle undercarriage, and another 240 earlier-model aircraft were modified with this."Model 18 Specifications."''Beechcraft Heritage Museum''. Retrieved: August 24, 2008. Construction of the Beechcraft Model 18 ended in 1970 with a final Model H18 going to Japan Airlines. Through the years, 32 variations of the basic design had flown, over 200 improvement modification kits were developed, and almost 8,000 aircraft were built. In one case, the aircraft was modified to a triple tail, trigear, humpbacked configuration and appeared similar to a miniature Lockheed Constellation. Another distinctive conversion was carried out by Pacific Airmotive as the PacAero Tradewind. This featured a lengthened nose to accommodate the tricycle nosewheel, and the Model 18's twin tailfins were replaced by a single fin."Beechcraft 3NMT Expeditor."
''Canadian Museum of Flight.'' Retrieved: August 13, 2012.
Operational history
 Production got an early boost when Nationalist China paid the company US$750,000 for six M18R light bombers,"Beechcraft page."
Production got an early boost when Nationalist China paid the company US$750,000 for six M18R light bombers,"Beechcraft page."''Aerofiles.'' Retrieved: August 12, 2008. but by the time of the U.S. entry into World War II, only 39 Model 18s had been sold, of which 29 were for civilian customers. Work began in earnest on a variant specifically for training United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) military pilots, bombardiers, and navigators. The effort resulted in the Army AT-7. Further development led to the AT-11 navigation trainer, C-45 military transport, and F-2 (the "F" standing for "Fotorecon", short for "photographic reconnaissance"). The United States Navy first adopted the Beech 18 as the JRB-1, equivalent to the F-2, followed by the JRB-2 transport; the JRB was initially named the Voyager, but this name did not enter common use, and JRBs were generally called Expeditors like their USAAF counterparts. The first JRB-1 obtained by the Navy, bureau number (BuNo) ''09771'', was converted from the last civil Model 18 built before production was earmarked solely for the military for the duration of the war. The Navy subsequently obtained more Model 18s as the JRB-3 (C-45B), JRB-4 (UC-45F), SNB-1 Kansan (AT-11), SNB-2 (AT-7), and SNB-2C (AT-7C). Existing naval Twin Beeches were subsequently modified into the SNB-2H air ambulance, SNB-2P reconnaissance trainer, and SNB-3Q electronic countermeasures trainer. The United States Coast Guard acquired seven JRB-4 and JRB-5 aircraft from the Navy between 1943 and 1947; they were primarily used as utility transports, with one aircraft later converted for aerial mapping, and another used for proficiency flying. After the war, the USAAF became the United States Air Force (USAF), and the USAF
Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile ...
had Model 18 variants (AT-11 Kansans, C-45 Expeditors, F-2 Expeditors, and UC-45 Expeditors) from 1946 until 1951. In 1950, the Navy still had around 1,200 JRB and SNB aircraft in inventory. From 1951 to 1955, the USAF had many of its aircraft remanufactured with new fuselages, wing center sections, and undercarriages to take advantage of the improvements to the civil models since the end of World War II. Eventually, 900 aircraft were remanufactured to be similar to the then-current Model D18S and given new designations, constructor's numbers, and Air Force serial numbers."C-45H."''Beechcraft Heritage Museum''. Retrieved: August 24, 2008. The USN had many of its surviving aircraft remanufactured as well, resulting in the JRB-6, the SNB-5, and SNB-5P. The Coast Guard retired its JRBs in 1956 and sold most of them as surplus in 1959, but one was retained by the United States Coast Guard Reserve until at least 1972. With the adoption of the
1962 United States Tri-Service aircraft designation system
The Tri-Service aircraft designation system is a unified system introduced in 1962 by the United States Department of Defense for designating all U.S. military aircraft. Previously, the U.S. armed services used separate nomenclature systems.
...
, the Navy's SNB-5 and SNB-5P became the TC-45J and RC-45J respectively, later becoming the UC-45J as their primary mission shifted from aircrew training to utility transport work. The C-45 flew in USAF service until 1963, the USN retired its last UC-45J in 1972, while the U.S. Army flew its C-45s until 1976. In later years, the military called these aircraft "bug smashers" in reference to their extensive use supplying mandatory flight hours for desk-bound aviators in the Pentagon.O'Rourke, G.G, CAPT USN. "Of Hosenoses, Stoofs, and Lefthanded Spads." ''United States Naval Institute Proceedings'', July 1968.
Beech 18s were used extensively by Air America during the Vietnam War; initially more-or-less standard ex-military C-45 examples were used, but then the airline had 12 aircraft modified by Conrad Conversions in 1963 and 1964 to increase performance and load-carrying capacity. The modified aircraft were known as Conrad Ten-Twos, as the maximum takeoff weight (MTOW) was increased to . The increase was achieved by several airframe modifications, including increased horizontal stabilizer angle-of-incidence, redesigned undercarriage doors, and aerodynamically improved wingtips. Air America then had Volpar convert 14 aircraft to turboprop power, fitted with Garrett AiResearch TPE-331 engines; modified aircraft were called Volpar Turbo Beeches, and also had a further increase in MTOW to ."Air America: Beech/Volpar Turbo Beech 18".''University of Texas at Dallas'', 2006. Retrieved: August 5, 2017.
Spar problems
The wing spar of the Model 18 was fabricated by welding an assembly of tubular steel. The configuration of the tubes in combination with drilled holes from aftermarket STC modifications on some of these aircraft have allowed the spar to become susceptible to corrosion and cracking while in service. This prompted the FAA to issue an Airworthiness Directive in 1975, mandating the fitting of a spar strap to some Model 18s. This led, in turn, to the retirement of a large number of STC-modified Model 18s when owners determined the aircraft were worth less than the cost of the modifications. The corrosion on unmodified spars was not a problem; it occurred due to the additional exposed surface area created through the STC hole-drilling process. Further requirements have been mandated by the FAA and other national airworthiness authorities, including regular removal of the spar strap to allow the strap to be checked for cracks and corrosion and the spar to beX-rayed
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 ...
. In Australia, the airworthiness authority has placed a life limit on the airframe, beyond which aircraft are not allowed to fly.
Variants
Manufacturer models
Unless otherwise noted, the engines fitted arePratt & Whitney R-985
The Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior is a series of nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engines built by the Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Company from the 1930s to the 1950s. These engines have a displacement of ; initial versions produced , ...
radials.
;Model 18A
:First production model with seating for two pilots and seven or eight passengers, fitted with Wright R-760E-2 engines of , MTOW: Four built.Pelletier 1995, p. 68
*Model S18A
:Version of Model 18A capable of being fitted with skis or Edo
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a ''jōkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of ...
55-7170 floats; MTOW:
;Model A18A
:Version fitted with Wright R-760E-2 engines, MTOW:
*Model SA18A
:Seaplane version of Model A18A, MTOW:
;Model 18B
:Version powered with Jacobs L-5
The Jacobs R-830 or L-5 is a seven-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft manufactured in the United States, production started in 1935.Gunston 1989, p.85.
Design and development
The R-830 was effectively an enlargement of the R-755 ...
engines. Four built.McKillop, Jack"Beech JRB Expedition (sic), Beech SNB Kansan and Navigator".
''microworks.ne.'' Retrieved: August 28, 2008. *Model S18B :Version of Model 18B capable of being fitted with skis or floats. ;Model 18D :Variant with seating for two pilots and nine passengers, fitted with
Jacobs L-6
The Jacobs R-915 or Jacobs L-6 is a seven-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft manufactured in the United States, production started in 1936.
Design and development
The R-915 was effectively an enlargement of the R-755 with strengt ...
engines of , MTOW: . Twelve aircraft built.
*Model S18D
:Version of Model 18D capable of being fitted with skis or , MTOW: "S18D."''Beechcraft Heritage Museum.'' Retrieved: August 12, 2008. ;Model A18D :Variant of 18D with MTOW increased by to . *Model SA18D :Seaplane version of Model A18D, but same MTOW as S18D. ;Model 18R :Model with
Pratt and Whitney R-985
The Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior is a series of nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engines built by the Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Company from the 1930s to the 1950s. These engines have a displacement of ; initial versions produced ...
, , seven built, one to Sweden as an air ambulance, six to Nationalist China as M18R light bombers
;Model 18S
:Nine-passenger pre-World War II civil variant, powered by served as basis for USAAF C-45C
;Model B18S
:Nine-passenger pre-World War II civil variant, served as basis for USAAF F-2
;Model C18S
:Variant of B18S with seating for eight passengers, and equipment and minor structural changes"Beech C18S Type Certificate."''Federal Aviation Administration''. Retrieved: August 12, 2008. ;Model D18S :First post-World War II variant introduced in 1945, with seating for eight passengers and MTOW of , 1,035 built"Aircraft Serial Number Lists 1945–2008."
''Hawker Beechcraft''. Retrieved: August 8, 2008. ;Model D18C :Variant with Continental R9-A engines of and MTOW of , introduced in 1947, 31 built.FAA Beech D18/E18/G18/H18 Series Type Certificate.
Retrieved 8 August 2008."Beech 18".
''Airliners.net''. Retrieved: August 8, 2008. ;Model E18S :Variant with redesigned wing and MTOW of ; 403 built ;Model E18S-9700 :Variant of E18S with MTOW of ; 57 built ;Model G18S
 :Superseded E18S, MTOW of ; 155 built
;Model G18S-9150
:Lightweight version of G18, MTOW of ; one built
;Model H18
:Last production version, fitted with optional tricycle undercarriage developed by Volpar and MTOW of ; 149 built, of which 109 were manufactured with tricycle undercarriage
:Superseded E18S, MTOW of ; 155 built
;Model G18S-9150
:Lightweight version of G18, MTOW of ; one built
;Model H18
:Last production version, fitted with optional tricycle undercarriage developed by Volpar and MTOW of ; 149 built, of which 109 were manufactured with tricycle undercarriage
Military versions
USAAC/USAAF designations
;C-45 :Six-seat staff transport based on C18S; 11 builtDonald 1995, p. 7.Swanborough and Bowers 1963, p. 36. ;C-45A :Eight-seat utility transport based on C18S; 20 built ;RC-45A :Redesignation of all surviving F-2, F-2A, and F-2B aircraft by the USAF in 1948 ;C-45B :Based on C18S, but with modified internal layout; 223 ordered, redesignated UC-45B in 1943 ;C-45C :Two Model 18S aircraft impressed into the USAAF, redesignated UC-45C in January 1943"USA Warplanes C-45 page."''uswarplanes.net''. Retrieved 24 August 2008.Baugher, Joe
''USAAS-USAAC-USAAF-USAF Aircraft Serial Numbers–1908 to Present''. Retrieved: June 11, 2011. ;C-45D :Designation given to two AT-7 aircraft converted as passenger transports during manufacture, redesignated UC-45D in January 1943Baugher, Joe
''USAAS-USAAC-USAAF-USAF Aircraft Serial Numbers–1908 to Present''. Retrieved: June 11, 2011. ;C-45E :Designation given to two AT-7 and four AT-7B aircraft converted as passenger transports during manufacture, redesignated UC-45E in January 1943 ;C-45F :Standardized seven-seat version based on C18S, with longer nose than preceding models; 1,137 ordered, redesignated UC-45F ;C-45G :AT-7s and AT-11s remanufactured in the early 1950s for the USAF to similar standard as civil D18S with autopilot and R-985-AN-3 engines; 372 aircraft rebuilt ;TC-45G :Multiengine crew trainer variant of C-45G; AT-7s and AT-11s remanufactured in the early 1950s for the USAF to similar standard as civil D18S, 96 aircraft rebuiltBaugher, Joe
"USAF 1951 Serial Number List."
''USAAS-USAAC-USAAF-USAF Aircraft Serial Numbers–1908 to Present''. Retrieved 11 June 2011. ;C-45H :AT-7s and AT-11s remanufactured in the early 1950s for the USAF to similar standard as civil D18S, with no autopilot and R-985-AN-14B engines; 432 aircraft rebuiltBaugher, Joe
''USAAS-USAAC-USAAF-USAF Aircraft Serial Numbers–1908 to Present''. Retrieved: August 24, 2008. ;TC-45H ;RC-45J :In 1962, all surviving U.S. Navy SNB-5Ps were redesignated RC-45J ;TC-45J :In 1962 all surviving U.S. Navy SNB-5s were redesignated TC-45J ;UC-45J :Subsequent redesignation of RC-45J and TC-45J ;AT-7 Navigator :Navigation trainer based on C18S, with an astrodome and positions for three students, powered by 450-hp
Pratt & Whitney R-985-25
The Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior is a series of nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engines built by the Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Company from the 1930s to the 1950s. These engines have a displacement of ; initial versions produced ...
engines; 577 built
;AT-7A
:Floatplane version of AT-7; six built
;AT-7B
:Winterised AT-7; nine built
;AT-7C
:Based on C18S with R-985-AN3 engines; 549 built
;AT-11 Kansan
:Bombing and gunnery trainer for USAAF derived from AT-7, fuselage had small, circular cabin windows, bombardier position in nose, and bomb bay; gunnery trainers were also fitted with two or three .30-caliber machine guns, early models (the first 150 built) had a single .30-cal AN-M2 in a Beechcraft-manufactured top turret, later models used a Crocker Wheeler twin .30-cal top turret, a bottom tunnel gun was used for tail gunner training, 1,582 built for USAAF orders, with 24 ordered by Netherlands repossessed by USAAF and used by the Royal Netherlands Military Flying School at Jackson, Mississippi.Donald 1995, pp. 7–8.Swanborough and Bowers 1963, p. 37.
;AT-11A
:Conversion of AT-11 as navigation trainer; 36 converted
;CQ-3
:Conversion of UC-45F, modified to act as drone
Drone most commonly refers to:
* Drone (bee), a male bee, from an unfertilized egg
* Unmanned aerial vehicle
* Unmanned surface vehicle, watercraft
* Unmanned underwater vehicle or underwater drone
Drone, drones or The Drones may also refer to:
...
control aircraft, redesignated as DC-45F in June 1948
 ;F-2
:Photo-reconnaissance version based on B18
;F-2A
:Improved version
;F-2B
;F-2
:Photo-reconnaissance version based on B18
;F-2A
:Improved version
;F-2B
US Navy designations

 ;JRB-1
:Photographic aircraft, based on the C18S, fitted with fairing over cockpit for improved visibility, 11 obtained,Swanborough and Bowers 1976, p. 41. at least one conversion from impressed civil B18S
;JRB-2
:Light transport, based on the C18S; 15 obtained, at least one conversion from JRB-1, some transferred from USAAF C-45A stocks
;JRB-3
:Photographic version, similar to C-45B; 23 obtained, some transferred from USAAF C-45B stocks
;JRB-4
:Utility transport version, equivalent to UC-45F; 328 obtained from USAAF
;JRB-6
:Remanufactured JRB
;SNB-1
:Similar to AT-11; 110 built
;SNB-2
:Navigation trainer similar to AT-7, 299 built
;SNB-2C
:Navigation trainer similar to AT-7C, 375 built
;SNB-2H
:Ambulance conversion
;SNB-2P
:Photo-reconnaissance trainer conversion
;SNB-3Q
:Electronic countermeasures trainer conversion
;SNB-5
:Remanufactured SNB or JRB
;SNB-5P
:Remanufactured SNB-2P
;JRB-1
:Photographic aircraft, based on the C18S, fitted with fairing over cockpit for improved visibility, 11 obtained,Swanborough and Bowers 1976, p. 41. at least one conversion from impressed civil B18S
;JRB-2
:Light transport, based on the C18S; 15 obtained, at least one conversion from JRB-1, some transferred from USAAF C-45A stocks
;JRB-3
:Photographic version, similar to C-45B; 23 obtained, some transferred from USAAF C-45B stocks
;JRB-4
:Utility transport version, equivalent to UC-45F; 328 obtained from USAAF
;JRB-6
:Remanufactured JRB
;SNB-1
:Similar to AT-11; 110 built
;SNB-2
:Navigation trainer similar to AT-7, 299 built
;SNB-2C
:Navigation trainer similar to AT-7C, 375 built
;SNB-2H
:Ambulance conversion
;SNB-2P
:Photo-reconnaissance trainer conversion
;SNB-3Q
:Electronic countermeasures trainer conversion
;SNB-5
:Remanufactured SNB or JRB
;SNB-5P
:Remanufactured SNB-2P
RAF/RCAF Lend-lease designations
;Expeditor I: C-45Bs supplied to the RAF underLend-Lease
Lend-Lease, formally the Lend-Lease Act and introduced as An Act to Promote the Defense of the United States (), was a policy under which the United States supplied the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union and other Allied nations with food, oil, ...
;Expeditor II: C-45Fs supplied to the RAF and Royal Navy under Lend-Lease
;Expeditor III: C-45Fs supplied to the RCAF under Lend-Lease
Post-war RCAF designations
C-45Ds delivered between 1951 and 1952 ;Expeditor 3N: navigation trainer - 88 built ;Expeditor 3NM: navigational trainer that could be converted to a transport - 59 built ;Expeditor 3NMT: 3NM converted to a transport aircraft - 67 built ;Expeditor 3NMT(Special): navigation trainer/personnel transport - 19 built ;Expeditor 3TM: transport with fittings so it could be converted to a navigation trainer - 44 built"FAA Type Certificate A-765 (Beech D18/E18/G18/H18 Series)." ''Federal Aviation Administration'', p. 48. ;Expeditor 3TM(Special): modified RCAF Expeditors used overseas in conjunction with Project WPB6 - three builtCanadian Armed Forces
;CT-128 Expeditor: 1968 redesignation of existing RCAF aircraft upon unification of the Canadian Armed ForcesConversions
 ;Conrad 9800
:Modification increasing the gross weight to 9,800 pounds with a single piece windshield
;Dumod I
: Executive conversion with Volpar tricycle landing gear, new wing tips, enlarged fight deck and refurbished 6–7 seat cabin with larger windows. Originally named Infinité I. 37 converted by 1966.Taylor 1967, p. 250.
;Dumod Liner
:Stretched airliner conversion. Similar to Dumod I but with forward fuselage stretched by , allowing up to 15 passengers to be carried. Originally named Infinité II.
;Hamilton HA-1
:conversion of a TC-45J aircraft
;Hamilton Little Liner
:Modification of D18S with aerodynamic improvements and new, retractable tailwheel, capable of carrying 11 seatsTaylor 1965, p. 280.
;Hamilton Westwind
:Turboprop conversions with various engines
;Conrad 9800
:Modification increasing the gross weight to 9,800 pounds with a single piece windshield
;Dumod I
: Executive conversion with Volpar tricycle landing gear, new wing tips, enlarged fight deck and refurbished 6–7 seat cabin with larger windows. Originally named Infinité I. 37 converted by 1966.Taylor 1967, p. 250.
;Dumod Liner
:Stretched airliner conversion. Similar to Dumod I but with forward fuselage stretched by , allowing up to 15 passengers to be carried. Originally named Infinité II.
;Hamilton HA-1
:conversion of a TC-45J aircraft
;Hamilton Little Liner
:Modification of D18S with aerodynamic improvements and new, retractable tailwheel, capable of carrying 11 seatsTaylor 1965, p. 280.
;Hamilton Westwind
:Turboprop conversions with various engines
PT6A
The Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6 is a turboprop aircraft engine produced by Pratt & Whitney Canada.
Its design was started in 1958, it first ran in February 1960, first flew on 30 May 1961, entered service in 1964 and has been continuously up ...
s, and with accommodation for up to 17 passengersTaylor 1976, p. 300.
;Hamilton Westwind III:two 579-hp PT6A-20s or 630-hp PT6A-27s or 630-hp Lycoming LTS101
The Lycoming (now Honeywell) LTS101 is a turboshaft engine family ranging from 650 to 850 shaft horsepower, used in a number of popular helicopters, and, as the LTP101 turboprop, light aircraft. Both models carry the US military designation T702 ...
s.
;Hamilton Westwind IV:two 570-hp Lycoming LTP101s or 680-hp PT6A-28s or 750-hp PT6A-34s or 1020-hp PT6A-45s
;PacAero Tradewind
:Conversion of Beech D18S/C-45 to five- to 11-seat executive transport with single fin by Pacific Airmotive
Gulfstream Aerospace Corporation is an American aircraft company and a wholly owned subsidiary of General Dynamics.
Gulfstream designs, develops, manufactures, markets, and services business jet aircraft. Gulfstream has produced more than 2,000 ...
;Rausch Star 250
:Built as C-45F 44-47231, this aircraft was re-manufactured at Wichita by Beech in 1952, to become TC-45G 51-11544. From 1959 Rausch Engineering Inc. of South San Francisco, California, converted N8186H to tricycle undercarriage, using forward retracting main gear from a P-51 and rearward-retracting nose-leg from a T-28, adding a nose extension, rear fuselage extension, re-roofed fuselage for increased headroom and enlarged cabin windows. The modifications did not obtain FAA certification despite 58 hours of flight testing, with the aircraft eventually being broken up at Antioch, CA, in 1978.
;SFERMA-Beechcraft PD.18S
:Modification of Beech 18S powered by two Turboméca Bastan
The Turbomeca Bastan was a turboprop engine developed in France in 1957. Early models developed 650 shp (485 kW), but by 1965 this had been increased to 1,048 shp (780 kW) with the Bastan VII.
Flight tests of some Bastan models were c ...
turbopropsTaylor 1982, p. 67.
;Volpar (Beechcraft) Model 18
:Conversion of Model 18 with nosewheel undercarriageTaylor 1965, p. 316.Taylor 1982, p. 483.
;Volpar (Beechcraft) Super 18:
;Volpar (Beechcraft) Turbo 18:Beech Model 18s fitted with the Volpar MkIV tricycle undercarriage and powered by two 705-hp Garrett TPE331-1-101B
The Honeywell TPE331 (military designation: T76) is a turboprop engine. It was originally designed in the 1950s by Garrett AiResearch, and produced since 1999 by Honeywell Aerospace. The engine's power output ranges from .
Design and develo ...
turboprop engines, flat-rated to , driving Hartzell HC-B3TN-5 Hartzell is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Andy Hartzell, American cartoonist
* Curt Hartzell (1891–1975), Swedish gymnast
*Eric Hartzell (born 1989), American ice hockey player
*James Hartzell (1931–2010), American advert ...
three-bladed, reversible-pitch, constant-speed feathering propellers
;Volpar (Beechcraft) Super Turbo 18
:2x Garrett TPE331
;Volpar (Beechcraft) C-45G
:C-45G aircraft modified with tricycle undercarriage
;Volpar (Beechcraft) Turboliner
: 15-passenger version of the Turbo 18 with extended fuselage, powered by 2 705-hp Garrett TPE331-1-101B
The Honeywell TPE331 (military designation: T76) is a turboprop engine. It was originally designed in the 1950s by Garrett AiResearch, and produced since 1999 by Honeywell Aerospace. The engine's power output ranges from .
Design and develo ...
sTaylor 1982, p. 484.
;Volpar (Beechcraft) Turboliner II
:Turboliners modified to meet SFAR 23
Operators
Civil
, the Beechcraft Model 18 remains popular with air charter companies and small feeder airlines worldwide.Military



Brazilian Air Force
"Wings that protect the country"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march = Hino dos Aviadores
, mascot =
, anniversaries = 22 May (anniver ...
;
* Royal Canadian Air Force 394 examples from 1941 to 1972Griffin 1969, pp. 5–6.
* Royal Canadian Navy 10 examples from 1952 to 1960
** VX-10 Squadron
** VU-32 Squadron
*Canadian Armed Forces
}
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; french: Forces armées canadiennes, ''FAC'') are the unified military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air elements referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army, and Royal Canadian Air Force.
...
;
* Chilean Air ForceBridgman 1951, p. 6a.
* Chilean Army
* Chilean Navy
;
* Colombian Air ForcePelletier 1995, pp. 81–82.
;
* Public Force of Costa RicaPelletier 1995, p. 82.
;Pelletier 1995, p. 83.
;
* Cuban Air Force - received two AT-7s, two AT-11s, a F-2B and a UC-45F in 1947
;
*Dominican Air Force
The Air Force of the Dominican Republic ( es, Fuerza Aérea de República Dominicana), is one of the three branches of the Armed Forces of the Dominican Republic, together with the Army and the Navy.
History
At the end of the United States ...
Bridgman 1951, p. 7a.
;
* Ecuadorian Air Force
;
* Air Force of El SalvadorBridgman 1951, p. 17a.
;
*French Air Force
The French Air and Space Force (AAE) (french: Armée de l'air et de l'espace, ) is the air and space force of the French Armed Forces. It was the first military aviation force in history, formed in 1909 as the , a service arm of the French Army; ...
* French Naval Aviation
;
* Guatemalan Air ForceBridgman 1951, p. 11a.
;
* Haiti Air Corps
;
* Honduran Air ForceBridgman 1951, p. 12a.
;
*Indonesian Army
The Indonesian Army ( id, Tentara Nasional Indonesia Angkatan Darat (TNI-AD), ) is the land branch of the Indonesian National Armed Forces. It has an estimated strength of 300,000 active personnel. The history of the Indonesian Army has its ...
*Indonesian National Police
''
, mottotranslated = (Serving the Nation)
, formed =
, preceding1 =
, dissolved =
, superseding =
, employees = 440,000 (2020)
, volunteers =
, budget =
, nongovernment ...
;
;
* Italian Air Force operated 125 aircraft from 1949 until the 1970s
;
* Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force
* Japan Coast Guard
;
* Mexican Air ForceBridgman 1951, p. 14a.
* Mexican Navy
;
*Royal Netherlands Air Force
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march = ''Parade March of the Royal Netherlands Air Force''
, mascot =
, anniversaries =
, equipment ...
* Dutch Naval Aviation Service
;
* Nicaraguan Air Force
;
*Niger Air Force
The Niger Armed Forces (french: Forces armées nigériennes) (FAN) includes military armed force service branches ( Niger Army and Niger Air Force), paramilitary services branches (National Gendarmerie of Niger and National Guard of Niger) and ...
;
;
* Paraguayan Air ForceBridgman 1951, p. 16a.
;
* Peruvian Air Force
;
* Philippine Army Air Corps
;
* Forca Aerea PortuguesaPelletier 1995, p. 84.
* Portuguese Navy
;
* Somali Air Force – Withdrawn in 1991
;
* South African Air Force
;
* Republic of Vietnam Air Force
;
;
*Sri Lanka Air Force
The Sri Lanka Air Force (SLAF) ( si, ශ්රි ලංකා ගුවන් හමුදාව, Śrī Laṃkā guwan hamudāva; ta, இலங்கை விமானப்படை, Ilaṅkai vimāṉappaṭai) is the air arm and the yo ...
;
*Swedish Air Force
The Swedish Air Force ( sv, Svenska flygvapnet or just ) is the air force branch of the Swedish Armed Forces.
History
The Swedish Air Force was created on 1 July, 1926 when the aircraft units of the Army and Navy were merged. Because of the es ...
Bridgman 1951, p. 19a.
;
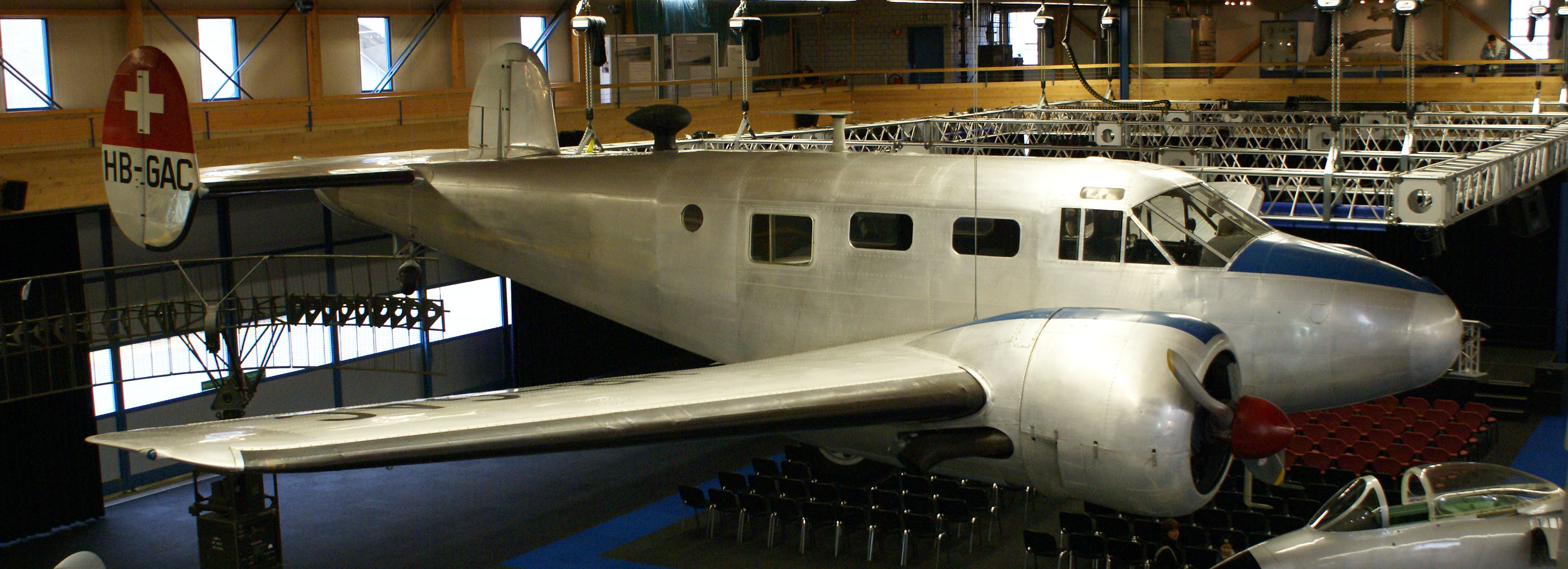
*Swiss Air Force
The Swiss Air Force (german: Schweizer Luftwaffe; french: Forces aériennes suisses; it, Forze aeree svizzere; rm, Aviatica militara svizra) is the air component of the Swiss Armed Forces, established on 31 July 1914 as a part of the army and ...
;
* Republic of China Air ForcePelletier 1995, p. 81.
;
* Royal Thai Air ForceBridgman 1951, p. 20a.
;
* Tongan Maritime Force Air Force
;
* Turkish Air Force
;
* Royal Air Force
* Royal Navy – Fleet Air Arm
;
* United States Army
** United States Army Air Corps
** United States Army Air Forces
* United States Air Force
* United States Coast Guard
** United States Coast Guard Reserve
* United States Marine Corps
* United States Navy
;
* Uruguayan Air ForcePelletier 1995, pp. 84–85.
;
* Venezuelan Air ForcePelletier 1995, p. 85.
;
* Zairian Air Force
Accidents and incidents
The Beechcraft Model 18 family has been involved in the following notable accidents and incidents: *April 25, 1951:Cubana de Aviación Flight 493
Cubana de Aviación Flight 493, registration was a Douglas DC-4 en route from Miami, Florida, to Havana, Cuba, on April 25, 1951. A US Navy Beechcraft SNB-1 Kansan, BuNo 39939, was on an instrument training flight in the vicinity of Nava ...
, a Douglas DC-4 bound from Miami to Havana, registration ''CU-T188'', collided with a U.S. Navy SNB-1, bureau number ''39939'', on a practice instrument approach to Naval Air Station Key West. The collision and ensuing crashes killed all 34 passengers and five crew aboard the DC-4 and all five crew aboard the SNB. The accident occurred at midday, weather was clear with unlimited visibility, and both flight crews had been cleared to fly under visual flight rules, being expected to "see and avoid" other aircraft; the student flying the SNB was wearing view-limiting goggles, but the other SNB crew were not, and were expected to keep watch. Ground witnesses said that neither aircraft took evasive action prior to the collision, and the Civil Aeronautics Board attributed the accident to the failure of both flight crews to see and avoid conflicting air traffic.
*1967: Mohammed bin Awad bin Laden
Muhammad Binladin ( ar, محمد بن لادن, translit=Muḥammad Binlādin; – 3 September 1967) was a Saudi tycoon who founded the Saudi Binladin Group. He worked primarily in the construction industry and became the wealthiest non-royal Sa ...
was killed in the crash of a Beechcraft 18 in Saudi Arabia.
*December 10, 1967: American soul music singer Otis Redding, four members of his backing band the Bar-Kays, the pilot, and another member of Redding's entourage were killed in the crash of Redding's H18, registration ''N390R'', into Lake Monona on approach to Truax Field in Wisconsin. The National Transportation Safety Board
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) is an independent U.S. government investigative agency responsible for civil transportation accident investigation. In this role, the NTSB investigates and reports on aviation accidents and incid ...
(NTSB) was unable to determine the cause of the crash, noting that the left engine and propeller were not recovered. Trumpet player Ben Cauley
Ben S. Cauley, Jr. (October 3, 1947 – September 21, 2015) was an American trumpet player, vocalist, songwriter, and founding member of the Stax recording group the Bar-Kays. He was the only survivor of the 1967 plane crash that claimed the live ...
, the sole survivor, subsequently revived the Bar-Kays together with another band member who was aboard a different aircraft.
*September 20, 1973: American folk music singer-songwriter Jim Croce, four members of his entourage, and the pilot were killed when their chartered E18S, registration ''N50JR'', crashed into a tree on takeoff from Natchitoches Regional Airport in Louisiana. The NTSB attributed the accident to reduced visibility due to fog, and to physical impairment of the pilot, who had severe coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pla ...
and had run to the airport. An investigation conducted for a lawsuit against the charter company attributed the accident solely to pilot error, citing his downwind takeoff into a "black hole" of severe darkness, causing him to experience spatial disorientation
Spatial disorientation results in a person being unable to determine their position or relative motion, commonly occurring during periods of challenging visibility, since vision is the dominant sense for orientation. The auditory system, vestibular ...
.
*September 26, 1978: Air Caribbean Flight 309, an air taxi flight by a D18S, registration ''N500L'', crashed on approach to Isla Verde International Airport
Isla or ISLA may refer to:
Organizations
* International Securities Lending Association, a trade association
* International School of Los Angeles
* International Bilingual School, later named International School of Los Angeles
People
* Isla (g ...
in Puerto Rico, killing the pilot and the five passengers aboard the aircraft and causing substantial property damage and injuries to bystanders on the ground. The pilot could not communicate with approach control and was following directions relayed by local tower controllers, who told the pilot to make a turn and maintain separation from a Lockheed L-1011 that was overtaking the flight, but the pilot did not turn, and the D18S passed underneath and very close to the L-1011. Both the NTSB and a U.S. District Court ruling attributed the crash to the D18S pilot's failure to correctly follow visual flight rules and air traffic control instructions to maintain separation from the much larger L-1011, causing a loss of aircraft control due to wake turbulence. A contributing factor was the pilot's difficulties in communication with controllers.
Aircraft on display
Argentina
* AT-11A ''3495'' – at the Museo Nacional de Aeronáutica de Argentina in Buenos Aires. * C-45H ''5621'' – at the Museo Nacional de Aeronáutica de Argentina in Buenos Aires. * C-45H ''AF-555'' – at the Museo Nacional de Aeronáutica de Argentina in Buenos Aires. * H18S c/no. BA-752 (former ''LV-JFH'') – at the Museo Nacional de Aeronáutica de Argentina in Buenos Aires.Australia
* E18S c/no. BA-81 (former ''N3781B'') - at the Queensland Air Museum in Caloundra, Queensland.Belgium
* 3NM floatplane c/no CA-191 (former ''C-FGNR'') – at Pairi Daiza.Brazil
* AT-11 ''4615'' - at the Museu Aeroespacial in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. * C-45F ''2856'' - at the Museu Aeroespacial inRio de Janeiro, Brazil
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
.
Canada
* C-45H ''459'' – at theCanadian Bushplane Heritage Centre
Canadian Bushplane Heritage Centre (CBHC), located on the north bank of the St. Marys River in Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Canada, is dedicated to preserving the history of bush flying and forest protection in Canada. It was founded in 1987 by a ...
in Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario. Tail code CF-MJY
* 3TM ''8034'' – at the Canadian Bushplane Heritage Centre in Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario.
* D18S c/no. A-141 (former ''CF-MPH'') – at the RCMP Academy, Depot Division in Regina, Saskatchewan.
* D18S c/no. A-142 (former ''CF-MPI'') – at the Bomber Command Museum of Canada in Nanton, Alberta.
* D18S c/no. A-156 – at the Canadian Warplane Heritage Museum in Hamilton, Ontario.
* 3N c/no. A-652 (former RCAF ''1477'') – at the Royal Aviation Museum of Western Canada
The Royal Aviation Museum of Western Canada (formerly the Western Canada Aviation Museum) is a museum in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The museum opened to the public in its new location on 21 May 2022.
History
The Western Canada Aviation Museum w ...
in Winnipeg, Manitoba.
* 3NMT c/no. A-700 – at the Canadian Air Land Sea Museum
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
at Toronto/Markham Airport in Markham, Ontario.
* 3NM c/no. A-710 – at the North Atlantic Aviation Museum in Gander, Newfoundland and Labrador.
* 3NMT c/no. A-782 (former ''CF-CKT'') – at the Canadian Museum of Flight in Langley, British Columbia.
* 3NMT c/no. A-872 – at the TransCanada Highway in Ignace, Ontario.
* 3NM c/no. A-895 – at the Alberta Aviation Museum in Edmonton, Alberta.
Chile
* D18S c/no. A-1024 (former FACh ''465'') – at theMuseo Aeronautico y del Espacio Museo may refer to:
* Museo, 2018 Mexican drama heist film
*Museo (Naples Metro)
Museo is a station on line 1 of the Naples Metro. It was opened on 5 April 2001 as the eastern terminus of the section of the line between Vanvitelli and Museo. O ...
in Santiago, Chile
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile, is the capital (political), capital and largest city of Chile as well as one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is the center of Chile's most densely populated Regions of Chile, region, t ...
.
India
* D18S VT-CNY former aircraft of the Raja of Mayurbhanj and later sold to Coal India Limited- at the Hotel Mayfair Lagoon in Bhubaneswar, Orissa.Italy
* C-45F ''6668'' – suspended inside the Olbia Costa Smeralda Airport passenger terminal inOlbia, Sardinia
Olbia (, ; sc, Terranoa; sdn, Tarranoa) is a city and commune of 60,346 inhabitants (May 2018) in the Italian insular province of Sassari in northeastern Sardinia, Italy, in the historical region of Gallura. Called ''Olbia'' in the Roman age, ...
. This was the first aircraft owned by Alisarda Airlines and was used in the filming of the movie '' The Last Emperor''.
Malta
* C-45H ''8304'' – under restoration at the Malta Aviation Museum in Ta' Qali, Malta.Mexico
* UC-45J Expeditor "ETL-1320" (S/N): 18 - at theMuseo Militar de Aviación Museo may refer to:
* Museo, 2018 Mexican drama heist film
* Museo (Naples Metro), station on line 1 of the Naples Metro
* Museo, Seville, neighborhood of Seville, Spain
{{disambiguation ...
.
Netherlands
* C-45G ''51-11665'' – at the Aviodrome inLelystad, Netherlands
Lelystad () is a municipality and a city in the centre of the Netherlands, and it is the capital of the province of Flevoland. The city, built on reclaimed land, was founded in 1967 and was named after Cornelis Lely, who engineered the Afsluitdi ...
.
New Zealand
* AT-11 ''3691'' - at the Museum of Transport and Technology in Auckland, New Zealand.Portugal
* AT-11 ''2504'' - at the Museu do Ar in Sintra, Portugal.Spain
* C-45H ''AF-752''– atFundación Infante de Orleans
Fundación is a town and municipality of the Colombian Department of Magdalena. Its people are known as Fundanenses. The primary economic activity is livestock-raising, for production of both meat and milk. Other crops are: corn, yuca, ora ...
in Madrid, Spain.
Turkey
* AT-11 Kansan ''6390/9-930'' – atIstanbul Aviation Museum
The Istanbul Aviation Museum, a.k.a. Turkish Air Force Museum, ( tr, Havacılık Müzesi or Hava Kuvvetleri Müzesi) is a military-based museum for aviation, owned and operated by the Turkish Air Force. The museum is located in Yeşilköy neighbo ...
.
United Kingdom
* E18S ''G-ASUG'' c/no. BA-111 – at theNational Museum of Flight
The National Museum of Flight is Scotland's national aviation museum, at East Fortune Airfield, just south of the village of East Fortune, Scotland. It is one of the museums within National Museums Scotland. The museum is housed in the original ...
in East Lothian, Scotland.
United States
* AT-11 ''41‐27561'' – at theNational Museum of the USAF
The National Museum of the United States Air Force (formerly the United States Air Force Museum) is the official museum of the United States Air Force located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, northeast of Dayton, Ohio. The NMUSAF is the ...
in Dayton, Ohio. ''or'' 42-37493
* AT-11B ''41-27616'' – at the Travis Air Force Base Heritage Center
The Travis Air Force Base Aviation Museum (former names include Travis Air Museum, Jimmy Doolittle Air & Space Museum, and Travis Air Force Base Heritage Center) is an aviation museum located at Travis Air Force Base in Fairfield, California. The ...
at Travis AFB, California.
* AT-11 ''42-36887'' – at the Barksdale Global Power Museum in Bossier City, Louisiana
Bossier City ( ) is a city in Bossier Parish in the northwestern region of the U.S. state of Louisiana in the United States. It is the second most populous city in the Shreveport–Bossier City metropolitan statistical area. In 2020, it had a ...
.
* AT-11 ''42-37240'' – at the Lone Star Flight Museum in Galveston, Texas
Galveston ( ) is a coastal resort city and port off the Southeast Texas coast on Galveston Island and Pelican Island in the U.S. state of Texas. The community of , with a population of 47,743 in 2010, is the county seat of surrounding Galvesto ...
.
* UC-45 ''42-37496'' – at the Wings Over the Rockies Air and Space Museum
The Wings Over the Rockies Air and Space Museum (WOTR) is located on the former Lowry Air Force Base in Denver, Colorado, United States. The museum preserves the history of Lowry AFB's operations from 1938 to 1994 in its collections, archives, and ...
in Denver, Colorado. This aircraft was originally an AT-11 before being remanufactured.
* UC-45F ''44-47342'' – at the Alaska Aviation Heritage Museum
The Alaska Aviation Museum, previously the Alaska Aviation Heritage Museum, is located on Lake Hood Seaplane Base in Anchorage, Alaska. Its mission since 1988, is to preserve, display, and honor Alaska's aviation heritage, by preserving and displ ...
in Anchorage, Alaska
Anchorage () is the largest city in the U.S. state of Alaska by population. With a population of 291,247 in 2020, it contains nearly 40% of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring Ma ...
.
* C-45G ''51-11467'' – at the EAA Chapter 1241 Air Museum at the Florida Keys Marathon Airport in Marathon, Florida
Marathon is a city spread over Knight's Key, Boot Key, Key Vaca, Fat Deer Key, Long Point Key, Crawl Key and Grassy Key islands in the middle of the Florida Keys, in Monroe County, Florida, United States. As of the 2010 census, the city had a to ...
.
* TC-45H ''51-11529'' – at the Tri-State Warbird Museum
The Tri-State Warbird Museum is a private, not-for-profit aviation museum located in Batavia, Ohio, in Clermont County next to the Clermont County Airport.
Overview
The focus of the museum is on World War II, therefore, all aircraft at the mus ...
in Batavia, Ohio
Batavia ( ) is a village in and the county seat of Clermont County, Ohio, United States. The population was 1,509 at the 2010 census.
Geography
Batavia is located at (39.077332, -84.179160).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the ...
.
* C-45H ''51-11696'' – at the Museum of Flight in Seattle, Washington.
* C-45G ''51-11795'' – at the Air Mobility Command Museum in Dover, Delaware
Dover () is the capital and second-largest city of the U.S. state of Delaware. It is also the county seat of Kent County and the principal city of the Dover, DE, Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Kent County and is part of ...
.
* C-45G ''51-11897'' – at the Castle Air Museum in Atwater, California.
* C-45H ''52-10539'' – at the 1941 Historical Aircraft Group Museum
The National Warplane Museum is a warbird and military history museum currently located on the grounds of the Geneseo Airport in Geneseo, New York. Founded in 1994, the museum restores, flies, and displays vintage military aircraft from the Second ...
in Geneseo, New York.
* C-45H ''52-10865'' – at the Travis Air Force Base Heritage Center at Travis AFB, California.
* C-45H ''52-10893'' – at the National Museum of the USAF
The National Museum of the United States Air Force (formerly the United States Air Force Museum) is the official museum of the United States Air Force located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, northeast of Dayton, Ohio. The NMUSAF is the ...
in Dayton, Ohio.
* UC-45J ''09771'' – at the National Museum of Naval Aviation in Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal ...
. This aircraft was converted from the last civil Beech 18 built prior to WWII.
* UC-45J ''23774'' – at Laughlin AFB in Del Rio, Texas
Del Rio is a city and the county seat of Val Verde County in southwestern Texas, United States. The city is 152 miles west of San Antonio. As of 2020, Del Rio had a population of 34,673.
History
The Spanish established a small settlement south o ...
.
* RC-45J ''51233'' – at the Tennessee Museum of Aviation
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to the ...
in Sevierville, Tennessee.
* UC-45J ''51242'' – at the CAF Central Texas Wing
CAF or caf may refer to:
Armed forces
*Canadian Armed Forces (Canadian Forces), the Canadian Air Force, Army, and Navy
*Canadian Air Force, now the Royal Canadian Air Force
*Republic of China Air Force
The Republic of China Air Force, retro ...
in San Marcos, Texas
San Marcos ( ) is a city and the county seat of Hays County, Texas, United States. The city's limits extend into Caldwell and Guadalupe Counties, as well. San Marcos is within the Austin–Round Rock metropolitan area and on the Interstate 35 ...
.
* UC-45J ''51291'' – at the Aerospace Museum of California in Sacramento, California.
* UC-45J ''51338'' – at the Minnesota Air National Guard Museum in St. Paul, Minnesota
Saint Paul (abbreviated St. Paul) is the capital of the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of Ramsey County. Situated on high bluffs overlooking a bend in the Mississippi River, Saint Paul is a regional business hub and the center o ...
.
* S18D c/no. 178 – at the Beechcraft Heritage Museum in Tullahoma, Tennessee.
* D18S c/no. A-935 – at the Beechcraft Heritage Museum at Tullahoma Regional Airport in Tullahoma, Tennessee.
* C-45H ''AF-824'' – at the Beechcraft Heritage Museum in Tullahoma, Tennessee.
* E18S c/no. BA-453 – at the Beechcraft Heritage Museum in Tullahoma, Tennessee.
* H18 c/no. BA-670 – at the Lone Star Flight Museum in Galveston, Texas
Galveston ( ) is a coastal resort city and port off the Southeast Texas coast on Galveston Island and Pelican Island in the U.S. state of Texas. The community of , with a population of 47,743 in 2010, is the county seat of surrounding Galvesto ...
.
Specifications (UC-45 Expeditor)

See also
* Air Caribbean Flight 309References
Notes
Bibliography
* Bridgeman, Leonard, ed. “The Beechcraft Expeditor.” ''Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II''. London: Studio, 1946. . * Bridgeman, Leonard. ''Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1951–52''. London: Samson Low, Marston & Company, Ltd., 1951. * Donald, David, ed.''American Warplanes of World War II''. London: Aerospace, 1995. . * Griffin, John A. ''Canadian Military Aircraft Serials & Photographs 1920 - 1968''. Ottawa: Queen's Printer, Publication No. 69-2, 1969. * Hagedorn, Daniel P. ''Central American and Caribbean Air Forces''. Tonbridge, UK: Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd., 1993. * Mesko, Jim. "The Rise...and Fall of the Vietnamese AF". '' Air Enthusiast'', August–November 1981, No. 16. pp. 1–12, 78–80. . * Mondey, David. ''American Aircraft of World War II'' (Hamlyn Concise Guide). London: Bounty Books, 2006. . * Ogden, Bob. ''Aviation Museums and Collections of North America''. Tonbridge, Kent, UK: Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd., 2007. . * Pelletier, A. J. ''Beech Aircraft and their Predecessors''. Annapolis, Maryland, USA: Naval Institute Press, 1995. . * * Pettipas, Leo. ''Canadian Naval Aviation 1945-1968''. L. Pettipas/Canadian Naval Air Group, Winnipeg: 1986. * * Swanborough, F. Gordon and Peter M. Bowers. ''United States Military Aircraft since 1909''. London: Putnam, 1963. * * Taylor, John W. R. ''Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1961–62''. London: Sampson Low, Marston & Company, 1961. * Taylor, John W. R. ''Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1965–66''. London: Sampson Low, Marston & Company, 1965. * Taylor, John W. R. ''Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1967–68''. London: Sampson Low, Marston & Company, 1967. * Taylor, John W. R. ''Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1976–77''. London: Jane's Yearbooks, 1976. . * Taylor, John W. R. ''Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1982-83''. London: Jane's Publishing Company, 1982. . * ''United States Air Force Museum Guidebook''. Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio: Air Force Museum Foundation, 1975.External links
Experimental Aircraft Association (Chapter 1000) Beech E18S overview and pictorial tour
{{Authority control 0018 1930s United States military trainer aircraft C-45, Beechcraft 1930s United States civil utility aircraft World War II trainer aircraft of the United States Aircraft first flown in 1937 Twin piston-engined tractor aircraft Low-wing aircraft Twin-tail aircraft