Tyrol on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a
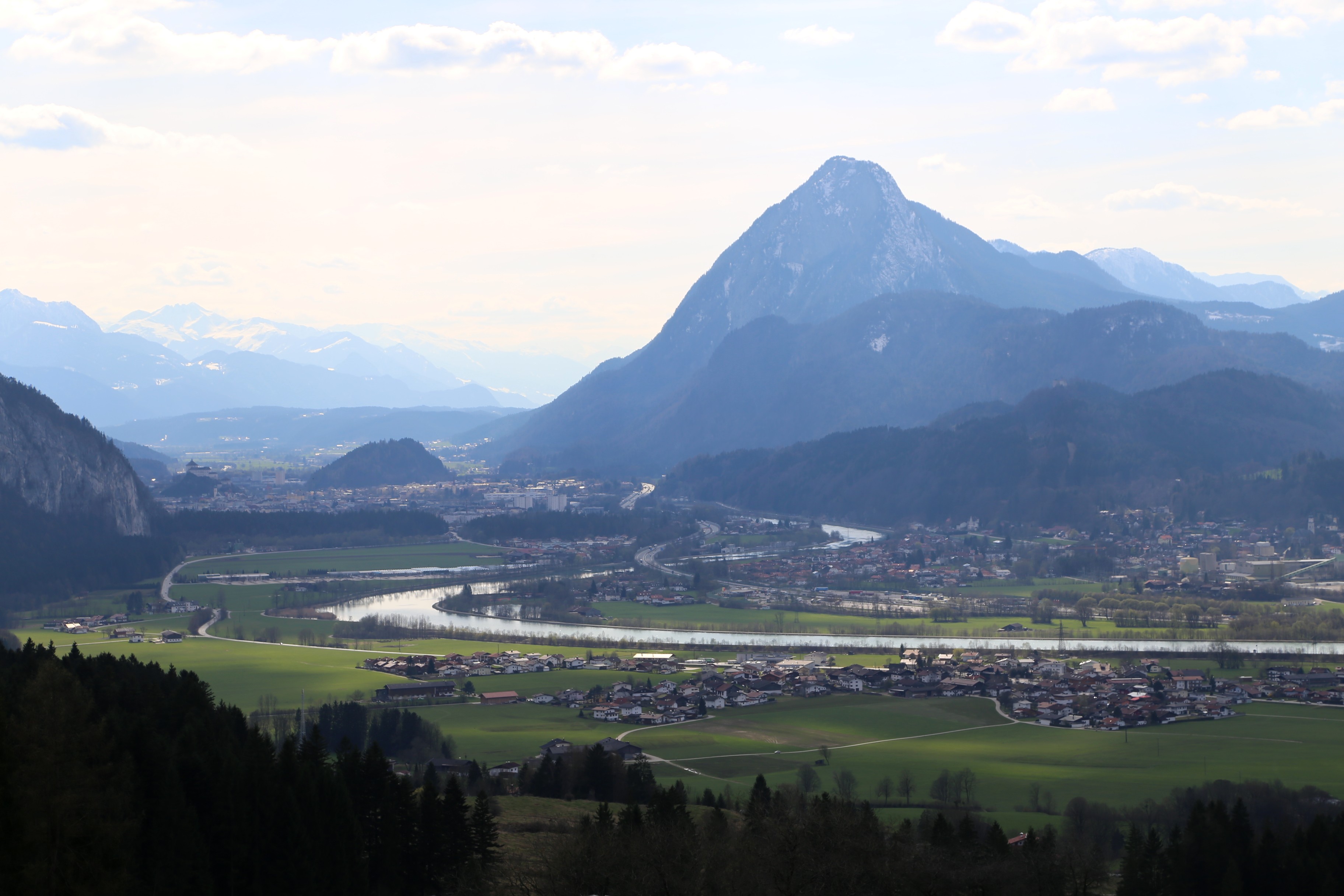 Tyrol has an area of 26,673 km2. The region consists of the State of Tyrol, the Province of South Tyrol and the
Tyrol has an area of 26,673 km2. The region consists of the State of Tyrol, the Province of South Tyrol and the
 As the Tyrolean region is located in the
As the Tyrolean region is located in the



 Municipalities of Tyrol with over 10,000 inhabitants:
Austria: 1 January 2017
Municipalities of Tyrol with over 10,000 inhabitants:
Austria: 1 January 2017
Italy: 31 December 2016
File:AUT Tirol COA.svg, Coat of arms of
 The earliest archaeological records of human settlement in Tyrol have been found in the
The earliest archaeological records of human settlement in Tyrol have been found in the
 In 1027, Emperor Conrad II, in order to secure the important route through the
In 1027, Emperor Conrad II, in order to secure the important route through the
 The Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion was founded in 1998. The aim is to strengthen cooperation between the separated countries. In several areas, such as mobility, agriculture, education and culture will be tried to promote exchange and to raise the awareness of the cultural and historical heritage of the region of Tyrol in the minds of the population. Cross-border projects will be initiated to improve the relationship between the different language groups. To represent common ideas and values in Europe, the Euroregion has a joint office in
The Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion was founded in 1998. The aim is to strengthen cooperation between the separated countries. In several areas, such as mobility, agriculture, education and culture will be tried to promote exchange and to raise the awareness of the cultural and historical heritage of the region of Tyrol in the minds of the population. Cross-border projects will be initiated to improve the relationship between the different language groups. To represent common ideas and values in Europe, the Euroregion has a joint office in
 Agriculture and forestry occupy a special position in Tyrol. The many small and medium-sized farms have shaped the landscape and culture in Tyrol for many centuries. In order to be competitive with larger farms outside Tyrol, there is a strong
Agriculture and forestry occupy a special position in Tyrol. The many small and medium-sized farms have shaped the landscape and culture in Tyrol for many centuries. In order to be competitive with larger farms outside Tyrol, there is a strong
 The most important sector in Tyrol is the tertiary sector. Especially tourism has a special position in this region. Due to the connection of the areas by the railway in the 19th century, many villages in Tyrol developed into popular tourism locations. The construction of the Brenner motorway in the 1960s gave the region in the 20th century a renewed upswing in the tourism branch. Today, Merano, Kitzbühel,
The most important sector in Tyrol is the tertiary sector. Especially tourism has a special position in this region. Due to the connection of the areas by the railway in the 19th century, many villages in Tyrol developed into popular tourism locations. The construction of the Brenner motorway in the 1960s gave the region in the 20th century a renewed upswing in the tourism branch. Today, Merano, Kitzbühel,
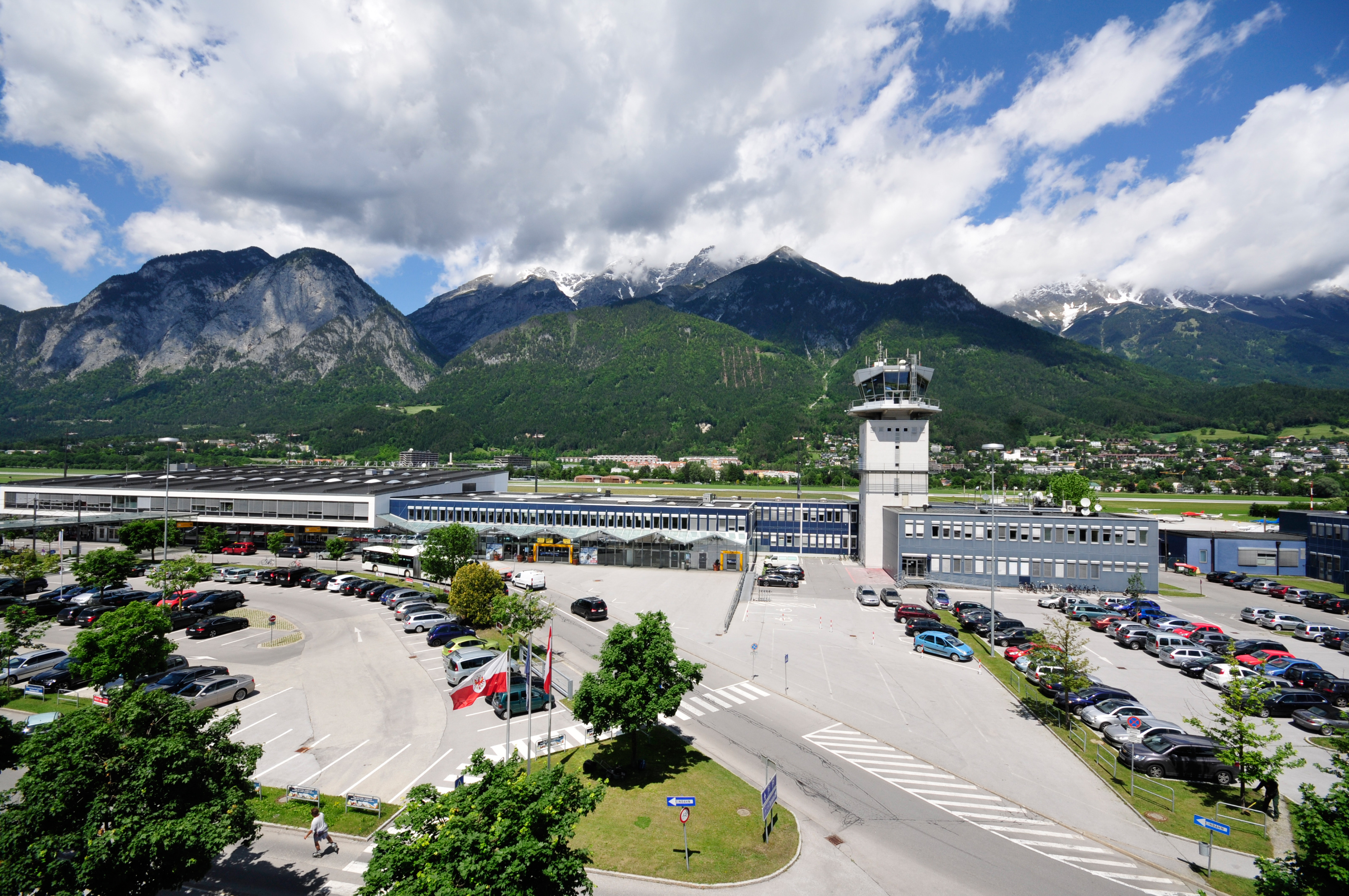 The most important airport in Tyrol is Innsbruck Airport. With over one million passengers, it is the third largest airport in Austria. Other airports in the region are in
The most important airport in Tyrol is Innsbruck Airport. With over one million passengers, it is the third largest airport in Austria. Other airports in the region are in
 The most important railway line in Tyrol is the Brenner Line via the
The most important railway line in Tyrol is the Brenner Line via the
 The Tyrolean cuisine has similarities with the
The Tyrolean cuisine has similarities with the
 The Tyrolean Rifles were a militia organized in case of an attack on
The Tyrolean Rifles were a militia organized in case of an attack on
File:Krampus2.jpg, Krampus in Dobbiaco. Typical in the alpine region.
File:Imst Schemenlaufen 2016 34.jpg, ''Imster Schemenlaufen'' in Imst
File:Ifinger Mountain - Herz Jesu Fires - South Tyrol.jpg, Herz Jesu Fire in whole Tyrol
 In Tyrol, the Olympic Winter Games have been organized three times so far. In
In Tyrol, the Olympic Winter Games have been organized three times so far. In



historical region
Historical regions (or historical areas) are geographical regions which at some point in time had a cultural, ethnic, linguistic or political basis, regardless of latterday borders. They are used as delimitations for studying and analysing soci ...
in the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, ...
- in Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative Regions ...
and western Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised pr ...
, part of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, from its formation in the 12th century until 1919. In 1919, following World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, it was divided into two modern administrative parts through the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye:
* State of Tyrol: Formed through the merger of North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''no ...
and East Tyrol
East Tyrol, occasionally East Tirol (german: Osttirol), is an exclave of the Austrian state of Tyrol, separated from the main North Tyrol part by the short common border of Salzburg and Italian South Tyrol (''Südtirol'', it, Alto Adige). It ...
, as part of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
* Region of Trentino-Alto Adige: At that time still with Souramont (Cortina d'Ampezzo
Cortina d'Ampezzo (; lld, Anpezo, ; historical de-AT, Hayden) is a town and ''comune'' in the heart of the southern (Dolomites, Dolomitic) Alps in the Province of Belluno, in the Veneto region of Northern Italy. Situated on the Boite (river), ...
, Livinallongo del Col di Lana and Colle Santa Lucia) and the municipalities Valvestino
Valvestino ( Brescian: ) is a '' comune'' in the province of Brescia, in Lombardy in northern Italy.
Historical and cultural profile
The Stoni and the Gallic Cenomani The Gaulish name Cenomani can refer to:
* Aulerci Cenomani, an ancient Ga ...
, Magasa, and Pedemonte, seized in 1918 by the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and ...
, and thus since 1946 part of the Italian Republic
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
.
With the founding of the European region Tyrol-South Tyrol-Trentino the area has its own legal entity since 2011 in the form of a European Grouping for Territorial Cooperation
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
.
Etymology
According to , the name ''Tyrol'' derives from a root word meaning ''terrain'' (i.e. area, ground or soil; compare la, terra andOld Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic ( sga, Goídelc, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ga, Sean-Ghaeilge; gd, Seann-Ghàidhlig; gv, Shenn Yernish or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive writte ...
: ''tir''); first from the village of Tirol, and its castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
; from which the County of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised pr ...
grew. Some sources suggest it derives from the Slavic language "ta rola" meaning "this land, farming terrain/farming ground." According to Karl Finsterwalder Karl may refer to:
People
* Karl (given name), including a list of people and characters with the name
* Karl der Große, commonly known in English as Charlemagne
* Karl Marx, German philosopher and political writer
* Karl of Austria, last Austrian ...
, the name ''Tyrol'' derives from , a late-Roman fort and travellers' hostel in Zirl, Tyrol
Zirl is a market town in the district of Innsbruck-Land in the Austrian state of Tyrol located 10 km west of Innsbruck at the bottom of a pass up the side of the Zirler Berg, leading to Seefeld and ultimately to Germany. The location was ment ...
. There seems to be no scholarly consensus.
Geography
Location
 Tyrol has an area of 26,673 km2. The region consists of the State of Tyrol, the Province of South Tyrol and the
Tyrol has an area of 26,673 km2. The region consists of the State of Tyrol, the Province of South Tyrol and the Province of Trento
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous regi ...
. In addition to the region belong the municipalities Cortina d'Ampezzo
Cortina d'Ampezzo (; lld, Anpezo, ; historical de-AT, Hayden) is a town and ''comune'' in the heart of the southern (Dolomites, Dolomitic) Alps in the Province of Belluno, in the Veneto region of Northern Italy. Situated on the Boite (river), ...
, Livinallongo del Col di Lana, Colle Santa Lucia and Pedemonte from the Region of Veneto
it, Veneto (man) it, Veneta (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 = ...
and Valvestino
Valvestino ( Brescian: ) is a '' comune'' in the province of Brescia, in Lombardy in northern Italy.
Historical and cultural profile
The Stoni and the Gallic Cenomani The Gaulish name Cenomani can refer to:
* Aulerci Cenomani, an ancient Ga ...
and Magasa from the Region of Lombardy. The largest cities in Tyrol are Innsbruck, Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
and Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
.
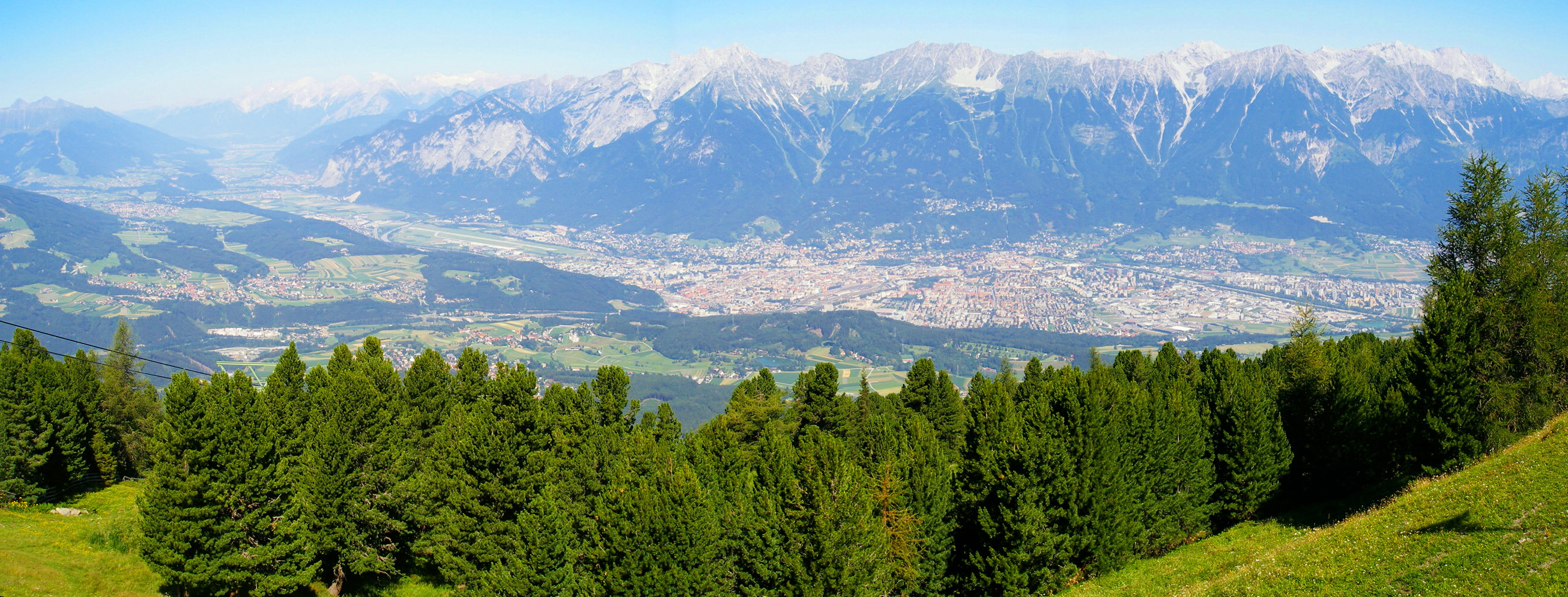
The whole region of Tyrol is located in the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, ...
. Tyrol is bordered to the north by the state of Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
and to the east by the states of Carinthia and Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
. West of Tyrol lies the state of Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the ...
and the canton of Grisons. On the southern side of Tyrol, the land is bordered by the regions of Veneto
it, Veneto (man) it, Veneta (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 = ...
and Lombardy.
Important rivers in Tyrol are the Adige, Inn
Inns are generally establishments or buildings where travelers can seek lodging, and usually, food and drink. Inns are typically located in the country or along a highway; before the advent of motorized transportation they also provided accommo ...
and . The region is characterized by many valleys. Some of these valleys are still difficult to reach today. The most important valleys are the Inn Valley and Adige Valley. A large part of the population lives in these two valleys and also the five largest cities of Tyrol ( Innsbruck, Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
, Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
, Merano, and Rovereto) lie in these valleys. For centuries, the region has been known for transit trade. The most important trade route across the Alps, namely the Brenner Route, traverses the whole of Tyrol and is regarded as a connecting link between the Italian and German-speaking areas.
Mountains
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, ...
, the landscape is heavily influenced by the mountains. The highest mountains in Tyrol include:
* the Ortler - 3,905 m a.s.l.
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance ( height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as '' orthometric heights''.
T ...
* the Königspitze - 3,851 m a.s.l.
* the Großglockner - 3,798 m AA
* the Monte Cevedale - 3,769 m a.s.l.
* the Wildspitze - 3,768 m AA
Across Tyrol, on the border between North and South Tyrol, runs the main chain of the Alps. The main chain of the Alps geographically divides the Alps into a southern and northern half.
Biggest municipalities



 Municipalities of Tyrol with over 10,000 inhabitants:
Austria: 1 January 2017
Municipalities of Tyrol with over 10,000 inhabitants:
Austria: 1 January 2017 Italy: 31 December 2016
Society

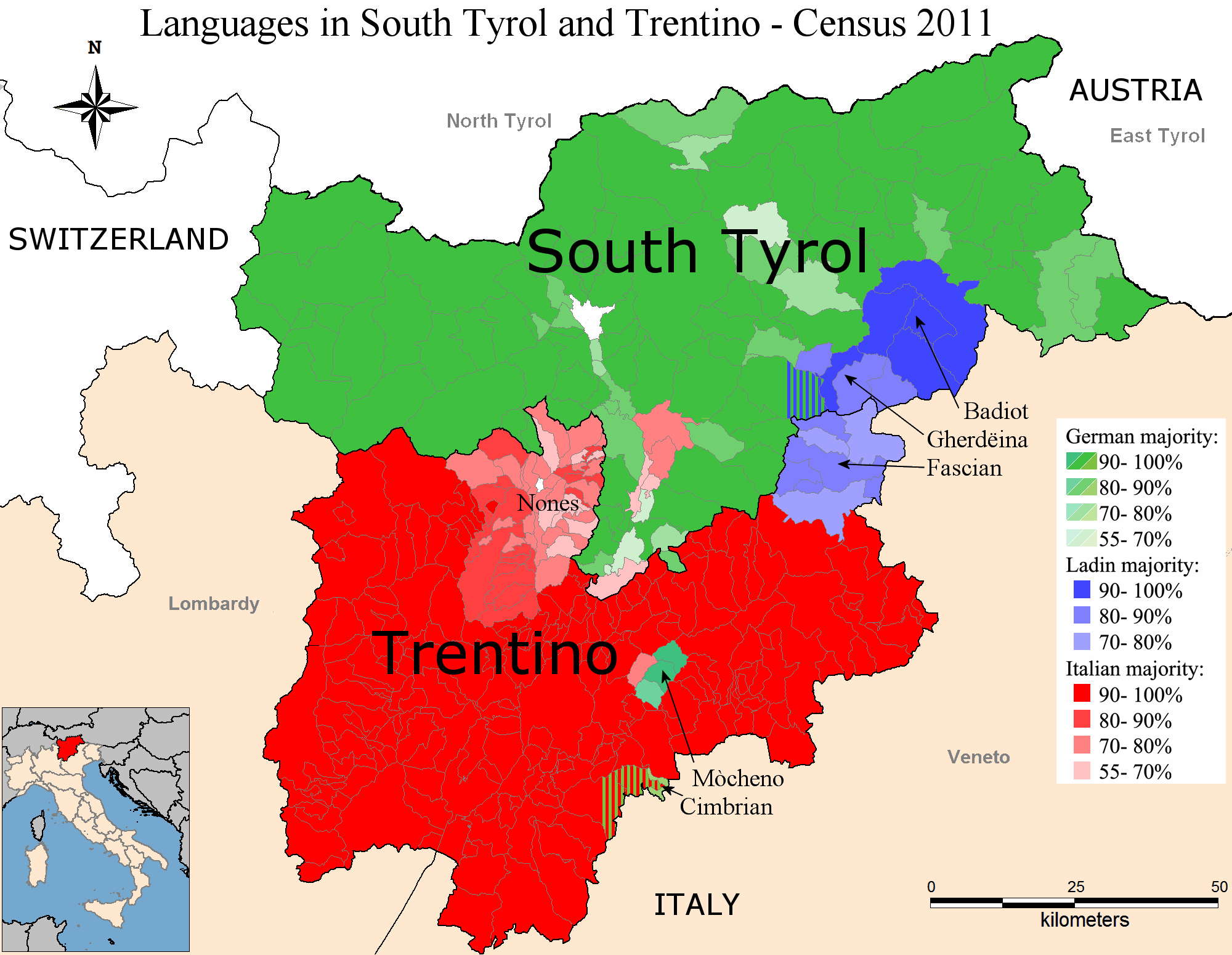
Language distribution
Tyrol can be subdivided into 5 different language groups. In addition to the majority languages such as German and Italian, languages such as Ladin,Cimbrian
Cimbrian ( cim, zimbar, links=no, ; german: Zimbrisch; it, cimbro) refers to any of several local Upper German varieties spoken in northeastern Italy. The speakers of the language are known as ''Zimbern'' in German.
Cimbrian is a German ...
and Mócheno are also spoken. The last three languages are recognized as minority languages. These language groups are mostly located in the Trentino-Alto Adige region and are thus promoted and protected by the region.
The Ladin language is also spoken outside the region in Souramont ( Province of Belluno). Ladin is considered a Rhaeto-Romance language
Rhaeto-Romance, Rheto-Romance, or Rhaetian, is a purported subfamily of the Romance languages that is spoken in south-eastern Switzerland and north-eastern Italy. The name "Rhaeto-Romance" refers to the former Roman province of Raetia. The qu ...
.
The Cimbrian language
Cimbrian ( cim, zimbar, links=no, ; german: Zimbrisch; it, cimbro) refers to any of several local Upper German varieties spoken in northeastern Italy. The speakers of the language are known as ''Zimbern'' in German.
Cimbrian is a Germani ...
is also used in various linguistic islands ( Sette Comuni) outside the region of Trentino-South Tyrol. The Cimbrian and the Mòcheno languages are considered as upper-Bavarian dialects.
The majority in Trentino
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous regio ...
two romance languages are spoken: Lombard in western valleys, and is Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
eastern ones, in central Trentino a transitional dialect between the lombard language and the venetian language is spoken.
Dialects
In the Austrian state of Tyrol, the German language is used by a large majority. As in many other regions in German-speaking countries, Tyrol also has its own German-language dialect. The Tyrolean dialect comes from the Bavarian language. In South Tyrol, the Tyrolean dialect was mixed with a few individual Italian words. Due to the difficult accessibility of the valleys in earlier years, many other valleys developed a slightly differentiated dialect compared to the Tyrolean. The Ladin language also has no uniform language, so every valley also has a slight difference in Ladinia.Heraldry
Although the details of the arms of Tyrol have changed over the centuries, one feature has remained more-or-less constant: ''argent
In heraldry, argent () is the tincture of silver, and belongs to the class of light tinctures called "metals". It is very frequently depicted as white and usually considered interchangeable with it. In engravings and line drawings, regions t ...
'', an eagle displayed ''gules
In heraldry, gules () is the tincture with the colour red. It is one of the class of five dark tinctures called "colours", the others being azure (blue), sable (black), vert (green) and purpure (purple).
In engraving, it is sometimes depi ...
'', armed (and sometimes crowned) '' or''. Since 1983, the Province of South Tyrol has its own coat of arms. It is very similar to the coat of arms of the State of Tyrol. The Province wanted to emphasize the historical commonality of the countries. The Province of Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
received its coat of arms in 1340 and refers to the prince-bishopric of Trento. The former County of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised pr ...
had a uniform coat of arms, which was slightly changed over the centuries.
Tyrol (State)
Tyrol (; german: Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a state (''Land'') in western Austria. It comprises the Austrian part of the historical Princely County of Tyrol. It is a constituent part of the present-day Euroregion Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino (t ...
File:Suedtirol CoA.svg, Coat of arms of the Province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
of South Tyrol
File:Trentino CoA.svg, Coat of arms of the Province of Trentino
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous regio ...
File:Coat of arms of Trentino-South Tyrol.svg, Coat of arms of the Region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
of Trentino–South Tyrol
File:Wappen Gefürstete Grafschaft Tirol.png, Coat of arms of the former County of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised pr ...
during the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with t ...
History
Prehistory
 The earliest archaeological records of human settlement in Tyrol have been found in the
The earliest archaeological records of human settlement in Tyrol have been found in the Tischofer Cave
The Tischofer Cave (german: Tischofer Höhle) is a cave in the Kaisertal valley in the Kaisergebirge mountains in Austria. It was a locally important gathering place and weapons cache during the Tyrolean Rebellion in the Napoleonic Wars.
The roug ...
. They date from the Palaeolithic, about 28,000–27,000 BP. The same cave has also yielded evidence of human occupation during the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
(very roughly, 4000–3000 BP (2000–1000 BC)).
In 1991, the mummified remains of a man who had died around 3300–3100 BC were discovered in a glacier in the Ötztal Alps, in Tyrol. Researchers have called him Ötzi
Ötzi, also called the Iceman, is the natural mummy of a man who lived some time between 3350 and 3105 BC, discovered in September 1991 in the Ötztal Alps (hence the nickname "Ötzi") on the border between Austria and Italy.
Ötzi is believed to ...
(and also other names, including "The Iceman"). He lived during the Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', " copper" and ''líthos'', " stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin ''aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regul ...
or Copper Age, after man had learned how to exploit copper but before man had learned how to make bronze. His body and belongings were very well-preserved, and have been subjected to detailed scientific study. They are preserved in the South Tyrol Museum of Archaeology, Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
, South Tyrol, Italy.
There is evidence that Tyrol was a center for copper mining in the 4th millennium BC; for example, at Brixlegg. There is also evidence of the Urnfield culture
The Urnfield culture ( 1300 BC – 750 BC) was a late Bronze Age culture of Central Europe, often divided into several local cultures within a broader Urnfield tradition. The name comes from the custom of cremating the dead and p ...
(roughly 1300–750 BC).
Evidence of the La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any defi ...
(roughly 450–100 BC, during the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
) has also been found; as has evidence of the Fritzens-Sanzeno culture from about the same period. Toward the end of that time, Tyrol began to be noted in Roman written records. The inhabitants may have been Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan populations, a ...
, in the process of being displaced by Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
(perhaps themselves displaced from Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the nort ...
by Slavs). There are also indications that Adriatic Veneti may have been present in the south of the region. The Romans called them Rhaetians; although it is not clear whether that then meant a specific tribe or confederation of tribes, or was a broader term for the inhabitants of the area. They made wine barrels (an idea which the Romans took from them), and had their own alphabet.
Roman times
In 15 BC, Tyrol was conquered by Roman forces commanded by Drusus andTiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
. The Romans established Raetia and Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the nort ...
as province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
s of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
. Raetia included Vinschgau, Burggrafenamt, Eisacktal, Wipptal, Oberinntal and parts of the Unterinntal. Noricum included Pustertal, Defereggen and parts of the Unterinntal to the right of the Ziller and the Inn. Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
and the extreme south of Tyrol belonged to the province of Venetia et Histria.
The inhabitants adopted the Latin Language called vulgar Latin or the everyday spoken version vs. the standardized written formal form, and combined it with their own languages. The result was Romansh, which is still spoken today and is one of the official languages of Switzerland.
The Romans constructed metaled roads guarded by fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
s through Tyrol to connect the Italian peninsula and the lands beyond; notably the Via Claudia Augusta and the . The Romans did not seem to find Tyrol an attractive area in which to build new towns, because there are few of them. One town they did build was Aguntum, near modern Lienz.
In late antiquity (from AD 476), Tyrol belonged to the Ostrogoths, and it was included in the Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), existed under the control of the Germanic Ostrogoths in Italy and neighbouring areas from 493 to 553.
In Italy, the Ostrogoths led by Theodoric the Great killed and replaced Odoacer ...
. In 534, the Ostrogoths lost Merrano, Val Venosta and Passer to the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
. The Ostrogothic Kingdom collapsed in 553, after being overrun by Bajuvarians
The Baiuvarii or Bavarians (german: Bajuwaren) were a Germanic people. The Baiuvarii had settled modern-day Bavaria (which is named after them), Austria, and South Tyrol by the 6th century AD, and are considered the ancestors of modern-day Bavar ...
from the north and Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
from the south. The Lombards established the Duchy of Tridentum (or, Trent; roughly corresponding to modern Trentino
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous regio ...
) in south Tyrol. Slavic people
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic language, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout ...
s, who had recently taken Carinthia from the Bajuvarians, settled in east Tyrol.
Middle Ages
Most of Tyrol came under the control of theDuchy of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria ( German: ''Herzogtum Bayern'') was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (''duces'') under ...
(created ). The southern parts, including Bolzano, Salorno, and the right bank of the Adige (including Eppan and Kaltern) remained under the Lombards. Tyrol was Christianized through the bishoprics of Brixen
Brixen (, ; it, Bressanone ; lld, Porsenù or ) is a town in South Tyrol, northern Italy, located about north of Bolzano.
Geography
First mentioned in 901, Brixen is the third largest city and oldest town in the province, and the artistic and ...
and Triento. The frontier remained the same though Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
and Ottonian times. The area was subject to ''Stammensgerechte'' ( Ancient Germanic laws), such as ''Lex Romana Curiensis
The ''Lex Romana Curiensis'' ("Roman Law of Chur"), also known as the ''Lex Romana Raetica'', ''Lex Romana Utinensis'' or ''Epitome Sancti Galli'', is a Latin legal treatise of the eighth century from the region of Churraetia.Floyd Seyward Lear (1 ...
'', '' Lex Alamannorum'', '' Lex Baiuvariorum'' and '' Leges Langobardorum''.
 In 1027, Emperor Conrad II, in order to secure the important route through the
In 1027, Emperor Conrad II, in order to secure the important route through the Brenner Pass
The Brenner Pass (german: link=no, Brennerpass , shortly ; it, Passo del Brennero ) is a mountain pass through the Alps which forms the border between Italy and Austria. It is one of the principal passes of the Eastern Alpine range and ha ...
, allotted the left bank of the Adige (from Lana to Mezzocorona) to the Duchy of Bavaria. During the 12th century, the local nobility went further: they built Tyrol Castle
Tyrol Castle, less commonly Tirol Castle (german: Schloss Tirol, it, Castel Tirolo) is a castle in the ''comune'' (municipality) of Tirol near Merano, in the Burggrafenamt district of South Tyrol, Italy. It was the ancestral seat of the Counts o ...
in the modern ''comune
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces ('' province''). The can ...
'' of Tirol in South Tyrol, near modern Merano; and around 1140, established the County of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised pr ...
as a state within the Holy Roman Empire.
The Counts of Tyrol were at first ''Vogt
During the Middle Ages, an (sometimes given as modern English: advocate; German: ; French: ) was an office-holder who was legally delegated to perform some of the secular responsibilities of a major feudal lord, or for an institution such as ...
'' (underlords) subject to the Bishoprics of Brixen and Triento; but they had other ideas. They expanded their holdings at those bishoprics' expense. They displaced competing nobles like the , and declared their independence from the Duchy of Bavaria; though not without dispute. In 1228, they conceded the to the House of Wittelsbach, rulers of Bavaria; as a result, that area remains part of Bavaria to this day.
In 1253, rulership of the County passed by inheritance to the Meinhardiner family. In 1335, the last male heir to the Meinhardiner lands, Henry of Bohemia, died. His daughter, Margaret, thereupon became Countess of Tyrol; but her title was in doubt because of different laws in different lands as to what a woman could or could not inherit. She navigated her way between the competing claims of the Houses of Wittelsbach, Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small land ...
and Habsburg by, in 1342, marrying Louis of Wittelsbach. Louis died in 1361. Margaret died in 1369, and bequeathed Tyrol to Rudolf of Habsburg. The various dynastic squabbles were resolved that same year by the , under which (for suitable compensation) the Wittelsbachs agreed to relinquish their claims to Tyrol in favour of the Habsburgs.
When the Habsburgs took control of Tyrol, it had roughly its modern size. However, the Unterinntal
The Lower Inn Valley (german: Unterinntal) is that part of the Inntal valley through which the Inn river flows from a point a few kilometres west of Innsbruck near its confluence with the Melach downstream to a few kilometres before Rosenheim. A ...
downstream from Schwaz
Schwaz () is a city in the Austrian state of Tyrol. It is the administrative center of the Schwaz district. Schwaz is located in the lower Inn valley.
Location
Schwaz lies in the middle of the Lower Inn Valley at the foot of the Kellerjoch a ...
still belonged to Bavaria; the Zillertal and Brixental to Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
; Brixen
Brixen (, ; it, Bressanone ; lld, Porsenù or ) is a town in South Tyrol, northern Italy, located about north of Bolzano.
Geography
First mentioned in 901, Brixen is the third largest city and oldest town in the province, and the artistic and ...
and the Pustertal were episcopal territories, or part of the County of Gorizia
The County of Gorizia ( it, Contea di Gorizia, german: Grafschaft Görz, sl, Goriška grofija, fur, Contee di Gurize), from 1365 Princely County of Gorizia, was a State of the Holy Roman Empire. Originally mediate '' Vogts'' of the Patriarch ...
. On the other hand, the Montafon and the Unterengadin
The Engadin or Engadine ( rm, ;This is the name in the two Romansh idioms that are spoken in the Engadin, Vallader and Puter, as well as in Sursilvan and Rumantsch Grischun. In Surmiran, the name is ''Nagiadegna'', and in Sutsilvan, it is ''G ...
were Tyrolean.
Tyrol was of great strategic importance to the Habsburgs. It controlled several important Alpine passes. It connected their landholdings in Further Austria. In 1406, as the Habsburg lands were split up by inheritance, Tyrol once again became a separate entity (a '' Landstand''), in which the greater landowners had the right to be consulted (''Mitspracherecht''). During a confusing succession of events, in 1420 Frederick IV, Duke of Austria
Frederick IV (1382 – 24 June 1439), also known as Frederick of the Empty Pockets (german: Friedrich mit der leeren Tasche), a member of the House of Habsburg, was Duke of Austria from 1402 until his death. As a scion of the Habsburg Leopoldian ...
moved the capital of Tyrol from Meran
Merano (, , ) or Meran () is a city and ''comune'' in South Tyrol, northern Italy. Generally best known for its spa resorts, it is located within a basin, surrounded by mountains standing up to above sea level, at the entrance to the Passeier ...
to Innsbruck, and Meran lost its earlier importance.
Politics
Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion
 The Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion was founded in 1998. The aim is to strengthen cooperation between the separated countries. In several areas, such as mobility, agriculture, education and culture will be tried to promote exchange and to raise the awareness of the cultural and historical heritage of the region of Tyrol in the minds of the population. Cross-border projects will be initiated to improve the relationship between the different language groups. To represent common ideas and values in Europe, the Euroregion has a joint office in
The Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion was founded in 1998. The aim is to strengthen cooperation between the separated countries. In several areas, such as mobility, agriculture, education and culture will be tried to promote exchange and to raise the awareness of the cultural and historical heritage of the region of Tyrol in the minds of the population. Cross-border projects will be initiated to improve the relationship between the different language groups. To represent common ideas and values in Europe, the Euroregion has a joint office in Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
since 1995. The headquarters of the office is in Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
. Joint decisions are taken by organized three diet (in German: ''Dreier-Landtag''), which have been held since 1991 mostly every two to three years with the state Diets of Trento (provincial council of Trentino), Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
(provincial council of South Tyrol) and Innsbruck (state council of Tyrol (State)). In 2011, the region was institutionalized and since then has its own legal entity.
Political parties
Political parties in the Italian part of Tyrol (provinces of Bolzano and Trento) include: * Partito Democratico (PD) *Südtiroler Volkspartei
The South Tyrolean People's Party (german: Südtiroler Volkspartei, SVP) is a regionalist and autonomist political party in South Tyrol, an autonomous province with a German-speaking majority in northern Italy.
Founded on 8 May 1945, the ...
(SVP)
* Movimento Cinque Stelle
The Five Star Movement ( it, Movimento 5 Stelle , M5S) is a political party in Italy. Its leader and president is Giuseppe Conte, Prime Minister of Italy from 2018 until 2021. The M5S was founded on 4 October 2009 by Beppe Grillo, a comedian an ...
(M5S)
* Lega Nord (LN)
* Greens
Greens may refer to:
*Leaf vegetables such as collard greens, mustard greens, spring greens, winter greens, spinach, etc.
Politics Supranational
* Green politics
* Green party, political parties adhering to Green politics
* Global Greens
* Europ ...
* South Tyrolean Freedom
South Tyrolean Freedom (german: Süd-Tiroler Freiheit, STF) is a regionalist, separatist and national-conservative political party in South Tyrol, Italy. The party, which is part of the South Tyrolean independence movement, seeks to represent t ...
* Die Freiheitlichen
* Trentino Tyrolean Autonomist Party (PATT)
The Austrian part of Tyrol shares the Austrian party system:
* Tiroler Volkspartei; organization of the ÖVP
The Austrian People's Party (german: Österreichische Volkspartei , ÖVP ) is a Christian-democratic and liberal-conservative political party in Austria.
Since December 2021, the party has been led provisionally by Karl Nehammer. It is curr ...
in the state of Tyrol, which has dominated local politics since 1945
* Social Democratic Party of Austria
The Social Democratic Party of Austria (german: Sozialdemokratische Partei Österreichs , SPÖ), founded and known as the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Austria (german: link=no, Sozialdemokratische Arbeiterpartei Österreichs, SDAPÖ) unti ...
(SPÖ)
* Freedom Party of Austria
The Freedom Party of Austria (german: Freiheitliche Partei Österreichs, FPÖ) is a right-wing populist and national-conservative political party in Austria. It was led by Norbert Hofer from September 2019 to 1 June 2021.Staff (1 June 2021"Au ...
(FPÖ)
* The Greens – The Green Alternative
* NEOS
The multiplicity of parties is due to the fact that Tyrol lies in two different nation states and thus are politically independent of each other. Another reason for the large number of parties is the great independence of the two Provinces of Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
and Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
. By the second statute of autonomy in 1972, the province of Bolzano acquired much of the region's competences and since then has been mostly independent of the province of Trento. The second autonomy statute enabled the linguistic minorities to be better protected. The regional council of Trentino-South Tyrol
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
, which consists of the two provincial councils of Bolzano and Trento, has less influence and competences. Thus, many parties determine their focus within the provinces. Other parties in Trentino-South Tyrol, especially in South Tyrol, were founded on the example of Austrian parties and have many similarities with the parties in Austria.
Economy
In the economic sector statistics are shown, which are based largely on numbers and data of the Euroregion Tyrol-South Tyrol-Trentino. It lacks individual communities that are outside the Euroregion. As there are no 10,000 inhabitants living in these communities, the statistics hardly distort the territory of Tyrol and the remaining 1.8 million inhabitants. Tyrol had a total GDP of 67.6 billion euros in 2014. Divided into individual countries, the State of Tyrol generated 28.8 billion euros, the Province of South Tyrol 20.6 billion euros and the Province ofTrentino
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous regio ...
18.2 billion euros. In GDP per capita (2015), that means 39,300 euros/capita in the State of Tyrol, 42,400 euros/capita in South Tyrol and 35,500 euros/capita in Trentino. The unemployment rate in the State of Tyrol is 3.2% (2014), in South Tyrol 3.4% (2017) and in Trentino 4.6% (2017).
The Tyrol region is one of the wealthiest regions in Europe and, in terms of GDP/capita, is above the EU average, which amounted to 28,900 euros/capita in 2015.
The Region of Trentino-South Tyrol is, in terms of GDP/capita, the wealthiest region in Italy with 37,813 euros/capita in 2015.
Primary sector
 Agriculture and forestry occupy a special position in Tyrol. The many small and medium-sized farms have shaped the landscape and culture in Tyrol for many centuries. In order to be competitive with larger farms outside Tyrol, there is a strong
Agriculture and forestry occupy a special position in Tyrol. The many small and medium-sized farms have shaped the landscape and culture in Tyrol for many centuries. In order to be competitive with larger farms outside Tyrol, there is a strong cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-contro ...
system in Tyrol.
South of Tyrol, in the Region of Trentino-South Tyrol, the cultivation of apples and wine plays an important role. So every tenth apple in Europe comes from South Tyrol. Known wines in Trentino-South Tyrol are the Vernatsch
Trollinger, Schiava, or Vernatsch, is a red German/Italian wine grape variety that was likely first originally cultivated in the wine regions of South Tyrol and Trentino, but today is almost exclusively cultivated on steep, sunny locations in t ...
, the Lagrein, the Gewürztraminer and the Weißburgunder.
Livestock, grazing and forestry are important at higher elevations and in more northerly areas. Mainly cattle, sheep, goats and pigs are kept. Accordingly, the production of milk and Tyrolean Speck in the farms is very important. Horses also play an increasingly important role in livestock, for equestrian sports and farm holidays. The Haflinger horses are known in the Tyrolean region and originate from Hafling, near Merano.
Secondary sector
The first industrialization reached Tyrol late in the 19th century. Most of these were small businesses that were important only in the local area. A second wave of industrialization took place at the beginning of the 20th century. Particularly affected at that time was the city ofBolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
with the Italianization policy under Fascism in the 1920s.
In 2011, approximately 10% of the workplaces in all parts of the country were active in the manufacturing sector. Thus lies Tyrol in the EU average at 10.3% (2011). Important branches of industry in Tyrol are the food industry, wood processing and mechanical engineering.
The industry in Tyrol consists mostly of small and medium-sized companies. The craft still plays a special role throughout the region. A large part of these craft businesses are still partially small-structured and family businesses. From an economic point of view, the energy sector is important in the secondary sector. Much of the electricity produced is generated by hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of ...
.
Tertiary sector
 The most important sector in Tyrol is the tertiary sector. Especially tourism has a special position in this region. Due to the connection of the areas by the railway in the 19th century, many villages in Tyrol developed into popular tourism locations. The construction of the Brenner motorway in the 1960s gave the region in the 20th century a renewed upswing in the tourism branch. Today, Merano, Kitzbühel,
The most important sector in Tyrol is the tertiary sector. Especially tourism has a special position in this region. Due to the connection of the areas by the railway in the 19th century, many villages in Tyrol developed into popular tourism locations. The construction of the Brenner motorway in the 1960s gave the region in the 20th century a renewed upswing in the tourism branch. Today, Merano, Kitzbühel, Cortina
Cortina may refer to:
Things
* Cortina (tango), a short piece of music played during a tango dance event
* Ford Cortina, a medium-sized family car built by Ford of Britain from 1962 to 1982
**Lotus Cortina, a 1963–1968 performance variant on the ...
or Riva del Garda are among the most important tourism destinations in the Alpine region. In 2013, the Euroregion
In European politics, the term Euroregion usually refers to a transnational co-operation structure between two (or more) contiguous territories located in different European countries. Euroregions represent a specific type of cross-border regi ...
counted over 80 million overnight stays in the Tyrolean region (to compare - Province of Rome in 2011: 25.8 million overnight stays).
Also important for Tyrol is the trade. Among other things, the Exhibition of Bolzano has been a meeting point for Italian and German economy already for centuries. As a transit route country, more than 2.25 million trucks (2017) drove over the Brenner Pass
The Brenner Pass (german: link=no, Brennerpass , shortly ; it, Passo del Brennero ) is a mountain pass through the Alps which forms the border between Italy and Austria. It is one of the principal passes of the Eastern Alpine range and ha ...
. This means that two times more trucks travel on the Brenner Route than in all four Alpine crossing roads in Switzerland together.
Transport
Tyrol is known as a transit route. The most important route between northern and southern Europe, the Brenner route, traverses the entire region. At 1370 m above the Adriatic, theBrenner Pass
The Brenner Pass (german: link=no, Brennerpass , shortly ; it, Passo del Brennero ) is a mountain pass through the Alps which forms the border between Italy and Austria. It is one of the principal passes of the Eastern Alpine range and ha ...
is the lowest pass crossing of the main chain of the Alps.
Due to the linguistic diversity and the climatic transition from temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
(alpine climate
Alpine climate is the typical weather ( climate) for elevations above the tree line, where trees fail to grow due to cold. This climate is also referred to as a mountain climate or highland climate.
Definition
There are multiple definitions ...
) to mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
, the area is regarded as a bridge between the Italian and German speaking countries.
Airports
 The most important airport in Tyrol is Innsbruck Airport. With over one million passengers, it is the third largest airport in Austria. Other airports in the region are in
The most important airport in Tyrol is Innsbruck Airport. With over one million passengers, it is the third largest airport in Austria. Other airports in the region are in Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
and Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
. These do not offer regular scheduled flights and the Bolzano Airport currently offers charter flights. There are other small airfields in Toblach
Toblach (; it, Dobbiaco ) is a ''comune''/''Gemeinde'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located in the Puster Valley about northeast of the city of Bolzano, on the border with Austria.
Geography
As of November 30, 2010, it h ...
, Kufstein
Kufstein (; Central Bavarian: ''Kufstoa'') is a town in the Austrian state of Tyrol, the administrative seat of Kufstein District. With a population of about 19,600 it is the second largest Tyrolean town after the state capital Innsbruck. The gr ...
, St. Johann in Tirol, Reutte and Cortina
Cortina may refer to:
Things
* Cortina (tango), a short piece of music played during a tango dance event
* Ford Cortina, a medium-sized family car built by Ford of Britain from 1962 to 1982
**Lotus Cortina, a 1963–1968 performance variant on the ...
. The airfield in Cortina was closed in 1976 due to a crash.
Road transport
Highways in Tyrol are the Brenner motorway and the Inntal motorway. The Brenner motorway runs from Innsbruck (in Austria A13) to Modena (in Italy A22). Together with the Inntal motorway from Innsbruck toKufstein
Kufstein (; Central Bavarian: ''Kufstoa'') is a town in the Austrian state of Tyrol, the administrative seat of Kufstein District. With a population of about 19,600 it is the second largest Tyrolean town after the state capital Innsbruck. The gr ...
is the part of the European route E45. The dual carriageway from Merano to Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
(MeBo) ends in Bolzano South in the Brenner motorway. Important road section in Trentino
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous regio ...
, next to the Brenner motorway, is the SS 47 (Strada Statale 47), which connects via Sugana Valley Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
with Padova
Padua ( ; it, Padova ; vec, Pàdova) is a city and ''comune'' in Veneto, northern Italy. Padua is on the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice. It is the capital of the province of Padua. It is also the economic and communications hub of the ...
. A large part of this route is dual-lane and flows into the Brenner state road (SS 12).
Due to the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, ...
, there are many mountain passes that connect valleys. The most important pass roads for transit trade are the Reschen Pass and Brenner Pass
The Brenner Pass (german: link=no, Brennerpass , shortly ; it, Passo del Brennero ) is a mountain pass through the Alps which forms the border between Italy and Austria. It is one of the principal passes of the Eastern Alpine range and ha ...
. Popular pass roads include the Stelvio Pass, Arlberg Pass
Arlberg () is a massif between Vorarlberg and Tyrol in Austria. The highest peak is the Valluga at . The name ''Arlberg'' derives from the tradition of the "Arlenburg", who are said to have once established themselves on the Tyrolean side of the A ...
, Karer Pass, Mendel Pass
The Mendel Pass (german: Mendelpass or , it, Passo della Mendola, or ) is a 1,362 metre-high mountain pass
A mountain pass is a navigable route through a mountain range or over a ridge. Since many of the world's mountain ranges have p ...
and the Gardena Pass. The Provinces of Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
and Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
have been responsible for the preservation and management of the state roads in their provinces since 1998.
Railways
Brenner Pass
The Brenner Pass (german: link=no, Brennerpass , shortly ; it, Passo del Brennero ) is a mountain pass through the Alps which forms the border between Italy and Austria. It is one of the principal passes of the Eastern Alpine range and ha ...
. The Brenner Railway was opened in 1867 and runs from Innsbruck to Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
via the cities of Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
and Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
. Together with the Lower Inn Valley Railway in North Tyrol, this section of the route is part of the important European railway axis Berlin-Palermo, which connects northern Europe with southern Europe across the Alps. With the construction of the Brenner Base Tunnel and its completion in 2027, transit traffic on the rail will be promoted and relocated. After completion, the Brenner Base Tunnel, together with the Innsbruck bypass, will be the longest railway tunnel in the world at 64 km and will reduce the travel time between Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
and Innsbruck from 2 hours to 45 minutes.
Further important railway lines in Tyrol are the Arlberg railway, Zillertal railway, Salzburg-Tyrol railway, Pustertal railway with continuation of the Drautal railway, the railway line Bolzano-Merano and the continuation of the Vinschgau railway, the Trento–Malè–Mezzana railway and the Valsugana railway, which leads from Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
to Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
over the Sugana Valley. Cross-border connections are offered only a few. The ÖBB travels over the Brenner Pass on the Eurocity trains and several regional trains connect South Tyrol with North Tyrol an East Tyrol
East Tyrol, occasionally East Tirol (german: Osttirol), is an exclave of the Austrian state of Tyrol, separated from the main North Tyrol part by the short common border of Salzburg and Italian South Tyrol (''Südtirol'', it, Alto Adige). It ...
. The Euroregion Tyrol-South Tyrol-Trentino has set itself the goal of promoting and expanding cross-border connections. The aim is to shift traffic through the Alps to sustainable means of transport, thus protecting the Alpine environment.
Local public transport
Many villages and communities are difficult to reach because of the large differences in altitude, so the region sets much on ropeway concepts. Although most of the cable cars are located in ski resorts, they are also used for the local public transport. Known cable cars in Tyrol are the Ritten cable car inBolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
, the Sardagna cable car in Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
and the Nordkette cable car in Innsbruck. Also funicular
A funicular (, , ) is a type of cable railway system that connects points along a railway track laid on a steep slope. The system is characterized by two counterbalanced carriages (also called cars or trains) permanently attached to opposite e ...
railways are being built to cope with the differences in altitude more quickly. Famous funiculars are among others the Hungerburgbahn in Innsbruck and the Mendel funicular in Kaltern.
Local public transport is usually offered with intercity buses or city buses. The city of Innsbruck has its own tram network. Another tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport ...
is located in Ritten. The cities of Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
, Merano and Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
formerly had their own tram network, but these were displaced and replaced by the city buses and private transport in the 50s and 60s.
Culture
The Tyrolean culture has been cultivated for several centuries and passed on to future generations. The state border between South and North Tyrol is more a political border and is considered less as a cultural border. Many traditions are cultivated throughout the Tyrolean region and show little differences. In all cultural areas such as food, dress or customs there are many similarities. Nevertheless, the individual language groups, especially the minority languages, try to maintain and promote their own linguistic identity.Tyrolean cuisine
 The Tyrolean cuisine has similarities with the
The Tyrolean cuisine has similarities with the Austrian cuisine
Austrian cuisine () is a style of cuisine native to Austria and composed of influences from Central Europe and throughout the former Austro-Hungarian Empire. Austrian cuisine is most often associated with Viennese cuisine, but there are signific ...
and is characterized by its alpine influence. Also the historical influence of the former K.U.K. Monarchy
The phrase Imperial and Royal ( German: ''kaiserlich und königlich'', ), typically abbreviated as ''k. u. k.'', ''k. und k.'', ''k. & k.'' in German (the "und" is always spoken unabbreviated), ''cs. és k. (császári és királyi)'' in Hungar ...
can be found in the Tyrolean dishes. These include dishes such as goulash, Kaiserschmarrn
''Kaiserschmarrn'' or ''Kaiserschmarren'' (Emperor's Mess) is a lightly sweetened pancake that takes its name from the Austrian emperor (Kaiser) Franz Joseph I, who was fond of this fluffy shredded pancake. It is served as a dessert or as a li ...
and apple strudel which are consumed in large parts of the Danube monarchy and today still in Tyrol. Since the region is still relatively strong agricultural and peasant today, also many peasant dishes are offered on the farms. Schlutzkrapfen, boiled dumplings or cold cuts with bacon (in German: ''Speck'') or grey cheese is eaten on the farms.
The Tyrolean dishes show only slight differences throughout Tyrol. Due to the Mediterranean conditions in the southern part of Tyrol, a lot of wine is grown and is therefore also an important part of the Tyrolean dish, especially in South Tyrol and Trentino
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous regio ...
. Famous wines from this area are the Gewürztraminer, Pinot Blanc
Pinot blanc is a white wine grape. It is a point genetic mutation of Pinot noir. Pinot noir is genetically unstable and will occasionally experience a point mutation in which a vine bears all black fruit except for one cane which produces ...
, Pinot Grigio and Chardonnay
Chardonnay (, , ) is a green-skinned grape variety used in the production of white wine. The variety originated in the Burgundy wine region of eastern France, but is now grown wherever wine is produced, from England to New Zealand. For new ...
. Furthermore, a lot of apples are grown in the Region of Trentino-South Tyrol. In this region also a food culture is cultivated with a mixture of Italian and Tyrolean specialties.Tyrolean Rifles
 The Tyrolean Rifles were a militia organized in case of an attack on
The Tyrolean Rifles were a militia organized in case of an attack on crown land
Crown land (sometimes spelled crownland), also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it ...
, which required Tyrol to defend its territory. The militia consisted mostly of citizens and peasants who were responsible only for the defence of their own land and were not obliged to go to war on behalf of the Habsburg monarchy. They were authorized by an order signed by Emperor Maximilian I in 1511 that remained valid until 1918. The Tyrolean Rifles became known in 1809 when Tyrolese peasants rose up and fought against the French-Bavarian occupation under Napoleon. The ensuing four Battles of Bergisel were led by Andreas Hofer. The Rifles were also used in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
in 1915 on the Dolomite front. After the separation of Tyrol and the downfall of the monarchy, the companies also lost their task of defending their country. Nevertheless, they remained as a non-governmental organization. Today, the Rifles are responsible as an organization for the preservation of the Tyrolean culture and are always present at important political events in Tyrol.
Customs
Many Tyrolean customs were created centuries ago and are passed on by the population for the next generations. Typical in the Alpine region are the many individual customs in the valleys. Due to the seclusion of the valleys, the locals developed their own customs. Many customs have been created by legends and narratives, others by the close connection to the church. There are also traditions that are cultivated everywhere in the Tyrolean region and do not differ from other valleys and villages. These customs give local people an identity and thus feel the community more connected.Sports
Tyrol is traditionally a winter sports country. Many athletes, such asGustav Thoeni
Gustav, Gustaf or Gustave may refer to:
*Gustav (name), a male given name of Old Swedish origin
Art, entertainment, and media
* ''Primeval'' (film), a 2007 American horror film
* ''Gustav'' (film series), a Hungarian series of animated short cart ...
, Benjamin Raich, Carolina Kostner, Gregor Schlierenzauer, Toni Sailer and Armin Zoeggeler
Armin (Armyn) is a given name or surname, and is:
* An ancient Indo-European name:
** a German/Dutch given name,
*** a modern form of the name Arminius (18/17 BC–AD 21), a German prince who defeated a Roman army in the Battle of the Teutoburg F ...
have already won overall World Cups and medals at World Championships and Olympic Games.
Even in summer sports, several athletes from Tyrol were and still are among the best in the world. In water jumping Tania Cagnotto and Klaus Dibiasi
Klaus Dibiasi (born 6 October 1947) is a former diver from Italy, who competed in four consecutive Summer Olympics for his country, starting in 1964. He dominated the platform event from the late 1960s to the mid-1970s, winning a total number of ...
won several medals. In cycling, Francesco Moser won the Giro d'Italia. Andreas Seppi played against the best tennis players in the world for many years. In bouldering Anna Stöhr
Anna Stöhr (born 25 April 1988 in Reith im Alpbachtal, Austria) is a professional climber. She is a champion in bouldering climbing competitions. She won four Bouldering World Cups, in 2008, 2011, 2012 and 2013 and two World Championships, in 20 ...
was one of the best in the world.
Many Tyrolean mountaineers such as Reinhold Messner and Hans Kammerlander influenced the alpinism.
Football
The FC Wacker Innsbruck is one of the most traditional and successful clubs in Austria. Since the club was founded in 1915 and several name changes, the football club has won ten times the Austrian Championship and seven times the Austrian Cup. In 1987, it reached the semi-finals of theUEFA CUP
A cup is an open-top used to hold hot or cold liquids for pouring or drinking; while mainly used for drinking, it also can be used to store solids for pouring (e.g., sugar, flour, grains, salt). Cups may be made of glass, metal, china, cla ...
. In 1970, the team defeated Real Madrid in Madrid. Currently (2018) Wacker Innsbruck plays in the "Erste Liga In sports, 1. Liga, 1. liga, I Liga or Erste Liga may refer to:
Association football
* 1. Bundesliga, football league in Germany
* Latvian First League, (1. līga), football league in Latvia
* I liga, football league in Poland
* I liga (women's ...
" (second highest category of Austria).
In the Region of Trentino-South Tyrol, the FC Südtirol and AC Trento
A.C. Trento 1921 (nicknamed ' or ') is an Football in Italy, Italian football club, and the major club in Trento. Currently they play in .
In 2014 Società Sportiva Dilettantistica Trento Calcio 1921 S.r.l. went bankrupt. The sports title was t ...
are the two most important clubs. Both teams participated in the Italian Serie C
The Serie C () is the third-highest division in the Italian football league system after the Serie B and Serie A. The Lega Italiana Calcio Professionistico (Lega Pro) is the governing body that runs the Serie C.
The unification of the Lega ...
(third highest league in Italy) for several seasons. The AC Trento has a long history until 1921. FC Südtirol was founded in 1995. AC Trento are currently (2018) playing in the Italian Serie D
The Serie D () is the top level of semi-professional football in the country. The fourth tier of the Italian league system, the competition sits beneath the third professional league, Serie C. It is administered by the Lega Nazionale Dilettant ...
(fourth highest league in Italy) and FC Südtirol in Serie C
The Serie C () is the third-highest division in the Italian football league system after the Serie B and Serie A. The Lega Italiana Calcio Professionistico (Lega Pro) is the governing body that runs the Serie C.
The unification of the Lega ...
. Thus, the FC Südtirol is the only professional football club in the region.
Ice hockey
Ice hockey is a very popular sport in Tyrol. Important clubs are the HC Bolzano and the HC Innsbruck. Both teams play in the EBEL. The HC Innsbruck, formerly EV Innsbruck, won the Austrian championship seven times. With 19 won Italian championships, the HC Bolzano is the record champion in Italy. The club celebrated the biggest international successes by winning theAlpenliga
The Alpenliga was an international professional ice hockey league which existed between 1991 and 1999. It was contested by club teams from Austria, Italy and Slovenia.
In 1994-95 and 1995–96, the Alpenliga was part of a larger competition ...
, the EBEL and the Six Nations Tournament
The Six Nations Championship (known as the Guinness Six Nations for sponsorship reasons) is an annual international men's rugby union competition between the teams of England, France, Ireland, Italy, Scotland and Wales. The current champions ar ...
with Jaromír Jágr. The Italian ice hockey league consists mostly of South Tyrolean teams. 5 of the 8 Italian teams in the Alps Hockey League come from South Tyrol (HC Neumarkt-Egna
HC Neumarkt-Egna is an ice hockey team in Neumarkt, Italy. They play in the Alps Hockey League and formerly the Serie A. The club was founded in 1963.
Honours
*Inter-National League
The Inter-National League was an international ice hock ...
, HC Pustertal, Ritten Sport, HC Gardena and WSV Sterzing Broncos). In this league three more Tyrolean teams play ( SG Cortina, HC Fassa and EC Kitzbühel).
In 2005, the Ice Hockey World Championship was held in Innsbruck and Vienna. The 1994 Ice Hockey World Championship took place in Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
, Canazei
Canazei ( Ladin: ''Cianacéi'') is a ''comune'' (municipality) in Trentino in the northern Italian region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, located in the upper part of the Val di Fassa, about northeast of Trento. Its name derives from the Lat ...
and Milan.
Volleyball
In volleyball, Trentino Volley is one of the best teams in the world. Three times the Champions league title, four times the clubworld championship
A world championship is generally an international competition open to elite competitors from around the world, representing their nations, and winning such an event will be considered the highest or near highest achievement in the sport, game, ...
title and four times the Italian championship title could win the club from Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
. Founded in 2000, the club quickly established itself at the top of the league. In 2011, Trentino Volley won the CEV Champions League ahead of its own fans at the PalaOnda in Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
.
Hypo Tirol Innsbruck
Hypo Tirol Innsbruck is a professional volleyball team based in Innsbruck
Innsbruck (; bar, Innschbruck, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian ) is the capital of Tyrol (state), Tyrol and the List of cities and towns in Austria, fifth-la ...
conquered the Austrian title 10 times. Of the last 13 seasons, the team won 10 times the Austrian championship. Since the season 2017/18 the club plays in the German volleyball league under the name "Hypo Tirol Alpenvolleys Haching". The club went into cooperation with the German team TSV Unterhaching.
Sports events
 In Tyrol, the Olympic Winter Games have been organized three times so far. In
In Tyrol, the Olympic Winter Games have been organized three times so far. In 1964
Events January
* January 1 – The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarc ...
and 1976 they were held in Innsbruck and 1956 in Cortina
Cortina may refer to:
Things
* Cortina (tango), a short piece of music played during a tango dance event
* Ford Cortina, a medium-sized family car built by Ford of Britain from 1962 to 1982
**Lotus Cortina, a 1963–1968 performance variant on the ...
.
Most of the big annual sporting events in Tyrol take place in winter. The Alpine Skiing World Cup is held in Kitzbühel, Val Gardena, Cortina
Cortina may refer to:
Things
* Cortina (tango), a short piece of music played during a tango dance event
* Ford Cortina, a medium-sized family car built by Ford of Britain from 1962 to 1982
**Lotus Cortina, a 1963–1968 performance variant on the ...
and Madonna di Campiglio. These races are classics in the Ski World Cup and have a long tradition.
A famous biathlon
The biathlon is a winter sport that combines cross-country skiing and rifle shooting. It is treated as a race, with contestants skiing through a cross-country trail whose distance is divided into shooting rounds. The shooting rounds are not ti ...
location is in Antholz. There were often held the Biathlon World Championships. Several Nordic Combined
Nordic combined is a winter sport in which athletes compete in cross-country skiing and ski jumping. The Nordic combined at the Winter Olympics has been held since the first ever Winter Olympics in 1924, while the FIS Nordic Combined World Cup ...
World Championships were organized in Val di Fiemme. Part of the Four Hills Tournament is the Bergisel Ski Jump in Innsbruck. A stage of the Tour de Ski is also located in Toblach
Toblach (; it, Dobbiaco ) is a ''comune''/''Gemeinde'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located in the Puster Valley about northeast of the city of Bolzano, on the border with Austria.
Geography
As of November 30, 2010, it h ...
.
Some summer sports events are also held in Tyrol. The Tour of the Alps take place every year in Tyrol. The tour was launched by the Euroregion Tyrol-South Tyrol-Trentino. It is the successor of the Giro del Trentino
The Tour of the Alps is an annual professional cycling stage race in Italy and Austria. First held in 1962, it was named Giro del Trentino ( en, Tour of Trentino) until 2016, and run over four stages in the Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol region o ...
, which has been around for over 40 years. In 2017, the UCI Downhill World Championships took place in Val di Sole, near Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
. The BOclassic in Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
takes place on New Year's Eve and is one of the best occupied New Year's Eve races in the world. Every year, an ATP World Series tennis tournament is organized in Kitzbühel.
Universities and research institutions



Universities
*University of Innsbruck
The University of Innsbruck (german: Leopold-Franzens-Universität Innsbruck; la, Universitas Leopoldino Franciscea) is a public research university in Innsbruck, the capital of the Austrian federal state of Tyrol, founded on October 15, 1669.
...
* University of Trento
* Free University of Bozen-Bolzano
* UMIT – Private University for Health Sciences, Medical Informatics and Technology
* Medical University of Innsbruck
The Medical University of Innsbruck (german: Medizinische Universität Innsbruck) is a university in Innsbruck, Austria. It used to be one of the four historical faculties of the Leopold-Franzens-Universität Innsbruck and became an independent un ...
Colleges
* Philosophical-theological Academy Brixen * Conservatory "Claudio Monteverdi" * Tyrolean State Conservatory * University of Applied Sciences Kufstein * Health university of Applied Science Tyrol * MCI Management Center Innsbruck * Pedagogical University of Applied Science Tyrol * Ecclesiastical Pedagogical University of Applied Science – Edith Stein * State College of Health Professions "Claudiana"Independent research institutions
* Institute for Interdisciplinary Mountain Research, a facility of Austrian Academy of Sciences * Eurac Research *NOI Techpark
NOI Techpark is the science and technology park of South Tyrol that hosts 4 research institutes ( Fraunhofer Italia, Eurac Research, ClimateHouse and Research Centre Laimburg), 4 Faculties of the Free University of Bozen-Bolzano, 40 scientific ...
* Foundation Bruno Kessler
* Edmund Mach Foundation
* Research-Center Laimburg
See also
*County of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised pr ...
* Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion
The Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion (german: Europaregion Tirol–Südtirol–Trentino; it, Euregio Tirolo–Alto Adige–Trentino) is a Euroregion formed by three different regional authorities in Austria and Italy: the Aust ...
* Austria–Italy border
References
{{Authority control Divided regions