Tuberculosis Deaths In West Virginia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''
 The main cause of TB is ''
The main cause of TB is ''
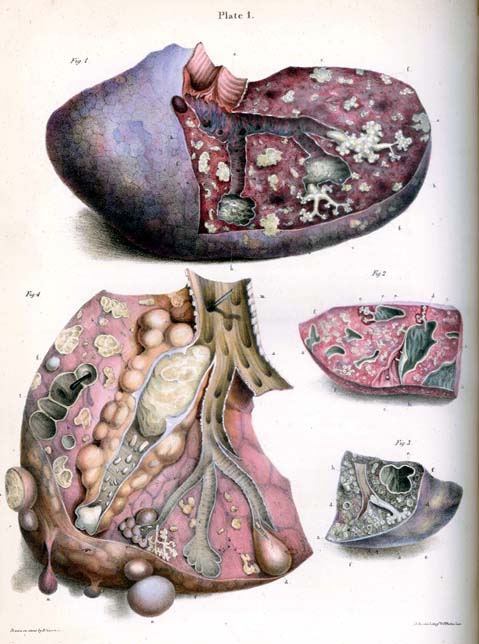 About 90% of those infected with ''M. tuberculosis'' have
About 90% of those infected with ''M. tuberculosis'' have  TB infection begins when the mycobacteria reach the alveolar air sacs of the lungs, where they invade and replicate within endosomes of alveolar macrophages. Macrophages identify the bacterium as foreign and attempt to eliminate it by phagocytosis. During this process, the bacterium is enveloped by the macrophage and stored temporarily in a membrane-bound vesicle called a phagosome. The phagosome then combines with a lysosome to create a phagolysosome. In the phagolysosome, the cell attempts to use reactive oxygen species and acid to kill the bacterium. However, ''M. tuberculosis'' has a thick, waxy mycolic acid capsule that protects it from these toxic substances. ''M. tuberculosis'' is able to reproduce inside the macrophage and will eventually kill the immune cell.
The primary site of infection in the lungs, known as the Ghon focus, is generally located in either the upper part of the lower lobe, or the lower part of the upper lobe. Tuberculosis of the lungs may also occur via infection from the blood stream. This is known as a Simon focus and is typically found in the top of the lung. This hematogenous transmission can also spread infection to more distant sites, such as peripheral lymph nodes, the kidneys, the brain, and the bones. All parts of the body can be affected by the disease, though for unknown reasons it rarely affects the heart,
TB infection begins when the mycobacteria reach the alveolar air sacs of the lungs, where they invade and replicate within endosomes of alveolar macrophages. Macrophages identify the bacterium as foreign and attempt to eliminate it by phagocytosis. During this process, the bacterium is enveloped by the macrophage and stored temporarily in a membrane-bound vesicle called a phagosome. The phagosome then combines with a lysosome to create a phagolysosome. In the phagolysosome, the cell attempts to use reactive oxygen species and acid to kill the bacterium. However, ''M. tuberculosis'' has a thick, waxy mycolic acid capsule that protects it from these toxic substances. ''M. tuberculosis'' is able to reproduce inside the macrophage and will eventually kill the immune cell.
The primary site of infection in the lungs, known as the Ghon focus, is generally located in either the upper part of the lower lobe, or the lower part of the upper lobe. Tuberculosis of the lungs may also occur via infection from the blood stream. This is known as a Simon focus and is typically found in the top of the lung. This hematogenous transmission can also spread infection to more distant sites, such as peripheral lymph nodes, the kidneys, the brain, and the bones. All parts of the body can be affected by the disease, though for unknown reasons it rarely affects the heart,

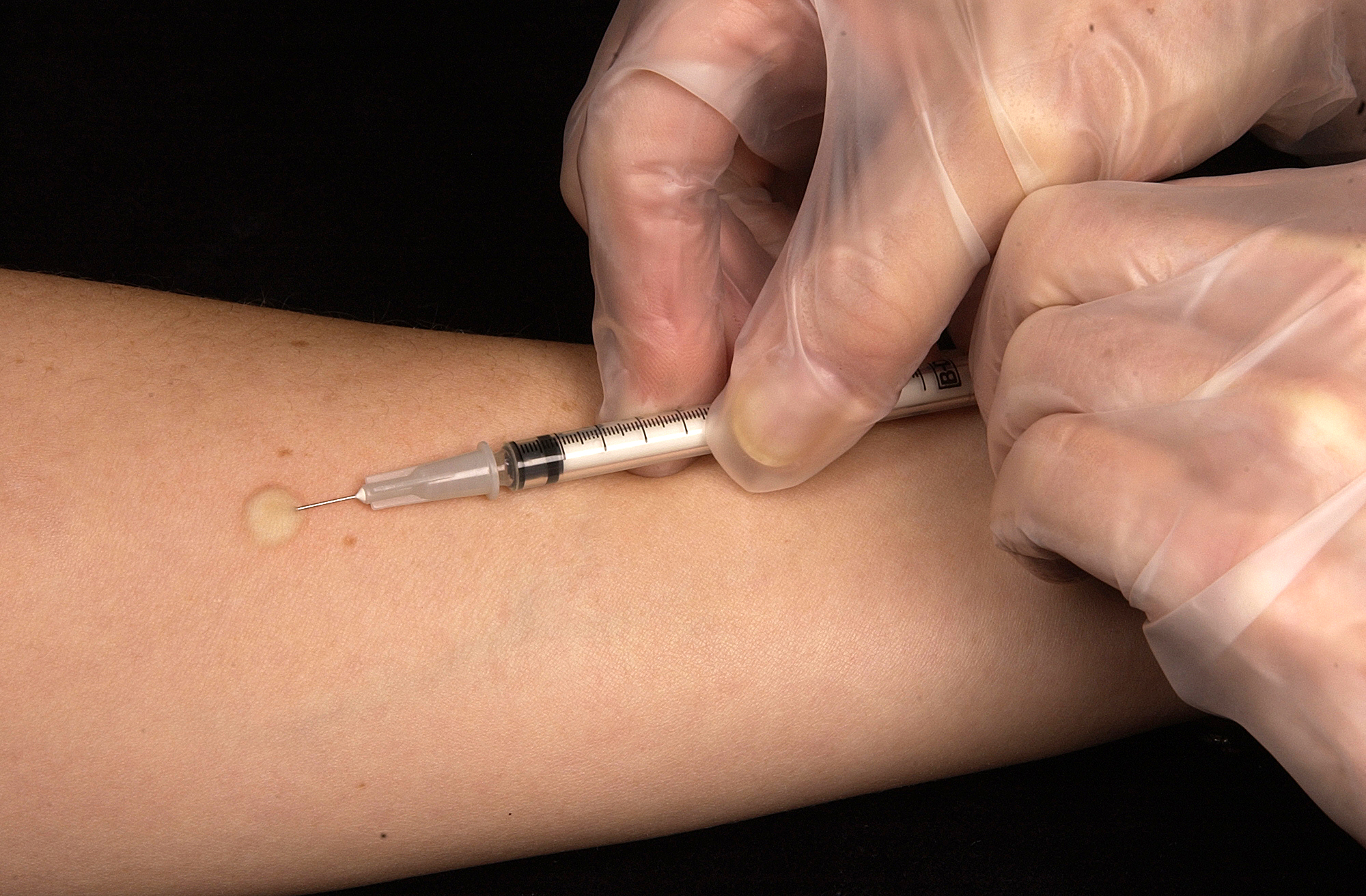 The Mantoux tuberculin skin test is often used to screen people at high risk for TB. Those who have been previously immunized with the Bacille Calmette-Guerin vaccine may have a false-positive test result. The test may be falsely negative in those with sarcoidosis, Hodgkin's lymphoma, malnutrition, and most notably, active tuberculosis. Interferon gamma release assays, on a blood sample, are recommended in those who are positive to the Mantoux test. These are not affected by immunization or most environmental mycobacteria, so they generate fewer false-positive results. However, they are affected by ''M. szulgai'', ''M. marinum'', and ''M. kansasii''. IGRAs may increase sensitivity when used in addition to the skin test, but may be less sensitive than the skin test when used alone.
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has recommended screening people who are at high risk for latent tuberculosis with either tuberculin skin tests or interferon-gamma release assays. While some have recommend testing health care workers, evidence of benefit for this is poor . The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) stopped recommending yearly testing of health care workers without known exposure in 2019.
The Mantoux tuberculin skin test is often used to screen people at high risk for TB. Those who have been previously immunized with the Bacille Calmette-Guerin vaccine may have a false-positive test result. The test may be falsely negative in those with sarcoidosis, Hodgkin's lymphoma, malnutrition, and most notably, active tuberculosis. Interferon gamma release assays, on a blood sample, are recommended in those who are positive to the Mantoux test. These are not affected by immunization or most environmental mycobacteria, so they generate fewer false-positive results. However, they are affected by ''M. szulgai'', ''M. marinum'', and ''M. kansasii''. IGRAs may increase sensitivity when used in addition to the skin test, but may be less sensitive than the skin test when used alone.
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has recommended screening people who are at high risk for latent tuberculosis with either tuberculin skin tests or interferon-gamma release assays. While some have recommend testing health care workers, evidence of benefit for this is poor . The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) stopped recommending yearly testing of health care workers without known exposure in 2019.
 Tuberculosis prevention and control efforts rely primarily on the vaccination of infants and the detection and appropriate treatment of active cases. The World Health Organization (WHO) has achieved some success with improved treatment regimens, and a small decrease in case numbers. Some countries have legislation to involuntarily detain or examine those suspected to have tuberculosis, or involuntarily treat them if infected.
Tuberculosis prevention and control efforts rely primarily on the vaccination of infants and the detection and appropriate treatment of active cases. The World Health Organization (WHO) has achieved some success with improved treatment regimens, and a small decrease in case numbers. Some countries have legislation to involuntarily detain or examine those suspected to have tuberculosis, or involuntarily treat them if infected.
 Treatment of TB uses antibiotics to kill the bacteria. Effective TB treatment is difficult, due to the unusual structure and chemical composition of the mycobacterial
Treatment of TB uses antibiotics to kill the bacteria. Effective TB treatment is difficult, due to the unusual structure and chemical composition of the mycobacterial
 Progression from TB infection to overt TB disease occurs when the bacilli overcome the immune system defenses and begin to multiply. In primary TB disease (some 1–5% of cases), this occurs soon after the initial infection. However, in the majority of cases, a
Progression from TB infection to overt TB disease occurs when the bacilli overcome the immune system defenses and begin to multiply. In primary TB disease (some 1–5% of cases), this occurs soon after the initial infection. However, in the majority of cases, a
, World Health Organization, 2011. however, mortality rate increased to 24 per 100,000 in 2005 and then recoiled to 11 per 100,000 by 2015.
File:Tuberculosis incidence (per 100,000 people), OWID.svg, Number of new cases of tuberculosis per 100,000 people in 2016.
File:Tuberculosis world map-Deaths per million persons-WHO2012.svg, Tuberculosis deaths per million persons in 2012
File:Tuberculosis deaths by region, OWID.svg, Tuberculosis deaths by region, 1990 to 2017.
 Tuberculosis has existed since
Tuberculosis has existed since 
 Tuberculosis was for centuries associated with poetic and artistic qualities among those infected, and was also known as "the romantic disease". Major artistic figures such as the poets
Tuberculosis was for centuries associated with poetic and artistic qualities among those infected, and was also known as "the romantic disease". Major artistic figures such as the poets
WHO global 2016 TB report (infographic)
WHO tuberculosis country profiles
"Tuberculosis Among African Americans"
1990-11-01, '' In Black America''; KUT Radio, American Archive of Public Broadcasting (
Working Group on New TB drugs
tracking clinical trials and drug candidates {{Authority control Airborne diseases Articles containing video clips Health in Africa Healthcare-associated infections Infectious causes of cancer Mycobacterium-related cutaneous conditions Vaccine-preventable diseases Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full)
 Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb) is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its c ...
'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms.
Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air
''Through the Air'' (French title: ''La résistance de l'air'') is a 2015 French-Belgian drama film directed by Fred Grivois. The film concerns an air rifle champion who becomes embroiled in a dangerous plot after accepting a well-paid job offer. ...
when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active TB is based on chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
s, as well as microscopic examination and culture of body fluids. Diagnosis of Latent TB relies on the tuberculin skin test (TST) or blood tests.
Prevention of TB involves screening those at high risk, early detection and treatment of cases, and vaccination with the bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine. Those at high risk include household, workplace, and social contacts of people with active TB. Treatment requires the use of multiple antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s over a long period of time. Antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
is a growing problem with increasing rates of multiple drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB).
In 2018, one quarter of the world's population was thought to have a latent infection of TB. New infections occur in about 1% of the population each year. In 2020, an estimated 10 million people developed active TB, resulting in 1.5 million deaths, making it the second leading cause of death from an infectious disease after COVID-19. As of 2018, most TB cases occurred in the regions of South-East Asia (44%), Africa (24%), and the Western Pacific (18%), with more than 50% of cases being diagnosed in seven countries: India (27%), China (9%), Indonesia (8%), the Philippines (6%), Pakistan (6%), Nigeria (4%), and Bangladesh (4%). By 2021 the number of new cases each year was decreasing by around 2% annually. About 80% of people in many Asian and African countries test positive while 5–10% of people in the United States population test positive via the tuberculin test. Tuberculosis has been present in humans since ancient times.
Signs and symptoms
Tuberculosis may infect any part of the body, but most commonly occurs in the lungs (known as pulmonary tuberculosis). Extrapulmonary TB occurs when tuberculosis develops outside of the lungs, although extrapulmonary TB may coexist with pulmonary TB. General signs and symptoms include fever,chills
Chills is a feeling of coldness occurring during a high fever, but sometimes is also a common symptom which occurs alone in specific people. It occurs during fever due to the release of cytokines and prostaglandins as part of the inflammatory r ...
, night sweats, loss of appetite, weight loss, and fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
. Significant nail clubbing may also occur.
Pulmonary
If a tuberculosis infection does become active, it most commonly involves the lungs (in about 90% of cases). Symptoms may includechest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
and a prolonged cough producing sputum. About 25% of people may not have any symptoms (i.e., they remain asymptomatic). Occasionally, people may cough up blood in small amounts, and in very rare cases, the infection may erode into the pulmonary artery or a Rasmussen's aneurysm Rasmussen's aneurysm is a pulmonary artery aneurysm associated with a cavitary lung lesion. It was originally described by Fritz Valdemar Rasmussen in association with cavitary lung lesions of tuberculosis,Rasmussen, V. On hemoptysis, especially wh ...
, resulting in massive bleeding. Tuberculosis may become a chronic illness and cause extensive scarring in the upper lobes of the lungs. The upper lung lobes are more frequently affected by tuberculosis than the lower ones. The reason for this difference is not clear. It may be due to either better air flow, or poor lymph drainage within the upper lungs.
Extrapulmonary
In 15–20% of active cases, the infection spreads outside the lungs, causing other kinds of TB. These are collectively denoted as extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Extrapulmonary TB occurs more commonly in people with a weakened immune system and young children. In those with HIV, this occurs in more than 50% of cases. Notable extrapulmonary infection sites include the pleura (in tuberculous pleurisy), the central nervous system (in tuberculous meningitis), thelymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid o ...
(in scrofula of the neck), the genitourinary system
The genitourinary system, or urogenital system, are the organs of the reproductive system and the urinary system. These are grouped together because of their proximity to each other, their common embryological origin and the use of common pathwa ...
(in urogenital tuberculosis), and the bones and joints (in Pott disease of the spine), among others. A potentially more serious, widespread form of TB is called "disseminated tuberculosis", it is also known as miliary tuberculosis. Miliary TB currently makes up about 10% of extrapulmonary cases.
Causes
Mycobacteria
 The main cause of TB is ''
The main cause of TB is ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb) is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its c ...
'' (MTB), a small, aerobic, nonmotile bacillus. The high lipid content of this pathogen accounts for many of its unique clinical characteristics. It divides every 16 to 20 hours, which is an extremely slow rate compared with other bacteria, which usually divide in less than an hour. Mycobacteria have an outer membrane lipid bilayer. If a Gram stain is performed, MTB either stains very weakly "Gram-positive" or does not retain dye as a result of the high lipid and mycolic acid content of its cell wall. MTB can withstand weak disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than st ...
s and survive in a dry state for weeks. In nature, the bacterium can grow only within the cells of a host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
People
*Jim Host (born 1937), American businessman
* Michel Host ...
organism, but ''M. tuberculosis'' can be cultured in the laboratory.
Using histological stains on expectorated samples from phlegm (also called sputum), scientists can identify MTB under a microscope. Since MTB retains certain stains even after being treated with acidic solution, it is classified as an acid-fast bacillus. The most common acid-fast staining techniques are the Ziehl–Neelsen stain and the Kinyoun stain, which dye acid-fast bacilli a bright red that stands out against a blue background. Auramine-rhodamine staining and fluorescence microscopy are also used.
The ''M. tuberculosis'' complex (MTBC) includes four other TB-causing mycobacteria
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis ('' M. tuberculosis'') and ...
: '' M. bovis'', ''M. africanum
''Mycobacterium africanum'' is a species of ''Mycobacterium'' that is most commonly found in West African countries, where it is estimated to cause up to 40% of pulmonary tuberculosis. The symptoms of infection resemble those of ''M. tuberculosi ...
'', '' M. canetti'', and ''M. microti
''Mycobacterium microti''
*Member of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC)
*Also known as the 'Vole bacillus'
*Etymology: microtus is a genus that includes small field rodents such as the vole. This mycobacterium species was first descri ...
''. ''M. africanum'' is not widespread, but it is a significant cause of tuberculosis in parts of Africa. ''M. bovis'' was once a common cause of tuberculosis, but the introduction of pasteurized milk has almost eliminated this as a public health problem in developed countries. ''M. canetti'' is rare and seems to be limited to the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, although a few cases have been seen in African emigrants. ''M. microti'' is also rare and is seen almost only in immunodeficient people, although its prevalence may be significantly underestimated.
Other known pathogenic mycobacteria include ''M. leprae
''Mycobacterium leprae'' (also known as the leprosy bacillus or Hansen's bacillus), is one
of the two species of bacteria that cause Hansen’s disease (leprosy), a chronic but curable infectious disease that damages the peripheral nerves and ...
'', ''M. avium
''Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare'' infection (MAI) is an atypical mycobacterial infection, i.e. one with nontuberculous mycobacteria or NTM, caused by ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex (MAC), which is made of two ''Mycobacterium'' species, ''M. ...
'', and ''M. kansasii
''Mycobacterium kansasii'' is a bacterium in the ''Mycobacterium'' genus. It is an environmental bacteria that causes opportunistic infections in humans, and is the one of the leading mycobacterial causes of human disease after tuberculosis and ...
''. The latter two species are classified as " nontuberculous mycobacteria" (NTM) or atypical mycobacteria. NTM cause neither TB nor leprosy, but they do cause lung diseases that resemble TB.
Transmission
When people with active pulmonary TB cough, sneeze, speak, sing, or spit, they expel infectiousaerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog o ...
droplets 0.5 to 5.0 µm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Unit ...
in diameter. A single sneeze can release up to 40,000 droplets. Each one of these droplets may transmit the disease, since the infectious dose of tuberculosis is very small (the inhalation of fewer than 10 bacteria may cause an infection).
Risk of transmission
People with prolonged, frequent, or close contact with people with TB are at particularly high risk of becoming infected, with an estimated 22% infection rate. A person with active but untreated tuberculosis may infect 10–15 (or more) other people per year. Transmission should occur from only people with active TB – those with latent infection are not thought to be contagious. The probability of transmission from one person to another depends upon several factors, including the number of infectious droplets expelled by the carrier, the effectiveness of ventilation, the duration of exposure, the virulence of the ''M. tuberculosis'' strain, the level of immunity in the uninfected person, and others. The cascade of person-to-person spread can be circumvented by segregating those with active ("overt") TB and putting them on anti-TB drug regimens. After about two weeks of effective treatment, subjects with nonresistant active infections generally do not remain contagious to others. If someone does become infected, it typically takes three to four weeks before the newly infected person becomes infectious enough to transmit the disease to others.Risk factors
A number of factors make individuals more susceptible to TB infection and/or disease.Active disease risk
The most important risk factor globally for developing active TB is concurrent HIV infection; 13% of those with TB are also infected with HIV. This is a particular problem insub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
, where HIV infection rates are high. Of those without HIV infection who are infected with tuberculosis, about 5–10% develop active disease during their lifetimes; in contrast, 30% of those co-infected with HIV develop the active disease.
Use of certain medications, such as corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involve ...
and infliximab (an anti-αTNF monoclonal antibody), is another important risk factor, especially in the developed world.
Other risk factors include: alcoholism, diabetes mellitus (3-fold increased risk), silicosis
Silicosis is a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust. It is marked by inflammation and scarring in the form of nodular lesions in the upper lobes of the lungs. It is a type of pneumoconiosis. Silicos ...
(30-fold increased risk), tobacco smoking (2-fold increased risk), indoor air pollution, malnutrition, young age, recently acquired TB infection, recreational drug use, severe kidney disease, low body weight, organ transplant, head and neck cancer, and genetic susceptibility (the overall importance of genetic risk factors remains undefined).
Infection susceptibility
Tobacco smoking increases the risk of infections (in addition to increasing the risk of active disease and death). Additional factors increasing infection susceptibility include young age.Pathogenesis
 About 90% of those infected with ''M. tuberculosis'' have
About 90% of those infected with ''M. tuberculosis'' have asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asy ...
, latent TB infections (sometimes called LTBI), with only a 10% lifetime chance that the latent infection will progress to overt, active tuberculous disease. In those with HIV, the risk of developing active TB increases to nearly 10% a year. If effective treatment is not given, the death rate for active TB cases is up to 66%.
 TB infection begins when the mycobacteria reach the alveolar air sacs of the lungs, where they invade and replicate within endosomes of alveolar macrophages. Macrophages identify the bacterium as foreign and attempt to eliminate it by phagocytosis. During this process, the bacterium is enveloped by the macrophage and stored temporarily in a membrane-bound vesicle called a phagosome. The phagosome then combines with a lysosome to create a phagolysosome. In the phagolysosome, the cell attempts to use reactive oxygen species and acid to kill the bacterium. However, ''M. tuberculosis'' has a thick, waxy mycolic acid capsule that protects it from these toxic substances. ''M. tuberculosis'' is able to reproduce inside the macrophage and will eventually kill the immune cell.
The primary site of infection in the lungs, known as the Ghon focus, is generally located in either the upper part of the lower lobe, or the lower part of the upper lobe. Tuberculosis of the lungs may also occur via infection from the blood stream. This is known as a Simon focus and is typically found in the top of the lung. This hematogenous transmission can also spread infection to more distant sites, such as peripheral lymph nodes, the kidneys, the brain, and the bones. All parts of the body can be affected by the disease, though for unknown reasons it rarely affects the heart,
TB infection begins when the mycobacteria reach the alveolar air sacs of the lungs, where they invade and replicate within endosomes of alveolar macrophages. Macrophages identify the bacterium as foreign and attempt to eliminate it by phagocytosis. During this process, the bacterium is enveloped by the macrophage and stored temporarily in a membrane-bound vesicle called a phagosome. The phagosome then combines with a lysosome to create a phagolysosome. In the phagolysosome, the cell attempts to use reactive oxygen species and acid to kill the bacterium. However, ''M. tuberculosis'' has a thick, waxy mycolic acid capsule that protects it from these toxic substances. ''M. tuberculosis'' is able to reproduce inside the macrophage and will eventually kill the immune cell.
The primary site of infection in the lungs, known as the Ghon focus, is generally located in either the upper part of the lower lobe, or the lower part of the upper lobe. Tuberculosis of the lungs may also occur via infection from the blood stream. This is known as a Simon focus and is typically found in the top of the lung. This hematogenous transmission can also spread infection to more distant sites, such as peripheral lymph nodes, the kidneys, the brain, and the bones. All parts of the body can be affected by the disease, though for unknown reasons it rarely affects the heart, skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
s, pancreas, or thyroid.
Tuberculosis is classified as one of the granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious ...
tous inflammatory diseases. Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s, epithelioid cells, T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, and fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound ...
s aggregate to form granulomas, with lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adap ...
surrounding the infected macrophages. When other macrophages attack the infected macrophage, they fuse together to form a giant multinucleated cell in the alveolar lumen. The granuloma may prevent dissemination of the mycobacteria and provide a local environment for interaction of cells of the immune system. However, more recent evidence suggests that the bacteria use the granulomas to avoid destruction by the host's immune system. Macrophages and dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. ...
s in the granulomas are unable to present antigen to lymphocytes; thus the immune response is suppressed. Bacteria inside the granuloma can become dormant, resulting in latent infection. Another feature of the granulomas is the development of abnormal cell death (necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated dige ...
) in the center of tubercles. To the naked eye, this has the texture of soft, white cheese and is termed caseous necrosis.
If TB bacteria gain entry to the blood stream from an area of damaged tissue, they can spread throughout the body and set up many foci of infection, all appearing as tiny, white tubercles in the tissues. This severe form of TB disease, most common in young children and those with HIV, is called miliary tuberculosis. People with this disseminated TB have a high fatality rate even with treatment (about 30%).
In many people, the infection waxes and wanes. Tissue destruction and necrosis are often balanced by healing and fibrosis. Affected tissue is replaced by scarring and cavities filled with caseous necrotic material. During active disease, some of these cavities are joined to the air passages ( bronchi) and this material can be coughed up. It contains living bacteria and thus can spread the infection. Treatment with appropriate antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s kills bacteria and allows healing to take place. Upon cure, affected areas are eventually replaced by scar tissue.
Diagnosis

Active tuberculosis
Diagnosing active tuberculosis based only on signs and symptoms is difficult, as is diagnosing the disease in those who have a weakened immune system. A diagnosis of TB should, however, be considered in those with signs of lung disease or constitutional symptoms lasting longer than two weeks. Achest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
and multiple sputum cultures for acid-fast bacilli are typically part of the initial evaluation. Interferon-γ release assays (IGRA) and tuberculin skin tests are of little use in most of the developing world. IGRA have similar limitations in those with HIV.
A definitive diagnosis of TB is made by identifying ''M. tuberculosis'' in a clinical sample (e.g., sputum, pus, or a tissue biopsy). However, the difficult culture process for this slow-growing organism can take two to six weeks for blood or sputum culture. Thus, treatment is often begun before cultures are confirmed.
Nucleic acid amplification tests and adenosine deaminase testing may allow rapid diagnosis of TB. Blood tests to detect antibodies are not specific or sensitive, so they are not recommended.
Latent tuberculosis
 The Mantoux tuberculin skin test is often used to screen people at high risk for TB. Those who have been previously immunized with the Bacille Calmette-Guerin vaccine may have a false-positive test result. The test may be falsely negative in those with sarcoidosis, Hodgkin's lymphoma, malnutrition, and most notably, active tuberculosis. Interferon gamma release assays, on a blood sample, are recommended in those who are positive to the Mantoux test. These are not affected by immunization or most environmental mycobacteria, so they generate fewer false-positive results. However, they are affected by ''M. szulgai'', ''M. marinum'', and ''M. kansasii''. IGRAs may increase sensitivity when used in addition to the skin test, but may be less sensitive than the skin test when used alone.
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has recommended screening people who are at high risk for latent tuberculosis with either tuberculin skin tests or interferon-gamma release assays. While some have recommend testing health care workers, evidence of benefit for this is poor . The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) stopped recommending yearly testing of health care workers without known exposure in 2019.
The Mantoux tuberculin skin test is often used to screen people at high risk for TB. Those who have been previously immunized with the Bacille Calmette-Guerin vaccine may have a false-positive test result. The test may be falsely negative in those with sarcoidosis, Hodgkin's lymphoma, malnutrition, and most notably, active tuberculosis. Interferon gamma release assays, on a blood sample, are recommended in those who are positive to the Mantoux test. These are not affected by immunization or most environmental mycobacteria, so they generate fewer false-positive results. However, they are affected by ''M. szulgai'', ''M. marinum'', and ''M. kansasii''. IGRAs may increase sensitivity when used in addition to the skin test, but may be less sensitive than the skin test when used alone.
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has recommended screening people who are at high risk for latent tuberculosis with either tuberculin skin tests or interferon-gamma release assays. While some have recommend testing health care workers, evidence of benefit for this is poor . The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) stopped recommending yearly testing of health care workers without known exposure in 2019.
Prevention
 Tuberculosis prevention and control efforts rely primarily on the vaccination of infants and the detection and appropriate treatment of active cases. The World Health Organization (WHO) has achieved some success with improved treatment regimens, and a small decrease in case numbers. Some countries have legislation to involuntarily detain or examine those suspected to have tuberculosis, or involuntarily treat them if infected.
Tuberculosis prevention and control efforts rely primarily on the vaccination of infants and the detection and appropriate treatment of active cases. The World Health Organization (WHO) has achieved some success with improved treatment regimens, and a small decrease in case numbers. Some countries have legislation to involuntarily detain or examine those suspected to have tuberculosis, or involuntarily treat them if infected.
Vaccines
The only available vaccine is bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG). In children it decreases the risk of getting the infection by 20% and the risk of infection turning into active disease by nearly 60%. It is the most widely used vaccine worldwide, with more than 90% of all children being vaccinated. The immunity it induces decreases after about ten years. As tuberculosis is uncommon in most of Canada, Western Europe, and the United States, BCG is administered to only those people at high risk. Part of the reasoning against the use of the vaccine is that it makes the tuberculin skin test falsely positive, reducing the test's usefulness as a screening tool. Several vaccines are being developed. Intradermal MVA85A vaccine in addition to BCG injection is not effective in preventing tuberculosis.Public health
Public health campaigns which have focused on overcrowding, public spitting and regular sanitation (including hand washing) during the 1800s helped to either interrupt or slow spread which when combined with contact tracing, isolation and treatment helped to dramatically curb the transmission of both tuberculosis and other airborne diseases which led to the elimination of tuberculosis as a major public health issue in most developed economies. Other risk factors which worsened TB spread such as malnutrition were also ameliorated, but since the emergence of HIV a new population of immunocompromised individuals was available for TB to infect. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared TB a "global health emergency" in 1993, and in 2006, the Stop TB Partnership developed a Global Plan to Stop Tuberculosis that aimed to save 14 million lives between its launch and 2015. A number of targets they set were not achieved by 2015, mostly due to the increase in HIV-associated tuberculosis and the emergence of multiple drug-resistant tuberculosis. A tuberculosis classification system developed by the American Thoracic Society is used primarily in public health programs. In 2015, it launched the End TB Strategy to reduce deaths by 95% and incidence by 90% before 2035. The goal of tuberculosis elimination is hampered by the lack of rapid testing, of short and effective treatment courses, and of completely effective vaccines. The benefits and risks of giving anti-tubercular drugs in those exposed to MDR-TB is unclear. Making HAART therapy available to HIV-positive individuals significantly reduces the risk of progression to an active TB infection by up to 90% and can mitigate the spread through this population.Treatment
 Treatment of TB uses antibiotics to kill the bacteria. Effective TB treatment is difficult, due to the unusual structure and chemical composition of the mycobacterial
Treatment of TB uses antibiotics to kill the bacteria. Effective TB treatment is difficult, due to the unusual structure and chemical composition of the mycobacterial cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech ...
, which hinders the entry of drugs and makes many antibiotics ineffective.
Active TB is best treated with combinations of several antibiotics to reduce the risk of the bacteria developing antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
. The routine use of rifabutin instead of rifampicin
Rifampicin, also known as rifampin, is an ansamycin antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis (TB), mycobacterium avium complex, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, leprosy, and Legionnaires’ disease. ...
in HIV-positive people with tuberculosis is of unclear benefit .
Latent TB
Latent TB is treated with either isoniazid or rifampin alone, or a combination of isoniazid with either rifampicin or rifapentine. The treatment takes three to nine months depending on the medications used. People with latent infections are treated to prevent them from progressing to active TB disease later in life. Education or counselling may improve the latent tuberculosis treatment completion rates.New onset
The recommended treatment of new-onset pulmonary tuberculosis, , is six months of a combination of antibiotics containing rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol for the first two months, and only rifampicin and isoniazid for the last four months. Where resistance to isoniazid is high, ethambutol may be added for the last four months as an alternative. Treatment with anti-TB drugs for at least 6 months results in higher success rates when compared with treatment less than 6 months, even though the difference is small. Shorter treatment regimen may be recommended for those with compliance issues. There is also no evidence to support shorter anti-tuberculosis treatment regimens when compared to a 6-month treatment regimen. However recently, results from an international, randomized, controlled clinical trial indicate that a four-month daily treatment regimen containing high-dose, or "optimized," rifapentine with moxifloxacin (2PHZM/2PHM) is as safe and effective as the existing standard six-month daily regimen at curing drug-susceptible tuberculosis (TB) disease.Recurrent disease
If tuberculosis recurs, testing to determine which antibiotics it is sensitive to is important before determining treatment. If multiple drug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) is detected, treatment with at least four effective antibiotics for 18 to 24 months is recommended.Medication administration
Directly observed therapy, i.e., having a health care provider watch the person take their medications, is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) in an effort to reduce the number of people not appropriately taking antibiotics. The evidence to support this practice over people simply taking their medications independently is of poor quality. There is no strong evidence indicating that directly observed therapy improves the number of people who were cured or the number of people who complete their medicine. Moderate quality evidence suggests that there is also no difference if people are observed at home versus at a clinic, or by a family member versus a health care worker. Methods to remind people of the importance of treatment and appointments may result in a small but important improvement. There is also not enough evidence to support intermittent rifampicin-containing therapy given two to three times a week has equal effectiveness as daily dose regimen on improving cure rates and reducing relapsing rates. There is also not enough evidence on effectiveness of giving intermittent twice or thrice weekly short course regimen compared to daily dosing regimen in treating children with tuberculosis.Medication resistance
Primary resistance occurs when a person becomes infected with a resistant strain of TB. A person with fully susceptible MTB may develop secondary (acquired) resistance during therapy because of inadequate treatment, not taking the prescribed regimen appropriately (lack of compliance), or using low-quality medication. Drug-resistant TB is a serious public health issue in many developing countries, as its treatment is longer and requires more expensive drugs. MDR-TB is defined as resistance to the two most effective first-line TB drugs: rifampicin and isoniazid. Extensively drug-resistant TB is also resistant to three or more of the six classes of second-line drugs. Totally drug-resistant TB is resistant to all currently used drugs. It was first observed in 2003 in Italy, but not widely reported until 2012, and has also been found in Iran and India. There is some efficacy for linezolid to treat those with XDR-TB but side effects and discontinuation of medications were common. Bedaquiline is tentatively supported for use in multiple drug-resistant TB. XDR-TB is a term sometimes used to define ''extensively resistant'' TB, and constitutes one in ten cases of MDR-TB. Cases of XDR TB have been identified in more than 90% of countries. For those with known rifampicin or MDR-TB, molecular tests such as the Genotype® MTBDRsl Assay (performed on culture isolates or smear positive specimens) may be useful to detect second-line anti-tubercular drug resistance.Prognosis
latent infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
occurs with no obvious symptoms. These dormant bacilli produce active tuberculosis in 5–10% of these latent cases, often many years after infection.
The risk of reactivation increases with immunosuppression, such as that caused by infection with HIV. In people coinfected with ''M. tuberculosis'' and HIV, the risk of reactivation increases to 10% per year. Studies using DNA fingerprinting of ''M. tuberculosis'' strains have shown reinfection contributes more substantially to recurrent TB than previously thought, with estimates that it might account for more than 50% of reactivated cases in areas where TB is common. The chance of death from a case of tuberculosis is about 4% , down from 8% in 1995.
In people with smear-positive pulmonary TB (without HIV co-infection), after 5 years without treatment, 50-60% die while 20-25% achieve spontaneous resolution (cure). TB is almost always fatal in those with untreated HIV co-infection and death rates are increased even with antiretroviral treatment of HIV.
Epidemiology
Roughly one-quarter of the world's population has been infected with ''M. tuberculosis'', with new infections occurring in about 1% of the population each year. However, most infections with ''M. tuberculosis'' do not cause disease, and 90–95% of infections remain asymptomatic. In 2012, an estimated 8.6 million chronic cases were active. In 2010, 8.8 million new cases of tuberculosis were diagnosed, and 1.20–1.45 million deaths occurred (most of these occurring in developing countries). Of these, about 0.35 million occur in those also infected with HIV. In 2018, tuberculosis was the leading cause of death worldwide from a single infectious agent. The total number of tuberculosis cases has been decreasing since 2005, while new cases have decreased since 2002. Tuberculosis incidence is seasonal, with peaks occurring every spring and summer. The reasons for this are unclear, but may be related to vitamin D deficiency during the winter. There are also studies linking tuberculosis to different weather conditions like low temperature, low humidity and low rainfall. It has been suggested that tuberculosis incidence rates may be connected to climate change.At-risk groups
Tuberculosis is closely linked to both overcrowding and malnutrition, making it one of the principal diseases of poverty. Those at high risk thus include: people who inject illicit drugs, inhabitants and employees of locales where vulnerable people gather (e.g., prisons and homeless shelters), medically underprivileged and resource-poor communities, high-risk ethnic minorities, children in close contact with high-risk category patients, and health-care providers serving these patients. The rate of tuberculosis varies with age. In Africa, it primarily affects adolescents and young adults. However, in countries where incidence rates have declined dramatically (such as the United States), tuberculosis is mainly a disease of the elderly and immunocompromised (risk factors are listed above). Worldwide, 22 "high-burden" states or countries together experience 80% of cases as well as 83% of deaths. In Canada and Australia, tuberculosis is many times more common among the aboriginal peoples, especially in remote areas. Factors contributing to this include higher prevalence of predisposing health conditions and behaviours, and overcrowding and poverty. In some Canadian aboriginal groups, genetic susceptibility may play a role. Socioeconomic status (SES) strongly affects TB risk. People of low SES are both more likely to contract TB and to be more severely affected by the disease. Those with low SES are more likely to be affected by risk factors for developing TB (e.g. malnutrition, indoor air pollution, HIV co-infection, etc.), and are additionally more likely to be exposed to crowded and poorly ventilated spaces. Inadequate healthcare also means that people with active disease who facilitate spread are not diagnosed and treated promptly; sick people thus remain in the infectious state and (continue to) spread the infection.Geographical epidemiology
The distribution of tuberculosis is not uniform across the globe; about 80% of the population in many African, Caribbean, South Asian, and eastern European countries test positive in tuberculin tests, while only 5–10% of the U.S. population test positive. Hopes of totally controlling the disease have been dramatically dampened because of many factors, including the difficulty of developing an effective vaccine, the expensive and time-consuming diagnostic process, the necessity of many months of treatment, the increase in HIV-associated tuberculosis, and the emergence of drug-resistant cases in the 1980s. In developed countries, tuberculosis is less common and is found mainly in urban areas. In Europe, deaths from TB fell from 500 out of 100,000 in 1850 to 50 out of 100,000 by 1950. Improvements in public health were reducing tuberculosis even before the arrival of antibiotics, although the disease remained a significant threat to public health, such that when the Medical Research Council was formed in Britain in 1913 its initial focus was tuberculosis research. In 2010, rates per 100,000 people in different areas of the world were: globally 178, Africa 332, the Americas 36, Eastern Mediterranean 173, Europe 63, Southeast Asia 278, and Western Pacific 139.Russia
Russia has achieved particularly dramatic progress with a decline in its TB mortality rate—from 61.9 per 100,000 in 1965 to 2.7 per 100,000 in 1993;Global Tuberculosis Control, World Health Organization, 2011. however, mortality rate increased to 24 per 100,000 in 2005 and then recoiled to 11 per 100,000 by 2015.
China
China has achieved particularly dramatic progress, with about an 80% reduction in its TB mortality rate between 1990 and 2010. The number of new cases has declined by 17% between 2004 and 2014.Africa
In 2007, the country with the highest estimated incidence rate of TB wasEswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
, with 1,200 cases per 100,000 people. In 2017, the country with the highest estimated incidence rate
In epidemiology, incidence is a measure of the probability of occurrence of a given medical condition in a population within a specified period of time. Although sometimes loosely expressed simply as the number of new cases during some time p ...
as a % of the population was Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked country, landlocked as an Enclave and exclave, enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the Thabana Ntlenyana, highest mountains in Sou ...
, with 665 cases per 100,000 people.
India
As of 2017, India had the largest total incidence, with an estimated 2,740,000 cases. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2000–2015, India's estimated mortality rate dropped from 55 to 36 per 100,000 population per year with estimated 480 thousand people died of TB in 2015. In India a major proportion of tuberculosis patients are being treated by private partners and private hospitals. Evidence indicates that the tuberculosis national survey does not represent the number of cases that are diagnosed and recorded by private clinics and hospitals in India.North America
In the United States Native Americans have a fivefold greater mortality from TB, and racial and ethnic minorities accounted for 84% of all reported TB cases. In the United States, the overall tuberculosis case rate was 3 per 100,000 persons in 2017. In Canada, tuberculosis is still endemic in some rural areas.Western Europe
In 2017, in the United Kingdom, the national average was 9 per 100,000 and the highest incidence rates in Western Europe were 20 per 100,000 in Portugal.History
 Tuberculosis has existed since
Tuberculosis has existed since antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
. The oldest unambiguously detected ''M. tuberculosis'' gives evidence of the disease in the remains of bison in Wyoming dated to around 17,000 years ago. However, whether tuberculosis originated in bovines, then transferred to humans, or whether both bovine and human tuberculosis diverged from a common ancestor, remains unclear. A comparison of the genes of ''M. tuberculosis'' complex (MTBC) in humans to MTBC in animals suggests humans did not acquire MTBC from animals during animal domestication, as researchers previously believed. Both strains of the tuberculosis bacteria share a common ancestor, which could have infected humans even before the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
. Skeletal remains show some prehistoric humans (4000 BC) had TB, and researchers have found tubercular decay in the spines of Egyptian mummies dating from 3000 to 2400 BC. Genetic studies suggest the presence of TB in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
from about AD 100.
Before the Industrial Revolution, folklore often associated tuberculosis with vampires. When one member of a family died from the disease, the other infected members would lose their health slowly. People believed this was caused by the original person with TB draining the life from the other family members.
Although Richard Morton established the pulmonary form associated with tubercles as a pathology in 1689, due to the variety of its symptoms, TB was not identified as a single disease until the 1820s. Benjamin Marten conjectured in 1720 that consumptions were caused by microbes which were spread by people living close to each other. In 1819, René Laennec claimed that tubercles were the cause of pulmonary tuberculosis. J. L. Schönlein first published the name "tuberculosis" (German: ''Tuberkulose'') in 1832. Between 1838 and 1845, John Croghan, the owner of Mammoth Cave in Kentucky from 1839 onwards, brought a number of people with tuberculosis into the cave in the hope of curing the disease with the constant temperature and purity of the cave air; each died within a year. Hermann Brehmer opened the first TB sanatorium in 1859 in Görbersdorf (now Sokołowsko) in Silesia. In 1865, Jean Antoine Villemin demonstrated that tuberculosis could be transmitted, via inoculation, from humans to animals and among animals. (Villemin's findings were confirmed in 1867 and 1868 by John Burdon-Sanderson.)

Robert Koch
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch ( , ; 11 December 1843 – 27 May 1910) was a German physician and microbiologist. As the discoverer of the specific causative agents of deadly infectious diseases including tuberculosis, cholera (though the Vibrio ...
identified and described the bacillus causing tuberculosis, ''M. tuberculosis'', on 24 March 1882. In 1905, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for this discovery. Koch did not believe the cattle and human tuberculosis diseases were similar, which delayed the recognition of infected milk as a source of infection. During the first half of the 1900s, the risk of transmission from this source was dramatically reduced after the application of the pasteurization
Pasteurization or pasteurisation is a process of food preservation in which packaged and non-packaged foods (such as milk and fruit juices) are treated with mild heat, usually to less than , to eliminate pathogens and extend shelf life.
The ...
process. Koch announced a glycerine extract of the tubercle bacilli as a "remedy" for tuberculosis in 1890, calling it "tuberculin". Although it was not effective, it was later successfully adapted as a screening test for the presence of pre-symptomatic tuberculosis. World Tuberculosis Day is marked on 24 March each year, the anniversary of Koch's original scientific announcement.
Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin achieved the first genuine success in immunization against tuberculosis in 1906, using attenuated bovine-strain tuberculosis. It was called bacille Calmette–Guérin (BCG). The BCG vaccine was first used on humans in 1921 in France, but achieved widespread acceptance in the US, Great Britain, and Germany only after World War II.
Tuberculosis caused widespread public concern in the 19th and early 20th centuries as the disease became common among the urban poor. In 1815, one in four deaths in England was due to "consumption". By 1918, TB still caused one in six deaths in France. After TB was determined to be contagious, in the 1880s, it was put on a notifiable-disease list in Britain; campaigns started to stop people from spitting in public places, and the infected poor were "encouraged" to enter sanatoria that resembled prisons (the sanatoria for the middle and upper classes offered excellent care and constant medical attention). Whatever the benefits of the "fresh air" and labor in the sanatoria, even under the best conditions, 50% of those who entered died within five years ( 1916). When the Medical Research Council formed in Britain in 1913, it initially focused on tuberculosis research.
In Europe, rates of tuberculosis began to rise in the early 1600s to a peak level in the 1800s, when it caused nearly 25% of all deaths. In the 18th and 19th century, tuberculosis had become epidemic in Europe, showing a seasonal pattern. By the 1950s mortality in Europe had decreased about 90%. Improvements in sanitation, vaccination, and other public-health measures began significantly reducing rates of tuberculosis even before the arrival of streptomycin and other antibiotics, although the disease remained a significant threat. In 1946, the development of the antibiotic streptomycin made effective treatment and cure of TB a reality. Prior to the introduction of this medication, the only treatment was surgical intervention, including the " pneumothorax technique", which involved collapsing an infected lung to "rest" it and to allow tuberculous lesions to heal.
In India, tuberculosis prevalence was first investigated by Dr. Arthur Colborne Lankester, an English medical missionary and physician. He was selected by the government to undertake the study for one year and collaborate with all the provincial governments of India to expand the reach of the research. He eventually published a book titled ''Tuberculosis in India.''
'
Because of the emergence of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), surgery has been re-introduced for certain cases of TB infections. It involves the removal of infected chest cavities ("bullae") in the lungs to reduce the number of bacteria and to increase exposure of the remaining bacteria to antibiotics in the bloodstream. Hopes of eliminating TB ended with the rise of drug-resistant
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, ...
strains in the 1980s. The subsequent resurgence of tuberculosis resulted in the declaration of a global health emergency by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1993.
Society and culture
Names
Tuberculosis has been known by many names from the technical to the familiar. () is a Greek word for consumption, an old term for pulmonary tuberculosis; around 460 BCE, Hippocrates described phthisis as a disease of dry seasons. The abbreviation ''TB'' is short for ''tubercle bacillus''. ''Consumption'' was the most common nineteenth century English word for the disease. The Latin root meaning 'completely' is linked to meaning 'to take up from under'. In '' The Life and Death of Mr Badman'' by John Bunyan, the author calls consumption "the captain of all these men of death." "Great white plague" has also been used.Art and literature
 Tuberculosis was for centuries associated with poetic and artistic qualities among those infected, and was also known as "the romantic disease". Major artistic figures such as the poets
Tuberculosis was for centuries associated with poetic and artistic qualities among those infected, and was also known as "the romantic disease". Major artistic figures such as the poets John Keats
John Keats (31 October 1795 – 23 February 1821) was an English poet of the second generation of Romantic poets, with Lord Byron and Percy Bysshe Shelley. His poems had been in publication for less than four years when he died of tuberculo ...
, Percy Bysshe Shelley
Percy Bysshe Shelley ( ; 4 August 17928 July 1822) was one of the major English Romantic poets. A radical in his poetry as well as in his political and social views, Shelley did not achieve fame during his lifetime, but recognition of his achie ...
, and Edgar Allan Poe, the composer Frédéric Chopin
Frédéric François Chopin (born Fryderyk Franciszek Chopin; 1 March 181017 October 1849) was a Polish composer and virtuoso pianist of the Romantic period, who wrote primarily for solo piano. He has maintained worldwide renown as a leadin ...
, the playwright Anton Chekhov
Anton Pavlovich Chekhov (; 29 January 1860 Old Style date 17 January. – 15 July 1904 Old Style date 2 July.) was a Russian playwright and short-story writer who is considered to be one of the greatest writers of all time. His career ...
, the novelists Franz Kafka, Katherine Mansfield, Charlotte Brontë, Fyodor Dostoevsky
Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky (, ; rus, Фёдор Михайлович Достоевский, Fyódor Mikháylovich Dostoyévskiy, p=ˈfʲɵdər mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪdʑ dəstɐˈjefskʲɪj, a=ru-Dostoevsky.ogg, links=yes; 11 November 18219 ...
, Thomas Mann, W. Somerset Maugham, George Orwell
Eric Arthur Blair (25 June 1903 – 21 January 1950), better known by his pen name George Orwell, was an English novelist, essayist, journalist, and critic. His work is characterised by lucid prose, social criticism, opposition to totalitar ...
, and Robert Louis Stevenson, and the artists Alice Neel
Alice Neel (January 28, 1900 – October 13, 1984) was an American visual artist, who was known for her portraits depicting friends, family, lovers, poets, artists, and strangers. Her paintings have an expressionistic use of line and color, psyc ...
, Jean-Antoine Watteau
Jean-Antoine Watteau (, , ; baptised October 10, 1684died July 18, 1721) Alsavailablevia Oxford Art Online (subscription needed). was a French painter and draughtsman whose brief career spurred the revival of interest in colour and movement, as ...
, Elizabeth Siddal, Marie Bashkirtseff, Edvard Munch
Edvard Munch ( , ; 12 December 1863 – 23 January 1944) was a Norwegian painter. His best known work, ''The Scream'' (1893), has become one of Western art's most iconic images.
His childhood was overshadowed by illness, bereavement and the dr ...
, Aubrey Beardsley and Amedeo Modigliani
Amedeo Clemente Modigliani (, ; 12 July 1884 – 24 January 1920) was an Italian painter and sculptor who worked mainly in France. He is known for portraits and nudes in a modern style characterized by a surreal elongation of faces, necks, and ...
either had the disease or were surrounded by people who did. A widespread belief was that tuberculosis assisted artistic talent. Physical mechanisms proposed for this effect included the slight fever and toxaemia that it caused, allegedly helping them to see life more clearly and to act decisively.
Tuberculosis formed an often-reused theme in literature, as in Thomas Mann's '' The Magic Mountain'', set in a sanatorium; in music, as in Van Morrison's song " T.B. Sheets"; in opera, as in Puccini's '' La bohème'' and Verdi's ''La Traviata
''La traviata'' (; ''The Fallen Woman'') is an opera in three acts by Giuseppe Verdi set to an Italian libretto by Francesco Maria Piave. It is based on ''La Dame aux camélias'' (1852), a play by Alexandre Dumas ''fils'' adapted from his own 18 ...
''; in art, as in Monet's painting of his first wife Camille on her deathbed; and in film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere ...
, such as the 1945 '' The Bells of St. Mary's'' starring Ingrid Bergman
Ingrid Bergman (29 August 191529 August 1982) was a Swedish actress who starred in a variety of European and American films, television movies, and plays.Obituary ''Variety'', 1 September 1982. With a career spanning five decades, she is often ...
as a nun with tuberculosis.
Public health efforts
In 2014, the WHO adopted the "End TB" strategy which aims to reduce TB incidence by 80% and TB deaths by 90% by 2030. The strategy contains a milestone to reduce TB incidence by 20% and TB deaths by 35% by 2020. However, by 2020 only a 9% reduction in incidence per population was achieved globally, with the European region achieving 19% and the African region achieving 16% reductions. Similarly, the number of deaths only fell by 14%, missing the 2020 milestone of a 35% reduction, with some regions making better progress (31% reduction in Europe and 19% in Africa). Correspondingly, also treatment, prevention and funding milestones were missed in 2020, for example only 6.3 million people were started on TB prevention short of the target of 30 million. The World Health Organization (WHO), the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, and the U.S. government are subsidizing a fast-acting diagnostic tuberculosis test for use in low- and middle-income countries as of 2012. In addition to being fast-acting, the test can determine if there is resistance to the antibiotic rifampicin which may indicate multi-drug resistant tuberculosis and is accurate in those who are also infected with HIV. Many resource-poor places have access to only sputum microscopy. India had the highest total number of TB cases worldwide in 2010, in part due to poor disease management within the private and public health care sector. Programs such as the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program are working to reduce TB levels among people receiving public health care. A 2014 EIU-healthcare report finds there is a need to address apathy and urges for increased funding. The report cites among others Lucica Ditui " Bis like an orphan. It has been neglected even in countries with a high burden and often forgotten by donors and those investing in health interventions." Slow progress has led to frustration, expressed by the executive director of the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria – Mark Dybul: "we have the tools to end TB as a pandemic and public health threat on the planet, but we are not doing it." Several international organizations are pushing for more transparency in treatment, and more countries are implementing mandatory reporting of cases to the government as of 2014, although adherence is often variable. Commercial treatment providers may at times overprescribe second-line drugs as well as supplementary treatment, promoting demands for further regulations. The government of Brazil provides universal TB care, which reduces this problem. Conversely, falling rates of TB infection may not relate to the number of programs directed at reducing infection rates but may be tied to an increased level of education, income, and health of the population. Costs of the disease, as calculated by the World Bank in 2009 may exceed US$150 billion per year in "high burden" countries. Lack of progress eradicating the disease may also be due to lack of patient follow-up – as among the 250 million rural migrants in China. There is insufficient data to show that active contact tracing helps to improve case detection rates for tuberculosis. Interventions such as house-to-house visits, educational leaflets, mass media strategies, educational sessions may increase tuberculosis detection rates in short-term. There is no study that compares new methods of contact tracing such as social network analysis with existing contact tracing methods.Stigma
Slow progress in preventing the disease may in part be due to stigma associated with TB. Stigma may be due to the fear of transmission from affected individuals. This stigma may additionally arise due to links between TB and poverty, and in Africa, AIDS. Such stigmatization may be both real and perceived; for example, in Ghana, individuals with TB are banned from attending public gatherings. Stigma towards TB may result in delays in seeking treatment, lower treatment compliance, and family members keeping cause of death secret – allowing the disease to spread further. In contrast, in Russia stigma was associated with increased treatment compliance. TB stigma also affects socially marginalized individuals to a greater degree and varies between regions. One way to decrease stigma may be through the promotion of "TB clubs", where those infected may share experiences and offer support, or through counseling. Some studies have shown TB education programs to be effective in decreasing stigma, and may thus be effective in increasing treatment adherence. Despite this, studies on the relationship between reduced stigma and mortality are lacking , and similar efforts to decrease stigma surrounding AIDS have been minimally effective. Some have claimed the stigma to be worse than the disease, and healthcare providers may unintentionally reinforce stigma, as those with TB are often perceived as difficult or otherwise undesirable. A greater understanding of the social and cultural dimensions of tuberculosis may also help with stigma reduction.Research
The BCG vaccine has limitations, and research to develop new TB vaccines is ongoing. A number of potential candidates are currently in phase I and II clinical trials. Two main approaches are used to attempt to improve the efficacy of available vaccines. One approach involves adding a subunit vaccine to BCG, while the other strategy is attempting to create new and better live vaccines. MVA85A, an example of a subunit vaccine, is in trials in South Africa as of 2006, is based on a genetically modified vaccinia virus. Vaccines are hoped to play a significant role in treatment of both latent and active disease. To encourage further discovery, researchers and policymakers are promoting new economic models of vaccine development as of 2006, including prizes, tax incentives, and advance market commitments. A number of groups, including theStop TB Partnership The Stop TB Partnership was established in 2001 to eliminate tuberculosis as a public health problem. Its 1500 partner organizations include international, nongovernmental and governmental organizations and patient groups. The secretariat is based ...
, the South African Tuberculosis Vaccine Initiative, and the Aeras Global TB Vaccine Foundation, are involved with research. Among these, the Aeras Global TB Vaccine Foundation received a gift of more than $280 million (US) from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation to develop and license an improved vaccine against tuberculosis for use in high burden countries.
A number of medications are being studied as of 2012 for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, including bedaquiline and delamanid. Bedaquiline received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in late 2012. The safety and effectiveness of these new agents are uncertain as of 2012, because they are based on the results of relatively small studies. However, existing data suggest that patients taking bedaquiline in addition to standard TB therapy are five times more likely to die than those without the new drug, which has resulted in medical journal articles raising health policy questions about why the FDA approved the drug and whether financial ties to the company making bedaquiline influenced physicians' support for its use.
Steroids add-on therapy has not shown any benefits for active pulmonary tuberculosis infection.
Other animals
Mycobacteria infect many different animals, including birds, fish, rodents, and reptiles. The subspecies ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', though, is rarely present in wild animals. An effort to eradicate bovine tuberculosis caused by '' Mycobacterium bovis'' from the cattle and deer herds of New Zealand has been relatively successful. Efforts in Great Britain have been less successful. , tuberculosis appears to be widespread among captive elephants in the US. It is believed that the animals originally acquired the disease from humans, a process called reverse zoonosis. Because the disease can spread through the air to infect both humans and other animals, it is a public health concern affecting circuses and zoos.References
External links
* * *WHO global 2016 TB report (infographic)
WHO tuberculosis country profiles
"Tuberculosis Among African Americans"
1990-11-01, '' In Black America''; KUT Radio, American Archive of Public Broadcasting (
WGBH WGBH may refer to:
* WGBH Educational Foundation, based in Boston, Massachusetts, United States
** WGBH (FM), a public radio station at Boston, Massachusetts on 89.7 MHz owned by the WGBH Educational Foundation
** WGBH-TV
WGBH-TV (channel 2), ...
and the Library of Congress)
Working Group on New TB drugs
tracking clinical trials and drug candidates {{Authority control Airborne diseases Articles containing video clips Health in Africa Healthcare-associated infections Infectious causes of cancer Mycobacterium-related cutaneous conditions Vaccine-preventable diseases Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full)