|
Interferon-gamma Release Assay
Interferon-γ release assays (IGRA) are medical tests used in the diagnosis of some infectious diseases, especially tuberculosis. Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) release assays rely on the fact that T-lymphocytes will release IFN-γ when exposed to specific antigens. These tests are mostly developed for the field of tuberculosis diagnosis, but in theory, may be used in the diagnosis of other diseases which rely on cell-mediated immunity, e.g. cytomegalovirus and leishmaniasis. For example, in patients with cutaneous adverse drug reactions, challenge of peripheral blood lymphocytes with the drug causing the reaction produced a positive test result for half of the drugs tested. There are currently two IFN-γ release assays available for the diagnosis of tuberculosis: * QuantiFERON-TB Gold (licensed in US, Europe and Japan); and * T-SPOT.TB, a form of ELISpot, the variant of ELISA (licensed in Europe, US, Japan and China). The former test quantitates the amount of IFN-γ produced in response ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active TB is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly a protein) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries. In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample to be tested are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme and then any unbound antibodies are removed. In the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's substrate is added. If there was binding, the subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change. Performing an ELISA involves at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
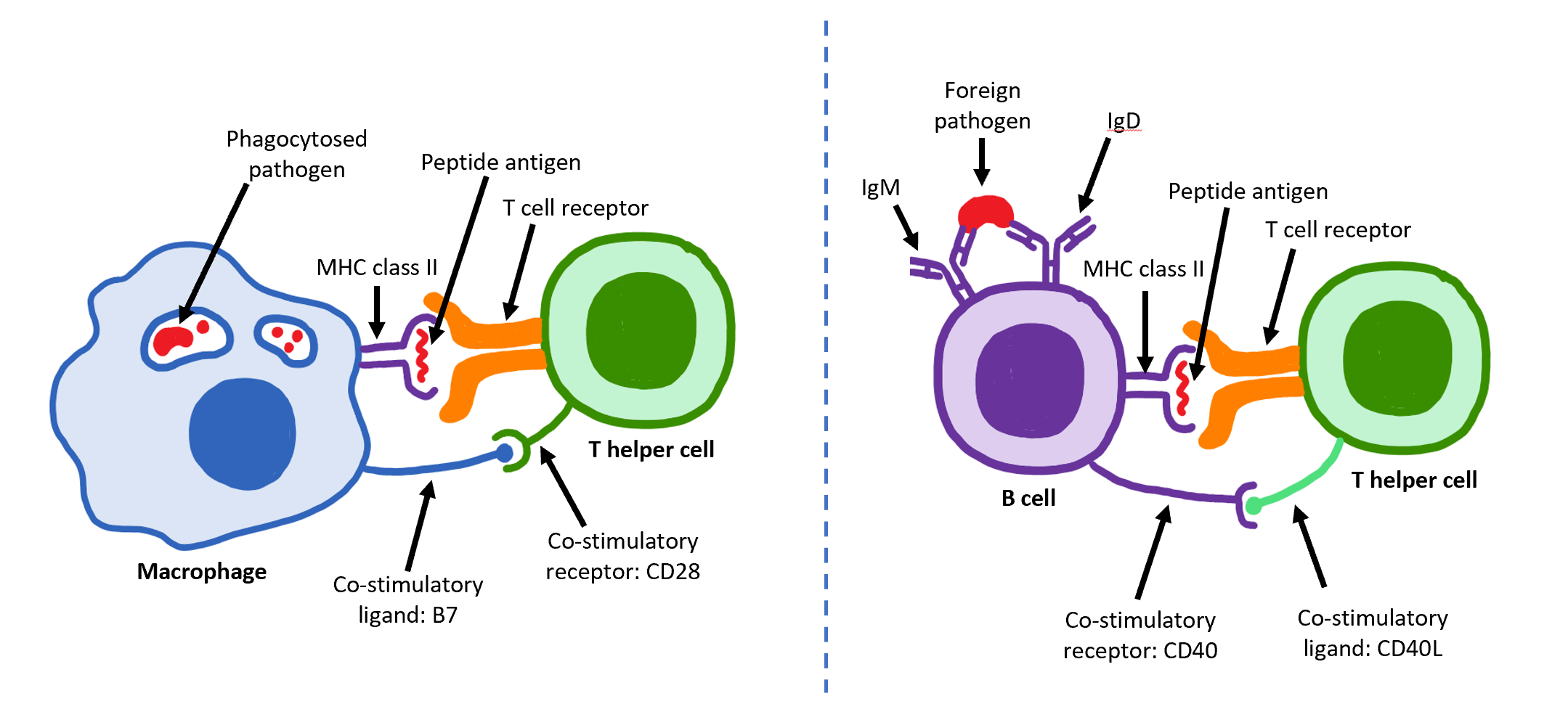
Effector T Cells
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell antibody class switching, breaking cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polarize the immune response depending on the nature of the immunological insult ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacteria
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis ('' M. tuberculosis'') and leprosy ('' M. leprae'') in humans. The Greek prefix ''myco-'' means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with Gram-positive and Gram-negative features, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types. Metabolism and Morphology Mycobacteria are aerobic with 0.2-0.6 µm wide and 1.0-10 µm long rod shapes. They are generally non-motile, except for the species ''Mycobacterium marinum'', which has been shown to be motile within macrophages. Mycobacteria possess capsules and most do not form endospores. ''M. marinum'' and perhaps ''M. bovis'' have been shown to sporulate; however, this has been contested by further research. The disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacille Calmette-Guérin
Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccine is a vaccine primarily used against tuberculosis (TB). It is named after its inventors Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin. In countries where tuberculosis or leprosy is common, one dose is recommended in healthy babies as soon after birth as possible. In areas where tuberculosis is not common, only children at high risk are typically immunized, while suspected cases of tuberculosis are individually tested for and treated. Adults who do not have tuberculosis and have not been previously immunized, but are frequently exposed, may be immunized, as well. BCG also has some effectiveness against Buruli ulcer infection and other nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Additionally, it is sometimes used as part of the treatment of bladder cancer. Rates of protection against tuberculosis infection vary widely and protection lasts up to 20 years. Among children, it prevents about 20% from getting infected and among those who do get infected, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-react and bind more than one antigen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CFP-10
CFP-10 within bacterial proteins (also known as ESAT-6-like protein esxB or secreted antigenic protein MTSA-10 or 10 kDa culture filtrate antigen CFP-10) is a protein that is encoded by the ''esxB'' gene. CFP-10 is a 10 kDa secreted antigen from ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. It forms a 1:1 heterodimeric complex with ESAT-6. Both genes are expressed from the RD1 region of the bacterial genome and play a key role in the virulence of the infection. Function 10-kDa culture filtrate protein (CFP-10) is an antigen that contributes to the virulence Mycobacterium tuberculosis. CFP-10 forms a tight 1:1 heterodimeric complex with 6kDaA early secreted antigen target (ESAT-6). In the mycobacterial cell, these two proteins are interdependent on each other for stability. The ESAT-6/CFP-10 complex is secreted by the ESX-1 secretion system, also known as the RD1 region. Mycobacterium tuberculosis uses this ESX-1 secretion system to deliver virulence factors into host macrophage and monoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESAT-6
ESAT-6 or Early Secreted Antigenic Target 6 kDa, is produced by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', it is a secretory protein and potent T cell antigen. It is used in tuberculosis diagnosis by the whole blood interferon γ test QuantiFERON-TB Gold, in conjunction with CFP-10 and TB7.7. ESAT-6 has been shown to directly bind to the TLR2 receptor, inhibiting downstream signal transduction. It has also been studied that the inactivation of ESAT-6 leads to decreased virulence of ''M. Tuberculosis''. Secretion of the ESAT-6 protein is one of the main determining factors in the virulence of the ''M. Tuberculosis.'' ESAT-6 has more commonly become a marker for the TB diagnosis and treatment. There is also the use of the ESAT increase the production of virulent factors that cause for the increase in pathogenicity of TB. ESAT-6 is one of the main proteins that is inhibited in the production of vaccines for ''M. Tuberculosis'' with the combination of the increased antigenic factors agβ5-A a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IFN-γ
Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. Wheelock as a product of human leukocytes stimulated with phytohemagglutinin, and by others as a product of antigen-stimulated lymphocytes. It was also shown to be produced in human lymphocytes. or tuberculin-sensitized mouse peritoneal lymphocytes challenged with Mantoux test (PPD); the resulting supernatants were shown to inhibit growth of vesicular stomatitis virus. Those reports also contained the basic observation underlying the now widely employed IFN-γ release assay used to test for tuberculosis. In humans, the IFN-γ protein is encoded by the ''IFNG'' gene. Through cell signaling, IFN-γ plays a role in regulating the immune response of its target cell. A key signaling pathway that is activated by type II IFN is the JAK-STAT sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELISpot
The enzyme-linked immune absorbent spot (ELISpot) is a type of assay that focuses on quantitatively measuring the frequency of cytokine secretion for a single cell. The ELISpot Assay is also a form of immunostaining since it is classified as a technique that uses antibodies to detect a protein analyte, with the word analyte referring to any biological or chemical substance being identified or measured. The FluoroSpot Assay is a variation of the ELISpot assay. The FluoroSpot Assay uses fluorescence in order to analyze multiple analytes, meaning it can detect the secretion of more than one type of protein. History Cecil Czerkinsky first described ELISpot in 1983 as a new way to quantify the production of an antigen-specific immunoglobulin by hybridoma cells. In 1988, Czerkinsky developed an ELISA spot assay that quantified the secretion of a lymphokine by T cells. In the same year, dual-color ELISpot was combined with computer imaging for the first time, which allowed for the enu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon-γ
Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. Wheelock as a product of human leukocytes stimulated with phytohemagglutinin, and by others as a product of antigen-stimulated lymphocytes. It was also shown to be produced in human lymphocytes. or tuberculin-sensitized mouse peritoneal lymphocytes challenged with Mantoux test (PPD); the resulting supernatants were shown to inhibit growth of vesicular stomatitis virus. Those reports also contained the basic observation underlying the now widely employed IFN-γ release assay used to test for tuberculosis. In humans, the IFN-γ protein is encoded by the ''IFNG'' gene. Through cell signaling, IFN-γ plays a role in regulating the immune response of its target cell. A key signaling pathway that is activated by type II IFN is the JAK-STAT signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |