Titanium Enterprises ALPG Players Championship on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Titanium is a chemical element with the
As a metal, titanium is recognized for its high
Commercially pure (99.2% pure)
 Like aluminium and magnesium, the surface of titanium metal and its alloys oxidize immediately upon exposure to air to form a thin non-porous passivation layer that protects the bulk metal from further oxidation or corrosion. When it first forms, this protective layer is only 1–2 nm thick but it continues to grow slowly, reaching a thickness of 25 nm in four years. This layer gives titanium excellent resistance to corrosion, almost equivalent to platinum.
Titanium is capable of withstanding attack by dilute
Like aluminium and magnesium, the surface of titanium metal and its alloys oxidize immediately upon exposure to air to form a thin non-porous passivation layer that protects the bulk metal from further oxidation or corrosion. When it first forms, this protective layer is only 1–2 nm thick but it continues to grow slowly, reaching a thickness of 25 nm in four years. This layer gives titanium excellent resistance to corrosion, almost equivalent to platinum.
Titanium is capable of withstanding attack by dilute
 The +4 oxidation state dominates titanium chemistry, but compounds in the +3 oxidation state are also numerous. Commonly, titanium adopts an octahedral coordination geometry in its complexes, but tetrahedral TiCl4 is a notable exception. Because of its high oxidation state, titanium(IV) compounds exhibit a high degree of
The +4 oxidation state dominates titanium chemistry, but compounds in the +3 oxidation state are also numerous. Commonly, titanium adopts an octahedral coordination geometry in its complexes, but tetrahedral TiCl4 is a notable exception. Because of its high oxidation state, titanium(IV) compounds exhibit a high degree of
 Titanium tetrachloride (titanium(IV) chloride, TiCl4) is a colorless volatile liquid (commercial samples are yellowish) that, in air, hydrolyzes with spectacular emission of white clouds. Via the Kroll process, TiCl4 is used in the conversion of titanium ores to titanium metal. Titanium tetrachloride is also used to make titanium dioxide, e.g., for use in white paint. It is widely used in organic chemistry as a
Titanium tetrachloride (titanium(IV) chloride, TiCl4) is a colorless volatile liquid (commercial samples are yellowish) that, in air, hydrolyzes with spectacular emission of white clouds. Via the Kroll process, TiCl4 is used in the conversion of titanium ores to titanium metal. Titanium tetrachloride is also used to make titanium dioxide, e.g., for use in white paint. It is widely used in organic chemistry as a
 Titanium was discovered in 1791 by the clergyman and geologist William Gregor as an inclusion of a mineral in Cornwall, Great Britain. Gregor recognized the presence of a new element in ilmenite when he found black sand by a stream and noticed the sand was attracted by a magnet. Analyzing the sand, he determined the presence of two metal oxides:
Titanium was discovered in 1791 by the clergyman and geologist William Gregor as an inclusion of a mineral in Cornwall, Great Britain. Gregor recognized the presence of a new element in ilmenite when he found black sand by a stream and noticed the sand was attracted by a magnet. Analyzing the sand, he determined the presence of two metal oxides:  Titanium of very high purity was made in small quantities when
Titanium of very high purity was made in small quantities when

 The processing of titanium metal occurs in four major steps: reduction of titanium ore into "sponge", a porous form; melting of sponge, or sponge plus a master alloy to form an ingot; primary fabrication, where an ingot is converted into general mill products such as billet, bar, plate,
The processing of titanium metal occurs in four major steps: reduction of titanium ore into "sponge", a porous form; melting of sponge, or sponge plus a master alloy to form an ingot; primary fabrication, where an ingot is converted into general mill products such as billet, bar, plate, 2FeTiO3 + 7Cl2 + 6C -> 00^oC2FeCl3 + 2TiCl4 + 6CO
:TiCl4 + 2Mg ->
Common titanium alloys are made by reduction. For example, cuprotitanium (rutile with copper added is reduced), ferrocarbon titanium (ilmenite reduced with coke in an electric furnace), and manganotitanium (rutile with manganese or manganese oxides) are reduced.
About fifty grades of titanium alloys are designed and currently used, although only a couple of dozen are readily available commercially. The ASTM International recognizes 31 grades of titanium metal and alloys, of which grades one through four are commercially pure (unalloyed). Those four vary in tensile strength as a function of oxygen content, with grade 1 being the most ductile (lowest tensile strength with an oxygen content of 0.18%), and grade 4 the least ductile (highest tensile strength with an oxygen content of 0.40%). The remaining grades are alloys, each designed for specific properties of ductility, strength, hardness, electrical resistivity,
 Titanium is used in steel as an alloying element (
Titanium is used in steel as an alloying element (
 About 95% of all titanium ore is destined for refinement into titanium dioxide (), an intensely white permanent pigment used in paints, paper, toothpaste, and plastics. It is also used in cement, in gemstones, as an optical opacifier in paper, and a strengthening agent in graphite composite fishing rods and golf clubs.
pigment is chemically inert, resists fading in sunlight, and is very opaque: it imparts a pure and brilliant white color to the brown or grey chemicals that form the majority of household plastics. In nature, this compound is found in the minerals anatase, brookite, and rutile. Paint made with titanium dioxide does well in severe temperatures and marine environments. Pure titanium dioxide has a very high
About 95% of all titanium ore is destined for refinement into titanium dioxide (), an intensely white permanent pigment used in paints, paper, toothpaste, and plastics. It is also used in cement, in gemstones, as an optical opacifier in paper, and a strengthening agent in graphite composite fishing rods and golf clubs.
pigment is chemically inert, resists fading in sunlight, and is very opaque: it imparts a pure and brilliant white color to the brown or grey chemicals that form the majority of household plastics. In nature, this compound is found in the minerals anatase, brookite, and rutile. Paint made with titanium dioxide does well in severe temperatures and marine environments. Pure titanium dioxide has a very high
 Welded titanium pipe and process equipment (heat exchangers, tanks, process vessels, valves) are used in the chemical and petrochemical industries primarily for corrosion resistance. Specific alloys are used in oil and gas downhole applications and nickel hydrometallurgy for their high strength (e. g.: titanium beta C alloy), corrosion resistance, or both. The
Welded titanium pipe and process equipment (heat exchangers, tanks, process vessels, valves) are used in the chemical and petrochemical industries primarily for corrosion resistance. Specific alloys are used in oil and gas downhole applications and nickel hydrometallurgy for their high strength (e. g.: titanium beta C alloy), corrosion resistance, or both. The
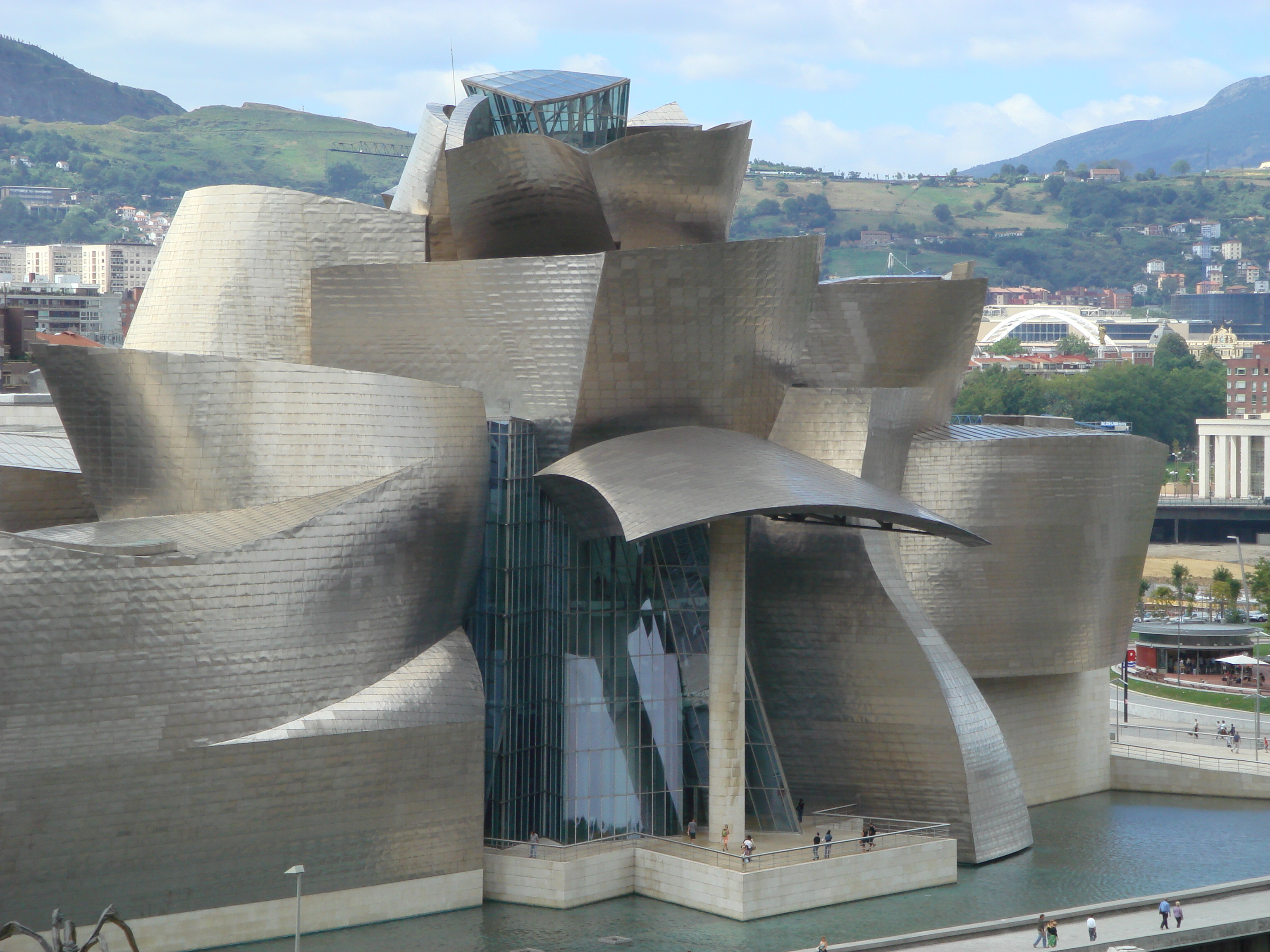 Titanium has occasionally been used in architecture. The
Titanium has occasionally been used in architecture. The
 Because of its durability, titanium has become more popular for designer jewelry (particularly,
Because of its durability, titanium has become more popular for designer jewelry (particularly,
 Titanium has the inherent ability to
Titanium has the inherent ability to
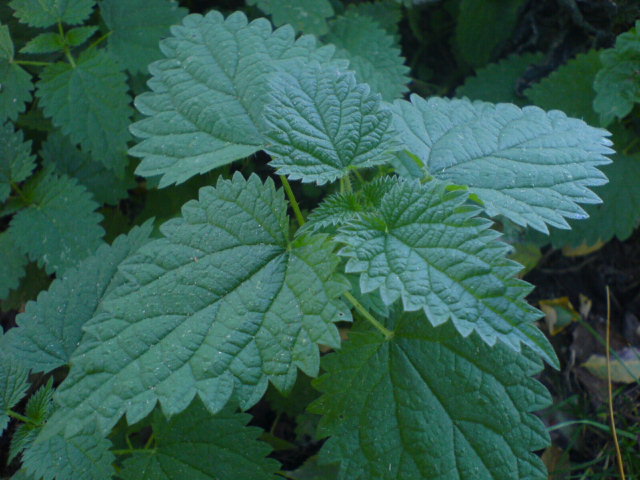 An unknown mechanism in plants may use titanium to stimulate the production of carbohydrates and encourage growth. This may explain why most plants contain about 1 part per million (ppm) of titanium, food plants have about 2 ppm, and horsetail and nettle contain up to 80 ppm.
An unknown mechanism in plants may use titanium to stimulate the production of carbohydrates and encourage growth. This may explain why most plants contain about 1 part per million (ppm) of titanium, food plants have about 2 ppm, and horsetail and nettle contain up to 80 ppm.
"Titanium: Our Next Major Metal"
''
Titanium
at '' The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
Titanium
at The Essential Chemical Industry – online (CIEC Promoting Science at the University of York)
International Titanium Association
Metal of the gods
{{Authority control Aerospace materials Biomaterials Chemical elements with hexagonal close-packed structure Chemical elements Native element minerals Pyrotechnic fuels Transition metals
symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approx ...
, aqua regia, and chlorine.
Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
and lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust (geology), crust and the portion of the upper mantle (geology), mantle that behaves elastically on time sca ...
; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and catalysts; and titanium trichloride (TiCl3), which is used as a catalyst in the production of polypropylene.
Titanium can be alloyed with iron, aluminium, vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer ( pas ...
, and molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lea ...
, among other elements, to produce strong, lightweight alloys for aerospace (jet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term ...
s, missiles, and spacecraft), military, industrial processes (chemicals and petrochemicals, desalination plants, pulp, and paper), automotive, agriculture (farming), medical prostheses, orthopedic implants
Implant can refer to:
Medicine
*Implant (medicine), or specifically:
**Brain implant
**Breast implant
**Buttock implant
**Cochlear implant
**Contraceptive implant
**Dental implant
**Fetal tissue implant
**Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
** ...
, dental and endodontic instruments and files, dental implants, sporting goods, jewelry, mobile phones, and other applications.
The two most useful properties of the metal are corrosion resistance and strength-to-density ratio, the highest of any metallic element. In its unalloyed condition, titanium is as strong as some steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
s, but less dense. There are two allotropic forms and five naturally occurring isotopes of this element, Ti through Ti, with Ti being the most abundant (73.8%).
Characteristics
Physical properties
strength-to-weight ratio
The specific strength is a material's (or muscle's) strength (force per unit area at failure) divided by its density. It is also known as the strength-to-weight ratio or strength/weight ratio or strength-to-mass ratio. In fiber or textile applic ...
. It is a strong metal with low density that is quite ductile (especially in an oxygen-free environment), lustrous, and metallic-white in color. The relatively high melting point (1,668 °C or 3,034 °F) makes it useful as a refractory metal. It is paramagnetic and has fairly low electrical and thermal conductivity compared to other metals. Titanium is superconducting when cooled below its critical temperature of 0.49 K.grades
Grade most commonly refers to:
* Grade (education), a measurement of a student's performance
* Grade, the number of the year a student has reached in a given educational stage
* Grade (slope), the steepness of a slope
Grade or grading may also r ...
of titanium have ultimate tensile strength of about 434 MPa (63,000 psi), equal to that of common, low-grade steel alloys, but are less dense. Titanium is 60% denser than aluminium, but more than twice as strong as the most commonly used 6061-T6 aluminium alloy. Certain titanium alloys (e.g., Beta C) achieve tensile strengths of over 1,400 MPa (200,000 psi). However, titanium loses strength when heated above .
Titanium is not as hard as some grades of heat-treated steel; it is non-magnetic and a poor conductor of heat and electricity. Machining requires precautions, because the material can gall
Galls (from the Latin , 'oak-apple') or ''cecidia'' (from the Greek , anything gushing out) are a kind of swelling growth on the external tissues of plants, fungi, or animals. Plant galls are abnormal outgrowths of plant tissues, similar to be ...
unless sharp tools and proper cooling methods are used. Like steel structures, those made from titanium have a fatigue limit that guarantees longevity in some applications.
The metal is a dimorphic allotrope
Allotropy or allotropism () is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical state, known as allotropes of the elements. Allotropes are different structural modifications of an element: the ...
of an hexagonal α form that changes into a body-centered cubic (lattice) β form at . The specific heat of the α form increases dramatically as it is heated to this transition temperature but then falls and remains fairly constant for the β form regardless of temperature.
Chemical properties
 Like aluminium and magnesium, the surface of titanium metal and its alloys oxidize immediately upon exposure to air to form a thin non-porous passivation layer that protects the bulk metal from further oxidation or corrosion. When it first forms, this protective layer is only 1–2 nm thick but it continues to grow slowly, reaching a thickness of 25 nm in four years. This layer gives titanium excellent resistance to corrosion, almost equivalent to platinum.
Titanium is capable of withstanding attack by dilute
Like aluminium and magnesium, the surface of titanium metal and its alloys oxidize immediately upon exposure to air to form a thin non-porous passivation layer that protects the bulk metal from further oxidation or corrosion. When it first forms, this protective layer is only 1–2 nm thick but it continues to grow slowly, reaching a thickness of 25 nm in four years. This layer gives titanium excellent resistance to corrosion, almost equivalent to platinum.
Titanium is capable of withstanding attack by dilute sulfuric
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
and hydrochloric acids, chloride solutions, and most organic acids. However, titanium is corroded by concentrated acids. As indicated by its negative redox potential, titanium is a very reactive metal that burns in normal air at lower temperatures than the melting point. Melting is possible only in an inert atmosphere or vacuum. At , it combines with chlorine. It also reacts with the other halogens and absorbs hydrogen.
Titanium readily reacts with oxygen at in air, and at in pure oxygen, forming titanium dioxide. Titanium is one of the few elements that burns in pure nitrogen gas, reacting at to form titanium nitride, which causes embrittlement. Because of its high reactivity with oxygen, nitrogen, and many other gases, titanium that is evaporated from filaments is the basis for titanium sublimation pumps, in which titanium serves as a scavenger for these gases by chemically binding to them. Such pumps inexpensively produce extremely low pressures in ultra-high vacuum systems.
Occurrence
Titanium is the ninth-most abundant element in Earth's crust (0.63% by mass) and the seventh-most abundant metal. It is present as oxides in most igneous rocks, in sediments derived from them, in living things, and natural bodies of water. Of the 801 types of igneous rocks analyzed by the United States Geological Survey, 784 contained titanium. Its proportion in soils is approximately 0.5 to 1.5%. Common titanium-containing minerals are anatase, brookite, ilmenite, perovskite, rutile, and titanite (sphene). Akaogiite is an extremely rare mineral consisting of titanium dioxide. Of these minerals, only rutile and ilmenite have economic importance, yet even they are difficult to find in high concentrations. About 6.0 and 0.7 million tonnes of those minerals were mined in 2011, respectively. Significant titanium-bearing ilmenite deposits exist inAustralia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, Canada, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, India, Mozambique, New Zealand, Norway, Sierra Leone, South Africa, and Ukraine. About 210,000 tonnes of titanium metal sponge
Regular foamed aluminium
A metal foam is a cellular structure consisting of a solid metal (frequently aluminium) with gas-filled pores comprising a large portion of the volume. The pores can be sealed (closed-cell foam) or interconnected (open-c ...
were produced in 2020, mostly in China (110,000 t), Japan (50,000 t), Russia (33,000 t) and Kazakhstan (15,000 t). Total reserves of anatase, ilmenite, and rutile are estimated to exceed 2 billion tonnes.
The concentration of titanium is about 4 picomolar in the ocean. At 100 °C, the concentration of titanium in water is estimated to be less than 10−7 M at pH 7. The identity of titanium species in aqueous solution remains unknown because of its low solubility and the lack of sensitive spectroscopic methods, although only the 4+ oxidation state is stable in air. No evidence exists for a biological role, although rare organisms are known to accumulate high concentrations of titanium.
Titanium is contained in meteorite
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the ...
s, and it has been detected in the Sun and in M-type star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
s (the coolest type) with a surface temperature of . Rocks
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's ...
brought back from the Moon during the Apollo 17
Apollo 17 (December 7–19, 1972) was the final mission of NASA's Apollo program, the most recent time humans have set foot on the Moon or traveled beyond low Earth orbit. Commander Gene Cernan and Lunar Module Pilot Harrison Schmitt walked on ...
mission are composed of 12.1% TiO2. Native titanium (pure metallic) is very rare.
Isotopes
Naturally occurring titanium is composed of five stable isotopes: 46Ti, 47Ti, 48Ti, 49Ti, and 50Ti, with 48Ti being the most abundant (73.8% natural abundance). At least 21 radioisotopes have been characterized, the most stable of which are 44Ti with a half-life of 63 years; 45Ti, 184.8 minutes; 51Ti, 5.76 minutes; and 52Ti, 1.7 minutes. All other radioactive isotopes have half-lives less than 33 seconds, with the majority less than half a second. The isotopes of titanium range in atomic weight from 39.002 u (39Ti) to 63.999 u (64Ti). The primarydecay mode
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
for isotopes lighter than 46Ti is positron emission (with the exception of 44Ti which undergoes electron capture), leading to isotopes of scandium, and the primary mode for isotopes heavier than 50Ti is beta emission, leading to isotopes of vanadium.
Titanium becomes radioactive upon bombardment with deuterons
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being protium, or hydrogen-1). The nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one n ...
, emitting mainly positrons
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. It has an electric charge of +1 '' e'', a spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same mass as an electron. When a positron collides w ...
and hard gamma rays.
Compounds
 The +4 oxidation state dominates titanium chemistry, but compounds in the +3 oxidation state are also numerous. Commonly, titanium adopts an octahedral coordination geometry in its complexes, but tetrahedral TiCl4 is a notable exception. Because of its high oxidation state, titanium(IV) compounds exhibit a high degree of
The +4 oxidation state dominates titanium chemistry, but compounds in the +3 oxidation state are also numerous. Commonly, titanium adopts an octahedral coordination geometry in its complexes, but tetrahedral TiCl4 is a notable exception. Because of its high oxidation state, titanium(IV) compounds exhibit a high degree of covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms ...
ing.
Oxides, sulfides, and alkoxides
The most important oxide is TiO2, which exists in three important polymorphs; anatase, brookite, and rutile. All three are white diamagnetic solids, although mineral samples can appear dark (see rutile). They adopt polymeric structures in which Ti is surrounded by sixoxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
ligands that link to other Ti centers.
The term '' titanates'' usually refers to titanium(IV) compounds, as represented by barium titanate (BaTiO3). With a perovskite structure, this material exhibits piezoelectric properties and is used as a transducer in the interconversion of sound and electricity. Many minerals are titanates, such as ilmenite (FeTiO3). Star sapphires and rubies get their asterism (star-forming shine) from the presence of titanium dioxide impurities.
A variety of reduced oxides ( suboxides) of titanium are known, mainly reduced stoichiometries of titanium dioxide obtained by atmospheric plasma spraying. Ti3O5, described as a Ti(IV)-Ti(III) species, is a purple semiconductor produced by reduction of TiO2 with hydrogen at high temperatures, and is used industrially when surfaces need to be vapor-coated with titanium dioxide: it evaporates as pure TiO, whereas TiO2 evaporates as a mixture of oxides and deposits coatings with variable refractive index. Also known is Ti2O3, with the corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the pres ...
structure, and TiO
Titanium(II) oxide ( Ti O) is an inorganic chemical compound of titanium and oxygen. It can be prepared from titanium dioxide and titanium metal at 1500 °C. It is non-stoichiometric in a range TiO0.7 to TiO1.3 and this is caused by vacancie ...
, with the rock salt structure, although often nonstoichiometric.
The alkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, whe ...
s of titanium(IV), prepared by treating TiCl4 with alcohols, are colorless compounds that convert to the dioxide on reaction with water. They are industrially useful for depositing solid TiO2 via the sol-gel process. Titanium isopropoxide is used in the synthesis of chiral organic compounds via the Sharpless epoxidation.
Titanium forms a variety of sulfides, but only TiS2 has attracted significant interest. It adopts a layered structure and was used as a cathode in the development of lithium batteries. Because Ti(IV) is a "hard cation", the sulfides of titanium are unstable and tend to hydrolyze to the oxide with release of hydrogen sulfide.
Nitrides and carbides
Titanium nitride (TiN) is a refractory solid exhibiting extreme hardness, thermal/electrical conductivity, and a high melting point. TiN has a hardness equivalent to sapphire and carborundum (9.0 on the Mohs scale), and is often used to coat cutting tools, such as drill bits. It is also used as a gold-colored decorative finish and as a barrier layer in semiconductor fabrication. Titanium carbide (TiC), which is also very hard, is found in cutting tools and coatings.Halides
 Titanium tetrachloride (titanium(IV) chloride, TiCl4) is a colorless volatile liquid (commercial samples are yellowish) that, in air, hydrolyzes with spectacular emission of white clouds. Via the Kroll process, TiCl4 is used in the conversion of titanium ores to titanium metal. Titanium tetrachloride is also used to make titanium dioxide, e.g., for use in white paint. It is widely used in organic chemistry as a
Titanium tetrachloride (titanium(IV) chloride, TiCl4) is a colorless volatile liquid (commercial samples are yellowish) that, in air, hydrolyzes with spectacular emission of white clouds. Via the Kroll process, TiCl4 is used in the conversion of titanium ores to titanium metal. Titanium tetrachloride is also used to make titanium dioxide, e.g., for use in white paint. It is widely used in organic chemistry as a Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
, for example in the Mukaiyama aldol condensation
The Mukaiyama aldol addition is an organic reaction and a type of aldol reaction between a silyl enol ether and an aldehyde or formate. The reaction was discovered by Teruaki Mukaiyama (1927–2018) in 1973. His choice of reactants allows for ...
. In the van Arkel–de Boer process, titanium tetraiodide (TiI4) is generated in the production of high purity titanium metal.
Titanium(III) and titanium(II) also form stable chlorides. A notable example is titanium(III) chloride (TiCl3), which is used as a catalyst for production of polyolefin
A polyolefin is a type of polymer with the general formula (CH2CHR)n where R is an alkyl group. They are usually derived from a small set of simple olefins (alkenes). Dominant in a commercial sense are polyethylene and polypropylene. More speciali ...
s (see Ziegler–Natta catalyst) and a reducing agent in organic chemistry.
Organometallic complexes
Owing to the important role of titanium compounds as polymerization catalyst, compounds with Ti-C bonds have been intensively studied. The most common organotitanium complex is titanocene dichloride ((C5H5)2TiCl2). Related compounds include Tebbe's reagent and Petasis reagent. Titanium forms carbonyl complexes, e.g. (C5H5)2Ti(CO)2.Anticancer therapy studies
Following the success of platinum-based chemotherapy, titanium(IV) complexes were among the first non-platinum compounds to be tested for cancer treatment. The advantage of titanium compounds lies in their high efficacy and low toxicity '' in vivo''. In biological environments, hydrolysis leads to the safe and inert titanium dioxide. Despite these advantages the first candidate compounds failed clinical trials due to insufficient efficacy to toxicity ratios and formulation complications. Further development resulted in the creation of potentially effective, selective, and stable titanium-based drugs.History
 Titanium was discovered in 1791 by the clergyman and geologist William Gregor as an inclusion of a mineral in Cornwall, Great Britain. Gregor recognized the presence of a new element in ilmenite when he found black sand by a stream and noticed the sand was attracted by a magnet. Analyzing the sand, he determined the presence of two metal oxides:
Titanium was discovered in 1791 by the clergyman and geologist William Gregor as an inclusion of a mineral in Cornwall, Great Britain. Gregor recognized the presence of a new element in ilmenite when he found black sand by a stream and noticed the sand was attracted by a magnet. Analyzing the sand, he determined the presence of two metal oxides: iron oxide
Iron oxides are chemical compounds composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. All are black magnetic solids. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of whic ...
(explaining the attraction to the magnet) and 45.25% of a white metallic oxide he could not identify. Realizing that the unidentified oxide contained a metal that did not match any known element, in 1791 Gregor reported his findings in both German and French science journals:'' Crell's Annalen'' and ''Observations et Mémoires sur la Physique''.
Around the same time, Franz-Joseph Müller von Reichenstein produced a similar substance, but could not identify it. The oxide was independently rediscovered in 1795 by Prussian chemist Martin Heinrich Klaproth in rutile from Boinik (the German name of Bajmócska), a village in Hungary (now Bojničky in Slovakia).
Klaproth found that it contained a new element and named it for the Titans of Greek mythology. After hearing about Gregor's earlier discovery, he obtained a sample of manaccanite and confirmed that it contained titanium.
The currently known processes for extracting titanium from its various ores are laborious and costly; it is not possible to reduce the ore by heating with carbon (as in iron smelting) because titanium combines with the carbon to produce titanium carbide. Pure metallic titanium (99.9%) was first prepared in 1910 by Matthew A. Hunter
Matthew Albert Hunter (1878-1961) was a metallurgist and inventor of the Hunter process for producing titanium metal.
Hunter was born in Auckland, New Zealand in 1878 and received his early education in local public schools. He completed his Secon ...
at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute () (RPI) is a private research university in Troy, New York, with an additional campus in Hartford, Connecticut. A third campus in Groton, Connecticut closed in 2018. RPI was established in 1824 by Stephen Van ...
by heating TiCl4 with sodium at 700–800 °C under great pressure in a batch process known as the Hunter process. Titanium metal was not used outside the laboratory until 1932 when William Justin Kroll produced it by reducing titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) with calcium. Eight years later he refined this process with magnesium and with sodium in what became known as the Kroll process. Although research continues to seek cheaper and more efficient routes, such as the FFC Cambridge process, the Kroll process is still predominantly used for commercial production.
 Titanium of very high purity was made in small quantities when
Titanium of very high purity was made in small quantities when Anton Eduard van Arkel
Anton Eduard van Arkel, (19 November 1893 – 14 March 1976) was a Dutch chemist.
Van Arkel suggested the names "pnictogen" and "pnictide" to refer to chemical elements in group 15 (the nitrogen group or nitrogen family) of the periodic table.
...
and Jan Hendrik de Boer discovered the iodide process in 1925, by reacting with iodine and decomposing the formed vapors over a hot filament to pure metal.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the Soviet Union pioneered the use of titanium in military and submarine applications (Alfa class
The Alfa class, Soviet designation Project 705 Lira (russian: Лира, meaning "Lyre", NATO reporting name Alfa), was a class of nuclear-powered attack submarines in service with the Soviet Navy from 1971 into the early 1990s, with one servin ...
and Mike class) as part of programs related to the Cold War. Starting in the early 1950s, titanium came into use extensively in military aviation, particularly in high-performance jets, starting with aircraft such as the F-100 Super Sabre
The North American F-100 Super Sabre is an American supersonic jet fighter aircraft that served with the United States Air Force (USAF) from 1954 to 1971 and with the Air National Guard (ANG) until 1979. The first of the Century Series of ...
and Lockheed A-12 and SR-71
The Lockheed SR-71 "Blackbird" is a Range (aeronautics), long-range, high-altitude, Mach number, Mach 3+ military strategy, strategic reconnaissance aircraft developed and manufactured by the American aerospace company Lockheed Corporati ...
.
Throughout the Cold War period, titanium was considered a strategic material
Strategic material is any sort of raw material that is important to an individual's or organization's strategic plan and supply chain management. Lack of supply of strategic materials may leave an organization or government vulnerable to disru ...
by the U.S. government, and a large stockpile of titanium sponge (a porous form of the pure metal) was maintained by the Defense National Stockpile Center, until the stockpile was dispersed in the 2000s. As of 2021, the four leading producers of titanium sponge were China (52%), Japan (24%), Russia (16%) and Kazakhstan (7%).
Production

 The processing of titanium metal occurs in four major steps: reduction of titanium ore into "sponge", a porous form; melting of sponge, or sponge plus a master alloy to form an ingot; primary fabrication, where an ingot is converted into general mill products such as billet, bar, plate,
The processing of titanium metal occurs in four major steps: reduction of titanium ore into "sponge", a porous form; melting of sponge, or sponge plus a master alloy to form an ingot; primary fabrication, where an ingot is converted into general mill products such as billet, bar, plate, sheet
Sheet or Sheets may refer to:
* Bed sheet, a rectangular piece of cloth used as bedding
* Sheet of paper, a flat, very thin piece of paper
* Sheet metal, a flat thin piece of metal
* Sheet (sailing), a line, cable or chain used to control the cle ...
, strip, and tube; and secondary fabrication of finished shapes from mill products.
Because it cannot be readily produced by reduction of titanium dioxide, titanium metal is obtained by reduction of TiCl4 with magnesium metal in the Kroll process. The complexity of this batch production in the Kroll process explains the relatively high market value of titanium, despite the Kroll process being less expensive than the Hunter process. To produce the TiCl4 required by the Kroll process, the dioxide is subjected to carbothermic reduction in the presence of chlorine. In this process, the chlorine gas is passed over a red-hot mixture of rutile or ilmenite in the presence of carbon.
After extensive purification by fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation to ...
, the TiCl4 is reduced with molten magnesium in an argon atmosphere. Titanium metal can be further purified by the van Arkel–de Boer process, which involves thermal decomposition of titanium tetraiodide.
:100^oC
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. ...
Ti + 2MgCl2creep
Creep, Creeps or CREEP may refer to:
People
* Creep, a creepy person
Politics
* Committee for the Re-Election of the President (CRP), mockingly abbreviated as CREEP, an fundraising organization for Richard Nixon's 1972 re-election campaign
Art ...
resistance, specific corrosion resistance, and combinations thereof.
In addition to the ASTM specifications, titanium alloys are also produced to meet aerospace and military specifications (SAE-AMS, MIL-T), ISO standards, and country-specific specifications, as well as proprietary end-user specifications for aerospace, military, medical, and industrial applications.
Titanium powder is manufactured using a flow production process known as the Armstrong process that is similar to the batch production Hunter process. A stream of titanium tetrachloride gas is added to a stream of molten sodium; the products (sodium chloride salt and titanium particles) is filtered from the extra sodium. Titanium is then separated from the salt by water washing. Both sodium and chlorine are recycled to produce and process more titanium tetrachloride.
Fabrication
All welding of titanium must be done in an inert atmosphere of argon or helium to shield it from contamination with atmospheric gases (oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen). Contamination causes a variety of conditions, such as embrittlement, which reduce the integrity of the assembly welds and lead to joint failure. Titanium is very difficult to solder directly, and hence a solderable metal or alloy such as steel is coated on titanium prior to soldering. Titanium metal can be machined with the same equipment and the same processes asstainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corros ...
.
Forming and forging
Commercially pure flat product (sheet, plate) can be formed readily, but processing must take into account of the tendency of the metal tospringback
Bending is a manufacturing process that produces a V-shape, U-shape, or channel shape along a straight axis in ductile materials, most commonly sheet metal.Manufacturing Processes Reference Guide, Industrial Press Inc., 1994. Commonly used equi ...
. This is especially true of certain high-strength alloys. Exposure to the oxygen in air at the elevated temperatures used in forging results in formation of an brittle oxygen-rich metallic surface layer called " alpha case" that worsens the fatigue properties, so it must be removed by milling, etching, or electrochemical treatment.
Applications
 Titanium is used in steel as an alloying element (
Titanium is used in steel as an alloying element (ferro-titanium
Ferrotitanium is a ferroalloy, an alloy of iron and titanium with between 10–20% iron and 45–75% titanium and sometimes a small amount of carbon. It is used in steelmaking as a cleansing agent for iron and steel; the titanium is highly reactive ...
) to reduce grain size
Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. This is different from the crystallite size, which refer ...
and as a deoxidizer, and in stainless steel to reduce carbon content. Titanium is often alloyed with aluminium (to refine grain size), vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer ( pas ...
, copper (to harden), iron, manganese, molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lea ...
, and other metals. Titanium mill products (sheet, plate, bar, wire, forgings, castings) find application in industrial, aerospace, recreational, and emerging markets. Powdered titanium is used in pyrotechnics
Pyrotechnics is the science and craft of creating such things as fireworks, safety matches, oxygen candles, explosive bolts and other fasteners, parts of automotive airbags, as well as gas-pressure blasting in mining, quarrying, and demolition. ...
as a source of bright-burning particles.
Pigments, additives, and coatings
 About 95% of all titanium ore is destined for refinement into titanium dioxide (), an intensely white permanent pigment used in paints, paper, toothpaste, and plastics. It is also used in cement, in gemstones, as an optical opacifier in paper, and a strengthening agent in graphite composite fishing rods and golf clubs.
pigment is chemically inert, resists fading in sunlight, and is very opaque: it imparts a pure and brilliant white color to the brown or grey chemicals that form the majority of household plastics. In nature, this compound is found in the minerals anatase, brookite, and rutile. Paint made with titanium dioxide does well in severe temperatures and marine environments. Pure titanium dioxide has a very high
About 95% of all titanium ore is destined for refinement into titanium dioxide (), an intensely white permanent pigment used in paints, paper, toothpaste, and plastics. It is also used in cement, in gemstones, as an optical opacifier in paper, and a strengthening agent in graphite composite fishing rods and golf clubs.
pigment is chemically inert, resists fading in sunlight, and is very opaque: it imparts a pure and brilliant white color to the brown or grey chemicals that form the majority of household plastics. In nature, this compound is found in the minerals anatase, brookite, and rutile. Paint made with titanium dioxide does well in severe temperatures and marine environments. Pure titanium dioxide has a very high index of refraction
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
and an optical dispersion higher than diamond. In addition to being a very important pigment, titanium dioxide is also used in sunscreens.
Aerospace and marine
Because titanium alloys have high tensile strength to density ratio, high corrosion resistance, fatigue resistance, high crack resistance, and ability to withstand moderately high temperatures without creeping, they are used in aircraft, armor plating, naval ships, spacecraft, and missiles. For these applications, titanium is alloyed with aluminium, zirconium, nickel, vanadium, and other elements to manufacture a variety of components including critical structural parts, fire walls, landing gear, exhaust ducts (helicopters), and hydraulic systems. In fact, about two thirds of all titanium metal produced is used in aircraft engines and frames. Thetitanium 6AL-4V
Titanium alloys are alloys that contain a mixture of titanium and other chemical elements. Such alloys have very high tensile strength and toughness (even at extreme temperatures). They are light in weight, have extraordinary corrosion resistance a ...
alloy accounts for almost 50% of all alloys used in aircraft applications.
The Lockheed A-12 and its development the SR-71 "Blackbird" were two of the first aircraft frames where titanium was used, paving the way for much wider use in modern military and commercial aircraft. A large amount of titanium mill products are used in the production of many aircraft, such as (following values are amount of raw mill products used ... only a fraction of this ends up in the finished aircraft): 116 metric tons are used in the Boeing 787, 77 in the Airbus A380, 59 in the Boeing 777, 45 in the Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet times its size, t ...
, 18 in the Boeing 737, 32 in the Airbus A340, 18 in the Airbus A330, and 12 in the Airbus A320. In aero engine applications, titanium is used for rotors, compressor blades, hydraulic system components, and nacelles. An early use in jet engines was for the Orenda Iroquois in the 1950s.
Because titanium is resistant to corrosion by sea water, it is used to make propeller shafts, rigging, and heat exchangers in desalination plants; heater-chillers for salt water aquariums, fishing line and leader, and divers' knives. Titanium is used in the housings and components of ocean-deployed surveillance and monitoring devices for science and the military. The former Soviet Union developed techniques for making submarines with hulls of titanium alloys forging titanium in huge vacuum tubes.
Titanium is used in the walls of the Juno spacecraft's vault to shield on-board electronics.
Industrial
 Welded titanium pipe and process equipment (heat exchangers, tanks, process vessels, valves) are used in the chemical and petrochemical industries primarily for corrosion resistance. Specific alloys are used in oil and gas downhole applications and nickel hydrometallurgy for their high strength (e. g.: titanium beta C alloy), corrosion resistance, or both. The
Welded titanium pipe and process equipment (heat exchangers, tanks, process vessels, valves) are used in the chemical and petrochemical industries primarily for corrosion resistance. Specific alloys are used in oil and gas downhole applications and nickel hydrometallurgy for their high strength (e. g.: titanium beta C alloy), corrosion resistance, or both. The pulp and paper industry
The pulp and paper industry comprises companies that use wood as raw material and produce pulp, paper, paperboard and other cellulose-based products.
Manufacturing process
The pulp is fed to a paper machine where it is formed as a paper web an ...
uses titanium in process equipment exposed to corrosive media, such as sodium hypochlorite or wet chlorine gas (in the bleachery). Other applications include ultrasonic welding, wave soldering, and sputtering targets.
Titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a colorless liquid, is important as an intermediate in the process of making TiO2 and is also used to produce the Ziegler–Natta catalyst. Titanium tetrachloride is also used to iridize glass and, because it fumes strongly in moist air, it is used to make smoke screens.
Consumer and architectural
Titanium metal is used in automotive applications, particularly in automobile and motorcycle racing where low weight and high strength and rigidity are critical. The metal is generally too expensive for the general consumer market, though some late model Corvettes have been manufactured with titanium exhausts, and a Corvette Z06's LT4 supercharged engine uses lightweight, solid titanium intake valves for greater strength and resistance to heat. Titanium is used in many sporting goods: tennis rackets, golf clubs, lacrosse stick shafts; cricket, hockey, lacrosse, and football helmet grills, and bicycle frames and components. Although not a mainstream material for bicycle production, titanium bikes have been used by racing teams and adventure cyclists. Titanium alloys are used in spectacle frames that are rather expensive but highly durable, long lasting, light weight, and cause no skin allergies. Many backpackers use titanium equipment, including cookware, eating utensils, lanterns, and tent stakes. Though slightly more expensive than traditional steel or aluminium alternatives, titanium products can be significantly lighter without compromising strength. Titanium horseshoes are preferred to steel by farriers because they are lighter and more durable. Titanium has occasionally been used in architecture. The
Titanium has occasionally been used in architecture. The Monument to Yuri Gagarin
Monument to Yuri Gagarin is a 42.5-meter high pedestal and statue of Yuri Gagarin, the first person to travel in space. It is located at Leninsky Prospekt in Moscow. The pedestal is designed to be reminiscent of a rocket exhaust. The statue is ma ...
, the first man to travel in space (), as well as the Monument to the Conquerors of Space on top of the Cosmonaut Museum in Moscow are made of titanium for the metal's attractive color and association with rocketry. The Guggenheim Museum Bilbao and the Cerritos Millennium Library were the first buildings in Europe and North America, respectively, to be sheathed in titanium panels. Titanium sheathing was used in the Frederic C. Hamilton Building in Denver, Colorado.
Because of titanium's superior strength and light weight relative to other metals (steel, stainless steel, and aluminium), and because of recent advances in metalworking techniques, its use has become more widespread in the manufacture of firearms. Primary uses include pistol frames and revolver cylinders. For the same reasons, it is used in the body of laptop computers (for example, in Apple's PowerBook line).
Some upmarket lightweight and corrosion-resistant tools, such as shovels, knife handles and flashlights, are made of titanium or titanium alloys.
Jewelry
 Because of its durability, titanium has become more popular for designer jewelry (particularly,
Because of its durability, titanium has become more popular for designer jewelry (particularly, titanium ring
Titanium rings are jewelry rings or bands which have been primarily constructed from titanium. The actual compositions of titanium can vary, such as "commercial pure" (99.2% titanium) or "aircraft grade" (primarily, 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, 4% v ...
s). Its inertness makes it a good choice for those with allergies or those who will be wearing the jewelry in environments such as swimming pools. Titanium is also alloyed with gold to produce an alloy that can be marketed as 24-karat
The fineness of a precious metal object (coin, bar, jewelry, etc.) represents the weight of ''fine metal'' therein, in proportion to the total weight which includes alloying base metals and any impurities. Alloy metals are added to increase hardne ...
gold because the 1% of alloyed Ti is insufficient to require a lesser mark. The resulting alloy is roughly the hardness of 14-karat gold and is more durable than pure 24-karat gold.
Titanium's durability, light weight, and dent and corrosion resistance make it useful for watch cases. Some artists work with titanium to produce sculptures, decorative objects and furniture.
Titanium may be anodized to vary the thickness of the surface oxide layer, causing optical interference fringes and a variety of bright colors. With this coloration and chemical inertness, titanium is a popular metal for body piercing
Body piercing, which is a form of body modification, is the practice of puncturing or cutting a part of the human body, creating an opening in which jewelry may be worn, or where an implant could be inserted. The word ''piercing'' can refer to ...
.
Titanium has a minor use in dedicated non-circulating coins and medals. In 1999, Gibraltar released the world's first titanium coin for the millennium celebration. The Gold Coast Titans, an Australian rugby league team, award a medal of pure titanium to their player of the year.
Medical
Because titanium is biocompatible (non-toxic and not rejected by the body), it has many medical uses, including surgical implements and implants, such as hip balls and sockets ( joint replacement) and dental implants that can stay in place for up to 20 years. The titanium is often alloyed with about 4% aluminium or 6% Al and 4% vanadium. Titanium has the inherent ability to
Titanium has the inherent ability to osseointegrate
Osseointegration (from Latin ''osseus'' "bone, bony" and ''integrare'' "to make whole") is the direct structural and functional connection between living bone and the surface of a load-bearing Implant (medicine), artificial implant ("load-bearing ...
, enabling use in dental implants that can last for over 30 years. This property is also useful for orthopedic implant applications. These benefit from titanium's lower modulus of elasticity ( Young's modulus) to more closely match that of the bone that such devices are intended to repair. As a result, skeletal loads are more evenly shared between bone and implant, leading to a lower incidence of bone degradation due to stress shielding and periprosthetic bone fractures, which occur at the boundaries of orthopedic implants. However, titanium alloys' stiffness is still more than twice that of bone, so adjacent bone bears a greatly reduced load and may deteriorate.
Because titanium is non-ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) which results in a large observed magnetic permeability, and in many cases a large magnetic coercivity allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials ...
, patients with titanium implants can be safely examined with magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(convenient for long-term implants). Preparing titanium for implantation in the body involves subjecting it to a high-temperature plasma
Plasma or plasm may refer to:
Science
* Plasma (physics), one of the four fundamental states of matter
* Plasma (mineral), a green translucent silica mineral
* Quark–gluon plasma, a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics
Biology
* Blood pla ...
arc which removes the surface atoms, exposing fresh titanium that is instantly oxidized.
Modern advancements in additive manufacturing techniques have increased potential for titanium use in orthopedic implant applications. Complex implant scaffold designs can be 3D-printed using titanium alloys, which allows for more patient-specific applications and increased implant osseointegration.
Titanium is used for the surgical instruments used in image-guided surgery, as well as wheelchairs, crutches, and any other products where high strength and low weight are desirable.
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles are widely used in electronics and the delivery of pharmaceuticals
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and rel ...
and cosmetics.
Nuclear waste storage
Because of its corrosion resistance, containers made of titanium have been studied for the long-term storage of nuclear waste. Containers lasting more than 100,000 years are thought possible with manufacturing conditions that minimize material defects. A titanium "drip shield" could also be installed over containers of other types to enhance their longevity.Precautions
Titanium is non-toxic even in large doses and does not play any natural role inside thehuman body
The human body is the structure of a Human, human being. It is composed of many different types of Cell (biology), cells that together create Tissue (biology), tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the life, viabi ...
. An estimated quantity of 0.8 milligrams of titanium is ingested by humans each day, but most passes through without being absorbed in the tissues. It does, however, sometimes bio-accumulate
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance at a rate faster than that at which the substance is lost or eliminated ...
in tissues that contain silica. One study indicates a possible connection between titanium and yellow nail syndrome
Yellow nail syndrome, also known as "primary lymphedema associated with yellow nails and pleural effusion", is a very rare medical syndrome that includes pleural effusions, lymphedema (due to under development of the lymphatic vessels) and yellow d ...
.
As a powder or in the form of metal shavings, titanium metal poses a significant fire hazard and, when heated in air, an explosion hazard. Water and carbon dioxide are ineffective for extinguishing a titanium fire; Class D dry powder agents must be used instead.
When used in the production or handling of chlorine, titanium should not be exposed to dry chlorine gas because it may result in a titanium–chlorine fire.
Titanium can catch fire when a fresh, non-oxidized surface comes in contact with liquid oxygen.
Function in plants
See also
* List of countries by titanium production * Suboxide *Titanium in Africa
Titanium mining in Africa has been beset by environmental problems due to the polluting nature of processing rutile, a principal titanium ore. Titanium production in Africa includes the following principal countries and companies.
Kenya
* ...
* Titanium in zircon geothermometry
Titanium in zircon geothermometry is a form of a geothermometry technique by which the crystallization temperature of a zircon crystal can be estimated by the amount of titanium atoms which can only be found in the crystal lattice. In zircon cry ...
* Titanium Man
* VSMPO-AVISMA
Footnotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * *External links
"Titanium: Our Next Major Metal"
''
Popular Science
''Popular Science'' (also known as ''PopSci'') is an American digital magazine carrying popular science content, which refers to articles for the general reader on science and technology subjects. ''Popular Science'' has won over 58 awards, incl ...
'', October 1950—one of first general public detailed articles on Titanium
Titanium
at '' The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
Titanium
at The Essential Chemical Industry – online (CIEC Promoting Science at the University of York)
International Titanium Association
Metal of the gods
{{Authority control Aerospace materials Biomaterials Chemical elements with hexagonal close-packed structure Chemical elements Native element minerals Pyrotechnic fuels Transition metals